Soil Erosion Processes in European Vineyards: A Qualitative Comparison of Rainfall Simulation Measurements in Germany, Spain and France
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Qualitative Comparison with Different Data of Rainfall Simulations in Vineyards
- (1)
- Suspended sediment load (SSL) =
- (2)
- Surface flow =
- (3)
- Suspended sediment load concentration (SSC)
3. Results
3.1. Ruwer-Mosel Valley (Trier, Germany)
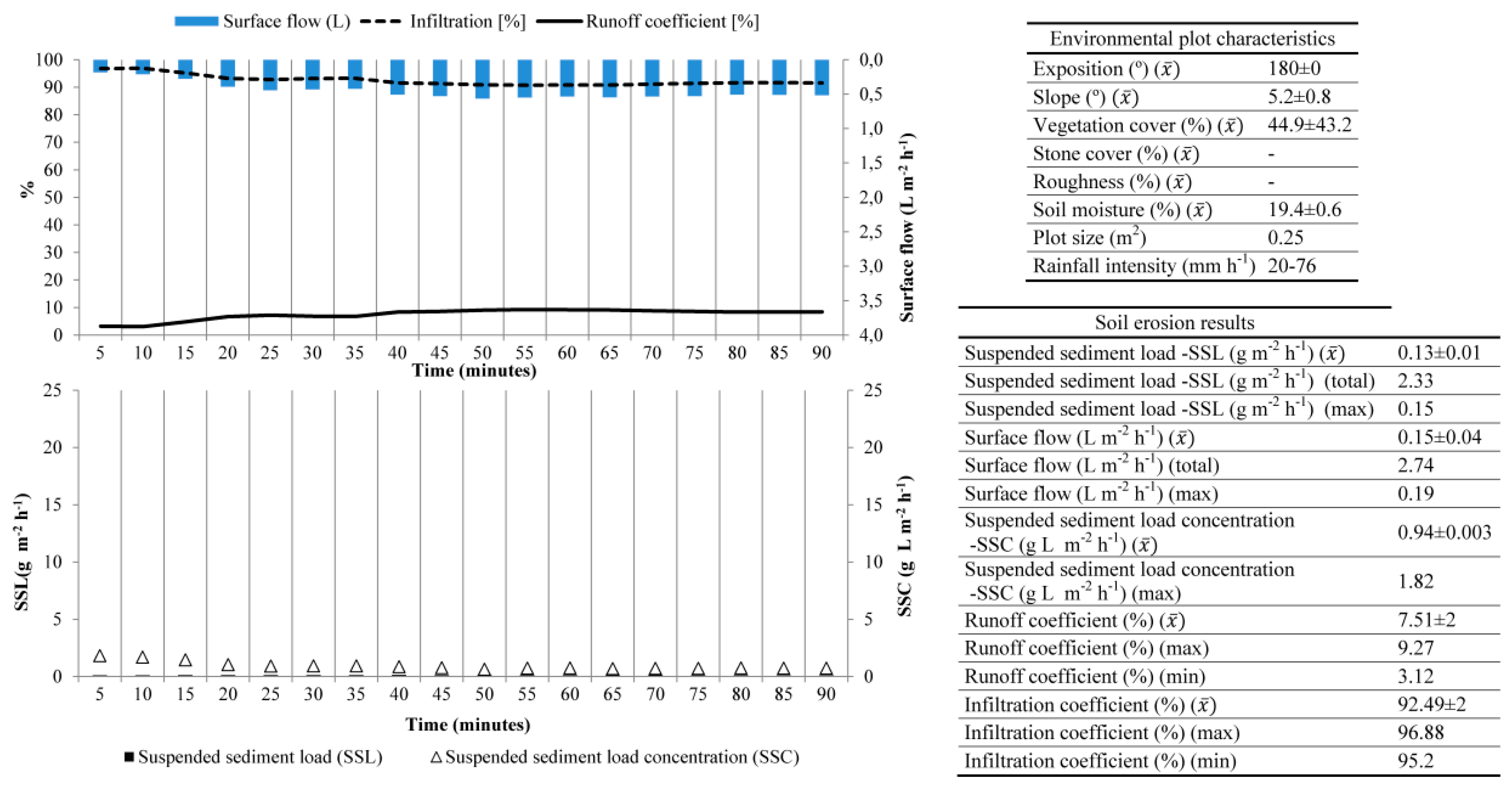
3.2. Montagne de Reims (Champagne, France)
3.3. Spain
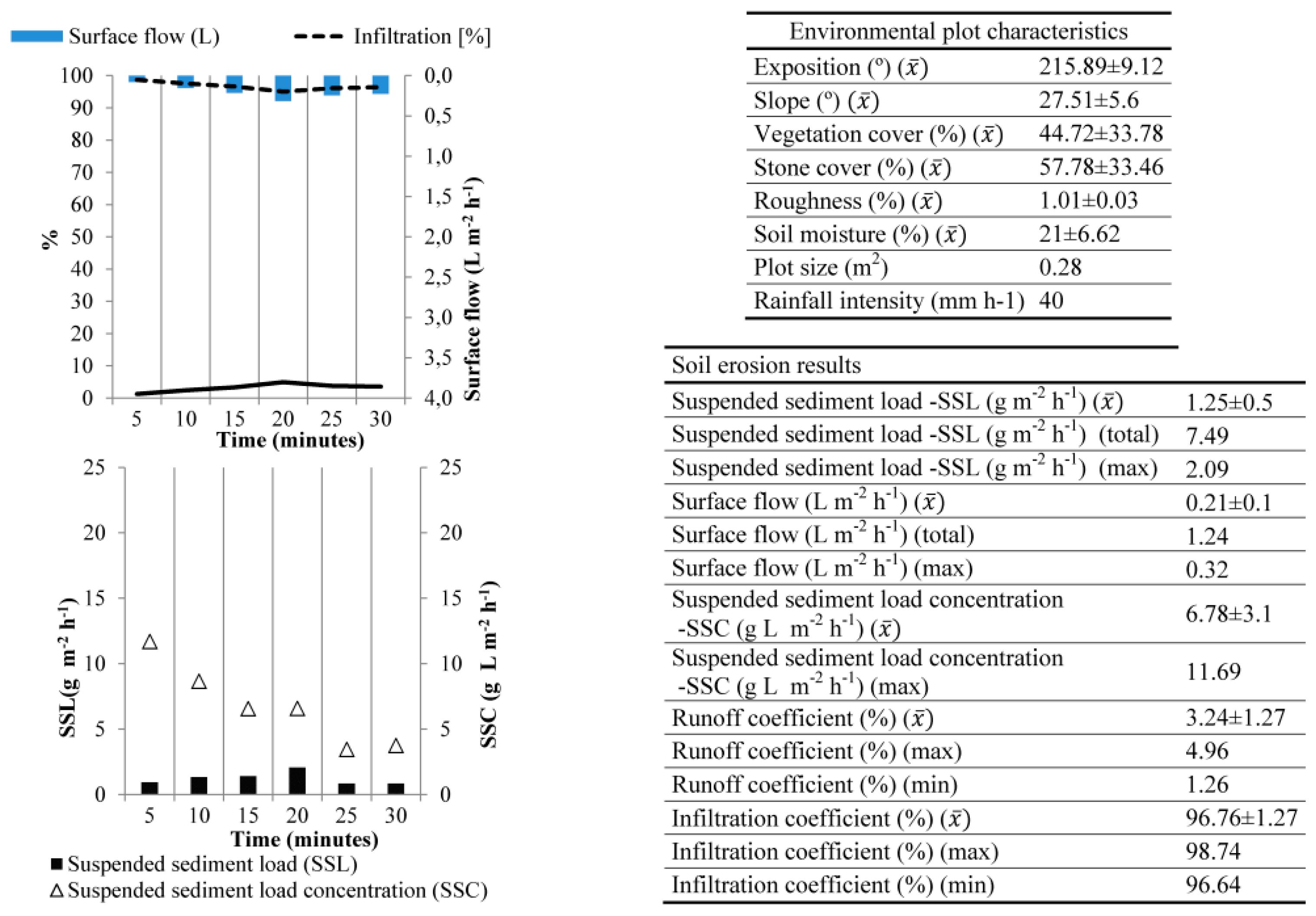
3.3.1. Montes de Málaga
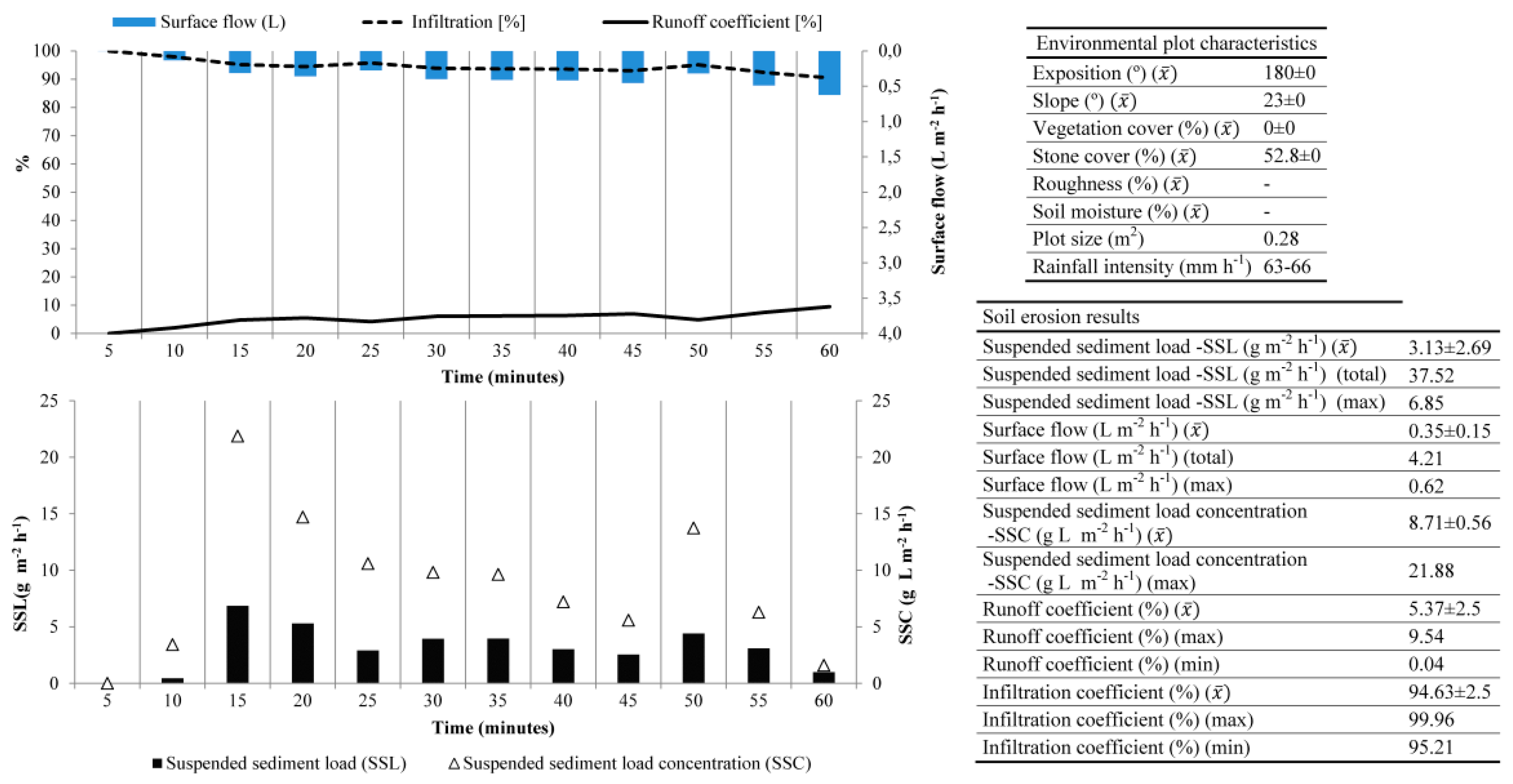
3.3.2. Els Hostalest de Pierola (Penedès)
3.3.3. Moixent (Valencia, Spain)
3.3.4. Villamediana de Iregua (La Rioja)
3.3.5. Campo Real (Madrid)
3.4. Final Comparison
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fischer, U.; Roth, D.; Christmann, M. The impact of geographic origin, vintage and wine estate on sensory properties of Vitis vinifera cv. Riesling wines. Food Qual. Prefer. 1999, 10, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resolution OIV/VITI 333/2010 Definition of vitivinicultural “Terroir”. The General Director of the OIV. In; Tbilisi (Georgia). 2010.
- Van Leeuwen, C.; Bois, B.; de Resseguier, L.; Roby, J.P. New Methods and Technologies to Describe the Environment in Terroir Studies. Available online: http://terroir2010.entecra.it/atti/pdf/session2.pdf (accessed on 6 February 2016).
- Cadot, Y.; Caillé, S.; Thiollet-Scholtus, M.; Samson, A.; Barbeau, G.; Cheynier, V. Characterisation of typicality for wines related to terroir by conceptual and by perceptual representations: An application to red wines from the Loire Valley. Food Qual. Prefer. 2012, 24, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Casasnovas, J.A.; Ramos, M.C.; García-Hernández, D. Effects of land-use changes in vegetation cover and sidewall erosion in a gully head of the Penedès region (northeast Spain). Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1927–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Piñeiro, A.; Muñoz, A.; Zamora, E.; Ramírez, M. Influence of the management regime and phenological state of the vines on the physicochemical properties and the seasonal fluctuations of the microorganisms in a vineyard soil under semi-arid conditions. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 126, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salome, C.; Coll, P.; Lardo, E.; Villenave, C.; Blanchart, E.; Hinsinger, P.; Marsden, C.; Le Cadre, E. Relevance of use-invariant soil properties to assess soil quality of vulnerable ecosystems: The case of Mediterranean vineyards. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 43, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likar, M.; Vogel-Mikuš, K.; Potisek, M.; Hančević, K.; Radić, T.; Nečemer, M.; Regvar, M. Importance of soil and vineyard management in the determination of grapevine mineral composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo Comino, J.; Senciales González, J.M. Ratio LE para el ajuste de perfiles longitudinales en cursos fluviales de montaña. Aplicación a la cuenca del río Almáchar (Málaga, España). Cuaternario Geomorfol. 2015, 29, 31–56. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudour, E.; Costantini, E.; Jones, G.V.; Mocali, S. An overview of the recent approaches to terroir functional modelling, footprinting and zoning. Soil 2015, 1, 287–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.; Danalatos, N.; Cammeraat, L.H.; Chabart, M.; Diamantopoulos, J.; Farand, R.; Gutierrez, L.; Jacob, A.; Marques, H.; Martinez-Fernandez, J.; et al. The effect of land use on runoff and soil erosion rates under Mediterranean conditions. Catena 1997, 29, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieskovský, J.; Kenderessy, P. Modelling the effect of vegetation cover and different tillage practices on soil erosion in vineyards: a case study in Vráble (Slovakia) using WATEM/SEDEM. Land Degrad. Dev. 2014, 25, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novara, A.; Gristina, L.; Saladino, S.S.; Santoro, A.; Cerdà, A. Soil erosion assessment on tillage and alternative soil managements in a Sicilian vineyard. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 117, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, A.; Gristina, L.; Crescimanno, M.; Barone, E.; Novara, A. Towards More Efficient Incentives for Agri-environment Measures in Degraded and Eroded Vineyards. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, E.A.C.; Agnelli, A.E.; Fabiani, A.; Gagnarli, E.; Mocali, S.; Priori, S.; Simoni, S.; Valboa, G. Short-term recovery of soil physical, chemical, micro- and mesobiological functions in a new vineyard under organic farming. Soil 2015, 1, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnarli, E.; Goggioli, D.; Tarchi, F.; Guidi, S.; Nannelli, R.; Vignozzi, N.; Valboa, G.; Lottero, M.R.; Corino, L.; Simoni, S. Case study of microarthropod communities to assess soil quality in different managed vineyards. Soil 2015, 1, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrón, J.M.; Blanco, J.; Moral, F.J.; Mancha, L.A.; Uriarte, D.; Marques da Silva, J.R. Evaluation of vineyard growth under four irrigation regimes using vegetation and soil on-the-go sensors. Soil 2015, 1, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarolli, P.; Sofia, G.; Calligaro, S.; Prosdocimi, M.; Preti, F.; Dalla Fontana, G. Vineyards in Terraced Landscapes: New Opportunities from Lidar Data. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bissonnais, Y.; Benkhadra, H.; Chaplot, V.; Fox, D.; King, D.; Daroussin, J. Crusting, runoff and sheet erosion on silty loamy soils at various scales and upscaling from m2 to small catchments. Soil Tillage Res. 1998, 46, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morvan, X.; Naisse, C.; Malam Issa, O.; Desprats, J.F.; Combaud, A.; Cerdan, O. Effect of ground-cover type on surface runoff and subsequent soil erosion in Champagne vineyards in France. Soil Use Manag. 2014, 30, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortigosa Izquierdo, L.M.; Lasanta Martínez, T. El papel de la escorrentía en la organización textural de suelos cultivados en pendiente: modelos en viñedos de La Rioja. Cuad. Investig. Geográfica 1984, 10, 99–112. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, J.; Andrieux, P. Infiltration characteristics of soils in Mediterranean vineyards in Southern France. Catena 1998, 32, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.C.; Martínez-Casasnovas, J.A. Impact of land levelling on soil moisture and runoff variability in vineyards under different rainfall distributions in a Mediterranean climate and its influence on crop productivity. J. Hydrol. 2006, 321, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbane, C.; Jacob, F.; Raclot, D.; Albergel, J.; Andrieux, P. Multitemporal analysis of hydrological soil surface characteristics using aerial photos: A case study on a Mediterranean vineyard. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 18, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddoccu, M.; Ferraris, S.; Cavallo, E.; Opsi, F.; Previati, M.; Canone, D. Hillslope Vineyard Rainfall-Runoff Measurements in Relation to Soil Infiltration and Water Content. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 19, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; González-Pelayo, A.; Giménez Morera, A.; Jordán, A.; Pereira, P.; Novara, A.; Brevik, E.C.; Prosdocimi, M.; Mahmoodabadi, M.; Keesstra, S.; et al. The use of barley straw residues to avoid high erosion and runoff rates on persimmon plantations in Eastern Spain under low frequency – high magnitude simulated rainfall events. Soil Res. 2015, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Casalí, J.; Giménez, R.; De Santisteban, L.; Álvarez-Mozos, J.; Mena, J.; Del Valle de Lersundi, J. Determination of long-term erosion rates in vineyards of Navarre (Spain) using botanical benchmarks. Catena 2009, 78, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggisser, O.T.; Schmidt-Entling, M.H.; Bacher, S. Effects of vineyard management on biodiversity at three trophic levels. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navel, A.; Martins, J.M.F. Effect of long term organic amendments and vegetation of vineyard soils on the microscale distribution and biogeochemistry of copper. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466–467, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiquerez, A.; Chevigny, E.; Allemand, P.; Curmi, P.; Petit, C.; Grandjean, P. Assessing the impact of soil surface characteristics on vineyard erosion from very high spatial resolution aerial images (Côte de Beaune, Burgundy, France). Catena 2014, 116, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A. Soil erosion after land abandonment in a semiarid environment of southeastern Spain. Arid Soil Res. Rehabil. 1997, 11, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A. The effect of patchy distribution of Stipa tenacissim aL. on runoff and erosion. J. Arid Environ. 1997, 36, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A. Effect of climate on surface flow along a climatological gradient in Israel: a field rainfall simulation approach. J. Arid Environ. 1998, 38, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A. Relationships between climate and soil hydrological and erosional characteristics along climatic gradients in Mediterranean limestone areas. Geomorphology 1998, 25, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; Giménez Morera, A.; Bodí, M.B.; Burguet, M.; García López, J.; Jovani, C.; Segura, M. Pérdida de suelo y agua bajo cubierta de Quercus Coccifera en la Sierra de Enguera. Valencia. Cuaternario Geomorfol. Rev. Soc. Esp. Geomorfol. Asoc. Esp. Para El Estud. Cuaternario 2010, 24, 11–21. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- De Lima, J.L.M.P.; Singh, V.P. The influence of the pattern of moving rainstorms on overland flow. Adv. Water Resour. 2002, 25, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, J.L.M.P.; Singh, V.P.; de Lima, M.I.P. The influence of storm movement on water erosion: storm direction and velocity effects. Catena 2003, 52, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, A.A.A.; Abrantes, J.R.C.B.; de Lima, J.L.M.P.; Singh, V.P.; Santos, T.E.M. Impact of mulching on soil and water dynamics under intermittent simulated rainfall. Catena 2013, 109, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaez, J.; Lasanta, T.; Ruiz-Flaño, P.; Ortigosa, L. Factors affecting runoff and erosion under simulated rainfall in Mediterranean vineyards. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 93, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, M. Uncertainty of factors determining runoff and erosion processes as quantified by rainfall simulations. Catena 2007, 71, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordán, A.; Martínez-Zavala, L. Soil loss and runoff rates on unpaved forest roads in southern Spain after simulated rainfall. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 255, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, J.; Echeverría, M.T.; Badía, D.; Martí, C.; Álvarez, C.J. Effectiveness of wood chips cover at reducing erosion in two contrasted burnt soils. Z. Für Geomorphol. Suppl. 2013, 57, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, S.; Iserloh, T.; Rock, G.; Hansen, R.; Marzen, M.; Seeger, M.; Betz, S.; Remke, A.; Wengel, R.; Butzen, V.; et al. Soil Erosion on Abandoned Land in Andalusia: A Comparison of Interrill- and Rill Erosion Rates. ISRN Soil Sci. 2012, 2012, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juras, R.; Pavlásek, J.; Ded, P.; Tomásek, V.; Máca, P. A portable simulator for investigating rain-on-snow events. Z. Geomorphol. Suppl. 2013, 57, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassu, T.; Seeger, M.; Peters, P.; Keesstra, S.D. The Wageningen Rainfall Simulator: Set-up and Calibration of an Indoor Nozzle-Type Rainfall Simulator for Soil Erosion Studies. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Hu, Y.; Greenwood, P.; Kuhn, N.J. A Combined Raindrop Aggregate Destruction Test-Settling Tube (RADT-ST) Approach to Identify the Settling Velocity of Sediment. Hydrology 2015, 2, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Tang, Z.; Zeng, G.; Huang, J.; Guo, W.; Chen, X.; Hirsh, A. Effects of water erosion on the redistribution of soil organic carbon in the hilly red soil region of southern China. Geomorphology 2013, 197, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Cornelis, W.M.; Gabriels, D.; Baert, M.; Wu, H.J.; Schiettecatte, W.; Cai, D.X.; de Neve, S.; Jin, J.Y.; Hartmann, R.; et al. Residue cover and rainfall intensity effects on runoff soil organic carbon losses. Catena 2009, 78, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iserloh, T.; Ries, J.B.; Arnáez, J.; Boix-Fayos, C.; Butzen, V.; Cerdà, A.; Echeverría, M.T.; Fernández-Gálvez, J.; Fister, W.; Geißler, C.; et al. European small portable rainfall simulators: A comparison of rainfall characteristics. Catena 2013, 110, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iserloh, T.; Ries, J.B.; Cerdà, A.; Echeverría, M.T.; Fister, W.; Geis sler, C.; Kuhn, N.J.; León, F.J.; Peters, P.; Schindewolf, M.; et al. Comparative measurements with seven rainfall simulators on uniform bare fallow land. Z. Für Geomorphol. Suppl. 2013, 57, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, J.B.; Iserloh, T.; Seeger, M.; Gabriels, D. Rainfall simulations - constraints, needs and challenges for a future use in soil erosion research. Z. Für Geomorphol. Suppl. 2013, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, J.B.; Seeger, M.; Iserloh, T.; Wistorf, S.; Fister, W. Calibration of simulated rainfall characteristics for the study of soil erosion on agricultural land. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 106, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo Comino, J.; Lassu, T.; González, J.M.S.; Sinoga, J.D.R.; Seeger, K.M.; Ries, J.B. Estudio de procesos geomorfodinámicos en campos cultivados de viñedos sobre laderas en pendientes en el valle del Ruwer (Alemania). Cuad. Geográficos 2015, 54, 6–26. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigo Comino, J.; Brings, C.; Lassu, T.; Iserloh, T.; Senciales, J.; Martínez Murillo, J.; Ruiz Sinoga, J.; Seeger, M.; Ries, J. Rainfall and human activity impacts on soil losses and rill erosion in vineyards (Ruwer Valley, Germany). Solid Earth 2015, 6, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Murillo, J.F.; Ruiz Sinoga, J.D. Incidencia de algunas propiedades físicas de suelos en su respuesta hidrológica ante diferentes usos bajo condiciones mediterráneas (Montes de Málaga). Edafología 2003, 10, 57–62. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Prosdocimi, M.; Jordán, A.; Tarolli, P.; Keesstra, S.; Novara, A.; Cerdà, A. The immediate effectiveness of barley straw mulch in reducing soil erodibility and surface runoff generation in Mediterranean vineyards. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, M.C.; Mulligan, M. Spatial modelling of the impact of climate variability on the annual soil moisture regime in a mechanized Mediterranean vineyard. J. Hydrol. 2005, 306, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.C. Soil water content and yield variability in vineyards of Mediterranean northeastern Spain affected by mechanization and climate variability. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 2271–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.C.; Martínez-Casasnovas, J.A. Soil loss and soil water content affected by land levelling in Penedès vineyards, NE Spain. Catena 2007, 71, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.C.; Martínez-Casasnovas, J.A. Impacts of annual precipitation extremes on soil and nutrient losses in vineyards of NE Spain. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.C.; Martínez-Casasnovas, J.A. Effects of field reorganisation on the spatial variability of runoff and erosion rates in vineyards of Northeastern Spain. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, J.O.; Ramos, M.C. Grape harvest and yield responses to inter-annual changes in temperature and precipitation in an area of north-east Spain with a Mediterranean climate. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, M.C.; Benito, C.; Martínez-Casasnovas, J.A. Simulating soil conservation measures to control soil and nutrient losses in a small, vineyard dominated, basin. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 213, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnáez Vadillo, J.; Ruiz Flaño, P.; Lasanta Martínez, T.; Ortigosa Izquierdo, L.M.; Llorente Adán, J.A.; Pascual Bellido, N.E.; Lana-Renault Monreal, N. Efectos de las rodadas de tractores en la escorrentía y erosión de suelos en laderas cultivadas con viñedos. Cuad. Investig. Geográfica 2012, 38, 115–130. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz Colmenero, M. Influencia del empleo de cubiertas vegetales en viñedos en pendiente sobre el control de la erosión. Available online: http://dspace.uah.es/dspace/handle/10017/17161 (accessed on 6 February 2016).
- Ruiz-Colmenero, M.; Bienes, R.; Marques, M.J. Soil and water conservation dilemmas associated with the use of green cover in steep vineyards. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 117, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienes, R.; Pérez, M.J.M.; Colmenero, M.R. Cultivos herbáceos, viñedos y olivares: el manejo tradicional del suelo y sus consecuencias en la erosión hídrica. Cuad. Investig. Geográfica 2012, 38, 49–74. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.J.; Bienes, R.; Cuadrado, J.; Ruiz-Colmenero, M.; Barbero-Sierra, C.; Velasco, A. Analysing perceptions attitudes and responses of winegrowers about sustainable land management in Central Spain. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
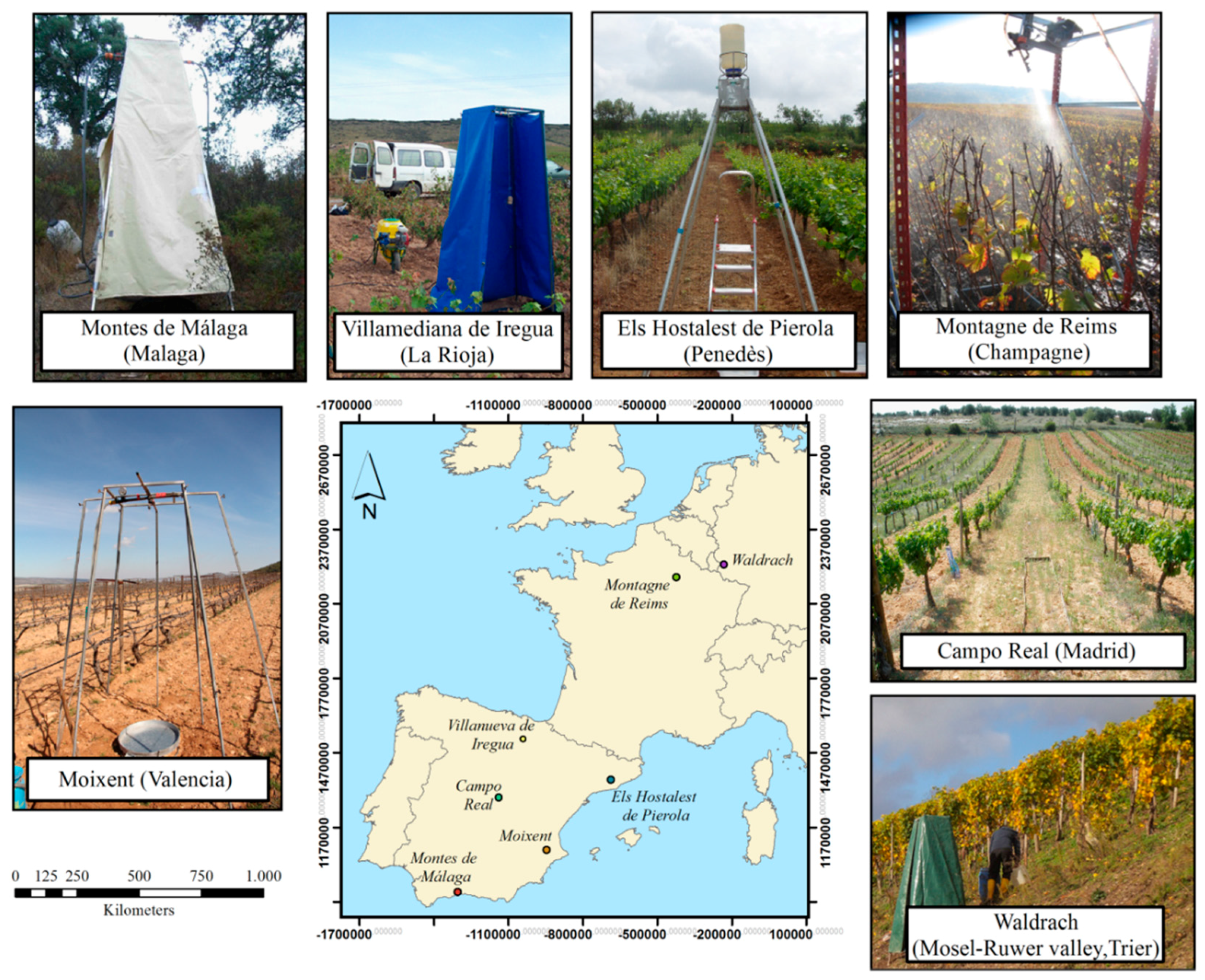
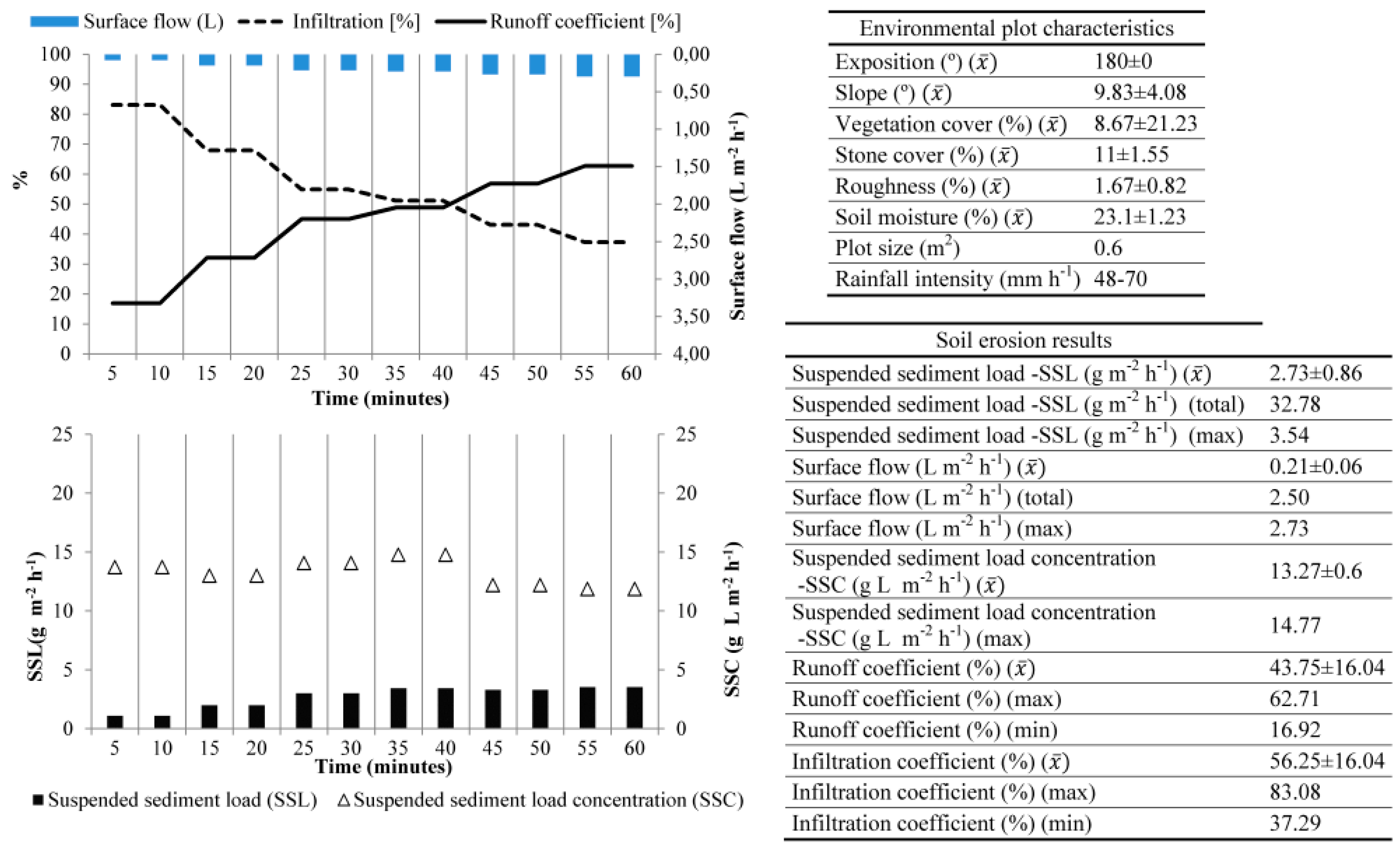
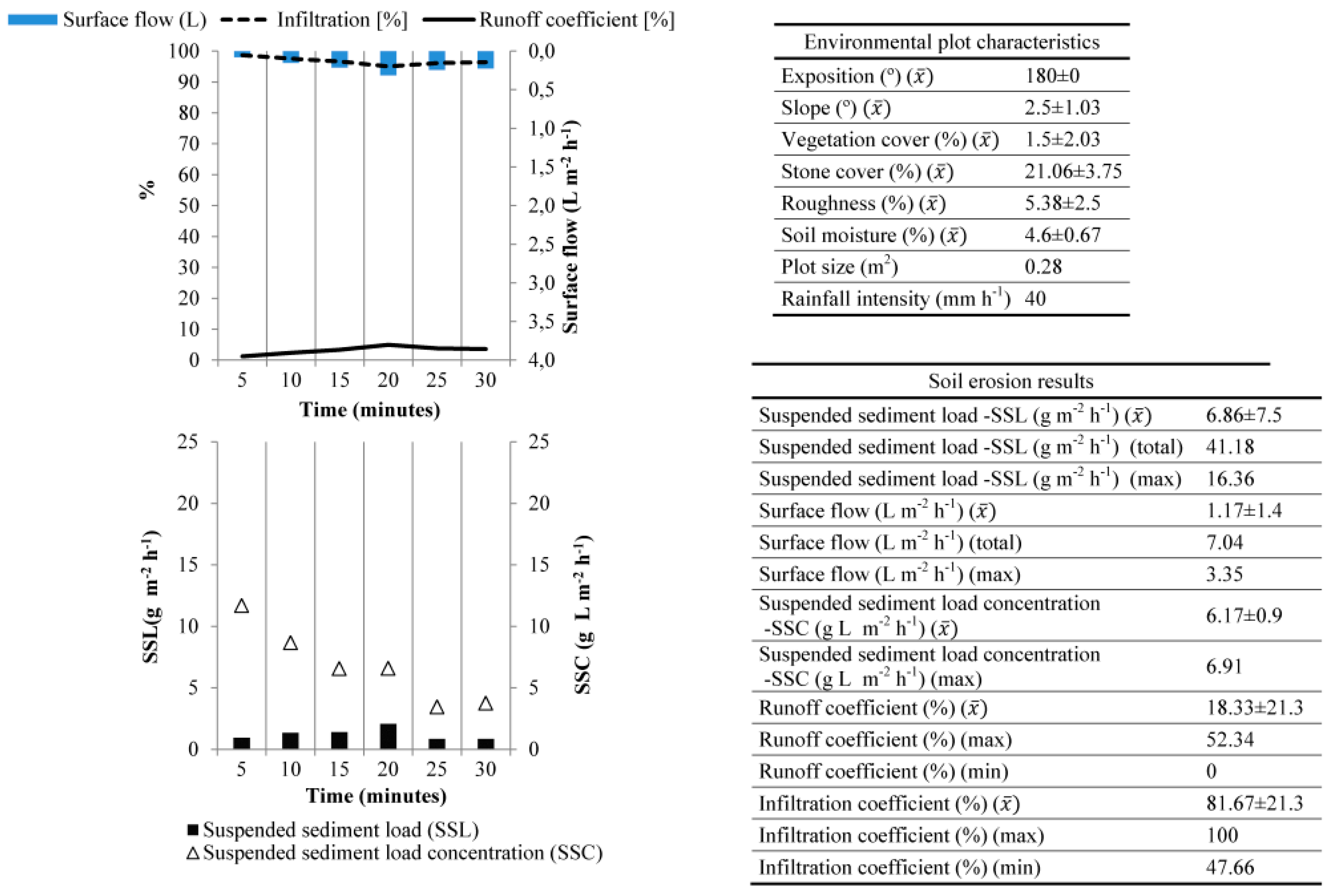
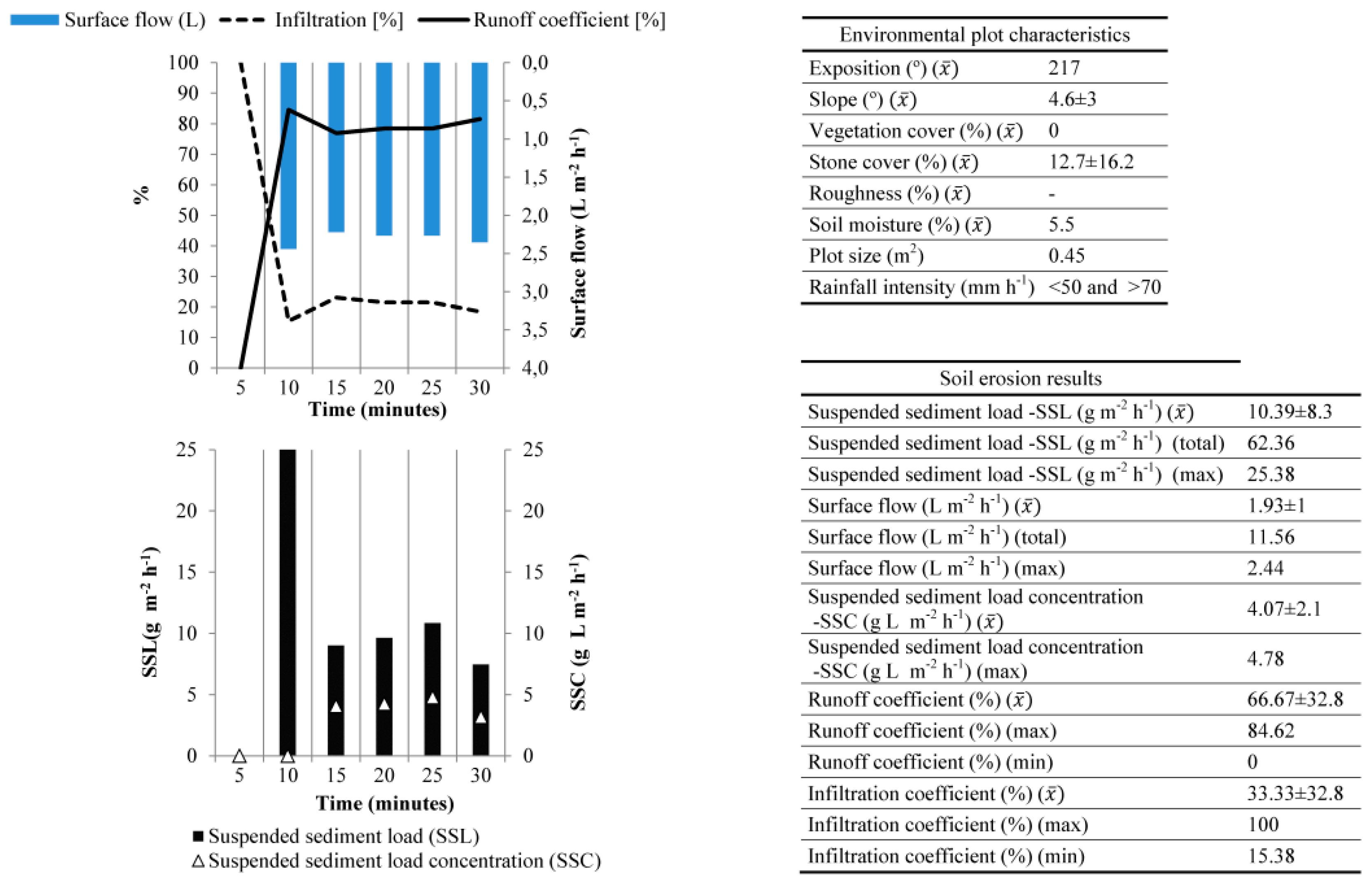
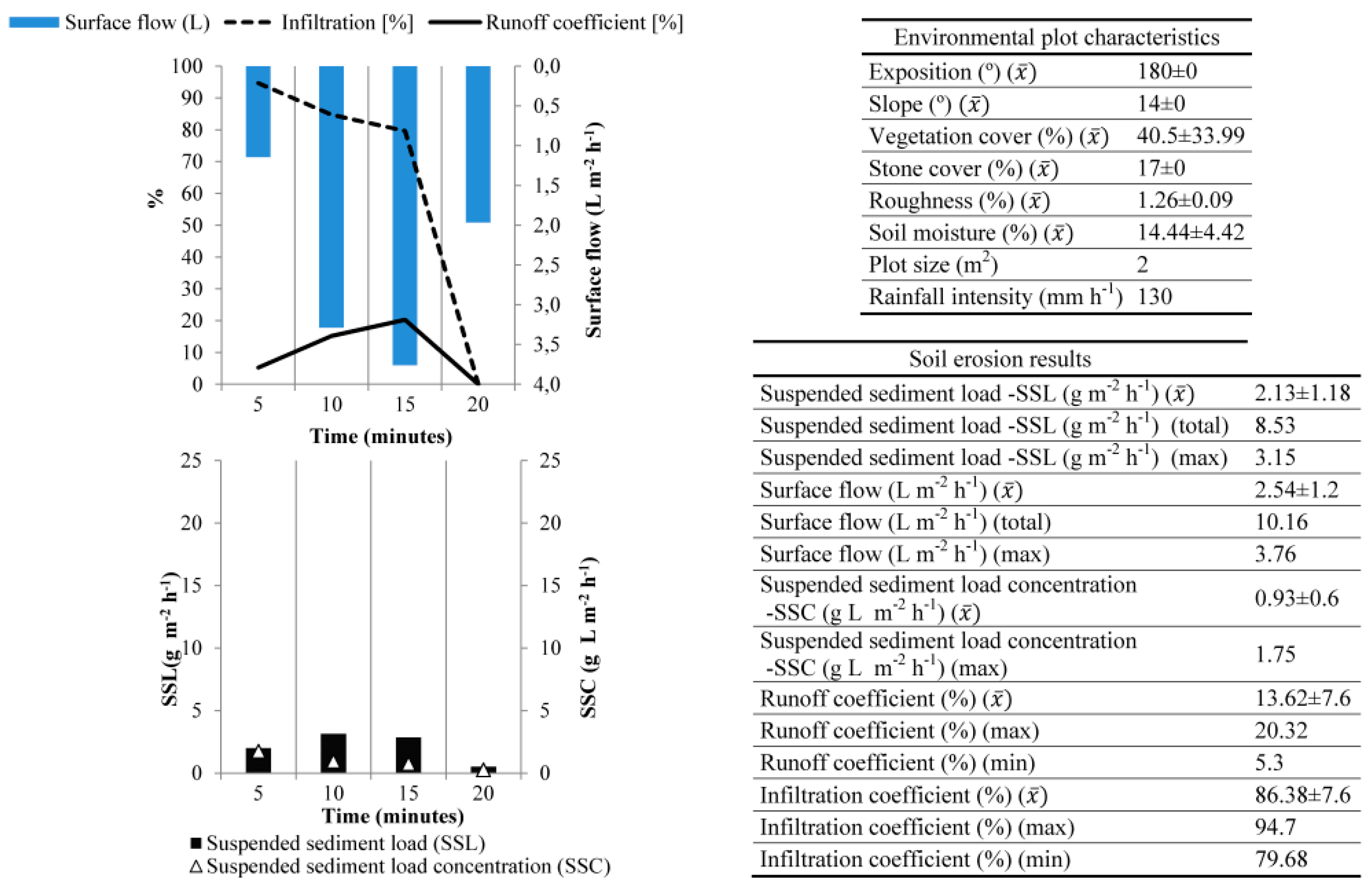
| Place | Ruwer-Mosel Valley (Trier) | Montagne de Reims (Champagne) | Montes de Málaga (Málaga)* | ElsHostalest de Pierola (Penedès) | Moixent (Valencia) | Villamedianade Iregua (La Rioja) | Campo Real (Madrid) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay (%) | 9.4 | 6–12 | - | 10.6 | 8 | 19.9 | 24 |
| Silt (%) | 64.7 | 45–55 | - | 25.8 | 32 | 40.4 | 18 |
| Sand (%) | 26 | 33–45 | - | 63.6 | 60 | 39.9 | 58 |
| SOM7 | 6.1 | 3.9–8.3 | 2 | 1.2 | 1.01 | 0.9 | 1.7 |
| pH | 7.2 | 8 | - | 8.6 | 7.8 | 8.4 | 8.5 |
| Coordinates (WGS 1984) | 49.74N; 6.75E | 49.16N; 4.12E | 36.76N; −4.39E | 41.59N, 1.77E | 38.78N; 0.87E | 42.26N; 2.23 E | 40.35N; −3.37E |
| Altitude (m.a.s.l.) | 220-250 | 170 | 500 | 330-360 | 550 | 425–450 | 820 |
| Grape variety | Riesling | Pinot noir, Pinot meunier and Chardonnay | Muscat of Alexandria | Parellada, Macabeo, Xarello and Chardonnay | Monastrell | Tempranillo | Tempranillo |
| Soiltillage | Machinery, grass/pruning cover | Machinery, grass/pruning cover (ecological and conventional) | Conventional with animals and ploughing | Machiniery and herbicids. | Ploughing | Terrace (1-2 m height), machiniery, soil tillage and herbicids | Machinery |
| T° 1 | 9.3 | - | 15.6 | 15 | 14.2 | 14.6 | 14.4 |
| T° (max_)2 | 17.6 | - | - | 31.4 | 25 | 21.1 | 21,1 |
| T° (min_)3 | 1.5 | - | - | 1.5 | 9.2 | 1.2 | 7.9 |
| Pp (total)4 | 765 | 757 | 586.1 | 520 | 420 | 419 | 371 |
| Pp (max_)5 | 71.2 | 72.9 | - | 76.6 | 42 | 75 | 51 |
| Pp (min_)6 | 50.6 | 33.2 | - | 22.6 | 5 | 42.3 | 9 |
| Flow Control | Nozzle | Electricbilge Pump | Plot | Current Method | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manometer Pressure (bar or kg·cm2) | Type | Head of the Pump (m) | Voltage (V) | Area (m2) | Form | Height (m) | Total Time (min) | Interval (min) | Investigation | |
| Ruwer-Mosel valley Moixent | 0.2 bars | Lechler 460.608 | 4.5 | 12 | 0.28 | Ring | 2 | 30–60 | 5 | Ruwer-Mosel valley: [53,54]. Alforins: [26,56] |
| Campo Real | 1.5 ± 0.2 kg·cm−2 | Spraying systems 1/3 HH 35 W. Two nozzles separated 1.5 m apart | 7 | 6.5 | 2 | Rectangle | 2 | 15 | 1 | [65,66,67,68] |
| Montes de Málaga | - | Hardi 1553-20 | - | - | 0.28 | Ring | 2 | 60 | 5 | [55] |
| Villamediana de Iregua | 20 bars | Lechler 460.728 (<50 mm·h−1) Lechler 460.608 (50–70 mm·h−1) Lechler 460.880 (70 mm·h−1) | - | - | 0.45 | Ring | 2.5 | 30–45 | 3–5 | [39,64] |
| ElsHostalest de Pierola | 2.5 mm diameter drops of deionised water freely | Rainfall intensity was controlled by modifying the water column above the droppers, using an inverted Mariotte’s bottle | - | - | 0.6 | Rectangle | 2.5 | 60 | 10 | [57,58,59,60,61,62,63] |
| Montagne de Reims | 2-3 bars | Teejet 6501- Teejet 6508 | Max. 2.5 m | 220 | 0.25 | Square | 2.5 | 90 | Mostly 10 min | [20] |
| Waldrach (Mosel-Ruwer, Trier) | Montagne de Reims (Champagne) | Montes de Málaga (Málaga) | Els Hostalest de Pierola (Penedés) | Moixent (Valencia) | Villamediana de Iregua (La Rioja) | Campo Real (Madrid) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RI1 | 0.9 ± 1.4 | 0.77 ± 0.1 | 1.83 ± 0 | 0.29 ± 0 | 0.9 ± 1.4 | 0.65 ± 0 | 10.29 ± 0.9 | |
| Plot2 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.6 | 0.28 | 0.45 | 2 | |
| SSL3 | 0.17 ± 0 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 2.44 ± 3.8 | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 0.11 ± 0.2 | 2.58 ± 2.9 | 1.33 ± 0.3 | |
| SF4 | 0.15 ± 0.1 | 0.08 ± 0.1 | 0.15 ± 1 | 0.1 ± 0 | 0.12 ± 0.2 | 1.56 ± 1.6 | 1.37 ± 0.7 | |
| SSC5 | 8.97 ± 2.6 | 1.65 ± 0.2 | 8.44 ± 11.8 | 13.48 ± 0.4 | 2.15 ± 3.8 | 1.35 ± 2.3 | 1.15 ± 0.5 | |
| RC6 | 2.3 ± 1.1 | 3.7 ± 0.9 | 2.3 ± 2.4 | 22 ± 8.8 | 2 ± 3.3 | 53.9 ± 46.8 | 13.6 ± 7.6 | |
| IC7 | 97.7 ± 1.1 | 96.3 ± 0.9 | 97.7 ± 2.4 | 78 ± 8.8 | 98.1 ± 3.3 | 46.2 ± 46.8 | 86.4 ± 7.6 |
| SSL3 | SF4 | SSC5 | RC6 | IC7 | Slope | Vegetation cover (%) | Stone cover (%) | Roughness (%) | Soil moisture (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RI1 | −0.18 | 0.324 | −0.36 | −0.541 | 0.541 | 0.227 | 0.338 | 0.391 | −0.026 | −0.426 |
| Plot2 | 0.482 | 0.519 | −0.185 | 0.593 | −0.593 | −0.449 | −0.368 | −0.823 | 0.395 | 0.044 |
| SSL3 | - | 0.536 | −0.036 | 0.607 | −0.607 | −0.126 | −0.406 | −0.523 | −0.051 | 0.232 |
| SF4 | 0.536 | - | −0.464 | 0.321 | −0.321 | −0.216 | −0.464 | −0.252 | 0.051 | −0.522 |
| SSC5 | −0.036 | −0.464 | - | 0.179 | −0.179 | −0.613 | −0.667 | −0.432 | 0.41 | −0.725 |
| RC6 | 0.607 | 0.321 | 0.179 | - | 0.321 | 0.018 | −0.116 | −0.018 | 0.205 | 0.406 |
| IC7 | 0.541 | −0.593 | −0.607 | -0.321 | - | −0.018 | 0.116 | 0.018 | −0.205 | −0.406 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigo Comino, J.; Iserloh, T.; Morvan, X.; Malam Issa, O.; Naisse, C.; Keesstra, S.D.; Cerdà, A.; Prosdocimi, M.; Arnáez, J.; Lasanta, T.; et al. Soil Erosion Processes in European Vineyards: A Qualitative Comparison of Rainfall Simulation Measurements in Germany, Spain and France. Hydrology 2016, 3, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology3010006
Rodrigo Comino J, Iserloh T, Morvan X, Malam Issa O, Naisse C, Keesstra SD, Cerdà A, Prosdocimi M, Arnáez J, Lasanta T, et al. Soil Erosion Processes in European Vineyards: A Qualitative Comparison of Rainfall Simulation Measurements in Germany, Spain and France. Hydrology. 2016; 3(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology3010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigo Comino, Jesús, Thomas Iserloh, Xavier Morvan, Oumarou Malam Issa, Christophe Naisse, Saskia D. Keesstra, Artemio Cerdà, Massimo Prosdocimi, José Arnáez, Teodoro Lasanta, and et al. 2016. "Soil Erosion Processes in European Vineyards: A Qualitative Comparison of Rainfall Simulation Measurements in Germany, Spain and France" Hydrology 3, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology3010006
APA StyleRodrigo Comino, J., Iserloh, T., Morvan, X., Malam Issa, O., Naisse, C., Keesstra, S. D., Cerdà, A., Prosdocimi, M., Arnáez, J., Lasanta, T., Ramos, M. C., Marqués, M. J., Ruiz Colmenero, M., Bienes, R., Ruiz Sinoga, J. D., Seeger, M., & Ries, J. B. (2016). Soil Erosion Processes in European Vineyards: A Qualitative Comparison of Rainfall Simulation Measurements in Germany, Spain and France. Hydrology, 3(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology3010006












