Numerical Simulation of Typical River Closure Process and Sensitivity Analysis of Influencing Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of the Study Area and Numerical Model
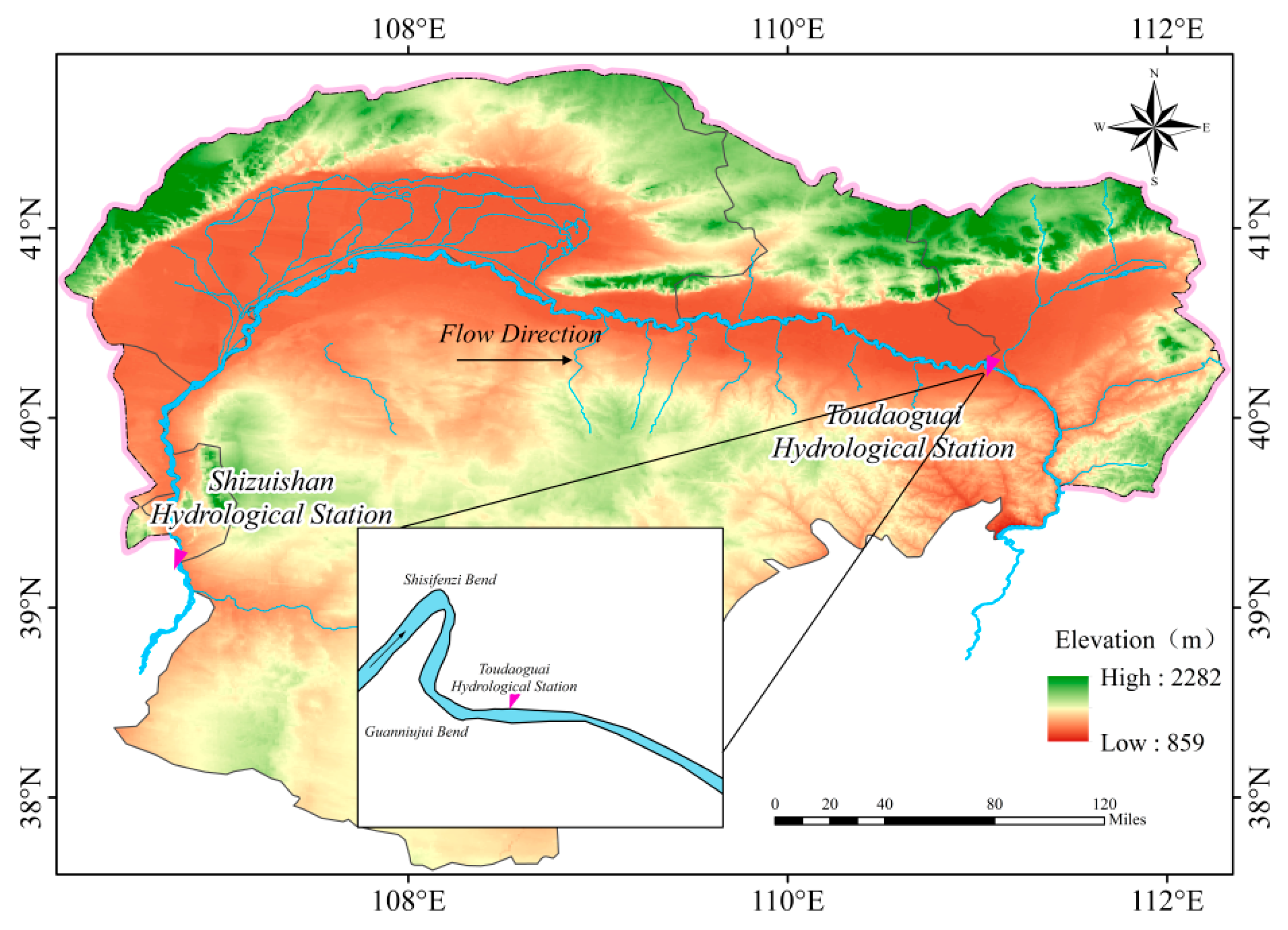
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Numerical Model
2.2.1. Governing Equation
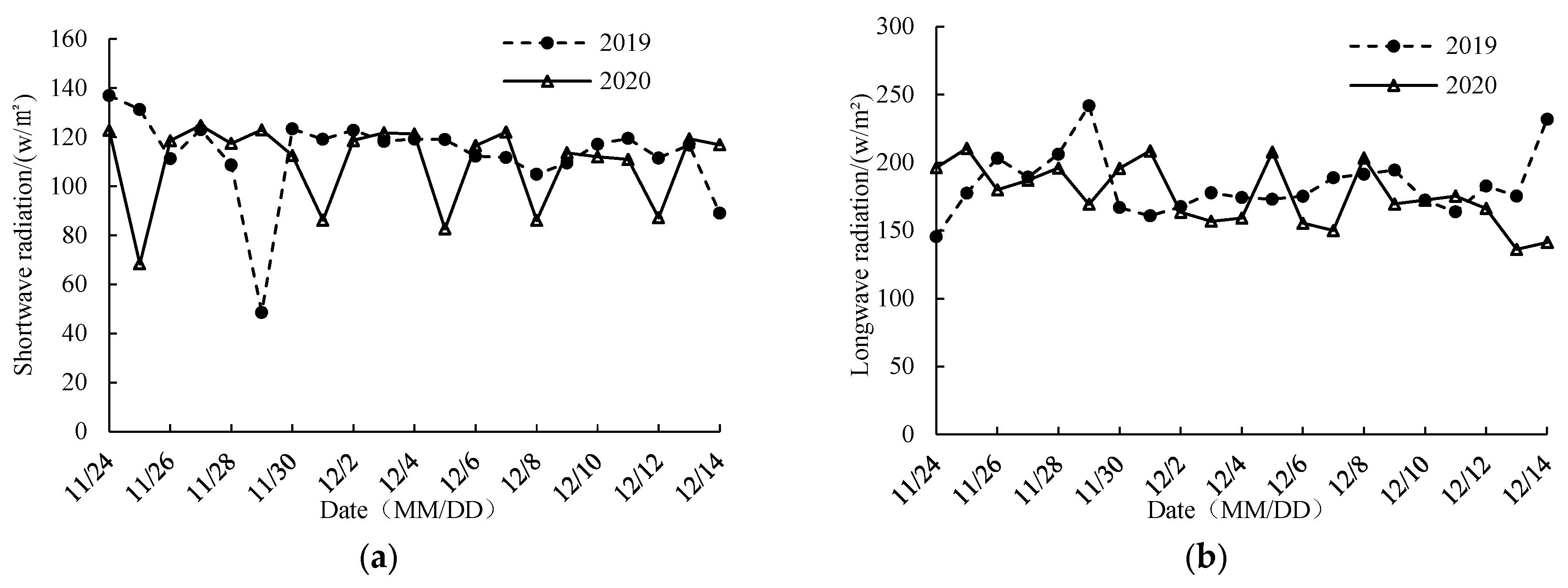
2.2.2. Initial and Boundary Conditions
2.2.3. Model Solution and Time Step
3. Simulation Results and Verification
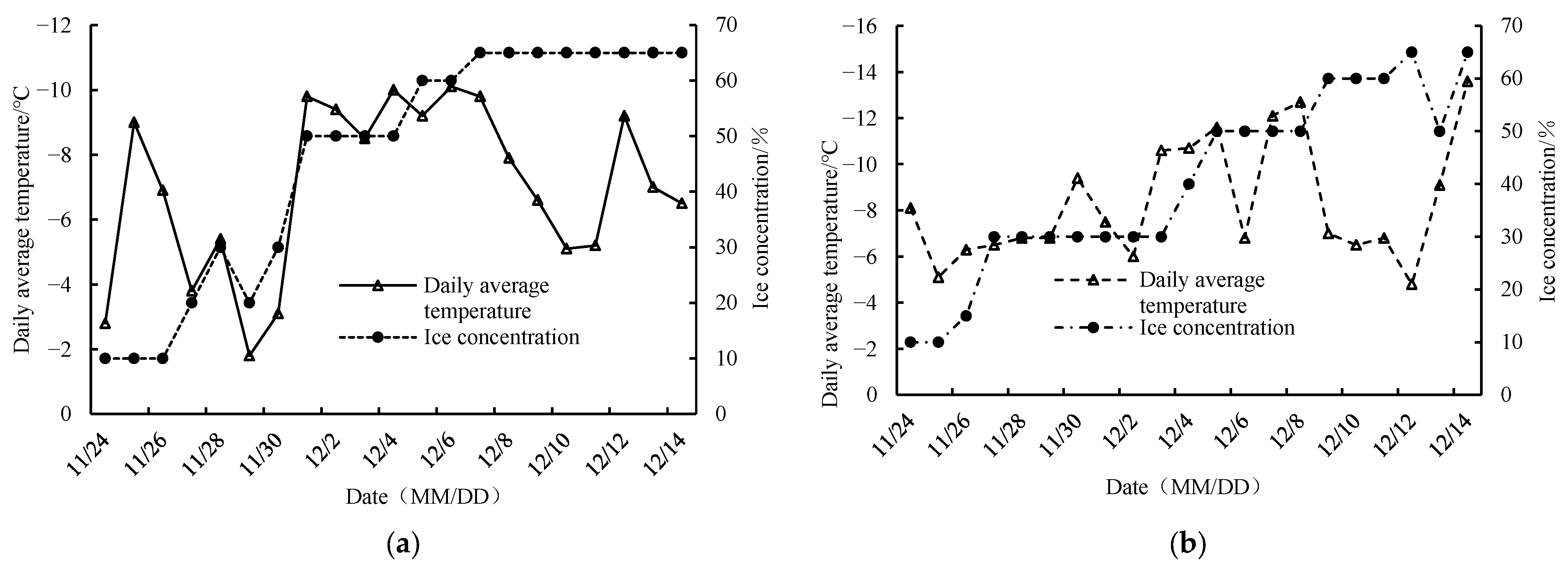
3.1. Ice Process Numerical Simulation Under Thermal-Dynamic Coupling
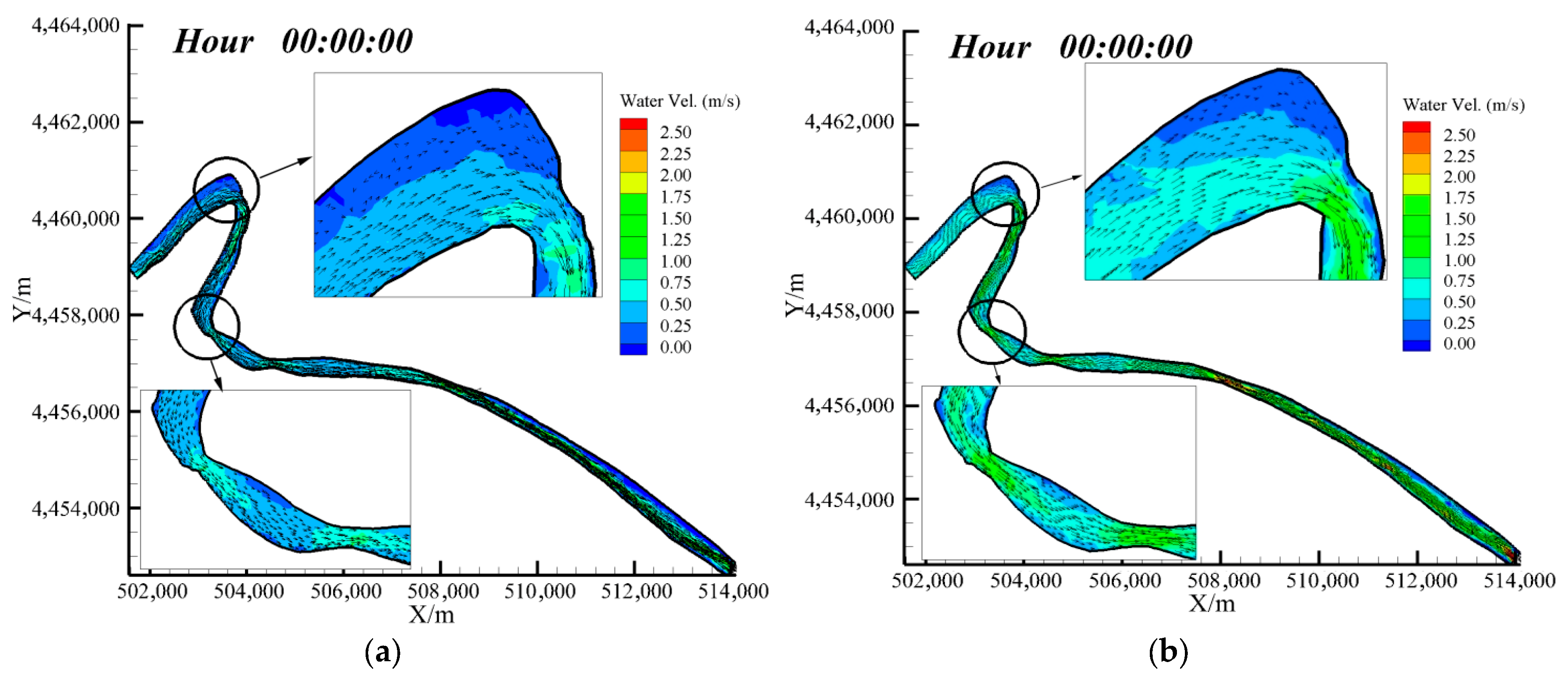
3.2. Water Level Variation Along the Course and Validation of Simulation Result
4. Discussion on Key Parameters of the Model and Sensitivity Analysis
4.1. Hydrodynamic Parameter
4.2. Border Ice Parameters
4.3. Heat Exchange Coefficient
4.4. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beltaos, S. Hydraulics of Ice-Covered Rivers. In Issues and Directions in Hydraulics; Nakato, T., Ettema, R., Eds.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ze, Y.M.; Jian, J.W.; Yun, T.S. River Ice Processes. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2002, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.T. Mathematical modeling of river ice processes. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.T.; Chiang, L. Simulation of growth and decay of river ice cover. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1984, 110, 958–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, G.D. Deterioration of floating ice covers. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 1985, 107, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.T.; Su, J.; Liu, L. SPH Simulation of River Ice Dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 2000, 165, 752–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.T.; Lu, S. Dynamics of River Ice Jam Release. In Cold Regions Engineering: The Cold Regions Infrastructure—An International Imperative for the 21st Century; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Knack, I.M.; Huang, F.; Shen, H.T. A Numerical Model Study on St. Marys River Ice Conditions. In Proceedings of the 21st IAHR International Symposium on Ice, Dalian, China, 11–15 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Shen, H.T.; Knack, I. Modeling Border Ice Formation and Cover Progression in Rivers. In Proceedings of the 21st IAHR International Symposium on Ice, Dalian, China, 11–15 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wazney, L.; Clark, S.P.; Malenchak, J.; Knack, I.; Shen, H.T. Numerical simulation of river ice cover formation and consolidation at freeze-up. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2019, 168, 102884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.B. One-dimensional mathematical models of river ice evolving process. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2011, 22, 78–83+87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Research on Prediction Mathematical Model of Freeze-up of River Ice Cover. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2001, 23, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K. Heat exchange model between river-lake and atmosphere during ice age. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2021, 52, 556–564+577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K. Water temperature models of open channels in glacial period. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2022, 53, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, B.; Liu, L.; Shen, H.T.; Ji, S. A numerical model for river ice dynamics based on discrete element method. J. Hydraul. Res. 2022, 60, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, B.; Shen, H.T.; Liu, L.; Pan, J.; Jia, D. DEM simulation of wave-generated river ice cover breakup. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2024, 218, 104084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.C.; Ji, H.L.; Gao, G.M.; Zhang, B.S.; Mou, X.Y. Study on the characteristics of flow and ice jam formation in Shisifenzi bend in the Yellow River during the freeze-up period. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2020, 51, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Shi, X.; Zhao, S. Processes of river ice and ice-jam formation in Shensifenzi Bend of the Yellow River. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2017, 48, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.K.; Ji, H.L.; Mou, X.Y.; Zhang, B.S. Effects of ice cover on flow and sediment characteristics of the Shisifenzi reach in the Yellow River. J. Sediment. Res. 2021, 46, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhou, R.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Ma, J.; Li, C.; Ma, B. The simulation study of wind erosion characteristics of different soils in Inner Mongolia reach of Yellow River. J. Desert Res. 2020, 40, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Yin, H.; Li, W. Nonlinear thermodynamic analysis of water surface-atmosphere during freeze-up period of the Inner Mongolia reach of the Yellow River. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2021, 32, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.T.; Lu, S.; Crissman, R.D. Numerical simulation of ice transport over the Lake Erie-Niagara River ice boom. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 1997, 26, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, J.J.; Brebbia, C.A. Finite Element Techniques for Fluid Flow; Newnes: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, C.; Shen, H.T. Characteristics of surface ice movement in a channel bend with intake and the layout of ice deflection booms. Adv. Water Sci. 2014, 25, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.T.; Gao, L.; Kolerski, T.; Liu, L. Dynamics of ice jam formation and release. J. Coast. Res. 2008, 10052, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Karney, B.W.; Fang, D. Variation in water level under ice-jammed condition—Field investigation and experimental study. Hydrol. Res. 2005, 36, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L. Study on Characteristics of River Ice Evolution and Numerical Simulation of the Yellow River (Inner Mongolia Reach). Ph.D. Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, B.; Marcotte, N.; Fonseca, F.; Rivard, G. Formation of border ice in the St. Anne River. In Proceedings of the 2nd CRIPE Workshop, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 6–9 June 1982; pp. 38–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Shen, H.T.; Shi, X.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Zhao, S. Winter time surface heat exchange for the Inner Mongolia reach of the Yellow River. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2020, 56, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, A.W.; Shen, H.T. A Mathematical model for river ice processes. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1991, 117, 851–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, J.; She, Y. A comprehensive public-domain river ice process model and its application to a complex natural river. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2019, 163, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, T.L.; Zong, X.X.; Chen, L.Y. Parameter sensitivity analysis methods of Storm Water Management Model. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2022, 41, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Pang, P.C.; Shu, Y.L.; Wang, J. Experimental study of critical condition of ice jam formation in a curved channel. South-to-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 14, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Module | Parametric | Define | Typical Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrodynamics module | River bed roughness | 0.025 | ||
| Drying depth | 0.2 | m | ||
| Wet depth | 0.2 | m | ||
| Density of water | 1000 | |||
| Ice dynamics module | Maximum flow density | 65 | % | |
| Porosity between ice cubes | 0.4 | |||
| Angle of friction within the ice | 46 | ° | ||
| Empirical constant | 15 | |||
| Coefficient of friction between riverbank and ice | 1.04 | |||
| Coefficient of friction between riverbed and ice | 1.04 | |||
| Internal stresses during freezing of ice | 0~100,000 | Pa | ||
| Ice sheet roughness | 0.020 | |||
| Velocity of ice uplift in water | 0.1 | |||
| Water drag coefficient | , when when, , when | |||
| Wind drag coefficient | 0.0015 | |||
| Critical erosion rate of drift ice | 1.5 | |||
| Critical Froude number for the Hydraulic thickening of the ice sheet | 0.09 | |||
| River ice thermodynamic module | Heat exchange coefficient between atmosphere and water surface | 21.38 | ||
| Heat exchange coefficient between atmosphere and ice | 15 | |||
| Heat exchange coefficient between ice and water | 32.547 | |||
| Thermal conductivity of ice | 2.47 | |||
| Thermal conductivity of water | 2.24 | |||
| Thermal conductivity of snow surfaces | 0.3 | |||
| Critical water surface temperature for the formation of border ice | −0.5 | |||
| Critical flow velocities at which static border ice does not form | 0.35 | |||
| Critical flow velocity for non-development of alluvial border ice | 0.5 | |||
| Maximum density of border ice formation | 1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Ma, L.; Li, C.; Yao, Z.; Ji, X. Numerical Simulation of Typical River Closure Process and Sensitivity Analysis of Influencing Factors. Hydrology 2026, 13, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology13010029
Ma L, Li C, Yao Z, Ji X. Numerical Simulation of Typical River Closure Process and Sensitivity Analysis of Influencing Factors. Hydrology. 2026; 13(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology13010029
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Lan, Chao Li, Zhanquan Yao, and Xuefei Ji. 2026. "Numerical Simulation of Typical River Closure Process and Sensitivity Analysis of Influencing Factors" Hydrology 13, no. 1: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology13010029
APA StyleMa, L., Li, C., Yao, Z., & Ji, X. (2026). Numerical Simulation of Typical River Closure Process and Sensitivity Analysis of Influencing Factors. Hydrology, 13(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology13010029






