Abstract
The efficacy of water resource management and protection hinges on a profound understanding of the controlling factors and regulatory mechanisms that shape groundwater chemistry within aquifers. Despite this, our comprehension of how groundwater chemistry and ion sources vary across diverse aquifer types remained limited. To bridge this gap, our study conducted a detailed hydrochemical and statistical investigation of porous, fissured, and karst aquifers. By applying multivariate statistical techniques, including principal component analysis (PCA) and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA), the hydrochemical characteristics and main ion sources of each aquifer type, as well as distinct controlling factors and regulation patterns, were determined. Notably, evaporation predominantly affected the hydrochemistry of porous aquifers, whereas mineral dissolution and rock weathering processes played a pivotal role in shaping the groundwater evolution of fissured and karst aquifers. HCO3− and SO42− are the most common anions of all types, while Na+ is dominant in porous and fissured aquifers and Ca2+ is dominant in karst aquifers. The most common hydrochemical types identified were HCO3-Ca·Mg (accounting for approximately 56.84%) and SO4·Cl-Na (constituting approximately 21.75%). PCA results revealed that lateral recharge from fissured aquifers in hilly regions into the groundwater of porous aquifer, and wastewater discharge and agricultural fertilizer application, significantly impact the groundwater chemistry across all three aquifer types. It is worth noting that the dissolution of carbonate minerals, often influenced by human activities, had a profound effect on the hydrochemistry of each aquifer. Conversely, the dissolution of evaporitic minerals affected groundwater chemistry primarily through cation exchange processes. In summary, the hydrochemical characteristics of these aquifer types were predominantly shaped by a complex interplay of mineral dissolution, cation exchange, evaporation, and anthropogenic activities, with notable contributions from fissured aquifer recharge and pollution. These insights were critical for informing national-level strategies for groundwater resource protection and management.
1. Introduction
Groundwater stands as a pivotal element within the Earth’s precious freshwater reserves, with an impressive 90% of it safely sequestered within aquifers [1,2]. These aquifers, based on their porosity and the distinct characteristics of voids within the water-bearing medium, can be categorized into porous, fissured, and karst aquifers [2,3,4]. Predominantly, porous aquifers consist of gravels, sands, silt, and moderately cemented clays [5], whereas fissured aquifers are composed of diverse hard rocks. Meanwhile, karst aquifers predominantly form within carbonate rocks [6]. Remarkably, despite the extensive research conducted on these aquifer varieties, there remains a significant gap in our understanding of the controlling factors and regulatory mechanisms that shape groundwater chemistry. This knowledge gap is paramount in guiding effective management strategies and guaranteeing the sustainability of the groundwater resources.
The chemical composition of groundwater offers invaluable insights into its development, shedding light on the intricate hydrogeochemical processes that underlie it [7]. When compared to trace ions, which serve as indicators of these processes, variations in major ion concentrations emerge more distinctly, providing a clearer picture of the primary origins of groundwater components [8]. Typically, the pH ranges observed across various aquifer types share similarities, often exhibiting alkaline characteristics [9,10,11]. However, it is important to note that groundwater pH is highly vulnerable to anthropogenic disturbances; for instance, the use of fertilizers and pesticides can significantly lower pH levels. Within groundwater, Na+ and Ca2+ emerge as the predominant cations, while HCO3− and Cl− occupy prominent positions among anions, with other ions appearing in lower concentrations [12,13]. Geological conditions exert a profound influence on the concentrations and composition of these ions. For instance, seawater intrusion can lead to a significant elevation in levels of TDS, Na+, Mg2+, K+, and Cl− within porous aquifers [14]. In both porous and fissured aquifers, Ca-HCO3 emerges as the prevalent water type, exhibiting strong correlations between Cl− and Na+, as well as between NO3− and SO42− [5]. Karst aquifers, distinguished by their unique geological structures and dissolution dynamics, are primarily shaped by carbonate mineral dissolution, ion exchange, and external water inputs such as seawater intrusion and fracture upwelling. These processes result in elevated concentrations of Ca2+, Mg2+, and HCO3− [15]. These observations underscore the intimate relationship between groundwater chemistry and the geological and evolutionary contexts of various aquifer types. Hence, a comprehensive and meticulous analysis of the groundwater’s chemical attributes, along with the primary origins of its constituents across these three aquifer types, is immensely valuable for precisely depicting the present condition of the groundwater environment and for discerning avenues towards its efficient regulation and stewardship.
Extensive research has conclusively shown that both natural and anthropogenic factors exert a considerable influence on the chemical composition of groundwater. Natural processes, including evaporation driven by climatic conditions, rock weathering, mineral dissolution, and cation exchange, play a crucial role in shaping groundwater chemistry. Simultaneously, anthropogenic activities such as the discharge of industrial and domestic wastewater and the application of agricultural fertilizers have a profound impact on groundwater quality [14,16,17]. Within the complex matrix of porous, fissured, and karst aquifers, cation exchange and the dissolution of minerals like calcite, dolomite, and gypsum emerge as primary hydrogeochemical processes [18]. Agricultural practices, specifically the use of nitrogenous fertilizers, and domestic sewage discharge contribute to increased concentrations of NO3− in groundwater, posing potential health and environmental risks [19,20]. However, it is important to note that there exist distinct differences in the hydrogeochemical processes and controlling factors among various aquifer types. The dissolution of minerals, particularly carbonates, plays a pivotal role in determining the chemical properties of groundwater [21,22]. In karst aquifers, the aquifer matrix itself is a key determinant, as the dissolution of carbonate minerals leads to elevated concentrations of Ca2+, Mg2+, and HCO3− [15,23]. Conversely, porous aquifers exhibit relatively simpler hydrochemical characteristics, often dominated by Ca·Mg-HCO3 types, reflecting limited water–rock interaction. The solutes in groundwater within these aquifers are primarily derived from rock weathering and evaporation processes [24]. The evaporation process, in particular, contributes to the enrichment of salts in groundwater, thereby influencing its overall chemical composition [25]. Therefore, a comprehensive evaluation of water chemical properties is essential to identify and quantitatively assess the controlling factors and potential sources of ions, providing valuable insights for effective groundwater management and protection strategies.
Currently, there are many research methods for the chemical evolution of groundwater, and multivariate statistical analysis techniques have been widely used in regional-scale groundwater chemical analysis. Techniques such as Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA) help to identify the major hydrogeochemical processes, group similar water types, and realize the downscaling of the data by extracting the major components among them [26,27], and infer the underlying natural and anthropogenic processes that control groundwater chemistry. The dissolution processes of some minerals are understood by calculating the mineral saturation index (SI), as well as cation exchange processes [28]. Geographic Information System (GIS) is widely used to visualize the spatial and temporal distribution of chemical ions in groundwater [29]. The application of these methods has helped to improve the accuracy of geographic distribution and sources of water chemical ions in different aquifers.
China’s diverse natural geographical landscapes and intricate geological structures have given rise to a wide array of groundwater systems across its vast regions. Notably, the distribution of porous, fissured, and karst aquifers varies distinctly. Porous aquifers, for instance, are predominantly present in the expansive plains of China, with the North China Plain emerging as a prime example. On the other hand, fissured aquifers tend to occur in mountainous and hilly terrains, while karst aquifers are predominantly scattered within the southwestern karst regions. Currently, most of the studies on the chemical characteristics of groundwater focus on aquifers in specific regions within China, and there is still a lack of research on the comprehensive comparison of the chemical characteristics of different aquifers and their evolutionary patterns throughout the country. This comprehensive study aims to delve into the spatial patterns of groundwater chemistry within these three aquifer types at a national level, focusing specifically on the aquifer media types. Moreover, it seeks to unravel the impact of geological factors and hydrogeochemical processes, including mineral dissolution, on these aquifers. The primary objectives of this study are twofold: (1) to examine the spatial distribution of groundwater chemistry in different aquifer types across various regions of the country; and (2) to investigate the driving forces and regulatory mechanisms influencing groundwater chemistry in these aquifers. The insights gained from this study are expected to enhance our understanding of sustainable groundwater conservation and management practices at the national scale.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.1.1. Geographical Conditions and Climate
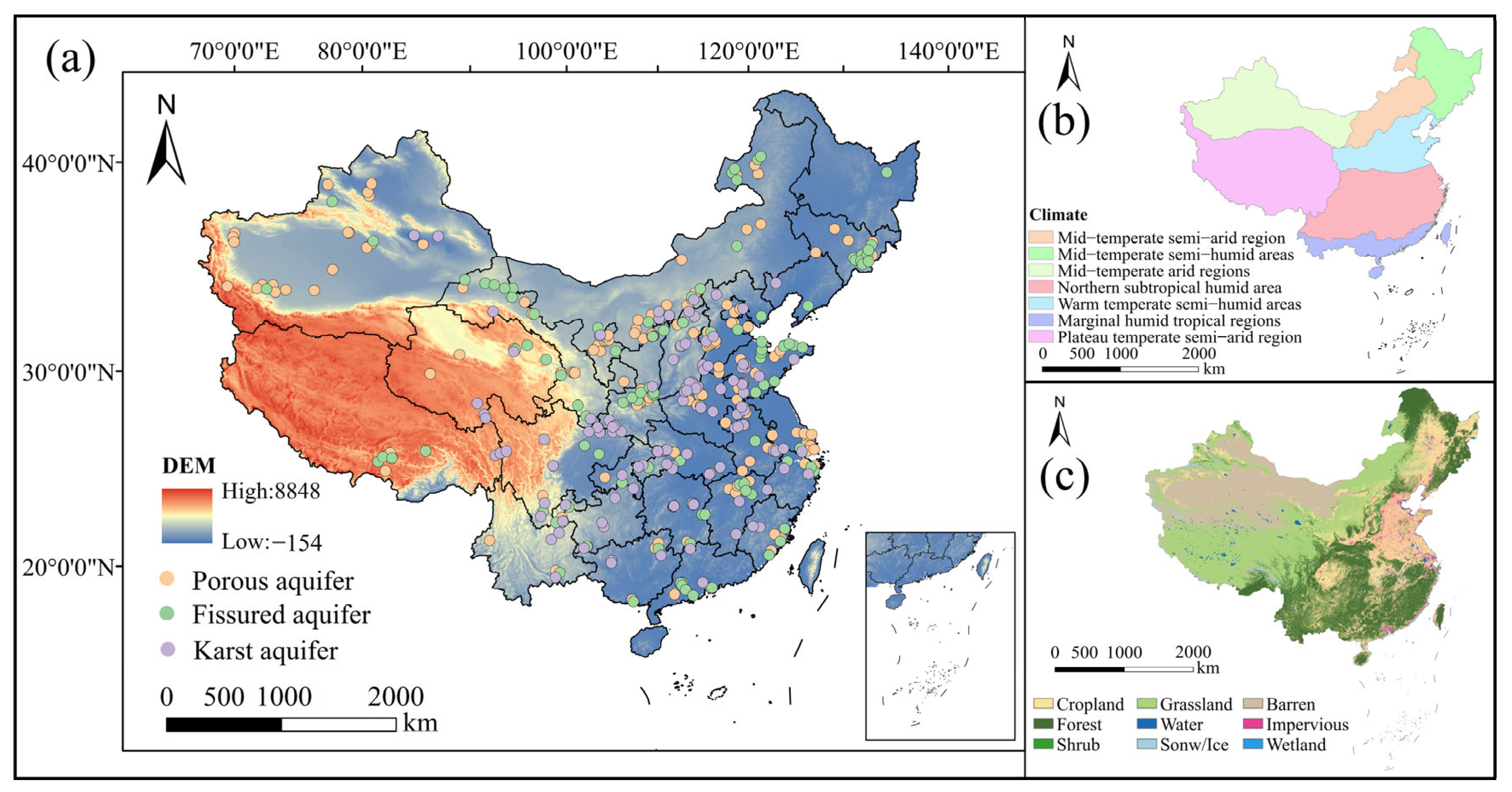
China is located in eastern Asia, on the west side of the Pacific Ocean, between longitudes 73°33′ E and 135°05′ E and latitudes 3°51′ N and 53°33′ N. The land area is about 9.6 million km2. Topographically, China’s terrain is complex and varied, dominated by mountains, plateaus and hills, with the terrain high in the west and low in the east, distributed in a three-tiered gradient (Figure 1a), including 33.3% mountains, 26% plateaus, 18.8% basins, 12% plains and 9.9% hills. The western terrain is dominated by mountains and basin plateaus. The central terrain is dominated by plateaus, and mainly the flowing water erosion landforms of the Loess Plateau in the north. The eastern terrain is dominated by plains, mostly sedimentary alluvial plains. The study area is located in the East Asian monsoon region, which is significantly influenced by the monsoon. In terms of temperature types, there are different divisions such as tropical, subtropical, warm-temperate, mesothermal, cold-temperate and Tibetan Plateau zones. In terms of wet and dry conditions, there are humid, semi-humid, semi-arid and arid regions. The average annual temperature in the study area is about 11.2 °C, while the average annual precipitation is 642 mm. Interannual variations in temperature and precipitation are large, with the spatial distribution of annual precipitation decreasing from southeast to northwest, and the average annual temperature decreasing from south to north.
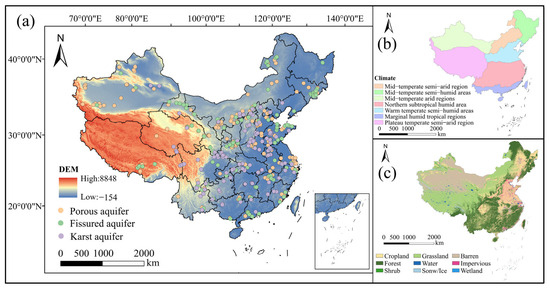
Figure 1.
(a) Study area and distribution of groundwater sampling sites, (b) climate zoning map of the study area, (c) land-use types in the study area.
2.1.2. Hydrogeological Condition and Land-Use Types
China’s hydrogeological distribution has obvious regional differences, mainly influenced by topography, climate and geological structure. The eastern plains (North China, Northeast China, and the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River) are dominated by loose sedimentary strata, and the lithology is dominated by sand and gravel strata; loose rock pore water is abundant, but over-exploitation is serious in some areas. In the western arid region (Xinjiang, Gansu, Qinghai), groundwater is mainly stored in granite, metamorphic rocks and other fissures and sedimentary layers in the basin, mainly in sand and gravel layers and bedrock fissure water, relying on glacial meltwater recharge, and water resources are scarce and unevenly distributed. The southwestern karst region (Guizhou, Guangxi, Yunnan) is dominated by carbonate rocks, with complex water flow channels and abundant but unevenly distributed groundwater. The Qinghai–Tibet Plateau and mountainous areas (Tianshan Mountains, Qinling Mountains and Greater Khingan Mountains) are mainly dominated by glaciers, lakes and bedrock fissure water, with small reserves, and recharging is dependent on precipitation and glacial meltwater. The central mountainous and northeastern regions are dominated by bedrock fissure water and loose sedimentary layers, respectively.
China has a distribution of multiple tectonic units and strata of different geological ages, ranging from Precambrian basement rock systems to Cenozoic sedimentary basins. Porous aquifers are mainly distributed in large quaternary alluvial plains such as the North China Plain, Songliao Plain, and Yangtze River Delta. They are composed of loose quaternary sediments (such as sand, gravel, silt and clay), and the lithology is mainly alluvial and diluvial. They are usually phreatic or weakly confined aquifers, with a burial depth of generally 10–100 m, a cover layer thickness of less than 50 m, good permeability, slow groundwater flow rate, and good shallow groundwater storage and migration conditions. Groundwater is mainly recharged through vertical seepage from precipitation and agricultural irrigation, and lateral flow of bedrock groundwater in hilly and river areas during the rainy season [30]. The mean residence times are short, generally from a few months to a few years [31]. It is widely distributed in densely populated areas with frequent agricultural activities and is significantly affected by human activities.
Fissured aquifers are mainly developed in weathered and broken bedrock such as granite, basalt, gneiss and schist [32]. They are confined or weakly confined aquifers and are distributed in the igneous and metamorphic mountains of the Taihang Mountains, Qinling–Dabie Mountains, parts of the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau, and the arid areas of the northwest (such as the Qilian Mountains and the Tianshan Mountains). Their burial depth varies greatly (30–200 m), and permeability mainly depends on the development of fractures. The mean residence times are several years to several decades [33]. The recharge source is precipitation infiltration and lateral runoff. It is common in hilly or mountainous areas with a small population.
Karst aquifers are widely distributed in the southwest, including Guangxi, Guizhou, Yunnan, and parts of Hunan and Sichuan. They are mainly developed in Paleozoic limestone and dolomite [34]. This type of aquifer is a non-confined aquifer. The rock mass is dissolved for a long time to form complex groundwater circulation systems, such as caves, sinkholes, underground rivers, etc., with highly uneven permeability. The burial depth is usually more than 100 m, and the thickness of the cover layer varies greatly. The mean residence times vary greatly, ranging from a few days to several decades [34,35]. The recharge mainly comes from precipitation and sinkholes, with fast flow but complex flow directions. The degree of human activities in the karst outcrop area varies greatly, and agriculture and rural development have a significant impact on it.
More than 70% of the land in the study area has been developed and utilized, and at this stage the developed land-use types are mainly arable land, forest land, grassland, water and construction land, while the remaining land types that are difficult to develop and utilize are mainly bare land, glacier, tundra, etc. (Figure 1c). Forests are mainly located in the south and the northeast, and agricultural land is the main source in the east. Forests are mainly distributed in the south as well as in the northeast, with barren land dominating in the northwest and farmland in the east. Along with economic and social development, the pattern of land use has been changing.
2.1.3. Coastal Aquifers and River–Groundwater Interaction
Some of the porous, fissured and karst aquifers in the study area are located in coastal areas, mainly along the coast of Bohai Bay, the Yangtze River Delta, and the southeastern coastal areas of Fujian and Guangdong, etc. Restricted by the overexploitation of groundwater resources and insufficient natural recharge [36], the aquifers in these areas are susceptible to seawater intrusion, which significantly alters groundwater salinity, hydrochemical characteristics and major ionic compositions [14,37]. In addition, the aquifers are clearly hydraulically connected to the major river systems of the Yellow, Yangtze and Pearl Rivers in the region. Through the processes of bankside percolation, seasonal flooding and river recharge, surface water bodies may not only transport dissolved substances to the groundwater system, but also change its redox environment, which in turn has an important impact on the hydrochemical evolution of groundwater.
2.2. Search Strategy
Groundwater data of different aquifers across China were collected from websites such as Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure and China Wanfang Literature Database. The papers on groundwater data of different aquifers in China from 1991 to 2024 were collected by searching the keywords “China”, “groundwater chemistry”, “aquifer”, “porous aquifer”, “fissured aquifer” and “karst aquifer”. A total of 15 water chemistry parameters were collected, including pH, EC, TDS, F−, NH4+, NO2−, TH, major cations (e.g., Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+) and anions (e.g., Cl−, SO42−, HCO3−, NO3−). However, not all papers reported all these parameters. If some parameters were missing, these samples were excluded from the analysis, which required complete data. For the parameters used in the main statistical or graphical analysis, consistency between data sets was ensured. Finally, 10 groundwater chemical parameters (Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl−, SO42−, HCO3−, NO3−, pH and TDS) were determined for analysis.
The qualifying criteria for the included literature include the following: (a) the study objects are porous aquifers, fissured aquifers and karst aquifers, including pore water, fissure water and karst water; (b) the study area is within the territory of China; (c) the latitude and longitude coordinates of the sampling points are recorded; (d) the average content or median value of the hydrochemical parameter is specific or can be obtained by calculation; (e) the sampling process and the analytical method are strictly in accordance with scientific procedures; and (f) the year is based on the year of sampling. If the year of sampling is not mentioned, the date of receipt of the manuscript will be used. If neither was mentioned, the date of publication of the full paper was used. Finally, 140 documents were identified, and the samples collected were groundwater samples collected multiple times from 2010 to 2024, with a total of 28,351 sampling points. A total of 462 sets of water samples were taken, including 192 sets from porous aquifers, 129 sets from fissured aquifers and 141 sets from karst aquifers, covering both dry and rainy seasons. Included were 19,507 samples of porous aquifers, 5506 samples of fissured aquifers and 3338 samples of karst aquifers. According to the different types of aquifers, the groundwater data in the papers about each province and city in China were counted, and the latitude and longitude coordinates of the sampling points were recorded.
Groundwater chemical parameters were mainly determined by the following methods: major cations (K+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+) were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). HCO3− was determined by acid–base titration, and anions (Cl−, SO42−, NO3−) were determined by ion chromatography (IC). pH values were measured on site using a calibrated portable meter, and total dissolved solids (TDS) were determined gravimetrically. The charge balance error of each sample was calculated, and water chemical sample data with an error within ±5% were retained.
2.3. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis
Hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) is a multivariate statistical method used to analyze multidimensional water chemistry datasets. It can classify groundwater into groups that are similar to each other and cluster chemical components from different sources [38,39,40]. To ensure that each parameter is equally weighted, all input parameters used for HCA are normalized. HCA technology reduces the data to a single cluster containing all individuals. It starts with each instance in its cluster and gradually links the clusters together until only one cluster remains [41]. In this study, Ward’s systematic cluster analysis method was applied. The distance between samples was measured by squared Euclidean distance [42]. The groundwater samples from three types of aquifers were analyzed separately, and cluster dendrograms of hydrochemical indicators were obtained. Dendrograms are widely used to display hierarchical clustering and linkage distances. By constructing dendrograms, the cohesion and correlation between hydrochemical parameters and groundwater samples can be observed. The clustering results show strong consistency within the clusters and significant differences between different clusters [43]. HCA was implemented using SPSS 27.0.
2.4. Principal Component Analysis(PCA)
Principal component analysis can be used to identify relevant factors affecting the evolution of groundwater chemistry [44,45,46]. Prior to generating the principal components, the Z-Score method in SPSS software was used to standardize the data based on the mean and standard deviation of the raw data (Equation (1)) to ensure that each variable was equally weighted [44]. PCA was then performed using SPSS software. Factor rotation was performed using the maximum variance method to extract factors with eigenvalues greater than 1 [47], and factors with eigenvalues greater than 1 explained more of the total variance than individual groundwater quality variables and were considered significant to select for data interpretation [45].
The Z-Score standardization method was calculated using the following formula:
where zi represents the standard score of sample i, xi is the value of sample i, is the mean of all samples under this parameter and s is the standard deviation [13].
The mathematical formula for PCA is expressed as
where Z = component score; α = component loading; X = measured value of the variables; i = number of components; j = number of samples; and m = total number of variables [48].
2.5. Saturation Index (SI) and Chloroalkaline Indices (CAI)
The saturation index is an important indicator of whether the minerals in groundwater are saturated or not, and changes in SI values can be used to identify the hydrochemical evolution occurring in groundwater and the dissolution of minerals [22,49]. Mineral saturation indices were calculated using PHREEQCI software [50] to evaluate the effect of dissolution of minerals on the groundwater chemistry of different aquifers and mineral saturation status [51].
The Saturation Index (SI) of a mineral is calculated using the following formula:
where IAP is the ionic activity product of the mineral and K is the equilibrium constant of the solubility product at temperature T. When SI > 0, it indicates that the groundwater is supersaturated, leading to precipitation; when SI < 0, it signifies that the groundwater is unsaturated, resulting in the dissolution of minerals; and when SI = 0, it means that the groundwater is in equilibrium with the dissolved minerals in the aquifer [51,52].
Certain cations adsorbed on the geotechnical surface can be ion-exchanged with certain cations in the groundwater, and the chlor-alkali indices (CAI-I and CAI-II) determine the manner and extent of cation exchange in groundwater [48], calculated using Equations (4) and (5). When the CAI value is negative, then forward cation exchange is carried out (Equation (8)), where Ca2+ and Mg2+ in the groundwater exchange Na+ and K+ in the aquifer minerals, and reverse cation exchange is carried out when the CAI value is positive (Equation (9)), where Na+ and K+ in the groundwater exchange Ca2+ and Mg2+ in the aquifer minerals [53,54].
2.6. Structural Equation Modeling
SEM is a comprehensive statistical analysis method used to test hypotheses about the relationships between observed variables and latent variables, which can be employed to understand the covariant relationships among variables [55]. It is categorized into measurable and latent variables and includes measurement and structural models, where measurement models refer to the relationship between observable indicators and latent variables, while structural models are the links between variables [56,57]. The path coefficient between the latent variable and the dependent variable represents the standardized regression coefficient, and the larger the path coefficient, the greater the effect of the latent variable on the dependent variable [55].
In order to clarify the pathways of different influencing factors on the groundwater chemistry of the aquifer, it was analyzed by structural equation modeling. Four categories of factors, namely mineral dissolution (carbonate minerals, evaporite minerals), cation exchange, evaporation, and human activities, were selected as influencing factors to be analyzed. After obtaining the final acceptable model, it was ensured that the assumptions of normality and linearity were met. Several metrics—chi-square (χ2), generalized fit index (GFI), root-mean-square error of approximation (RMSEA), chi-square minimum discrepancy (CMIN) and degree of freedom (DF)—were used to assess the effectiveness of the SEM fit [57].
χ2 was used to assess the significance of differences between multiple constructed models, and GFI was used to assess the fit of the model to the sample observations, with a fit value between 0 and 1. RMSEA is a composite indicator that integrates the mean and variance of the fit metrics, and the smaller the value, the better, and a value of RMSEA higher than 0.1 indicates that the model is poorly fitting; usually, RMSEA ≤ 0.08 is considered a well-fitted model [55]. Where the value of CMIN/DF is less than 3, the values of the other indices are close to 1, indicating a well-fitted model [58].
3. Results
3.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Classification of Groundwater
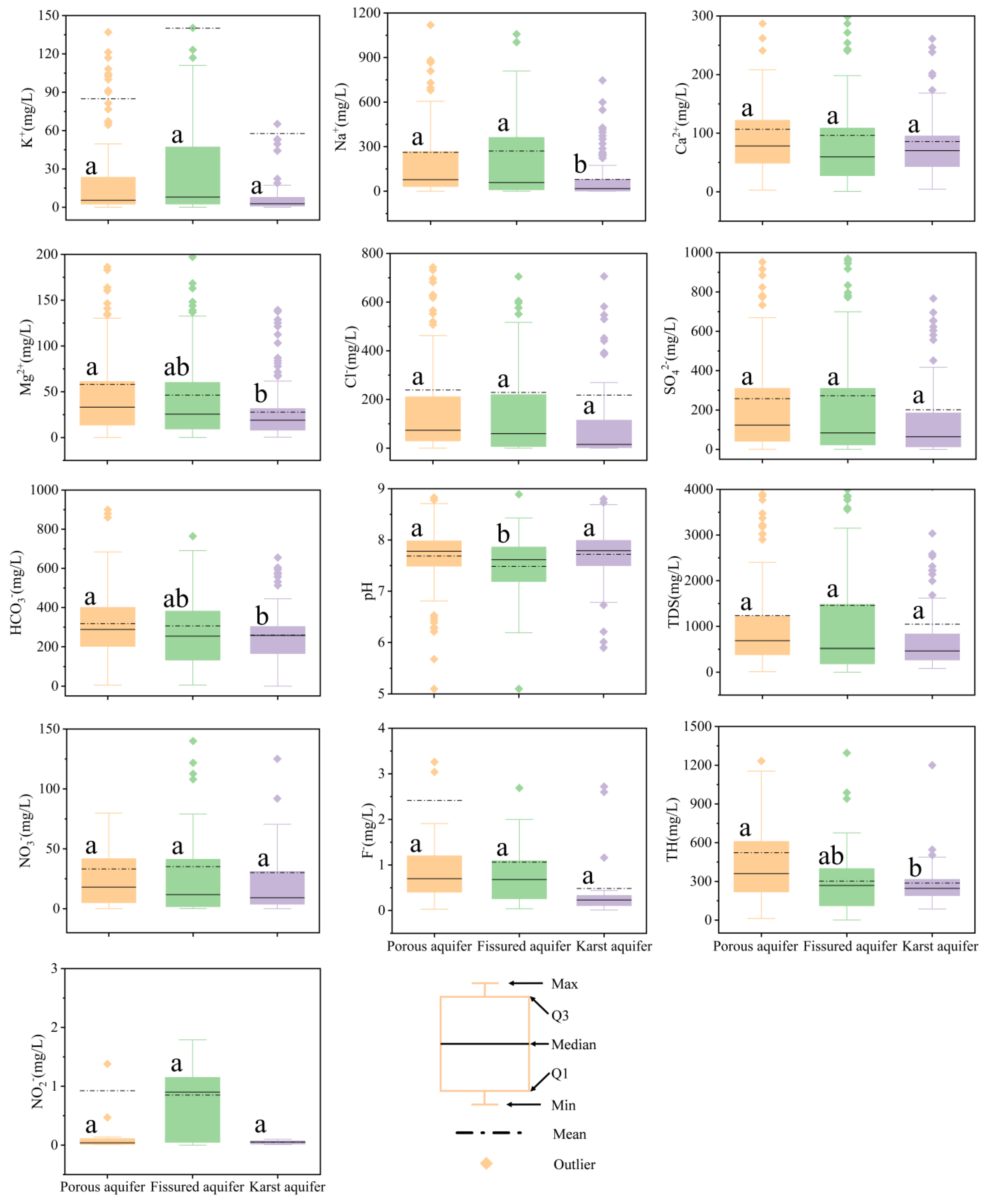
The order of cation concentration (mg/L) dominance varied slightly between aquifers, with Na+ > Ca2+ > K+ > Mg2+ in porous aquifers, Na+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+ > K+ in fissured aquifers and Ca2+>Na+>K+>Mg2+ in karst aquifers. In the three types of aquifers, the overall anion concentration (mg/L) was HCO3− > SO42− > Cl− > NO3− > F− > NO2−. The pH values of groundwater samples from the three types of aquifers ranged from 5.1 to 9.37, with an average value of 7.64, and were weakly alkaline overall (Figure 2). Among them, the pH values of the porous aquifers and karst aquifers were slightly higher than those of the fissured aquifers. The pH values were 7.69, 7.72 and 7.48, respectively. The total dissolved solids (TDS) value of the fissured aquifer was the highest (average value of 1565.49 mg/L), higher than that of the porous aquifer (average value of 1236.07 mg/L) and the karst aquifer (average value of 1047.2 mg/L). The average concentrations of K+, Na+ and SO42− were the highest in the fissured aquifer, while the average concentrations of Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl− and HCO3− in the porous aquifer were higher than those of the other two types of aquifers.
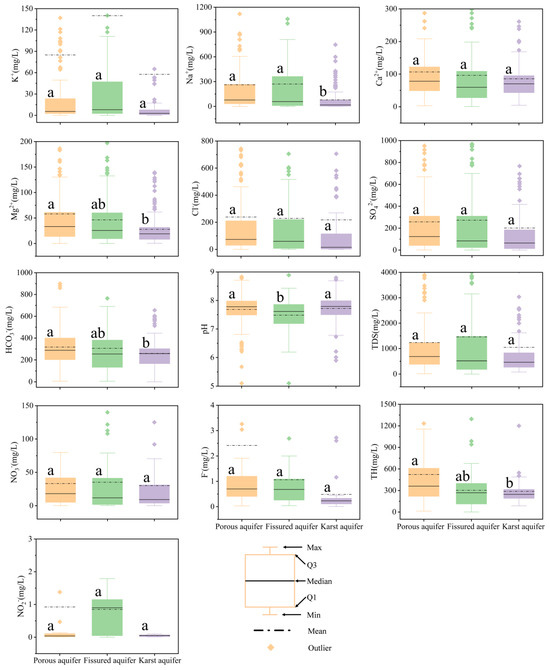
Figure 2.
Box plots of groundwater parameters for different types of aquifers. The same letter indicates significant differences in the same water chemical ions in different aquifers (p < 0.05).
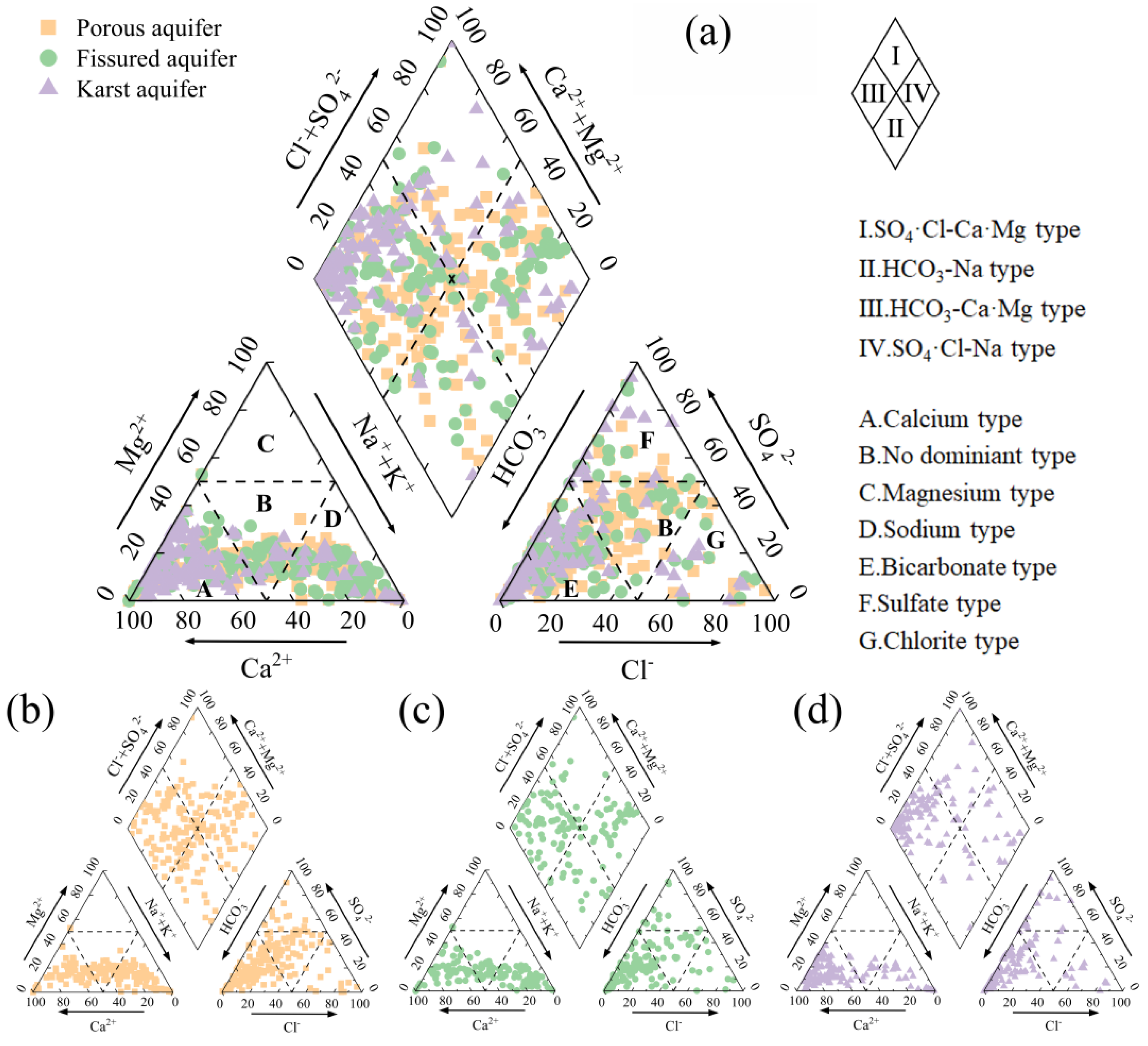
The Piper diagram (Piper, 1944) is a simple and effective method for water type classification, which identifies water types based on the relative proportions of major cations and anions and is widely used in water chemistry analysis and classification [30,59]. The Piper diagram analysis results (Figure 3) showed that various types of aquifers had obvious hydrochemical characteristics. The dominant water chemistry type in all three aquifers was the HCO3-Ca·Mg type, reflecting the widespread influence of carbonate dissolution processes, while SO4·Cl-Na-type water mostly appeared in areas with significant evaporite dissolution. In the porous aquifer, the groundwater was mainly HCO3-Ca·Mg-type (46.88%), and the rest were SO4·Cl-Na-type (27.60%), HCO3-Na-type (15.10%) and SO4·Cl-Ca·Mg-type (10.42%). The fissured aquifer is mainly HCO3-Ca·Mg-type (52.71%), and the others were SO4·Cl-Na-type (25.58%), HCO3-Na-type (13.96%) and SO4·Cl-Ca·Mg-type (7.75%). In the karst aquifer, HCO3-Ca·Mg-type accounted for the highest proportion (70.92%), followed by SO4·Cl-Na-type (12.06%), SO4·Cl-Ca·Mg-type (11.35%) and HCO3-Na-type (5.67%).
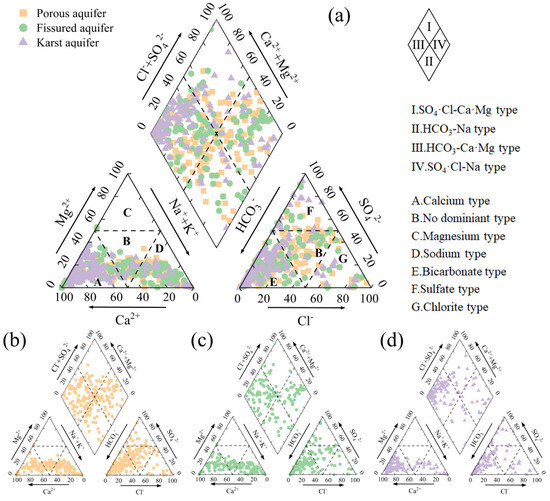
Figure 3.
Piper diagram of groundwater in the study area: (a) summary of the three types of aquifers, (b) porous aquifers, (c) fissured aquifers and (d) karst aquifers.
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Groundwater Chemistry in Different Types of Aquifers
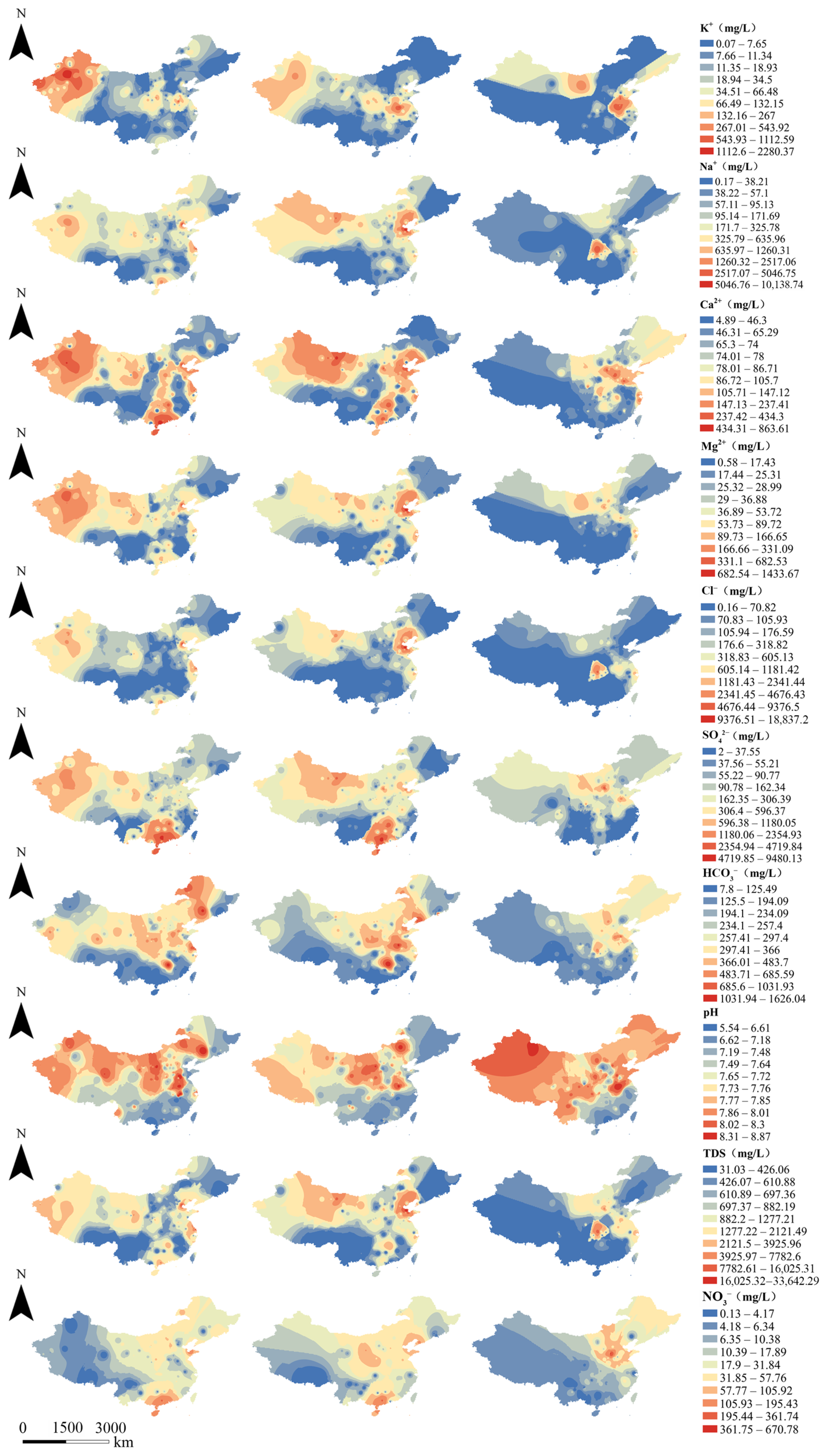
Interpolation of the spatial distribution of groundwater ions in various types of aquifers was performed using the inverse distance weighting method of ArcGIS 10.8. There were obvious differences between karst aquifers and porous aquifers and fissured aquifers. The distribution of K+, Ca2+, SO42−, HCO3−, pH, TDS and NO3− in the latter two was relatively consistent (Figure 4). In porous and fissured aquifers, K+ was higher in the northwest, while in karst aquifers it was mainly distributed in East China. High values of Na+ in porous aquifers were mainly distributed in the northwest, East China and coastal areas of South China, while in fissured aquifers they were concentrated in the northwest, North China and parts of East China. Na+ in karst aquifers was only high in Central China. Ca2+ was high in porous and fissured aquifers in the northwest, South China and coastal cities of the Bohai Sea, while high values in karst aquifers were located in East China and North China. Mg2+ was high in porous aquifers in the northwest and fissured aquifers in coastal cities of the Bohai Sea, while in karst aquifers it was concentrated in North China.
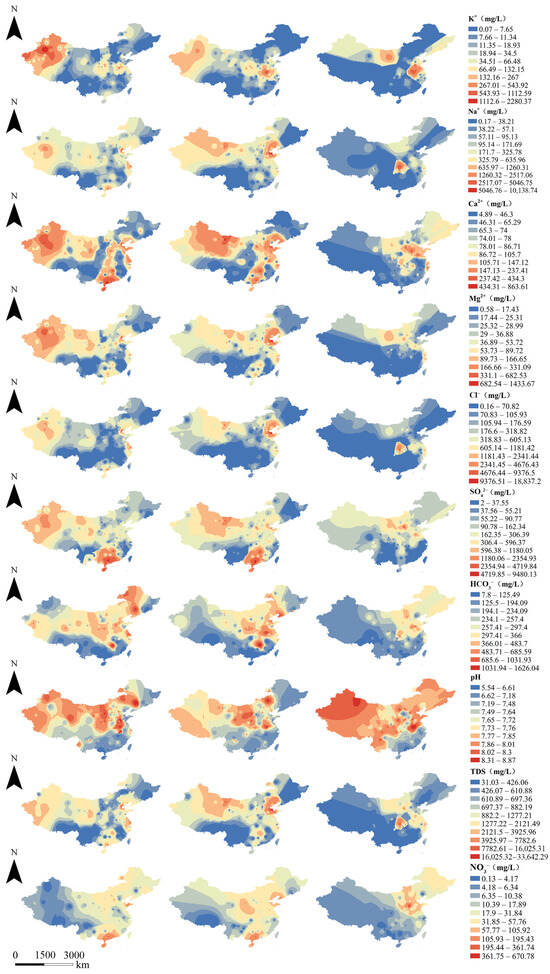
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of groundwater chemical composition in three types of aquifers (first column: porous aquifer; second column: fissured aquifer; third column: karst aquifer).
Cl− was high in porous aquifers in the northwest, fissured aquifers in coastal cities of the Bohai Sea and karst aquifers in Central China. SO42− and NO3− were high in porous and fissured aquifers in South China, and high in karst aquifers in North China. HCO3− was high in porous aquifers in Northeast China and fissured aquifers in East China and Central China, while karst aquifers in Northeast China were higher than those in the west and south. High pH values were found in porous and fissured aquifers in Northwest and North China, and karst aquifers in most areas except South China. High TDS values were mainly distributed in porous and fissured aquifers in coastal areas of the Bohai Sea and karst aquifers in Central China.
3.3. Source Allocation of Chemical Constituents of Groundwater from Different Types of Aquifers
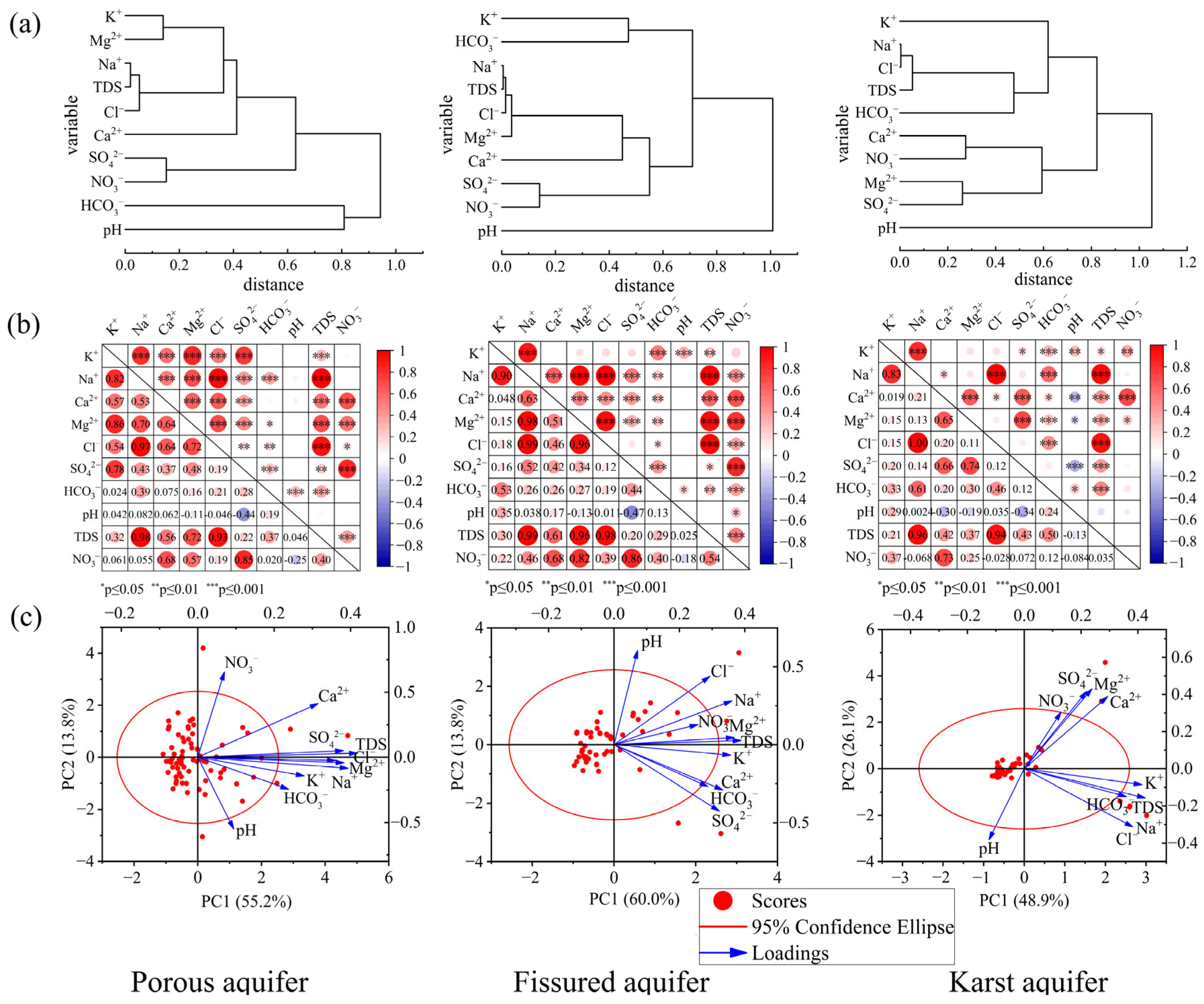
In order to reveal the relationship between the main hydrochemical parameters in the three types of aquifers, a hierarchical cluster analysis was performed on 10 hydrochemical indicators of the three types of aquifers (Figure 5a). The results showed that in different types of aquifers, the hydrochemical parameters can generally be divided into three main groups, but there were certain differences in their internal structures. From the clustering results, there was a high similarity between porous aquifers and fissured aquifers. Na+, Cl−, TDS, Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions were divided into a large category in both porous and fissured aquifers, showing their strong clustering relationship, reflecting their similar geochemical sources or migration processes. NO3− and SO42− were usually classified as an independent subclass in porous and fissured aquifers, which may be related to anthropogenic inputs such as agricultural fertilization or mining activities. HCO3− was either clustered with other ions or classified separately in different aquifers, reflecting the spatial differences in carbonate buffering. pH formed a separate cluster in each aquifer type, indicating that it was controlled by a different mechanism than other ions.
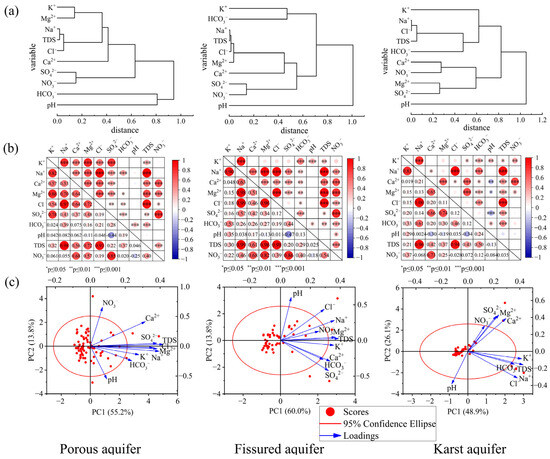
Figure 5.
(a) Hierarchical clustering diagrams of water chemical parameters, (b) correlation coefficient diagrams, (c) principal component analysis biplot.
In the three types of aquifers, there was a general significant correlation between the main ions. Overall, the porous aquifer and the fissured aquifer showed a high consistency in the correlation characteristics between ions, reflecting the similarity of their water chemical processes. In addition, there was a strong correlation between K+ and Na+, Na+ and Cl−, TDS, Ca2+ and NO3−, and Cl− and TDS in all three aquifers (Figure 5b). In the three types of aquifers, Na+ and Cl− and TDS were all extremely significantly positively correlated (r > 0.9, p < 0.001); Ca2+ and NO3− also showed a stable correlation (r > 0.6, p < 0.001). Cl− and TDS also had a strong positive correlation. In porous aquifers, TDS was strongly correlated with Mg2+ and Cl− (r > 0.7). Na+, Mg2+ and SO42− were strongly correlated with K+ (r > 0.7). In fissured aquifers, Na+ was strongly correlated with Mg2+ and Cl− (r > 0.9). TDS also showed significant correlation with Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+ and Cl− (r > 0.6). In karst aquifers, Na+ was highly correlated with K+ (r > 0.8), and had a strong positive correlation with Cl−, TDS (r > 0.9) and HCO3− (r > 0.6), and SO42− also showed significant correlation with Ca2+ and Mg2+.
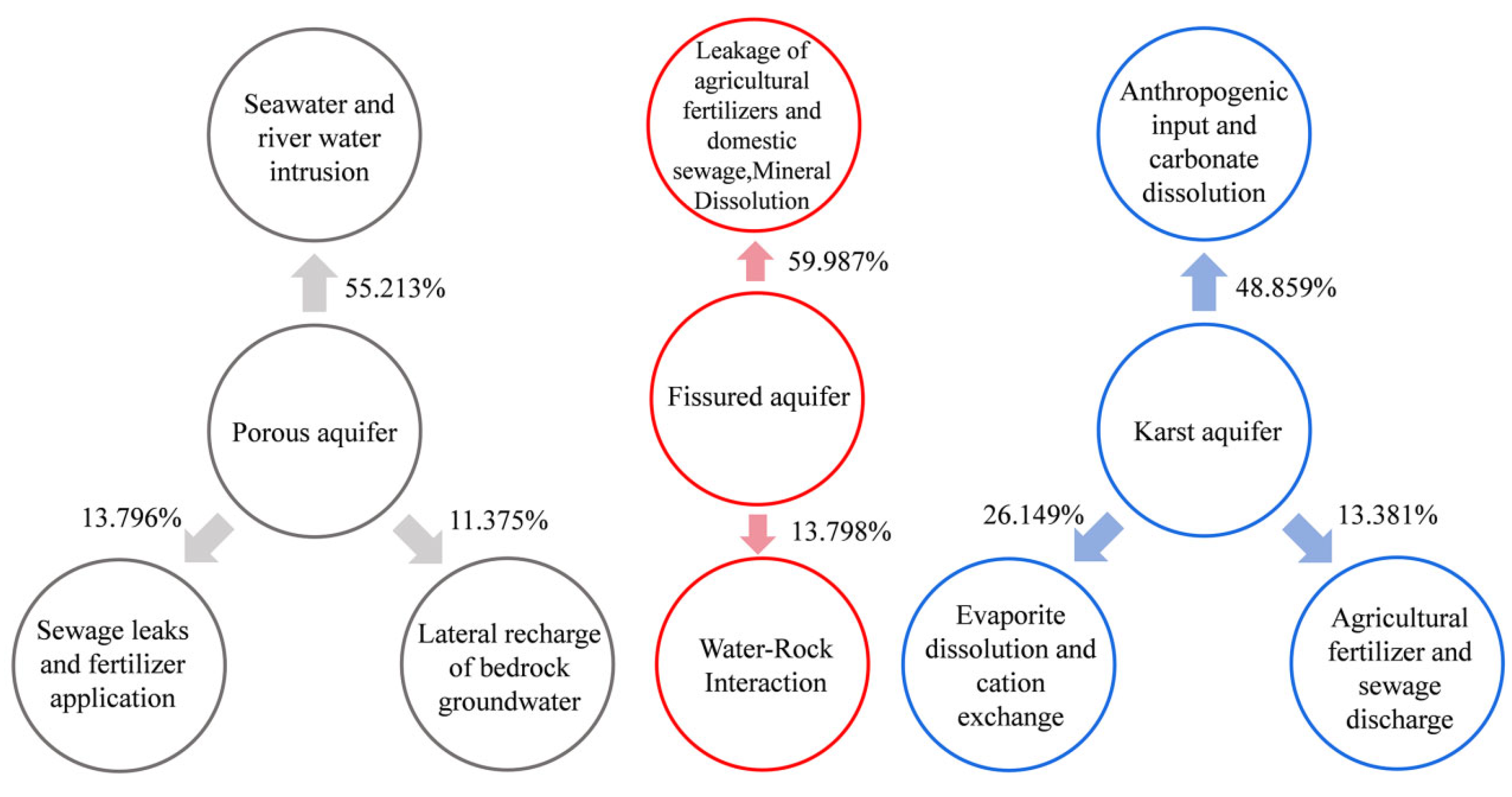
Principal component analysis (PCA) revealed the main factors that had controlled the groundwater chemistry of the three aquifers (Table 1). In the porous aquifer, the three principal components explained 80.384% of the total variance, of which PC1 (55.213%) was dominated by Na+, Mg2+, Cl−, SO42−, Ca2+ and TDS, PC2 (13.796%) mainly represented NO3− and pH, and PC3 (11.375%) reflected the influence of HCO3−. In the fissured aquifer, the two principal components cumulatively explained 73.785% of the variance (Figure 5c), of which PC1 (59.987%) contained strong loadings of Mg2+, TDS, K+, Na+, SO42−, Cl− and Ca2+, and PC2 (13.798%) mainly represented pH. In the karst aquifer, three principal components explained 88.389% of the total variance, PC1 (48.859%) contained TDS, K+, Na+, Cl−, Ca2+ and strong HCO3− loadings, PC2 (26.149%) represented Mg2+ and SO42−, and PC3 (13.381%) mainly reflected the influence of NO3−.

Table 1.
Principal component matrix and loading, variance contribution rate and cumulative contribution rate of groundwater chemical indicators.
3.4. Controlling Factors of Water Chemistry in Different Aquifers
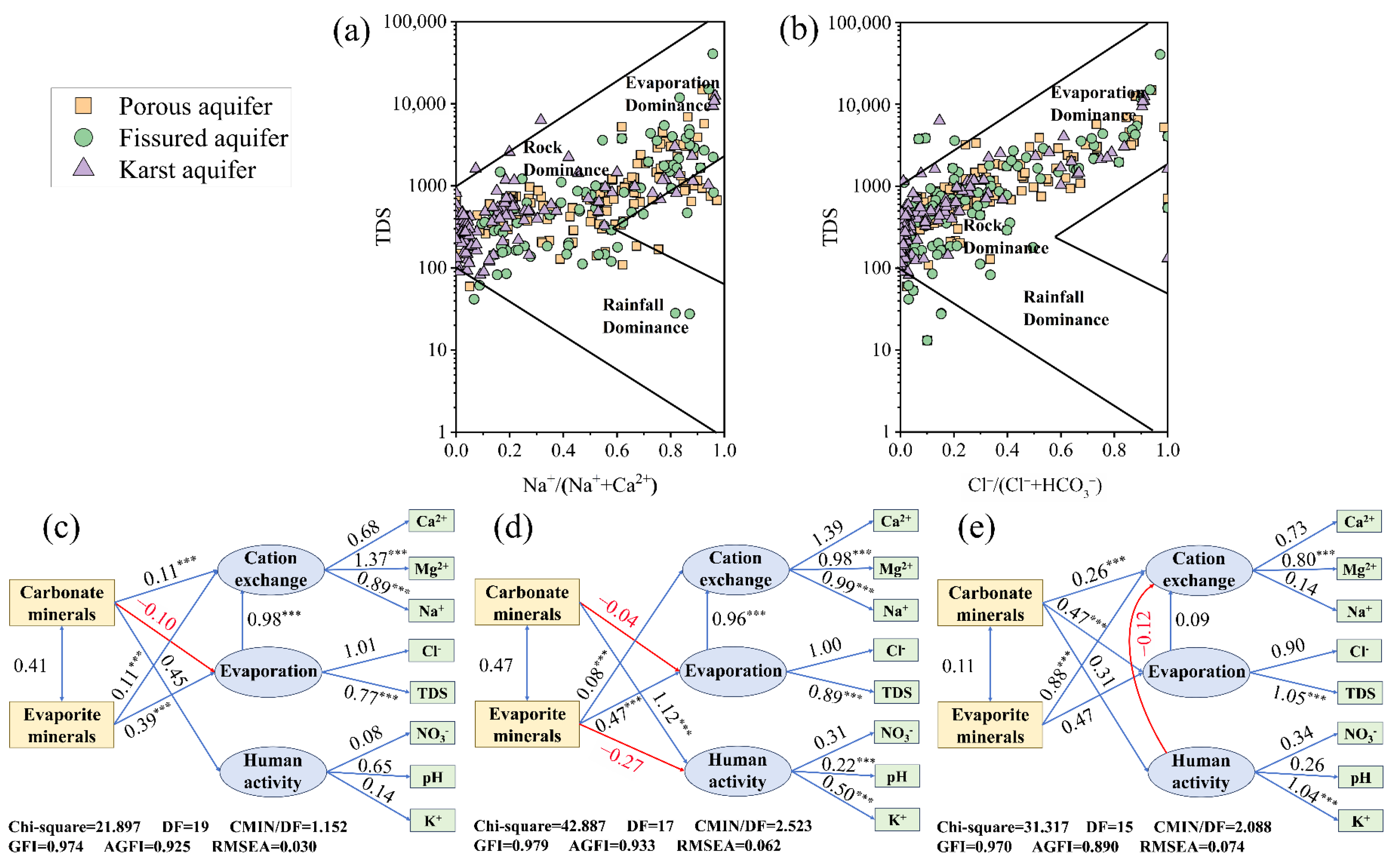
A Gibbs diagram analysis showed that groundwater in the study area was mainly controlled by rock weathering (such as silicate and carbonate rocks) and evaporation (Figure 6). Among them, water samples of porous aquifers and fissured aquifers were mostly distributed in areas affected by rock weathering and evaporation, and fissured aquifers were particularly affected by rock weathering. Karst aquifer samples were mainly concentrated in rock weathering-controlled areas, and a few water samples were affected by evaporation.
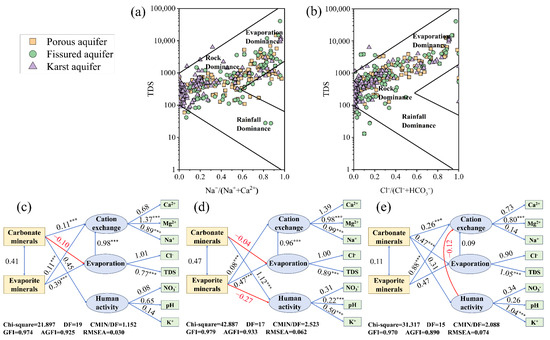
Figure 6.
Gibbs diagrams and structural equation modeling of groundwater samples. (a) Na+/(Na++Ca2+) versus TDS, and (b) Cl−/(Cl−+HCO3−) versus TDS, (c) porous aquifer, (d) fissured aquifer, (e) karst aquifer (the blue line indicates a positive impact, and the red line and red numbers indicates negative impact, *** p < 0.001).
Combining the results of the correlation analysis and PCA, the correlation analysis showed that there was a significant correlation between the cations Na+ and Ca2+ and Mg2+ in the porous aquifers and the fissured aquifers, and the three ions Na+, Ca2+ and Mg2+ were used as a set of measurement variables. There was a significant correlation between Cl− and TDS in all three types of aquifers, so these two water chemical indicators were used as a set of measurement variables (Figure 5). In addition, K+ and NO3− were considered to be pollution caused by human activities [60], and they were used as a set of measurement variables together with pH.
The structural equation model (SEM) showed good fit in all three aquifers (CMIN/DF < 3, GFI > 0.9, RMSEA < 0.08). The model showed that carbonate mineral and evaporite mineral dissolution significantly affected the hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater through three pathways: cation exchange, evaporation and human activities (Figure 6). Among them, Ca2+, Mg2+ and Na+ were important factors in cation exchange, while Cl− and TDS reflected the influence of the evaporation process. The dissolution of carbonate minerals had the greatest impact on the three aquifers through human activities. The dissolution of evaporite minerals not only significantly affected the hydrochemistry of aquifers through cation exchange (p < 0.001), but also played an important role in porous and fissured aquifers through the evaporation pathway. The effect of the evaporation process on cation exchange was also very significant. It was worth noting that the dissolution of carbonate minerals had a negative effect on porous and fissured aquifers through the evaporation pathway, and the evaporite minerals in fissured aquifers also showed a negative effect through the human activity pathway. The contribution of cation exchange to Mg2+ (SC ≥ 0.8, p < 0.001) and the contribution of evaporation to TDS (SC > 0.75, p < 0.001) in the three types of aquifers were significant, reflecting their key roles in the evolution of groundwater chemistry.
4. Discussion
4.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Different Types of Aquifers
Due to the existence of fissures at the surface and the mutual recharge and discharge movement between the water-conducting channels and the water storage network within the karst aquifer, seawater and river water with high pH values had infiltrated into the aquifers [60], resulting in a neutral to nearly alkaline pH of groundwater in China. Bi et al. found that the mineralization of organic matter in marine sediments (vadose zone) produced a large amount of bicarbonate, which increased the pH value of groundwater through the conversion of the carbonate equilibrium system “H2CO3 ↔ HCO3− + H+” [37]. Therefore, large-scale irrigation with high pH seawater and river water led to an increase in the pH values of porous and karst aquifers [14]. The mineralization degree of groundwater in porous aquifers and karst aquifers is lower than that in fissured aquifers, indicating that the groundwater chemistry in the porous and karst aquifers is relatively homogeneous [22]. In addition, seawater with high TDS values entered the fissured aquifers, causing the TDS values of the fissured aquifers in coastal cities of the Bohai Sea to be higher [61]. The dissolution of carbonate minerals (calcite, dolomite) was the main reason for the higher average values of Ca2+ and HCO3− in the groundwater of porous aquifers compared to in groundwater of fissured aquifers and karst aquifers [14,62]. The high K+ content in the fissured aquifer might have been related to human input such as domestic sewage [60]. In addition, seawater and river water intrusion resulted in higher contents of Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl− and HCO3− in porous aquifers compared to in fissured and karst aquifers because calcium, magnesium, chloride ions and bicarbonate ions are widely present in seawater [14]. The main sources of NO3− in groundwater were human activities, including pesticide and fertilizer use and sewage spills and discharges [63,64], which resulted in higher content of NO3− in fissured aquifers than in porous and karst aquifers.
Compared with the results of relevant studies in other countries, this study found that most groundwater samples were alkaline [9,10], similar to aquifers in the United States (pH = 7.42) and Iran (pH = 6.25–8.25). Anthropogenic contaminants such as fertilizer and pesticide application had ultimately altered the groundwater pH [65,66]. There was consistency with the acidity and alkalinity of groundwater aquifers in China. The groundwater cations in the Omdel aquifer in the Oamaru Basin, Namibia, Africa, had been dominated by Na+ and Ca2+. Cation exchange occurred in Oamaru catchment groundwater, with Na+ replaced by Ca2+ due to seawater intrusion [12]. The cation order was consistent with that of the porous aquifer. These international cases show that the phenomenon of groundwater hydrochemical characteristics in China’s aquifers is universal and consistent with the laws of similar hydrogeological environments around the world.
4.2. Main Sources of Groundwater Chemical Composition
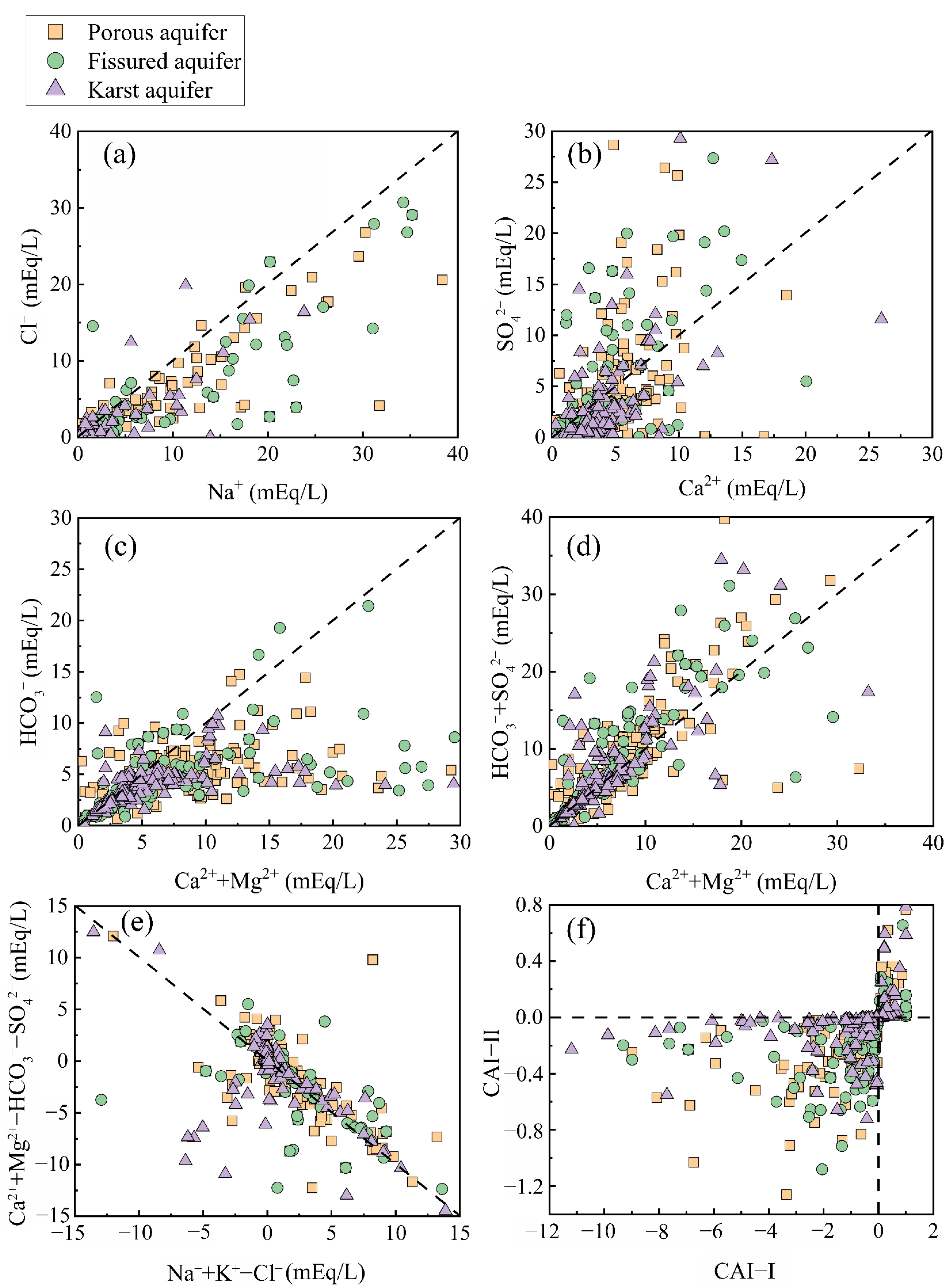
There was a high correlation between Na+ and Cl− in the three types of aquifers (r > 0.99), and the spatial distribution of high-value areas was relatively consistent. Coastal cities had elevated Na+ and Cl− contents due to seawater intrusion [67]. Qiao et al. found that the sources of Na+ and Cl− in karst aquifers were similar. Clastic rocks and other rock salt minerals dissolve, thus generating Na+ and Cl− in groundwater [68]. In this study, the higher Na+ and Cl− contents in karst aquifers had mainly been distributed in Hubei, Chongqing and Shaanxi regions, and halite dissolution may be the main source of Na+ and Cl− in karst aquifers in these regions (Equation (6)).
The contents of Ca2+ and NO3− in porous and fissured aquifers were high in the Pearl River Delta region, where the groundwater pH was mainly acidic to near-neutral [69]. On the one hand, the frequency of acid rain in the region was very high, which was likely to be the cause of groundwater acidification in the region [70]. Acid rain may have also been a source of NO3− in groundwater. On the other hand, the soil in the Pearl River Delta was generally acidic [71]. Fertilizers were applied in agriculture to neutralize the acidity in the soil [72]. Calcium nitrate is easily soluble in water. Excessive use of Ca(NO3)2 fertilizers was likely to be the source of Ca2+ and NO3− in the region (Equation (7)). The dissolution of gypsum may have been an important process in karst aquifers (Equation (8)) [22]. Cl− and Ca2+, Mg2+ in porous and fissured aquifers had a high correlation, which may be due to the cation exchange that occurs after the dissolution of rock salt [73]. Similarly, the correlation between Mg2+ and SO42− in karst aquifers was high (r = 0.739). This indicates that cation exchange may occur in karst aquifers after the dissolution of gypsum.
The majority of the groundwater samples were located below the y = x line, indicating significant Na+ content in all three types of aquifers (Figure 7a). If the Na content is much higher than Cl, this may be caused by ion exchange or silicate dissolution. If the Cl content is higher than Na, it may be caused by human factors [74]. In addition to halite dissolution and the dissolution of Na-bearing silicates, additional Na+ inputs may have resulted from the dissolution of other Na-bearing minerals (Glauber’s salt and feldspars) (Equations (9) and (10)) or from the effects of positive cation exchange between Ca2+ and Na+ (Equation (13)) [22].
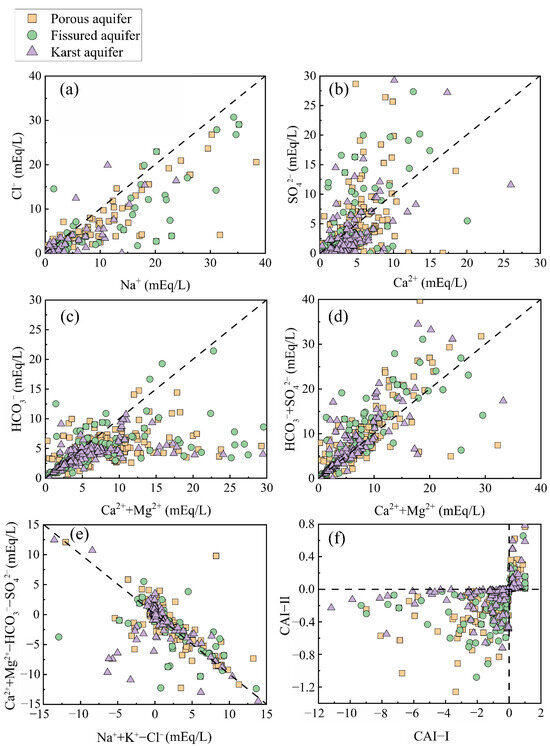
Figure 7.
Scatter plots of ion pairs in groundwater. (a) Na+ vs. Cl−, (b) Ca2+ vs. SO42−, (c) (Ca2++Mg2+) vs. HCO3−, (d) (Ca2++Mg2+) vs. (HCO3−+SO42−), (e) (Na++K+-Cl−) vs. (Ca2++Mg2+- HCO3−-SO42−), (f) CAI-I vs. CAI-II.
The ionic ratios of Ca2+ to SO42− in most sample points were less than 1 (Figure 7b), indicating that the dissolution of gypsum occurs in all three aquifers, and the excess Ca2+ may have resulted from cation exchange after the dissolution of rock salts, which led to the elevation of the Ca2+ content. Most of the sample points were distributed on the right side of the 1:1 line (Figure 7c), indicating an excess of Ca2+ and Mg2+ and the presence of dissolved carbonate minerals (calcite, dolomite) in the groundwater (Equations (11) and (12)) [30]. In addition, the dissolution of gypsum and reverse ion exchange (Equation (14)) may have also led to the release of Ca2+ into the aquifer system. In the ion ratios of Ca2++Mg2+ and HCO3−+SO42− (Figure 7d), the vast majority of sample points in the three types of aquifers were distributed above or along the 1:1 line. This indicated that dissolved carbonates and gypsum were present in the groundwater [49]. Compared with Figure 7c, it could be seen that the addition of SO42− caused the sample points to shift from below the 1:1 line to above it, with a larger shift in the porous and fissured aquifers, while the karst aquifers showed a smaller change. This indicated that the dissolution of gypsum and Glauber salt (Na2SO4·10H2O) provided a large amount of SO42− in the porous and fissured aquifers. In addition, positive cation exchange also leads to a decrease in Ca2+ content in groundwater, which in turn leads to an excess of HCO3−+SO42− over Ca2++Mg2+.
The CAI values of most sample points in the three types of aquifers were less than zero (Figure 7f), indicating that the degree of positive cation exchange was greater than that of reverse cation exchange [75]. In addition, the groundwater samples were roughly linearly distributed and had an approximate slope of −1 (Figure 7e). This indicated that Ca2+ and Mg2+ replaced Na+ that had been previously adsorbed on the mineral surfaces within the aquifer matrix, leading to a decrease in the distribution of (Ca2++Mg2+-HCO3−-SO42−) and an increase in (Na++K+-Cl−). This further confirms that cation exchange was one of the primary reasons for the elevated Na+ concentrations in the three types of aquifers [72].
NaCl→Na+ + Cl−
Ca(NO3)2→Ca2+ + 2NO3−
CaSO4·2H2O⇔Ca2+ + SO42− + 2H2O
Na2SO4·10H2O⇔2Na++SO42− + 10H2O
Na2Al2Si6O16 + 2H2O+CO2→Na2CO3 + H2Al2Si2O8 + H2O + 4Si2O
CaCO3+CO2 + H2O⇔Ca2+ + 2HCO3−
CaMg(CO3)2 + 2CO2 + 2H2O⇔Ca2+ + Mg2+ + 4HCO3−
2NaX + Ca2+→CaX2 + 2Na+
CaX2 + 2Na+→2NaX + Ca2+
4.3. Hydrogeochemical Mechanisms of Groundwater Evolution in Different Aquifers
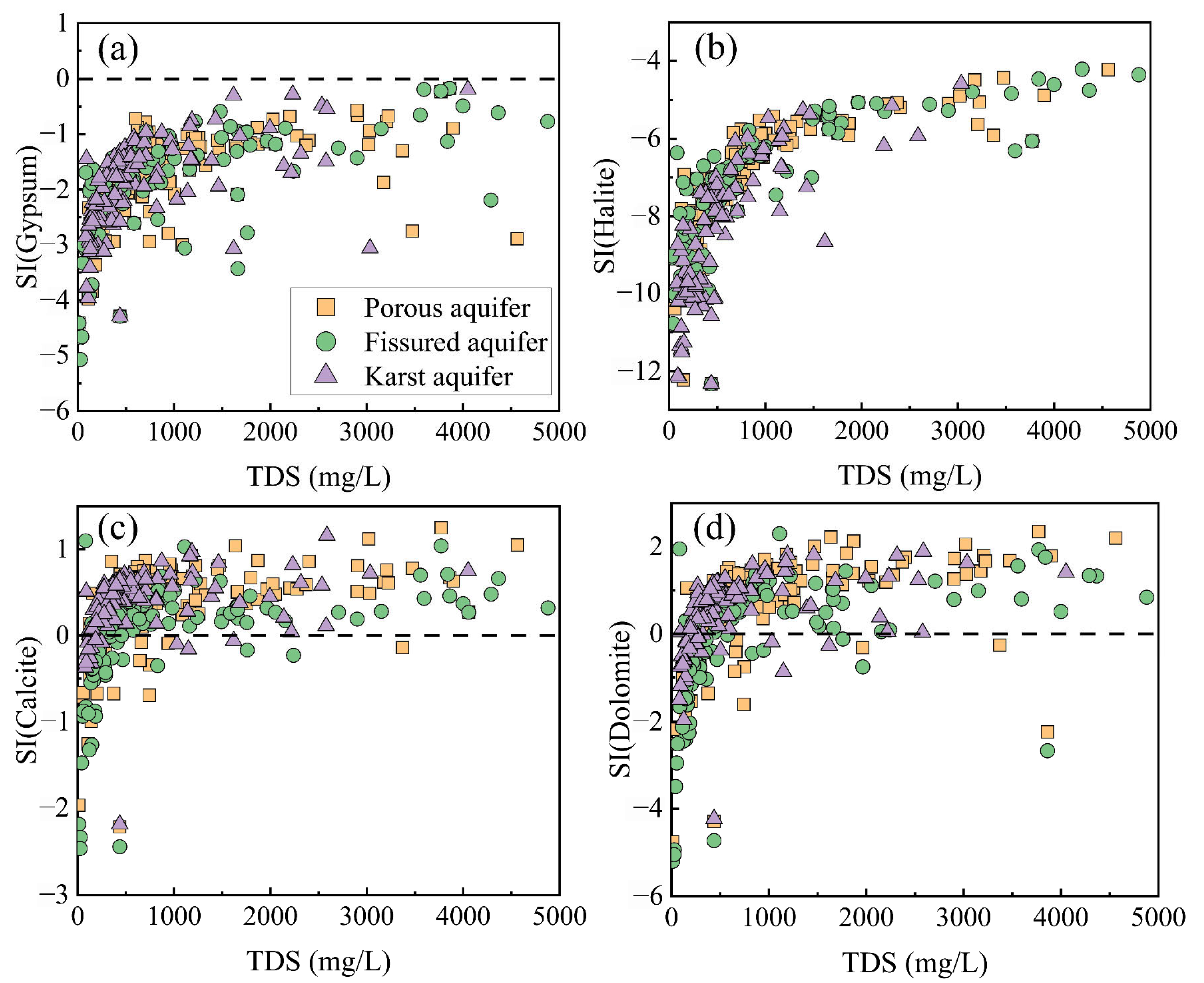
To ascertain whether geochemical reactions involving evaporites and carbonate minerals were the primary factors influencing groundwater chemistry, the saturation index (SI) was computed for various mineral phases, namely calcite, dolomite, gypsum, and halite. As shown in Figure 8a, the SI values of gypsum in all three types of aquifers were less than 0, and gypsum in groundwater was in an unsaturated state. As the TDS increased, the saturation index of gypsum gradually approached 0, indicating that the dissolution of gypsum occurred in all three types of aquifers, but that the dissolution potential was decreasing [76]. Moreover, gypsum dissolution in water samples with TDS below 1000 mg/L increased rapidly with increasing TDS, suggesting that evaporite minerals might have been the main contributor to groundwater salinity, as indicated by TDS. The SI values in 87% of the water samples from the karst aquifer when TDS was below 1000 mg/L showed a significant increase with increasing TDS (Figure 8b). This finding suggested that the dissolution of halite was notably more prominent within the karst aquifer.
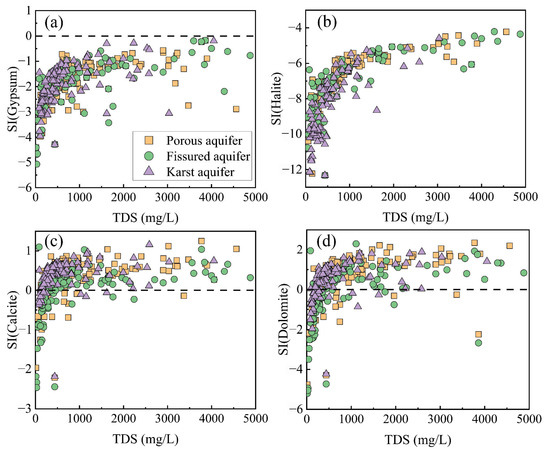
Figure 8.
Relationship between saturation index and TDS, (a) gypsum, (b) halite, (c) calcite, and (d) dolomite.
In the three types of aquifers, calcite was in a supersaturated state in most water samples and precipitation occurred (Figure 8c). The rest of the water samples exhibited SI values below 0, thereby indicating the dissolution of calcite. Similarly, the presence of a majority (about 90%) of the porous aquifer water samples with dolomite in supersaturation indicated that groundwater precipitation was occurring. Roughly 10% of the pore groundwater samples had negative SI values, indicating that the dolomite present in these samples was unsaturated, suggesting a potential dissolution of dolomite. Dolomite precipitation occurred at about 85% of the water sample sites in the karst aquifer. Compared with the other two aquifers, about one third of the groundwater samples from the fissured aquifer had negative SI values, indicating that dolomite dissolution occurred at more sample points in the water chemistry samples from the fissured aquifer than in the other two aquifers.
The dissolution of evaporite minerals increased the content of Ca2+ and Na+ in groundwater [77], which had a more significant positive effect on the porous aquifer through evaporation (Figure 6). This resulted in a transition of groundwater samples from the porous aquifer to the evaporation-dominated zone, thereby implying that evaporation served as the primary natural process dictating the groundwater’s development within the porous aquifers. Fissure groundwater samples were mainly distributed in the upper middle right, suggesting that evaporation and rock weathering may have been the main factors influencing groundwater chemistry in the fissured aquifers. Furthermore, over half of the groundwater samples collected from the karst aquifers were located within the rock weathering zone, which demonstrates a significant impact of rock weathering on the karst aquifers. Previous studies also found that all ion components of karst groundwater were concentrated in the rock weathering zone, indicating that the ions of karst groundwater in the study area mainly originated from rock weathering [68]. Consistent with the results obtained from the structural equation modeling, the influence paths of mineral dissolution on the karst aquifers were all positive, resulting in a shift in groundwater samples from the karst aquifers to the rock dominant zone. It was noteworthy that with the significant increase in TDS, the groundwater TDS values were consistent with the increasing trend of the ratio of Cl−/(Cl− + HCO3−), which further demonstrated that evaporate salts were enriched in the fissured and karst aquifers [22], suggesting that mineral dissolution as well as rock weathering were the main mechanisms controlling the evolution of groundwater in the fissured and karst aquifers. The relative increase in the ratio of Cl− to HCO3− can be attributed to a confluence of evaporation, halite dissolution, precipitation of carbonate minerals and the influx of chlorinated effluents [23], and also suggests that evapotranspiration and rock dominance processes had a significant effect on groundwater quality [78].
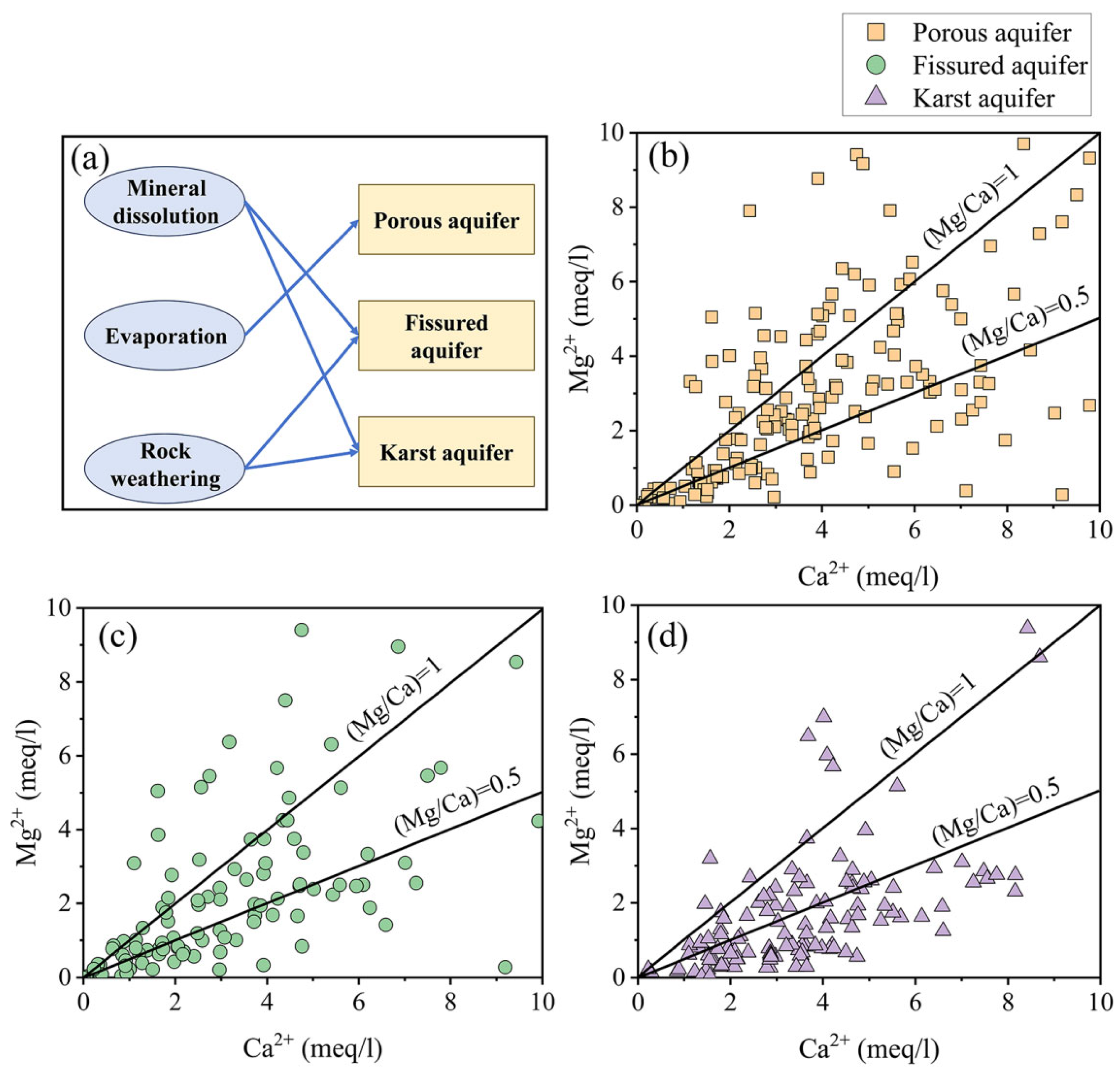
The (Mg2+/Ca2+) index depicted in Figure 9 served as a valuable indicator for determining the comparative dispersal of calcite and dolomite in carbonate rocks traversed by groundwater [11,79,80]. Most of the groundwater samples from the porous aquifers were below the (Mg2+/Ca2+) = 1 line, indicating that both calcite and dolomite were present in the groundwater from the porous aquifers. Nearly half of the sample points in the fissured aquifers lay below the 0.5 line, indicating that calcite was dominant in the groundwater in the carbonate rocks [11]. Only a small number of points lay on the (Mg2+/Ca2+) = 1 line, which suggests that the groundwater in this type of aquifer was part of an aquifer that flows through an aquifer that was influenced by the dissolution of dolomite. Most of the karst aquifer’s groundwater samples were distributed below the 0.5 line, which indicates that calcite is dominant in the groundwater of the karst aquifer in carbonate rocks. The latest research also confirmed that in limestone-dominated karst aquifer systems, the dissolution of calcite led to higher concentrations of Ca2+ and lower concentrations of Mg2+ [81]. Some samples above the 0.5 line were affected by the dissolution of dolomitic tuff or dolomite in the bedrock [79].
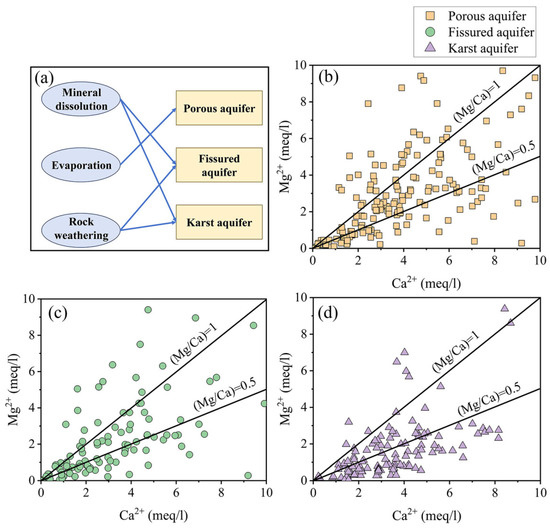
Figure 9.
Groundwater chemical control mechanisms in different types of aquifers (a) and groundwater chemical (Mg2+/Ca2+) index of different types of aquifer: (b) porous aquifer, (c) fissured aquifer, (d) karst aquifer.
In addition to rock weathering, mineral dissolution and evaporation, the mean residence times of the aquifer and the conditions of the catchment area also played an important role in the evolution of groundwater. Porous aquifers were composed of loose quaternary sediments, were shallowly buried, received vertical recharge from precipitation or irrigation, recharged rapidly, and usually had a short residence time (months to years), which made them more sensitive to human influences [31]. The residence time of fissured aquifers varied more, resulting in greater chemical evolution and buffering capacity, especially in areas with low permeability lithologies such as granite and schist. Studies found that the longer the transit time of fissured aquifers, the greater the degree of groundwater mineralization. It was also found that Mg2+ concentration was related to the mean residence times of groundwater and water–rock interaction. Water–rock interaction developed with increasing residence time. A lower average residence time indicated a rapid response to precipitation, suggesting high permeability and connectivity of the aquifer, while a higher residence time indicated a longer flow path or slower velocity, reflecting the influence of the aquifer medium [33]. Karst aquifers had a wide range of mean residence times (days to decades) [35]. Previous studies showed that the Mg/Ca ratio of groundwater in karst aquifers usually increased with the extension of groundwater residence time, and the saturation index (SI) of dolomite also changed due to the mean residence times [34]. These differences indicated that the mean residence times of groundwater in aquifers and the unique water collection system of aquifers played an important role in water–rock interactions, thus affecting the evolution of groundwater.
4.4. Influencing Factors Across Different Aquifer Types
The high loads of Cl− and TDS also indicated the possible existence of seawater intrusion [12]. Seawater and river water intrusion were the main reasons why the concentrations of Mg2+, Cl− and HCO3− in porous aquifers were higher than those in the other two types of aquifers [14]. PC2, accounting for 13.796% of the variance, was primarily influenced by elevated NO3− levels, coupled with a substantial negative loading on pH. This component reflects anthropogenic influences, predominantly arising from the leaching of inorganic fertilizers from agricultural soils, domestic sewage and industrial effluent discharges [25], as well as the intensive use of the acidic soil quick-acting fertilizer Ca(NO3)2. Tziritis et al. found that groundwater pH affected nitrate concentration, with increased nitrate retention and reduction reactions occurring under acidic conditions, converting it to nitrogen oxides (NOx) and ammonia (NH3), leading to a decrease in NO3− concentration, whereas under alkaline conditions, nitrate was more stable and less prone to such reactions [13]. In contrast to the fissured aquifers (pH = 7.48), the higher pH (pH = 7.69) and lower NO3− concentration in the porous aquifers were not consistent with the above; thus, PC2 was mainly sewage spillage and fertilizer application. PC3 (11.375%) mainly represents the strong load of HCO3−. Porous aquifers were usually recharged by the lateral flow of bedrock groundwater (fissured aquifer groundwater) from hilly areas where carbonate minerals such as limestone are common [14]. Therefore, PC3 mainly indicated a lateral recharge of bedrock groundwater (Figure 10).
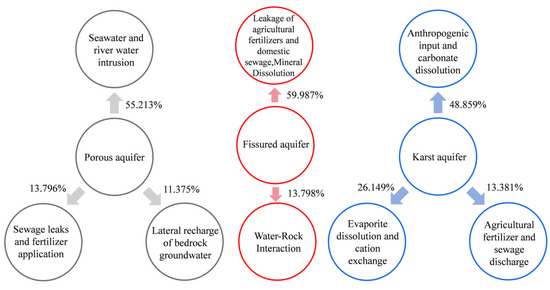
Figure 10.
Control factors of groundwater chemistry in different types of aquifers.
PC1 explained 59.987% of the total variance (Table 1). The presence of K+ and Na+ in fissured aquifer groundwater commonly originated from the infiltration of agricultural fertilizers and domestic sewage [82]. Moreover, the concentrations of Cl−, SO42− and NO3− in groundwater were typically attributed to the precipitation of industrial waste gases and percolation of agricultural fertilizers and domestic sewage [5,14,60,83]. The dissolution of basalt and carbonate minerals (calcite, aragonite, dolomite) in fissured aquifers led to elevated concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ [25,62]. SO42− may also have originated from the dissolution of minerals, including gypsum and hard gypsum [25]. PC1 represented the leakage of agricultural fertilizers and domestic wastewater, as well as the dissolution of minerals. PC2 comprised pH, which accounted for 13.798% of the total variance, and the pH of the groundwater reflected the concentration of H+ in the groundwater (pH = −logH+), and H+ was absorbed by water–rock interaction processes [82], resulting in alkaline groundwater pH in fissured aquifers. Therefore, PC2 mainly indicated water–rock interaction.
The growth trend of Na+ and Cl− in karst water is usually consistent. Na+ in groundwater naturally arises from the dissolution of rock salts within aquifers as well as from Na-bearing minerals present in metamorphic rocks [84]. Guo et al. found that the carbonate rock layers in karst areas had extremely low contents of rock salt minerals, so the background concentrations of K+ and Na+ were generally low [85]. Possible anthropogenic sources of these ions included mineral fertilizers and potash fertilizers that were highly soluble and easily leached from the soil, as well as the discharge of domestic sewage [81]. Therefore, it was inferred that the unusually elevated concentrations of Na+ and Cl− in karst water were influenced by anthropogenic inputs [21]. Ca2+ and HCO3− indicated that the basic environment for karst groundwater development was calcite-dominated chert dissolution [86]. Therefore, PC1 mainly represented anthropogenic inputs and the dissolution of carbonate minerals. PC2 mainly represented Mg2+ and SO42−, accounting for 26.149% of the total variance. Mg2+ and SO42− originated from the dissolution of evaporite minerals such as gypsum in the aquifer, as well as from cation exchange [86]. PC3 mainly represented a strong loading of NO3−, accounting for 13.381% of the total variance, and it is generally believed that NO3− has no known lithologic source or atmospheric deposition. In addition, several preceding studies have indicated that an excessive application of nitrogen fertilizers often constituted a significant source of NO3− in groundwater [60,87], and thus NO3− in karst aquifers may mainly have come from an excessive application of agricultural fertilizers and sewage discharge [82,86].
4.5. Suggestions for Groundwater Protection
This study found that the controlling factors for groundwater chemistry can be roughly divided into two categories: natural factors and human factors [5,88]. Natural factors were difficult to control, while human factors could be effectively controlled through some means [14]. Human factors such as fertilization and sewage discharge play an important role in affecting the chemical properties of groundwater in all aquifer types. Groundwater vulnerability is closely related to the intensity of human activities. Therefore, groundwater protection measures should give priority to areas with intensive land use and weak infrastructure, such as suburban areas and agricultural areas. To achieve effective management, local governments should focus on upgrading and transforming aging sewage treatment systems, implement sewage treatment in underserved areas, and formulate scientific fertilization plans and promote the use of organic fertilizers in agricultural areas with a high degree of land development and utilization. Environmentally sustainable agricultural practices should also be promoted. The expansion of construction land will also lead to changes in land cover, increase surface runoff, and make it easier for pollutants to infiltrate groundwater with rainwater. In the early stages of urban land development and expansion, groundwater protection should be included in the preliminary planning assessment, and land use control in key recharge areas should be strengthened. In the suburban transition zone, priority should be given to building green infrastructure (such as permeable paved roads) and accelerating the construction of sewage collection and treatment systems to reduce direct pollution loads on groundwater. These targeted measures, based on the specific pathways identified in this study (nitrate and sulfate enrichment caused by human factors), are expected to mitigate the further deterioration of groundwater.
5. Conclusions
This study revealed significant differences in hydrochemical characteristics, spatial distribution, main controlling factors and evolution mechanisms among porous, fissured and karst aquifers in China. The study found that groundwater in the three types of aquifers was weakly alkaline, and the hydrochemical type was mainly HCO3-Ca·Mg. The concentrations of K+, Na+, SO42− and NO3− in the fissured aquifer were relatively high, mainly due to anthropogenic factors such as agricultural fertilization and domestic sewage leakage. The HCO3− content in the porous aquifer was relatively high, which may be affected by the lateral recharge of fissure water in the hilly area. The dissolution of carbonate and evaporite minerals jointly affected groundwater chemistry through cation exchange, evaporation and anthropogenic activities. The hydrochemistry of porous aquifers was affected by evaporation, while that of fissured and karst aquifers was mainly controlled by rock weathering and mineral dissolution. Sewage discharge and fertilizer application were the main anthropogenic factors in the three types of aquifers. In addition, the groundwater chemical characteristics of different types of aquifers showed obvious differences at the regional scale. Porous aquifers and fissured aquifers had similar spatial distribution characteristics in multiple ion indicators, with high values mainly concentrated in northwest and coastal areas of China. The chemical composition distribution of karst aquifers was more regionally heterogeneous. High values of Na+, Ca2+, Cl− and TDS were distributed in the central region, while high pH values were distributed in the northwest and northeast. These differences reflect the combined effects of multiple factors including lithology, recharge conditions and human activities.
Despite regional differences, natural and anthropogenic factors such as mineral dissolution, evaporation and anthropogenic activities generally affect groundwater quality. Changes in industrial activities, agricultural activities and pollutant input methods have led to an increasing number of anthropogenic factors playing a dominant role in some areas. These findings help deepen the understanding of groundwater systems in complex geological settings and provide a reference for groundwater management in other areas with similar hydrogeological conditions. Future research needs to develop water resource management strategies for different aquifers according to local conditions, especially in areas of rapid urbanization and agricultural expansion. At the same time, future research should focus on long-term monitoring and seasonal changes to better understand the evolution of groundwater under climate change and human activities.
Author Contributions
C.L.: Writing—review and editing, Data curation, Formal analysis. J.F.: Writing—review and editing, Supervision, Conceptualization. F.F.: Writing—original draft, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis, Data curation. T.Y.: Investigation, Project administration. Y.S.: Methodology, Conceptualization, Supervision. W.S.: Funding acquisition, Software, Supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Open Fund for the State Key Laboratory of Water Resources Protection and Utilization in Coal Mining (No.GJNY-21-41-08).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Wanli Su was employed by the company CHN ENERGY Investment Group Co Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Gleeson, T.; Befus, K.M.; Jasechko, S.; Luijendijk, E.; Cardenas, M.B. The global volume and distribution of modern groundwater. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 9, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, F.A.S.; Brait, L.A.S.; Coutinho, F.H.; Ferreira, C.M.; Moreira, E.F.; de Queiroz Salles, L.; Meirelles, P.M. Ecological landscape explains aquifers microbial structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 862, 160822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, P.; Pei, L.; Huang, G.; Han, D.; Song, J. Identification of Groundwater Contamination in a Rapidly Urbanized Area on a Regional Scale: A New Approach of Multi-Hydrochemical Evidences. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazakis, N.; Oikonomidis, D.; Voudouris, K.S. Groundwater vulnerability and pollution risk assessment with disparate models in karstic, porous, and fissured rock aquifers using remote sensing techniques and GIS in Anthemountas basin, Greece. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 6199–6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de León-Gómez, H.; Martin del Campo-Delgado, M.A.; Esteller-Alberich, M.V.; Velasco-Tapia, F.; Alva-Niño, E.; Cruz-López, A. Assessment of nitrate and heavy metal contamination of groundwater using the heavy metal pollution index: Case study of Linares, Mexico. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fandel, C.; Ferré, T.; Chen, Z.; Renard, P.; Goldscheider, N. A model ensemble generator to explore structural uncertainty in karst systems with unmapped conduits. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 29, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Gao, L.; Ge, Z.; Li, M. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in a plain river network region: Establishing linkages between source and water quality variables. Chemosphere 2023, 331, 138809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, G.; Zhan, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, M. Identification of hydrogeochemical processes and transport paths of a multi-aquifer system in closed mining regions. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhaei, M.; Dadgar, M.A.; Amiri, V. Geochemical processes analysis and evaluation of groundwater quality in Hamadan Province, Western Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, A.D.; Kirk, M.F.; Whittemore, D.O.; Stotler, R.; Hildebrand, J.; Feril, O. Long-term (1970s–2016) changes in groundwater geochemistry in the High Plains aquifer in south-central Kansas, USA. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 28, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.A.; Goeppert, N.; Goldscheider, N. Use of major ion chemistry and trace and rare earth elements to characterize hydraulic relations, mixing processes and water–rock interaction in the Dong Van karst aquifer system, Northern Vietnam. Hydrogeol. J. 2023, 31, 1735–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matengu, B.; Xu, Y.; Tordiffe, E. Hydrogeological characteristics of the Omaruru Delta Aquifer System in Namibia. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 857–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziritis, E.; Sachsamanoglou, E.; Güler, C. Evaluating spatiotemporal groundwater quality changes in the Rhodope coastal aquifer system (NE Greece) employing a GIS-assisted hybrid approach of multivariate statistics and inverse geochemical modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, M.; Jing, J.; Li, L. A regional scale investigation on factors controlling the groundwater chemistry of various aquifers in a rapidly urbanized area: A case study of the Pearl River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellman, P.; Pain, A.; Breithaupt, C.; Bremner, P.M. Using multivariate statistics to link major ion chemistry changes at karst springs to agriculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 170573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamari, H.; Mesbah, M.; Cherchali, M.E.-H. Groundwater chemistry origin and quality assessment of the Sahel−Soummam aquifer, in northeast Algeria: A combined hydrochemical and isotopic approach. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 26, 101294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, P.; Wang, G.; Mao, H.; Feng, X.; Huang, H. Groundwater chemistry and isotope for interpreting the hydrogeological conditions and hydrochemical evolution of multilayer aquifer system of Donghai island, China. Appl. Geochem. 2023, 159, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, L.; Yao, D.; Hou, X.; Zhang, J.; Qin, H.; Ren, X.; Zheng, X. Hydrogeochemical Processes and Inverse Modeling for a Multilayer Aquifer System in the Yuaner Coal Mine, Huaibei Coalfield, China. Mine Water Environ. 2022, 41, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio Torres-Martínez, J.; Mahlknecht, J.; Mora, A.; Kaown, D.; Koh, D.-C.; Mayer, B.; Tetzlaff, D. Unveiling nitrate origins in semiarid aquifers: A comparative analysis of Bayesian isotope mixing models using nitrate and boron isotopes and a Positive Matrix Factorization model. J. Hydrol. 2024, 639, 131622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumaiza, L.; Walter, J.; Chesnaux, R.; Zahi, F.; Huneau, F.; Garel, É.; Stotler, R.L.; Bordeleau, G.; Johannesson, K.H.; Vystavna, Y.; et al. Combined effects of seawater intrusion and nitrate contamination on groundwater in coastal agricultural areas: A case from the Plain of the El-Nil River (North-Eastern Algeria). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, S.A.; Jeelani, G.; Mukherjee, A. Hydrogeochemical controls on contrasting co-occurrence of geogenic Arsenic (As) and Fluoride (F−) in complex aquifer system of Upper Indus Basin, (UIB) western Himalaya. Environ. Res. 2024, 260, 119675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zou, J.W.; Liu, J.R.; Zhang, J.K.; Zhen, P.N. Factors controlling groundwater chemical evolution with the impact of reduced exploitation. Catena 2022, 214, 106261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Yu, J.; Wu, D.; Han, Y.; Sun, B.; Zheng, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, R. Isotopic and Hydrochemical Characteristics of the Changqing-Xiaolipu Water Resource, Jinan, Eastern China: Implications for Water Resources in the Yellow River Basin. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Ma, R. Influence of permafrost and hydrogeology on seasonal and spatial variations in water chemistry of an alpine river in the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 834, 155227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishaye, H.A.; Tait, D.R.; Befus, K.M.; Maher, D.T.; Reading, M.J.; Jeffrey, L.; Tewolde, T.G.; Asfaw, A.T. Development of an improved hydrogeological and hydro-geochemical conceptualization of a complex aquifer system in Ethiopia. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 2727–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Han, D.; Song, J.; Li, L.; Pei, L. A sharp contrasting occurrence of iron-rich groundwater in the Pearl River Delta during the past dozen years (2006–2018): The genesis and mitigation effect. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Hou, Q.; Han, D.; Liu, R.; Song, J. Large scale occurrence of aluminium-rich shallow groundwater in the Pearl River Delta after the rapid urbanization: Co-effects of anthropogenic and geogenic factors. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2023, 254, 104130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba Rao, N.; Das, R.; Sahoo, H.K.; Gugulothu, S. Hydrochemical characterization and water quality perspectives for groundwater management for urban development. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 24, 101071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S.; Subba Rao, N.; Chaudhary, M.; Das, R. Assessing sources of groundwater quality and health risks using graphical, multivariate, and index techniques from a part of Rajasthan, India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 27, 101356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Sun, T.; Fan, H.; Wu, B.; Li, M.; Qian, L. Hydrochemical evaluation of groundwater quality and human health risk assessment of nitrate in the largest peninsula of China based on high-density sampling: A case study of Weifang. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 322, 129164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reischer, M.; Bichler, B.; Spötl, C.; Höfer-Öllinger, G.; Wyhlidal, S. Karst hydrogeology of the Untersberg massif and its interaction with the porous aquifer in the adjacent Salzburg Basin. Austrian J. Earth Sci. 2015, 108, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, J.C.M.; Velásquez, L.N.M.; de Paula, R.S. Horizontal and vertical compartmentalization in the fissure and karstic aquifers of the Lagoa Santa Karst Environmental Protection Area and surroundings, Minas Gerais, Brazil. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2023, 123, 104219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaunat, J.; Huneau, F.; Dupuy, A.; Celle-Jeanton, H.; Vergnaud-Ayraud, V.; Aquilina, L.; Labasque, T.; Le Coustumer, P. Hydrochemical data and groundwater dating to infer differential flowpaths through weathered profiles of a fractured aquifer. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 2053–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musgrove, M.; Jurgens, B.C.; Opsahl, S.P. Karst Groundwater Vulnerability Determined by Modeled Age and Residence Time Tracers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, 102853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Luo, M.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhou, H. Dual-tracer analysis of stable isotopes and thermal signals to quantify groundwater residence times in karst rhythmic spring systems. J. Hydrol. 2025, 661, 133493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Q. Impact of groundwater overexploitation on karst aquifer and delineation of the critical zones: Case study of Jinci spring in Shanxi, China. Carbonates Evaporites 2022, 37, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, P.; Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Li, L. Geochemical factors controlling natural background levels of phosphate in various groundwater units in a large-scale urbanized area. J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-alnaeem, M.F.; Yusoff, I.; Ng, T.F.; Alias, Y.; Raksmey, M. Assessment of groundwater salinity and quality in Gaza coastal aquifer, Gaza Strip, Palestine: An integrated statistical, geostatistical and hydrogeochemical approaches study. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 972–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xie, X.; Hou, Q.; Han, D.; Song, J.; Huang, G. Spatial distribution, sources, and human health risk assessment of elevated nitrate levels in groundwater of an agriculture-dominant coastal area in Hainan Island, China. J. Hydrol. 2024, 634, 131088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Pei, L.; Li, L.; Liu, C. Natural background levels in groundwater in the Pearl River Delta after the rapid expansion of urbanization: A new pre-selection method. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 151890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Umar, R.; Ahmad, I. Assessment of groundwater quality using Entropy-Weighted Quality Index (EWQI) and multivariate statistical techniques in Central Ganga plain, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 26, 1615–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaibu, A.; Kalin, R.M.; Phoenix, V.; Lawal, I.M. Geochemical evolution and mechanisms controlling groundwater chemistry in the transboundary Komadugu–Yobe Basin, Lake Chad region: An integrated approach of chemometric analysis and geochemical modeling. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 57, 102098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanji, S.; Das, S.; Rajak, C. A comparative hydrochemical assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes using different statistical and ML models in lower gangetic alluvial plain, eastern India. Chemosphere 2025, 372, 144074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liang, X.; Liu, Y.; Jin, M.; Knappett, P.S.K.; Liu, Y. Hydrogeochemical Evolution Along Groundwater Flow Paths in the Manas River Basin, Northwest China. Groundwater 2018, 57, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, H. Application of multivariate statistical techniques in the assessment of groundwater quality in seawater intrusion area in Bafra Plain, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 185, 2439–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligavha-Mbelengwa, L.; Gomo, M. Investigation of factors influencing groundwater quality in a typical Karoo aquifer in Beaufort West town of South Africa. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Feng, F.; Sun, J.; Shan, Y.; Su, W.; Shang, W.; Li, Y. Distribution and source analysis of soil toxic organic compounds of coal-electricity production base in arid and semi-arid region of China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Zou, J.; Zhen, P. Multivariate statistical analysis of chemical and stable isotopic data as indicative of groundwater evolution with reduced exploitation. Geosci. Front. 2023, 14, 101476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Wang, J.D.; Liu, J.T. Geochemical factors controlling the occurrence of high-fluoride groundwater in the western region of the Ordos basin, northwestern China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, V.; Nwabisa, D.P.; Rajmohan, N. Evaluation of high fluoride contaminated fractured rock aquifer in South Africa—Geochemical and chemometric approaches. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jampani, M.; Liedl, R.; Hülsmann, S.; Sonkamble, S.; Amerasinghe, P. Hydrogeochemical and mixing processes controlling groundwater chemistry in a wastewater irrigated agricultural system of India. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfarrah, N.; Hweesh, A.; van Camp, M.; Walraevens, K. Groundwater flow and chemistry of the oases of Al Wahat, NE Libya. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, V.; Rajmohan, N.; Sithole, B.; Li, P.; Uthandi, S.; van Tol, J. Geochemical evolution and the processes controlling groundwater chemistry using ionic ratios, geochemical modelling and chemometric analysis in uMhlathuze catchment, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Venkatesh, A.S.; Singh, R.; Udayabhanu, G.; Saha, D. Geochemical signatures and isotopic systematics constraining dynamics of fluoride contamination in groundwater across Jamui district, Indo-Gangetic alluvial plains, India. Chemosphere 2018, 205, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shao, W.; Guan, Q.; Sun, Y.; Du, Q.; Zhang, E.; Yan, Y.; Yang, X. The structural equation modeling constructed for runoff change attribution analysis outperforms traditional methods. J. Hydrol. 2024, 636, 131317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lv, Y.; Lu, J. Structural equation modeling of the combined effect of urban population, gross regional product and area on air pollution in selected Chinese cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, J.B.; Keeley, J.E. A Structural Equation Model Analysis Of Postfire Plant Diversity In California Shrublands. Ecol. Appl. 2006, 16, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yinglan, A.; Wang, G.Q.; Liu, T.X.; Shrestha, S.; Xue, B.L.; Tan, Z.X. Vertical variations of soil water and its controlling factors based on the structural equation model in a semi-arid grassland. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, S. An investigation into the hydrochemistry, quality and risk to human health of groundwater in the central region of Shandong Province, North China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 282, 125416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, F. Impact of anthropogenic and natural processes on the evolution of groundwater chemistry in a rapidly urbanized coastal area, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiao, J.J. Origin of groundwater salinity and hydrogeochemical processes in the confined Quaternary aquifer of the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 438–439, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Rivas, R.M.; Santacruz-De Leon, G.; Ramos-Leal, J.A.; Alvarez-Bastida, C.; Moran-Ramirez, J. Hydrogeochemical processes, and health risk assessment of groundwater, in Santa María del rio aquifer: A case study of San Luis Potosí valley, Mexico. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 26, 101268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Rai, S.P.; Puthiyottil, N.; Singh, A.K.; Noble, J.; Singh, R.; Hagare, D.; Saravana Kumar, U.D.; Rai, N.; Venyo Akpataku, K. Refining aquifer heterogeneity and understanding groundwater recharge sources in an intensively exploited agrarian dominated region of the Ganga Plain. Geosci. Front. 2024, 15, 101808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Martínez, J.A.; Mora, A.; Knappett, P.S.K.; Ornelas-Soto, N.; Mahlknecht, J. Tracking nitrate and sulfate sources in groundwater of an urbanized valley using a multi-tracer approach combined with a Bayesian isotope mixing model. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menció, A.; Mas-Pla, J.; Otero, N.; Regàs, O.; Boy-Roura, M.; Puig, R.; Bach, J.; Domènech, C.; Zamorano, M.; Brusi, D.; et al. Nitrate pollution of groundwater; all right…, but nothing else? Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostad, H.; Mohammadi, Z.; Raeisi, E.; Azimi, M.H.; Liso, I.S.; Parise, M. An integrated approach for characterization of a fractured-rock carbonate aquifer in the Zagros Region of Iran. J. Hydrol. 2024, 640, 131681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satheeskumar, V.; Subramani, T.; Lakshumanan, C.; Roy, P.D.; Karunanidhi, D. Groundwater chemistry and demarcation of seawater intrusion zones in the Thamirabarani delta of south India based on geochemical signatures. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 43, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaojuan, Q.; Baoling, L.; Kai, L.; Xinyu, C.; Wenjin, Y. Hydrochemical characteristic and karst development in typical karst spring area, Northern China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 12, 1494730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Song, J.; Han, D.; Liu, R.; Liu, C.; Hou, Q. Assessing natural background levels of geogenic contaminants in groundwater of an urbanized delta through removal of groundwaters impacted by anthropogenic inputs: New insights into driving factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Groundwater acidification in shallow aquifers in Pearl River Delta, China: Distribution, factors, and effects. Geochem. J. 2017, 51, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.Y.; Yang, Z.F.; Ji, J.F.; Yu, T.; Yuan, J.X. Effects of Soil pH and Mineral Nutrients on Cadmium Uptake by Rice Grain in the Pearl River Delta, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Song, X.; Yang, L.; Han, D.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Bu, H. The role of anthropogenic and natural factors in shaping the geochemical evolution of groundwater in the Subei Lake basin, Ordos energy base, Northwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Li, P.; He, X.; Su, F.; Elumalai, V. Hydrogeochemical Processes Affecting Groundwater Chemistry in the Central Part of the Guanzhong Basin, China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 80, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghiri, M.; Mozafari, M. Characterization of karst aquifers of the Hashtgerd Basin (North Iran) using a combination of geological, hydrodynamical, hydrochemical and isotopic investigations. Hydrogeol. J. 2025, 33, 391–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liang, X.; Ma, B.; Liu, Y.; Jin, M.; Knappett, P.S.K.; Liu, Y. Using isotopes and hydrogeochemistry to characterize groundwater flow systems within intensively pumped aquifers in an arid inland basin, Northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 126048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Zhang, Q.L.; Chen, W.F.; Shi, W.W.; Cui, Y.L.; Chen, L.L.; Shao, J.L. Hydrogeochemical analysis and groundwater pollution source identification based on self-organizing map at a contaminated site. J. Hydrol. 2023, 616, 128839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Gao, X.; Jiang, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Duan, Y.; Luo, W.; Mao, Z.; Wang, Y. Multiple contamination sources, pathways and conceptual model of complex buried karst water system:constrained by hydrogeochemistry and δ2H, δ18O, δ34S, δ13C and 87Sr/86Sr isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2024, 639, 131614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, R.; Han, P.-F.; Wang, J.; Wan, L. Evolution of Hydrogeochemistry in the Haolebaojinao Watershed of the Ordos Basin, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyet, V.T.M.; Thanh, V.P.; Hai, V.D.; Roi, N.D.; Tra, D.T.T. Hydrogeochemical characterization and groundwater quality of the dong giao karst aquifer in Tam Diep, Ninh Binh, Vietnam. Acta Carsologica 2016, 45, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, A.L. Water-formed structures: Geomorphology and hydrology of karst terrains. Science 1989, 243, 1618–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Chiogna, G.; Chang, W.; Richieri, B.; Chen, L.; Luo, M.; Guo, X.; Huang, K. Investigating the structure of a multiple karst aquifer system and its hydrological process response using high-resolution multi-tracer data. J. Hydrol. 2025, 657, 133152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Groves, C.; Yuan, D.; Kambesis, P. Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the groundwater quality in the Nandong karst underground river system in Yunan, China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2009, 109, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abiriga, D.; Vestgarden, L.S.; Klempe, H. Groundwater contamination from a municipal landfill: Effect of age, landfill closure, and season on groundwater chemistry. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, S.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X. Silicate weathering contributed to arsenic enrichment in geotherm-affected groundwater in Pliocene aquifers of the Guide basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 606, 127444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, Q.; Huang, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Huang, K.; Zhou, H. Water source identification and circulation characteristics of intermittent karst spring based on hydrochemistry and stable isotope—An example from Southern China. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 141, 105309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, P.; Luo, Y.; Li, B.; Peng, J.; Jin, X. Behavior of Sb and As in the hydrogeochemistry of adjacent karst underground river systems and the responses of such systems to mining activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Tang, C.; Satake, S.; Orimo, M.; Fukumoto, K.; Cao, Y. Heterogeneity of hydrological connectivity in coral limestone groundwater pool from vertical, spatial and temporal tracing of groundwater chemicals and isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2023, 623, 129636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, I.; Abd-Elgawad, A.N.; Seleem, E.-M.M.; Zeid, S.A.M.; Salman, S.A. Multivariate statistics explaining groundwater chemistry, Asyut, Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).