Evaluation of Phosphate and E. coli Attenuation in a Natural Wetland Receiving Drainage from an Urbanized Catchment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
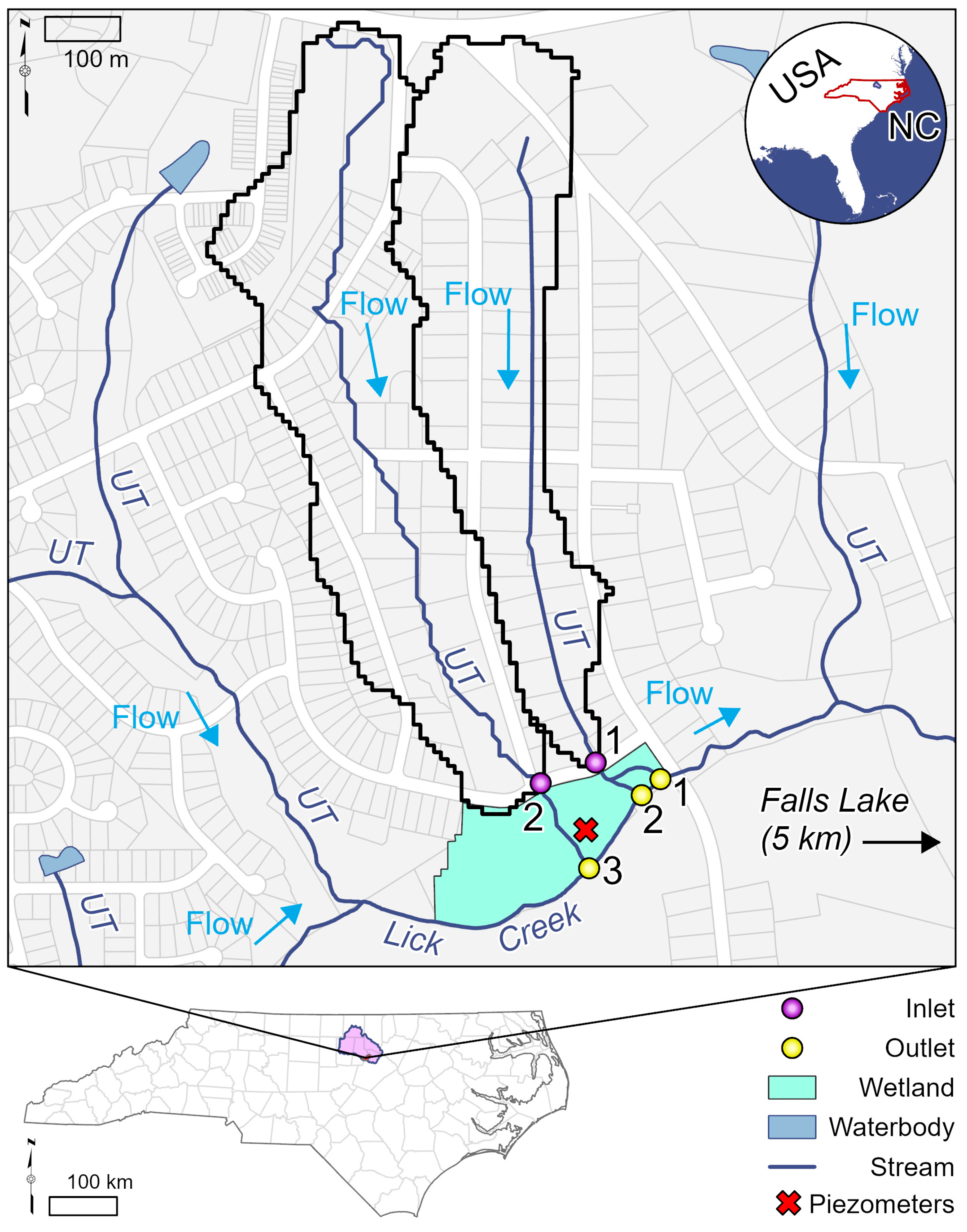
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Physicochemical Monitoring
2.3. Water Analyses
2.4. Pollutant Loading and Treatment Efficiency
2.5. Statistical Analyses
2.6. Drainageway Modifications and Onsite System Improvements
3. Results and Discussion
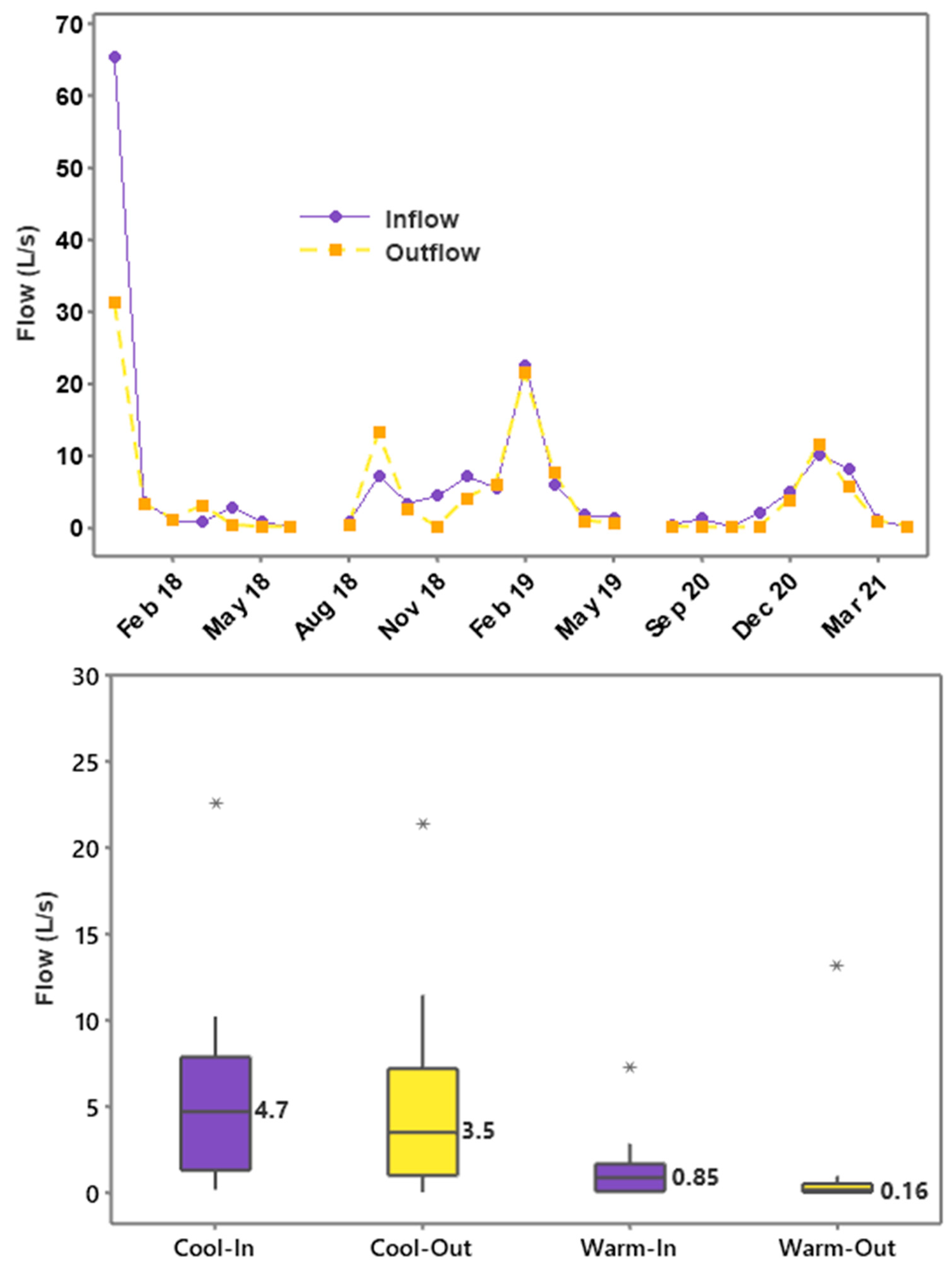
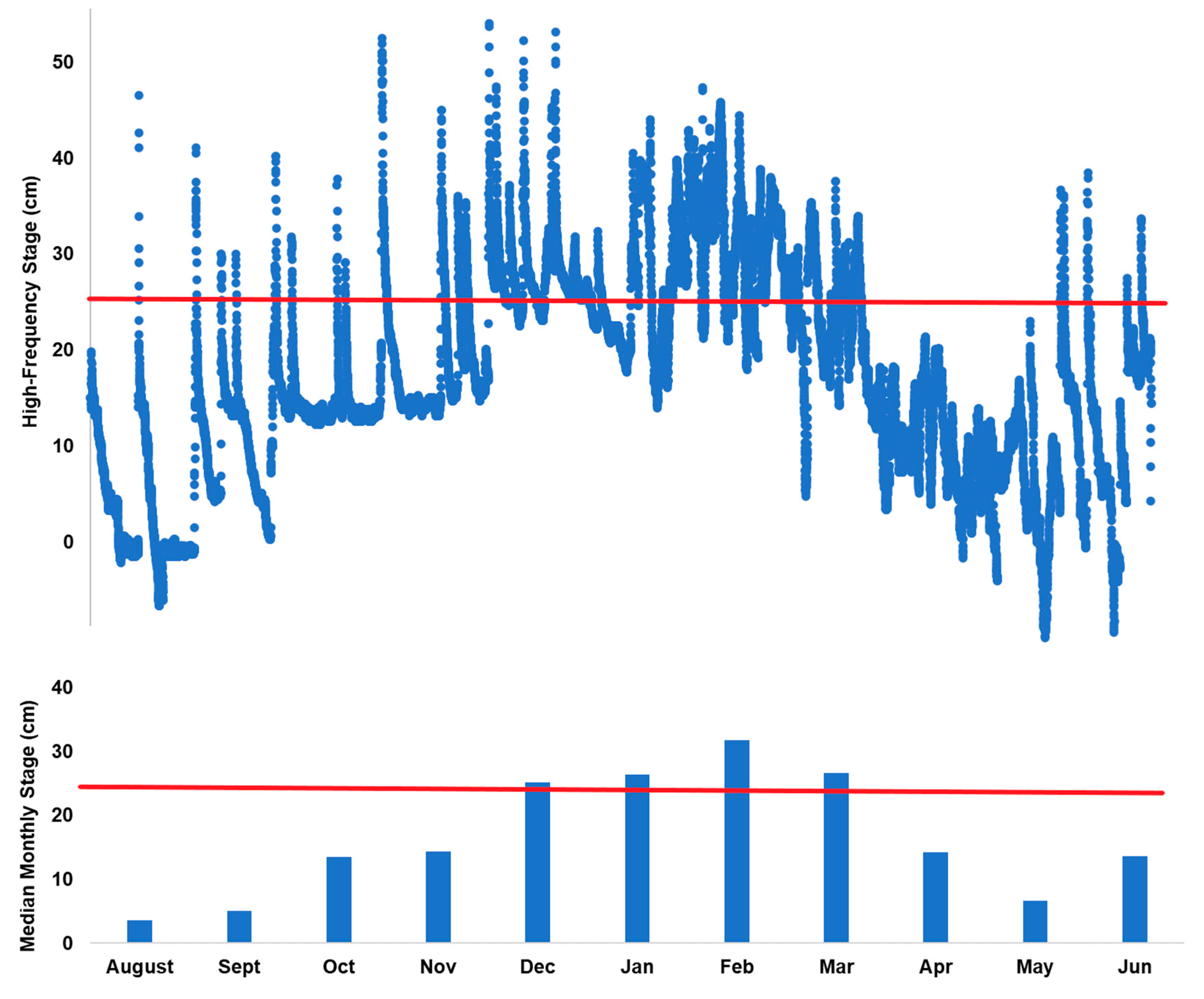
3.1. Flow Dynamics
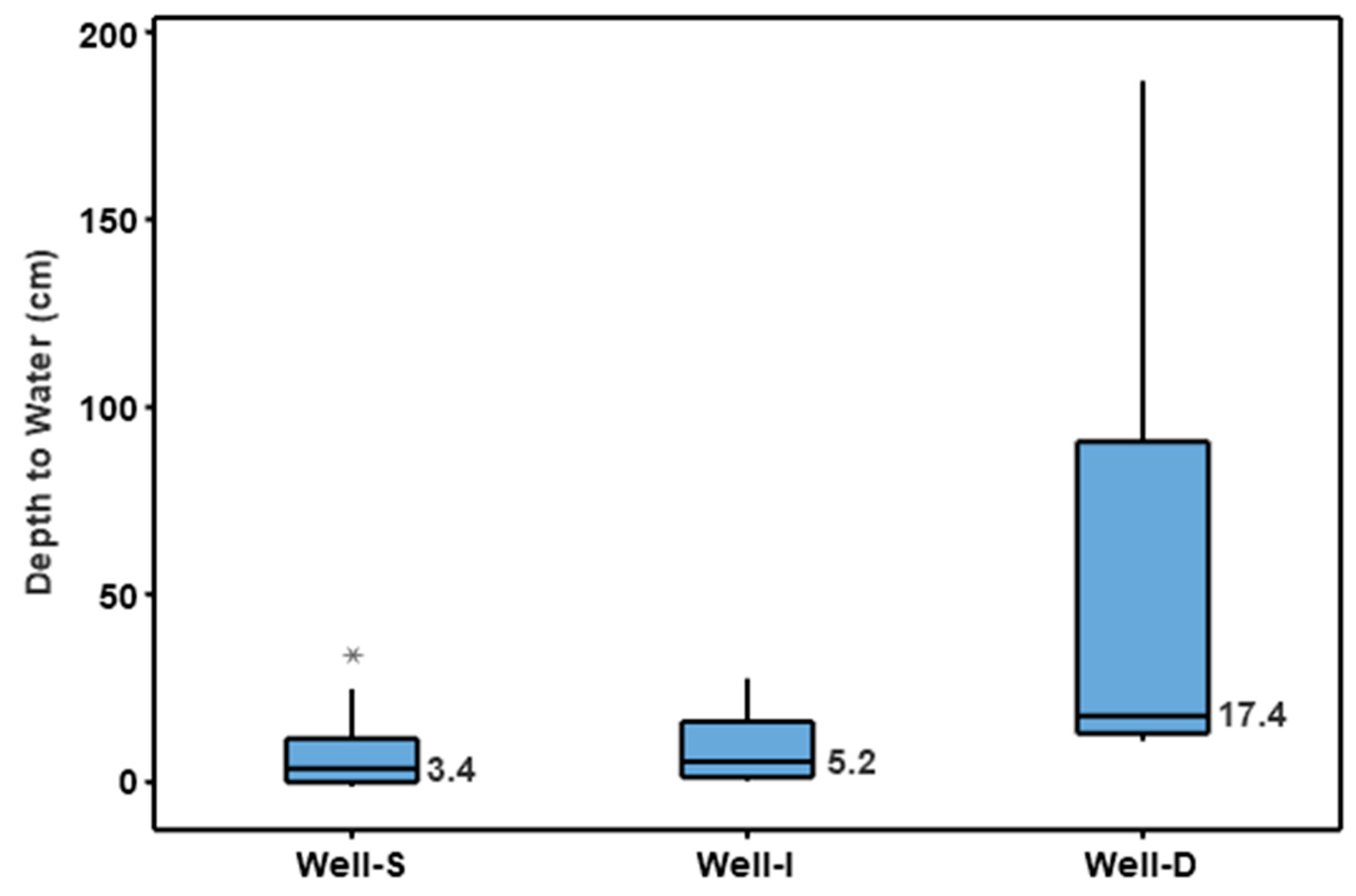
3.2. Physicochemical Characteristics
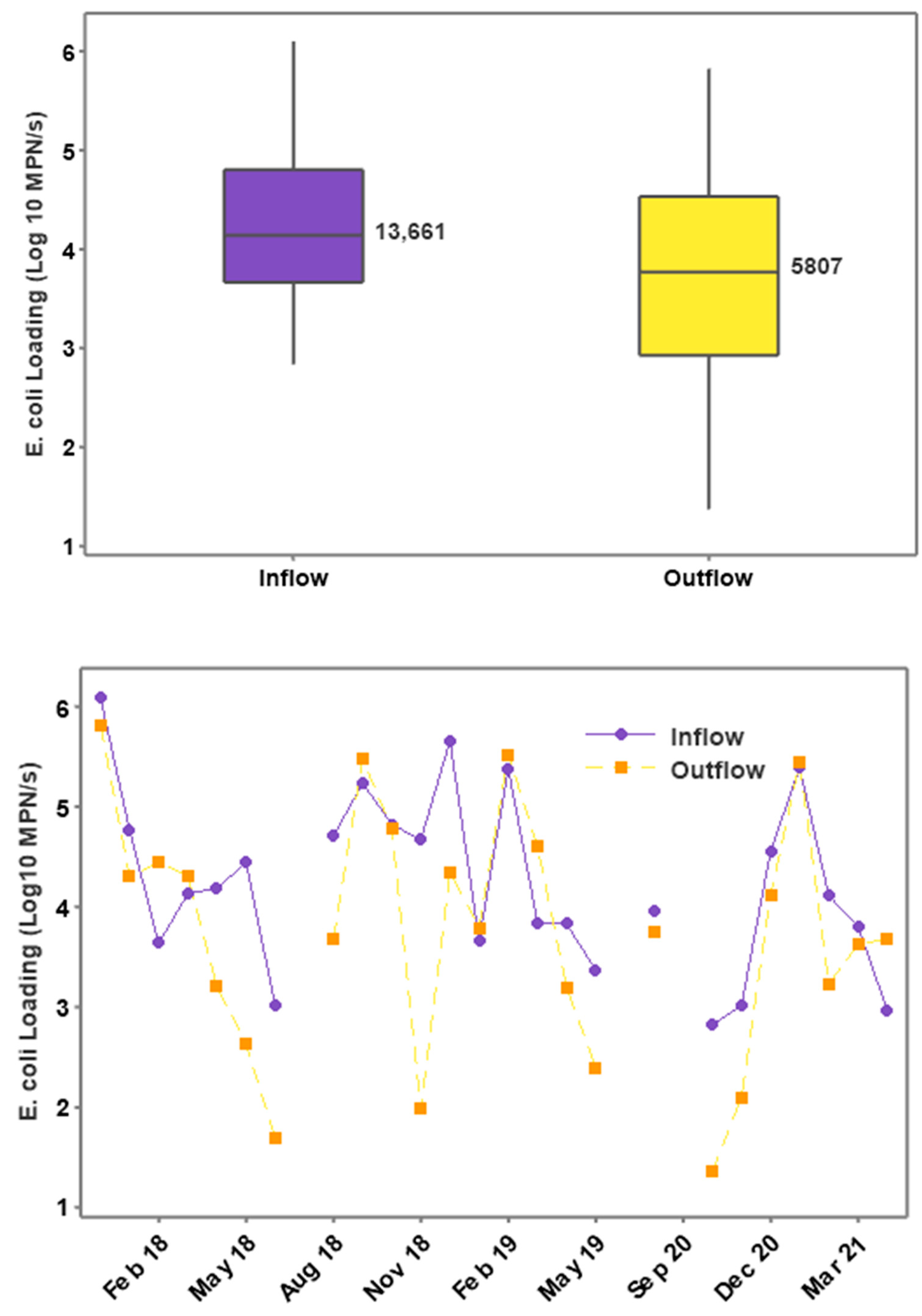
3.3. E. coli Concentrations and Loading
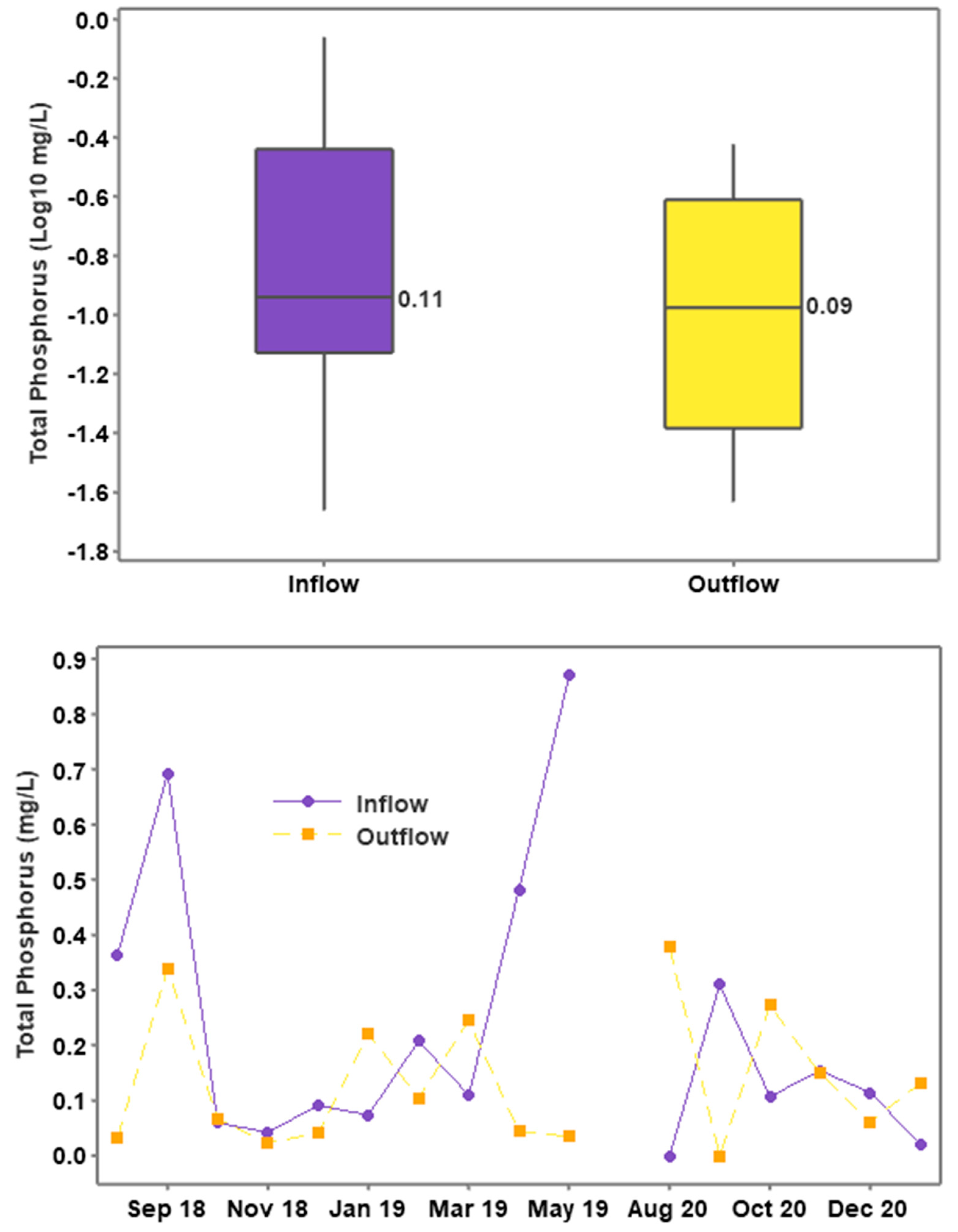
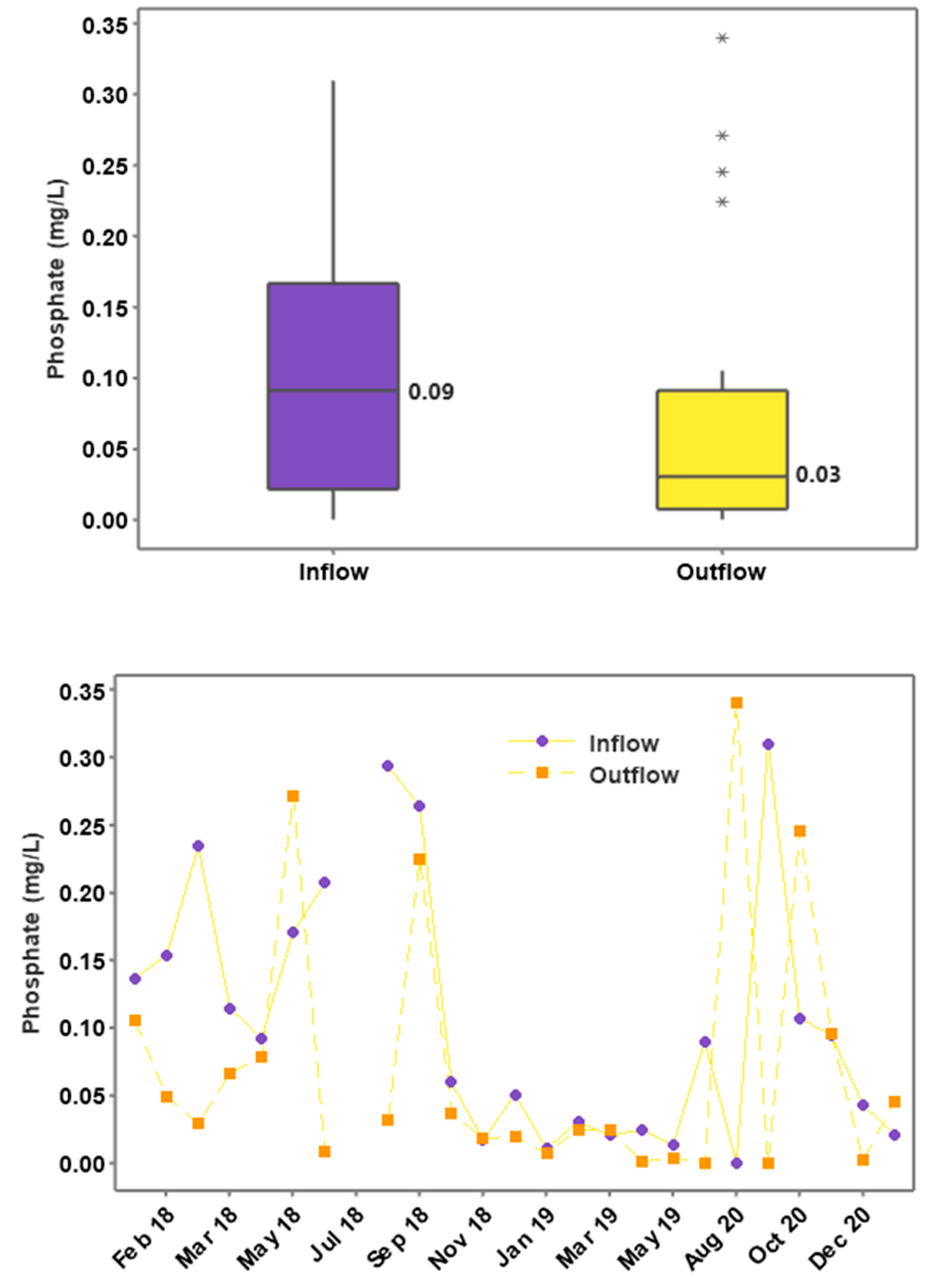
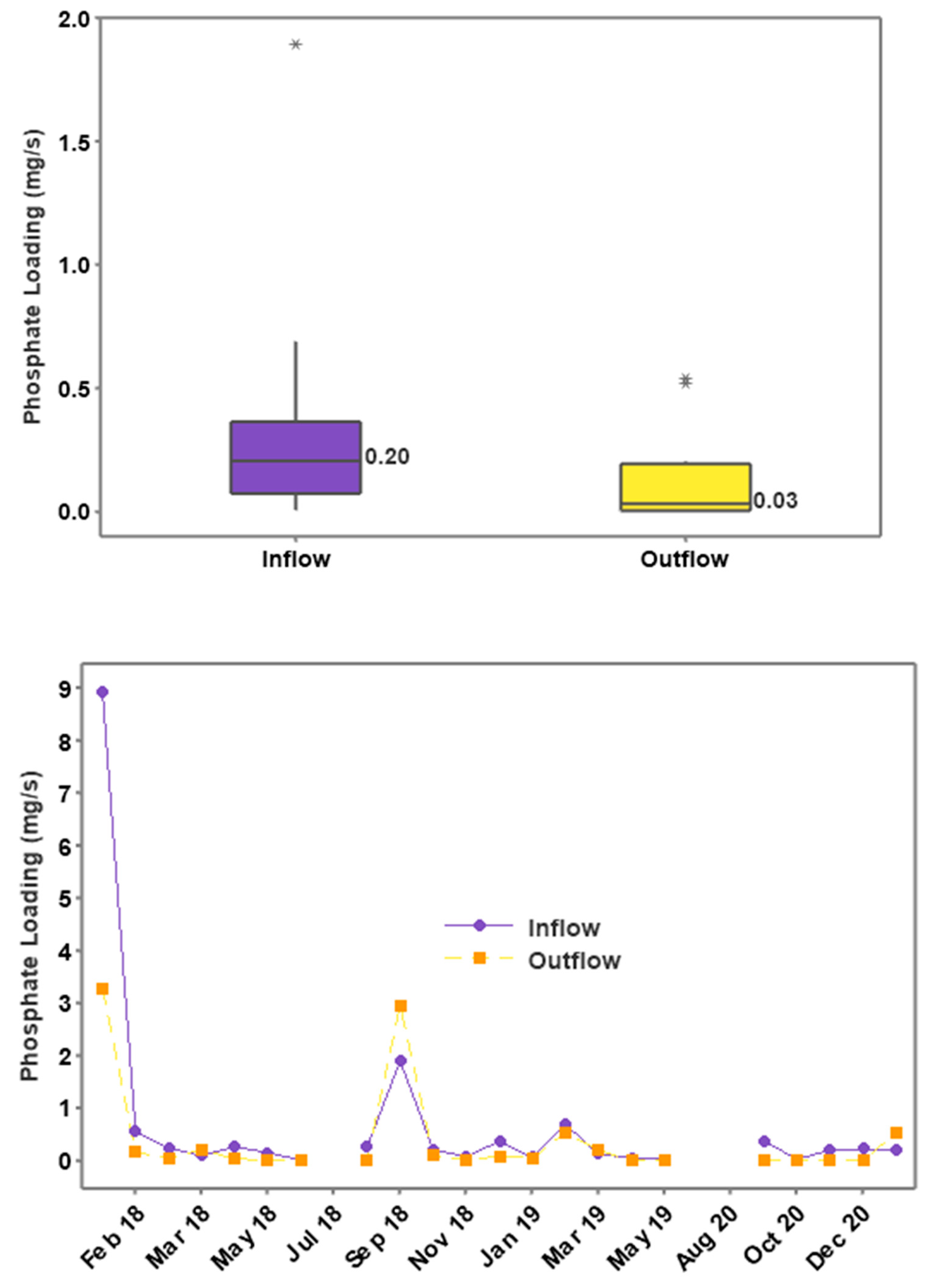
3.4. Phosphorus Concentrations and Loading
3.5. Mitigation Efforts
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- US EPA National Water Quality Inventory: Report to Congress. 2017. EPA 841-R-16-011. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2017-12/documents/305brtc_finalowow_08302017.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- Brooks, B.W.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Howard, M.D.; Johnson, M.-V.V.; Morton, S.L.; Perkins, D.A.; Reavie, E.D.; Scott, G.I.; Smith, S.A.; Steevens, J. Are Harmful Algal Blooms Becoming the Greatest Inland Water Quality Threat to Public Health and Aquatic Ecosystems? Environ. Toxicol. Chem 2016, 35, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Ecology: Controlling Eutrophication: Nitrogen and Phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapra, S.C.; Hecky, R.E.; Orihel, D.M. Reducing Phosphorus to Curb Lake Eutrophication is a Success. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8923–8929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, D.L. Phosphorus: A Rate Limiting Nutrient in Surface Waters. Poult. Sci. 1999, 78, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Ciais, P.; Goll, D.S.; Sardans, J.; Penuelas, J.; Cresto-Aleina, F.; Zhang, H. The shift of phosphorus transfers in global fisheries and aquaculture. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, X.; Qin, B.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Thomaz, S.M.; Deng, J. Global loss of aquatic vegetation in lakes. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, T.V.; David, M.B.; Gentry, L.E. Timing of Riverine Export of Nitrate and Phosphorus from Agricultural Watersheds in Illinois: Implications for Reducing Nutrient Loading to the Mississippi River. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4126–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jwaideh, M.A.A.; Sutanudjaja, E.H.; Dalin, C. Global impacts of nitrogen and phosphorus ferliser use for major crops on aquatic biodiversity. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2022, 27, 1058–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, E.; Kleinman, P.; Veith, T.; Stedman, R.; Sharpley, A. Phosphorus contributions from pastured dairy cattle to streams on the Cannonsville Watershed, New York. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2007, 62, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Janke, B.D.; Finlay, J.C.; Hobbie, S.E. Trees and Streets as Drivers of Urban Stormwater Nutrient Pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9569–9579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, C.; Anderson-Evans, E.; O’Driscoll, M.; Manda, A.; Iverson, G. Comparison of Phosphorus Concentrations in Coastal Plain Watersheds Served by Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems and a Municipal Sewer Treatment System. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preisner, M. Surface Water Pollution by Untreated Municipal Wastewater Discharge Due to Sewer Failure. Environ. Process. 2020, 7, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, C.; O’Driscoll, M.; Iverson, G.; Anderson-Evans, E. Is Onsite Wastewater a Significant Source of Phosphorus to Coastal Plain Streams? Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 1199–12110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillacheruvu, K.; Roy, D.; Tanacredi, J. Water Quality Characterization and Mathematical Modeling of Dissolved Oxygen in the East and West Ponds, Jamaica Bay Wildlife Refuge. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2003, 38, 1939–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA Recreational Water Quality Criteria. EPA-820-F-12-061. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-10/documents/rec-factsheet-2012.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- Humphrey, C.; Sanderford, C.; Iverson, G. Concentrations and Exports of Fecal Indicator Bacteria in Watersheds with Varying Densities of Onsite Wastewater Systems. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Hernandez, C.; Ryu, H.; Gonzalez-Nieves, J.; Huertas, E.; Toranzos, G.A.; Domingo, J.W.S. Tracking the primary sources of fecal pollution in a tropical watershed in a one-year study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2013, 79, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.E.; Solo-Gabriele, H.M.; Elmir, S.; Fleming, L.E. Microbial load from animal feces at a recreational beach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1649–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.H.; Senay, C.; Young, S.; Nayak, B.; Lobos, A.; Conrad, J.; Harwood, V.J. Determination of wild animal sources of fecal indicator bacteria by microbial source tracking (MST) influences regulatory decisions. Water Res. 2018, 144, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, C.P., Jr.; Lyons, N.; Bond, R.; Bean, E.; O’Driscoll, M.; White, A. Assessment and Mitigation of Fecal Bacteria Exports from a Coastal North Carolina Watershed. Hydrology 2023, 10, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fremaux, B.; Gritzfeld, J.; Boa, T.; Yost, C.K. Evaluation of host-specific Bacteroidales 16S rRNA gene markers as a complementary tool for detecting fecal pollution in a prairie watershed. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4838–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Carvalho, P.N.; Muller, J.A.; Manoj, V.R.; Dong, R. Sanitation in constructed wetlands: A review of the removal of human pathogens and fecal indicators. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, A.R.; Acharya, K.; Shanahan, S.A.; Zhou, X. Removal of nutrients and metals by constructed and naturally created wetlands in Las Vegas Valley, Nevada. Environ. Mon. Assess. 2011, 180, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, R.G.; Day, J.W.; Wiegman, A.R.; Lane, R.R. Municipal wastewater treatment costs with an emphasis on assimilation wetlands in the Louisiana coastal zone. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 137, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, W.D.; Van Stempvoort, D.R.; Schiff, S.L. Review of Phosphorus Attenuation in Groundwater Plumes from 24 Septic Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, J.; Acreman, M.C. Wetland nutrient removal: A review of evidence. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 8, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, M.; Graneli, W.; Grimvall, A.; Hoffman, C.C.; Mitsch, W.J.; Tonderski, K.S.; Verhoeven, J.T.A. How effective are created or restored wetlands for nitrogen and phosphorus removal? A systematic review. Environ. Evid. 2016, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.; Lane, R.; Day, J.; Lindsey, J.; Day, J.; Hunter, M. Nutrient Removal and Loading Rate Analysis of Louisiana Forested Wetlands Assimilating Treated Municipal Effluent. Environ. Manag. 2009, 44, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vymazal, J.; Brezinova, T.D. Treatment of a small stream impacted by agricultural drainage in a semi-constructed wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, V.L.; Bruland, G.L. Fecal Indicator Bacteria Dynamics in a Surface Flow Constructed Wetland in Southwestern Illinois, USA. Wetlands 2016, 36, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtchett, J.M.; Mallin, M.A.; Cahoon, L.B. Micro-zooplankton grazing as a means of fecal bacteria removal in stormwater BMPs. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 2702–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justino, S.; Calheiros, C.S.C.; Castro, P.M.L.; Goncalves, D. Constructed Wetlands as Nature-Based Solutions for Wastewater Treatment in the Hospitality Industry: A Review. Hydrology 2023, 10, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, C.; Chaplinski, N.; O’Driscoll, M.; Kelley, T.; Richards, S. Nutrient and E. coli Attenuation in a Constructed Stormwater Wetland in the North Carolina Coastal Plain. Environ. Nat. Resour. Res. 2014, 4, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Humphrey, C.; Iverson, G. Reduction in Nitrogen Exports from Stormflow after Conversion of a Dry Detention Basin to a Stormwater Wetland. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 9024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, C.P.; Iverson, G.; Nolan, M. Nitrogen Treatment by a Dry Detention Basin with Stormwater Wetland Characteristics. Hydrology 2022, 9, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, L.R.D.; Tonderski, K.; Iversen, B.V.; Kjaergaard, C. Phosphorus retention in surface-flow constructed wetlands targeting agricultural drainage water. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NC DEQ. Lick Creek Watershed Restoration Plan. 2009. Available online: https://www.deq.nc.gov/about/divisions/water-resources/water-planning/nonpoint-source-planning/319-grant-program/nc-watershed-restoration-plans (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- USDA. Web Soil Survey. Available online: https://websoilsurvey.nrcs.usda.gov/app/ (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- US Climate Data. Durham Climate Data. Available online: https://www.usclimatedata.com/climate/durham/north-carolina/united-states/usnc0192#google_vignette (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- Dawson, T.E. Determining water use by trees and forests from isotopic, energy balance and transpiration analyses: The roles of tree size and hydraulic lift. Tree Physiol. 1996, 16, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosetto, M.D.; Jobbagy, E.G.; Paruelo, J.M. Land-use change and water losses: The case of grassland afforestation across a soil textural gradient in central Argentina. Glob. Change Biol. 2005, 11, 1101–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.W.; Pangle, L.A.; Aulenbach, B.T. Evaluating the spatial and temporal variability of groundwater uptake by riparian vegetation in humid southeastern US catchment. Ecohydrology 2023, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, R. 2004 Basic Ground-Water Hydrology. Water-Supply Paper 2220. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/wsp/2220/report.pdf (accessed on 24 January 2024).
- Humphrey, C.P.; Finley, A.J.; O’Driscoll, M.A.; Manda, A.; Iverson, G. Groundwater and Stream E. coli Concentrations in Coastal Plain Watersheds Served by Onsite Wastewater and a Municipal Sewer Treatment System. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 1851–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, C.; Blackmon, J.; Kelley, T.; O’Driscoll, M.; Iverson, G. Environmental Health Threats Associated with Drainage from a Coastal Urban Watershed. Environ. Nat. Resour. Res. 2018, 8, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Iverson, G.; Humphrey, C.; Postma, M.H.; O’Driscoll, M.A.; Manda, A.K.; Finley, A. Influence of sewered versus septic systems on watershed exports of E. coli. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, G.F.; Matthai, C.; Fazeli, M.S.; Suh, J. Efficiency of a Constructed Wetland in Removing Contaminants from Stormwater. Wetlands 2004, 24, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathaway, J.M.; Hunt, W.F.; Jadlocki, S. Indicator Bacteria Removal in Storm-Water Best Management Practices in Charlotte, North Carolina. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 135, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, C.P.; Serozi, B.; Iverson, G.; Jernigan, J.; Pradhan, S.; O’Driscoll, M.; Bean, E. Phosphate treatment by onsite wastewater systems in nutrient sensitive watersheds of North Carolina’s Piedmont. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 1527–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanzyo, M.; Onedera, H.; Hasegawa, E.; Kanno, K.I.H. Formation and Dissolution of Vivianite in Paddy Field Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothe, M.; Kleeberg, A.; Hupfer, M. The occurrence, identification, and environmental relevance of vivianite in waterlogged soils and aquatic sediments. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 158, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmond, D.L. Riparian Buffers and Controlled Drainage to Reduce Agricultural Nonpoint Source Pollution; North Carolina Agricultural Research Service Technical Bulletin 318; North Carolina State University: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2023; Available online: https://content.ces.ncsu.edu/riparian-buffers-and-controlled-drainage-to-reduce-agricultural-nonpoint-source-pollution (accessed on 7 April 2024).
- Gordon, B.A.; Dorothy, O.; Lenhart, C.F. Nutrient Retention in Ecologically Functional Floodplains: A Review. Water 2020, 12, 2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, J.; Gascoign, M.; Bosanko, N.R. Erosion and natural revegetation associated with surface land drains in upland peatlands. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2007, 32, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, R.A.; Annable, W.K. Upstream River Responses to Low-Head Dam Removal. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2007, Tampa, FL, USA, 15–19 May 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, N.H.; Ahmad, Z. Evaluation of migration speed equations of the upstream nick of the sediment mining pit. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2023, 29, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.J.; Roy, A.H.; Feminella, J.W.; Cottingham, P.D.; Groffman, P.M.; Morgan, R.P., II. The urban stream syndrome: Current knowledge and the search for a cure. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 706–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardison, E.C.; O’Driscoll, M.; DeLoatch, J.P.; Howard, R.J.; Brinson, M.M. Urban Land Use, Channel Incision, and Water Table Decline Along Coastal Plain Streams, North Carolina. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2009, 45, 1032–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, E.; Toran, L. Effects of Bank Vegetation and Incision on Erosion Rates in an Urban Stream. Water 2018, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, R.J.; Powell, J.T.; Hunt, W.F. Retrofitting a grass swale with rock check dams: Hydrologic impacts. Urban Water J. 2019, 16, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Stagge, J.H.; Jamil, E.; Hunho, K. Hydraulic performance of grass swales for managing highway runoff. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6775–6786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, C.P.; O’Driscoll, M.A.; Zarate, M.A. Evaluation of On-site Wastewater System E. coli Contributions to Shallow Groundwater in Coastal North Carolina. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iverson, G.; Humphrey, C.P.; O’Driscoll, M.; Jernigan, J.; Serozi, B.; Sanderford, C. Quantifying Total Phosphorus and Heavy Metals in Residential Septage. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusk, M.; Toor, G.; Yang, Y.Y.; Mechtensimer, S.; De, M.; Obreza, T. A review of the fate and transport of nitrogen, phosphorus, pathogens, and trace organic chemicals in septic systems. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 455–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, K.E.; Habteselassie, M.Y.; Blackwood, A.D.; Noble, R.T. Microbial water quality before and after the repair of a failing onsite wastewater treatment system adjacent to coastal waters. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetra Tech Engineering, P.C. North Carolina Piedmont Nutrient Load Reducing Measures Technical Report. 2013. Available online: https://files.nc.gov/ncdeq/Water%20Quality/Planning/NPU/Nutrient%20Scientific%20Advisory%20Board/Final%20Nutrient%20Load%20Reduction%20report%20-%209-30-13.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2024).







| Location | Turbidity (NFU) | pH | Specific Conductance (µS/cm) | Temperature (°C) | Oxidation Reduction Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inlet 1 | 21.8 | 7.0 | 411.3 | 15 | 105.7 |
| Inlet 2 | 25.2 | 6.8 | 484.5 | 14.9 | 100.2 |
| Outlet 1 | 188.2 | 6.9 | 273.3 | 13.6 | 53.6 |
| Outlet 2 | 74.2 | 6.8 | 333.9 | 12.4 | 75.8 |
| Outlet 3 | 59.0 | 7.1 | 346.5 | 14.9 | 75.4 |
| Shallow | 6.6 | 260.6 | 13.3 | 26.8 | |
| Intermediate | 6.5 | 244.0 | 13.7 | −12.6 | |
| Deep | 6.5 | 512.7 | 13.2 | −48.7 | |
| Location | Turbidity (NFU) | pH | Specific Conductance (µS/cm) | Temperature (°C) | Oxidation Reduction Potential (mV) |
| Inlet 1 | 26.8 | 0.5 | 272.2 | 5.7 | 104.6 |
| Inlet 2 | 25.6 | 0.6 | 247.9 | 5.9 | 114.2 |
| Outlet 1 | 300.6 | 0.4 | 82.5 | 5.8 | 78.1 |
| Outlet 2 | 214 | 0.4 | 160.7 | 4.5 | 117.1 |
| Outlet 3 | 67.3 | 0.5 | 116.6 | 5.3 | 119.4 |
| Shallow | 0.3 | 50.2 | 5.8 | 72.4 | |
| Intermediate | 0.5 | 39.8 | 5.3 | 63.8 | |
| Deep | 0.6 | 119.1 | 3.9 | 108.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Humphrey, C.; Underwood, J.; Iverson, G.; Etheridge, R.; O’Driscoll, M.; White, A. Evaluation of Phosphate and E. coli Attenuation in a Natural Wetland Receiving Drainage from an Urbanized Catchment. Hydrology 2024, 11, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11060074
Humphrey C, Underwood J, Iverson G, Etheridge R, O’Driscoll M, White A. Evaluation of Phosphate and E. coli Attenuation in a Natural Wetland Receiving Drainage from an Urbanized Catchment. Hydrology. 2024; 11(6):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11060074
Chicago/Turabian StyleHumphrey, Charles, Jarrod Underwood, Guy Iverson, Randall Etheridge, Mike O’Driscoll, and Avian White. 2024. "Evaluation of Phosphate and E. coli Attenuation in a Natural Wetland Receiving Drainage from an Urbanized Catchment" Hydrology 11, no. 6: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11060074
APA StyleHumphrey, C., Underwood, J., Iverson, G., Etheridge, R., O’Driscoll, M., & White, A. (2024). Evaluation of Phosphate and E. coli Attenuation in a Natural Wetland Receiving Drainage from an Urbanized Catchment. Hydrology, 11(6), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11060074








