Abstract
Hydrogeological maps must synthesize scientific knowledge about the hydraulic features and the hydrogeological behavior of a specific area, and, at the same time, they must meet the expectations of land planners and administrators. Thus, hydrogeological maps can be fully effective when they are purpose-designed, especially in complex interconnected systems. In this case study, purpose-designed graphical solutions emphasize all the hydraulic interconnections that play significant roles in recharging the multilayered alluvial aquifer, where the majority of wells have been drilled for human purposes, artificial channels are used for agricultural purposes, and the shallow groundwater feeds protected groundwater-dependent ecosystems. The hydrogeological map was then designed to be the synthesis of three different and hydraulically interconnected main contexts: (i) the alluvial aquifer, (ii) the hydrographic basin of the Taro losing river, and (iii) those hard-rock aquifers whose springs feed the same river. The main hydrogeological map was integrated with two smaller sketches and one hydrogeological profile. One small map was drawn from a modeling perspective because it facilitates visualization of the alluvial aquifer bottom and the “no-flow boundaries.” The other small sketch shows the artificial channel network that emphasizes the hydraulic connection between water courses and groundwater within the alluvial aquifer. The hydrogeological profile was reconstructed to be able to (i) show the main heterogeneities within the aquifer system (both layered and discontinuous), (ii) visualize the coexistence of shallower and deeper groundwater, (iii) emphasize the hydraulic interconnections between subsystems, and (iv) suggest the coexistence of groundwater pathways with different mean residence times.
1. Introduction
The natural aquifer recharge is potentially made up of three different components (e.g., [1]): (i) direct recharge, coinciding with the effective infiltration of local precipitation; (ii) indirect recharge, due to losing streams (or occasionally floods from rivers); and (iii) indirect recharge, due to lateral inflow from adjacent upgradient aquifers. The existence of one or more of these components and their proportions where they coexist depend on geological, hydrogeological, hydrological, and geomorphological features. When studying interconnected surface and groundwater systems in vast areas, the groundwater availability in the downgradient aquifer is the net balance between the total input from all the components and the total output from each portion of the interconnected system. As a consequence, in agreement with the general suggestions of Struckmeier and Margat [2], when making hydrogeological maps in these hydraulically interconnected systems, graphic solutions must be used to enable “scientists” and “non-scientist users” (planners and administrators) to find the information they need to solve problems (applied science) or make decisions (planning and administration), also taking into account the possible cause–effect relationships at the system scale. For example, in terms of planning, a purpose-designed hydrogeological map provides the indispensable scientific knowledge for defining an order of priority when selecting the sub-areas where a vulnerability map must be implemented (more or less urgently) to find the best equilibrium between water resources protection and socio-economic growth. Regarding synthesis, hydrogeological maps must synthesize the scientific knowledge about the hydraulic features and the hydrogeological behavior of a specific area, and, at the same time, they must meet the expectations of the map users, who must find (fast and easily enough) the particular information they need to avoid experiencing negative domino effects when managing water resources in this sort of “basin-in-series” system. Thus, hydrogeological maps can be really and completely effective when they are purpose-designed, especially in complex interconnected systems. This approach to designing hydrogeological maps is of utmost importance in areas where the same water resources have an ecological relevance (e.g., groundwater-dependent ecosystems (GDEs)) and are utilized for human purposes.
The hydrogeological maps can be reconstructed by interpreting and synthesizing data and information from different investigations (e.g., geological surveys, well logging, geophysical investigations, pumping tests, hydraulic heads, discharge measurements, etc.). The type of data used in a specific case depends on several factors, such as (i) the hydrogeological and morphological context, (ii) the scale of the work (e.g., site, basin, regional scales), (iii) the main aims of the studies, and (iv) the available budget.
Based on these considerations, the main aim of the present work is to find and test new graphical solutions for reconstructing purpose-designed hydrogeological maps involving complex surface–groundwater systems where multiple uses and values are associated with water resources. The present map was obtained through a re-interpretation of available data (e.g., geological map, groundwater pathway within the alluvial aquifer, location of springs and “fontanili”, stratigraphic profiles, hydraulic properties of rocks) and the reconstruction of original hydrogeological profiles. The map was then used to speculate about the vulnerability of the heterogeneous alluvial aquifer as a function of possible contamination sources located within the Apennine chain, far from the plain, due to surface–groundwater interactions.
The choice of the test area fell on the wide system belonging to the Parma alluvial aquifer and the Taro River basin. From the hydrogeological point of view, it is characterized by several hard-rock mountain aquifers, a flat heterogeneous alluvial aquifer, and a losing river (e.g., [3]). On the other hand, at this site, water resources flowing within the heterogeneous alluvial aquifer feed GDEs and are utilized for drinking, industrial, and agricultural purposes. In agriculture, intensive models prevail in the flat areas, while organic techniques and protected areas and regional and national parks are prevalent within the mountainous Apennines (e.g., [4]). Some mountainous agri-food products (e.g., Parma Ham, Parmigiano Reggiano cheese, mushrooms from Borgotaro) are recognized as Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) or Protected Geographical Indication (PGI) (e.g., [5]), while others are traditional products linked to ancient varieties of animals and plants for which there is an increasing interest in the specific market [6,7]. Industrial activity in Parma is strongly oriented towards the agro-alimentary sector (e.g., large-scale pasta and baked goods and dairy manufacturers, which are world leaders in their sectors). The leading role of the Parma industry is also linked to the production of food machinery, packaging, and preservation machines and equipment. Other industrial sectors, such as pharmaceuticals and perfumery, belong to personal care and well-being [8].
2. Study Area
The research was carried out in the hydrogeological basin of the Taro River and the connected alluvial aquifer developing from the northern Apennine margin to the Parma plain (Northern Italy; Figure 1). The northern Apennines are a fold-and-thrust belt composed of a pile of NE-verging tectonic units that developed as a result of the Cenozoic collision between the European plate (Corso–Sardinian block) and the Adria plate [9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. The tectonic units belong to the Ligurian, Tuscan, and Umbria–Romagna domains. The Ligurian units represent the uppermost tectonic units in the Apennine nappe pile and correspond to allochthonous terrains initially deposited in an oceanic realm (the Ligurian–Piedmontese sector of the Alpine Tethyan ocean) composed of ophiolites and their Jurassic to Eocene sedimentary cover [16,17,18,19]. These units tectonically overlie the Tuscan and Umbria–Romagna units, originally deposited on the passive margin of the Adria Plate from the middle Triassic to early Cretaceous and convergent-to-collisional margin since the middle Cretaceous till the present, consisting of a lower succession of carbonate rocks of Mesozoic–Cenozoic age and a thick upper succession of siliciclastic foredeep sediments of the Oligocene–Miocene age [9]. During the orogenetic uplift from the Eocene to the Messinian, episutural and wedge-top basins were set on top of the Ligurian units, giving rise to the Epiligurian Succession [20,21].
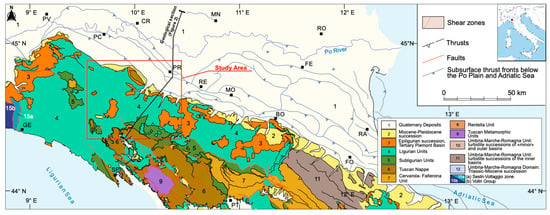
Figure 1.
Tectonic map of the northern Apennines (from [9], modified).
From the Messinian to the present, at the front of the chain, the Po Basin represents the northern Apennines foredeep, nowadays filled with Plio-Pleistocene turbidite and deltaic syntectonic marine-regressive sequences, heavily influenced by the uplifts of the several thrust fronts buried under the plain [9,22,23]. Similar to the upper Emilia–Romagna plain and Apennine foothills, the Parma plain is characterized mainly by this marine-to-continental regressive sedimentary succession. The sequence of units (or synthems sensu [24]) is characterized at the base by hectometric thicknesses of Pliocene-clay marine sediments, above which progressively more continental deposits from shallow marine and fan deltas to today’s plains and foothill alluvial fans discordantly overlapped during the Pleistocene till the present (Figure 2).
Due to their different lithological composition, the geological units of the study area may have different hydrogeological behaviors over the entire Apennines and Po Plain, as studied by several works (e.g., [25,26,27]) and extensively reported in the specific sections below.
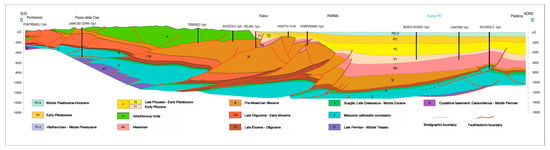
Figure 2.
Geological section (from [28], modified).
3. Hydrogeological Subsystems
The main subsystems within the study area are several hard-rock aquifers and one large heterogeneous alluvial aquifer (see details hereafter). Hard-rock aquifers are made mainly of ophiolitic rocks or turbiditic (carbonate and siliciclastic) successions. From the hydrogeological point of view, the alluvial aquifer is downstream of the hard-rock aquifers. Nevertheless, because of the interposition of Pliocene-clay marine sediments, there is no direct groundwater inflow from the ophiolitic or turbiditic aquifers toward the alluvial one (Figure 2). The alluvial aquifer is recharged directly through the effective infiltration of local precipitation and indirectly through the Taro losing river.
Ophiolitic aquifers in the Italian Apennine chain are characterized by hydraulic compartmentalization due to one or more of these factors (e.g., [29,30,31]; Figure 3): (i) low-permeability fault cores that partially or fully impede groundwater flow (e.g., [32,33]), and/or (ii) displacement of the aquifer bottom due to faulting. Ophiolitic rocks are sometimes characterized by vertical heterogeneity, causing the coexistence of shallow perched temporary groundwater and deeper groundwater [29,34].
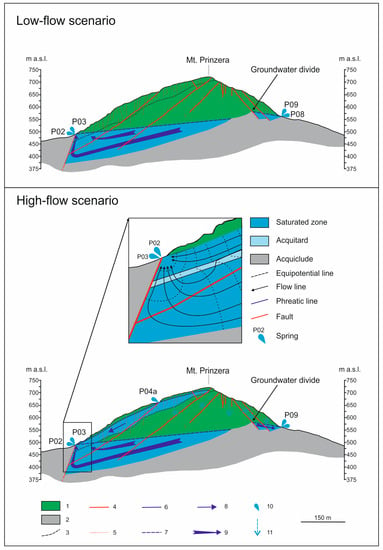
Figure 3.
Hydrogeologic conceptual model of the Mt. Prinzera aquifer system. Legend—1: ultramafic aquifer; 2: aquiclude; 3: discontinuous aquitard; 4: fault; 5: fracture; 6: perched groundwater phreatic surface; 7: basal groundwater piezometric surface; 8: flowline of the perched groundwater; 9: flow line of the basal groundwater; 10: springs and their code; 11: infiltration within the unsaturated ultramafic medium (from [29], modified).
Turbiditic aquifers in the Italian Apennine chain are mainly or exclusively made up of sandstones and/or marls. From the hydrogeological point of view, three main conceptual models have been defined, as synthesized below.
In some cases, turbiditic aquifers are characterized by significant vertical heterogeneity due to stress-release fracturing and/or weathering that enhances rock permeability in the near-surface bedrock ([35,36]; Figure 4), according to findings on other hard-rock aquifers (e.g., [37]). In this case, the upper bedrock is characterized by relatively high hydraulic conductivity (around 10−6 m/s; [36]) facilitating significant groundwater recharge and flow. Differently, the deeper bedrock is characterized by very low hydraulic conductivity (in the order of 10−8 m/s; [36]), and groundwater flow is more significant within possible networks of damage zones associated with faults.
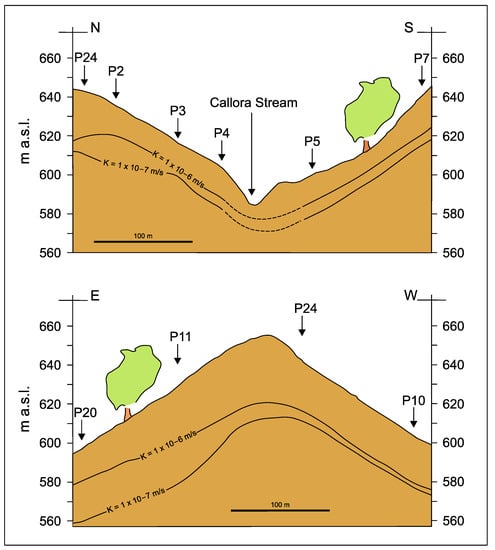
Figure 4.
Variation of hydraulic conductivity (K) with depth in a turbiditic aquifer (P2-5, P10, P11, P20, P24 are the codes of the boreholes used to carry out hydraulic tests; from [36], modified).
In other contexts, post-depositional processes increase rock permeability in larger volumes as a result of fracture development in the competent layers. Within these successions, there is no contrast in permeability with depth between a shallower and a deeper bedrock and unique groundwater flows in a low-permeability continuum at the basin scale. Despite the significant heterogeneity of the medium, the basin-scale hydraulic continuity is probably due to fracture networks associated with folds and faults that break the lower-permeability layers, therefore minimizing the aquiclude role potentially played by each one of these layers ([38]; Figure 5). In a broader context, this interpretation agrees with the link between fracture zones associated with thrust folds and fluid flow observed by other authors (e.g., [39]).
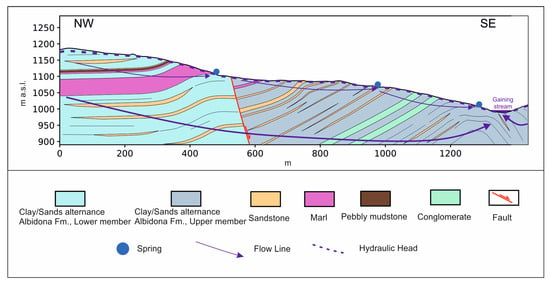
Figure 5.
Hydrogeological model of a turbiditic aquifer (from [38], modified).
The main features of the two models described above sometimes coexist and are further complicated by landslide processes, converging in a third conceptual model. In that case, a unique groundwater flows in a low-permeability continuum at the basin scale. Still, significant layered heterogeneity causes the whole system to be characterized by the coexistence of fast and shallow pathways and deeper and more prolonged ones [40]. As demonstrated by merging hydrogeological, microbial, and zoological data in a test site [41,42], rapid percolation is observed in the near-surface unsaturated zone, and fast groundwater flow is observed in the shallow bedrock. Differently, within the deeper bedrock, heterogeneities can cause a significant variation in the hydraulic head with depth [43], and the lower permeability causes the slowdown of groundwater flow. The variation in flow velocities and residence times within the whole heterogeneous system can be further emphasized by very low permeability slip surfaces of landslides that sometimes act as permeability barriers, as demonstrated by Petrella et al. [44] within the study area.
In the wider context of all the hard-rock aquifers, significant groundwater exchange is then possible between adjacent aquifers of the Apennine chain. However, detailed studies have yet to be carried out on this topic at this stage, and purpose-designed investigations must be developed shortly.
The alluvial aquifer corresponds to the Pleistocene alluvial synthem, lithologically defined by alternating gravels, sands, silts, and silty clays and generated in the area by the depositional dynamics of the ancient Taro River. At the bottom of the succession, the high thickness of Pliocene marine clays is considered an extensive regional-scale aquiclude [45]. The contact between the heterogeneous aquifer and bottom aquiclude corresponds to the Pliocene–Pleistocene boundary and is characterized by several undulations due to Apennine tectonic compressive action and subsequent erosion. At the southern end of this aquifer, the Taro River’s alluvial terrace (the area’s most recent unit) is settled with a stratification parallel to the topographic plane. Moving toward the valley (to the north), a fan of gravel–sand–silt strata open in depth, with gradually smaller angles of inclination as the more recent depositions have originated. The resulting geometric and physical feature of the aquifer arrangement validates its syntectonic nature, contemporaneous with the Apenninic tectonic activations (Figure 6). The groundwater flows from the southwest to the northeast at a basin scale (e.g., [46]) and is recharged by the effective local infiltration and the Taro River waters [3,46,47,48,49]. Concerning the hydraulic properties of the system, Zanini et al. [44,46] calculated a hydraulic conductivity varying from 1.2 × 10−5 to 4.9 × 10−5 m/s (mean 2.3 × 10−5 m/s; median 1.7 × 10−5 m/s) in coarse-grained horizons and from 9.3 × 10−9 to 1.3 × 10−7 m/s (mean 1.6 × 10−7 m/s; median 9.7 × 10−8 m/s) in fine-grained layers. The abundance of silt and fine sands, instead of clay, in the fine-grained outcropping layers [50] causes the groundwater to be semi-confined in some sub-areas.
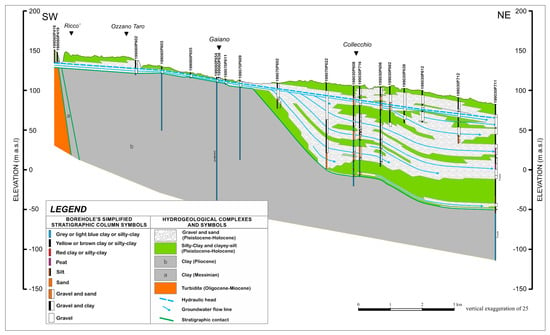
Figure 6.
Hydrogeological section showing arrangement of hydrogeological subsystems at the contact between Apennines chain and Parma plain.
In the northern end of the study area, the shallow groundwater feeds the so-called fontanili (e.g., [46,51,52]; see location in the supplementary Hydrogeological Map), which are small, semi-artificial aquatic ecosystems (sensu [53]). These GDEs are typical of the Po River basin, the largest Italian watershed. As demonstrated by Severini et al. [49], they are indirectly recharged also by the losing Taro River.
In the wide context of the whole interconnected system, the losing river causes the heterogeneous alluvial aquifer to be indirectly recharged by the entire hydrographic basin of the Taro, including the surface runoff and groundwater of those hard-rock aquifers whose springs flow out into the Taro River basin. The influence of Taro surface waters on the recharge of the alluvial aquifer is further emphasized by a network of losing artificial open channels used for agricultural purposes (Figure S1).
4. Materials and Methods
Starting from the lithological composition of the geological units composing this sector of the Apennines and Plains, four hydrogeological subsystems were divided at the basin scale. Official geological mapping (from ISPRA, Regione Emilia–Romagna, and Provincia di Parma), supplemented by outcrop inspections and related scientific literature, has formed the distinction’s main basis. To each single geological unit, an expected hydraulic behavior was attributed, and (i) ophiolitic, (ii) turbiditic, (iii) alluvial, and (iv) clay subsystems were defined as the main hydrogeological domains at the study-area scale. The International Hydrogeological Map of Europe 1:1,500,000 (IHME1500) provided by BGR and UNESCO (2019) was used as the standard color reference.
After the initial conceptual subdivision and the analysis of the possible hydraulic interconnection between the Taro River and the multilayered alluvial aquifer (through the reconstruction of original hydrogeological profiles), the main map (available as a supplementary file) was produced to graphically synthesize hydraulic features and interconnections at the basin scale. Mapping was executed with Corel Draw X6 graphic software, and the combination of multiple geological units has necessitated constant comparison with official geological cartography to accurately represent the contacts between the defined hydrogeological subsystems. The topographic chart has been used as the geographical reference base for the map to locate major population centers and anthropogenic structures as potential sources of impact. Geomorphological landforms (landslides, debris, colluvium, etc.) were mostly incorporated into the unit on which they were formed.
The boundary of the Taro River hydrogeological basin has been defined according to topography, surface drainage network, and extension of aquifer hydrogeological subsystems.
Once the representation of subsystems was completed, all the symbols capable of providing hydrogeological insights on a large scale were included in the map.
The main hydrogeological map was integrated with two smaller sketches and one hydrogeological profile. The two smaller maps enable visualizing in detail (i) the alluvial aquifer bottom and (ii) the network of artificial channels within the alluvial aquifer. Because numerical models are increasingly implemented in hydrogeological studies finalized to protect, use, and manage water resources, the small map focused on the aquifer bottom was designed to be easily used for modeling purposes by also emphasizing the “no-flow boundary.” Both the bottom and the “no-flow boundary” correspond to the Pliocene-clay marine sediments that act as (i) a hydraulic barrier between the hard-rock aquifers and the alluvial aquifer and (ii) the base of the whole heterogeneous alluvial succession.
The small map focused on the network of artificial channels facilitates an understanding of the wide and pervasive interaction between losing water courses and groundwater within the alluvial aquifer.
The hydrogeological section was added to improve subsurface information. It was reconstructed on the basis of a re-interpretation (from a hydrogeological perspective) of stratigraphic profiles derived from the published database by Regione Emilia–Romagna. At first, after an accurate selection of the above data, the stratigraphic section was constructed having an orthogonal direction to the Apennine front (SW–NE) to obtain a self-constructed perspective of the geological (and hydrogeological) context at the regional scale, considering the nodal zone of the Apennine to Parma Plain transition. In light of the multiple hydraulic interconnections existing within the whole test system and the significant layered heterogeneity of the main alluvial aquifer, the hydrogeological profile was reconstructed so as to be able to (i) show the main heterogeneities within the aquifer system (both layered and discontinuous), (ii) visualize the coexistence of shallower and deeper groundwater, (iii) emphasize the hydraulic interconnections between subsystems, and (iv) suggest the coexistence of groundwater pathways with different mean residence times.
The usual graphical approaches to creating hydrogeological maps could be incomplete and/or ineffective when working on interconnected aquifer systems, where the groundwater pumped for human purposes and feeding GDEs is recharged through direct (local effective infiltration) and indirect processes (losing streams, lateral underground inflow from upgradient aquifers). Therefore, according to other authors (e.g., [30]), in the case of complex systems and/or specific management/protection aims, new and purpose-designed graphical solutions must be applied to enhance the map’s effectiveness. In this case study, these solutions show and emphasize all the hydraulic interconnections playing significant roles in recharging the multilayered alluvial aquifer, where the majority of wells have been drilled for drinking/industrial/agricultural purposes, artificial channels are used for agricultural purposes, and the shallow groundwater feeds protected GDEs. The hydrogeological map was then designed to be the synthesis of three different and hydraulically interconnected main contexts: (i) the main heterogeneous alluvial aquifer (the main target of the purpose-designed map), (ii) the hydrographic basin of the Taro River (the losing river that feeds the main alluvial aquifer), and (iii) those hard-rock aquifers (mainly turbiditic and ophiolitic) within the Apennine chain whose springs feed the Taro River. As per the interconnection between the surface and groundwaters within the alluvial plain, a dedicated sketch was added to the main map to clearly show the network of artificial channels utilized for agricultural purposes.
5. Discussion
The purpose-designed hydrogeological map tested at the study area (i) provides effective and partially new graphical solutions to describe the main hydrogeological features and processes characterizing a complex surface–groundwater interconnected system and (ii) points out several important aspects that meet the needs of hydrogeologists and the expectations of the map’s users (with emphasis on planners and administrators).
In the latter case, this type of map can be used, for example, as a basis for reconstructing reliable vulnerability maps from the perspective of groundwater and GDE protection against pollution (considering both direct and indirect contamination sources). As a matter of fact, this test study highlights that the large alluvial aquifer (whose groundwater feeds GDEs and is used to support the economic growth of one of the most important industrial areas in Italy and Europe) is vulnerable to contaminants also coming from the wider upgradient Apennine chain because of the indirect hydraulic connection via the Taro River.
Even if the Parma Apennines are mainly characterized by organic agriculture and protected areas, they could also be of interest for new mining exploitation, taking into consideration the progressive increase in the demand for metals and minerals for lithium-ion batteries. This is the case, for example, in the abandoned Corchia mining district (see location in the supplementary file), which can be defined as mixed sulfide (mostly Cu-bearing) ore deposits set into ophiolitic aquifers. As a matter of fact, mining activities can produce several types of waste, such as wastewater, and have long-lasting and profound adverse effects on the downstream receiving aquatic environments (e.g., [54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61]). Therefore, there is an urgent need to learn from historical mine pollution issues to avoid the negative environmental impacts of new mining activities in the future. This goal can be achieved by understanding how potential mine pollution could be transported from its source through a downstream catchment, and purpose-designed hydrogeological maps give this information to planners and administrators. From a vulnerability perspective, the hydrogeological mapping strategy and solutions proposed here suggest, for example, that Corchia mine reactivation would cause severe environmental damage in the vast interconnected aquatic ecosystem (to groundwater and GDEs) in case of contaminant release.
At the same time, this map will be used to plan and carry out more detailed studies that can help to understand and estimate (i) the magnitude of the expected impact of the possible Corchia mine reactivation, (ii) the transport time between the potential contamination source and each of the subsystems coexisting at the system scale, and (iii) the influence of pumping activities within the heterogeneous alluvial aquifer on the underground contaminant migration pathways.
6. Conclusions
In a broader context, the mapping strategy and solutions presented here are of utmost importance (i) in managing and optimizing water resources abstraction for human purposes (as is evident) as well as (ii) when carrying out effective water–energy–food–land–climate nexus studies (WqEFLC nexus, sensu [62]) for sustainable development goals. For example, an effective WqEFLC nexus study must also consider the layered heterogeneity of an alluvial aquifer. In that scenario, groundwater can be pumped through wells drilled and screened at different depths, requiring a lower or higher energy demand. Regarding climate change in particular, graphically showing the hydraulic interconnections between different subsystems that coexist in a wide area facilitates the (rapid and easy) understanding that water availability, as well as the integrity of specific GDEs, in a specific subsystem are both also influenced by climate modifications circumscribed to upstream sub-basins. Therefore, in hydrogeological settings where a changing climate has already been verified at a regional scale (e.g., [63,64] at the study area), more detailed climate studies should be planned to refine this cause–effect relationship.
Even in terms of sustainable development goals, this type of hydrogeological map can be utilized to measure the gross ecosystem product (GEP), which summarizes the value of the contribution of an ecosystem to the economic activity of an area by evaluating the ecosystem services in a single monetary metric [65]. As is known, this approach can consider the contribution of Nature to economic growth and human well-being differently from the conventional gross domestic product (GDP).
The approach proposed here can be applied worldwide, also in hydrogeological settings made up of different lithologies. As a matter of fact, the solutions tested with this map can be used in an easy way in those systems where different factors cause a large aquifer system to be hydraulically interconnected.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/hydrology10060127/s1, Figure S1: Hydrogeological Map of the Interconnected Surface–Groundwater System of Parma Alluvial Aquifer and Taro River Basin.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.P., A.F., A.R. and F.C.; methodology, R.P., A.F. and F.C.; software, R.P., A.F. and F.C., validation, R.P., A.F., A.R. and F.C.; writing and reviewing the draft, R.P., A.F., A.R. and F.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received external funding from Provincia di Parma and is funded by the ‘Departments of Excellence’ program of the Italian Ministry for University and Research (MUR, 2023–2027).
Data Availability Statement
The relevant data can be found as follows: “Regione Emilia Romagna Borehole’s Database” at https://servizimoka.regione.emilia-romagna.it/mokaApp/apps/geg/index.html (accessed on 11 May 2023); “Regione Emilia Romagna Water Springs” at https://servizimoka.regione.emilia-romagna.it/mokaApp/apps/rocce_magazzino/index.html (accessed on 11 May 2023); “Regione Emilia Romagna Geological Cartography—Webgis” at https://ambiente.regione.emilia-romagna.it/it/geologia/cartografia/webgis-banchedati/webgis (accessed on 11 May 2023); “ISPRA Geological Cartography at a scale of 1:50.000” at https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/Media/carg/ (accessed on 11 May 2023); “Provincia di Parma PIAE” at http://www.provincia.parma.it/provincia/servizi-e-uffici/servizio-pianificazione-territoriale/ufficio-attivit%C3%A0-estrattive-0 (accessed on 11 May 2023); and “Consorzio Bonifica Parmense irrigation canal network” at https://portale.bonifica.pr.it/map/lizmap/www/index.php/view/map/?repository=pubblica&project=web (accessed on 11 May 2023).
Acknowledgments
This research benefited from the equipment and framework of the COMP-R Initiative.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Freeze, R.A.; Cherry, J.A. Groundwater; Prentice Hall Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Stuckmeier, W.F.; Margat, J. Hydrogeological Maps. A Guide and a Standard Legend; International Association of Hydrogeoiogist, Contributions to Hydrogeology, Cerlag Heinz Heisse: Hannover, Germany, 1995; Volume 17, 170p. [Google Scholar]
- Iacumin, P.; Venturelli, G.; Selmo, E. Isotopic features of rivers and groundwater of the Parma Province (Northern Italy) and their relationships with precipitation. J. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 102, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.C.; Arfini, F.; Guareschi, M. When Higher Education Meets Sustainable Development of Rural Areas: Lessons Learned from a Community–University Partnership. Soc. Sci. 2022, 11, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfini, F.; Cozzi, E.; Mancini, M.C.; Ferrer-Perez, H.; Gil, J.M. Are Geographical Indication Products Fostering Public Goods? Some Evidence from Europe. Sustainability 2019, 11, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.C.; Donati, M. Local Agri-Food Systems in a Global World: Market, Social and Environmental Challenges; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, M.C.; Consiglieri, C. Innovation and marketing strategies for PDO products: The case of “Parmigiano Reggiano” as an ingredient. Bio-Based Appl. Econ. J. 2016, 5, 153–174. [Google Scholar]
- Parma Manifactures Associations. Parma and Its Enterprises. 2020. Available online: www.upi.pr.it (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Conti, P.; Cornamusini, G.; Carmignani, L. An outline of the geology of the Northern Apennines (Italy), with geological map at 1:250,000 scale. Ital. J. Geosci. 2020, 139, 149–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elter, P.; Grasso, M.; Parotto, M.; Vezzani, L. Structural setting of the Apennine-Maghrebian thrust belt. Epis. J. Int. Geosci. 2003, 26, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remitti, F.; Vannucchi, P.; Bettelli, G.; Fantoni, L.; Panini, F.; Vescovi, P. Tectonic and sedimentary evolution of the frontal part of an ancient subduction complex at the transition from accretion to erosion: The case of the Ligurian wedge of the northern Apennines, Italy. GSA Bull. 2011, 123, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlini, M.; Artoni, A.; Vescovi, P.; Bernini, M.; Remitti, F.; Bettelli, G.; Vannucchi, P.; Aldega, L.; Balestrieri, M.L.; Corrado, S.; et al. Tectonic and erosional exhumation processes in the western Northern Apennines of Italy: Coeval compressional and extensional tectonics affecting an eroding orogenic wedge. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 7–12 April 2013; p. 12994. [Google Scholar]
- Molli, G.; Crispini, L.; Malusà, M.; Mosca, P.; Piana, F.; Federico, L. Geology of the Western Alps-Northern Apennine junction area: A regional review. Eds Marco Beltrando Angelo Peccerillo Massimo Mattei Sandro Conticelli Carlo Doglioni J. Virtual Explor. 2010, 36, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vescovi, P. Note Illustrative Della Carta Geologica d'Italia Alla Scala 1:50.000, Foglio 216 “Borgo Val Di Taro”; Servizio Geologico d'Italia-Regione Emilia Romagna; SELCA: Firenze, Italy, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Boccaletti, M.; Corti, G.; Martelli, L. Recent and active tectonics of the external zone of the Northern Apennines (Italy). Int. J. Earth Sci. 2011, 100, 1331–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marroni, M.; Molli, G.; Montanini, A.; Tribuzio, R. The association of continental crust rocks with ophiolites (northern Apen-nines, Italy): Implications for the continent-ocean transition. Tectonophysics 1998, 292, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marroni, M.; Molli, G.; Montanini, A.; Ottria, G.; Pandolfi, L.; Tribuzio, R. The External Liguride units (Northern Apennine, Italy): From rifting to convergence history of a fossil ocean-continent transition zone. Ofioliti 2002, 27, 119–132. [Google Scholar]
- Vescovi, P.; Fornaciari, E.; Rio, D.; Valloni, R. The basal complex stratigraphy of the Helminthoid Monte Cassio Flysch: A key to the eoalpine tectonics of the Northern Apennines. Riv. Ital. Di Paleontol. E Stratigr. (Res. Paleontol. Stratigr.) 1999, 105, 101–128. [Google Scholar]
- Marroni, M.; Meneghini, F.; Pandolfi, L. A revised subduction inception model to explain the Late Cretaceous, double-vergent orogen in the precollisional western Tethys: Evidence from the Northern Apennines. Tectonics 2017, 36, 2227–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorosi, A.; Ricci Lucchi, F.; Tateo, F. The Lower Miocene siliceous zone: A marker in the palaeogeographic evolution of the northern Apennines. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1995, 118, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, A.; Artoni, A.; Ogata, K. The Epiligurian wedge-top succession in the Enza Valley (Northern Apennines): Evidence of a syn-depositional transpressive system. Swiss J. Geosci. 2016, 109, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantoni, R.; Franciosi, R. Tectono-sedimentary setting of the Po Plain and Adriatic foreland. Rend. Lincei 2010, 21, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livani, M.; Scrocca, D.; Arecco, P.; Doglioni, C. Structural and stratigraphic control on salient and recess development along a thrust belt front: The Northern Apennines (Po Plain, Italy). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 4360–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, A. International Stratigraphic Guide: A Guide to Stratigraphic Classification, Terminology, and Procedure; Geological Society of America: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Tazioli, A.; Cervi, F.; Doveri, M.; Mussi, M.; Deiana, M.; Ronchetti, F. Estimating the isotopic altitude gradient for hydrogeo-logical studies in mountainous areas: Are the low-yield springs suitable? Insights from the northern Apennines of Italy. Water 2019, 11, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchetti, F.; Piccinini, L.; Deiana, M.; Ciccarese, G.; Vincenzi, V.; Aguzzoli, A.; Malavasi, G.; Fabbri, P.; Corsini, A. Tracer test to asses flow and transport parameters of an earth slide: The Montecagno landslide case study (Italy). Eng. Geol. 2020, 275, 105749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguzzoli, A.; Arosio, D.; Mulas, M.; Ciccarese, G.; Benedikt, B.; Gerfried, W.; Ronchetti, F. Multidisciplinary non-invasive in-vestigations to develop a hydrogeological conceptual model supporting slope kinematics at Fontana Cornia landslide, Northern Apennines, Italy. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, L.; Calabrese, L.; Ercolessi, G.; Molinari, F.C.; Severi, P.; Bonini, M. The New Seismotectonic Map of the Emilia-Romagna Region and Surrounding Areas. Atti del 36° Congresso del Gruppo Nazionale di Geofisicxa della Terra Solida. Atti. Del. 2017, 36, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Segadelli, S.; Vescovi, P.; Ogata, K.; Chelli, A.; Zanini, A.; Boschetti, T.; Petrella, E.; Toscani, L.; Gargini, A.; Celico, F. A con-ceptual hydrogeological model of ophiolitic aquifers (serpentinised peridotite): The test example of Mt. Prinzera (Northern Italy). Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 1058–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segadelli, S.; Vescovi, P.; Chelli, A.; Petrella, E.; De Nardo, M.T.; Gargini, A.; Celico, F. Hydrogeological mapping of hetero-geneous and multi-layered ophiolitic aquifers (Mountain Prinzera, northern Apennines, Italy). J. Maps 2017, 13, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segadelli, S.; Filippini, M.; Monti, A.; Celico, F.; Gargini, A. Estimation of recharge in mountain hard-rock aquifers based on discrete spring discharge monitoring during base-flow recession. Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caine, J.S.; Evans, J.P.; Forster, C.B. Fault zone architecture and permeability structure. Geology 1996, 24, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bense, V.F.; Gleeson, T.; Loveless, S.E.; Bour, O.; Scibek, J. Fault zone hydrogeology. Earth Sci. Rev. 2013, 127, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segadelli, S.; Adorni, M.; Carbognani, M.; Celico, F.; Tomaselli, M. Combining biological and hydrogeological approaches: The grass Molinia arundinacea as a possible bioindicator of temporary perched aquifers in ophiolitic systems. Catena 2022, 217, 106448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargini, A.; Vincenzi, V.; Piccinini, L.; Zuppi, G.M.; Canuti, P. Groundwater flow systems in turbidites of the Northern Ap-ennines (Italy): Natural discharge and high speed railway tunnel drainage. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, E.; Celico, F. Heterogeneous aquitard properties in sedimentary successions in the Apennine chain: Case studies in southern Italy. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2009, 23, 3365–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.N.; De Wiest, R.J.M. Hydrogeology; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, P.; Severini, E.; Bucci, A.; Bocchia, F.; Palladino, G.; Riboni, N.; Celico, F. How do turbidite systems behave from the hydrogeological point of view? New insights and open questions coming from an interdisciplinary work in southern Italy. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, M. Interrelations of mud volcanism, fluid venting, and thrust-anticline folding: Examples from the external northern Apennines (Emilia-Romagna, Italy). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2007, 112, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiana, M.; Cervi, F.; Pennisi, M.; Mussi, M.; Bertrand, C.; Tazioli, A.; Ronchetti, F. Chemical and isotopic investigations (δ 18 O, δ 2 H, 3 H, 87 Sr/86 Sr) to define groundwater processes occurring in a deep-seated landslide in flysch. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 2669–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remelli, S.; Petrella, E.; Chelli, A.; Conti, F.D.; Lozano Fondón, C.; Celico, F.; Francese, R.; Menta, C. Hydrodynamic and soil biodiversity characterization in an active landslide. Water 2019, 11, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, P.; Petrella, E.; Bucci, A.; Salvioli Mariani, E.; Chelli, A.; Sanangelantoni, A.M.; Raimondo, M.; Quagliarini, A.; Celico, F. Studying hydraulic interconnections in low-permeability media by using bacterial communities as natural tracers. Water 2020, 12, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelli, A.; Francese, R.; Petrella, E.; Carri, A.; Quagliarini, A.; Segalini, A.; Celico, F. A multi-parameter field monitoring system to investigate the dynamics of large earth slides–earth flows in the Northern Apennines, Italy. Eng. Geol. 2020, 275, 105780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, E.; Raimondo, M.; Chelli, A.; Valentino, R.; Severini, E.; Diena, M.; Celico, F. Processes and factors controlling the groundwater flow in a complex landslide: A case study in the Northern Italy. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37(5), e14891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regione Emilia-Romagna; ENI-AGIP. Riserve Idriche Sotterranee Della Regione Emilia-Romagna. A Cura di G.M. Di Dio; Regione Emilia-Romagna, ENI Agip Divisione Esplorazione e Produzione; SELCA: Firenze, Italy, 1998; p. 120. [Google Scholar]
- Zanini, A.; Petrella, E.; Sanangelantoni, A.M.; Angelo, L.; Ventosi, B.; Viani, L.; Celico, F. Groundwater characterization from an ecological and human perspective: An interdisciplinary approach in the Functional Urban Area of Parma, Italy. Rend. Lincei. Sci. Fis. E Nat. 2019, 30, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Dio, G.; Martini, A.; Lasagna, S.; Zanzucchi, G. Explanatory notes of the Geologic Map of Italy at the Scale 1:50,000, Sheet No. 199 Parma Sud-Ovest; Servizio Geologico della Regione Emilia-Romagna, Servizio Geologico Nazionale, ISPRA: Rome, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zanini, A.; Ghirardi, M.; Emiliani, R. A multidisciplinary approach to evaluate the effectiveness of natural attenuation at a contaminated site. Hydrology 2021, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severini, E.; Ducci, L.; Sutti, A.; Robottom, S.; Sutti, S.; Celico, F. River–Groundwater Interaction and Recharge Effects on Microplastics Contamination of Groundwater in Confined Alluvial Aquifers. Water 2022, 14, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducci, L.; Rizzo, P.; Pinardi, R.; Solfrini, A.; Maggiali, A.; Pizzati, M.; Balsamo, F.; Celico, F. What Is the Impact of Leaky Sewers on Groundwater Contamination in Urban Semi-Confined Aquifers? A Test Study Related to Fecal Matter and Personal Care Products (PCPs). Hydrology 2022, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, G.; Pieri, V.; Martens, K. Recent ostracods (Crustacea, Ostracoda) found in lowland springs of the provinces of Pia-cenza and Parma (Northern Italy). Hydrobiologia 2005, 542, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaposta, D.; Segadelli, S.; De Nardo, M.T.; Alessandrini, A.; Pezzoli, S. Le potenzialità geologiche dei dati storici am-bientali: Il caso delle sorgenti e dei fontanili in Emilia-Romagna. Il Geologo dell’Emilia Romagna 2011, 1, 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kløve, B.; Ala-Aho, P.; Bertrand, G.; Boukalova, Z.; Ertürk, A.; Goldscheider, N.; Widerlund, A. Groundwater dependent ecosystems. Part I: Hydroecological status and trends. Environ. Sci. Policy 2011, 14, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ji, J.; Mao, C.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Godwin, A.A.; Frost, R.L. Heavy metal contamination in suspended solids of Changjiang river—Environmental implications. Geoderma 2010, 159, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorslund, J.; Jarsjö, J.; Chalov, S.R.; Belozerova, E.V. Gold mining impact on riverine heavy metal transport in a sparsely monitored region: The upper Lake Baikal Basin case. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 2780–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Li, J.; Bi, N.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Wei, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, G.; Yin, X.; Liu, M.; et al. Seasonal variability and flux of patticulate trace elements from the Yellow River: Impacts of the anthropogenic flood event. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 91, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberholster, P.J.; Botha, A.M.; Hill, L.; Strydom, W.F. River catchment responses to anthropogenic acidification in relationship with sewage effluent: An ecotoxicology screening application. Chemosphere 2017, 189, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, N.; Li, Y.; Ren, B.; Ding, X.; Bian, H.; Yao, X. Total concentration and sources of heavy metal pollution in global river and lake water bodies from 1972 to 2017. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atangana, E.; Oberholster, P.J. Using heavy metal pollution indices to assess water quality of surface and groundwater on catchment levels in South Africa. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 182, 104254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, C.; Fatichi, S.; Burlando, P.; Weber, E.; Battista, G. Modeling distributed metal pollution transport in a mine impacted catchment: Short and long-term effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 151473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, P.N.; Petticrew, E.L.; Albers, S.J.; French, T.D.; Granger, B.; Laval, B.; Vagle, S. Annual pulses of copper-enriched sediment in a North American river downstream of a large lake following the catastrophic failure of a mine tailings storage facility. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 158927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei Kalvani, S.; Celico, F. The Water–Energy–Food Nexus in European Countries: A Review and Future Perspectives. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Oria, M.; Cozzi, C.; Tanda, M.G. Future precipitation and temperature changes over the Taro, Parma and Enza River Basins in Northern Italy. Ital. J. Eng. Geol. Environ. (Spec. Issue) 2018, 1, 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Todaro, V.; D’Oria, M.; Secci, D.; Zanini, A.; Tanda, M.G. Climate change over the Mediterranean region: Local temperature and precipitation variations at five pilot sites. Water 2022, 14, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Song, C.; Zheng, H.; Polasky, S.; Xiao, Y.; Bateman, I.J.; Daily, G.C. Using gross ecosystem product (GEP) to value nature in decision making. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14593–14601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).