Heterogeneous Photodegradation for the Abatement of Recalcitrant COD in Synthetic Tanning Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Photodegradation Experimental Set-Up
2.3. Kinetic Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
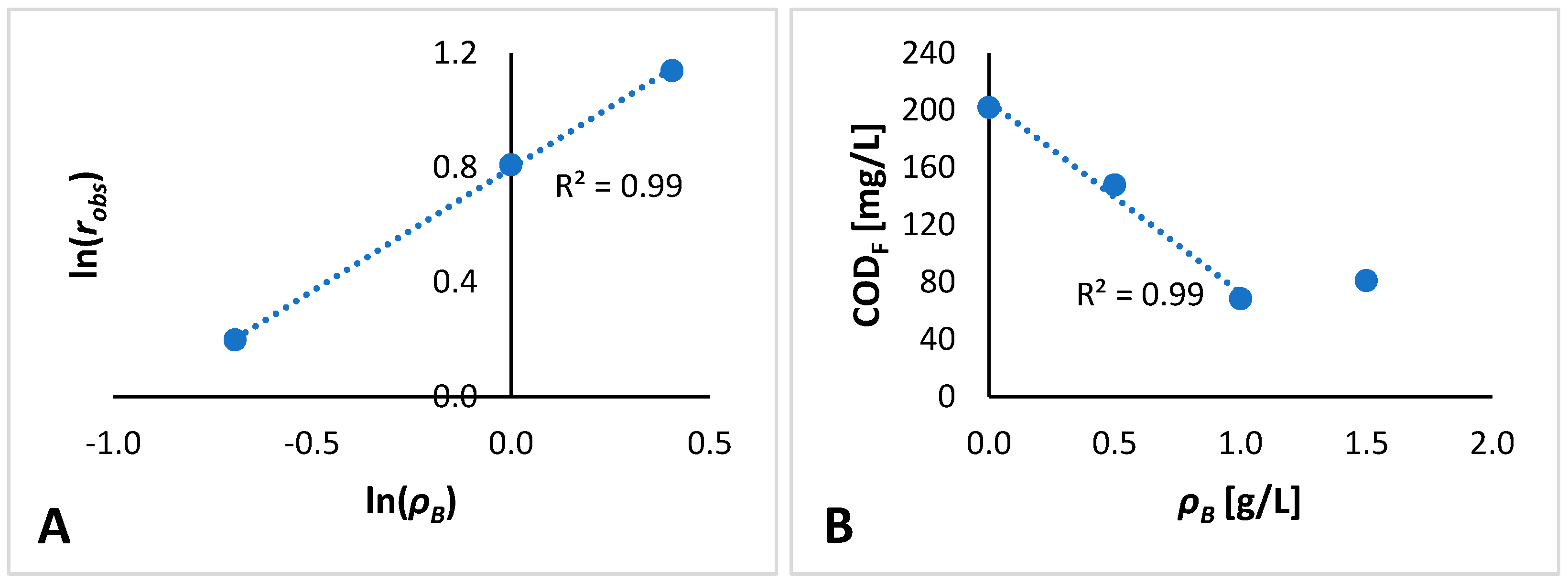
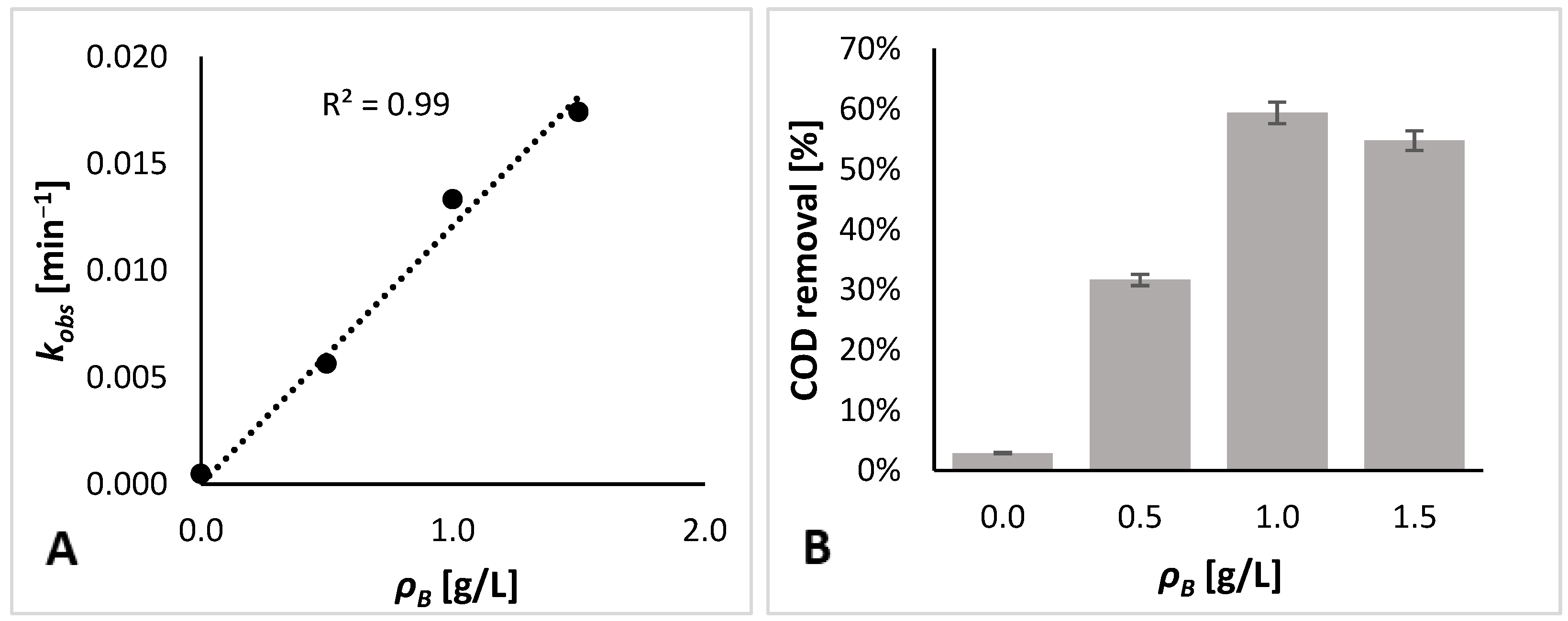
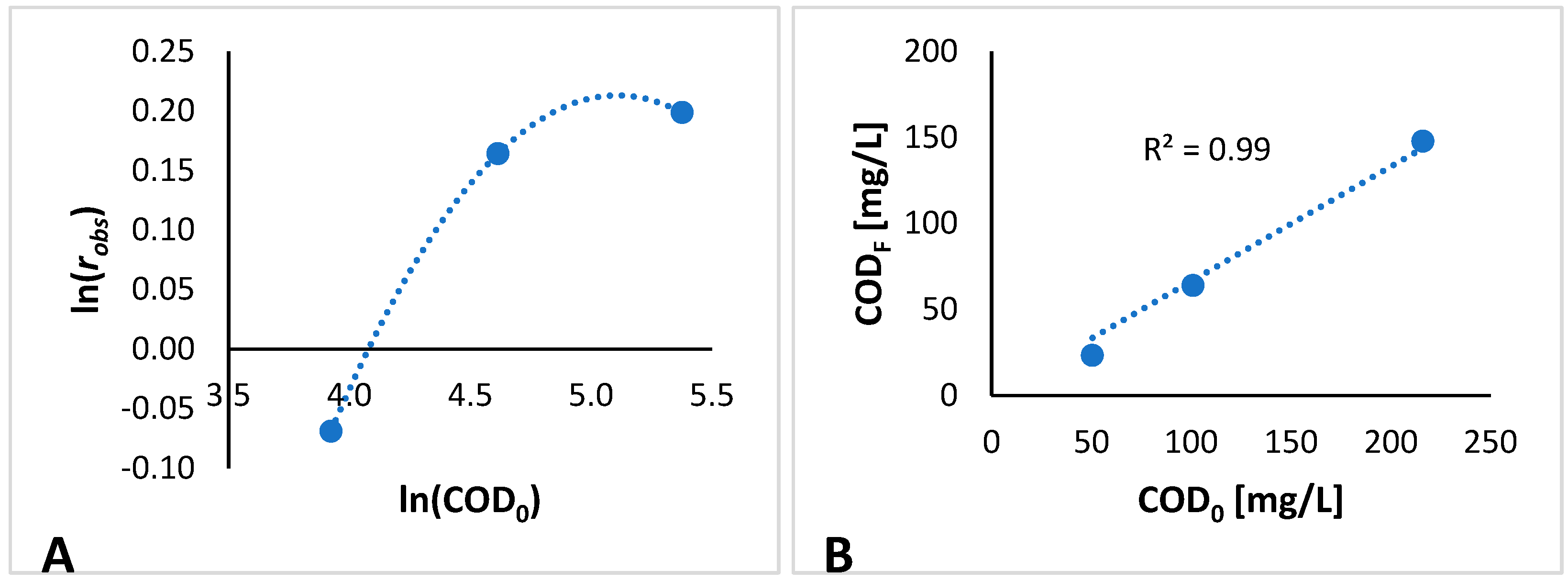
3.1. Photodegradation Experimental Results
3.2. Kinetic Modeling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sivaram, N.; Barik, D. Chapter 5—Toxic Waste from Leather Industries. In Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generatio; Barik, D., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolomaznik, K.; Adamek, M.; Andel, I.; Uhlirova, M. Leather waste—Potential threat to human health, and a new technology of its treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tariq, S.R.; Shah, M.H.; Shaheen, N. Comparative statistical analysis of chrome and vegetable tanning effluents and their effects on related soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.; Shahane, S.; Chauhan, D.; Rai, D.; Khan, Z.A.; Bhunia, B.; Chaudhary, V.K. Environmental Impact and Treatment of Tannery Waste. In Water Pollution and Remediation: Organic Pollutants; Inamuddin, M.I., Ahamed, E., Lichtfouse, Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharagava, R.N.; Saxena, G.; Mulla, S.I.; Patel, D.K. Characterization and Identification of Recalcitrant Organic Pollutants (ROPs) in Tannery Wastewater and Its Phytotoxicity Evaluation for Environmental Safety. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 75, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofrano, G.; Meric, S.; Zengin, G.E.; Orhon, D. Chemical and biological treatment technologies for leather tannery chemicals and wastewaters: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tünay, O.; Kabdasli, I.; Orhon, D.; Ates, E. Characterization and pollution profile of leather tanning industry in Turkey. Water Sci. Technol. 1995, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhon, D.; Çokgör, E.U. COD Fractionation in Wastewater Characterization—The State of the Art. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1997, 68, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardi, A.; Yuan, Q.; Tigini, V.; Spina, F.; Varese, G.C.; Spennati, F.; Becarelli, S.; Di Gregorio, S.; Petroni, G.; Munz, G. Recalcitrant Compounds Removal in Raw Leachate and Synthetic Effluents Using the White-Rot Fungus Bjerkandera adusta. Water 2017, 9, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishnamoorthy, G.; Sadulla, S.; Sehgal, P.; Mandal, A.B. Green chemistry approaches to leather tanning process for making chrome-free leather by unnatural amino acids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215–216, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Yao, K.; Sun, D.; Shi, B. Biodegradability of tannin-containing wastewater from leather industry. Biogeochemistry 2006, 18, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavlyanov, S.M.; Islambekov, S.Y.; Ismailov, A.I.; Dalimov, D.N.; Abdulladzhanova, N.G. Vegetable Tanning Agents. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2001, 37, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofrano, G.; Aydin, E.; Russo, F.; Guida, M.; Belgiorno, V.; Meric, S. Characterization, Fluxes and Toxicity of Leather Tanning Bath Chemicals in a Large Tanning District Area (IT). Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2008, 8, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, C.; Barbosa, A.; Takashima, K. Biotreatment of industrial tannery wastewater using Botryosphaeria rhodina. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2011, 76, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamersit, S.; Bouhidel, K.-E.; Zidani, Z. Investigation of electrodialysis anti-fouling configuration for desalting and treating tannery unhairing wastewater: Feasibility of by-products recovery and water recycling. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, W. A review for tannery wastewater treatment: Some thoughts under stricter discharge requirements. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 26102–26111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharan, V.K.; Pinjari, D.V.; Gogate, P.R.; Pandit, A.B. Chapter 3—Advanced Oxidation Technologies for Wastewater Treatment: An Overview. In Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse; Ranade, V.V., Bhandari, V.M., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 141–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, N.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Huo, S.; Cheng, P.; Peng, P.; Zhang, R.; et al. Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants using TiO2-based photocatalysts: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 121725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrank, S.; José, H.J.; Moreira, R.; Schröder, H. Elucidation of the behavior of tannery wastewater under advanced oxidation conditions. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandis, P.K.; Kalogirou, C.; Kanellou, E.; Vaitsis, C.; Savvidou, M.G.; Sourkouni, G.; Zorpas, A.A.; Argirusis, C. Key Points of Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) for Wastewater, Organic Pollutants and Pharmaceutical Waste Treatment: A Mini Review. ChemEngineering 2022, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, É.; de Aquim, P.M.; Gutterres, M. Current technologies for post-tanning wastewater treatment: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 113003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanowicz, M.; Bojanowska-Czajka, A.; Capodaglio, A.G. Can radiation chemistry supply a highly efficient AO(R)P process for organics removal from drinking and waste water? A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 20187–20208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouali, A.; Salhi, A.; Aguedach, A.; Lhadi, E.K.; El Krati, M.; Tahiri, S. Photo-catalytic degradation of polyphenolic tannins in continuous-flow reactor using titanium dioxide immobilized on a cellulosic material. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naraginti, S.; Thejaswini, T.; Prabhakaran, D.; Sivakumar, A.; Satyanarayana, V.; Prasad, A.A. Enhanced photo-catalytic activity of Sr and Ag co-doped TiO2 nanoparticles for the degradation of Direct Green-6 and Reactive Blue-160 under UV & visible light. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 149, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Removal of COD from olive mill wastewater by Fenton’s reagent: Kinetic study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, Z.; Younesi, H.; Zinatizadeh, A.A. Kinetics and thermodynamics of photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in petroleum refinery wastewater over nano-TiO2 supported on Fe-ZSM-5. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 65, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pirilä, M.; Saouabe, M.; Ojala, S.; Rathnayake, B.; Drault, F.; Valtanen, A.; Huuhtanen, M.; Brahmi, R.; Keiski, R.L. Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants in Wastewater. Top. Catal. 2015, 58, 1085–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanaprakasam, A.; Sivakumar, V.M.; Thirumarimurugan, M. Influencing Parameters in the Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Effluent via Nanometal Oxide Catalyst: A Review. Indian J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 2015, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.H.; Al-Afify, A.D.; Goher, M.E. Preparation and characterization of graphene—TiO2 nanocomposite for enhanced photodegradation of Rhodamine-B dye. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2018, 44, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidney Santana, C.; Nicodemos Ramos, M.D.; Vieira Velloso, C.C.; Aguiar, A. Kinetic Evaluation of Dye Decolorization by Fenton Processes in the Presence of 3-Hydroxyanthranilic Acid. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lair, A.; Ferronato, C.; Chovelon, J.-M.; Herrmann, J.-M. Naphthalene degradation in water by heterogeneous photocatalysis: An investigation of the influence of inorganic anions. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2008, 193, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Ray, A. Photodegradation kinetics of 4-nitrophenol in TiO2 suspension. Water Res. 1998, 32, 3223–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
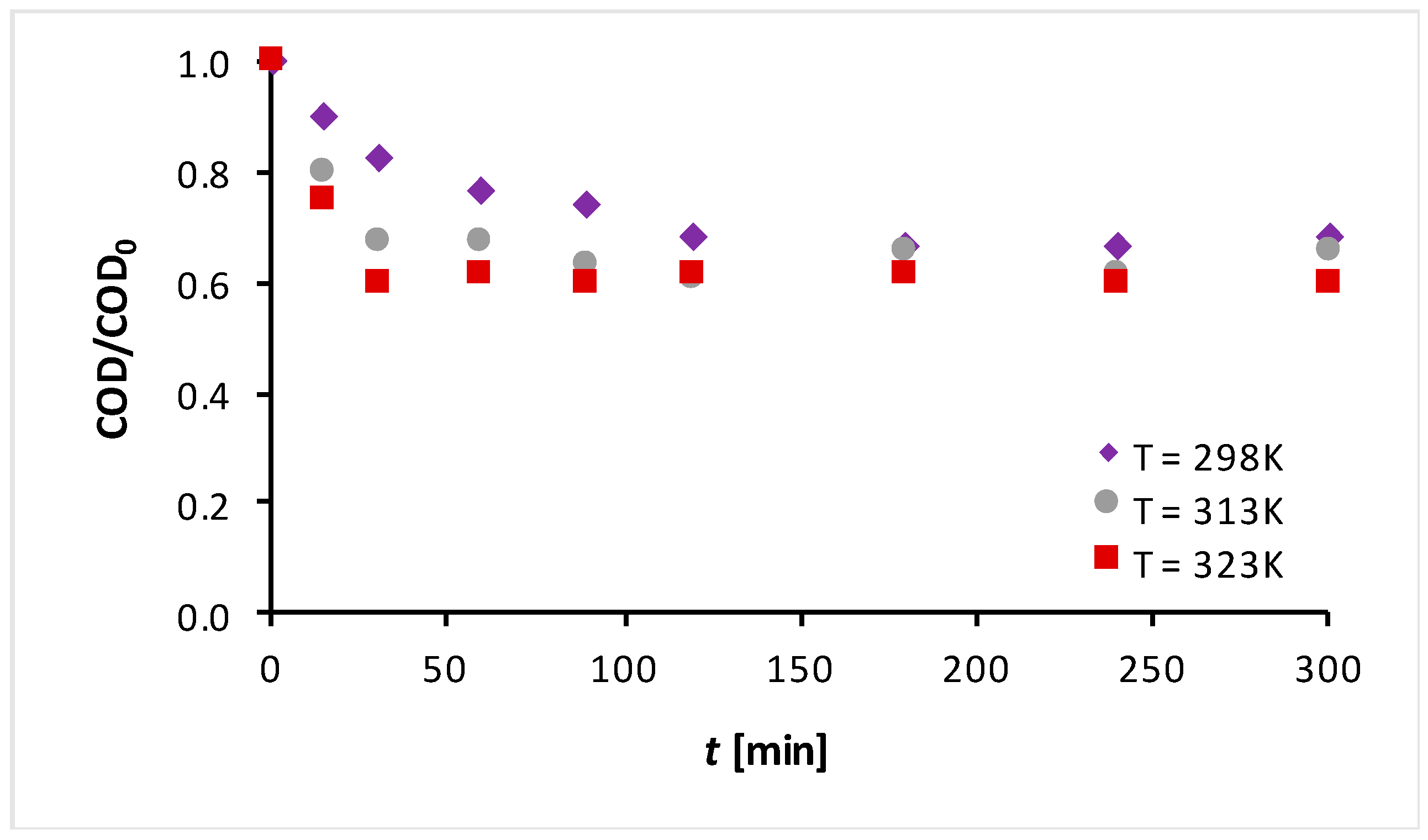
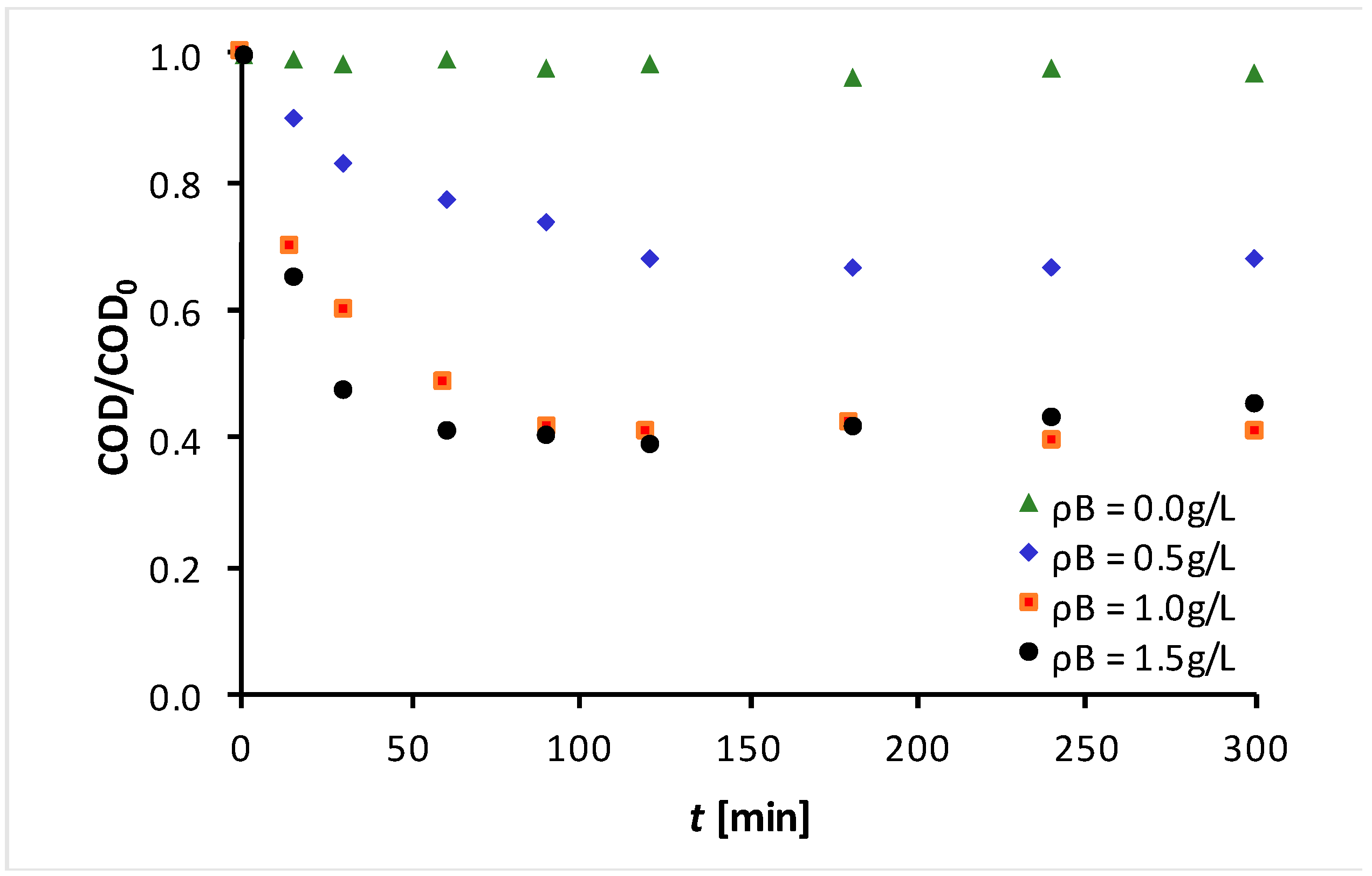
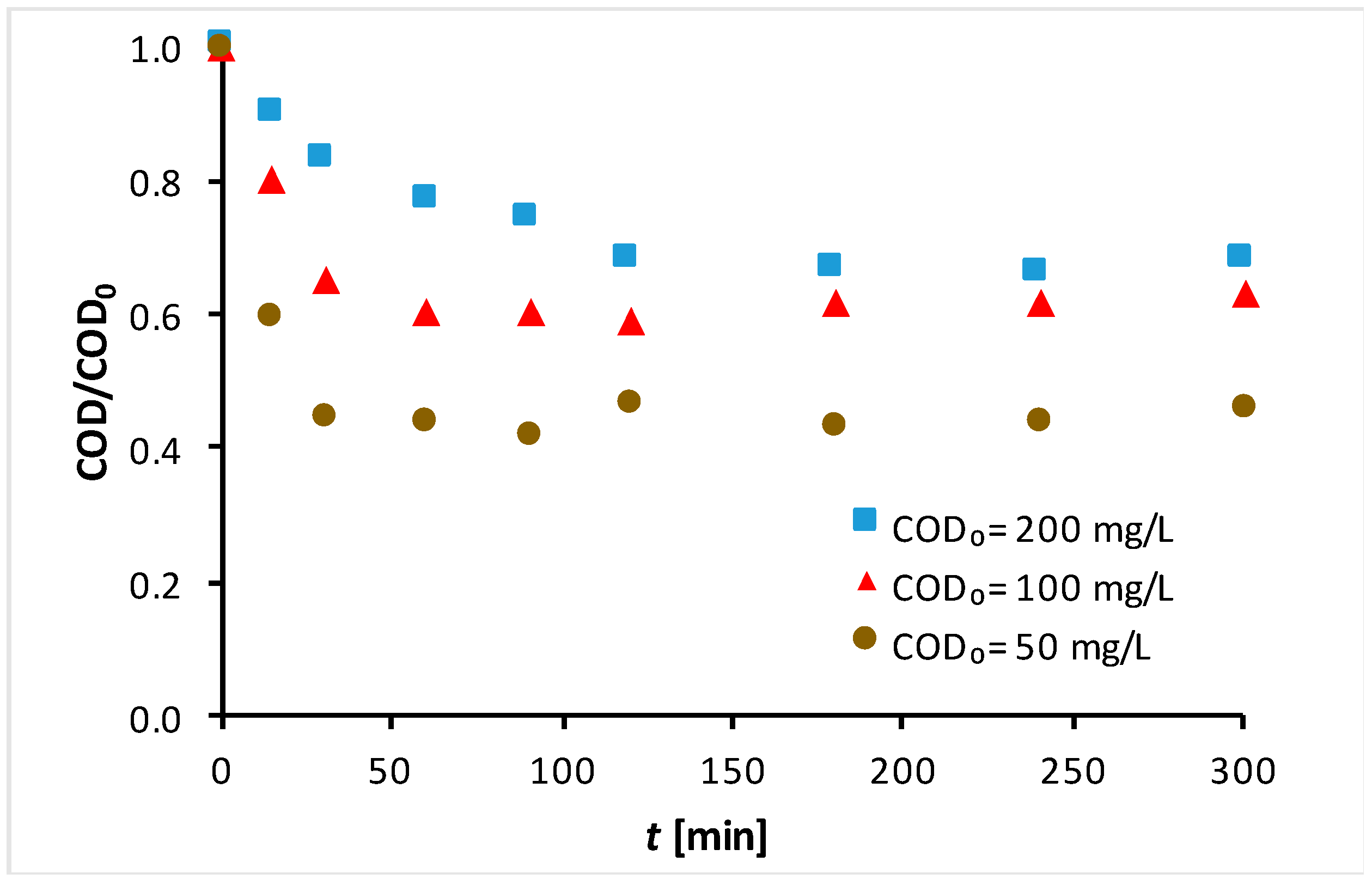
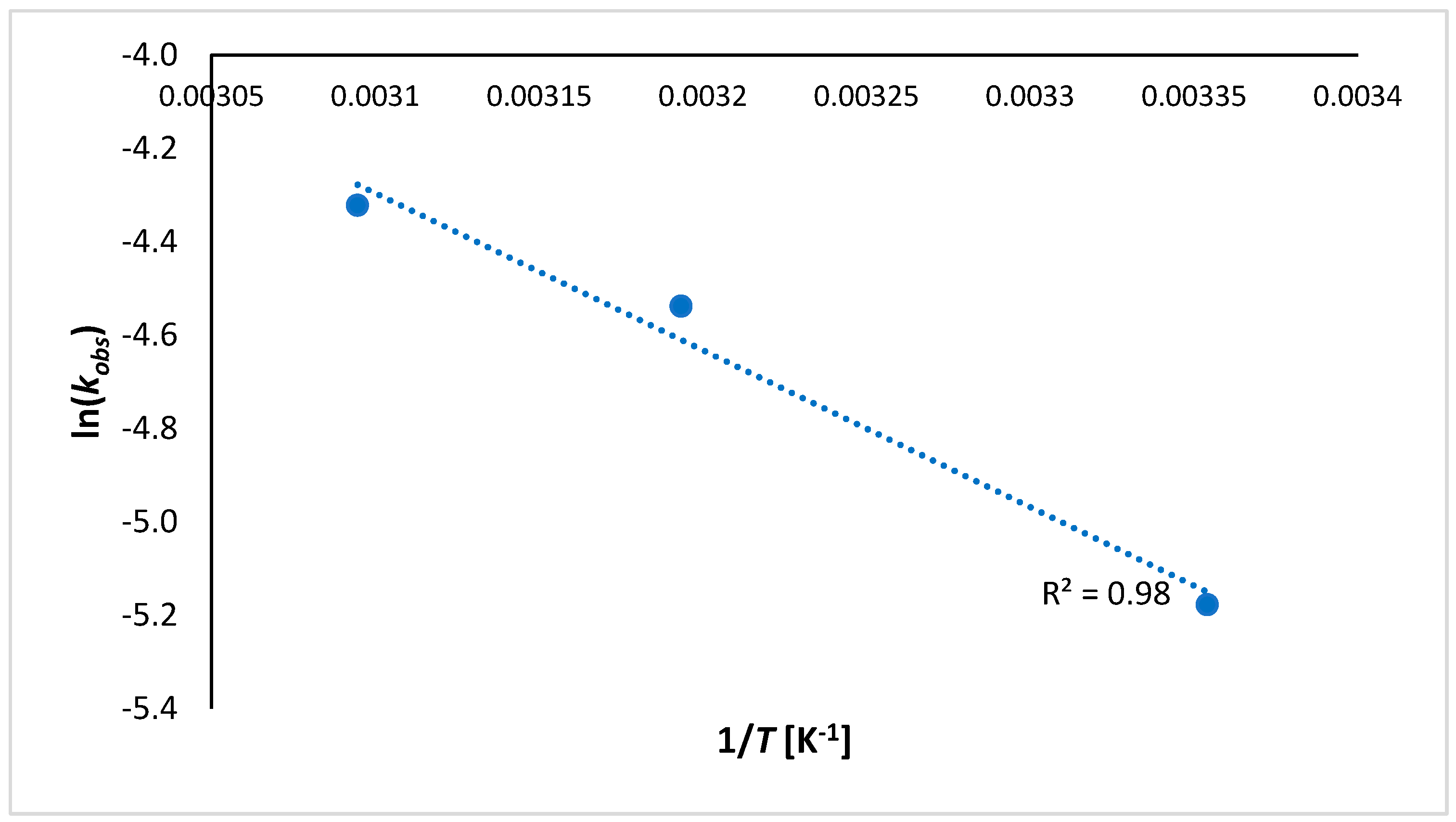
| Experiment No. | Temperature (K) | (g/L) | pH | TOC (mg/L) | COD (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 293 | 0 | 5.2 | 88.7 | 200 |
| 2 | 293 | 0.5 | 4.6 | 74.1 | 200 |
| 3 | 293 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 44.9 | 100 |
| 4 | 293 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 27.7 | 50 |
| 5 | 293 | 1.0 | 4.9 | 71.2 | 200 |
| 6 | 293 | 1.5 | 4.9 | 75.3 | 200 |
| 7 | 313 | 0.5 | 4.8 | 73.7 | 200 |
| 8 | 323 | 0.5 | 4.6 | 66.6 | 200 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toscanesi, M.; Russo, V.; Medici, A.; Giarra, A.; Hmoudah, M.; Di Serio, M.; Trifuoggi, M. Heterogeneous Photodegradation for the Abatement of Recalcitrant COD in Synthetic Tanning Wastewater. ChemEngineering 2022, 6, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6020025
Toscanesi M, Russo V, Medici A, Giarra A, Hmoudah M, Di Serio M, Trifuoggi M. Heterogeneous Photodegradation for the Abatement of Recalcitrant COD in Synthetic Tanning Wastewater. ChemEngineering. 2022; 6(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6020025
Chicago/Turabian StyleToscanesi, Maria, Vincenzo Russo, Antonio Medici, Antonella Giarra, Maryam Hmoudah, Martino Di Serio, and Marco Trifuoggi. 2022. "Heterogeneous Photodegradation for the Abatement of Recalcitrant COD in Synthetic Tanning Wastewater" ChemEngineering 6, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6020025
APA StyleToscanesi, M., Russo, V., Medici, A., Giarra, A., Hmoudah, M., Di Serio, M., & Trifuoggi, M. (2022). Heterogeneous Photodegradation for the Abatement of Recalcitrant COD in Synthetic Tanning Wastewater. ChemEngineering, 6(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6020025










