Rheology and Catastrophic Phase Inversion of Emulsions in the Presence of Starch Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
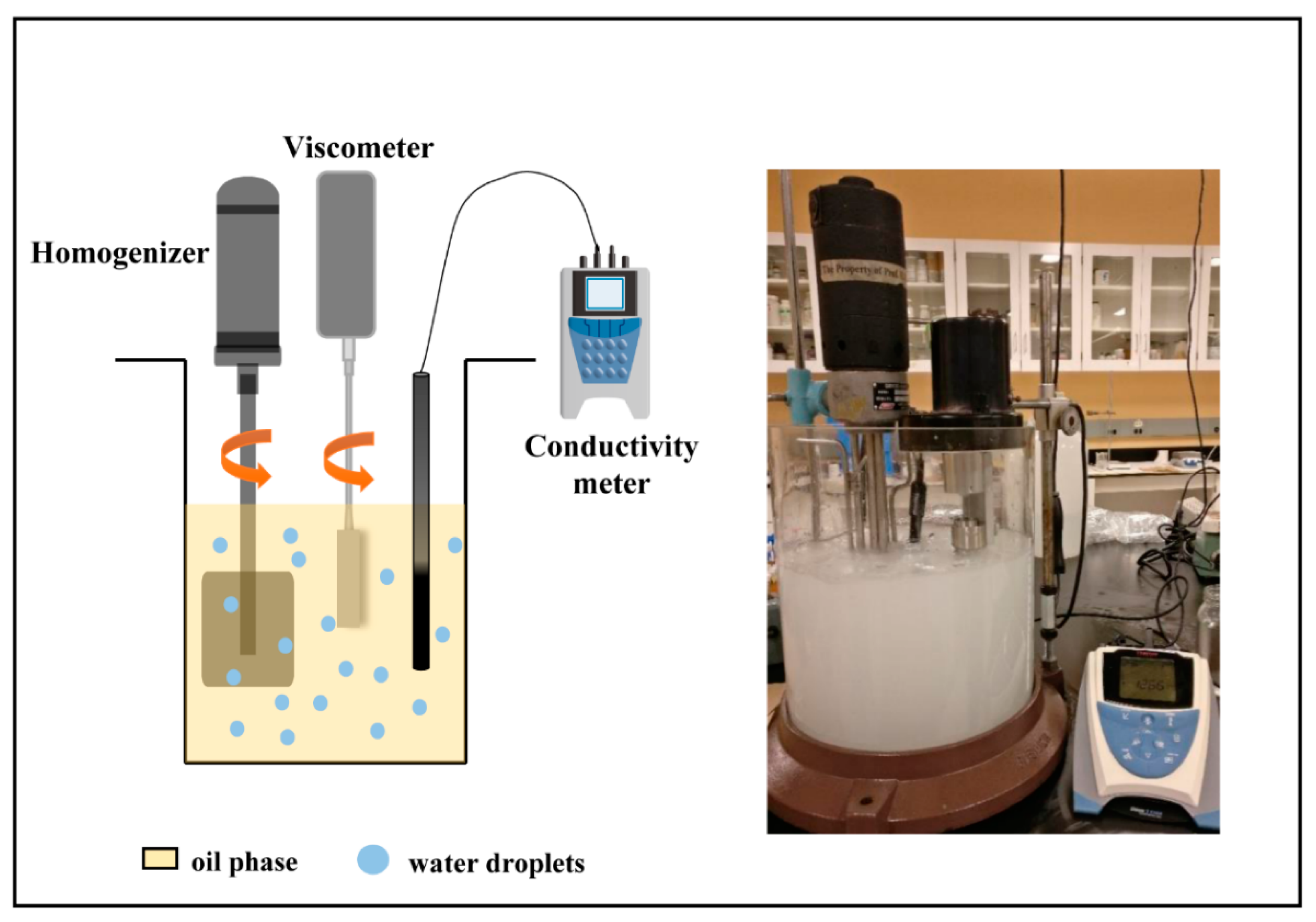
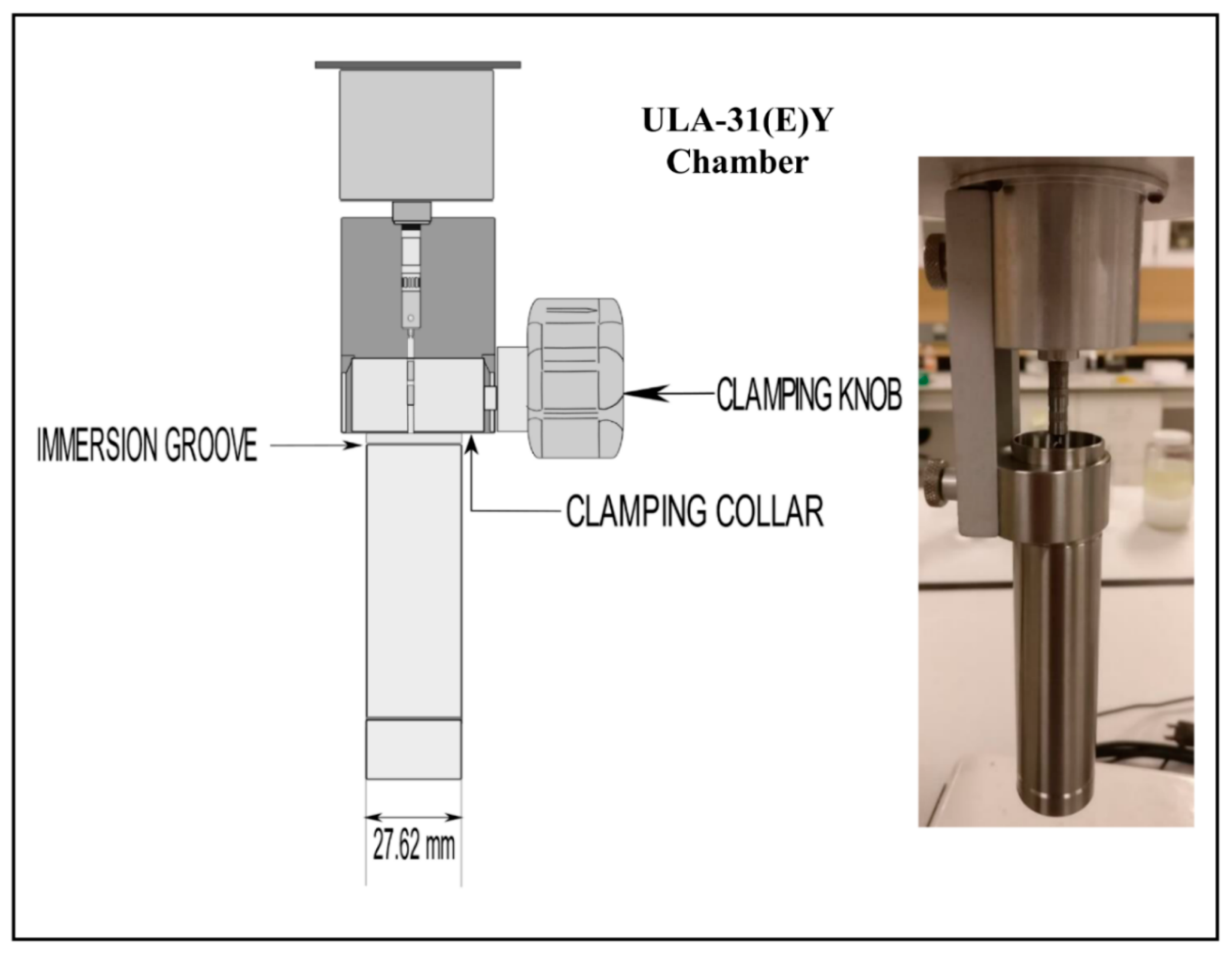
2. Experimental Setup
3. Experimental Work
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Starch Dispersions
3.3. Preparation of Emulsions
4. Results and Discussion
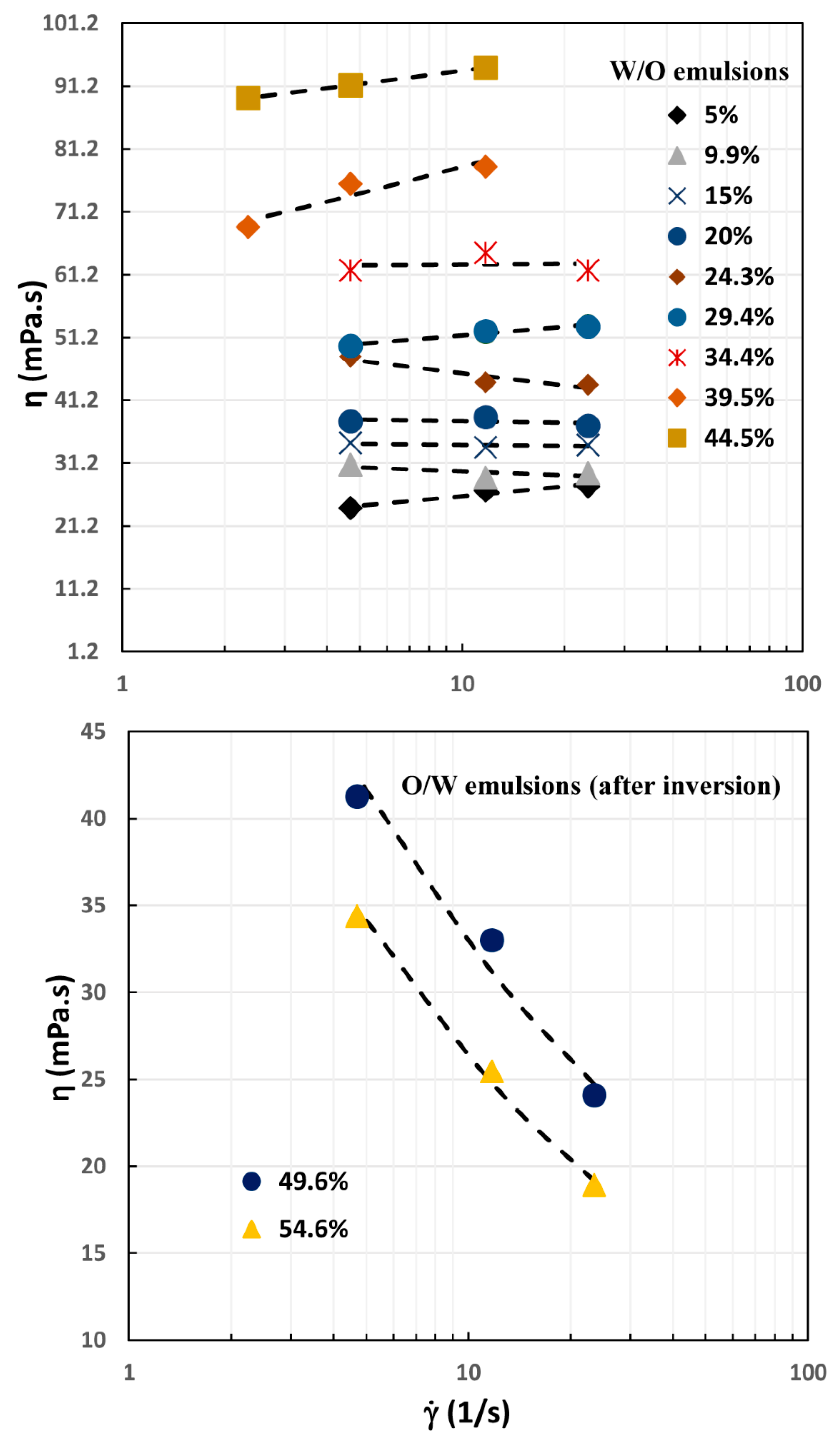
4.1. Rheological Behavior of Emulsions
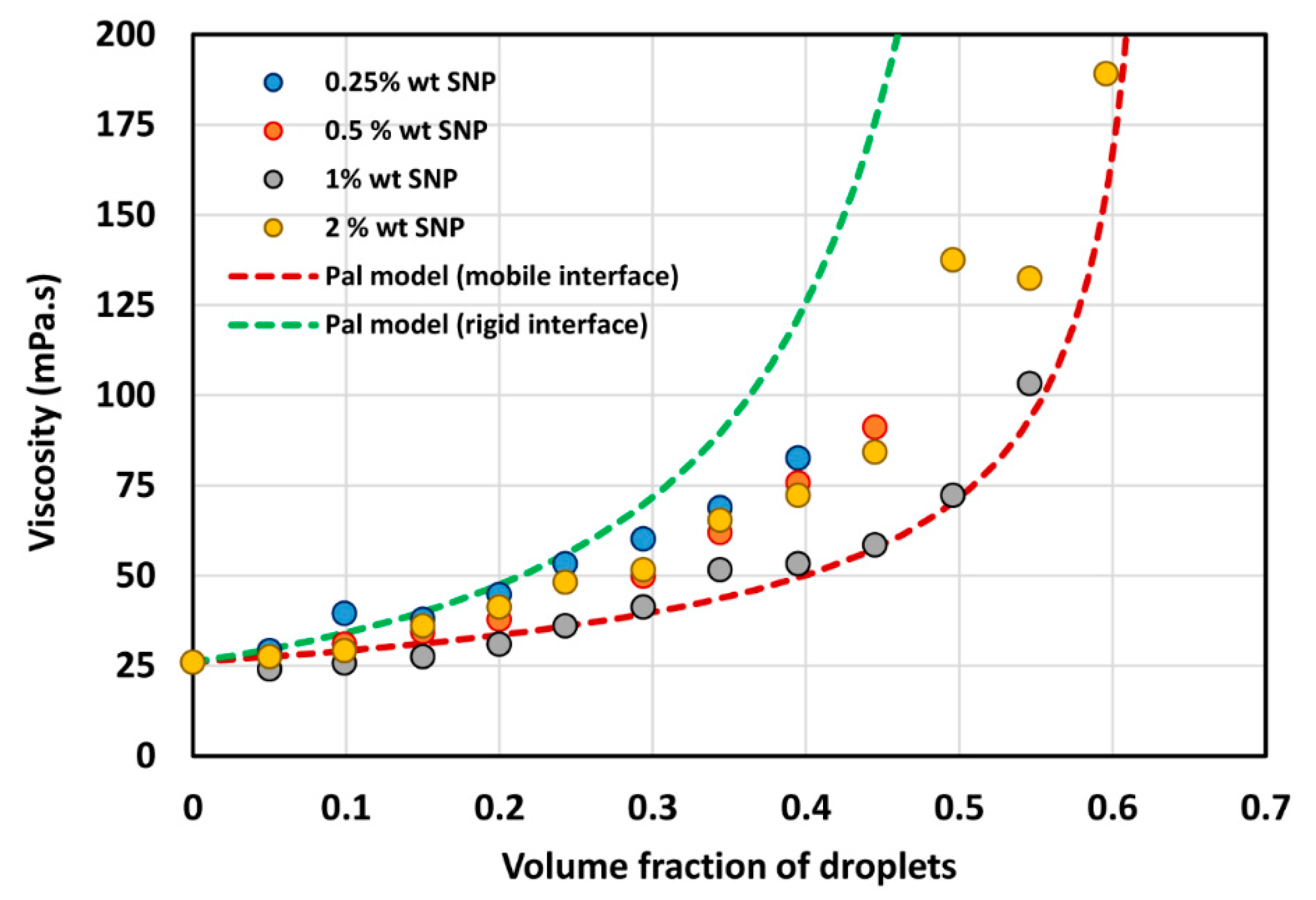
4.2. Viscosity-Concentration Behavior of Emulsions
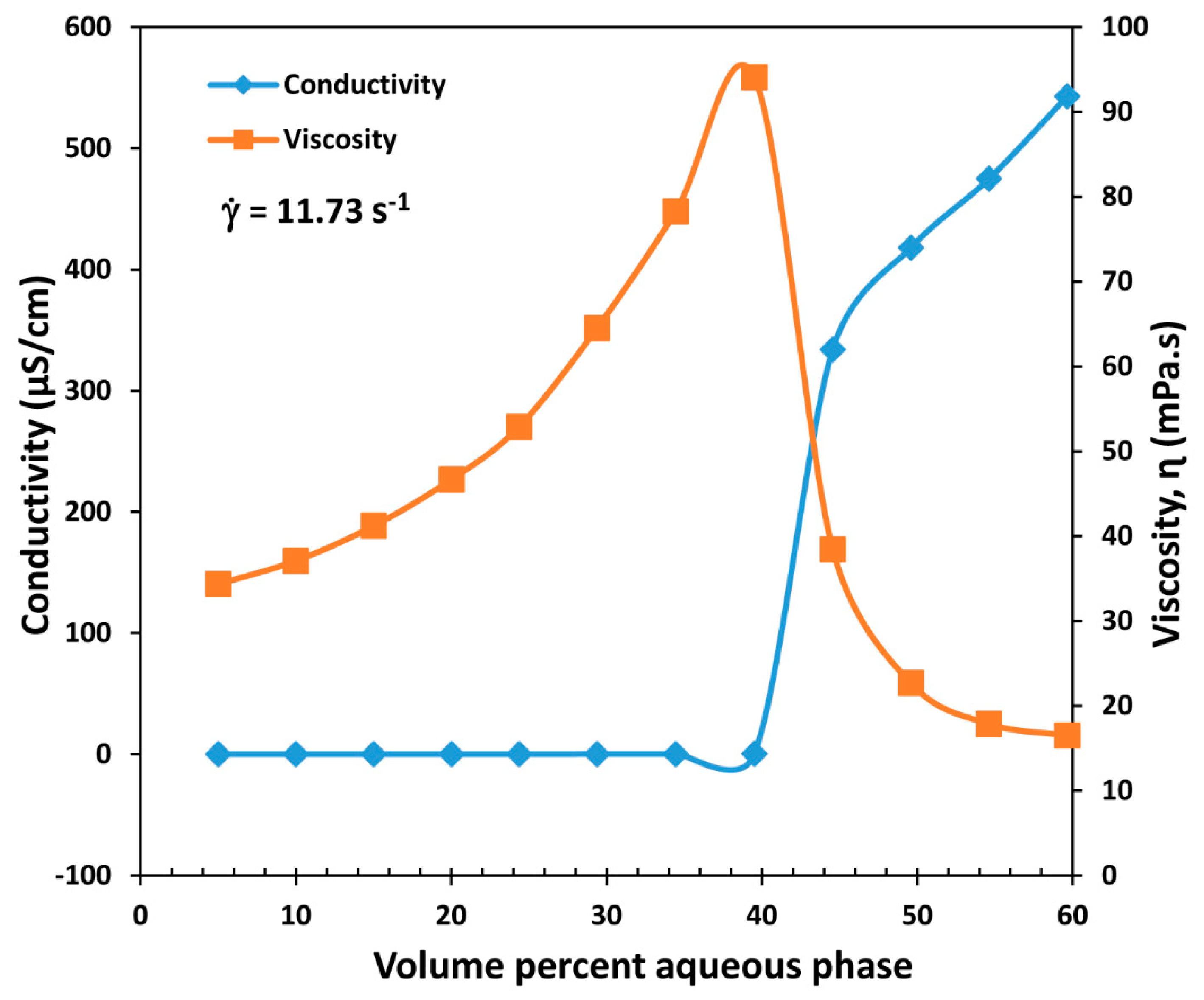
4.3. Catastrophic Phase Inversion in Emulsions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pal, R. Rheology of Particulate Dispersions and Composites; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Becher, P. Emulsions: Theory and Practice; Krieger Publishing Co.: Malabar, FL, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Torrey, S. Emulsions and Emulsifier Applications—Recent Developments; Noyes Data Corporation: Park Ridge, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Lissant, K.J. Emulsions and Emulsion Technology; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Friberg, S. Food Emulsions; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, R. Rheology of simple and multiple emulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R. Effect of droplet size on the rheology of emulsions. AIChE J. 1996, 42, 3181–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R. Techniques for measuring the composition (oil and water content) of emulsions-a state of the art review. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1994, 84, 141–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, W. An overview of Pickering emulsions: Solid-particle materials, classification, morphology, and applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berton-Carabin, C.C.; Schroen, K. Pickering emulsions for food applications: Background, trends, and challenges. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 263–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, Y.; Bolzinger, M.A. Emulsions stabilized with solid nanoparticles: Pickering emulsions. Colloids Surf. A 2013, 439, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timgren, A.; Rayner, M.; Dejmek, P.; Marku, D.; Sjoo, M. Emulsion stabilizing capacity of intact starch granules modified by heat treatment or octenyl succinic anhydride. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 1, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoppe, J.O.; Venditti, R.A.; Rojas, O.J. Pickering emulsions stabilized by cellulose nanocrystals grafted with thermos-responsive polymer brushes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 369, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Song, X.; Huang, J.; Wu, C.; Ma, D.; Tian, M.; Jiang, H.; Huang, P. Phase behavior of Pickering emulsions stabilized by graphene oxide sheets and resins. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 13439–13447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, B.P.; Fletcher, P.D.I.; Holt, B.L.; Beaussoubre, P. Phase inversion of particle-stabilized perfume oil-water emulsions: Experiment and theory. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 11954–11966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bains, U.; Pal, R. In-Situ Continuous Monitoring of the Viscosity of Surfactant-Stabilized and Nanoparticles-Stabilized Pickering Emulsions. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunlaja, S.B.; Pal, R.; Sarikhani, K. Effect of starch nanoparticles on phase inversion of Pickering emulsions. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 96, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R. A simple model for the viscosity of Pickering emulsions. Fluids 2018, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. Starch based Pickering emulsion: Fabrication, properties, and applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 85, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierulf, A.; Whaley, J.; Liu, W.; Enayati, M.; Tan, C.; Perez-Herrera, M.; You, Z.; Abbaspourrad, A. Protein content of amaranth and quinoa starch plays a key role in their ability as Pickering emulsifiers. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, B.; Lam, S.; Kirkland, M.; Frith, W.J. Shear-thickening of an emulsion stabilized with hydrophilic silica particles. J. Rheol. 2007, 51, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R. Novel viscosity equations for emulsions of two immiscible liquids. J. Rheol. 2001, 45, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazzo, A.; Preziosi, V.; Guido, S. Phase inversion emulsification: Current understanding and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 581–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bains, U.; Pal, R. Rheology and Catastrophic Phase Inversion of Emulsions in the Presence of Starch Nanoparticles. ChemEngineering 2020, 4, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4040057
Bains U, Pal R. Rheology and Catastrophic Phase Inversion of Emulsions in the Presence of Starch Nanoparticles. ChemEngineering. 2020; 4(4):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4040057
Chicago/Turabian StyleBains, Upinder, and Rajinder Pal. 2020. "Rheology and Catastrophic Phase Inversion of Emulsions in the Presence of Starch Nanoparticles" ChemEngineering 4, no. 4: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4040057
APA StyleBains, U., & Pal, R. (2020). Rheology and Catastrophic Phase Inversion of Emulsions in the Presence of Starch Nanoparticles. ChemEngineering, 4(4), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4040057




