Layered Double Hydroxide Sorbents for Removal of Selenium from Power Plant Wastewaters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sorbent Materials
2.2. Water Samples
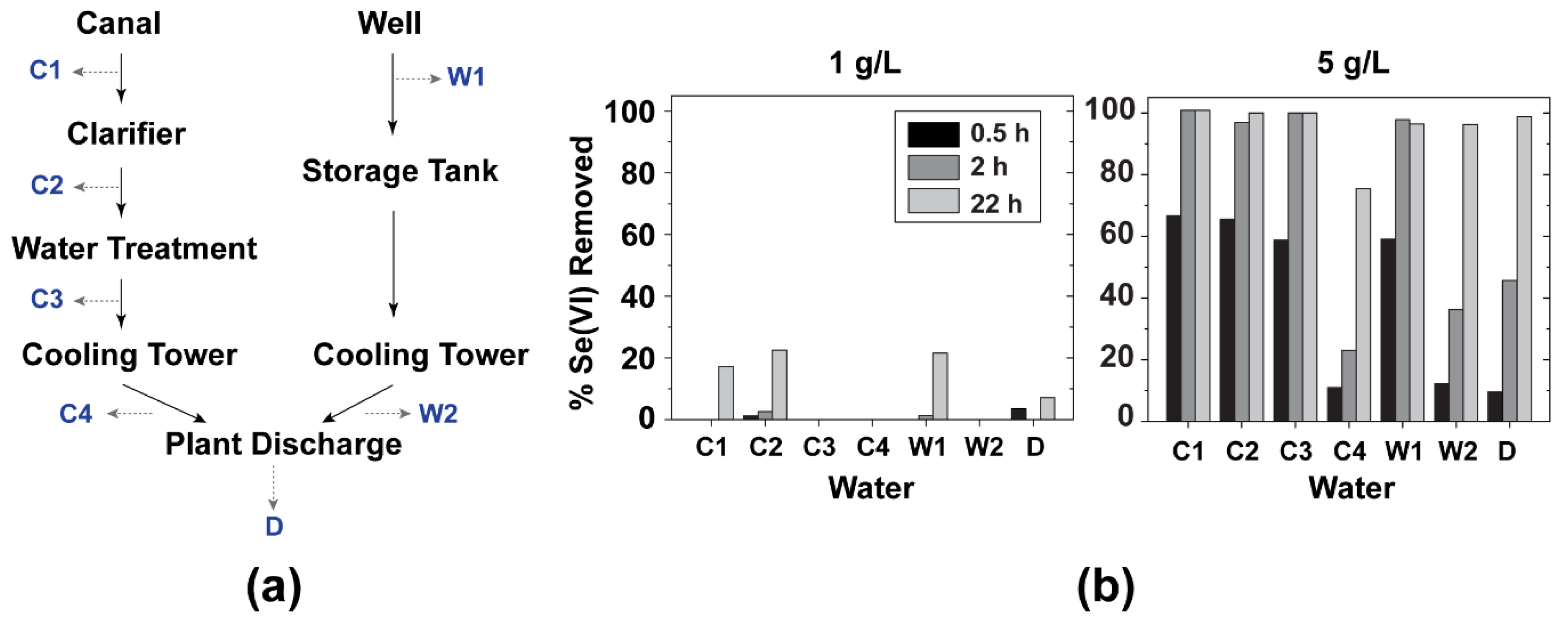
2.3. Jar Testing
2.4. Column Testing
3. Results
3.1. Physical Properties of LDH
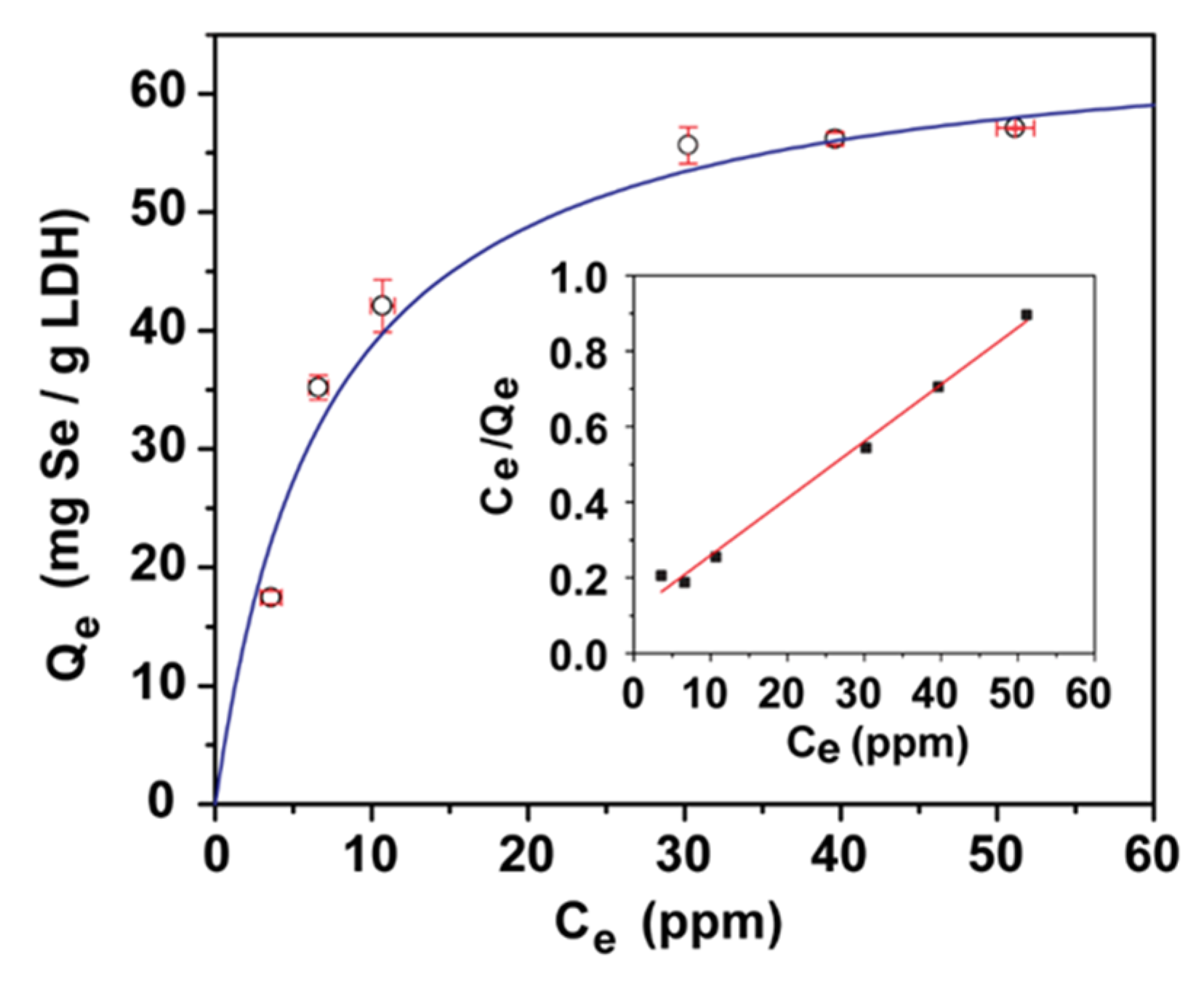
3.2. Jar Testing of LDH
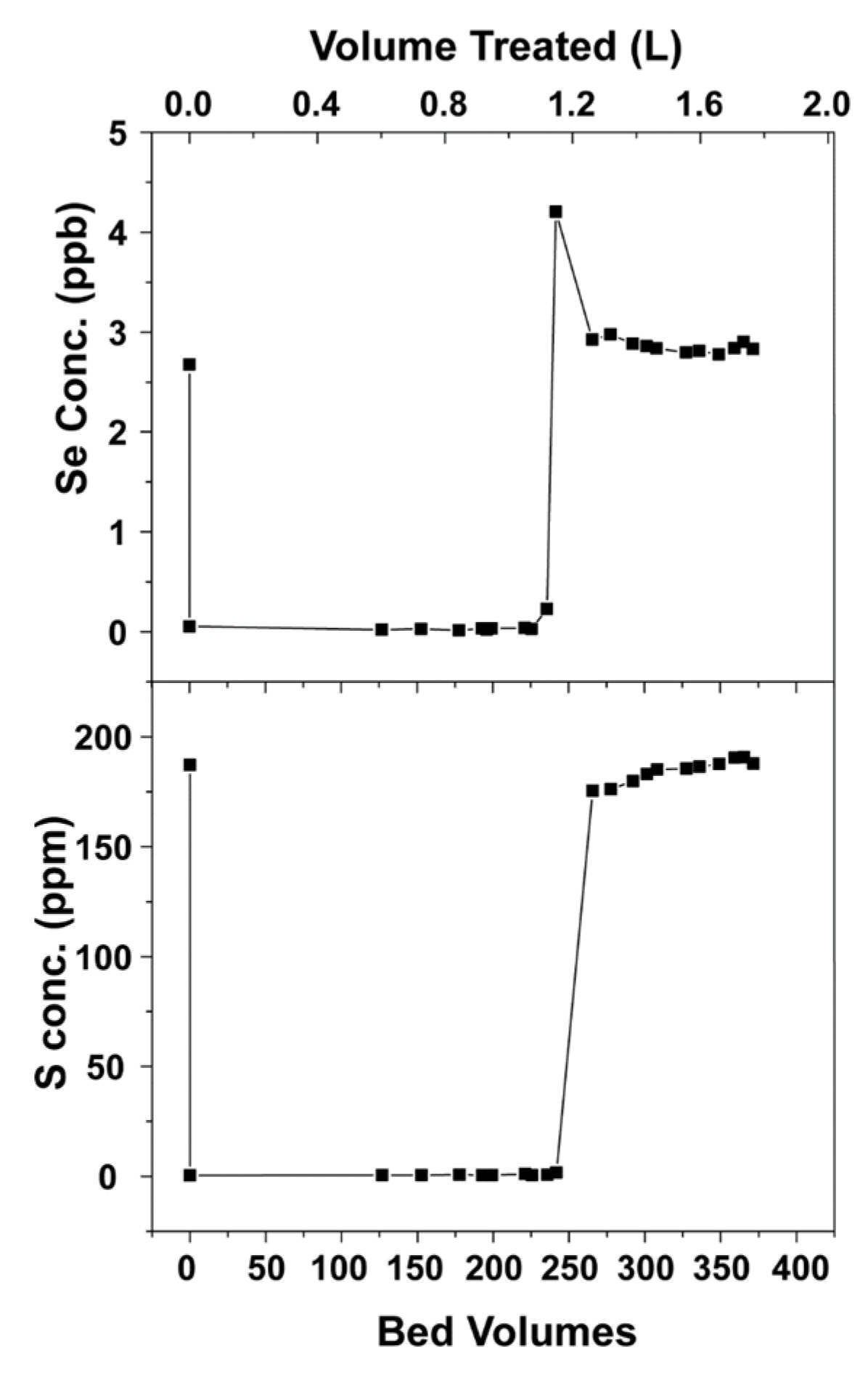
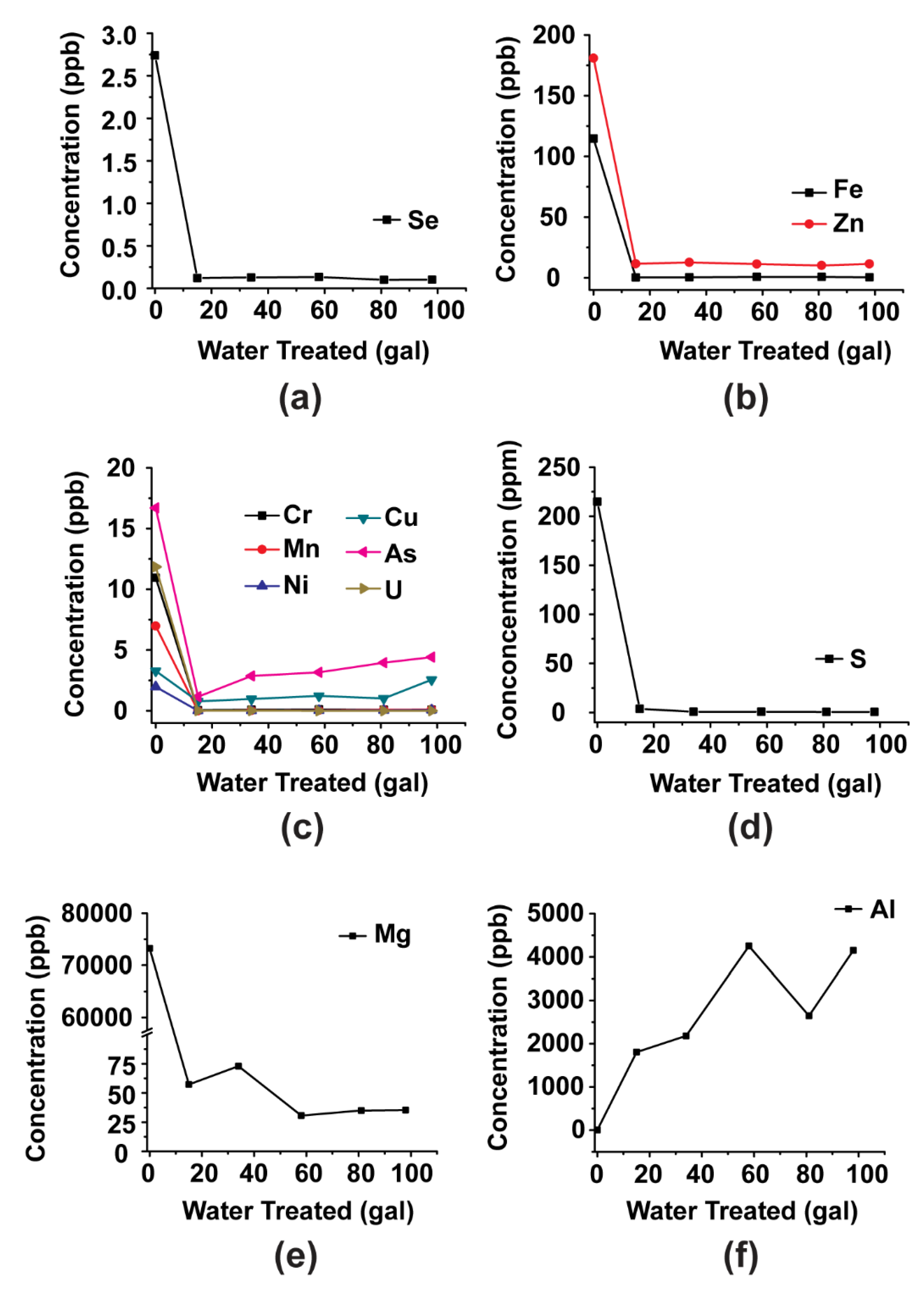
3.3. Small-Scale Column Test (1.1 cm Diameter)
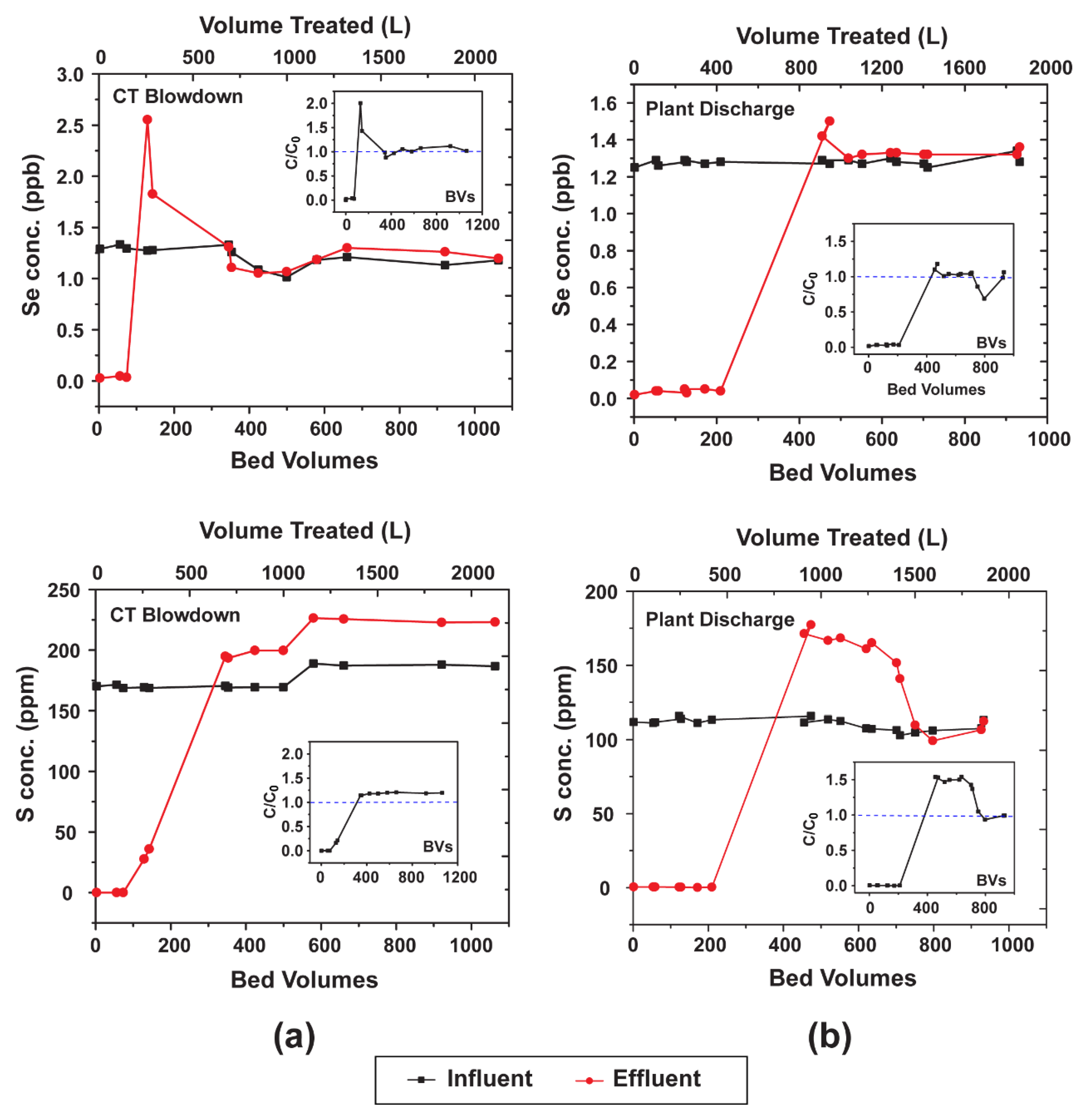
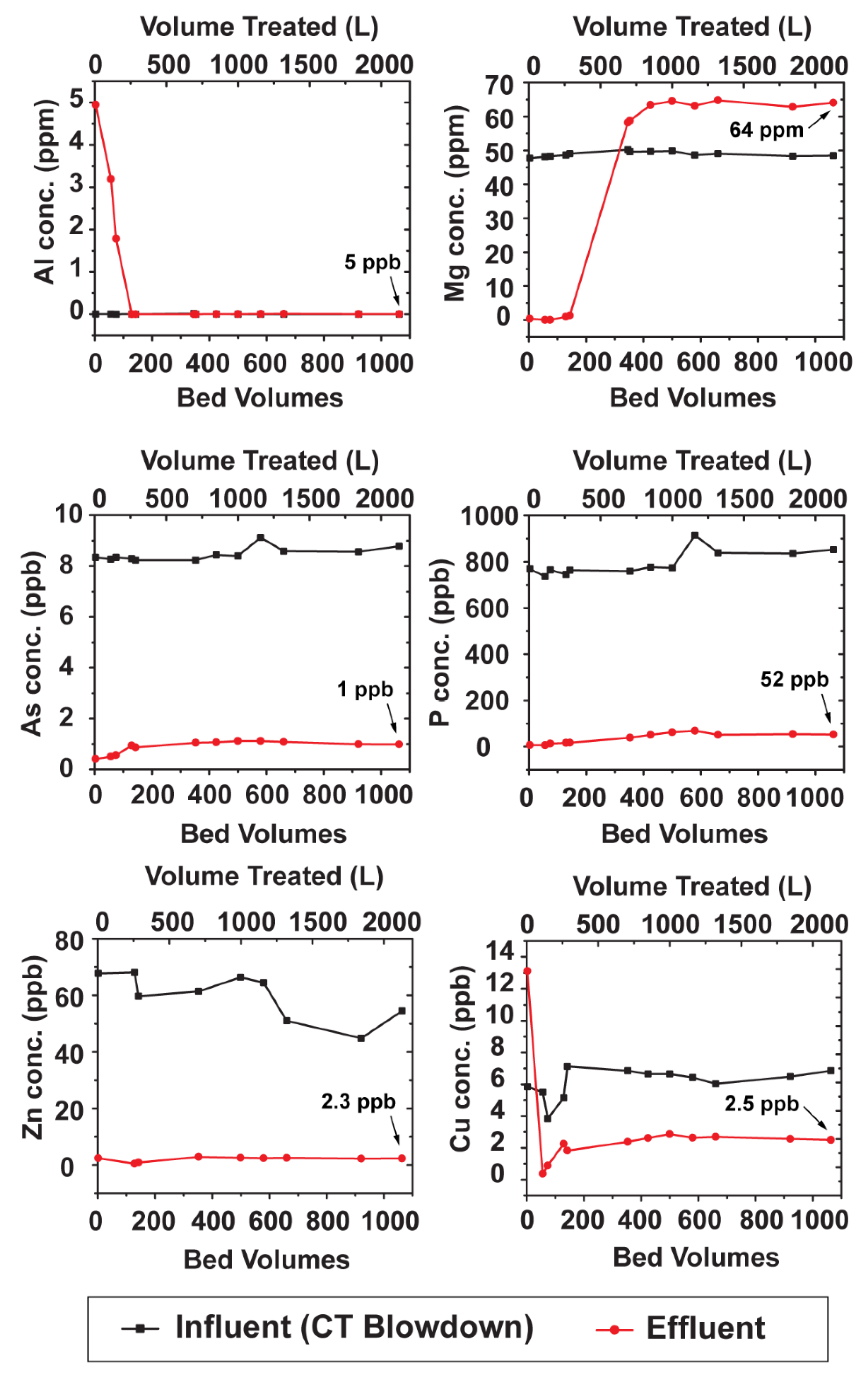
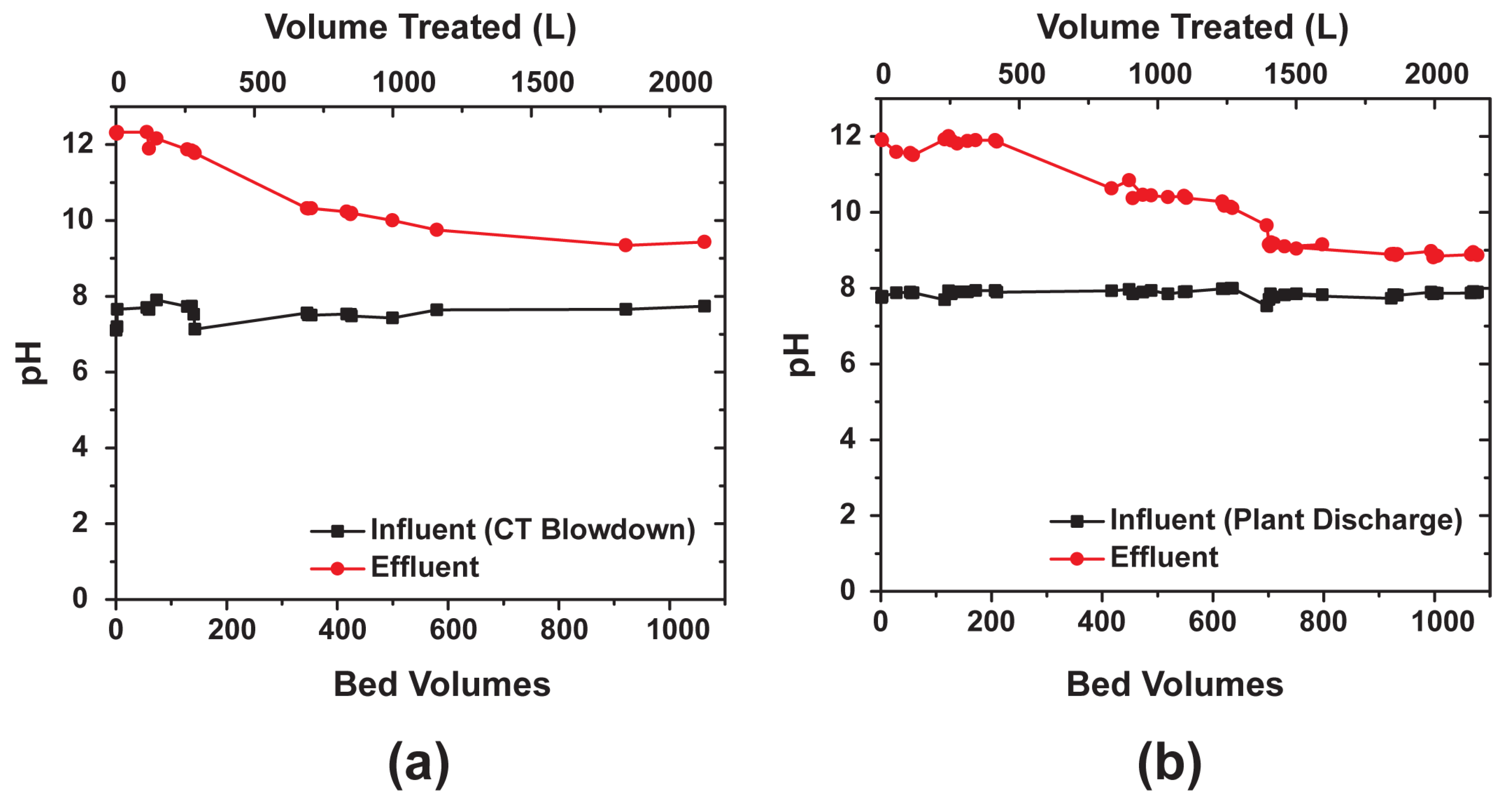
3.4. Column Testbed (2”= 5.08 cm Diameter)
3.5. Pilot-Scale Testing
3.6. LDH Post-Mortem Characterization
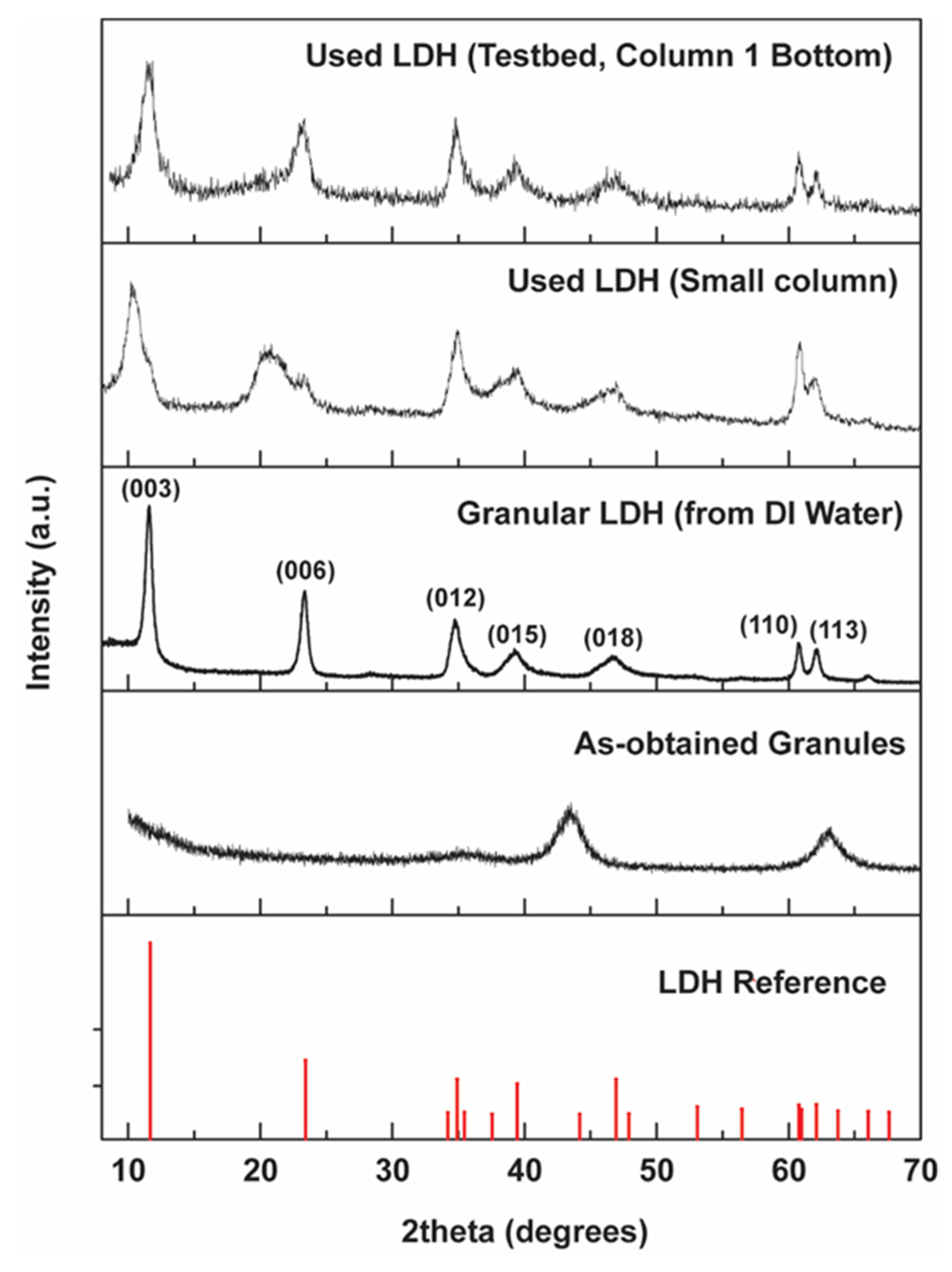
3.6.1. X-ray Characterization of LDH after Column Tests
3.6.2. Infrared Analysis of LDH
3.6.3. LDH Stability Tests
3.7. Regeneration of LDH Media
4. Discussion
4.1. Removal of Selenium and Sulfate Anions
4.2. Effect of pH
4.3. Removal of Other Species from the Water
4.4. Stability of LDH
5. Conclusions
- LDH granulated media were successfully evaluated under dynamic sorption conditions in laboratory columns and in the field for the removal of selenium from power plant wastewater.
- Continuous monitoring of influent and effluent pH showed the treated water increased to above pH 12 after startup, but gradually decreased after breakthrough of the bed.
- The LDH displayed good adsorption ability for Se(VI) in DI water solutions (66 mg/g equilibrium sorption capacity for calcined powdered media) but this was decreased in the real wastewaters < 1 μg/g due to the presence of competing anion species.
- Simultaneous removal of selenium, sulfate (~50 mg/g) and chromium (< 1 μg/g) was observed, likely occurring through anion-exchange with interlayer hydroxide and carbonate species in the LDH.
- Other species (Mg, Cu, Zn, P, As, Mn, Fe, Ni, U) were also removed from the wastewater, but likely through precipitation.
- Despite some Al3+ and Mg2+ leaching (< 0.5% of the original mass), the LDH materials retained their crystallinity after use. Calcination was demonstrated to be effective for regenerating the spent materials multiple times without losing selenate adsorption capacity.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roberts, C. Effluent Limitations Guidelines and Standards for the Steam Electric Power Generating Point Source Category, 40 CFR Part 423. Fed. Regist. 2015, 80, 67838–67903. Available online: https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2015-11-03/pdf/2015-25663.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2015).
- Gingerich, D.B.; Grol, E.; Mauter, M.S. Fundamental Challenges and Opportunities in Flue Gas Desulfurization Wastewater Treatment at Coal Fired Power Plants. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 909–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemly, A.D. Aquatic Selenium Pollution is a Global Environmental Safety Issue. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 59, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Title 18. Environmental Quality. Chapter 11. Department of Environmental Quality-Water Quality Standards. 2016. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2014-12/documents/az-chapter11-provisions.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2018).
- Ohlendorf, H.M. The Birds of Kesterson Reservoir: A Historical Perspective. Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L. Review of 15 Years of Research on Ecotoxicology and Remediation of Land Contaminated by Agricultural Drainage Sediment Rich in Selenium. Ecotoxicity Environ. Saf. 2004, 57, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.C.; Nancharaiah, Y.V.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Lens, P.N.L. Selenium: Environmental Significance, Pollution, and Biological Treatment Technologies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 886–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Review of Available Technologies for the Removal of Selenium from Water; Final Report prepared for North American Metals Council. CH2MHill: Englewood, CO, USA, 2010. Available online: http://www.namc.org/docs/00062756.PDF (accessed on 1 January 2013).
- Santos, S.; Ungureanu, G.; Boaventura, R.; Botelho, C. Selenium Contaminated Waters: An Overview of Analytical Methods, Treatment Options and Recent Advances in Sorption Methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521–522, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.B.; Gu, F.X. Emerging Nanomaterials for the Application of Selenium Removal for Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Sci. Nano 2014, 3, 982–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonstegard, J.; Pickett, T.; Harwood, J.; Johnson, D. Full Scale Operation of GE ABMet® Biological Technology for the Removal of Selenium from FGD Wastewaters. In 69th Annual International Water Conference; Curran Associates, Inc.: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Biological Treatment of Flue Gas Desulfurization Wastewater at a Power Plant Burning Powder River Basin Coal: Pilot Demonstration with the ABMet Technology; Final Report 3002006089; Electric Power Research Institute: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2017; Available online: https://www.epri.com/#/pages/product/3002006089/?lang=en-US (accessed on 15 December 2018).
- Peak, D.; Sparks, D.L. Mechanisms of Selenate Adsorption on Iron Oxides and Hydroxides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzinga, E.J.; Tang, Y.; McDonald, J.; Desisto, S.; Reeder, R.J. Macroscopic and Spectroscopic Characterization of Selenate, Selenite, and Chromate Adsorption at the Solid-Water Interface of Gamma-Al2O3. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 340, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.P.; Chrysochoou, M. Mechanisms of Chromate, Selenate, and Sulfate Adsorption on Al-Substituted Ferrihydrite: Implications for Ferrihydrite Surface Structure and Reactivity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Dianchen Gang, D.; Mcdonald, L.; Lin, L.-S. Background Electrolytes and pH Effects on Selenate Adsorption Using Iron-Impregnated Granular Activated Carbon and Surface Binding Mechanisms. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavani, F.; Trifirb, F.; Vaccari, A. Hydrotalcite-Type Anionic Clays: Preparation, Properties and Applications. Catal. Today 1991, 11, 172–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.H.; Lim, T.T.; Dong, Z. Application of Layered Double Hydroxides for Removal of Oxyanions: A Review. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1343–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Zang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Tan, X.; Hou, W.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y. Sorption of Metal Cations on Layered Double Hydroxides. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 433, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, A.; Sarina, S.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Gu, Y.; Ayoko, G.A.; Zhu, H. Efficient Removal of Cationic and Anionic Radioactive Pollutants from Water Using Hydrotalcite-Based Getters. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 16503–16510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, S. Anion-Exchange Properties of Hydrotalcite-Like Compounds. Clays Clay Miner. 1983, 31, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, S.J.; Christy, A.G.; Génin, J.-M.R.; Kameda, T.; Colombo, F. Nomenclature of the hydrotalcite supergroup: natural layered double hydroxides. Mineral. Mag. 2012, 76, 1289–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Vance, G.F.; Zhao, H. Selenium Adsorption on Mg-Al and Zn-Al Layered Double Hydroxides. Appl. Clay Sci. 2001, 20, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, M. -Selective Properties of Inorganic Materials Synthesized by the Soft Chemical Process. Solid State Ionics 2002, 151, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantino, L.V.; Nunes Quirino, J.; Monteiro, A.M.; Abrao, T.; Parreira, P.S.; Urbano, A.; Santos, M.J. Sorption-Desorption of Selenite and Selenate on Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxide in Competition with Nitrate, Sulfate and Phosphate. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chubar, N. New Inorganic (An)ion Exchangers Based on Mg-Al Hydrous Oxides: (Alkoxide-Free) Sol-Gel Synthesis and Characterisation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 357, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chubar, N.; Gerda, V.; Megantari, O.; Mičušík, M.; Omastova, M.; Heister, K.; Man, P.; Fraissard, J. Applications versus Properties of Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxides Provided by Their Syntheses Methods: Alkoxide and Alkoxide-Free Sol-Gel Syntheses and Hydrothermal Precipitation. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 234, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubar, N. EXAFS and FTIR Studies of Selenite and Selenate Sorption by Alkoxide-Free Sol-Gel Generated Mg-Al-CO3 Layered Double Hydroxide with Very Labile Interlayer Anions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 15995–16007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubar, N.; Szlachta, M. Static and Dynamic Adsorptive Removal of Selenite and Selenate by Alkoxide-Free Sol-Gel-Generated Mg-Al-CO3 Layered Double Hydroxide: Effect of Competing Ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubar, N.; Gilmour, R.; Gerda, V.; Mičušík, M.; Omastova, M.; Heister, K.; Man, P.; Fraissard, J.; Zaitsev, V. Layered Double Hydroxides as the Next Generation Inorganic Anion Exchangers: Synthetic Methods versus Applicability. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 245, 62–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubar, N. The Influence of Sulfate on Selenate Sorption on Mg-Al-CO3 Layered Double Hydroxides Prepared by Fine Inorganic Sol-Gel Synthesis Studied by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 459, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koilraj, P.; Kamura, Y.; Sasaki, K. Carbon-Dot-Decorated Layered Double Hydroxide Nanocomposites as a Multifunctional Environmental Material for Co-immobilization of and Sr2+ from Aqueous Solutions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9053–9064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koilraj, P.; Kamura, Y.; Sasaki, K. Cosorption Characteristics of and Sr2+ Radioactive Surrogates Using 2D/2D Graphene Oxide-Layered Double Hydroxide Nanocomposites. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 13854–13866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiabi, H.; Yamini, Y.; Shamsayei, M. Highly Selective and Efficient Removal of Arsenic(V), Chromium(VI) and Selenium(VI) Oxyanions by Layered Double Hydroxide Intercalated with Zwitterionic Glycine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 339, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.; Das, D.; Dash, G.P.; Parida, K.M. Studies on Mg/Fe Hydrotalcite-Like-Compound (HTlc) I. Removal of Inorganic Selenite () from Aqueous Medium. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 251, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-L.; An, M.-I. Selenium Adsorption and Speciation with Mg-FeCO3 Layered Double Hydroxides Loaded Cellulose Fibre. Talanta 2012, 95, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.N.; Konar, J.; Mohanta, M.K.; Srivastava, S.C. Adsorption of Cr(VI) and Se(IV) from their Aqueous Solutions onto Zr4+-Substituted ZnAl/MgAl-Layered Double Hydroxides: Effect of Zr4+ Substitution in the Layer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 270, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shahrivari, Z.; Liu, P.K.T.; Sahimi, M.; Tsotsis, T.T. Removal of Trace Levels of Arsenic and Selenium from Aqueous Solutions by Calcined and Uncalcined Layered Double Hydroxides (LDH). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 6804–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.; Sairam Patra, B.; Baliarsingh, N.; Parida, K. Calcined Mg-Fe-CO3 LDH as an Adsorbent for the Removal of Selenite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 316, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Frost, R.L.; Martens, W.N. Absorption of the Selenite Anion from Aqueous Solutions by Thermally Activated Layered Double Hydroxide. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paikaray, S.; Hendry, M.J.; Essilfie-Dughan, J. Controls on Arsenate, Molybdate, and Selenate Uptake by Hydrotalcite-Like Layered Double Hydroxides. Chem. Geol. 2013, 345, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Islam, S.M.; Xiao, C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Yuan, M.; Sun, G.; Li, H.; Ma, S.; Kanatzidis, M.G. Rapid Simultaneous Removal of Toxic Anions [HSeO3]−, [SeO3]2−, and [SeO4]2−, and Metals Hg2+, Cu2+, and Cd2+ by Intercalated Layered Double Hydroxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 12745–12757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, N.; Zhou, Z.; Tian, X.; Yang, C.; Li, Y. Superior Capability of MgAl2O4 for Selenite Removal from Contaminated Groundwater During its Reconstruction of Layered Double Hydroxides. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 176, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Farmen, L.M.; Chan, C.K. Selenium Removal from Sulfate-Containing Groundwater Using Granular Layered Double Hydroxide Materials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 2458–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeley, T.J.; Skone, T.J.; Stiegel, G.J.; McNemar, A.; Nemeth, M.; Schimmoller, B.; Murphy, J.T.; Manfredo, L. Water: A Critical Resource in the Thermoelectric Power Industry. Energy 2008, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Dopilka, A.; Kraetz, A.N.; Jing, H.; Chan, C.K. Layered Double Hydroxide/Chitosan Nanocomposite Beads as Sorbents for Selenium Oxoanions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 4978–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, S. Physico-Chemical Properties of Synthetic Hydrotalcites in Relation to Composition. Clays Clay Miner. 1980, 28, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Gallegos, S.; Pfeiffer, H.; Lima, E.; Espinosa, M.; Bosch, P.; Bulbulian, S. Cr(VI) Immobilization in Mixed (Mg, Al) Oxides. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 94, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Kim, Y.; Liu, P.K.T.; Sahimi, M.; Tsotsis, T.T. A Study by In Situ Techniques of the Thermal Evolution of the Structure of a Mg-Al-CO3 Layered Double Hydroxide. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2002, 57, 2945–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamani, J.S.; Lounsbury, A.W.; Zimmerman, J.B. Adsorption of Selenite and Selenate by Nanocrystalline Aluminum Oxide, Neat and Impregnated in Chitosan Beads. Water Res. 2014, 50, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, H. Water-Dispersible Magnetic Nanoparticle–Graphene Oxide Composites for Selenium Removal. Carbon 2014, 77, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Hendry, J.; Essilfie-Dughan, J. Adsorption of Selenate onto Ferrihydrite, Goethite, and Lepidocrocite under Neutral pH Conditions. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 28, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.; Giménez, J.; de Pablo, J.; Rovira, M.; Duro, L. Sorption of Selenium(IV) and Selenium(VI) onto Magnetite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 3767–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, C.M.; Hernandez, J.; Parsons, J.G.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Adsorption of Selenite and Selenate by a High- and Low- Pressure Aged Manganese Oxide Nanomaterial. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2011, 39, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, C.M.; Hernandez, J.; Parsons, J.G.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. A Study of the Removal of Selenite and Selenate from Aqueous Solutions using a Magnetic Iron/Manganese Oxide Nanomaterial and ICP-MS. Microchem. J. 2010, 96, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleiman, N.; Mishael, Y.G. Selenium Removal from Drinking Water by Adsorption to Chitosan—Clay Composites and Oxides: Batch and Columns Tests. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.T.; Kuan, W.H.; Chen, T.Y.; Wang, M.K. Adsorption Mechanism of Selenate and Selenite on the Binary Oxide Systems. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4412–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salt River Project (Tempe, AZ, USA). Personal communication, 2014.
- Jegadeesan, G.; Mondal, K.; Lalvani, S.B. Selenate Removal from Sulfate Containing Aqueous Solutions. Environ. Technol. 2005, 26, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, P.; Highfield, D.; Badruzzaman, M.; Yoon, Y. Rapid Small-Scale Column Tests for Arsenate Removal in Iron Oxide Packed Bed Columns. J. Environ. Eng. 2005, 131, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantino, V.R.L.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Basic Properties of Layered Double Hydroxides Intercalated by Carbonate, Hydroxide, Chloride, and Sulfate Anions. Inorg. Chem. 1995, 34, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cosimo, J.I.; Díez, V.K.; Xu, M.; Iglesia, E.; Apesteguía, C.R. Structure and Surface and Catalytic Properties of Mg-Al Basic Oxides. J. Catal. 1998, 178, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brungs, W.A. Effects of residual chlorine on aquatic life. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1973, 45, 2180–2193. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, F.; Fornes, V.; Rojo, J.M. Thermal Decomposition of Hydrotalcites An Infrared and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Study. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1992, 88, 2233–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millange, F.; Walton, R.I.; O’Hare, D. Time-Resolved In Situ X-ray Diffraction Study of the Liquid-Phase Reconstruction of Mg-Al-Carbonate Hydrotalcite-Like Compounds. J. Mater. Chem. 2000, 10, 1713–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, K.L.; Bostrom, T.E.; Frost, R.L. A Study of Structural Memory Effects in Synthetic Hydrotalcites Using Environmental SEM. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theiss, F.L.; Palmer, S.J.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L. Sulfate Intercalated Layered Double Hydroxides Prepared by the Reformation Effect. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 107, 1123–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhitova, E.S.; Krivovichev, S.V.; Pekov, I.V.; Yakovenchuk, V.N.; Pakhomovsky, Y.A. Correlation Between the d-value and the M2+:M3+ Cation Ratio in Mg-Al-CO3 Layered Double Hydroxides. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 130, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellotto, M.; Rebours, B.; Clause, O.; Lynch, J.; Bazin, D.; Elkaïm, E. A Reexamination of Hydrotalcite Crystal Chemistry. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 8527–8534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, L.M.; Milestone, N.B.; Newman, R.H. The Use of Hydrotalcite as an Anion Absorbent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1995, 34, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bookin, A.S.; Cherkashin, V.I.; Drits, V.A. Polytype Diversity of the Hydrotalcite-like Minerals II. Determination of the Polytypes of Experimentally Studied Varieties. Clays Clay Miner. 1993, 41, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimura, A.; Uchida, M.; Okuwaki, A. Synthesis and Sulfate Ion-Exchange Properties of a Hydrotalcite-Like Compound Intercalated by Chloride Ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustrowski, P.; Sułkowska, D.; Chmielarz, L.; Rafalska-Łasocha, A.; Dudek, B.; Dziembaj, R. Influence of Thermal Treatment Conditions on the Activity of Hydrotalcite-Derived Mg-Al Oxides in the Aldol Condensation of Acetone. Microporous Mesporous Mater. 2004, 78, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Moreno, M.J.; Ulibarri, M.A.; Rendon, J.L.; Serna, C.J. IR Characteristics of Hydrotalcite-like Compounds. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1985, 12, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gaini, L.; Lakraimi, M.; Sebbar, E.; Meghea, A.; Bakasse, M. Removal of Indigo Carmine Dye from Water to Mg-Al-CO3-Calcined Layered Double Hydroxides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.J.; Frost, R.L.; Nguyen, T. Hydrotalcites and Their Role in Coordination of Anions in Bayer Liquors: Anion Binding in Layered Double Hydroxides. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khitous, M.; Salem, Z.; Halliche, D. Effect of Interlayer Anions on Chromium Removal Using Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxides: Kinetic, Equilibrium and Thermodynamic Studies. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 24, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, S.V.; Kamath, P.V. Synthesis and Characterization of Arsenate-Intercalated Layered Double Hydroxides (LDHs): Prospects for Arsenic Mineralization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 331, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.-P.; Cao, C.-Y.; Wei, F.; Sun, Y.-B.; Song, W.-G. MgAl Layered Double Hydroxides with Chloride and Carbonate Ions as Interlayer Anions for Removal of Arsenic and Fluoride Ions in Water. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 10412–10417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, A.; Jones, M.I.; Kanezaki, E.; Metson, J.B. Complete Desorption of Interlayer Hydrogen Phosphate in Mg/Al-Layered Double Hydroxides by Means of Anion Exchange with 1-Octanesulfonate. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luengo, C.V.; Volpe, M.A.; Avena, M.J. High Sorption of Phosphate on Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxides: Kinetics and Equilibrium. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4656–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbágy, M.; Regazzoni, A.E. Dissolution of Nano-Size Mg-Al-Cl Hydrotalcite in Aqueous Media. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 51, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liao, M.-C.; Zeng, H.-Y.; Liu, X.-J.; Du, J.-Z.; Ding, P.-X.; Zhang, W. Surface Modification and Dissolution Behavior of Mg-Al Hydrotalcite Particles. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 56, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhalil, A.; Qourzal, S.; Mahjoubi, F.Z.; Elmoubarki, R.; Farnane, M.; Tounsadi, H.; Sadiq, M.; Abdennouri, M.; Barka, N. Defluoridation of Groundwater by Calcined Mg/Al Layered Double Hydroxide. Emerg. Contam. 2016, 2, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarneni, S.; Kozai, N.; Roy, R. Novel Function for Anionic Clays: Selective Transition Metal Cation Uptake by Diadochy. J. Mater. Chem. 1998, 8, 1329–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.C.; Braterman, P.S. Cation Exchange by Anion-Exchanging Clays: The Effects of Particle Aging. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 7965–7975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Sun, S.; Chen, X.; Chang, Y.; Zha, F.; Lei, Z. Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxides Modified Clay Adsorbents for Efficient Removal of Pb2+, Cu2+ and Ni2+ from Water. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 123, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, Z.; Lin, Z. Simultaneous Removal of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) by Mg-Al-Cl Layered Double Hydroxide and Mechanism Insight. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 53, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, T.W.J.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Fornasiero, D. Effect of pH, Concentration and Temperature on Copper and Zinc Hydroxide Formation/Precipitation in Solution. In CHEMECA 2011 - “Engineering a Better World”; Institution of Engineers Australia: Barton, Australia, 2011; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Um, N.; Hirato, T. Precipitation Behavior of Ca(OH)2, Mg(OH)2, and Mn(OH)2 from CaCl2, MgCl2, and MnCl2 in NaOH-H2O Solutions and Study of Lithium Recovery from Seawater via Two-Stage Precipitation Process. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 146, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boclair, J.W.; Braterman, P.S. Layered Double Hydroxide Stability. 1. Relative Stabilities of Layered Double Hydroxides and Their Simple Counterparts. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seida, Y.; Nakano, Y. Removal of Phosphate by Layered Double Hydroxides Containing Iron. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novillo, C.; Guaya, D.; Allen-Perkins Avendaño, A.; Armijos, C.; Cortina, J.L.; Cota, I. Evaluation of Phosphate Removal Capacity of Mg/Al Layered Double Hydroxides from Aqueous Solutions. Fuel 2014, 138, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ookubo, A.; Ooi, K.; Hayashi, H. Preparation and Phosphate Ion-Exchange Properties of a Hydrotalcite-like Compound. Langmuir 1993, 9, 1418–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftekhar, S.; Küçük, M.E.; Srivastava, V.; Repo, E.; Sillanpaa, M. Application of Zinc-Aluminium Layered Double Hydroxides for Adsorptive Removal of Phosphate and Sulfate: Equilibrium, Kinetic and Thermodynamic. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.T.K.; Zhang, Y.; De Corte, D.; Hannes, J.-B.; Ye, W.; Mondal, P.; Jullok, N.; Meesschaert, B.; Pinoy, L.; Van Der Bruggen, B. P-Recovery as Calcium Phosphate from Wastewater Using an Integrated Selectrodialysis/Crystallization Process. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 77, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekmene, O.; Quillard, S.; Rouillon, T.; Bouler, J.-M.; Piot, M.; Gaucheron, F. Effects of pH and Ca/P Molar Ratio on the Quantity and Crystalline Structure of Calcium Phosphates Obtained from Aqueous Solutions. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2009, 89, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Lu, P.; Ning, P.; Wang, Q. Arsenic Removal from Water/Wastewater Using Layered Double Hydroxide Derived Adsorbents, A Critical Review. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 22694–22709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violante, A.; Pucci, M.; Cozzolino, V.; Zhu, J.; Pigna, M. Sorption/Desorption of Arsenate on/from Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxides: Influence of Phosphate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 333, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun Moon, D.; Dermatas, D.; Menounou, N. Arsenic Immobilization by Calcium-Arsenic Precipitates in Lime Treated Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 330, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Violante, A.; Pigna, M.; Del Gaudio, S.; Cozzolino, V.; Banerjee, D. Coprecipitation of Arsenate with Metal Oxides. 3. Nature, Mineralogy, and Reactivity of Iron(III)-Aluminum Precipitates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parello, M.L.; Rojas, R.; Giacomelli, C.E. Dissolution Kinetics and Mechanism of Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxides: A Simple Approach to Describe Drug Release in Acid Media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 351, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rives, V.; Del Arco, M.; Martín, C. Layered Double Hydroxides as Drug Carriers and for Controlled Release of Non-Steroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): A Review. J. Control. Release 2013, 169, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rives, V.; Del Arco, M.; Martín, C. Intercalation of Drugs in Layered Double Hydroxides and Their Controlled Release: A Review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 88–89, 239–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, P.X.; Guo, Q.L. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Layered Double Hydroxides (LDHs) from Mixed MgO and Al2O3: LDH Formation Mechanism. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
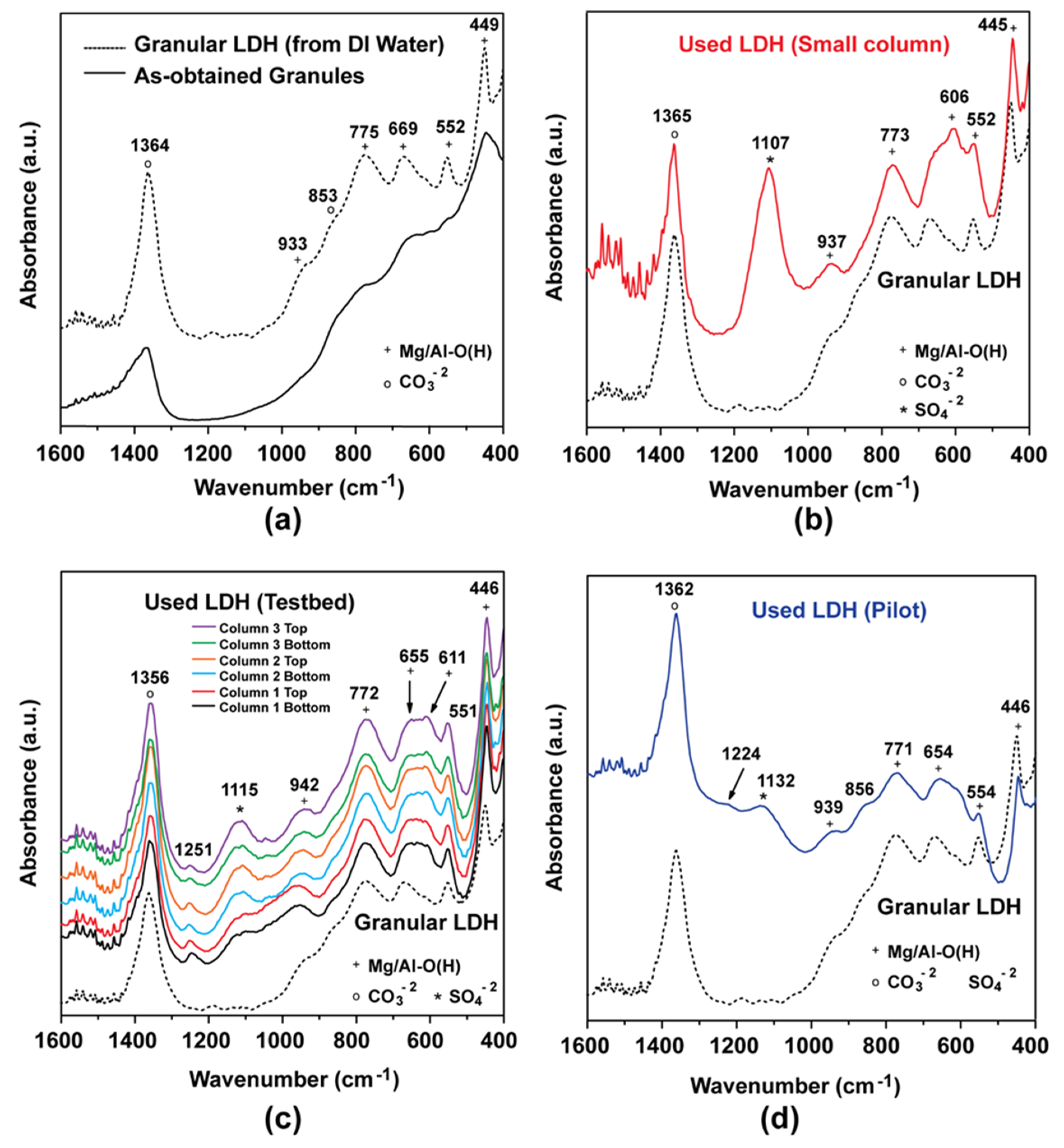
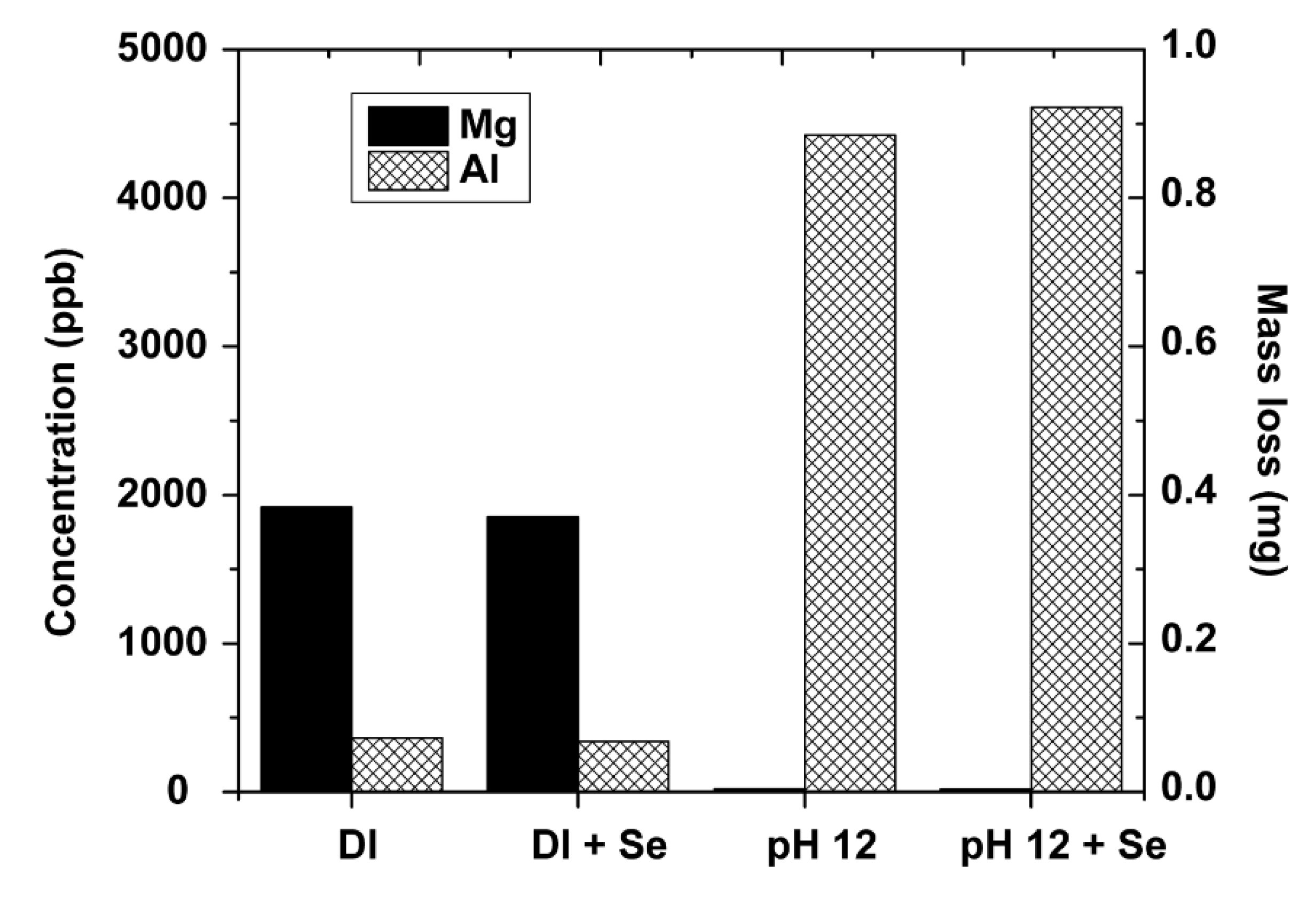
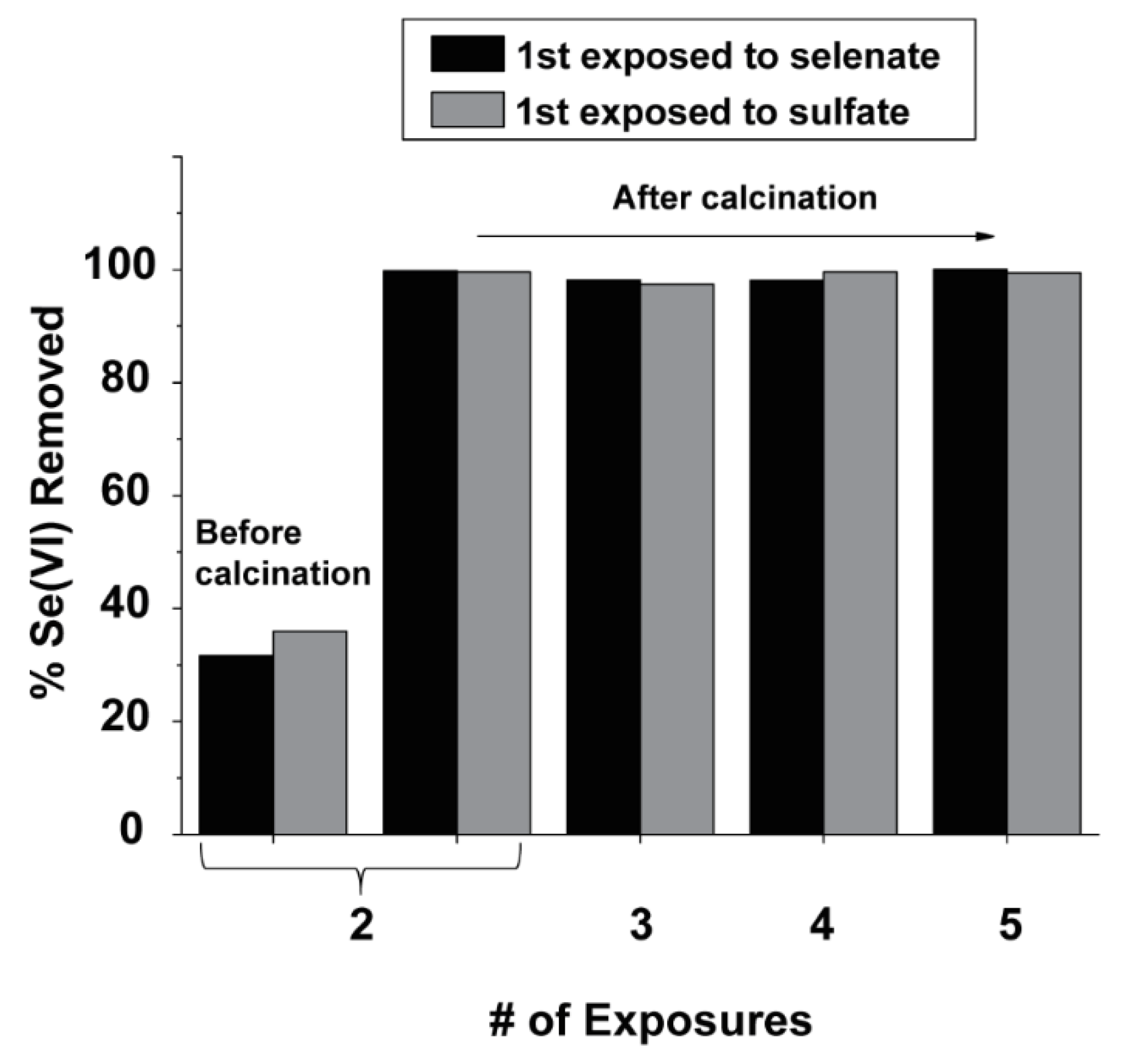
| Element | Vb1 | BVb2 | Qb3 | Ve4 | BVe5 | Qe6 | AER7 | V1g8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Se | 1.07 | 226 | 0.53 µg/g | 1.14 | 239 | 0.55 µg/g | 4.73 | 0.21 |
| S | 1.14 | 241 | 39.79 mg/g | 1.26 | 266 | 41.87 mg/g | 4.26 | 0.23 |
| Element | Vb1 | BVb2 | Qb3 | Ve4 | BVe5 | Qe6 | AER7 | V1g8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Se | 149 | 74 | 0.16 µg/g | 200 | 100 | 0.19 µg/g | 5.64 | 0.18 |
| S | 159 | 79 | 24.75 mg/g | 642 | 320 | 62.24 mg/g | 1.76 | 0.57 |
| Element | Vb1 | BVb2 | Qb3 | Ve4 | BVe5 | Qe6 | AER7 | V1g8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Se | 421 | 210 | 0.43 µg/g | 869 | 433 | 0.65 µg/g | 1.45 | 0.69 |
| S | 421 | 210 | 36.75 mg/g | 747 | 372 | 51.01 mg/g | 1.69 | 0.59 |
| Water | Nitrate 1 | Orthophosphate 2 | Chloride | Sulfate | Bicarbonate Alkalinity 3 | Total Dissolved Solids |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influent | 24 (0.20) | 4.2 (0.20) | 1300 (40) | 870 (40) | 74 (6.0) | 3700 (100) |
| Effluent | 22 (0.5) | 1.42 (0.50) | 1300 (40) | ND 4 (2.0) | ND 4 (6.0) | 3200 (20) |
| Wastewater | C0 (Se) 1 (μg/L) | C0 (S) 2 (mg/L) | [S]/[Se] | Qe (Se) 3 (µg/g) | Qe (S) 4 (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground water (small-scale column) | 1.75 | 37 | 21,000 | 0.65 | 18 |
| CT blowdown (small-scale column) | 2.67 | 187 | 70,000 | 0.55 | 42 |
| CT blowdown (testbed) | 1.22 | 175 | 144,000 | 0.19 | 62 |
| Plant discharge (testbed) | 1.28 | 110 | 86,000 | 0.65 | 51 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Chowdhury, T.; Kraetz, A.N.; Jing, H.; Dopilka, A.; Farmen, L.M.; Sinha, S.; Chan, C.K. Layered Double Hydroxide Sorbents for Removal of Selenium from Power Plant Wastewaters. ChemEngineering 2019, 3, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering3010020
Li M, Chowdhury T, Kraetz AN, Jing H, Dopilka A, Farmen LM, Sinha S, Chan CK. Layered Double Hydroxide Sorbents for Removal of Selenium from Power Plant Wastewaters. ChemEngineering. 2019; 3(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering3010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Man, Tanzil Chowdhury, Andrea N. Kraetz, Hangkun Jing, Andrew Dopilka, Lisa M. Farmen, Shahnawaz Sinha, and Candace K. Chan. 2019. "Layered Double Hydroxide Sorbents for Removal of Selenium from Power Plant Wastewaters" ChemEngineering 3, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering3010020
APA StyleLi, M., Chowdhury, T., Kraetz, A. N., Jing, H., Dopilka, A., Farmen, L. M., Sinha, S., & Chan, C. K. (2019). Layered Double Hydroxide Sorbents for Removal of Selenium from Power Plant Wastewaters. ChemEngineering, 3(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering3010020





