Effective Concentration of Ionic Liquids for Enhanced Saccharification of Cellulose
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Evaluation of IL Concentration Dependence of Cellulose Saccharification Activity
2.3. Measurement of Intrinsic Trp Fluorescence
3. Results and Discussion
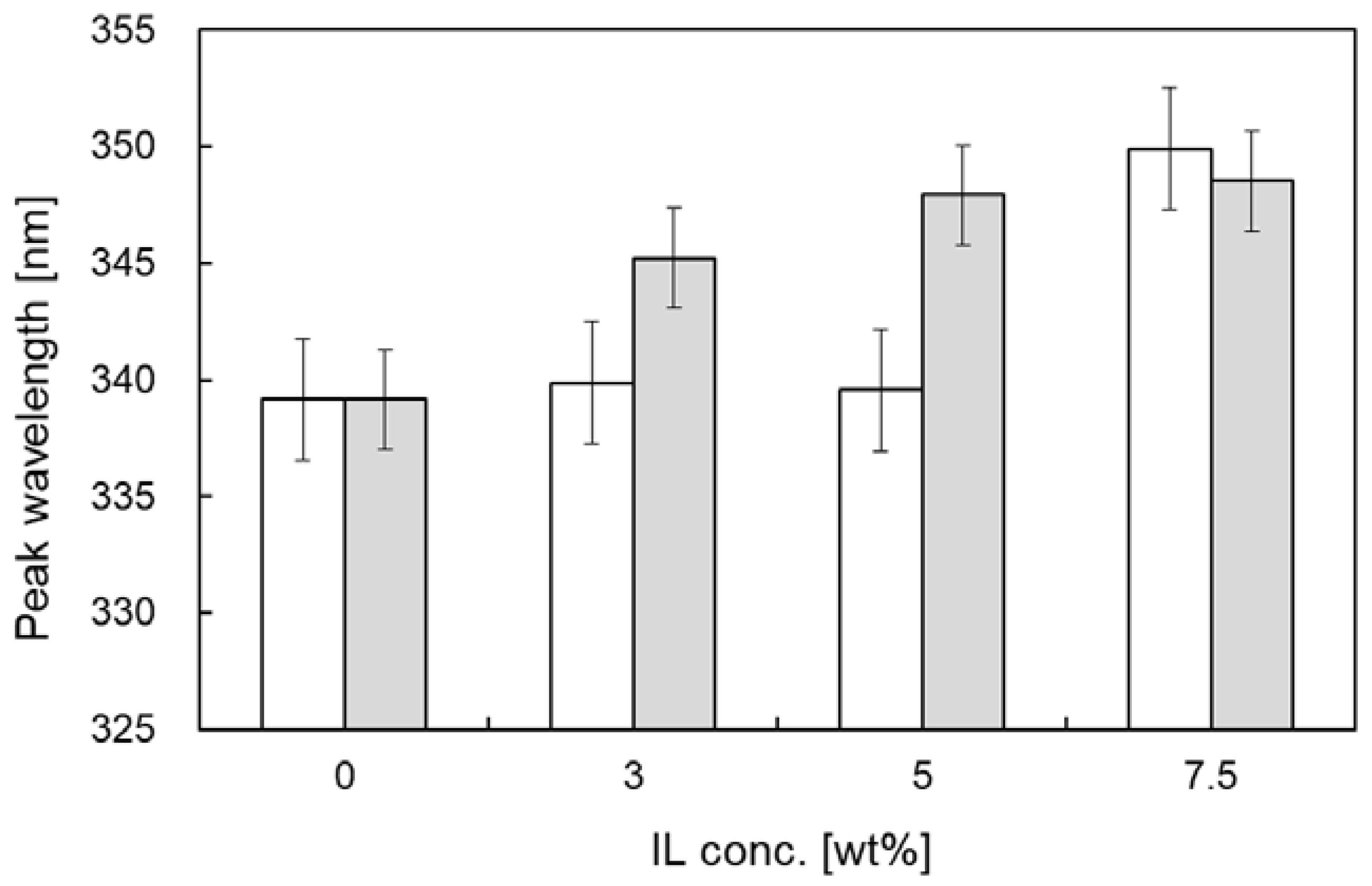
3.1. Effect of ILs on Ternary Structure of Cellulase
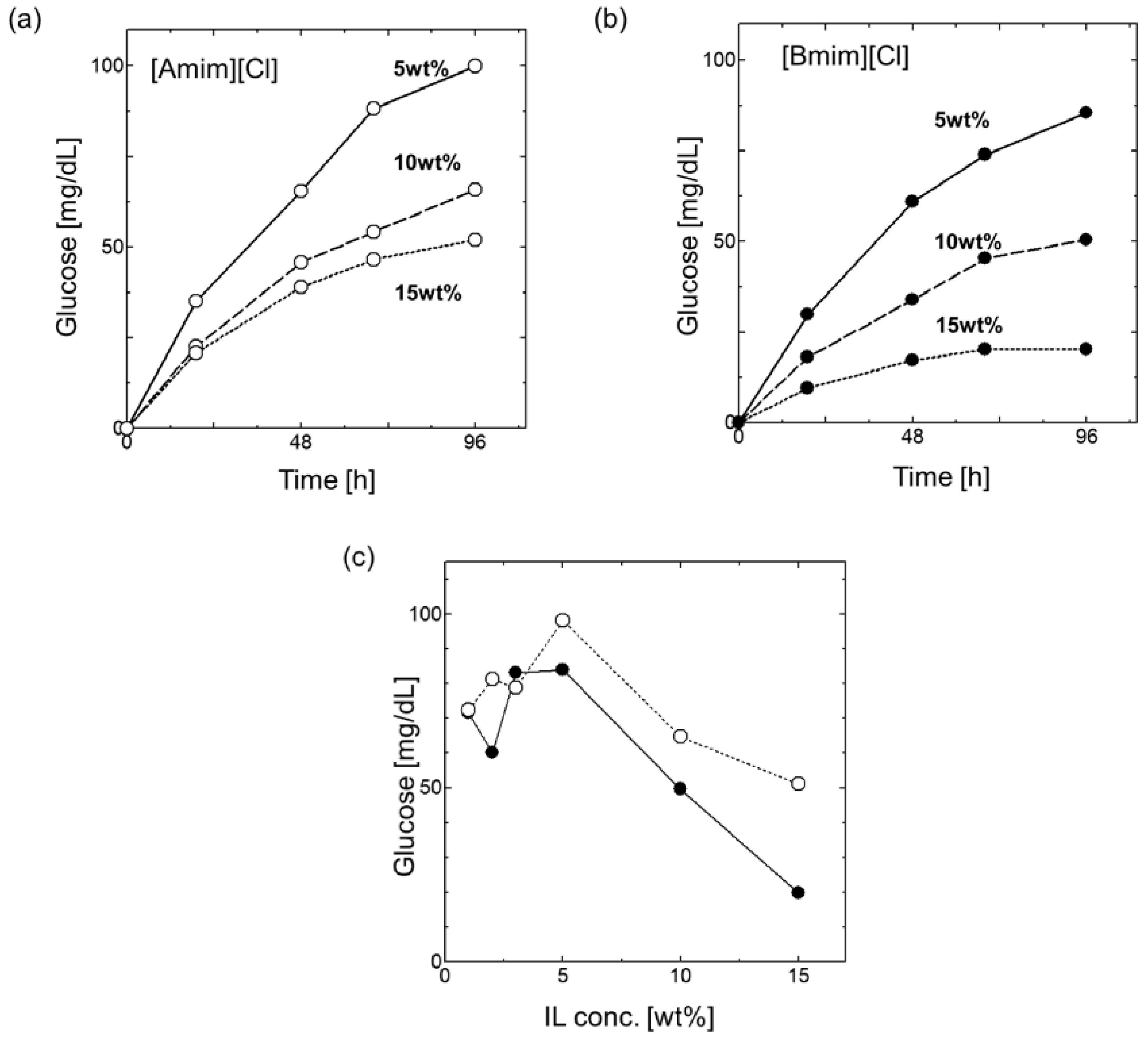
3.2. Effect of ILs on the Saccharification of Cellulose
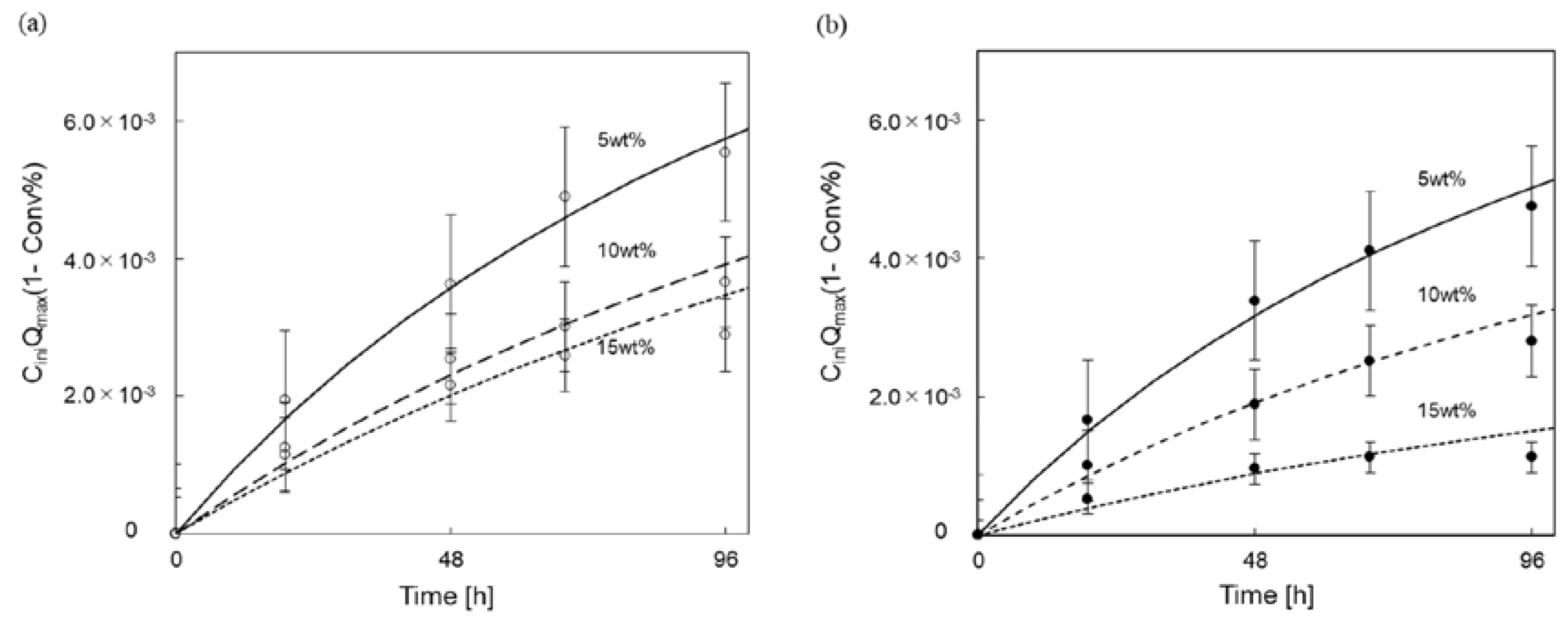
3.3. Kinetic Parameter Analysis for Enzymatic Saccharification of Cellulose
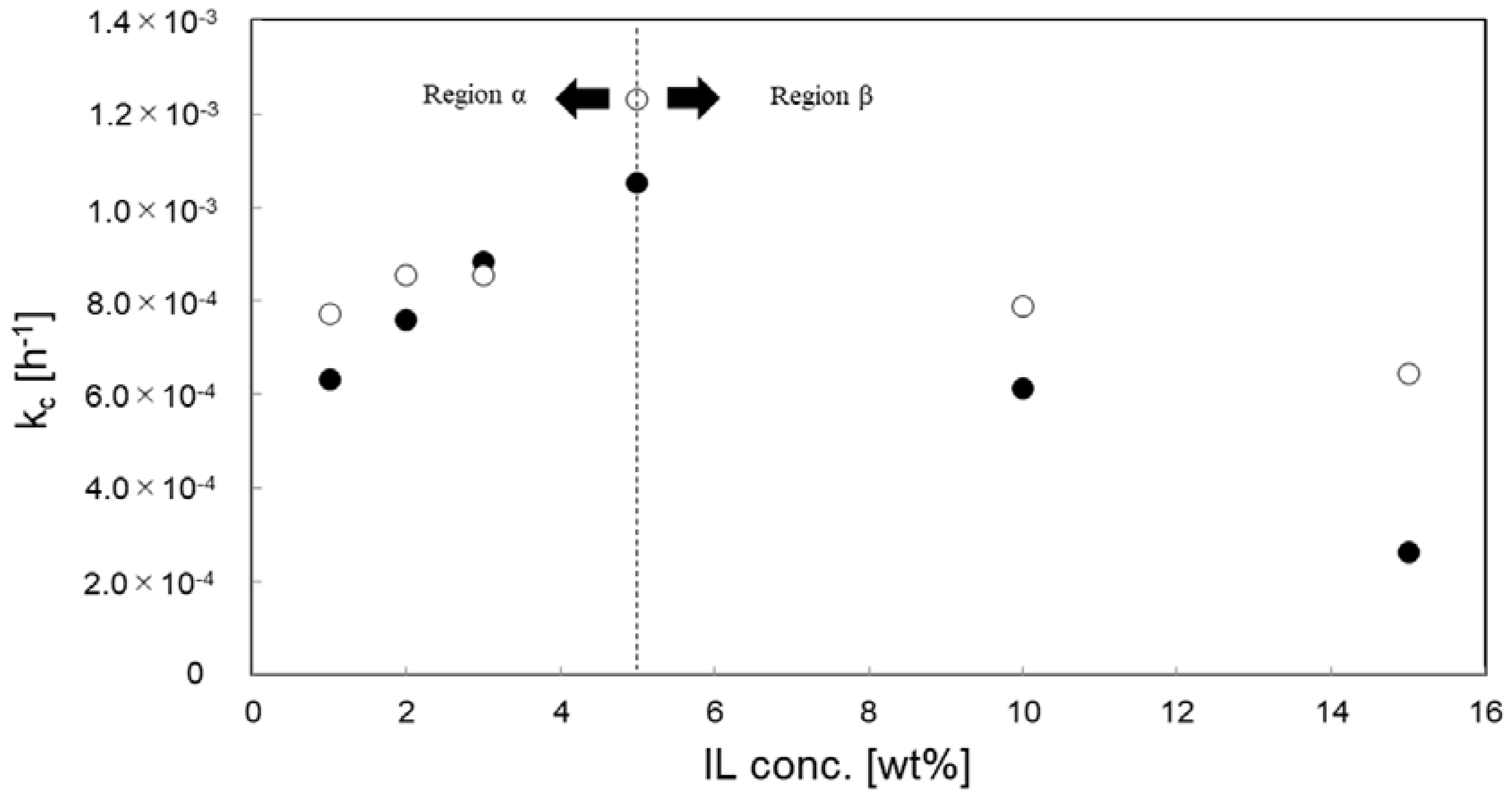
3.4. Effect of IL Species and Concentration for Kinetic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IL | ionic liquid |
| [Bmim][Cl] | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride |
| [Amim][Cl] | 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride |
| Trp | tryptophan |
References
- Mansfield, S.D.; Mooney, C.; Saddler, J.N. Substrate and enzyme characteristics that limit cellulose hydrolysis. Biotechnol. Prog. 1999, 15, 804–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beldman, G.; Voragen, A.G.; Rombouts, F.M.; Searle-van Leeuwen, M.F.; Pilnik, W. Adsorption and kinetic behavior of purified endoglucanases and exoglucanases from Trichoderma viride. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1987, 30, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, M.; Tsianou, M.; Alexandridis, P. Assessment of solvents for cellulose dissolution. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 228, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agbor, V.B.; Cicek, N.; Sparling, R.; Berlin, A.; Levin, D.B. Biomass pretreatment fundamentals toward application. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, K.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A critical review of analytical methods in pretreatment of lignocelluloses: Composition, imaging, and crystallinity. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadi, A.P.; Varanasi, S.; Schall, C.A. Enhancement of cellulose scarification kinetics using an ionic liquid pretreatment step. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2006, 95, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Pale, M.; Mwli, L.; Doherty, T.V.; Linhaardt, R.J.; Dordick, J.S. Room temperature ionic liquids as an emerging solvent for the pretreatment of lignocellulogic biomass. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 1229–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moniruzzaman, M.; Ono, T. Separation and characterization of cellulose fibers from cypress wood treated with ionic liquid prior to laccase treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 127, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vancouver, T.; Austin, A.-S.; Brown, T.; Mcintosh, S. Use of ionic liquids in converting lignocellulosic material to biofuels. Renew. Energy 2012, 45, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jones, C.L.; Baker, G.A.; Xia, S.; Olubajo, O.; Person, V.N. Regenerating cellulose from ionic liquids for an accelerated enzymatic hydrolysis. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 139, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.B.; Baker, G.A.; Cowins, J.V. Fast enzymatic scarification of switchgrass after pretreatment with ionic liquids. Biotechnol. Prog. 2010, 26, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.B.; Spear, S.K.; Huddleston, J.G.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquid salt-induced inactivation and unfolding of cellulase from Trichoderma reesei. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Barnes, C.A.; Petrich, J.W. Enhanced stability and activity of cellulase in an ionic liquid and the effect of pretreatment on cellulose hydrolysis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, D.; Singh, R. Pretreatment of lignocellulosic wastes for biofuel production: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 90, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.-L.; Qi, W.; Yuan, Z.-H.; Zhuang, Z.-S.; Liu, Y.; He, M.-C. A fractal-like kinetic equation to investigate temperature effect on cellulose hydrolysis by free and immobilized cellulase. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 168, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yoshimoto, M.; Tsukuda, N.; Fukunaga, K.; Nakao, K. A kinetic study on enzymatic hydrolysis of a variety of pulps for its enhancement with continuous ultrasonic irradiation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2004, 19, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlström, R.M.; Suurnäkki, A. Enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic polysaccharides in the presence of ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 694–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, M.; Tanimura, K.; Tokunaga, K.; Kamimura, A. Hydrolysis of insoluble cellulose to glucose catalyzed by cellulase-containing liposomes in an aqueous solution of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Biotechnol. Prog. 2013, 29, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miwa, I.; Okuda, J.; Maeua, K.; Okuda, G. Mutarotase effect on colorimetric determination of blood glucose with β-D-glucose oxidase. Clin. Chim. Acta 1972, 37, 538–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, N.I.; Abou-Zied, O.K.; Hashim, R. Evidence of basic medium in the polar nanochannels of the inverse bicontinuous cubic phase of a guerbet glycolipid: a steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 26636–26643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umakoshi, H.; Nishida, A. Modulation of yeast hexokinase on bio-inspired membranes. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 69, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.M.; Bermejo, M.D.; Martín, Á.; Cocero, M.J. Ionic liquid as reaction media for the production of cellulose-derived polymers from cellulosic biomass. ChemEngineering 2017, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Wu, Z.; Gong, G. Dissolution of cotton cellulose with ionic liquids 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride and 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride to prepare reducing sugar. J. Energy Eng. 2014, 140, 04013013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| IL | IL Conc. (wt%) | Qmax | K |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Amim][Cl] | 5 | 1.45 × 10−2 | 6.85 × 10−2 |
| [Amim][Cl] | 10 | 1.30 × 10−2 | 4.50 × 10−2 |
| [Amim][Cl] | 15 | 1.25 × 10−2 | 4.00 × 10−2 |
| [Bmim][Cl] | 5 | 1.20 × 10−2 | 7.50 × 10−2 |
| [Bmim][Cl] | 10 | 9.50 × 10−3 | 5.25 × 10−3 |
| [Bmim][Cl] | 15 | 5.00 × 10−3 | 4.50 × 10−3 |
| IL | Vmax | Km | Vmax/Km |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Amim][Cl] | 5.70 × 10−3 | 5.27 × 10−1 | 1.08 × 10−2 |
| [Bmim][Cl] | 5.80 × 10−3 | 8.70 × 10−1 | 0.67 × 10−2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanimura, K.; Ooe, Y.; Suga, K.; Umakoshi, H. Effective Concentration of Ionic Liquids for Enhanced Saccharification of Cellulose. ChemEngineering 2018, 2, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering2040047
Tanimura K, Ooe Y, Suga K, Umakoshi H. Effective Concentration of Ionic Liquids for Enhanced Saccharification of Cellulose. ChemEngineering. 2018; 2(4):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering2040047
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanimura, Kazuhiko, Yoshiko Ooe, Keishi Suga, and Hiroshi Umakoshi. 2018. "Effective Concentration of Ionic Liquids for Enhanced Saccharification of Cellulose" ChemEngineering 2, no. 4: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering2040047
APA StyleTanimura, K., Ooe, Y., Suga, K., & Umakoshi, H. (2018). Effective Concentration of Ionic Liquids for Enhanced Saccharification of Cellulose. ChemEngineering, 2(4), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering2040047






