Deterministic Assessment of the Risk of Phthalate Esters in Sediments of U-Tapao Canal, Southern Thailand
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
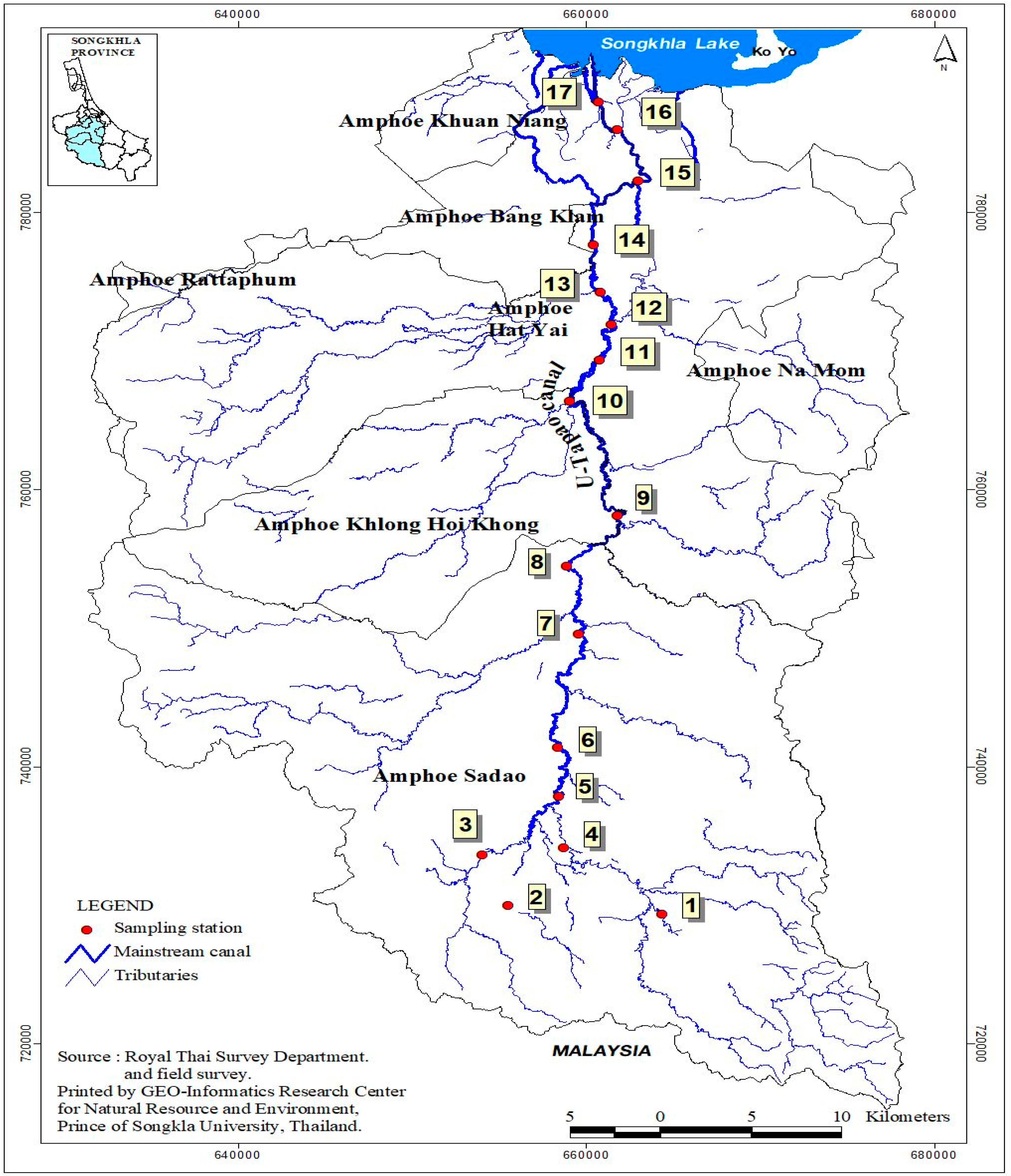
2.1. Study Site and Design
2.2. Chemicals and Material
2.3. Pretreatment in Sediments
2.4. Instrumental Analysis by GC-MS
2.5. Quality Control and Quality Assurance
2.6. Ecological Risk Assessment of PAEs in Sediments
2.6.1. Sediment Quality Guidelines (SQGs)
2.6.2. Risk Quotient Method
2.7. Analysis of Sediment Organic Matter
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Environmental Concentration of PAEs in Sediments
3.2. Correlation between the OM and pH of Sediments and PAEs Concentration
3.3. Comparison with Other Studies in the World
3.4. The Potential Ecological Risk of PAEs on Benthic Organisms
3.5. The Potential Ecological Risks of Individual PAEs to Algae, Crustacean and Fish
3.6. Mixture of Ecological Risks of PAEs by SQGs and RQ Methods
3.7. General Comparison among SQGs Approach and Assessment of the Toxicity Induced by PAEs
3.8. Uncertainty Analysis of Deterministic Risk Assessment by SQGs and RQ Approaches
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wormuth, M.; Scheringer, M.; Vollenweider, M.; Hungerbühler, K. What are the sources of exposure to eight frequently used phthalic acid esters in Europeans? Risk Anal. 2006, 26, 803–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Net, S.; Sempéré, R.; Delmont, A.; Paluselli, A.; Ouddane, B. Occurrence, fate, behavior and ecotoxicological state of phthalates in different environmental matrices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4019–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Wen, Z. A critical review of their occurrence, biodegradation, and removal during wastewater treatment processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, Y.; Ueda, K.; Kojima, N. Potential Risks of Phthalate Esters: Acquisition of Endocrine-disrupting Activity during Environmental and Metabolic Processing. J. Health Sci. 2011, 57, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Mao, W.; Shen, Y.; Feng, W.; Mao, G.; Zhao, T.; Yang, L.; Yang, L.; Meng, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Distribution, source, and environmental risk assessment of phthalate esters (PAEs) in water, suspended particulate matter, and sediment of a typical Yangtze River Delta City, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 24609–24619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staples, C.A.; Adams, W.J.; Parkerton, T.F.; Gorsuch, J.W.; Biddinger, G.R.; Reinert, K.H. Environmental Toxicology Review Aquatic toxicity of eighteen phthalate esters. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1997, 16, 875–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, G.F. A review of chemical-based sediment quality assessment methodologies for the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarazona, J.V.; Versonnen, B.; Janssen, C.; De Laender, F.; Vangheluwe, M.; Knight, D. Principles for Environmental Risk Assessment of the Sediment Compartment. In Proceedings of the Topical Scientific Workshop, Helsinki, Finland, 7–8 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Heyden, C.J.; New, M.G. Sediment chemistry: A history of mine contaminant remediation and an assessment of processes and pollution potential. J. Geochem. Explor. 2004, 82, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, A.; Liu, W.; Cheng, W. Occurrence of phthalate esters in sediments in Qiantang River, China and inference with urbanization and river flow regime. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 248, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Bo, L.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; Chen, G.; Christie, P.; Tenga, Y. Occurrence of phthalate esters in river sediments in areas with different land use patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 500, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfaeinia, H.; Fazlzadeh, M.; Taghizadeh, F.; Saeedi, R.; Spitz, J.; Dobaradaran, S. Phthalate acid esters (PAEs) accumulation in coastal sediments from regions with different land use configuration along the Persian Gulf. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramzi, A.; Gireeshkumar, T.R.; Rahman, K.H.; Manu, M.; Balachandran, K.K.; Chacko, J.; Chandramohanakumar, N. Distribution and contamination status of phthalic acid esters in the sediments of a tropical monsoonal estuary, Cochin—India. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cui, H.; Zeng, H.; Chen, H.; Cheng, Y.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, F.; Ouyang, G.; et al. Occurrence and distribution of phthalate esters in riverine sediments from the Pearl River Delta region, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brils, J. Sediment monitoring and the European Water Framework Directive. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2008, 44, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sirivithayapakorn, S.; Thuyviang, K. Dispersion and Ecological Risk Assessment of Di (2-Ethyl hexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) in the Surface Waters of Thailand. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malem, F.; Soonthondecha, P.; Khawmodjod, P.; Chunhakorn, V.; Whitlow, H.J.; Chienthavorn, O. Occurrence of phthalate esters in the eastern coast of Thailand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirinawin, W.; Sompongchaiyakul, P. Nondetrital and total metal distribution in core sediments. Mar. Chem. 2005, 94, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali, S.; Techato, K.; Yuangyai, C. Effects of Industrial Waste Disposal on the Surface Water Quality of U-tapao River, Thailand. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Environmental Science Engineering IPCBEE, Bangkok, Thailand, 24 March 2012; Volume 3, pp. 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley, O.; Witthayawirasak, B. Occurrence, ecological and health risk of phthalate esters in surface water of U-Tapao canal. Toxics 2020, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Technical Guidance Document in Support of Commission Directive 93/67/EEC on Risk Assessment for New Notified Substances and Commission Regulation (EC) No. 1488/94 on Risk Assessment for Existing Substance; Part II; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Liang, J.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, N.; Duan, H. Occurrence, spatial distribution, historical trend and ecological risk of phthalate esters in the Jiulong River, Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Tao, S.; Dawson, R.W.; Xu, F.L. Characterizing and comparing risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a Tianjin wastewater-irrigated area. Environ. Res. 2002, 90, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Chen, C.F.; Dong, C.D. Distribution of Phthalate Esters in Sediments of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Soil Sediment Contam. 2013, 22, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.M.; Mann, G.S. Sediment Quality Values (SQVs) and Ecological Risk Assessment (ERA). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1999, 38, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brien, G.O.; Behnke, H.F.; Poulson, H.D.; Ela, J.P.; Willett, S.D.; Hassett, S. Consensus-Based Sediment Quality Guidelines; Recommendations for Use and Application Interim Guidance; Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources: Madison, WI, USA, 2003; Volume 9, p. 722. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, H.W.; Batley, G.E.; Wenning, R.J.; Zhu, L.; Vangheluwe, M.; Lee, S. Sediment quality guidelines: Challenges and opportunities for improving sediment management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, D.D.; Carr, R.S.; Calder, F.D.; Long, E.R.; Ingersoll, C.G. Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters. Ecotoxicology 1996, 5, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, J.L.; MacDonald, D.D.; Ingersol, C.G.; Smorong, D.E.; Lindskoog, R.A.; Severn, C.G.; Berger, T.A.; Field, L.J. Development of a Framework for Evaluating Numerical Sediment Quality Targets and Sediment Contamination in the St. Louis River Area of Concern; Final Report; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Van Wezel, A.P.; Van Vlaardingen, P.; Posthumus, R.; Crommentuijn, G.H.; Sijm, D.T. Environmental Risk Limits for Two Phthalates, with Special Emphasis on Endocrine Disruptive Properties. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2000, 46, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, E.; Posthumus, R.; Wezel, A. Ecotoxicological Serious Risk Concentrations for Soil, Sediment and (Ground) Water: Updated Proposals for First Series of Compounds; Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu RIVM: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Liu, R.; Gao, H.; Tan, R.; Zeng, P.; Song, Y. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of phthalic acid esters and phenols in surface sediment from urban rivers in Northeast China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, M.; Wang, D.; Qi, H.; Shen, L.; Sverko, E.; Reiner, E.J.; Li, Y. Concentration and Bioaccumulation of Dechlorane Compounds in Coastal Environment of Northern China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2613–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.F.; Chen, C.W.; Ju, Y.R.; Dong, C.D. Determination and assessment of phthalate esters content in sediments from Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clara, M.; Windhofer, G.; Hart, W.; Braun, K.; Simon, M.; Gans, O.; Scheffknecht, C.; Chovane, A. Occurrence of phthalates in surface runoff, untreated and treated wastewater and fate during wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.; Xia, X.; Yang, Z.; Huang, G.H. Distribution of PAEs in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 124, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniyi, A.A.; Okedeyi, O.O.; Yusuf, K.A. Flame ionization gas chromatographic determination of phthalate esters in water, surface sediments and fish species in the Ogun river catchments, Ketu, Lagos, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 172, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirivithayapakorn, S.; Limtrakul, S. Distribution coefficient and adsorption-desorption rates of di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) onto and from the surface of suspended particles in fresh water. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2008, 190, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liang, J.; Duan, H.; Gong, Z. Spatial distribution and seasonal variation of phthalate esters in the Jiulong River estuary, Southeast China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.C.C.; Wang, C.; Chiu, Y. Occurrence and distribution of phthalate esters and pharmaceuticals in Taiwan river sediments. J. Soil Sediment. 2015, 15, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackintosh, C.E.; Maldonado, J.A.; Ikonomou, M.G.; Gobas, F.A. Sorption of phthalate esters and PCBs in a marine ecosystem. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3481–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Zhang, H.H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.W.; Yang, G.P. Occurrence, distribution, and ecological risks of phthalate esters in the seawater and sediment of Changjiang River Estuary and its adjacent area. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, Q.; Jia, J.; Wen, X. Heavy metals in wetland soils along a wetland-formingchronosequence in the Yellow River Delta of China: Levels, sourcesand toxic risks. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hu, J.; Chen, J.; Fan, Y.S.; Xing, B.; Tao, S. Distribution of persistent toxic substances in benthic bivalves from the inshore areas of the yellow sea. Environ. Toxic. Chem. 2008, 27, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, P.; Thur, A.; Gahnstr, G. Phthalate Esters Inhibit Microbial Activity in Aquatic Sediments. Environ. Pollut. 1986, 42, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.C.; Souza, A.O.; Bernardes, M.F.F.; Pazin, M.; Tasso, J.; Pereira, P.H.; Dorta, D.J. A perspective on the potential risks of emerging contaminants to human and environmental health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 13800–13823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; An, T.; Li, G.; Qiao, M.; Wei, D. Distribution, possible sources, and health risk assessment of SVOC pollution in small streams in Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 10083–10095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, E.R.; Ingersoll, C.G.; MacDonald, D.D. Calculation and Uses of Mean Sediment Quality Guideline Quotients: A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1726–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustavsson, B.M.; Magnér, J.; Carney Almroth, B.; Eriksson, M.K.; Sturve, J.; Backhaus, T. Chemical monitoring of Swedish coastal waters indicates common exceedances of environmental thresholds, both for individual substances as well as their mixtures. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Tan, T.; Lee, S.T.; Cheng, S.H. Toxicity and Estrogenic Endocrine Disrupting Activity of Phthalates and Their Mixtures. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 3156–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yu, G.; Huang, J.; Yu, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, L. Tiered aquatic ecological risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides and their mixture in Jiangsu reach of Huaihe River, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 157, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-gutiérrez, A.; Garnacho, E.; Bayona, J.M.; Albaigés, J. Screening ecological risk assessment of persistent organic pollutants in Mediterranean sea sediments. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binellia, A.; Sarkar, S.K.; Chatterje, M.; Riva, C.; Parolini, M.; Bhattacharya, B.; Bhattacharya, A.K.; Satpathy, K.K. A comparison of sediment quality guidelines for toxicity assessment in the Sunderban wetlands (Bay of Bengal, India). Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuvanich, S.; Thongnoo, K.; Chevakidagarn, P.; Phongdara, A. Evaluation of artificial neural networks for electrical conductivity-based and flow rate-based prediction of the nitrate nitrogen concentration in the u-tapao canal, Hat Yai, Thailand. Environ. Asia 2017, 10, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.S. Ecological risk assessment for aquatic species exposed to contaminants in Keelung River, Taiwan. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 1142–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannenbaum, L.V. A Critical Assessment of the Ecological Risk Assessment Process: A Review of Misapplied Concepts. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2005, 1, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PAEs | Linearity R2 | Target Ion (m/z) | Retention Time (min) | Recovery (%) (100 ng/g) n = 3 | RSD (%) | LOQ n = 7 ng/mL | LOD n = 7 ng/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBP | 0.999 | 223, 205, 167 | 7.57 | 81 | 5.9 | 1.88 | 0.32 |
| BBP | 0.999 | 205, 149, 91 | 8.77 | 83 | 6.2 | 1.78 | 0.12 |
| DEHP | 0.999 | 279, 167, 149 | 9.29 | 93 | 7.2 | 2.98 | 0.45 |
| DnOP | 0.999 | 279, 261, 149 | 9.84 | 89 | 6.8 | 2.34 | 0.42 |
| DiNP | 0.999 | 293, 127 | 9.93 | 105 | 7.6 | 2.76 | 0.84 |
| DIDP | 0.999 | 307, 141 | 10.44 | 90 | 8.4 | 2.82 | 1.04 |
| SITES | Latitude | Longitude | DBP | DEHP | DiNP | OM (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST1 | 6.979739 | 100.463408 | 180 | 620 | 840 | 2.56 |
| ST2 | 6.979740 | 100.463409 | 120 | 680 | 560 | 1.11 |
| ST3 | 7.002145 | 100.455991 | 50 | 580 | 260 | 1.41 |
| ST4 | 6.673192 | 100.433361 | 160 | 750 | 540 | 1.71 |
| ST5 | 6.639564 | 100.436129 | 80 | 290 | 580 | 1.00 |
| ST6 | 6.931202 | 100.439884 | 40 | 550 | 520 | 1.80 |
| ST7 | 6.596520 | 100.486966 | ND | 220 | 380 | 1.20 |
| ST8 | 7.108381 | 100.465011 | ND | 200 | 230 | 1.64 |
| ST9 | 6.705086 | 100.433163 | ND | 560 | ND | 2.86 |
| ST10 | 7.075167 | 100.475782 | 180 | 540 | 660 | 2.53 |
| ST11 | 6.823206 | 100.437958 | 130 | 520 | ND | 4.00 |
| ST12 | 6.779266 | 100.443868 | 90 | 220 | ND | 1.11 |
| ST13 | 6.602124 | 100.406920 | 280 | 890 | 760 | 3.72 |
| ST14 | 6.856377 | 100.464485 | 80 | 510 | 160 | 2.53 |
| ST15 | 7.033356 | 100.452362 | 40 | 190 | 140 | 1.00 |
| ST16 | 6.823206 | 100.437958 | ND | 640 | ND | 4.44 |
| ST17 | 7.126859 | 100.455496 | 60 | 270 | ND | 2.01 |
| Minimum | ND | 190 | ND | 1.00 | ||
| Maximum | 280 | 890 | 840 | 4.44 | ||
| Mean ± SD | 88.82 ± 78 | 484 ± 223 | 333 ± 292 | 2.16 ± 1.09 | ||
| Frequency of Detection | 77% | 100 | 71 | - |
| PAEs. | DBP | DEHP | DiNP | ∑PAEs | OM (%) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBP | 1 | |||||
| DEHP | 0.464 | 1 | ||||
| DiNP | 0.568 * | 0.414 | 1 | |||
| ∑PAEs | 0.675 ** | 0.759 ** | 0.854 ** | 1 | ||
| OM (%) | 0.171 | 0.484 * | −0.127 | 0.246 | 1 | |
| pH | −0.129 | −0.245 | −0.201 | −0.108 | 0.243 | 1 |
| Location | DBP | DEHP | DiNP | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kaoshiung Harbor Taiwan | 0.0–34.6 | 152.6–14,646.6 | 0.00–67,495.9 | [35] |
| False Creek Vancouver, Canada | 9320–63,900 | 7350–136,000 | 14,700–50,400 | [41] |
| Jiulong River Estuary, China | 1.6–92.8 | 4.3–394.7 | ND-110 | [39] |
| Dianbao River, Taiwan | 400–1865 | 494–1947 | 361–1277 | [40] |
| Jiulong River, China | 3.0–230 | 7.00–1160 | ND-470 | [22] |
| ChangJiang River Estuary, China | 340–7080 | 260–8550 | NA | [42] |
| Chao Phraya River, Thailand | NA | <8340–14,500 | NA | [16] |
| Eastern coast of Thailand | ND-800 | ND-16500 | NA | [17] |
| U-Tapao canal, Thailand | ND-280 | 190–890 | ND-840 | Present study |
| Standard Values of SQGs | Levels of DBP and DEHP in Sediments | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAEs | TEL (ng/g) | PEL (ng/g) | NSQGQ | TEC (ng/g) | MEC (ng/g) | PEC (ng/g) | PEC-Q | DBP (ng/g dw) | DEHP (ng/g dw) |
| DBP | NA | NA | NA | 2200 | 9600 | 17,000 | ≥0.25% | Level in sediment ND-230 TEC = 0% MEC = 0% PEC = 0% PEC-Q = 0.002–0.017% | 190–890 TEL = 100% PEL = 0% NSQGQ = 0.51–1.16 TEC = 29% MEC = 6% PEC-Q = 0.17–0.81% |
| DEHP | 182 | 2647 | <0.2<2,>2 | 610 | 855 | 1100 | ≥0.25% | ||
| PAEs | MPC (ng/g at 10% OM) | SRCeco (ng/g at 10% OM) | ERLs (ng/g at 10% OM) | DBP Level in Sediment (ng/g dw at 10% OM) | DEHP Levels in Sediment (ng/g dw at 10% OM) | ∑PAEs Level in Sediments (ng/g dw at 10% OM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBP | 2100 | 36,000 | 700 | 222–1081 MPC = 0% SRCeco = 0% ERLs = 41% sites | ||
| DEHP | 1000 | 10,000 | 1000 | 1219–6126 MPC = 100% sites SRCeco = 0% ERLs = 100% | ||
| ∑PAEs | 1400 | 57,000 | - | 1464–12, 252 MPC = 100% of sites SRCeco = 0% |
| PAEs/RQmix | Aquatic Biota | RQgeomean | RQmax |
|---|---|---|---|
| DBP | Algae | 4.0 × 10−2 | 1.2 × 10−2 |
| Crustacean | 3.0 × 10−2 | 1.0 × 10−1 | |
| Fish | 8.0 × 10−2 | 2.5 × 10−1 | |
| DEHP | Algae | 1.5 × 10−1 | 2.7 × 10−1 |
| Crustacean | 4.0 × 10−2 | 7.0 × 10−2 | |
| Fish | 2.0 × 10−2 | 3.0 × 10−2 | |
| DiNP | Crustacean | 2.0 × 10−2 | 5.0 × 10−3 |
| RQmixAlgae | 1.9 × 10−1 | 3.9 × 10−1 | |
| RQmixCrustacean | 7.0 × 10−2 | 1.8 × 10−1 | |
| RQ mix fish | 1.0 × 10−1 | 2.8 × 10−1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kingsley, O.; Witthayawirasak, B. Deterministic Assessment of the Risk of Phthalate Esters in Sediments of U-Tapao Canal, Southern Thailand. Toxics 2020, 8, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040093
Kingsley O, Witthayawirasak B. Deterministic Assessment of the Risk of Phthalate Esters in Sediments of U-Tapao Canal, Southern Thailand. Toxics. 2020; 8(4):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040093
Chicago/Turabian StyleKingsley, Okpara, and Banchong Witthayawirasak. 2020. "Deterministic Assessment of the Risk of Phthalate Esters in Sediments of U-Tapao Canal, Southern Thailand" Toxics 8, no. 4: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040093
APA StyleKingsley, O., & Witthayawirasak, B. (2020). Deterministic Assessment of the Risk of Phthalate Esters in Sediments of U-Tapao Canal, Southern Thailand. Toxics, 8(4), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8040093





