The Investigation of Unexpected Arsenic Compounds Observed in Routine Biological Monitoring Urinary Speciation Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Standards and Reagents
2.2. Instrumentation
2.2.1. Species Identification by µLC-ICP-MS
2.2.2. Species Identification by ESI-QqTOF-MS/MS
2.3. Sample Collection
3. Results
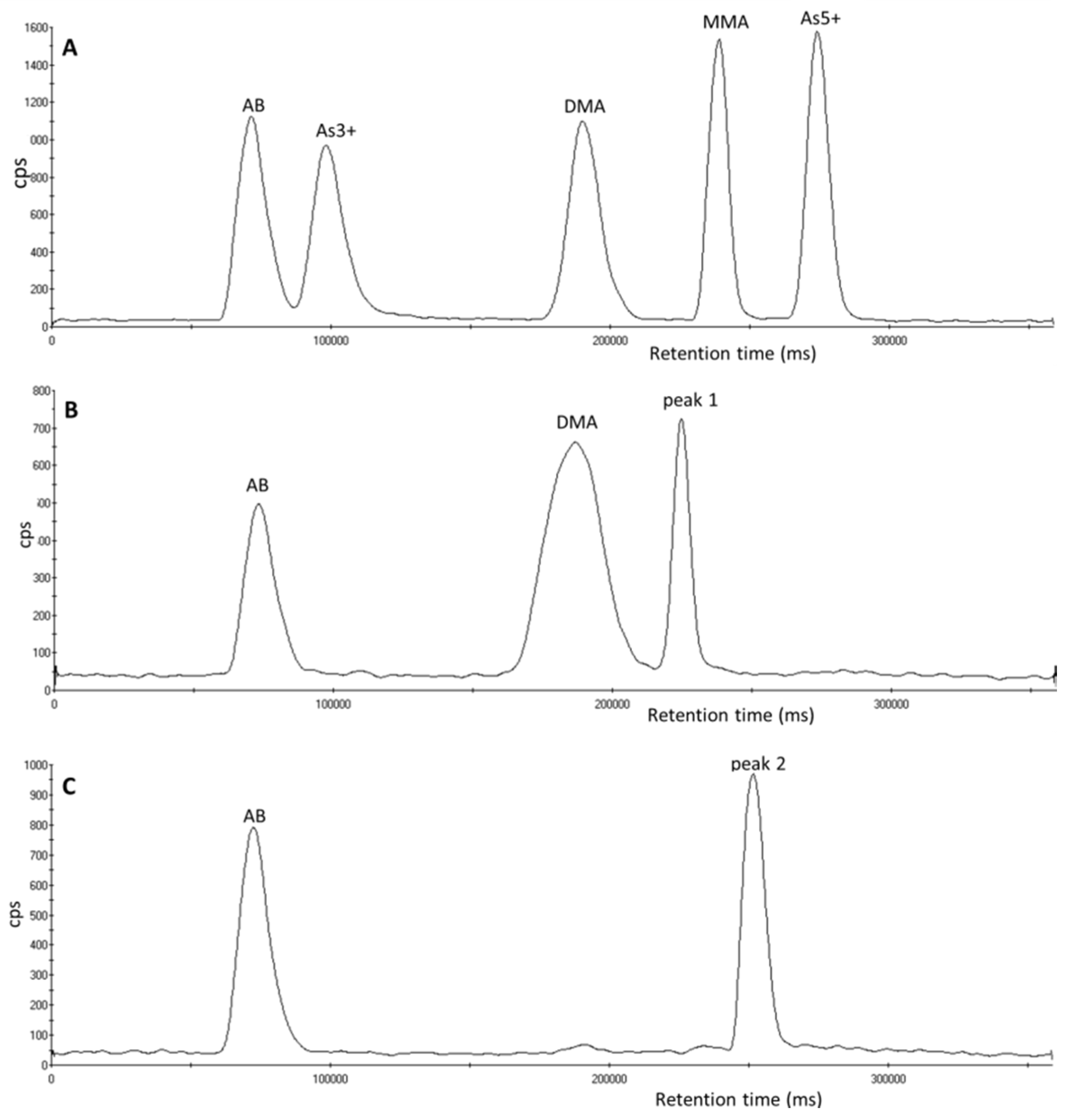
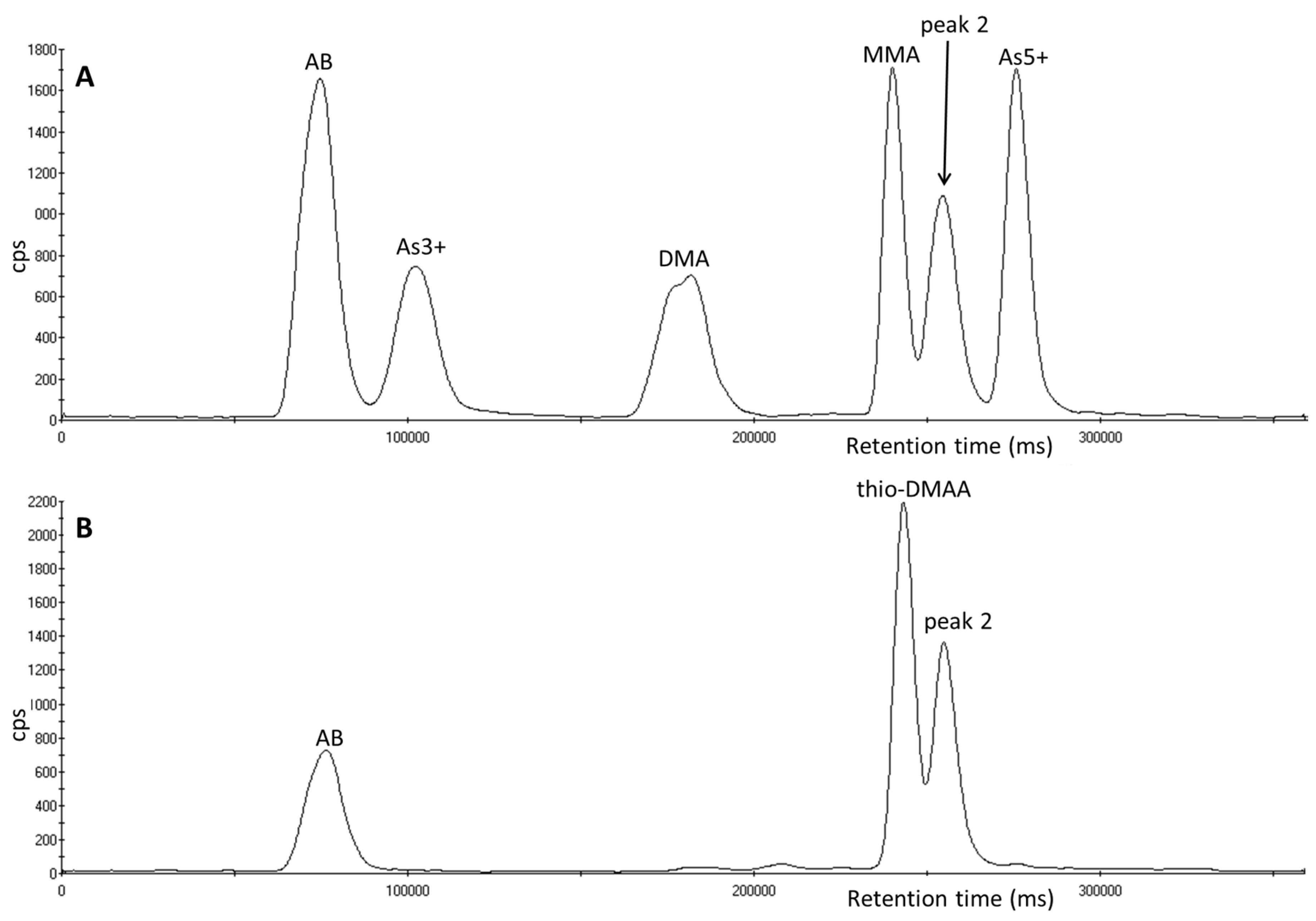
3.1. Identification of Unexpected Arsenic Peaks by µLC-ICP-MS
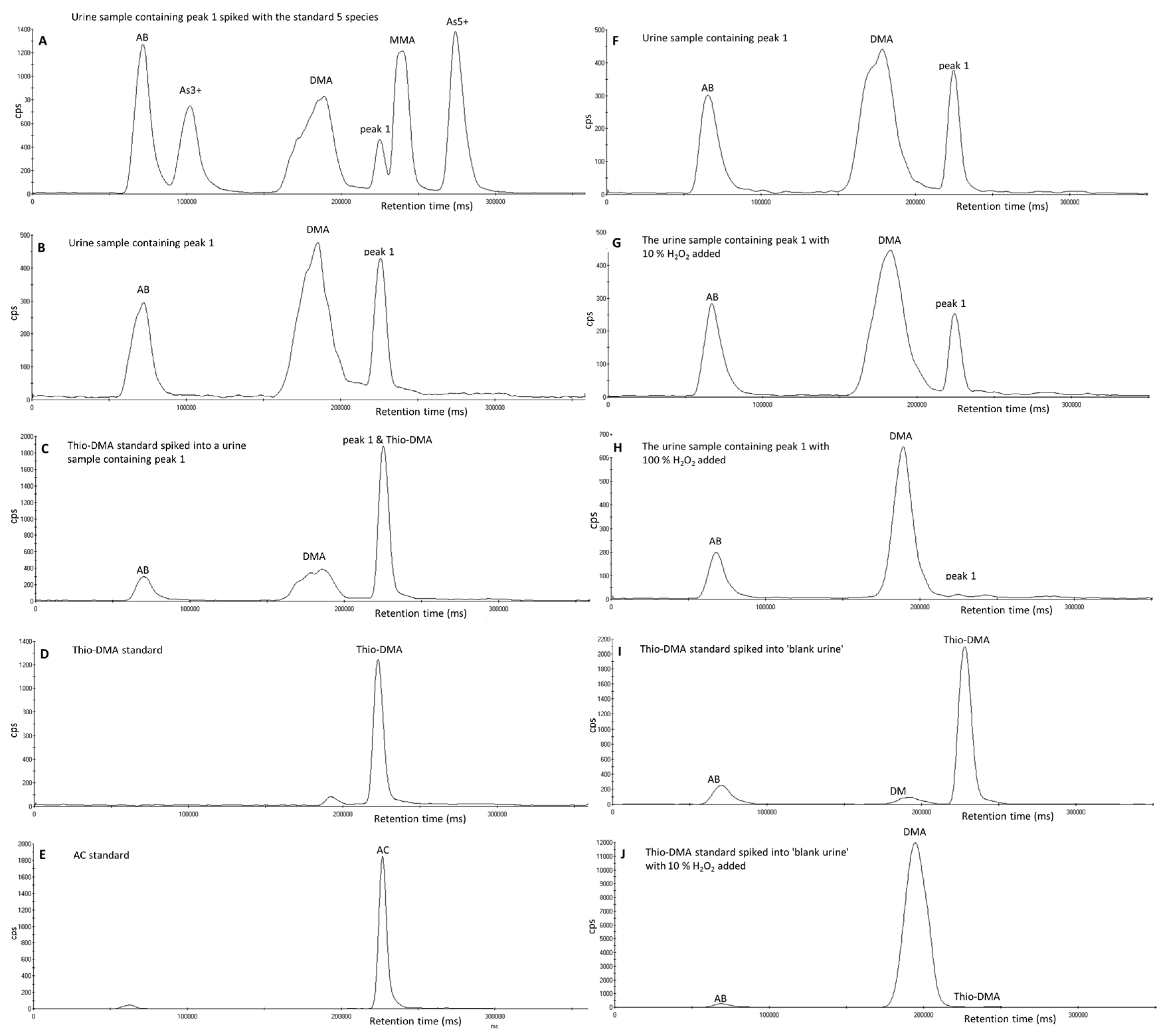
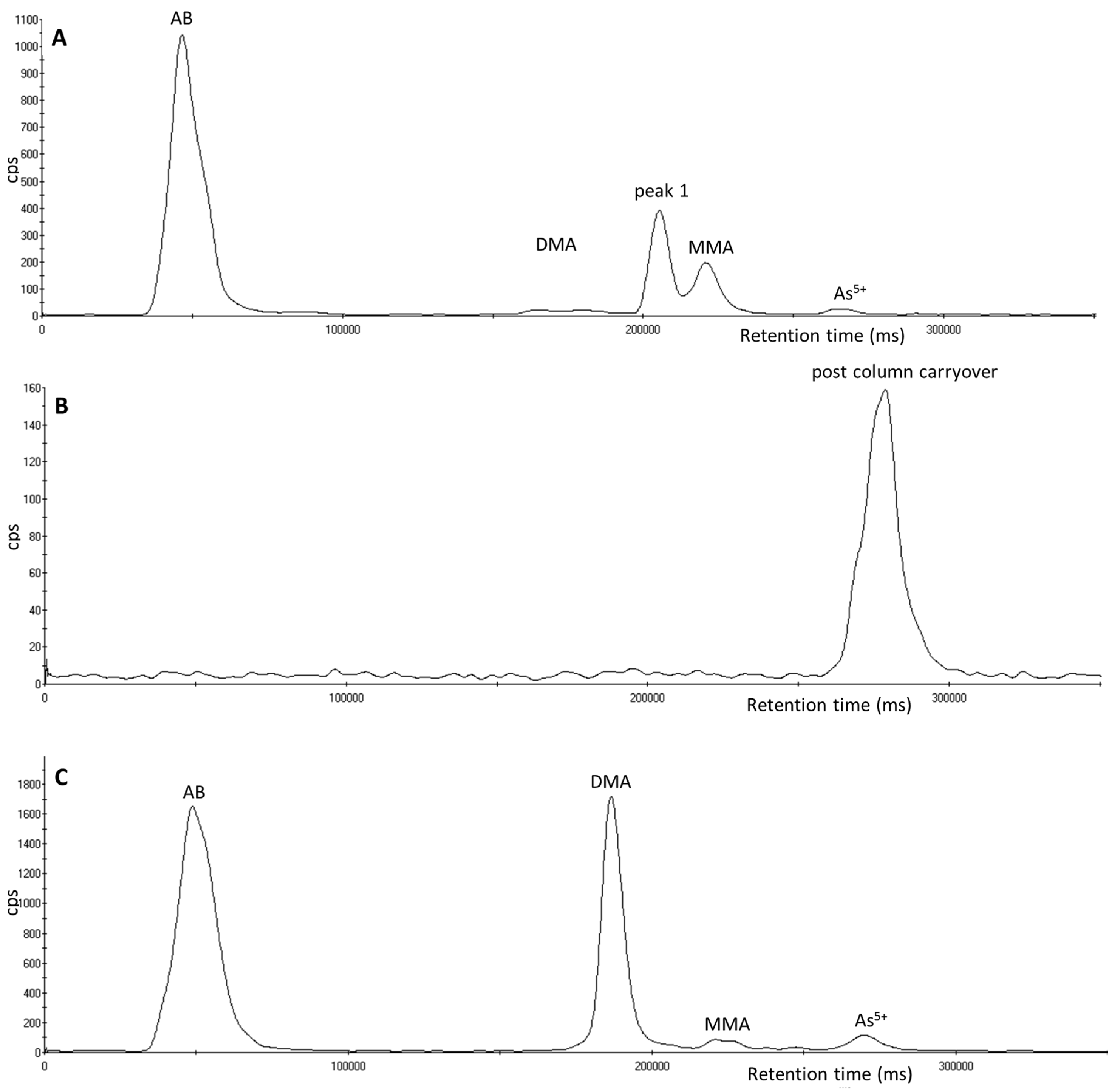
3.2. Investigation of Peak 1 by µLC-ICP-MS
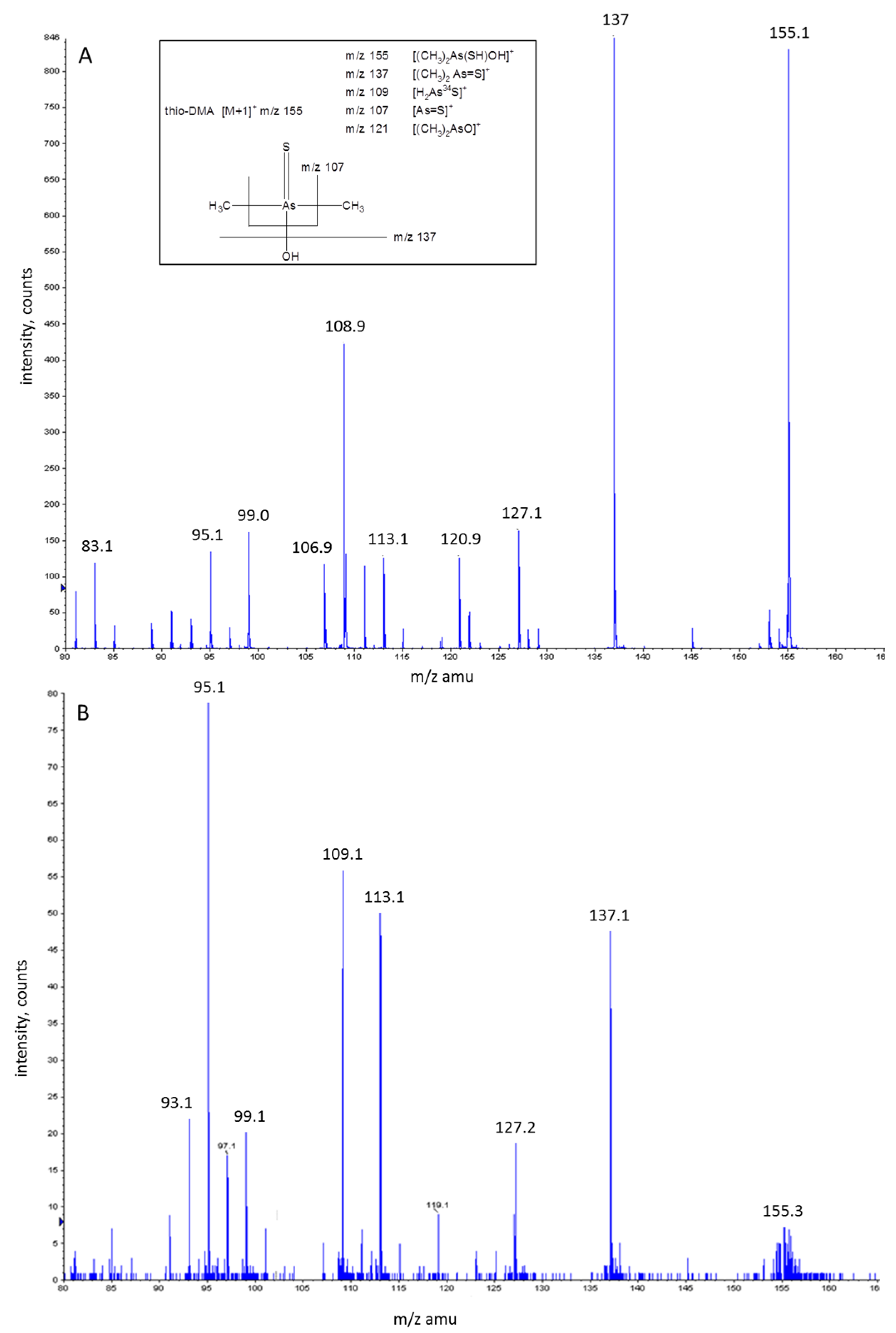
3.3. Investigation of Peak 1 by ESI-QqTOF-MS/MS
3.4. Investigation of Peak 2 by µLC-ICP-MS
3.5. Investigation of Peak 2 by ESI-QqTOF-MS/MS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rehman, K.; Naranmandura, H. Arsenic metabolism and thioarsenicals. Metallomics 2012, 4, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Cui, X.; Hirano, S. A new metabolic pathway of arsenite: Arsenic-glutathione complexes are substrates for human arsenic methyltransferase Cyt19. Arch. Toxicol. 2005, 79, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranmandura, H.; Suzuki, N.; Suzuki, K.T. Trivalent arsenicals are bound to proteins during reductive methylation. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2006, 19, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Song, X.; Geng, Z.; Hu, X.; Wang, Z. Rapid equilibrium kinetiv analysis of arsenite methylation catalysed by recombinant human arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase (hAS3MT). J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 38790–38799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challenger, F. Biological methylation. Chem. Rev. 1945, 36, 315–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobna, Z.; Naranmandura, H.; Kubachka, K.M.; Edwards, B.C.; Herbin-Davis, K.; Styblo, M.; Le, X.C.; Creed, J.T.; Maeda, N.; Hughes, M.F.; et al. Disruption of the arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase gene in the mouse alters the phenotype for methylation of arsenic and affects distribution and retention of orally administered arsenate. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 1713–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, M.F.; Edwards, B.C.; Herbin-Davis, K.M.; Saunders, J.; Styblo, M.; Thomas, D.J. Arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase genotype affects steady-state distribution and clearance of arsenic in arsenic-treated mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 249, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dopp, E.; Kligerman, A.D.; Diaz-Bone, R.A. Organoarsenicals. Uptake, metabolism and toxicity. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2010, 7, 231–265. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roy, P.; Saha, A. Metabolsim and toxicity of arsenic: A human carcinogen. Curr. Sci. 2002, 82, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, S.M.; Arnold, L.L. Methylated arsenicals: The implications of metabolism and carcinogenicity studies in rodents to human risk assessment. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2006, 36, 99–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drobna, Z.; Walton, F.S.; Paul, D.S.; Xing, W.; Thomas, D.J.; Stýblo, M. Metabolism of arsenic in human liver: The role of membrane transporters. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Waalkes, M.P. Liver is a target of arsenic carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 105, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.X.; Williams, P.N.; Zhu, Y.G.; Deacon, C.; Carey, A.M.; Raab, A.; Feldmann, J.; Meharg, A.A. Survey of arsenic and its speciation in rice products such as breakfast cereals, rice crackers and Japanese rice condiments. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Williams, P.N.; Meharg, A.A. Exposure to inorganic arsenic from rice: A global health issue? Environ. Pollut. 2008, 154, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francesconi, K.A.; Tanggaar, R.; McKenzie, C.J.; Goessler, W. Arsenic metabolites in human urine after ingestion of an arsenosugar. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Niegel, C.; Matysik, F.M. Analytical methods for the determination of arsenosugars—A review of recent trends and developments. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 11, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich-Ramm, R.; Mindt-Prufert, S.; Szadkowski, D. Arsenic species excretion after controlled seafood consumption. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 778, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, K.A. Arsenic species in seafood: Origin and human health implications. Pure Appl. Chem. 2010, 82, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, J.; Krupp, E.M. Critical review or scientific opinion paper: Arsenosugars—A class of benign arsenic species or justification for developing partly speciated arsenic fractionation in foodstuffs? Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 1735–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.J. The chemistry and metabolism of arsenic. In Arsenic: Exposure Sources, Health Risks, and Mechanisms of Toxicity; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 81–109. [Google Scholar]
- Pinyayev, T.S.; Kohan, M.J.; Herbin-Davis, K.; Creed, J.T.; Thomas, D.J. Preabsorptive metabolism of sodium arsenate by anaerobic microbiota of mouse cecum forms a variety of methylated and thiolated arsenicals. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranmandura, H.; Suzuki, N.; Suzuki, K.T. Reaction mechanism underlying the in vitro transformation of thioarsenicals. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 231, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranmandura, H.; Carew, M.W.; Xu, S.; Lee, J.; Leslie, E.M.; Weinfeld, M.; Le, X.C. Comparative toxicity of arsenic metabolites in human bladder cancer EJ-1 cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1586–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranmandura, H.; Suzuki, N.; Iwata, K.; Hirano, S.; Suzuki, K.T. Arsenic metabolism and thioarsenicals in hamsters and rats. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2007, 20, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranmandura, H.; Iwata, K.; Suzuki, K.T.; Ogra, Y. Distribution and metabolism of four different dimethylated arsenicals in hamsters. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 15, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, H.R.; Pickford, R.; Thomas-Oates, J.; Jaspars, M.; Feldmann, J. 2-Dimethylarsinothioyl acetic acid identified in a biological sample: The first occurrence of a mammalian arsinothioyl metabolite. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raml, R.; Goessler, W.; Traar, P.; Ochi, T.; Francesconi, A.K. Novel thioarsenic metabolites in human urine after ingestion of an arsenosugar, 2′,3′-dihydroxypropyl 5-deoxy-5-dimethylarsinoyl-beta-D-riboside. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raml, R.; Raber, G.; Rumpler, A.; Bauernhofer, T.; Goessler, W.; Francesconi, K.A. Individual variability in the human metabolism of an arsenic containing carbohydrate, 2′,3′-dihydroxypropyl 5-deoxy-5-dimethylarsinoyl-beta-D-riboside, a naturally occurring arsenical in seafood. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 1534–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, B.K.; Suzuki, K.T.; Anzai, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sei, Y. A SEC-HPLC-ICP MS hyphenated technique for identification of sulphur containing arsenic metabolites in biological samples. J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2008, 874, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raml, R.; Goessler, W.; Francesconi, K.A. Improved chromatographic separation of thio-arsenic compounds by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1128, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raml, R.; Rumpler, A.; Goessler, W.; Vahter, M.; Li, L.; Ochi, T.; Francesconi, K.A. Thio-dimethylarsinate is a common metabolite in urine samples from arsenic-exposed women in Bangladesh. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 222, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leffers, L.; Ebert, F.; Taleshi, M.S.; Francesconi, K.A.; Schwerdtle, T. In vitro toxicological characterization of two arsenosugars and their metabolites. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Kuroda, K.; Zhou, X.; Inoue, Y.; Date, Y.; Wanibuchi, H.; Fukushima, S.; Endo, G. Urinary sulphur containing metabolite produced by intestinal bacteria following oral administration of dimethylarsinic acid to rats. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2003, 16, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, K.; Yoshida, K.; Yoshimura, M.; Endo, Y.; Wanibuchi, H.; Fukushima, S.; Endo, G. Microbial metabolite of dimethylarsinic acid is highly toxic and genotoxic. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 198, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranmandura, H.; Ogra, Y.; Iwata, K.; Lee, J.; Suzuki, K.T.; Weinfeld, M.; Le, X.C. Evidence for toxicity differences between inorganic arsenite and thioarsenicals in human bladder cancer cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, F.; Leffers, L.; Weber, T.; Berndt, S.; Mangerich, A.; Beneke, S.; Burkle, A.; Schwerdtle, T. Toxicological properties of the thiolated inorganic arsenic and arsenosugar metabolite thio-dimethylarsinic acid in human bladder cells. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2014, 28, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leffers, L.; Unterberg, M.; Bartel, M.; Hoppe, C.; Pieper, I.; Stertmann, J.; Ebert, F.; Humpf, H.U.; Schwerdtle, T. In vitro toxicological characterisation of the S-containing arsenic metabolites thio-dimethylarsinic acid and dimethylarsinic glutathione. Toxicology 2013, 305, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, M.; Ebert, F.; Leffers, L.; Karst, U.; Schwerdtle, T. Toxicological characterization of the inorganic and organic arsenic metabolite Thio-DMA in cultured human lung cells. J. Toxicol. 2011, 2011, 373141. [Google Scholar]
- Unterberg, M.; Leffers, L.; Hubner, F.; Humpf, H.U.; Lepikhov, K.; Walter, J.; Ebert, F.; Schwerdtle, T. Toxicity of arsenite and thio-DMA(V) after long-term (21 days) incubation of human urothelial cells: Cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and epigenetics. Toxicol. Res. 2014, 3, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.S.; Le, X.C. Effect of arsenosugar ingestion on urinary arsenic speciation. Clin. Chem. 1998, 44, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Molin, M.; Ydersbond, T.A.; Ulven, S.M.; Holck, M.; Dahl, L.; Sloth, J.J.; Fliegel, D.; Goessler, W.; Alexander, J.; Meltzer, H.M. Major and minor arsenic compounds accouting for the total urinary excretion of arsenic following intake of blue mussels (Mytilus edulis): A controlled human study. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 2462–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmeisser, E.; Goessler, W.; Francesconi, A.K. Human metabolism of arsenolipids present in cod liver. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HSE. Biological Monitoring in the Workplace: A Guide to its Practical Application to Chemical Exposure; HSG 167; HSE Books, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Leese, E.; Morton, J.; Tan, E.; Gardiner, P.H.; Carolan, V.A. µLC-ICP-MS determinations of unexposed UK urinary arsenic speciation reference values. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2014, 38, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Conference of Government Industrial Hygienists. TLVs and BEIs: Threshold Limit Values for Chemical Substances and Physical Agents & Biological Exposure Indices; ACGIH Signature Publications: USA, 2016.
- Suzuki, K.T.; Katagiri, A.; Sakuma, Y.; Ogra, Y.; Ohmichi, M. Distributions and chemical forms of arsenic after intravenous administration of dimethylarsinic and monomethylarsonic acid to rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 198, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricke, M.; Zeller, M.; Cullen, W.; Witkowski, M.; Creed, J. Dimethylthioarsinic anhydride: A standard for arsenic speciation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 583, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Thomas, D.J.; Naranmandura, H. Importance of being thiomethylated: Formation, fate, and effects of methylated thioarsenicals. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conklin, S.D.; Fricke, M.W.; Creed, P.A.; Creed, J.T. Investigation of the pH effects on the formation of methylated thio-arsenicals, and the effects of pH and temperature on their stability. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2008, 23, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, K.A.; Edmonds, J.S. Arsenic and marine organisms. Adv. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 44, 147–189. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, H.R.; Raab, A.; Jaspars, M.; Milne, B.F.; Feldmann, J. Sulfur containing arsenical mistaken for dimethylarsinous acid [DMA(III)] and identified as a natural metabolite in urine: Major implications for studies on arsenic metabolism and toxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2004, 17, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerman, A.H.; Creed, P.A.; Parks, A.N.; Fricke, M.W.; Schwegel, C.A.; Creed, J.T.; Heitkemper, D.T.; Vela, N.P. Comparison of a chemical and enzymatic extraction of arsenic from rice and an assessment of the arsenic absorption from contaminated water by cooked rice. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5241–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, X.C.; Cullen, W.R.; Reimer, K.J. Human urinary arsenic excretion after one-time ingestion of seaweed, crab, and shrimp. Clin. Chem. 1994, 40, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.T.; Mandal, B.K.; Katagiri, A.; Sakuma, Y.; Kawakami, A.; Ogra, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sei, Y.; Yamanaka, K.; Anzai, K.; et al. Dimethylthioarsenicals as arsenic metabolites and their chemical preparations. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2004, 17, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubachka, K.M.; Kohan, M.C.; Herbin-Davis, K.; Creed, J.T.; Thomas, D.J. Exploring the in vitro formation of trimethylarsine sulfide from dimethylthioarsinic acid in anaerobic microflora of mouse cecum using HPLC-ICP-MS and HPLC-ESI-MS. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 239, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leese, E.; Clench, M.; Morton, J.; Gardiner, P.H.E.; Carolan, V.A. The Investigation of Unexpected Arsenic Compounds Observed in Routine Biological Monitoring Urinary Speciation Analysis. Toxics 2017, 5, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics5020012
Leese E, Clench M, Morton J, Gardiner PHE, Carolan VA. The Investigation of Unexpected Arsenic Compounds Observed in Routine Biological Monitoring Urinary Speciation Analysis. Toxics. 2017; 5(2):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics5020012
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeese, Elizabeth, Malcolm Clench, Jackie Morton, Philip H.E. Gardiner, and Vikki A. Carolan. 2017. "The Investigation of Unexpected Arsenic Compounds Observed in Routine Biological Monitoring Urinary Speciation Analysis" Toxics 5, no. 2: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics5020012
APA StyleLeese, E., Clench, M., Morton, J., Gardiner, P. H. E., & Carolan, V. A. (2017). The Investigation of Unexpected Arsenic Compounds Observed in Routine Biological Monitoring Urinary Speciation Analysis. Toxics, 5(2), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics5020012






