From Exposure to Dysfunction: The Intestinal Toxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. PFAS: Relevant Chemical and Physical Characteristics
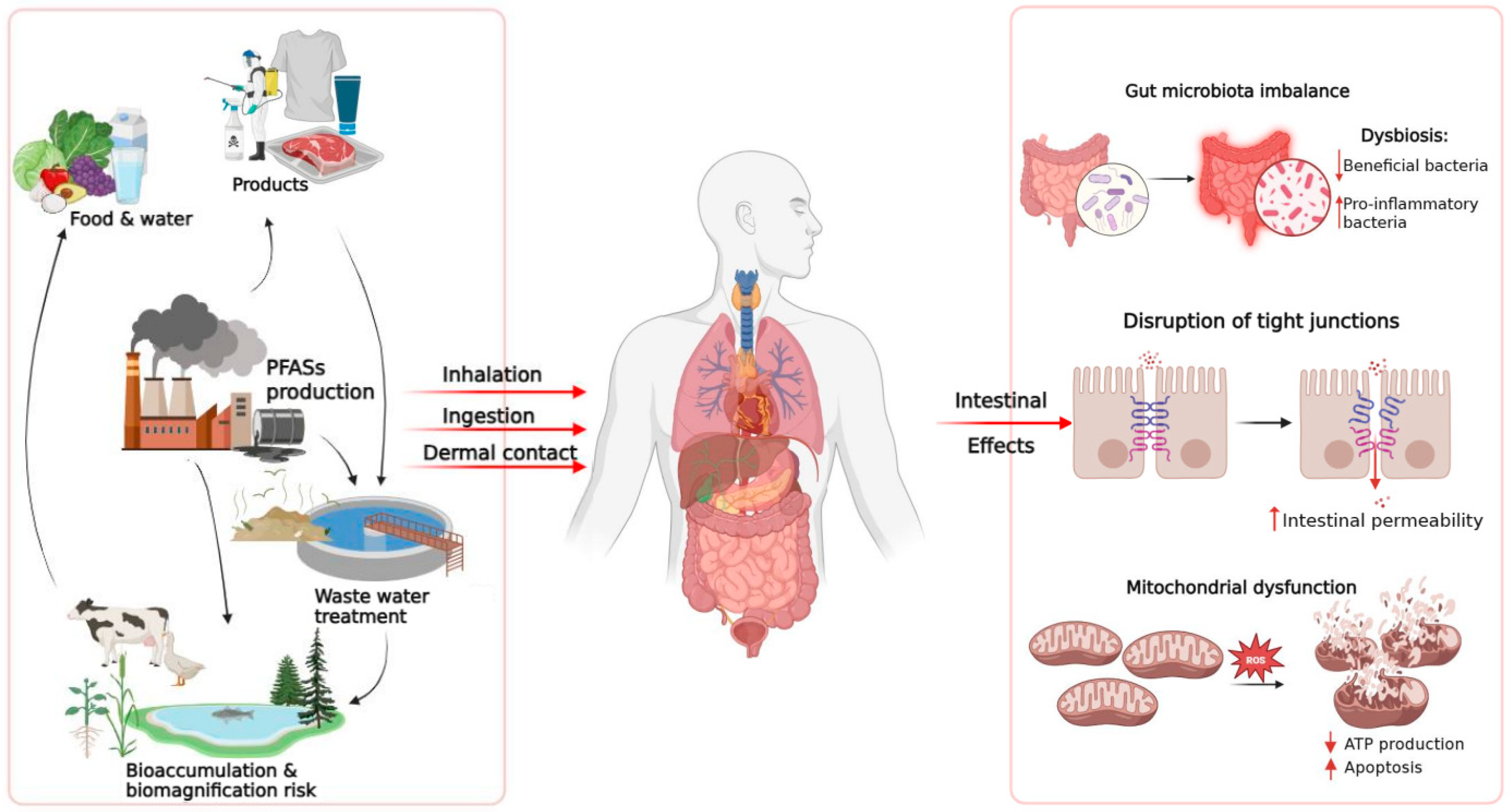
3. Human Exposure to PFAS
3.1. Human Bioaccumulation Insights
3.2. Environmental Exposure and Animal Studies
3.3. PFAS Combinations as a Critical Aspect of Environmental Toxicology
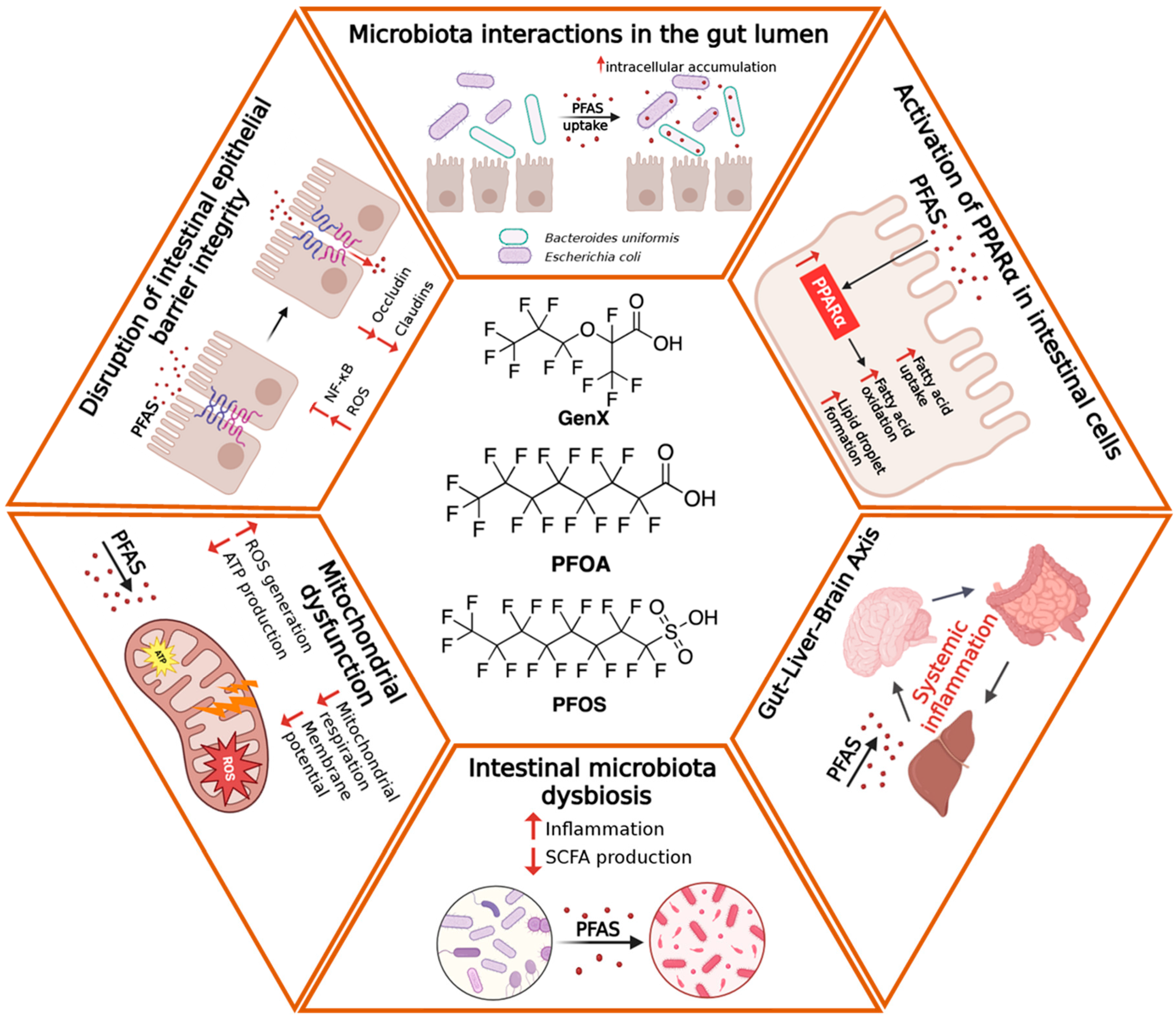
4. Effects of PFAS on the Intestinal Barrier
4.1. Structural Damage and Molecular Alterations
4.2. Activation of the Inflammatory Response
4.3. Functional Alterations and Effects on Epithelial Metabolism
5. Effects of PFAS on the Gut Microbiota
5.1. Compositional Alterations of the Gut Microbiota
5.2. Microbiota–Host Metabolic Interactions and Associated Diseases
5.3. Evidence from Alternative Model Organisms
6. Clinical and Epidemiological Evidence
Developing Strategies for the Treatment of PFAS-Induced Intestinal Damage
7. Conclusions
Future Directions
- Clarify mechanistic pathways: determine how variations in fluorinated chain length and terminal functional groups influence epithelial absorption, immune activation, and metabolic reprogramming, using well-established integrative in vitro and in vivo systems as well as novel intestinal organoids and gut-on-chip platforms.
- Assess realistic exposure scenarios: examine chronic, low-dose, and mixture exposures representative of environmental and dietary conditions encountered in human populations.
- Define microbiota-mediated mechanisms: apply integrative multi-omics (metagenomics, metabolomics, transcriptomics) to dissect how PFAS-induced dysbiosis drives intestinal inflammation and barrier dysfunction.
- Strengthen translational research: develop prospective human cohorts correlating PFAS exposure biomarkers with intestinal permeability, immune, and metabolic parameters, while standardizing analytical workflows for PFAS quantification in biological samples.
- Explore mitigation strategies: investigate nutritional, probiotic, and pharmacological interventions aimed at restoring microbial diversity and reinforcing epithelial barrier integrity under chronic PFAS exposure.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAA | Aromatic amino acids |
| AIM2 | Absent in melanoma 2 |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| BCAA | Branched-chain amino acids |
| BMD | Benchmark dose |
| EFSA | European Food Safety Authority |
| EPA | Environmental Protection Agency |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GenX | Perfluorohexanoic acid |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel diseases |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| miRNAs | microRNAs |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NLRP | NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein |
| NOAEL | No Observed Adverse Effect Level |
| PFBA | Perfluorobutanoic acid |
| PFAS | Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl substances |
| PFBS | Perfluorobutane sulfonic acid |
| PFOA | Perfluorooctanoic acid |
| PFOS | Perfluorooctane sulfonate |
| PPARα | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acids |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| Tjp | Tight junction protein |
References
- Li, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Deji, Z.; Xing, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, X.; Huang, Z. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Exposure and Its Influence on the Intestinal Barrier: An Overview on the Advances. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; He, H.; Han, T.; Wang, B.; Ji, P.; Wu, X.; Qian, J.; Shao, P. Environmental Explanation of Prostate Cancer Progression Based on the Comprehensive Analysis of Perfluorinated Compounds. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 263, 115267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.K.; Lai, M.Q.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zhong, M.T.; Zhang, J.J.; Chen, Y.Q.; Guo, X.F.; Wang, Q.; Xie, X.L. Inulin Alleviates Intestinal Changes Caused by Gestational PFOA and GenX Exposure in the Offspring of Mice through Reshaping Maternal Gut Microbiota and Vertically Inhibiting the TLR4/NF-ΚB/NLRP3 Inflammatory Pathway in the Pups. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 382, 126749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabal, E.; Azaizeh, M.; Baloni, P. Investigating Lipid and Energy Dyshomeostasis Induced by Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Congeners in Mouse Model Using Systems Biology Approaches. Metabolites 2025, 15, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, G.; Zhang, R.; Feng, L.; Zhang, J. Early Life Exposure to Low-Dose Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Disturbs Gut Barrier Homeostasis and Increases the Risk of Intestinal Inflammation in Offspring. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 329, 121708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Ahmad, S.; Irudayaraj, J.M.K. Effect of Perfluorooctanoic Acid on the Epigenetic and Tight Junction Genes of the Mouse Intestine. Toxics 2020, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; He, L.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z.; Cai, D.; Wang, Y.; Mo, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z.; et al. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Mixture Impairs Intestinal Barrier Function through Microbiota-Derived 21-Deoxycortisol and Cortisol Metabolism Dysregulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Midya, V.; Maroli, A.; Magee, J.; Petrick, L.; Colombel, J.F.; Valvi, D.; Ungaro, R.C.; Dolios, G.; Petralia, F.; et al. Per- and Poly-Fluoroalkyl Substances Exposure Is Associated With Later Occurrence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 1728–1730.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Dubinkina, V.; Ahmad, S.; Maslov, S.; Irudayaraj, J.M.K. Gut Microbiome-Host Metabolome Homeostasis upon Exposure to PFOS and GenX in Male Mice. Toxics 2023, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houde, M.; De Silva, A.O.; Muir, D.C.G.; Letcher, R.J. Monitoring of Perfluorinated Compounds in Aquatic Biota: An Updated Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7962–7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustsson, A.; Lennqvist, T.; Osbeck, C.M.G.; Tibblin, P.; Glynn, A.; Nguyen, M.A.; Westberg, E.; Vestergren, R. Consumption of Freshwater Fish: A Variable but Significant Risk Factor for PFOS Exposure. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Chi, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Ma, N.; Min, L.; Ji, S. Effects of Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid Exposure on Intestinal Microbial Community, Lipid Metabolism, and Liver Lesions in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodlief, T.; Vance, S.; Hu, Q.; Dewitt, J. Immunotoxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Insights into Short-Chain PFAS Exposure. Toxics 2021, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoike, O.E.; Pack, R.P.; Mamudu, H.M.; Liu, Y.; Strasser, S.; Zheng, S.; Okoro, J.; Wang, L. Association between per and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Markers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.G.; Wong, C.K.C.; Wong, M.H. Environmental Contamination, Human Exposure and Body Loadings of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS), Focusing on Asian Countries. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.M.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, L.; Liang-Ying, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, F.; Zeng, E.Y. Global Distribution of Perfluorochemicals (PFCs) in Potential Human Exposure Source—A Review. Environ. Int. 2017, 108, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, B.T.; Calkins, M.M. Occupational Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Scope Review of the Literature from 1980–2021. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2023, 33, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, E.M.; Hu, X.C.; Dassuncao, C.; Tokranov, A.K.; Wagner, C.C.; Allen, J.G. A Review of the Pathways of Human Exposure to Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) and Present Understanding of Health Effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 29, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, N.M.; Angrish, M.; Wilkins, A.; Thayer, K.; Cohen Hubal, E.A. Human Exposure Pathways to Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) from Indoor Media: A Systematic Review Protocol. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, G.B.; Cohn, P.D.; Cooper, K.R. Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA), an Emerging Drinking Water Contaminant: A Critical Review of Recent Literature. Environ. Res. 2012, 116, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, J.L. Health Risks of Dietary Exposure to Perfluorinated Compounds. Environ. Int. 2012, 40, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jogsten, I.E.; Perelló, G.; Llebaria, X.; Bigas, E.; Martí-Cid, R.; Kärrman, A.; Domingo, J.L. Exposure to Perfluorinated Compounds in Catalonia, Spain, through Consumption of Various Raw and Cooked Foodstuffs, Including Packaged Food. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.; Leblanc, J.C.; Nebbia, C.S.; et al. Risk to Human Health Related to the Presence of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Food. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ishaq, Z.; He, C.; Banks, A.P.W.; Bräunig, J.; Thai, P.K.; Jayarathne, A.; Mueller, J.F.; Wang, X. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Floor Dust from Different Indoor Environments in Australia: Levels, Variation, and Human Exposure Risks. Chemosphere 2024, 366, 143372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, N.; Kawashima, Y. Toxicity and Toxicockinetics of Perfluorooctanoic Acid in Humans and Animals. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 28, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Guan, R.; Zhu, N.; Hao, J.; Peng, H.; He, A.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G. A Critical Review on the Bioaccumulation, Transportation, and Elimination of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Human Beings. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 54, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, E.; Muensterman, D.; Carini, L.; Waite, I.; Payne, S.; Field, J.A.; Peterson, J.; Hafley, D.; Farrer, D.; Jones, G.D. Target and Suspect Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Fish from an AFFF-Impacted Waterway. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 906, 167798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestri, L.; Negri, S.; Ferrari, M.; Ghittori, S.; Fabris, F.; Danesino, P.; Imbriani, M. Determination of Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Perfluorooctanesulfonate in Human Tissues by Liquid Chromatography/Single Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 2728–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindell, A.E.; Grießhammer, A.; Michaelis, L.; Papagiannidis, D.; Ochner, H.; Kamrad, S.; Guan, R.; Blasche, S.; Ventimiglia, L.N.; Ramachandran, B.; et al. Human Gut Bacteria Bioaccumulate Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Nat. Microbiol. 2025, 10, 1630–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, P.; Rousselle, C.; Lange, R.; Sissoko, F.; Kolossa-Gehring, M.; Ougier, E. Human Biomonitoring Initiative (HBM4EU)—Strategy to Derive Human Biomonitoring Guidance Values (HBM-GVs) for Health Risk Assessment. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 230, 113622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenland, K.; Tinker, S.; Shankar, A.; Ducatman, A. Association of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) with Uric Acid among Adults with Elevated Community Exposure to PFOA. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, G.; Sartori, S.; Consonni, D. Thirty Years of Medical Surveillance in Perfluooctanoic Acid Production Workers. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2009, 51, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujic, E.; Ferguson, S.S.; Brouwer, K.L.R. Effects of PFAS on Human Liver Transporters: Implications for Health Outcomes. Toxicol. Sci. 2024, 200, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, S.E.; Ducatman, A.; Boobis, A.; De Witt, J.C.; Lau, C.; Ng, C.; Smith, J.S.; Roberts, S.M. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Toxicity and Human Health Review: Current State of Knowledge and Strategies for Informing Future Research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischel, H.N.; MacManus-Spencer, L.A.; Luthy, R.G. Noncovalent Interactions of Long-Chain Perfluoroalkyl Acids with Serum Albumin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5263–5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.A.; Hungerbühler, K. Bioconcentration of Perfluorinated Alkyl Acids: How Important Is Specific Binding? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7214–7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loccisano, A.E.; Campbell, J.L.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Andersen, M.E.; Clewell, H.J. Comparison and Evaluation of Pharmacokinetics of PFOA and PFOS in the Adult Rat Using a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argoul, C.M.; Toutain, P.L.; Berard, S.; Picard-Hagen, N.; Gayrard, V.; Lacroix, M.Z. Structure-Related Differences in Plasma Protein Binding of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Mice and Humans. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 120, 104879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, K.; Mertens, H.; Richter, L.; Mielke, H.; Schwerdtle, T.; Monien, B.H. Kinetics of 15 Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) after Single Oral Application as a Mixture—A Pilot Investigation in a Male Volunteer. Environ. Int. 2024, 193, 109047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzurro, D.M.; Seeley, M.; Kerper, L.E.; Beck, B.D. Interspecies Differences in Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Toxicokinetics and Application to Health-Based Criteria. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 106, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.C.; Dzierlenga, A.L.; Robinson, V.G.; Waidyanatha, S.; De Vito, M.J.; Eifrid, M.A.; Granville, C.A.; Gibbs, S.T.; Blystone, C.R. Toxicokinetics of Perfluorobutane Sulfonate (PFBS), Perfluorohexane-1-Sulphonic Acid (PFHxS), and Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (PFOS) in Male and Female Hsd:Sprague Dawley SD Rats after Intravenous and Gavage Administration. Toxicol. Rep. 2019, 6, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharpure, R.; Pramanik, S.; Pradhan, A. In Silico Analysis Decodes Transthyretin (TTR) Binding and Thyroid Disrupting Effects of per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, A.W.F.; Duivenvoorde, L.P.M.; Beekmann, K.; Pinckaers, N.; van der Hee, B.; Noorlander, A.; Leenders, L.L.; Louisse, J.; van der Zande, M. Transport of Perfluoroalkyl Substances across Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Intestinal Epithelial Cells in Comparison with Primary Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells and Caco-2 Cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2024, 98, 3777–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.; Jacob, S. A Simple Practice Guide for Dose Conversion between Animals and Human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iulini, M.; Russo, G.; Crispino, E.; Paini, A.; Fragki, S.; Corsini, E.; Pappalardo, F. Advancing PFAS Risk Assessment: Integrative Approaches Using Agent-Based Modelling and Physiologically-Based Kinetic for Environmental and Health Safety. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 23, 2763–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, K.; Yang, Z.; Agarwal, M.; Liu, W.; Peng, Z.; Long, Z.; Birbeck, J.; Westrick, J.; Liu, W.; Petriello, M.C. Exposure to a Mixture of Legacy, Alternative, and Replacement per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Results in Sex-Dependent Modulation of Cholesterol Metabolism and Liver Injury. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, C.J.; Leonard, R.C.; Kreckmann, K.H.; Slade, M.D.; Cullen, M.R. Longitudinal Study of Serum Lipids and Liver Enzymes in Workers with Occupational Exposure to Ammonium Perfluorooctanoate. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2007, 49, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, W.; Qian, Y.; Cai, X.; Wei, J.; Zhang, L. Mechanisms of Colon Toxicity Induced by Long-Term Perfluorooctanoic Acid Exposure in Mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 282, 116762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Liu, H.; An, Q.; Lei, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, C.; Lin, Y.; Dong, Q.; Yang, Z.; et al. Association of Adverse Fetal Outcomes with Placental Inflammation after Oral Gestational Exposure to Hexafluoropropylene Oxide Dimer Acid (GenX) in Sprague-Dawley Rats. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, J.M.; Lambright, C.S.; Evans, N.; Strynar, M.J.; Mc Cord, J.; McIntyre, B.S.; Travlos, G.S.; Cardon, M.C.; Medlock-Kakaley, E.; Hartig, P.C.; et al. Adverse Maternal, Fetal, and Postnatal Effects of Hexafluoropropylene Oxide Dimer Acid (GenX) from Oral Gestational Exposure in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 37008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.; Thibodeaux, J.R.; Hanson, R.G.; Narotsky, M.G.; Rogers, J.M.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Strynar, M.J. Effects of Perfluorooctanoic Acid Exposure during Pregnancy in the Mouse. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 90, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, S.J.; Bampidis, V.; Benford, D.; Bragard, C.; Halldorsson, T.I.; Hernández-Jerez, A.F.; Bennekou, S.H.; Koutsoumanis, K.; Lambré, C.; Machera, K.; et al. Guidance on the Use of the Benchmark Dose Approach in Risk Assessment. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindstrom, A.B.; Strynar, M.J.; Libelo, E.L. Polyfluorinated Compounds: Past, Present, and Future. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7954–7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee on the Guidance on PFAS Testing and Health Outcomes of the National Academies of Sciences, En-Gineering, and Medicine (Washington, DC, USA). Guidance on PFAS Exposure, Testing, and Clinical Follow-Up: PFAS Testing and Concentrations to Inform Clinical Care of Exposed Patients; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2022; p. 5. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/books/NBK584705/?report=reader (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Mahoney, H.; da Silva, F.; Brinkmann, M.; Giesy, J.P. Mixtures of Legacy and Replacement Perfluorosulphonic Acids (PFSAs) Demonstrate Ratio-, Concentration- and Endpoint-Dependent Synergistic Interactions in Vitro. Chemosphere 2024, 361, 142446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Bonilla, K.M.; Aga, D.S.; Lee, J.; König, M.; Qin, W.; Cristobal, J.R.; Atilla-Gokcumen, G.E.; Escher, B.I. Neurotoxic Effects of Mixtures of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) at Environmental and Human Blood Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 16774–16784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xu, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tao, M.; Chen, T.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z. Fate and Enzymatic Response of Co-Exposed Photoaged Nanoplastic and PFAS: Insights from a Human Gastrointestinal Simulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 496, 139274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, J.; Tessmann, J.W.; Deng, P.; Hennig, B.; Zaytseva, Y.Y. The Role of Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (PFOS) Exposure in Inflammation of Intestinal Tissues and Intestinal Carcinogenesis. Front. Toxicol. 2023, 5, 1244457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, M.; Zihler Berner, A.; Chervet, N.; Chassard, C.; Lacroix, C. Comparison of the Caco-2, HT-29 and the Mucus-Secreting HT29-MTX Intestinal Cell Models to Investigate Salmonella Adhesion and Invasion. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 94, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Pan, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, H.; Chu, X. Effects of Co-Exposure to Microplastics and Perfluorooctanoic Acid on the Caco-2 Cells. Toxicology 2025, 515, 154152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, M.; Leveque, M.; Stoffels, C.B.A.; Person, E.; Bruel, S.; Fourquaux, I.; Robert, H.; Cabaton, N.J.; Audinot, J.N.; Mercier-Bonin, M. Repeated in Vitro Exposure to PFOA Impairs Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Leads to Cytosolic Accumulation as Detected by Subcellular Chemical Imaging. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2025, 1003, 180666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.M.; Kim, T.O. Epigenetic Alterations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Cancer. Intest. Res. 2015, 13, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesueur, C.; Bôle-Feysot, C.; Bekri, S.; Husson, A.; Lavoinne, A.; Brasse-Lagnel, C. Glutamine Induces Nuclear Degradation of the NF-ΚB P65 Subunit in Caco-2/TC7 Cells. Biochimie 2012, 94, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Li, F.; Yu, C.; Guo, M.; Wu, Q.; Weng, Y.; Wu, M.; Tong, H.; Yan, J. Intestinal Inflammation Mediates PFOA-Induced Sleep Fragmentation and Growth Impairment in Drosophila. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 302, 118541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Yang, M.; Zeng, C.; Wu, W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y. Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Exerts Inflammatory Bowel Disease-like Intestinal Injury in Rats. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Rimal, B.; Nichols, R.G.; Tian, Y.; Smith, P.B.; Hatzakis, E.; Chang, S.C.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Peters, J.M.; Patterson, A.D. Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Alters Gut Microbiota-Host Metabolic Homeostasis in Mice. Toxicology 2020, 431, 152365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, R.; Yin, N.; Faiola, F. Effects of Per- and Poly-Fluorinated Alkyl Substances on Pancreatic and Endocrine Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domazet, S.L.; GrØntved, A.; Timmermann, A.G.; Nielsen, F.; Jensen, T.K. Longitudinal Associations of Exposure to Perfluoroalkylated Substances in Childhood and Adolescence and Indicators of Adiposity and Glucose Metabolism 6 and 12 Years Later: The European Youth Heart Study. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, O.E.; Sorini, C.; Morales, R.A.; Luo, X.; Frede, A.; Krais, A.M.; Chávez, M.N.; Wincent, E.; Das, S.; Villablanca, E.J. Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid Modulates Barrier Function and Systemic T-Cell Homeostasis during Intestinal Inflammation. Dis. Model. Mech. 2021, 14, dmm049104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Q.; Liu, T.; Yang, S.; Sun, L.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Li, L.Y.; She, Y.C.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Ye, X.Y.; Bao, Q.; et al. Perfluoroalkyl Substance Pollutants Activate the Innate Immune System through the AIM2 Inflammasome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominic, A.; Le, N.T.; Takahashi, M. Loop Between NLRP3 Inflammasome and Reactive Oxygen Species. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2022, 36, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yang, Q.; Fan, S.; He, Y.; Duan, J.; Zhang, S.; Xiong, H.; Zeng, D. PFOS Promotes Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Proliferation through PI3K/AKT/NF-ΚB Mediated EMT. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2025, 205, 115714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tursi, A.R.; Lindeman, B.; Kristoffersen, A.B.; Hjertholm, H.; Bronder, E.; Andreassen, M.; Husøy, T.; Dirven, H.; Andorf, S.; Nygaard, U.C. Immune Cell Profiles Associated with Human Exposure to Perfluorinated Compounds (PFAS) Suggest Changes in Natural Killer, T Helper, and T Cytotoxic Cell Subpopulations. Environ. Res. 2024, 256, 119221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.S.; Wang, J.; Yannie, P.J.; Ghosh, S. Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, LPS Translocation, and Disease Development. J. Endocr. Soc. 2020, 4, bvz039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.L.; Chen, Y.K.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Chen, L.J.; Zhang, K.K.; Li, J.H.; Liu, J.L.; Wang, Q.; Xie, X.L. Gestational Exposure to GenX Induces Hepatic Alterations by the Gut-Liver Axis in Maternal Mice: A Similar Mechanism as PFOA. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2022, 820, 153281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tian, Y.; Chen, B.; Xu, S.; Wu, L. PFOA/PFOS Facilitated Intestinal Fatty Acid Absorption by Activating the PPARα Pathway: Insights from Organoids Model. Environ. Health 2023, 2, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ling, X.; He, S.; Cui, H.; Yang, Z.; An, H.; Wang, L.; Zou, P.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.; et al. PPARα/ACOX1 as a Novel Target for Hepatic Lipid Metabolism Disorders Induced by per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: An Integrated Approach. Environ. Int. 2023, 178, 108138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jing, K.; He, L.; Song, P.; Yu, J. Impact of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Structure on Oxidative Stress and Lipid Metabolism Disruption in HepG2 Cells. Toxicology 2025, 517, 154218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.A.; Huang, C.W.; Wei, C.C. Early-Life Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (PFOS) Exposure Cause Obesity by Disrupting Fatty Acids Metabolism and Enhancing Triglyceride Synthesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 251, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. Function and Mechanisms of Enteroendocrine Cells and Gut Hormones in Metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Yang, L.; Jiang, S.; Qian, D.; Duan, J. Excessive Apoptosis in Ulcerative Colitis: Crosstalk Between Apoptosis, ROS, ER Stress, and Intestinal Homeostasis. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2022, 28, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, A.; Mishra, J.S.; Yadav, P.; Dangudubiyyam, S.V.; Blesson, C.S.; Kumar, S. PFOS Impairs Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Dynamics and Reduces Oxygen Consumption in Human Trophoblasts. J. Environ. Sci. Public Health 2023, 7, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanov, S.; Berlec, A.; Štrukelj, B. The Influence of Probiotics on the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in the Treatment of Obesity and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Gao, S.; Xu, M.; Shi, H.; Zhu, J. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Disrupt Gut Microbiome Composition and Metabolism in Metabolic Syndrome: Evidence from a Host-Free in Vitro Colonic Model. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 386, 127189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Hong, Y.; Xiao, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, E.; Li, H.; Cai, Z. The Role of Fecal Microbiota in Liver Toxicity Induced by Perfluorooctane Sulfonate in Male and Female Mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 67009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Kang, S.G.; Park, J.H.; Yanagisawa, M.; Kim, C.H. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Activate GPR41 and GPR43 on Intestinal Epithelial Cells to Promote Inflammatory Responses in Mice. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 396–406.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashitani, M.; Mizuno, A.; Kimura, T.; Shimbo, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Tokioka, S.; Kobayashi, D. Low Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)/Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) Ratio Associated with Increased Cardiovascular Disease and Its Risk Factors in Healthy Japanese Population. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2022, 31, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, A.B.; Michelsen-Correa, S.; Rosen, C.; Martin, C.F.; Blumberg, B. PFAS and Potential Adverse Effects on Bone and Adipose Tissue Through Interactions with PPARγ. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut Microbiota in Human Metabolic Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Cheng, S.; Rhee, E.P.; McCabe, E.; Lewis, G.D.; Fox, C.S.; Jacques, P.F.; Fernandez, C.; et al. Metabolite Profiles and the Risk of Developing Diabetes. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Olson, K.C.; Gao, C.; Prosdocimo, D.A.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Z.; Jeyaraj, D.; Youn, J.Y.; Ren, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Catabolic Defect of Branched-Chain Amino Acids Promotes Heart Failure. Circulation 2016, 133, 2038–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.-L.; Wu, G.; Zhu, W.-Y. Amino Acid Metabolism in Intestinal Bacteria: Links between Gut Ecology and Host Health. Front. Biosci. 2011, 16, 1768–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Host-Gut Microbiota Metabolic Interactions. Science 2012, 336, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, S.; Li, R.; Xia, H.; Jie, Z.; Wen, B.; Chen, X.; Yan, W.; Fan, Y.; et al. Integrated Metabolomics and Metagenomics Analysis of Plasma and Urine Identified Microbial Metabolites Associated with Coronary Heart Disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kori, M.; Aydln, B.; Unal, S.; Arga, K.Y.; Kazan, D. Metabolic Biomarkers and Neurodegeneration: A Pathway Enrichment Analysis of Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. OMICS 2016, 20, 645–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sako, W.; Abe, T.; Izumi, Y.; Harada, M.; Kaji, R. The Ratio of N-Acetyl Aspartate to Glutamate Correlates with Disease Duration of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 27, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Moriwaki, Y.; Takahashi, S. Effect of Ethanol on Metabolism of Purine Bases (Hypoxanthine, Xanthine, and Uric Acid). Clin. Chim. Acta 2005, 356, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Ang, K.Y.; Huang, S.; Hou, Q.; Su, X.; Qiao, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Intestinal Microbiota Distinguish Gout Patients from Healthy Humans. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, A.; Rivera, J.; Zapata, C.; Norambuena, J.; Sandoval, Á.; Chávez, R.; Orellana, O.; Levicán, G. Cobalamin Protection against Oxidative Stress in the Acidophilic Iron-Oxidizing Bacterium Leptospirillum Group II CF-1. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 196539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Yang, S.H.; Liu, Y.; Jamieson, P.; Shan, L.; Chu, K.H. Accumulation and Phytotoxicity of Perfluorooctanoic Acid and 2,3,3,3-Tetrafluoro-2-(Heptafluoropropoxy)Propanoate in Arabidopsis thaliana and Nicotiana benthamiana. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.D.; Bräunig, J.; Mueller, J.F.; Crompton, M.; Dunstan, R.H.; Nilsson, S. Metabolomic Profiles Associated with Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Aquatic Environments. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2019, 21, 1980–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nisio, A.; Sabovic, I.; Valente, U.; Tescari, S.; Rocca, M.S.; Guidolin, D.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Acquasaliente, L.; Pozzi, N.; Plebani, M.; et al. Endocrine Disruption of Androgenic Activity by Perfluoroalkyl Substances: Clinical and Experimental Evidence. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, A.; Belzer, C.; Geurts, L.; Ouwerkerk, J.P.; Druart, C.; Bindels, L.B.; Guiot, Y.; Derrien, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Cross-Talk between Akkermansia Muciniphila and Intestinal Epithelium Controls Diet-Induced Obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9066–9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover, J.S.; Ticer, T.D.; Engevik, M.A. Characterizing the Mucin-Degrading Capacity of the Human Gut Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Han, R.; Yuan, Y.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Mao, T. The Role of Akkermansia muciniphila in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Current Knowledge and Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1089600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Lai, H.; Tu, W. Comparative Chronic Toxicities of PFOS and Its Novel Alternatives on the Immune System Associated with Intestinal Microbiota Dysbiosis in Adult Zebrafish. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance (PFAS) Mixtures Induce Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis and Metabolic Disruption in Silkworm (Bombyx mori L.). Sci Tot Environ. 2024, 914, 169782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenland, K.; Kugathasan, S.; Barr, D.B. PFOA and Ulcerative Colitis. Environ. Res. 2018, 165, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitro, S.D.; Sagiv, S.K.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Calafat, A.M.; Fleisch, A.F.; Jaacks, L.M.; Williams, P.L.; Oken, E.; James-Todd, T.M. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Exposure, Gestational Weight Gain, and Postpartum Weight Changes in Project Viva. Obesity 2020, 28, 1984–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kew, S.; Ye, C.; Hanley, A.J.; Connelly, P.W.; Sermer, M.; Zinman, B.; Retnakaran, R. Cardiometabolic Implications of Postpartum Weight Changes in the First Year After Delivery. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1998–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkle, S.N.; Sharma, A.J.; Swan, D.W.; Schieve, L.A.; Ramakrishnan, U.; Stein, A.D. Excess Gestational Weight Gain Is Associated with Child Adiposity among Mothers with Normal and Overweight Prepregnancy Weight Status. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.H.T.; Ma, R.C.W.; Yuen, L.Y.; Ozaki, R.; Li, A.M.; Hou, Y.; Chan, M.H.M.; Ho, C.S.; Yang, X.; Chan, J.C.N.; et al. The Impact of Maternal Gestational Weight Gain on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Children. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2539–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jurkovic-Mlakar, S.; Li, Y.; Wahlberg, K.; Scott, K.; Pineda, D.; Lindh, C.H.; Jakobsson, K.; Engström, K. Association between Serum Concentrations of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Expression of Serum MicroRNAs in a Cohort Highly Exposed to PFAS from Drinking Water. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E.; Demir, F.T. Drosophila: A Promising Model for Evaluating the Toxicity of Environmental Pollutants. Karaelmas Sci. Eng. J. 2022, 12, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, Y.N.; Moustafa, J.S.E.S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Tomlinson, M.; Falchi, M.; Menni, C.; Bowyer, R.C.E.; Steves, C.J.; Small, K.S. Longitudinal Association of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid (PFOS) Exposure with Lipid Traits, in a Healthy Unselected Population. J. Exp. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2025, 35, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerville, M.; Boudry, G. Gastrointestinal and Hepatic Mechanisms Limiting Entry and Dissemination of Lipopolysaccharide into the Systemic Circulation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 311, G1–G15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Cai, X.; Fei, W.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, C. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Immunity, Inflammation and Metabolism. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Haens, G.; Dubinsky, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Irving, P.M.; Howaldt, S.; Pokrotnieks, J.; Krueger, K.; Laskowski, J.; Li, X.; Lissoos, T.; et al. Mirikizumab as Induction and Maintenance Therapy for Ulcerative Colitis. N. Eng. J. Med. 2023, 388, 2444–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qian, Y.; Cai, X.; He, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, L. Therapeutic Intervention with Anti-TNF Alleviates Colonic and Hepatic Toxicity Induced by Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 296, 118125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Hu, Z.; Luo, X.; Ge, C.; Lv, Y.; Zhan, S.; Huang, W.; Shen, X.; Yu, D.; Liu, B. Itaconic Acid Alleviates Perfluorooctanoic Acid-Induced Oxidative Stress and Intestinal Damage by Regulating the Keap1/Nrf2/Ho-1 Pathway and Reshaping the Gut Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, E.L.; Ryan, D.G.; Prag, H.A.; Dikovskaya, D.; Menon, D.; Zaslona, Z.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Costa, A.S.H.; Higgins, M.; Hams, E.; et al. Itaconate Is an Anti-Inflammatory Metabolite That Activates Nrf2 via Alkylation of KEAP1. Nature 2018, 556, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, S.; Del Bo, C.; Marino, M.; Gargari, G.; Cherubini, A.; Andrés-Lacueva, C.; Hidalgo-Liberona, N.; Peron, G.; González-Dominguez, R.; Kroon, P.; et al. Polyphenols and Intestinal Permeability: Rationale and Future Perspectives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 68, 1816–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagov, A.V.; Orekhova, V.A.; Sukhorukov, V.N.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Orekhov, A.N.; Blagov, A.V.; Orekhova, V.A.; Sukhorukov, V.N.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Orekhov, A.N. Potential Use of Antioxidant Compounds for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alander, M.; Korpela, R.; Saxelin, M.; Vilpponen-Salmela, T.; Mattila-Sandholm, T.; Von Wright, A. Recovery of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG from Human Colonic Biopsies. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 24, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, G.; Chen, S.; Li, R.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Ding, N.; Sun, Y. Mitigation of PFOA/PFOS Toxicity in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) by Oxidative Stress Modulation and Gut Microbial Metabolism through the Use of Aquatic Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus. Water Cycle 2025, 6, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.L.; Alvarado, D.A.; Swanson, K.S.; Holscher, H.D. The Prebiotic Potential of Inulin-Type Fructans: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 492–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, P.; Gasbarrini, A.; Gambassi, G.; Cianci, R. Pollutants, Microbiota and Immune System: Frenemies within the Gut. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1285186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Nukavarapu, S.P.; Jala, V.R. Effects of Heavy Metals on Gut Barrier Integrity and Gut Microbiota. Microbiota Host 2024, 2, e230015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kish, L.; Hotte, N.; Kaplan, G.G.; Vincent, R.; Tso, R.; Gänzle, M.; Rioux, K.P.; Thiesen, A.; Barkema, H.W.; Wine, E.; et al. Environmental Particulate Matter Induces Murine Intestinal Inflammatory Responses and Alters the Gut Microbiome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Aspect | Main Findings | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical nature and persistence | PFAS are highly stable, amphiphilic compounds with strong C–F bonds, resistant to degradation and prone to bioaccumulation. | Long-term persistence in environment and tissues enables chronic human exposure. |
| Exposure routes | Predominantly oral, via contaminated water, food, and indoor dust; PFAS detected in serum, urine, and breast milk. | Continuous low-dose intake contributes to cumulative systemic burden. |
| Epithelial damage | Downregulation of tight-junction molecules (occludin, claudins, Tjp-1); oxidative stress and apoptosis; altered stem-cell renewal. | Increased intestinal permeability (“leaky gut”), chronic inflammation, impaired regeneration. |
| Inflammatory and immune response | Activation of NF-κB, NLRP3, AIM2; TNF-α and IL-6 release; macrophage and neutrophil infiltration. | Sustained mucosal inflammation; potential contribution to IBD and metabolic inflammation. |
| Metabolic alterations | PPAR-α–dependent lipid reprogramming and mitochondrial dysfunction reduce ATP synthesis and energy balance. | Links PFAS exposure to dyslipidemia, obesity, and insulin resistance. |
| Microbiota dysbiosis | Reduced Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio; depletion of Lactobacillus and Akkermansia; loss of SCFA producers. | Amplifies inflammation and endotoxemia; may drive gut–liver–brain metabolic axis dysfunction. |
| Experimental evidence | Data from in vitro (Caco-2, organoids) and in vivo models (mice, Zebrafish, Drosophila, silkworms) reveal consistent gut toxicity. | Mechanisms are evolutionarily conserved, supporting translational validity. |
| Human evidence | Associations between serum PFAS levels and IBD, metabolic syndrome, and perinatal outcomes. | Suggests biologically plausible links between chronic exposure and systemic disease. |
| Research priorities | Need for multi-omics, low-dose mixture studies, longitudinal human cohorts, and mitigation strategies. | Essential for defining causal mechanisms and exposure thresholds. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Brunetti, K.; Galletti, G.S.; Catalani, E.; Cervia, D.; Del Quondam, S. From Exposure to Dysfunction: The Intestinal Toxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Toxics 2026, 14, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics14010039
Brunetti K, Galletti GS, Catalani E, Cervia D, Del Quondam S. From Exposure to Dysfunction: The Intestinal Toxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Toxics. 2026; 14(1):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics14010039
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrunetti, Kashi, Giulia Serena Galletti, Elisabetta Catalani, Davide Cervia, and Simona Del Quondam. 2026. "From Exposure to Dysfunction: The Intestinal Toxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances" Toxics 14, no. 1: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics14010039
APA StyleBrunetti, K., Galletti, G. S., Catalani, E., Cervia, D., & Del Quondam, S. (2026). From Exposure to Dysfunction: The Intestinal Toxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Toxics, 14(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics14010039







