Source Apportionment and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Urban Fringe Areas: A Case Study of Kaifeng West Lake, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Geo-Accumulation Index Method
2.3.2. Potential Ecological Risk Index Method
2.3.3. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) Method
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Heavy Metal Content in Surface Water and Sediment
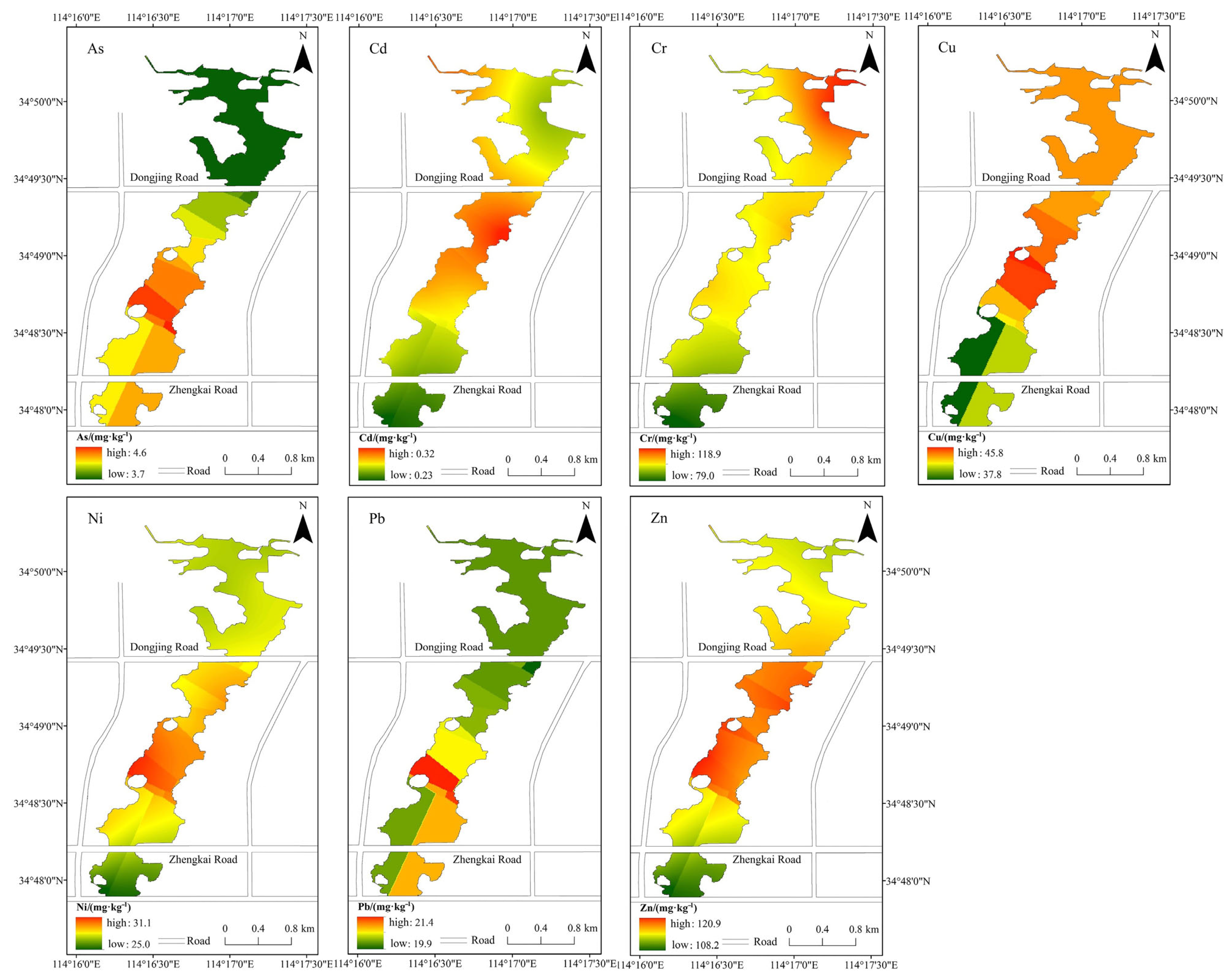
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metal Pollution in Sediment
3.3. Sediment Heavy Metal Pollution and Risk Assessment
3.3.1. Evaluation Results Using the Geo-Accumulation Index Method for Sediment Heavy Metal Pollution and Risk Assessment
3.3.2. Evaluation Results of the Potential Ecological Risk Index Method
3.4. Source Analysis of Heavy Metals
3.4.1. Pearson Correlation Analysis Results
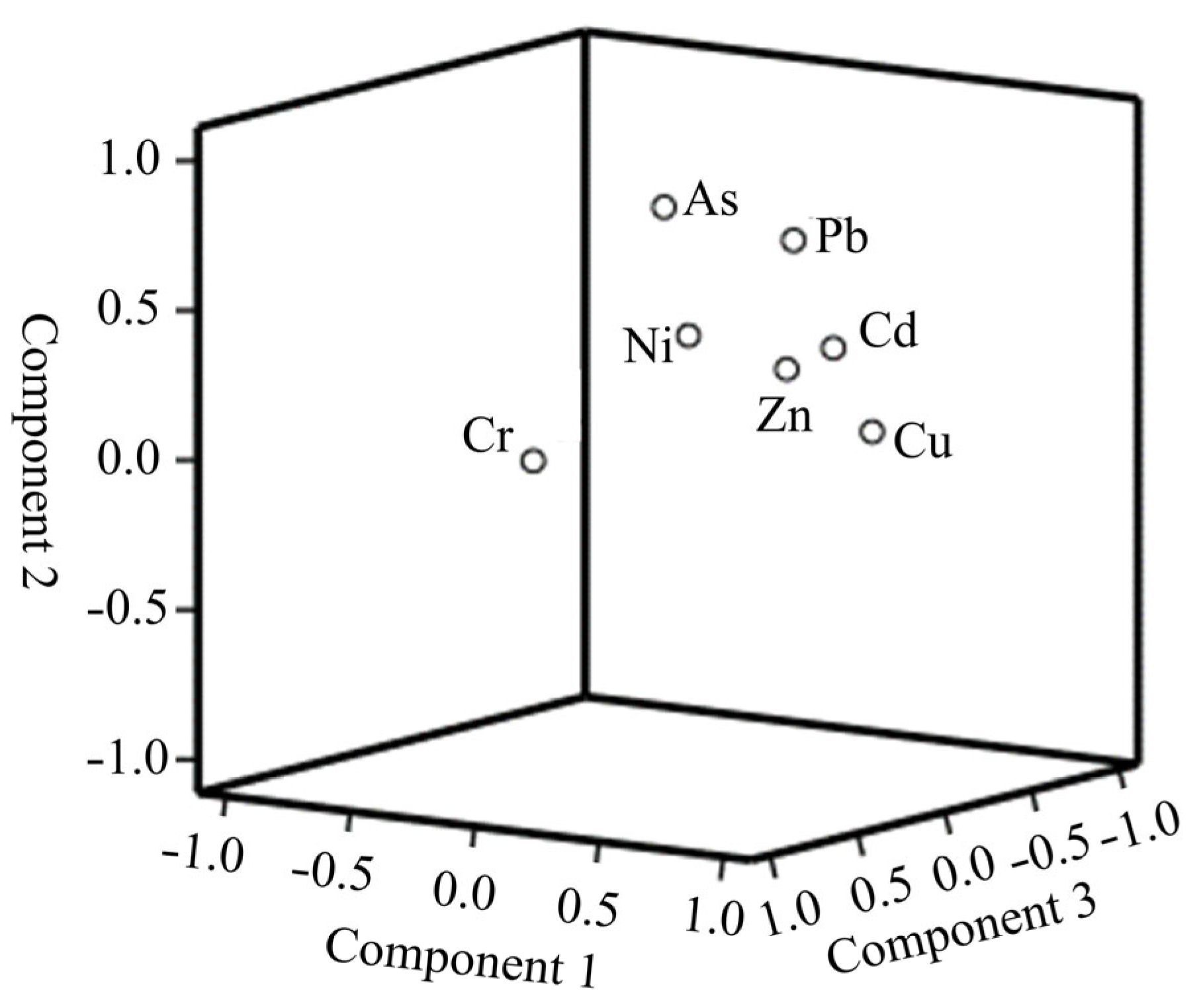
3.4.2. Principal Component Analysis Results
3.4.3. Cluster Analysis Results
3.4.4. PMF Analysis Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boase, K.; Santini, T.; Watkin, E. Microbes of biotechnological importance in acidic saline lakes in the Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1308797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Liu, D.X.; Ma, J.H.; Jin, B.Y.; Peng, J.; He, X.L. Assessing the influence of immobilization remediation of heavy metal contaminated farmland on the physical properties of soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ma, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y. Spatial distribution of soil magnetic susceptibility and correlation with heavy metal pollution in Kaifeng City, China. Catena 2016, 139, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Lou, W.; Wang, L.R.; Xu, J.L.; Pan, Y.F.; Peng, J.B.; Liu, D.X. Pollution, ecological risk and source identification of heavy metals in sediments from the Huafei River in the eastern suburbs of Kaifeng, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.L.; Liu, D.X.; Bu, T.X.; Zhang, M.Y.; Peng, J.; Ma, J.H. Assessment of pollution and health risks from exposure to heavy metals in soil, wheat grains, drinking water, and atmospheric particulate matter. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 376, 124448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.J.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, L.F.; Liang, T.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ma, C.X.; Xing, B.S. Multivariate geostatistical analysis and source identification of heavy metals in the sediment of Poyang Lake in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, Y.H.; Ding, M.J.; Xie, Z.L. Level, source identification, and risk analysis of heavy metal in surface sediments from river-lake ecosystems in the Poyang Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21902–21916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, Q.; Li, B.J.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, L.; Wu, S.H. One-century sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution in western Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bi, G.H.; Yang, Q.Y.; Wang, Z.L. Analyzing land use characteristics of rural settlements on the urban fringe of Liangjiang New Area, Chongqing, China. J. Mount. Sci. 2016, 13, 1855–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.J.; Wan, J. Land use and travel burden of residents in urban fringe and rural areas: An evaluation of urban-rural integration initiatives in Beijing. Land Use Policy 2021, 103, 105309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Lv, C.D. Construction and optimization of green space ecological networks in urban fringe areas: A case study with the urban fringe area of Tongzhou district in Beijing. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 276, 124266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Tian, M.; Zheng, L.R.; Li, X.M.; Jing, D.H. Characterisation and source apportionment of atmospheric organic and elemental carbon in an urban–rural fringe area of Taiyuan, China. Environ. Chemist. 2019, 16, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, J.; Yan, Q.X.; Guo, J.Q.; Liu, G.N.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Y.Y. Spatial distribution, sediment-water partitioning, risk assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in the Golmud River-Dabson Salt Lake ecosystem. Environ. Res. 2025, 268, 120792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, K.; Xia, J.d.; Jiao, W.; Niu, Y.; Yu, H. Meta analysis of heavy metal pollution and sources in surface sediments of Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, H. Spatial distribution and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediments of East Dongting Lake, China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- State Environmental Protection Administration of China, Total Station of China Environment Monitoring. Chinese Soil Element Background Values; Environment Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990.
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Han, C.; Jiang, Y. Some problems in the application of potential ecological risk index. Geogr. Res. 2020, 39, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Environmetrics 1994, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. EPA Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Xu, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, K. Characterization and source apportionment analysis of PM2.5 and ozone pollution over Fenwei Plain, China: Insights from PM2.5 component and VOC observations. Toxics 2025, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Gou, W.X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z.L.; Pei, X.J.; He, M.; Duo, J. Identifying hidden heavy metal sources in atmospheric dust of mining cities by integrating Cd isotopes and multivariate statistical method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 495, 138894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.W.; Kang, H.; Tao, W.D.; Li, H.Y.; He, D.; Ma, L.X.; Tang, H.J.; Wu, S.Q.; Yang, K.X.; Li, X.X. A spatial distribution—Principal component analysis (SD-PCA) model to assess pollution of heavy metals in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wu, X.; Tu, C.; Chen, Q.; Tao, L. Source apportionment and human health risks of potentially toxic elements in the surface water of coal mining areas. Toxics 2024, 12, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proshad, R.; Kormoker, T.; Al, M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Khadka, S.; Idris, A.M. Receptor model-based source apportionment and ecological risk of metals in sediments of an urban river in Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Xiang, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Lei, K.; Cao, Y. Heavy metal contamination risk assessment and correlation analysis of heavy metal contents in soil and crops. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macumu, P.H.; Gaiolini, M.; Ofori, A.; Micòl, M.; Nicolò, C. Additional sources of salinity and heavy metals from plant residues of peaty horizons in the Po River lowland (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Cao, G.; Cao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Jiang, G. Characteristics and potential ecological risks of heavy metal content in the soil of a plateau alpine mining area in the Qilian Mountains. Land 2023, 12, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Research of Heavy Metals and Their Fractions in Surface Sediments of Urban Water in Kaifeng. Master’s Thesis, Henan University, Zhengzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.X.; Qiao, Y.M.; Tang, M.Y.; Yang, H.Y. Heavy Metal pollution and potential ecological risk assessment in surface sediments from lakes located in Guangzhou City. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2019, 35, 600–607. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Li, P.; Xing, X.; Weng, M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Luo, H. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Longyang Lake and Moshui Lake in Wuhan. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 43, 6490–6499. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Zang, S.; Sun, H.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, K.; Sun, L. Pollution history and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in core sediments in Hulun Lake during the past 150 years. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2018, 37, 137–147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Fu, X. Enrichment characteristics and sources of heavy metals in surface sediments of Qinghai Lake, Northwest China. Chin. J. Ecol. 2013, 32, 1862–1869. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, E.; Zhang, E.; Lin, Q.; Shen, J.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. Spatio-temporal variations, contamination and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the sediments of Chenghai Lake. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 4169–4177. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Chang, Q.R.; Liu, J.; Clevers, J.; Kooistra, L. Identification of soil heavy metal sources and improvement in spatial mapping based on soil spectral information: A case study in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.D.; Lu, X.W.; Yang, G. Sources identification of heavy metals in urban topsoil from inside the Xi’an Second Ringroad, NW China using multivariate statistical methods. Catena 2012, 98, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Guo, X.; Tang, M.Y.; Zhu, D.; Wang, H.T.; Yang, X.; Chen, B. Variation in pollution status, sources, and risks of soil heavy metals in regions with different levels of urbanization. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, A.; Pandita, S.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.K.; Cerdà, A. A review of ecological risk assessment and associated health risks with heavy metals in sediment from India. Int. J. Sediment. Res. 2020, 35, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.P.; Wang, Q.Z.; Guan, Q.Y.; Ma, Y.R.; Ni, F.; Yang, E.Q.; Zhang, J. Heavy metal pollution levels, source apportionment and risk assessment in dust storms in key cities in Northwest China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 422, 126878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Zuo, Q.; Li, J.; Shi, S.; Li, B.; Zhao, X.N. A comprehensive exploration on distribution, risk assessment, and source quantification of heavy metals in the multi-media environment from Shaying River Basin, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, T.B. Source appointment of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) at an abandoned realgar mine: Combination of multivariate statistical analysis and three common receptor models. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| E | Ecological Risk Levels of a Single Metal | RI | Ecological Risk Levels of a Single Metal |
|---|---|---|---|
| <30 | Low ecological risk | <70 | Low ecological risk |
| 30~60 | Moderate ecological risk | 70~140 | Moderate ecological risk |
| 60~120 | Considerable ecological risk | 140~280 | Considerable ecological risk |
| 120~240 | High ecological risk | 280~560 | Very high ecological risk |
| ≥240 | Very high ecological risk |
| Elements (μg·L−1) | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean value | 0.030 | 6.180 | 3.350 | 4.400 | 0.010 | 10.170 | 0.940 |
| Maximum value | 0.090 | 9.410 | 6.370 | 6.390 | 0.050 | 21.250 | 1.760 |
| Minimum value | 0.010 | 3.750 | 1.520 | 2.830 | 0 | 4.150 | 0 |
| GB 3838-2002 * | ≤5 | ≤50 | ≤1000 | ≤20 | ≤50 | ≤2000 | ≤100 |
| Elements (mg·kg−1) | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean value | 0.280 | 99.950 | 41.400 | 28.070 | 20.410 | 115.230 | 3.990 |
| Maximum value | 0.410 | 152.500 | 73.730 | 39.220 | 29.140 | 147.850 | 5.750 |
| Minimum value | 0.140 | 47.230 | 22.090 | 9.260 | 17.070 | 68.700 | 2.030 |
| Standard deviation | 0.060 | 21.790 | 11.790 | 7.110 | 3.000 | 16.560 | 1.000 |
| Background value | 0.600 | 66.600 | 24.100 | 29.600 | 21.900 | 71.100 | 9.700 |
| Coefficient of variation/% | 21.64 | 21.80 | 28.48 | 25.32 | 14.72 | 14.37 | 25.08 |
Elements | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | As | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling Points | Igeo | Igeo Class | Igeo | Igeo Class | Igeo | Igeo Class | Igeo | Igeo Class | Igeo | Igeo Class | Igeo | Igeo Class | Igeo | Igeo Class |
| 1 | 0.970 | 1 | 0.360 | 1 | 0.110 | 1 | −0.930 | 0 | −0.700 | 0 | 0.060 | 1 | −2.030 | 0 |
| 2 | 0.580 | 1 | 0.650 | 1 | −0.030 | 0 | −0.300 | 0 | −0.810 | 0 | 0.030 | 1 | −2.310 | 0 |
| 3 | 0.910 | 1 | −0.130 | 0 | 0.160 | 1 | −0.670 | 0 | −0.710 | 0 | 0.200 | 1 | −1.930 | 0 |
| 4 | 1.150 | 2 | 0.070 | 1 | 1.000 | 1 | −0.500 | 0 | −0.660 | 0 | 0.380 | 1 | −2.270 | 0 |
| 5 | 1.440 | 2 | 0.480 | 1 | 0.340 | 1 | −0.340 | 0 | −0.420 | 0 | 0.230 | 1 | −1.410 | 0 |
| 6 | 1.600 | 2 | 0.030 | 1 | 1.100 | 2 | −0.200 | 0 | −0.200 | 0 | 0.370 | 1 | −1.370 | 0 |
| 7 | 1.030 | 2 | −0.040 | 0 | 0.290 | 1 | −0.600 | 0 | −0.690 | 0 | 0.050 | 1 | −1.720 | 0 |
| 8 | 0.800 | 1 | 0.130 | 1 | 0.07 | 1 | −0.600 | 0 | −0.760 | 0 | 0.070 | 1 | −1.580 | 0 |
| 9 | 1.050 | 2 | −0.020 | 0 | 0.100 | 1 | −0.620 | 0 | −0.610 | 0 | 0.170 | 1 | −1.670 | 0 |
| 10 | 0.740 | 1 | −0.250 | 0 | −0.010 | 0 | −0.740 | 0 | −0.620 | 0 | −0.040 | 0 | −1.540 | 0 |
| 11 | 0.830 | 1 | −0.180 | 0 | −0.130 | 0 | −1.000 | 0 | −0.860 | 0 | 0.080 | 1 | −1.800 | 0 |
| 12 | 0.080 | 1 | −1.040 | 0 | −0.640 | 0 | −2.190 | 0 | −0.750 | 0 | −0.570 | 0 | −2.780 | 0 |
| 13 | 1.110 | 2 | 0.130 | 1 | 0.280 | 1 | −0.250 | 0 | −0.080 | 0 | 0.390 | 1 | −1.630 | 0 |
| 14 | 1.310 | 2 | 0.210 | 1 | 0.600 | 1 | −0.110 | 0 | −0.480 | 0 | 0.410 | 1 | −1.390 | 0 |
| 15 | 0.800 | 1 | −0.070 | 0 | 0.360 | 1 | −0.550 | 0 | −0.710 | 0 | 0.220 | 1 | −1.780 | 0 |
| 16 | 1.360 | 2 | 0.300 | 1 | 0.390 | 1 | −0.100 | 0 | −0.460 | 0 | 0.540 | 1 | −1.280 | 0 |
| 17 | 1.170 | 2 | −0.230 | 0 | −0.150 | 0 | −1.010 | 0 | −0.790 | 0 | 0.160 | 1 | −2.350 | 0 |
| 18 | 1.080 | 2 | 0.040 | 1 | 0.130 | 1 | −0.730 | 0 | −0.710 | 0 | 0.040 | 1 | −1.990 | 0 |
| 19 | 0.930 | 1 | 0.010 | 1 | 0.170 | 1 | −0.730 | 0 | −0.690 | 0 | 0.190 | 1 | −1.860 | 0 |
| 20 | 1.080 | 2 | −0.230 | 0 | 0.060 | 1 | −0.940 | 0 | −0.620 | 0 | 0.300 | 1 | −2.250 | 0 |
| 21 | 1.390 | 2 | −0.130 | 0 | 0.420 | 1 | −0.420 | 0 | −0.520 | 0 | 0.160 | 1 | −1.970 | 0 |
| average Igeo | 1.020 | 2 | 0.000 | 0 | 0.220 | 1 | −0.640 | 0 | −0.610 | 0 | 0.160 | 1 | −1.850 | 0 |
| Elements | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 1 | ||||||
| Cr | 0.32 | 1 | |||||
| Cu | 0.71 ** | 0.26 | 1 | ||||
| Ni | 0.67 ** | 0.69 ** | 0.65 ** | 1 | |||
| Pb | 0.64 ** | 0.19 | 0.54 * | 0.62 ** | 1 | ||
| Zn | 0.75 ** | 0.42 | 0.67 ** | 0.79 ** | 0.58 ** | 1 | |
| As | 0.58 ** | 0.36 | 0.42 | 0.71 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.57 ** | 1 |
| Elements (mg·kg−1) | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | As | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| West Lake | 0.280 | 99.950 | 41.400 | 28.070 | 20.410 | 115.230 | 3.990 | This study |
| Baogong Lake | 0.430 | 65.820 | 117.600 | 31.140 | 81.960 | 173.990 | — | [31] |
| Longting Lake | 0.340 | 46.010 | 30.700 | 24.660 | 60.290 | 95.030 | — | [31] |
| Tieta Lake | 0.270 | 42.270 | 29.150 | 20.000 | 55.920 | 68.330 | — | [32] |
| Baiyun Lake | 4.900 | 143.100 | 275.900 | 117.300 | 89.500 | 594.400 | — | [32] |
| Longyang Lake | 0.580 | 59.200 | 55.610 | — | 33.200 | 176.940 | 14.270 | [33] |
| Moshui Lake | 0.620 | 85.530 | 53.670 | — | 41.690 | 266.640 | 19.260 | [33] |
| Hulun Lake | 0.190 | 37.070 | 25.360 | — | 21.840 | 50.560 | 21.440 | [34] |
| Qinghai Lake | — | 80.070 | 27.210 | 11.620 | 24.840 | 110.390 | — | [35] |
| Chenghai Lake | 0.680 | — | 56.200 | 47.600 | 28.100 | 109.000 | 12.100 | [36] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Jin, B.; Zhou, F. Source Apportionment and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Urban Fringe Areas: A Case Study of Kaifeng West Lake, China. Toxics 2025, 13, 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090720
Huang J, Jin B, Zhou F. Source Apportionment and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Urban Fringe Areas: A Case Study of Kaifeng West Lake, China. Toxics. 2025; 13(9):720. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090720
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jinting, Bingyan Jin, and Feng Zhou. 2025. "Source Apportionment and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Urban Fringe Areas: A Case Study of Kaifeng West Lake, China" Toxics 13, no. 9: 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090720
APA StyleHuang, J., Jin, B., & Zhou, F. (2025). Source Apportionment and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Urban Fringe Areas: A Case Study of Kaifeng West Lake, China. Toxics, 13(9), 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090720






