Inhibitory Effects of Aquadag, a Black Carbon Surrogate, on Microbial Growth via Surface-Mediated Stress: Evidence from Adenosine Triphosphate Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Particulate Matter
2.1.2. Aquadag—BC Reference Material
2.1.3. Bacterial Strains and Culture
2.2. Experiments
2.2.1. Cultivation Setup
2.2.2. Measurement of ATP Levels
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface and Size Characteristics of the Black Carbon Reference Material
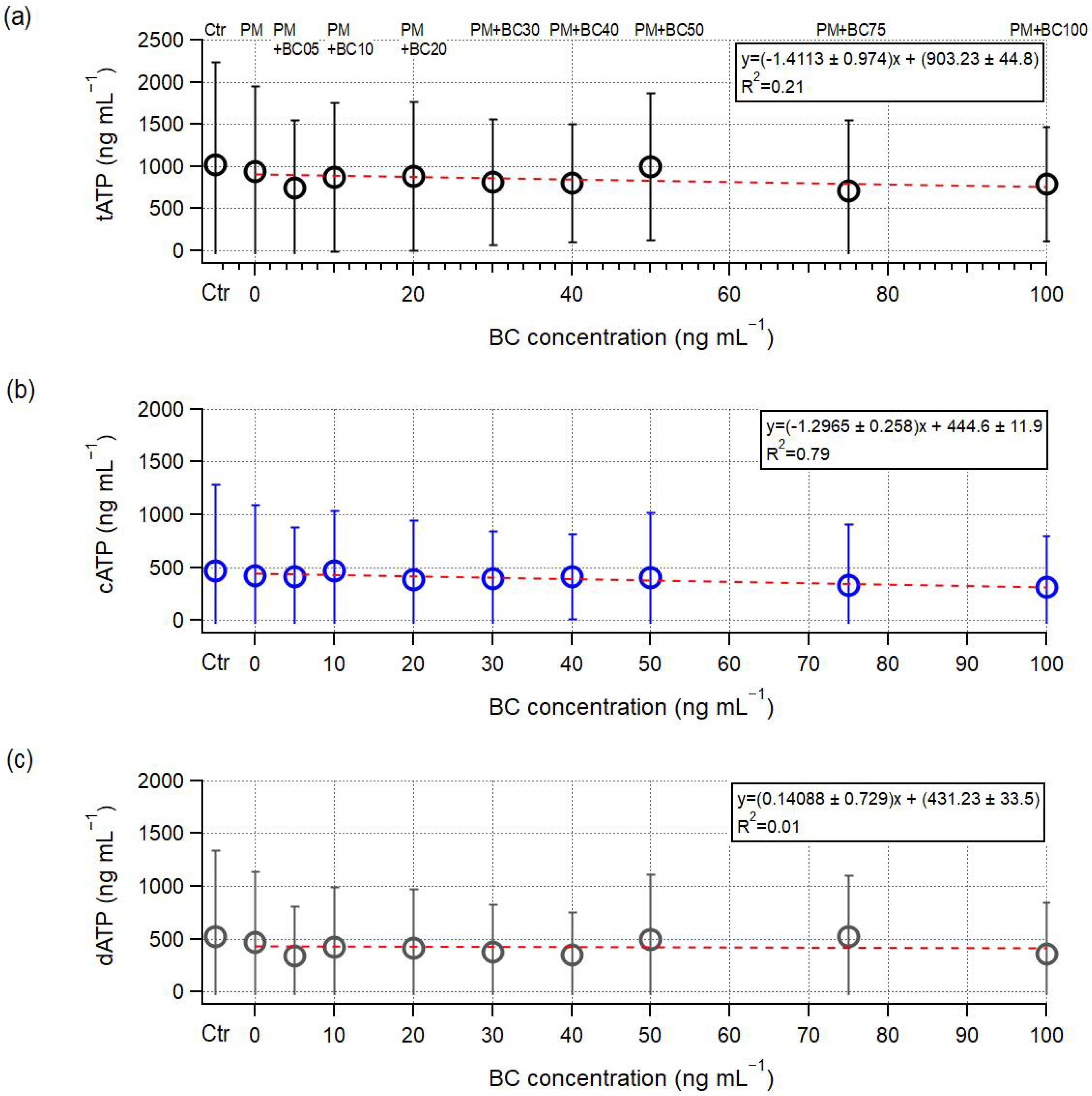
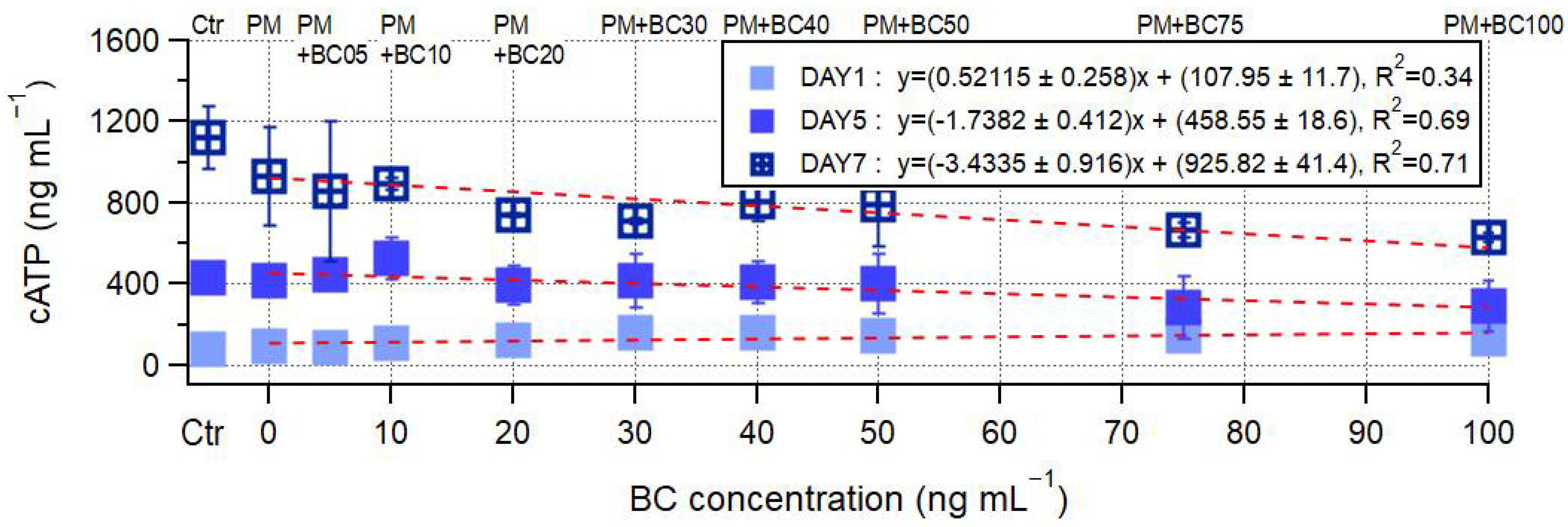
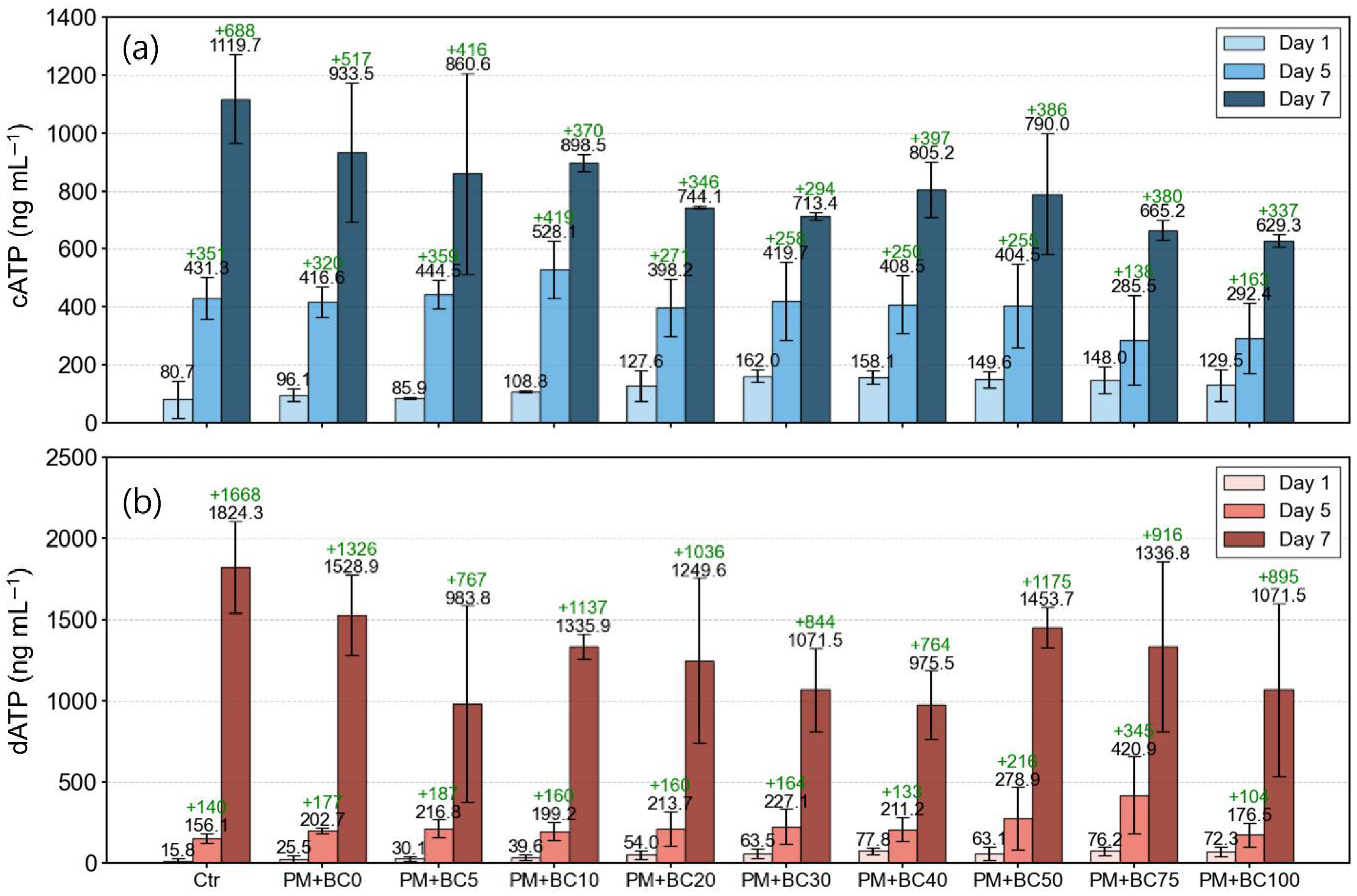
3.2. Microbial Growth Under the Presence of PM and BC
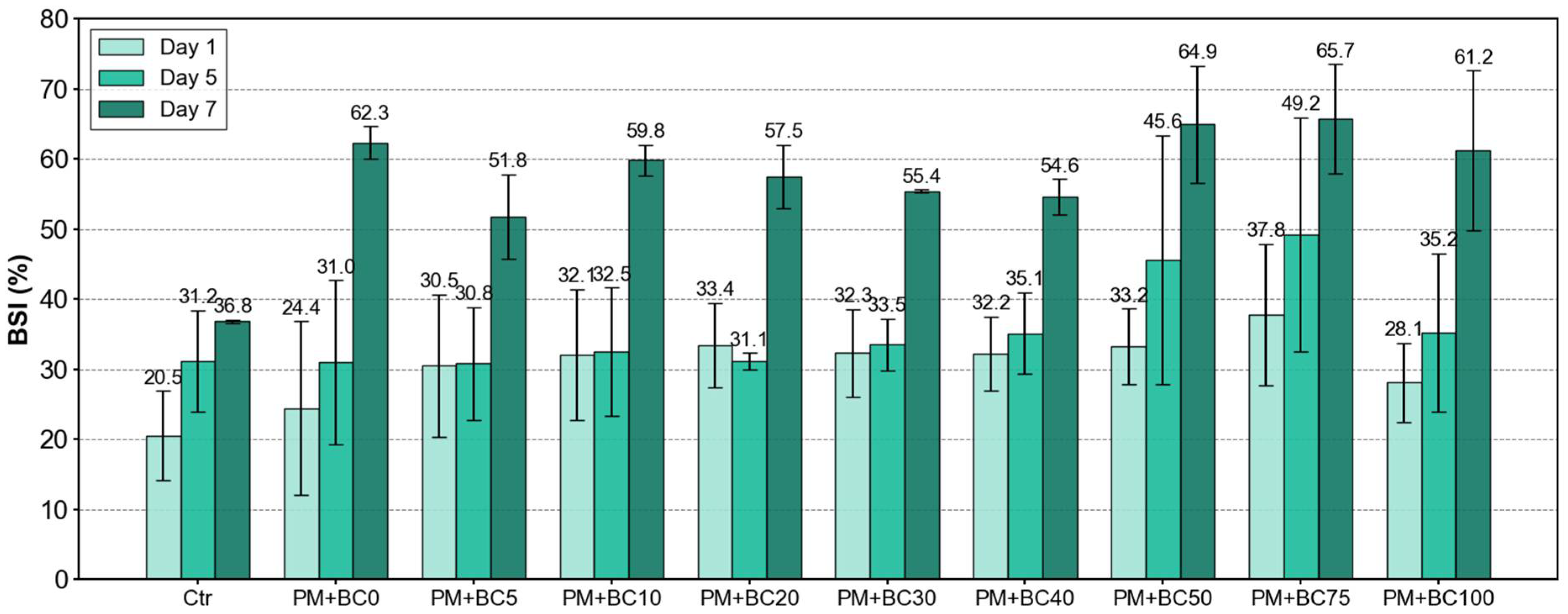
3.3. Stress Index of Bacterial Growth over Time (BSI)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bi, J.; D’Souza, R.R.; Moss, S.; Senthilkumar, N.; Russell, A.G.; Scovronick, N.C.; Chang, H.H.; Ebelt, S. Acute Effects of Ambient Air Pollution on Asthma Emergency Department Visits in Ten U.S. States. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 47003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Gao, D.; Liao, F.; Zhou, F.; Wang, X. The health effects of ambient PM2.5 and potential mechanisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 128, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, R.B.; Lim, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cromar, K.; Shao, Y.; Reynolds, H.R.; Silverman, D.T.; Jones, R.R.; Park, Y.; Jerrett, M.; et al. PM2.5 air pollution and cause-specific cardiovascular disease mortality. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krittanawong, C.; Qadeer, Y.K.; Hayes, R.B.; Wang, Z.; Virani, S.; Thurston, G.D.; Lavie, C.J. PM2.5 and Cardiovascular Health Risks. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2023, 48, 101670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Guo, X.; Cheung, F.M.H.; Yung, K.K.L. The association between PM2.5 exposure and neurological disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Wu, X.; Danesh Yazdi, M.; Braun, D.; Abu Awad, Y.; Wei, Y.; Liu, P.; Di, Q.; Wang, Y.; Schwartz, J.; et al. Long-term effects of PM2.5 on neurological disorders in the American Medicare population: A longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Planet. Health 2020, 4, e557–e565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ethan, C.J.; Mokoena, K.K.; Yu, Y.; Shale, K.; Fan, Y.; Rong, J.; Liu, F. Association between PM2.5 and mortality of stomach and colorectal cancer in Xi’an: A time-series study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 22353–22363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Pan, B.; Wu, J.; Chen, E.; Chen, L. Relationship between exposure to PM2.5 and lung cancer incidence and mortality: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 43322–43331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchett, N.; Spangler, E.C.; Gray, G.M.; Livinski, A.A.; Sampson, J.N.; Dawsey, S.M.; Jones, R.R. Exposure to Outdoor Particulate Matter Air Pollution and Risk of Gastrointestinal Cancers in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Epidemiologic Evidence. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 36001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Wan, X.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, K.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, L. Spatiotemporal analysis of PM2.5 and pancreatic cancer mortality in China. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-S.; Gui, Z.-H.; Zou, Z.-Y.; Yang, B.-Y.; Ma, J.; Jing, J.; Wang, H.-J.; Luo, J.-Y.; Zhang, X.; Luo, C.-Y.; et al. Long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: A national cross-sectional study in China. Environ. Int. 2021, 148, 106383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brines, M.; Dall’Osto, M.; Beddows, D.C.S.; Harrison, R.M.; Gómez-Moreno, F.; Núñez, L.; Artíñano, B.; Costabile, F.; Gobbi, G.P.; Salimi, F.; et al. Traffic and nucleation events as main sources of ultrafine particles in high-insolation developed world cities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5929–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.T.; Haywood, J.M.; Hawcroft, M.K. Are Changes in Atmospheric Circulation Important for Black Carbon Aerosol Impacts on Clouds, Precipitation, and Radiation? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 7930–7950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Hu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X.; Shi, A.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; et al. Is short-term and long-term exposure to black carbon associated with cardiovascular and respiratory diseases? A systematic review and meta-analysis based on evidence reliability. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e049516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanobetti, A.; Coull, B.A.; Gryparis, A.; Kloog, I.; Sparrow, D.; Vokonas, P.S.; Wright, R.O.; Gold, D.R.; Schwartz, J. Associations between arrhythmia episodes and temporally and spatially resolved black carbon and particulate matter in elderly patients. Occup. Environ. Med. 2014, 71, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Yin, Y.; Peng, L.; Du, L.; Geng, F.; Zhu, L. Acute effects of black carbon and PM2.5 on children asthma admissions: A time-series study in a Chinese city. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Huang, W.; Zhu, T.; Hu, M.; Brunekreef, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cheng, H.; Gehring, U.; Li, C.; et al. Acute Respiratory Inflammation in Children and Black Carbon in Ambient Air before and during the 2008 Beijing Olympics. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1507–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanbrabant, K.; Van Dam, D.; Bongaerts, E.; Vermeiren, Y.; Bové, H.; Hellings, N.; Ameloot, M.; Plusquin, M.; De Deyn, P.P.; Nawrot, T.S. Accumulation of Ambient Black Carbon Particles Within Key Memory-Related Brain Regions. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e245678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongaerts, E.; Lecante, L.L.; Bové, H.; Roeffaers, M.B.J.; Ameloot, M.; Fowler, P.A.; Nawrot, T.S. Maternal exposure to ambient black carbon particles and their presence in maternal and fetal circulation and organs: An analysis of two independent population-based observational studies. Lancet Planet. Health 2022, 6, e804–e811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, J.; Lawrence, W.R.; Chen, S.; Cheng, H.; Tang, H.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Gu, J.; et al. Potential causal associations of long-term exposure to PM2.5 constituents and all-cause mortality: Evidence from the Pearl River Cohort study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 291, 117897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, C.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, P.; Zhang, L. Does Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug Use Modify All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality Associated with PM2.5 and Its Components? A Nationally Representative Cohort Study (2007–2017). Environ. Health 2024, 3, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, S.J.K.; Purves, J.; Allcock, N.; Fernandes, V.E.; Monks, P.S.; Ketley, J.M.; Andrew, P.W.; Morrissey, J.A. Air pollution alters Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae biofilms, antibiotic tolerance and colonisation. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1868–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Li, X.; Sun, N.; He, F.; Cui, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, R. The combination of ultrafine carbon black and lead provokes cytotoxicity and apoptosis in mice lung fibroblasts through oxidative stress-activated mitochondrial pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Xue, W.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, X.; An, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; An, J. Ultrafine black carbon caused mitochondrial oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and mitophagy in SH-SY5Y cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 151899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas, M.E.; Gutiérrez, D.A.; Varela-Ramírez, A.; Garza, K.M. Continuous Exposure to Low Doses of Ultrafine Black Carbon Reduces the Vitality of Immortalized Lung-Derived Cells and Activates Senescence. J. Toxicol. 2020, 2020, 5702024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Tong, Z. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) bioluminescence-based strategies for monitoring atmospheric bioaerosols. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2022, 72, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.S.; Kim, H.R.; Ko, H.S.; Jeong, S.B.; Chan Kim, B.; Jung, J.H. Continuous Surveillance of Bioaerosols On-Site Using an Automated Bioaerosol-Monitoring System. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.; Choi, J.; Massoudifarid, M.; Park, J.Y.; Hwang, J.; Lim, J.; Byeon, J.H. Size-classified monitoring of ATP bioluminescence for rapid assessment of biological distribution in airborne particulates. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 234, 115356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yan, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Xing, D. Air sampling and ATP bioluminescence for quantitative detection of airborne microbes. Talanta 2024, 274, 126025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secka, F.; Allward, N.E.; Stoddart, A.K.; Gagnon, G.A. An automated and high-throughput method for adenosine triphosphate quantification. AWWA Water Sci. 2020, 2, e1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooij, D.v.d.; Bakker, G.L.; Italiaander, R.; Veenendaal, H.R.; Wullings, B.A. Biofilm Composition and Threshold Concentration for Growth of Legionella pneumophila on Surfaces Exposed to Flowing Warm Tap Water without Disinfectant. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e02737–02716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammes, F.; Goldschmidt, F.; Vital, M.; Wang, Y.; Egli, T. Measurement and interpretation of microbial adenosine tri-phosphate (ATP) in aquatic environments. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3915–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nescerecka, A.; Rubulis, J.; Vital, M.; Juhna, T.; Hammes, F. Biological Instability in a Chlorinated Drinking Water Distribution Network. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Yim, Y.-H.; Yoo, H.M. Particulate Matter Induces Oxidative Stress and Ferroptosis in Human Lung Epithelial Cells. Toxics 2024, 12, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gysel, M.; Laborde, M.; Olfert, J.S.; Subramanian, R.; Gröhn, A.J. Effective density of Aquadag and fullerene soot black carbon reference materials used for SP2 calibration. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2011, 4, 2851–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, M.; Schnaiter, M.; Linke, C.; Saathoff, H.; Naumann, K.H.; Möhler, O.; Berlenz, S.; Wagner, U.; Taylor, J.W.; Liu, D.; et al. Single Particle Soot Photometer intercomparison at the AIDA chamber. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2012, 5, 3077–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zeng, L.; Zhao, G.; Chen, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, W.; Hu, M. Significant changes in the physicochemical properties of BC-containing particles during the cold season in Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 151, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Alfarra, M.R.; Szpek, K.; Langridge, J.M.; Cotterell, M.I.; Belcher, C.; Rule, I.; Liu, Z.; Yu, C.; Shao, Y.; et al. Physical and chemical properties of black carbon and organic matter from different combustion and photochemical sources using aerodynamic aerosol classification. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 16161–16182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompalli, S.K.; Suresh Babu, S.N.; Satheesh, S.K.; Krishna Moorthy, K.; Das, T.; Boopathy, R.; Liu, D.; Darbyshire, E.; Allan, J.D.; Brooks, J.; et al. Seasonal contrast in size distributions and mixing state of black carbon and its association with PM1.0 chemical composition from the eastern coast of India. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3965–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moteki, N.; Kondo, Y. Dependence of Laser-Induced Incandescence on Physical Properties of Black Carbon Aerosols: Measurements and Theoretical Interpretation. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, A.; Sahu, R.; Owen, D.R.; Dennis, V.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa reference strains PAO1 and PA14: A genomic, phenotypic, and therapeutic review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1023523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, H.; McMullan, R.; Filloux, A. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa Reference Strain PA14 Displays Increased Virulence Due to a Mutation in ladS. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yam, J.K.H.; Cai, Z.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, L.-H.; Deng, Y.; Yang, L. Population dynamics and transcriptomic responses of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a complex laboratory microbial community. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2019, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Byun, Y.; Park, H.-D. 6-Gingerol reduces Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and virulence via quorum sensing inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viducic, D.; Murakami, K.; Amoh, T.; Ono, T.; Miyake, Y. RpoN Promotes Pseudomonas aeruginosa Survival in the Presence of Tobramycin. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydorn, A.; Nielsen, A.T.; Hentzer, M.; Sternberg, C.; Givskov, M.; Ersbøll, B.K.; Molin, S. Quantification of biofilm structures by the novel computer program comstat. Microbiology 2000, 146, 2395–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.R.; Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 4th ed.; Ingram International Inc.: Irvine, CA, USA, 2012; p. 448. [Google Scholar]
- Bisht, K.; Moore, J.L.; Caprioli, R.M.; Skaar, E.P.; Wakeman, C.A. Impact of temperature-dependent phage expression on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaBauve, A.E.; Wargo, M.J. Growth and Laboratory Maintenance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2012, 25, 6E.1.1–6E.1.8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistelok, F.; Pohl, A.; Wiera, B.; Stuczyński, T. Using the ATP test in wastewater treatment in the Silesia Province. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2016, 42, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, S.M.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G. Firefly bioluminescence: A mechanistic approach of luciferase catalyzed reactions. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shama, G.; Malik, D.J. The uses and abuses of rapid bioluminescence-based ATP assays. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2013, 216, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LIU, W. Application of Microbiological Monitoring Techniques at Biological Wastewater Treatment Plant in CSC. CSC China Steel Technol. Rep. 2019, 32, 55–60. Available online: https://www.csc.com.tw/csc/ts/ena/pdf/no32/pages/9-Application%20of%20Microbiological%20Monitoring.pdf (accessed on 28 October 2019).
- Mo, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, J.-G.; Cao, W.; Zhang, Y. Interactions and coupling mechanisms between Anammox, partial denitrification (PD) and hydroxyapatite (HAP) biomineralization in a PD/A-HAP system. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T. Measurement of the specific surface area and particle size distribution of atmospheric aerosol reference materials. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 75, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, K.; Smernik, R.J.; Skjemstad, J.O.; Schmidt, M.W.I. Characterisation and evaluation of reference materials for black carbon analysis using elemental composition, colour, BET surface area and 13C NMR spectroscopy. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 2113–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.H.; Gbadomosi, M.; Greytak, A.B.; Myrick, M.L. Measuring the Surface Area of Carbon Black Using BET Isotherms: An Experiment in Physical Chemistry. J. Chem. Educ. 2023, 100, 4838–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouf, F.X.; Bourrous, S.; Vallières, C.; Yon, J.; Lintis, L. Specific surface area of combustion emitted particles: Impact of primary particle diameter and organic content. J. Aerosol Sci. 2019, 137, 105436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Lee, M.; Yoo, H.-J. Size distributions, mixing state, and morphology of refractory black carbon in an urban atmosphere of northeast Asia during summer. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 158436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sager, T.M.; Castranova, V. Surface area of particle administered versus mass in determining the pulmonary toxicity of ultrafine and fine carbon black: Comparison to ultrafine titanium dioxide. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2009, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortimer, M.; Devarajan, N.; Li, D.; Holden, P.A. Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Induce More Pronounced Transcriptomic Responses in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PG201 than Graphene, Exfoliated Boron Nitride, or Carbon Black. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 2728–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimova, Y.; Zorina, A.; Nesterova, L. Oxidative Stress Response and E. coli Biofilm Formation under the Effect of Pristine and Modified Carbon Nanotubes. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirzadeh, N.; Mohammadian, Y.; Rasoulzadeh, Y.; Rezazadeh Azari, M.; Khodagholi, F. Toxicity of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials in the Human Lung: A Comparative In-Vitro Study. Tanaffos 2022, 21, 391–400. Available online: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10073947/ (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Varghese, S.; Kuriakose, S.; Jose, S. Antimicrobial Activity of Carbon Nanoparticles Isolated from Natural Sources against Pathogenic Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria. J. Nanosci. 2013, 2013, 457865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ude, J.; Tripathi, V.; Buyck, J.M.; Söderholm, S.; Cunrath, O.; Fanous, J.; Claudi, B.; Egli, A.; Schleberger, C.; Hiller, S.; et al. Outer membrane permeability: Antimicrobials and diverse nutrients bypass porins in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2107644118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, E.M.; Manges, R.; Parker, G.; Stone, E.A.; Peters, T.M.; Blount, R.J.; Noriega, J.; Li, X.; Zabner, J.; Polgreen, P.M.; et al. Indoor Particulate Matter from Smoker Homes Induces Bacterial Growth, Biofilm Formation, and Impairs Airway Antimicrobial Activity. A Pilot Study. Front. Public Health 2020, 7, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, L.M.; Cavaliere, R.; Turnbull, L.; Whitchurch, C.B. Extracellular ATP inhibits twitching motility-mediated biofilm expansion by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dsane, V.F.; An, S.; Oh, T.; Hwang, J.; Choi, Y.; Choi, Y. Saline conditions effect on the performance and stress index of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing (anammox) bacteria. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz Sierra, J.D.; Oosterkamp, M.J.; Spanjers, H.; van Lier, J.B. Effects of large salinity fluctuations on an anaerobic membrane bioreactor treating phenolic wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luján-Facundo, M.J.; Fernández-Navarro, J.; Alonso-Molina, J.L.; Amorós-Muñoz, I.; Moreno, Y.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A.; Pastor-Alcañiz, L. The role of salinity on the changes of the biomass characteristics and on the performance of an OMBR treating tannery wastewater. Water Res. 2018, 142, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Elemental Composition | Mass Fraction (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement * | Measurement Uncertainty | |
| Sb | 0.0679 | 0.0030 |
| Ca | 39.5 | 2.4 |
| Cr | 0.307 | 0.014 |
| Co | 0.01996 | 0.00070 |
| Cu | 4.01 | 0.30 |
| Pb | 0.293 | 0.013 |
| Mg | 9.43 | 0.54 |
| Sn | 0.191 | 0.012 |
| Zn | 8.17 | 0.44 |
| Benz(a)anthracene | 0.494 | 0.044 |
| Benzo(a)pyrene | 0.354 | 0.032 |
| Benzo(b)fluoranthene | 1.24 | 0.12 |
| Benzo(e)pyrene | 0.89 | 0.10 |
| Benzo(ghi)perylene | 1.11 | 0.12 |
| Benzo(j)fluoranthene | 0.466 | 0.046 |
| Benzo(k)fluoranthene | 0.420 | 0.045 |
| Chrysene | 1.019 | 0.097 |
| Indeno(1,2,3-cd)pyrene | 0.742 | 0.087 |
| Triphenylene | 0.399 | 0.039 |
| Analyze | ICP/MS (g·kg−1) | WD-XRF (g·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Na | 10.7 | 13.1 |
| Al | 37.0 | 45.5 |
| K | 17.7 | 15.1 |
| Ti | - | 4.1 |
| Mn | 1.5 | 1.2 |
| Fe | 99.0 | 81.2 |
| Sample ID | Cultured Strain | Concentration (ng mL−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PM | BC | ||
| Control | PA14 | 0 | 0 |
| PM | 5 | 0 | |
| PM + BC5 | 5 | 5 | |
| PM + BC10 | 5 | 10 | |
| PM + BC20 | 5 | 20 | |
| PM + BC30 | 5 | 30 | |
| PM + BC40 | 5 | 40 | |
| PM + BC50 | 5 | 50 | |
| PM + BC75 | 5 | 75 | |
| PM + BC100 | 5 | 100 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoo, H.; Lim, S.; Cho, I.S.; Im, H.; Lee, E.; Choi, S.; Kim, H.-S.; Jeong, S.; Choi, Y. Inhibitory Effects of Aquadag, a Black Carbon Surrogate, on Microbial Growth via Surface-Mediated Stress: Evidence from Adenosine Triphosphate Assay. Toxics 2025, 13, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090719
Yoo H, Lim S, Cho IS, Im H, Lee E, Choi S, Kim H-S, Jeong S, Choi Y. Inhibitory Effects of Aquadag, a Black Carbon Surrogate, on Microbial Growth via Surface-Mediated Stress: Evidence from Adenosine Triphosphate Assay. Toxics. 2025; 13(9):719. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090719
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoo, Hwangyu, Saehee Lim, I Seul Cho, Haneul Im, Euna Lee, Siyoung Choi, Han-Suk Kim, Sohee Jeong, and Younggyun Choi. 2025. "Inhibitory Effects of Aquadag, a Black Carbon Surrogate, on Microbial Growth via Surface-Mediated Stress: Evidence from Adenosine Triphosphate Assay" Toxics 13, no. 9: 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090719
APA StyleYoo, H., Lim, S., Cho, I. S., Im, H., Lee, E., Choi, S., Kim, H.-S., Jeong, S., & Choi, Y. (2025). Inhibitory Effects of Aquadag, a Black Carbon Surrogate, on Microbial Growth via Surface-Mediated Stress: Evidence from Adenosine Triphosphate Assay. Toxics, 13(9), 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13090719









