Presence of Micro- and Nanoplastics Affects Degradation of Chlorinated Solvents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of MP and NP Suspension Solutions
2.3. SDC-9 Culture and Growth Conditions
2.4. RDX Cultures and Growth Conditions
2.5. Adsorption/Desorption Experiment Setup
2.6. Impact of MPs and NPs on Reductive Dechlorination
2.7. Effect of MP and NP Presence on RDX Degradation
2.8. Analytical and Statistical Procedures
2.9. Quantitative Proteomics (qProt)
2.10. DNA Extraction and Quantitative PCR
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sorption/Desorption Studies
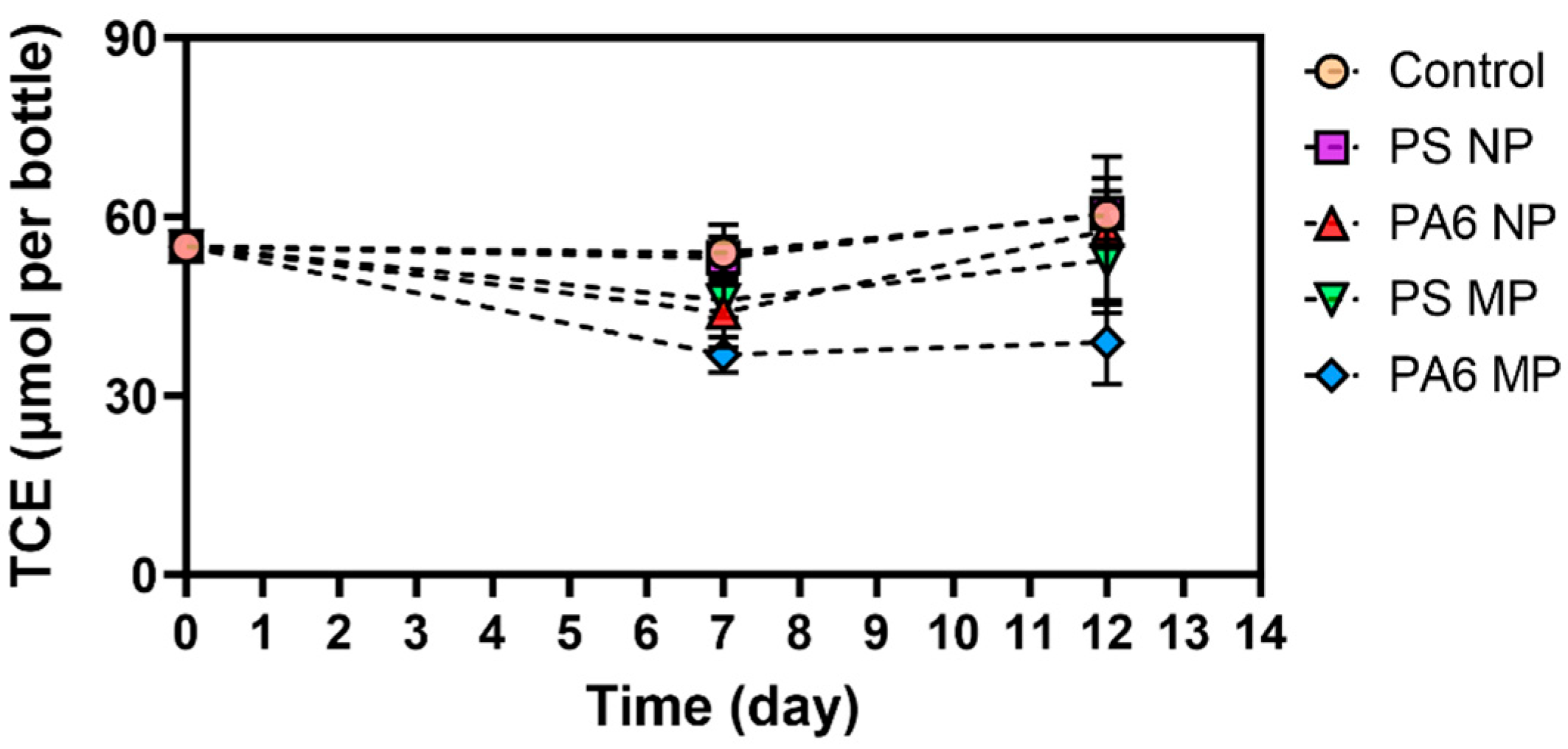
3.2. Presence of Plastic Particles Inhibits CVOC Degradation
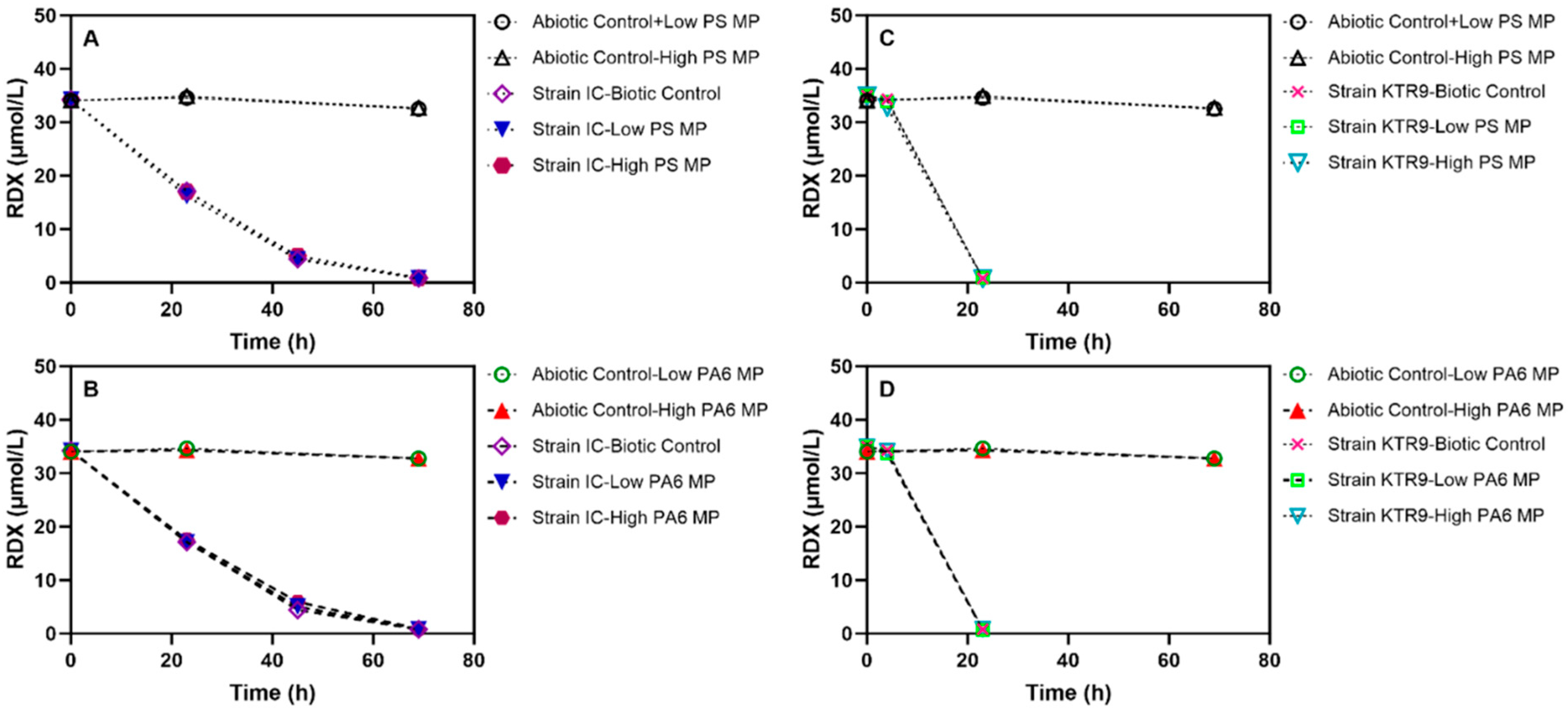
3.3. Presence of Plastic Particles Has No Effect on RDX Degradation
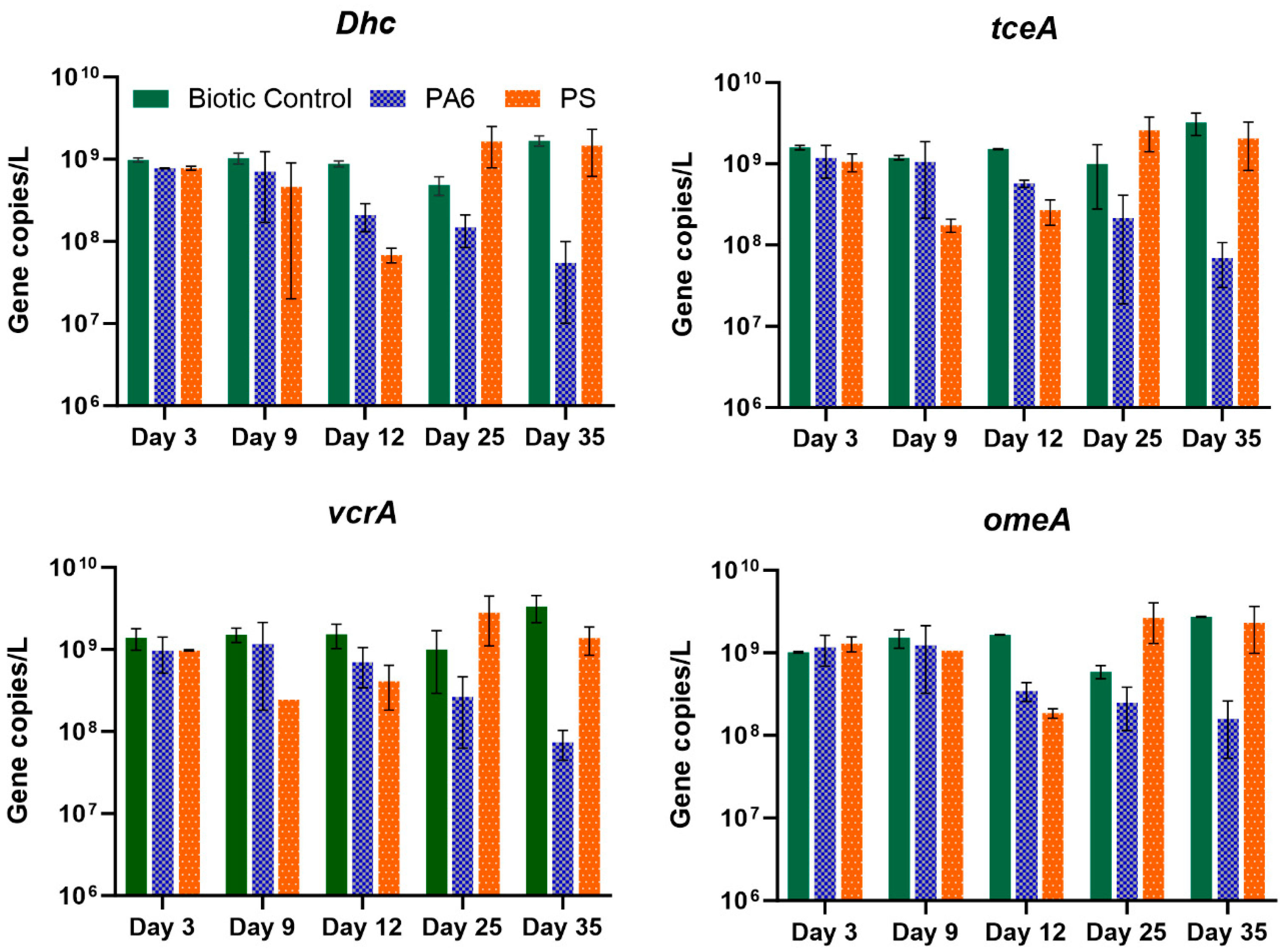
3.4. Effects of Plastic Particles on Dhc Abundance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Li, P.; Karunanidhi, D.; Subramani, T.; Srinivasamoorthy, K. Sources and consequences of groundwater contamination. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.S.; Morley, M.C.; Snow, D.D. Anaerobic biodegradation of RDX and TCE: Single-and dual-contaminant batch tests. Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste Manag. 2006, 10, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Sung, Y.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R.; Ritalahti, K.M.; Löffler, F.E. Isolation and characterization of Dehalococcoides sp. strain FL2, a trichloroethene (TCE)-and 1,2-dichloroethene-respiring anaerobe. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajmalnik-Brown, R.; Hölscher, T.; Thomson, I.N.; Saunders, F.M.; Ritalahti, K.M.; Löffler, F.E. Genetic Identification of a Putative Vinyl Chloride Reductase in Dehalococcoides sp. Strain BAV1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6347–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chin, Y.; Yang, H.; Lu, C.; Liu, M. Cometabolic biodegradation of chlorinated ethenes with methanotrophs in anaerobic/aerobic simulated aquifer. J. Environ. Biol. 2021, 42, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, M.E.; Hatzinger, P.B.; Condee, C.W.; Andaya, C.; Vainberg, S.; Michalsen, M.M.; Crocker, F.H.; Indest, K.J.; Jung, C.M.; Eaton, H. Laboratory evaluation of bioaugmentation for aerobic treatment of RDX in groundwater. Biodegradation 2015, 26, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, D.; Halasz, A.; Spain, J.; Spanggord, R.J.; Bottaro, J.C.; Hawari, J. Biodegradation of the hexahydro-1, 3, 5-trinitro-1, 3, 5-triazine ring cleavage product 4-nitro-2, 4-diazabutanal by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1123–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halasz, A.; Hawari, J. Degradation routes of RDX in various redox systems. In Aquatic Redox Chemistry; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 441–462. [Google Scholar]
- Halasz, A.; Spain, J.; Paquet, L.; Beaulieu, C.; Hawari, J. Insights into the formation and degradation mechanisms of methylenedinitramine during the incubation of RDX with anaerobic sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylott, E.L.; Jackson, R.G.; Edwards, J.; Womack, G.L.; Seth-Smith, H.M.B.; Rathbone, D.A.; Strand, S.E.; Bruce, N.C. An explosive-degrading cytochrome P450 activity and its targeted application for the phytoremediation of RDX. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, M.E.; McClay, K.; Hawari, J.; Paquet, L.; Malone, T.E.; Fox, B.G.; Steffan, R.J. Transformation of RDX and other energetic compounds by xenobiotic reductases XenA and XenB. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, C.; Shen, C.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, D. Effect of microplastics on microbial dechlorination of a polychlorinated biphenyl mixture (Aroclor 1260). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, G.; Zhao, S.; Chen, C.; Rogers, M.J.; He, J. Mechanistic and microbial ecological insights into the impacts of micro-and nano-plastics on microbial reductive dehalogenation of organohalide pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 448, 130895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosato, A.; Barone, M.; Negroni, A.; Brigidi, P.; Fava, F.; Xu, P.; Candela, M.; Zanaroli, G. Microbial colonization of different microplastic types and biotransformation of sorbed PCBs by a marine anaerobic bacterial community. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basumatary, T.; Biswas, D.; Boro, S.; Nava, A.R.; Narayan, M.; Sarma, H. Dynamics and Impacts of Microplastics (MPs) and Nanoplastics (NPs) on Ecosystems and Biogeochemical Processes: The Need for Robust Regulatory Frameworks. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 17051–17069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aralappanavar, V.K.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Bhatnagar, A.; Praveena, S.M.; Li, Y.; Paller, M.; Adyel, T.M.; Rinklebe, J.; et al. Effects of microplastics on soil microorganisms and microbial functions in nutrients and carbon cycling—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynaud, S.; Aynard, A.; Grassl, B.; Gigault, J. Nanoplastics: From model materials to colloidal fate. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 57, 101528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, E.; Zarfl, C. Sorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) to low and high density polyethylene (PE). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näkki, P.; Eronen-Rasimus, E.; Kaartokallio, H.; Kankaanpää, H.; Setälä, O.; Vahtera, E.; Lehtiniemi, M. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon sorption and bacterial community composition of biodegradable and conventional plastics incubated in coastal sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 143088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hoh, E.; Hentschel, B.T.; Kaye, S. Long-term field measurement of sorption of organic contaminants to five types of plastic pellets: Implications for plastic marine debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, L.; Zhao, X.; Song, K. An evaluation of the effects of nanoplastics on the removal of activated-sludge nutrients and production of short chain fatty acid. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 148, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; He, Q.; Guo, F.; Sun, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Vymazal, J.; Chen, Y. Nanoplastics disturb nitrogen removal in constructed wetlands: Responses of microbes and macrophytes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14007–14016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Huang, Q.-S.; Sun, J.; Dai, X.; Ni, B.-J. Revealing the mechanisms of polyethylene microplastics affecting anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9604–9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, L.; Cheng, Z.; Yao, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wang, L.; Sun, H. LDPE microplastics affect soil microbial communities and nitrogen cycling. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.-W.; Lee, E.-H. Interactions between bacteria and nano (micro)-sized polystyrene particles by bacterial responses and microscopy. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, J.; De, J.; Sur, S.; Banerjee, P. Interaction of Microbes with Microplastics and Nanoplastics in the Agroecosystems—Impact on Antimicrobial Resistance. Pathogens 2023, 12, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Dai, W.; Luan, Y. Bacterial Interactions with Nanoplastics and the Environmental Effects They Cause. Fermentation 2023, 9, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, B.; Li, Q.; Liu, N.; Xia, B.; Zhu, L.; Qu, K. Toxicities of polystyrene nano-and microplastics toward marine bacterium Halomonas alkaliphila. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okshevsky, M.; Gautier, E.; Farner, J.M.; Schreiber, L.; Tufenkji, N. Biofilm formation by marine bacteria is impacted by concentration and surface functionalization of polystyrene nanoparticles in a species-specific manner. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2020, 12, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Qian, H.; Cui, T.; Ren, Z.; Wang, X. Comprehensive meta-analysis reveals the impact of non-biodegradable plastic pollution on methane production in anaerobic digestion. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.M.M.; Hai, F.I.; Lu, W.; Al-Mamun, A.; Dhar, B.R. A review of mechanisms underlying the impacts of (nano) microplastics on anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 329, 124894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xu, G.; Zhao, S.; He, J. Resilience and functional redundancy of methanogenic digestion microbiome safeguard recovery of methanogenesis activity under the stress induced by microplastics. Mlife 2023, 2, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busch, P.L.; Stumm, W. Chemical interactions in the aggregation of bacteria bioflocculation in waste treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1968, 2, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Q.; Wang, D.; An, J.; Ding, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Wu, F.; You, J. Combined effects of nanosized polystyrene and erythromycin on bacterial growth and resistance mutations in Escherichia coli. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.T. The fate of microplastic in marine sedimentary environments: A review and synthesis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mammo, F.; Amoah, I.; Gani, K.; Pillay, L.; Ratha, S.; Bux, F.; Kumari, S. Microplastics in the environment: Interactions with microbes and chemical contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespy, D.; Landfester, K. Preparation of nylon 6 nanoparticles and nanocapsules by two novel miniemulsion/solvent displacement hybrid techniques. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2007, 208, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Gui, X.; Xu, X.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, H.; Cao, X. Microplastics in the soil-groundwater environment: Aging, migration, and co-transport of contaminants–a critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, R. Long-term effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on nitrogen and phosphorus removal from wastewater and bacterial community shift in activated sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7284–7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainberg, S.; Mcclay, K.; Schaefer, C.; Steffan, R. Dechlorination of mixed chlorinated solvents by a commercially available culture. In Proceedings of the 9th International In Situ and On-Site Bioremediation Symposium, Baltimore, MD, USA, 7–10 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, C.E.; Condee, C.W.; Vainberg, S.; Steffan, R.J. Bioaugmentation for chlorinated ethenes using Dehalococcoides sp.: Comparison between batch and column experiments. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzyk, K.H.; Meisel, J.E.; Kara-Murdoch, F.; Murdoch, R.W.; Higgins, S.A.; Vainberg, S.; Bartling, C.M.; Mullins, L.; Hatzinger, P.B.; Löffler, F.E. Metagenome-Guided Proteomic Quantification of Reductive Dehalogenases in the Dehalococcoides mccartyi-Containing Consortium SDC-9. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 1812–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritalahti, K.M.; Amos, B.K.; Sung, Y.; Wu, Q.; Koenigsberg, S.S.; Löffler, F.E. Quantitative PCR targeting 16S rRNA and reductive dehalogenase genes simultaneously monitors multiple Dehalococcoides strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2765–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.T.; Crocker, F.H.; Fredrickson, H.L. Mineralization of the cyclic nitramine explosive hexahydro-1, 3, 5-trinitro-1, 3, 5-triazine by Gordonia and Williamsia spp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8265–8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hareland, W.A.; Crawford, R.L.; Chapman, P.J.; Dagley, S. Metabolic function and properties of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid 1-hydroxylase from Pseudomonas acidovorans. J. Bacteriol. 1975, 121, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cápiro, N.L.; Marcet, T.F.; Yan, J.; Pennell, K.D.; Löffler, F.E. Organohalide respiration with chlorinated ethenes under low pH conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8579–8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, M.E.; Farquharson, E.M.; Hedman, P.C.; Chiu, P. Removal of munition constituents in stormwater runoff: Screening of native and cationized cellulosic sorbents for removal of insensitive munition constituents NTO, DNAN, and NQ, and legacy munition constituents HMX, RDX, TNT, and perchlorate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalsen, M.M.; Kara Murdoch, F.; Löffler, F.E.; Wilson, J.; Hatzinger, P.B.; Istok, J.D.; Mullins, L.; Hill, A.; Murdoch, R.W.; Condee, C. Quantitative Proteomics and Quantitative PCR as Predictors of cis-1, 2-Dichlorethene and Vinyl Chloride Reductive Dechlorination Rates in Bioaugmented Aquifer Microcosms. ACS EST Eng. 2021, 2, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalsen, M.; Kucharzyk, K.; Bartling, C.; Meisel, J.; Hatzinger, P.; Wilson, J.; Solutions, S.E.; Istok, L.J.; Murdoch, F.K.; Löffler, F. Validation of Advanced Molecular Biological Tools to Monitor Chlorinated Solvent Bioremediation and Estimate cVOC Degradation Rates. No. ER201726. 24 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Avila, M.A.S.; Breiter, R. Competitive sorption of cis-DCE and TCE in silica gel as a model porous mineral solid. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Luan, Y.; Dai, W. Adsorption behavior of organic pollutants on microplastics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 217, 112207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Sonne, C.; Brown, R.J.; Younis, S.A.; Kim, K.-H. Adsorption of environmental contaminants on micro-and nano-scale plastic polymers and the influence of weathering processes on their adsorptive attributes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 427, 127903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusseau, M.L.; Rao, P.S.C.; Gillham, R.W. Sorption nonideality during organic contaminant transport in porous media. Crit. Rev. Environ. Control. 1989, 19, 33–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velzeboer, I.; Kwadijk, C.J.A.F.; Koelmans, A.A. Strong Sorption of PCBs to Nanoplastics, Microplastics, Carbon Nanotubes, and Fullerenes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4869–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Dolan, M.E.; Semprini, L. Kinetics and Inhibition of Reductive Dechlorination of Chlorinated Ethylenes by Two Different Mixed Cultures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffler, F.E.; Ritalahti, K.M.; Tiedje, J.M. Dechlorination of chloroethenes is inhibited by 2-bromoethanesulfonate in the absence of methanogens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 4982–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natesan, U.; Vaikunth, R.; Kumar, P.; Ruthra, R.; Srinivasalu, S. Spatial distribution of microplastic concentration around landfill sites and its potential risk on groundwater. Chemosphere 2021, 277, 130263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Mohamed Nor, N.H.; Hermsen, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.M.; De France, J. Microplastics in freshwaters and drinking water: Critical review and assessment of data quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, S.; Mai, L.; Jeong, C.-B.; Lee, J.-S.; Zeng, E.Y.; Xu, E.G. Key mechanisms of micro-and nanoplastic (MNP) toxicity across taxonomic groups. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 247, 109056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-Q.; Li, Z.-L.; Wu, B.; Jin, Y.-R.; Cao, D.; Nan, J.; Chen, X.-Q.; Liu, W.-Z.; Gao, S.-H.; Wang, A.-J. Insights into the influence on 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol microbial reductive dechlorination process by exposure to microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.-H.; Reuther, J.; Liu, J.; Crocker, F.H.; Indest, K.J.; Eltis, L.D.; Mohn, W.W. The essential role of nitrogen limitation in expression of xplA and degradation of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) in Gordonia sp. strain KTR9. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickson, E.R.; Payne, J.A.; Young, R.M.; Starr, M.G.; Perry, M.P.; Fahnestock, S.; Ellis, D.E.; Ebersole, R.C. Molecular analysis of Dehalococcoides 16S ribosomal DNA from chloroethene-contaminated sites throughout North America and Europe. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, H.; Kanitkar, Y.H.; Stedtfeld, R.D.; Hatzinger, P.B.; Hashsham, S.A.; Cupples, A.M. Abundance of chlorinated solvent and 1, 4-dioxane degrading microorganisms at five chlorinated solvent contaminated sites determined via shotgun sequencing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13914–13924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygin, H.; Baysal, A. Biofilm formation of clinically important bacteria on bio-based and conventional micro/submicron-sized plastics. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 105, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, D.E.; Carroll, A.B.; Gossett, J.M.; Zinder, S.H. Assessment of indigenous reductive dechlorinating potential at a TCE-contaminated site using microcosms, polymerase chain reaction analysis, and site data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1830–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkness, M.R.; Bracco, A.A.; Brennan, M.J.; DeWeerd, K.A.; Spivack, J.L. Use of bioaugmentation to stimulate complete reductive dechlorination of trichloroethene in Dover soil columns. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhamel, M.; Wehr, S.D.; Yu, L.; Rizvi, H.; Seepersad, D.; Dworatzek, S.; Cox, E.E.; Edwards, E.A. Comparison of anaerobic dechlorinating enrichment cultures maintained on tetrachloroethene, trichloroethene, cis-dichloroethene and vinyl chloride. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4193–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R.; Fung, J.; Rahm, B.; Zhang, S.; Freedman, D.; Zinder, S.; Richardson, R. Comparative proteomics of Dehalococcoides spp. reveals strain-specific peptides associated with activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Wang, J.; Villalobos Solis, M.I.; Jin, H.; Chourey, K.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Hettich, R.L.; Löffler, F.E. Respiratory vinyl chloride reductive dechlorination to ethene in TceA-expressing Dehalococcoides mccartyi. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4831–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson Jon, K.; Romine Margaret, F.; Burris David, R.; Kingsley Mark, T. Trichloroethene Reductive Dehalogenase fromDehalococcoides ethenogenes: Sequence of tceA and Substrate Range Characterization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 5141–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijenhuis, I.; Zinder Stephen, H. Characterization of Hydrogenase and Reductive Dehalogenase Activities of Dehalococcoides ethenogenes Strain 195. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1664–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kara Murdoch, F.; Sun, Y.; Fuller, M.E.; Mullins, L.; Hill, A.; Lilly, J.; Wilson, J.; Löffler, F.E.; Kucharzyk, K.H. Presence of Micro- and Nanoplastics Affects Degradation of Chlorinated Solvents. Toxics 2025, 13, 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080656
Kara Murdoch F, Sun Y, Fuller ME, Mullins L, Hill A, Lilly J, Wilson J, Löffler FE, Kucharzyk KH. Presence of Micro- and Nanoplastics Affects Degradation of Chlorinated Solvents. Toxics. 2025; 13(8):656. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080656
Chicago/Turabian StyleKara Murdoch, Fadime, Yanchen Sun, Mark E. Fuller, Larry Mullins, Amy Hill, Jacob Lilly, John Wilson, Frank E. Löffler, and Katarzyna H. Kucharzyk. 2025. "Presence of Micro- and Nanoplastics Affects Degradation of Chlorinated Solvents" Toxics 13, no. 8: 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080656
APA StyleKara Murdoch, F., Sun, Y., Fuller, M. E., Mullins, L., Hill, A., Lilly, J., Wilson, J., Löffler, F. E., & Kucharzyk, K. H. (2025). Presence of Micro- and Nanoplastics Affects Degradation of Chlorinated Solvents. Toxics, 13(8), 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080656







