Visceral, Neural, and Immunotoxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Mini Review
Abstract
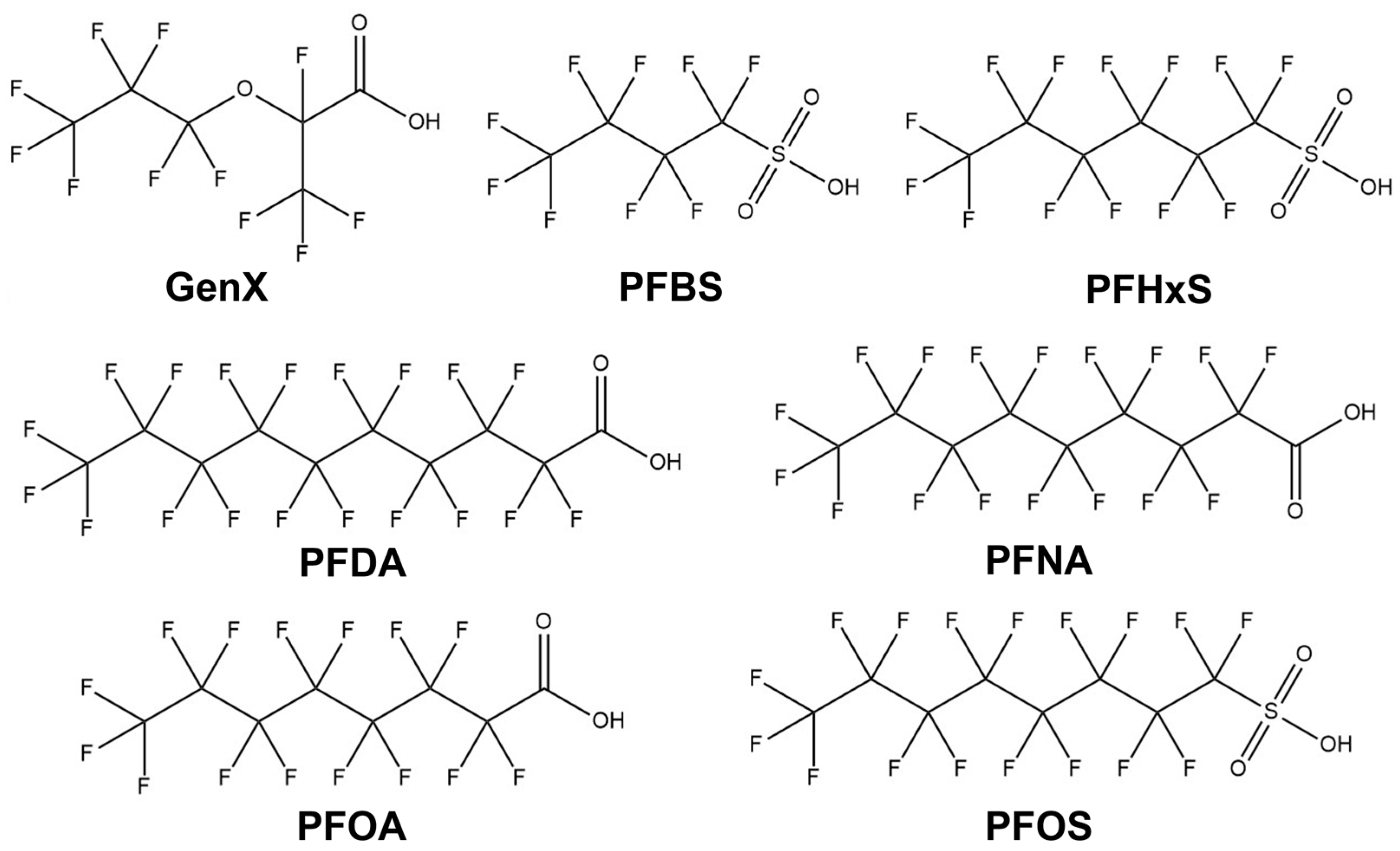
1. Introduction
2. Visceral Toxicity
2.1. Hepatotoxicity
2.2. Kidney Toxicity
2.3. Cardiovascular Impacts
3. Neurotoxicity
4. Immunotoxicity
Co-Exposure Toxicology with Other Contaminants
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liljestrand, C.T. PFAS Exposure: A Comprehensive Look at Emerging Facts and Studies, Risk and Liability Assessment, Litigation History, Evolving Regulations and Future Predictions. Def. Couns. J. 2022, 89, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Lyons, C. Stain Resistant, Nonstick, Waterproof, and Lethal; Praeger: Westport, CT, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Brennan, N.M.; Evans, A.T.; Fritz, M.K.; Peak, S.A.; von Holst, H.E. Trends in the regulation of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A scoping review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, S. 3M knew about the dangers of PFOA and PFOS decades ago, internal documents show. Intercept 2018, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Grandjean, P.; Clapp, R. Perfluorinated Alkyl Substances: Emerging Insights into Health Risks. New Solut. 2015, 25, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, L.G. Historical and current usage of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A literature review. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2023, 66, 353–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, J.A.; Sharp, E.; Yi, S.; Leitao, E.M.; Padhye, L.P.; Kah, M.; Chen, J.L.-Y.; Gobindlal, K. Public perceptions of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): Psycho-demographic characteristics differentiating PFAS knowledge and concern. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 442, 140866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Place, B.J.; Field, J.A. Identification of novel fluorochemicals in aqueous film-forming foams used by the US military. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7120–7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Reconciling terminology of the universe of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances: Recommendations and practical guidance. Ser. Risk Manag. 2021, 61, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, K.; Wong, L.-Y.; Jia, L.T.; Kuklenyik, Z.; Calafat, A.M. Trends in exposure to polyfluoroalkyl chemicals in the US population: 1999–2008. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8037–8045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharal, B.; Ruchitha, C.; Kumar, P.; Pandey, R.; Rachamalla, M.; Niyogi, S.; Naidu, R.; Kaundal, R.K. Neurotoxicity of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances: Evidence and future directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 176941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebe, G.O.; Anyaogu, E.V.; Ntomchukwu, A.D.A.R.C.; Oghenerhoro, S.O.; Jonathan, O.E. Health impacts and mechanisms of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from epidemiological to toxicological. J. Biosci. Med. 2023, 11, 218–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.S.; Yun, X.; McKenzie, E.R.; Heron, C.G.; Field, J.A.; Salice, C.J. Spatial and temporal variability of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in environmental media of a small pond: Toward an improved understanding of PFAS bioaccumulation in fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelch, K.E.; McKnight, T.; Reade, A. 70 analyte PFAS test method highlights need for expanded testing of PFAS in drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwichtenberg, T.; Bogdan, D.; Carignan, C.C.; Reardon, P.; Rewerts, J.; Wanzek, T.; Field, J.A. PFAS and dissolved organic carbon enrichment in surface water foams on a northern US freshwater lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14455–14464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, T.; Bond, D.; Foley, J. PFAS soil and groundwater contamination via industrial airborne emission and land deposition in SW Vermont and Eastern New York State, USA. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2021, 23, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusseau, M.L.; Anderson, R.H.; Guo, B. PFAS concentrations in soils: Background levels versus contaminated sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ren, C.; Wang, B.; Sun, H.; Alder, A.C.; Kannan, K. Multimedia distribution and transfer of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) surrounding two fluorochemical manufacturing facilities in Fuxin, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8263–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chang, S.; Sun, H.; Gan, Z.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Neutral and ionic per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in atmospheric and dry deposition samples over a source region (Tianjin, China). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambro, E.L.; Pye, H.O.; Bash, J.O.; Bowyer, J.; Allen, C.; Efstathiou, C.; Gilliam, R.C.; Reynolds, L.; Talgo, K.; Murphy, B.N. Characterizing the air emissions, transport, and deposition of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances from a fluoropolymer manufacturing facility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.B.; Conder, J.M.; Arblaster, J.A.; Higgins, C.P. Assessing human health risks from per-and polyfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS)-impacted vegetable consumption: A tiered modeling approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15202–15214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göckener, B.; Weber, T.; Rüdel, H.; Bücking, M.; Kolossa-Gehring, M. Human biomonitoring of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in German blood plasma samples from 1982 to 2019. Environ. Int. 2020, 145, 106123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunen, L.; Bervoets, L.; Belpaire, C.; De Jonge, M.; Groffen, T. PFAS accumulation in indigenous and translocated aquatic organisms from Belgium, with translation to human and ecological health risk. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Langberg, H.A.; Hale, S.E.; Kallenborn, R.; Hartz, W.F.; Mortensen, Å.-K.; Ciesielski, T.M.; McDonough, C.A.; Jenssen, B.M.; Breedveld, G.D. The fate of poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances in a marine food web influenced by land-based sources in the Norwegian Arctic. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2021, 23, 588–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiano, M.; Angelier, F.; Blévin, P.; Ribout, C.; Sagerup, K.; Descamps, S.; Herzke, D.; Moe, B.; Barbraud, C.; Bustnes, J.O. Exposure to PFAS is associated with telomere length dynamics and demographic responses of an arctic top predator. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10217–10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiano, M.; Jouanneau, W.; Blévin, P.; Angelier, F.; Parenteau, C.; Pallud, M.; Ribout, C.; Gernigon, J.; Lemesle, J.; Robin, F. Physiological effects of PFAS exposure in seabird chicks: A multi-species study of thyroid hormone triiodothyronine, body condition and telomere length in South Western France. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 165920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hearon, S.E.; Orr, A.A.; Moyer, H.; Wang, M.; Tamamis, P.; Phillips, T.D. Montmorillonite clay-based sorbents decrease the bioavailability of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from soil and their translocation to plants. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, Y.; Lu, H.; Grieger, K.D.; Munoz, G.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; He, Q.; Qian, S. Bioaccumulation and translocation of 6: 2 fluorotelomer sulfonate, GenX, and perfluoroalkyl acids by urban spontaneous plants. ACS EST Eng. 2022, 2, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.D.; Reh, C.M.; Breysse, P. Advancing per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) research: An overview of ATSDR and NCEH activities and recommendations. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2021, 31, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glüge, J.; Scheringer, M.; Cousins, I.T.; DeWitt, J.C.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lohmann, R.; Ng, C.A.; Trier, X.; Wang, Z. An overview of the uses of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 2345–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.-M.; Chen, D.; Han, F.-J.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, F. A short review on human exposure to and tissue distribution of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosato, I.; Bonato, T.; Fletcher, T.; Batzella, E.; Canova, C. Estimation of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) half-lives in human studies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2023, 242, 117743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, G.W.; Burris, J.M.; Ehresman, D.J.; Froehlich, J.W.; Seacat, A.M.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Zobel, L.R. Half-life of serum elimination of perfluorooctanesulfonate, perfluorohexanesulfonate, and perfluorooctanoate in retired fluorochemical production workers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batzella, E.; Rosato, I.; Pitter, G.; Da Re, F.; Russo, F.; Canova, C.; Fletcher, T. Determinants of PFOA serum half-life after end of exposure: A longitudinal study on highly exposed subjects in the Veneto region. Environ. Health Perspect. 2024, 132, 027002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radke, E.G.; Wright, J.M.; Christensen, K.; Lin, C.J.; Goldstone, A.E.; Lemeris, C.; Thayer, K.A. Epidemiology evidence for health effects of 150 per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances: A systematic evidence map. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 096003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, K.; Yang, Z.; Agarwal, M.; Liu, W.; Peng, Z.; Long, Z.; Birbeck, J.; Westrick, J.; Liu, W.; Petriello, M.C. Exposure to a mixture of legacy, alternative, and replacement per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) results in sex-dependent modulation of cholesterol metabolism and liver injury. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown-Leung, J.M.; Cannon, J.R. Neurotransmission targets of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substance neurotoxicity: Mechanisms and potential implications for adverse neurological outcomes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 35, 1312–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, J.J.; Callahan, C.L.; Calafat, A.M.; Huang, W.-Y.; Jones, R.R.; Sabbisetti, V.S.; Freedman, N.D.; Sampson, J.N.; Silverman, D.T.; Purdue, M.P. Serum concentrations of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances and risk of renal cell carcinoma. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 113, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Fisher, J.A.; VoPham, T.; Vasiliou, V.; Jones, R.R. Associations between per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances, liver function, and daily alcohol consumption in a sample of US adults. Environ. Res. 2023, 235, 116651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzanová, B.; Thon, V.c.; Vespalcová, H.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Piler, P.; Zvonař, M.; Klánová, J.; Bláha, L.k.; Adamovsky, O. Altered Transcriptome Response in PBMCs of Czech Adults Linked to Multiple PFAS Exposure: B Cell Development as a Target of PFAS Immunotoxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneguzzi, A.; Fava, C.; Castelli, M.; Minuz, P. Exposure to perfluoroalkyl chemicals and cardiovascular disease: Experimental and epidemiological evidence. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 706352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imir, O.B.; Kaminsky, A.Z.; Zuo, Q.-Y.; Liu, Y.-J.; Singh, R.; Spinella, M.J.; Irudayaraj, J.; Hu, W.-Y.; Prins, G.S.; Madak Erdogan, Z. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substance exposure combined with high-fat diet supports prostate cancer progression. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.M.; Zhang, S.; Hoffman, K.; Miranda, M.L.; Stapleton, H.M. Concentrations of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in human placental tissues and associations with birth outcomes. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.Q.Y.; Guo, T.L. Interaction between Per-and Polyfluorinated Substances (PFAS) and Acetaminophen in Disease Exacerbation—Focusing on Autism and the Gut–Liver–Brain Axis. Toxics 2024, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Rashid, F.; Fazal, Z.; Singh, R.; Spinella, M.J.; Irudayaraj, J. Nephrotoxicity of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS)—Effect on transcription and epigenetic factors. Environ. Epigenetics 2022, 8, dvac010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Yan, S.; Wang, P.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Cui, J.; Liang, Y.; Ren, S.; Gao, Y. Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) exposure in relation to the kidneys: A review of current available literature. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1103141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyyedsalehi, M.S.; Boffetta, P. Per-and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) exposure and risk of kidney, liver, and testicular cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. La Med. Del Lav. 2023, 114, e2023040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Ren, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, H.; Wang, L. Rutin ameliorate PFOA induced renal damage by reducing oxidative stress and improving lipid metabolism. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2024, 123, 109501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrabadi, F.; Alarcan, J.; Sprenger, H.; Braeuning, A.; Buhrke, T. Impact of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and PFAS mixtures on lipid metabolism in differentiated HepaRG cells as a model for human hepatocytes. Arch. Toxicol. 2024, 98, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, L.; Xu, H. Dietary exposure to per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances: Potential health impacts on human liver. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, N.; Dai, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Chen, D. Occurrence and distribution of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in human livers with liver cancer. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Pan, K.; Xu, S.; Wang, L. Dual-channel recognition of human serum albumin and glutathione by fluorescent probes with site-dependent responsive features. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 12391–12397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Death, C.; Bell, C.; Champness, D.; Milne, C.; Reichman, S.; Hagen, T. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in livestock and game species: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 144795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassler, J.; Ducatman, A.; Elliott, M.; Wen, S.; Wahlang, B.; Barnett, J.; Cave, M.C. Environmental perfluoroalkyl acid exposures are associated with liver disease characterized by apoptosis and altered serum adipocytokines. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solan, M.E.; Schackmuth, B.; Bruce, E.D.; Pradhan, S.; Sayes, C.M.; Lavado, R. Effects of short-chain per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) on toxicologically relevant gene expression profiles in a liver-on-a-chip model. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 337, 122610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, A.-C.; Plinsch, C.; Braeuning, A.; Buhrke, T. Activation of human nuclear receptors by perfluoroalkylated substances (PFAS). Toxicol. Vitr. 2020, 62, 104700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.M.; Roberts, S.M.; Gordon, D.S.; Stuchal, L.D. Derivation of a chronic reference dose for perfluorohexane sulfonate (PFHxS) for reproductive toxicity in mice. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 108, 104452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.; Qadri, S.; Luukkonen, P.K.; Ragnarsdottir, O.; McGlinchey, A.; Jäntti, S.; Juuti, A.; Arola, J.; Schlezinger, J.J.; Webster, T.F. Exposure to environmental contaminants is associated with altered hepatic lipid metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, V.; Cengo, A.; Gehres, F.; Sijm, D.; Vrolijk, M. Investigating the cytotoxicity of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in HepG2 cells: A structure-activity relationship approach. Toxicology 2022, 480, 153312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.R.; Reed, J.C. Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 1998, 281, 1309–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, A.F.; Xia, Q.; Peng, C.; Ng, J.C. Evaluation of the individual and combined toxicity of perfluoroalkyl substances to human liver cells using biomarkers of oxidative stress. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.J.; Pyo, M.C.; Park, Y.; Kim, B.Y.; Lee, K.-W. Hexafluoropropylene oxide dimer acid (GenX) exposure induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florentin, A.; Deblonde, T.; Diguio, N.; Hautemaniere, A.; Hartemann, P. Impacts of two perfluorinated compounds (PFOS and PFOA) on human hepatoma cells: Cytotoxicity but no genotoxicity? Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2011, 214, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, A.F.; Peng, C.; Ng, J.C. Combined effects and toxicological interactions of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances mixtures in human liver cells (HepG2). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruge, K.S.; Manage, P.M.; Yamanaka, N.; Miyazaki, S.; Taniyasu, S.; Yamashita, N. Species-specific concentrations of perfluoroalkyl contaminants in farm and pet animals in Japan. Chemosphere 2008, 73, S210–S215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestergren, R.; Orata, F.; Berger, U.; Cousins, I.T. Bioaccumulation of perfluoroalkyl acids in dairy cows in a naturally contaminated environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7959–7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Rogers, J.M. The developmental toxicity of perfluoroalkyl acids and their derivatives. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 198, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crebelli, R.; Caiola, S.; Conti, L.; Cordelli, E.; De Luca, G.; Dellatte, E.; Eleuteri, P.; Iacovella, N.; Leopardi, P.; Marcon, F. Can sustained exposure to PFAS trigger a genotoxic response? A comprehensive genotoxicity assessment in mice after subacute oral administration of PFOA and PFBA. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 106, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attema, B.; Janssen, A.W.; Rijkers, D.; van Schothorst, E.M.; Hooiveld, G.J.; Kersten, S. Exposure to low-dose perfluorooctanoic acid promotes hepatic steatosis and disrupts the hepatic transcriptome in mice. Mol. Metab. 2022, 66, 101602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ling, X.; He, S.; Cui, H.; Yang, Z.; An, H.; Wang, L.; Zou, P.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J. PPARα/ACOX1 as a novel target for hepatic lipid metabolism disorders induced by per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances: An integrated approach. Environ. Int. 2023, 178, 108138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, E.; Rock, S.; Stratakis, N.; Eckel, S.P.; Walker, D.I.; Valvi, D.; Cserbik, D.; Jenkins, T.; Xanthakos, S.A.; Kohli, R. Exposure to per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances and markers of liver injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 046001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintz, M.M.; Chappell, G.A.; Thompson, C.M.; Haws, L.C. Evaluation of transcriptomic responses in livers of mice exposed to the short-chain PFAS compound HFPO-DA. Front. Toxicol. 2022, 4, 937168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robarts, D.R.; Paine-Cabrera, D.; Kotulkar, M.; Venneman, K.K.; Gunewardena, S.; Foquet, L.; Bial, G.; Apte, U. Identifying novel mechanisms of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substance-induced hepatotoxicity using FRG humanized mice. Arch. Toxicol. 2024, 98, 3063–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Hinton, P.; Chen, J.; Jiang, J. Causal inference for the effect of environmental chemicals on chronic kidney disease. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Levin, A.; Coresh, J.; Rossert, J.; Zeeuw, D.D.; Hostetter, T.H.; Lameire, N.; Eknoyan, G. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: A position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.-I.D.; Cardenas, A.; Hauser, R.; Gold, D.R.; Kleinman, K.P.; Hivert, M.-F.; Calafat, A.M.; Webster, T.F.; Horton, E.S.; Oken, E. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances and kidney function: Follow-up results from the Diabetes Prevention Program trial. Environ. Int. 2021, 148, 106375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, M.; Kresna, A. Chronic Kidney Disease Among Workers Exposed To Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA). Indones. J. Community Occup. Med. 2021, 1, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Cancer Society. What Is Kidney Cancer? Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/kidney-cancer/about/what-is-kidney-cancer.html (accessed on 27 July 2025).
- Sood, S.; Ojo, A.O.; Adu, D.; Kannan, K.; Ghassabian, A.; Koshy, T.; Vento, S.M.; Pehrson, L.J.; Gilbert, J.F.; Arogundade, F.A. Association between perfluoroalkyl substance exposure and renal function in children with CKD enrolled in H3Africa kidney disease research network. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 1641–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soma-Pillay, P.; Nelson-Piercy, C.; Tolppanen, H.; Mebazaa, A. Physiological changes in pregnancy: Review articles. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2016, 27, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-R.; Lin, S.-B.; Lv, J.-Y.; Wu, Y.; Feng, W.-R. Dissect the association between per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and kidney function from the perspective of lipid molecules. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 361, 124865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Liang, X.; Li, J. GenX disturbs the indicators of hepatic lipid metabolism even at environmental concentration in drinking water via PPARα signaling pathways. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2023, 37, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Duan, Z.; He, W.; Chen, T.; Tang, H.; Du, S.; Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Hu, Y.; Iijima, Y. Kidney function decline mediates the adverse effects of per-and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) on uric acid levels and hyperuricemia risk. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 471, 134312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.S.; Liang, S.S.; Cheng, M.M.; Wu, M.T.; Li, S.Y.; Cheng, T.T.; Liu, T.Y.; Tsai, C.Y.; Lai, Y.T.; Lin, C.H. How renal toxins respond to renal function deterioration and oral toxic adsorbent in pH-controlled releasing capsule. Environ. Toxicol. 2024, 39, 3930–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-C.; Sakolish, C.; Moyer, H.L.; Carmichael, P.L.; Baltazar, M.T.; Ferguson, S.S.; Stanko, J.P.; Hewitt, P.; Rusyn, I.; Chiu, W.A. An in vitro-in silico workflow for predicting renal clearance of PFAS. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2024, 489, 117015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Yao, J.; Bi, J.; He, J. Associations between serum PFOA and PFOS levels and incident chronic kidney disease risk in patients with type 2 diabetes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 229, 113060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, J.; Zhao, R.; Xu, H.; Liu, X.; Guo, H.; Lu, C. Hyperuricemia is associated with metabolic syndrome: A cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Prev. Med. Rep. 2023, 36, 102520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.-W.; Lodge, C.J.; Dharmage, S.C.; Bloom, M.S.; Yu, Y.; Yang, M.; Chu, C.; Li, Q.-Q.; Hu, L.-W.; Liu, K.-K. Isomers of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances and uric acid in adults: Isomers of C8 Health Project in China. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah Soheimi, S.S.; Abdul Rahman, A.; Abd Latip, N.; Ibrahim, E.; Sheikh Abdul Kadir, S.H. Understanding the impact of perfluorinated compounds on cardiovascular diseases and their risk factors: A meta-analysis study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Wang, C.; Sung, F.-C.; Su, T.-C. Association between serum per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances and thrombograms in young and middle-aged Taiwanese populations. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 236, 113457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, E.; Stratakis, N.; Basagana, X.; Brantsæter, A.L.; Casas, M.; Fossati, S.; Gražulevičienė, R.; Haug, L.S.; Heude, B.; Maitre, L. Prenatal and postnatal exposure to PFAS and cardiometabolic factors and inflammation status in children from six European cohorts. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averina, M.; Brox, J.; Huber, S.; Furberg, A.-S. Exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and dyslipidemia, hypertension and obesity in adolescents. The Fit Futures study. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penson, P.E.; Pirro, M.; Banach, M. LDL-C: Lower is better for longer—Even at low risk. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, E.S.; Groth, S.W.; Preston, E.V.; Kinkade, C.; James-Todd, T. Endocrine-disrupting chemical exposures in pregnancy: A sensitive window for later-life cardiometabolic health in women. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2021, 8, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canova, C.; Di Nisio, A.; Barbieri, G.; Russo, F.; Fletcher, T.; Batzella, E.; Dalla Zuanna, T.; Pitter, G. PFAS concentrations and cardiometabolic traits in highly exposed children and adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitter, G.; Zare Jeddi, M.; Barbieri, G.; Gion, M.; Fabricio, A.S.; Daprà, F.; Russo, F.; Fletcher, T.; Canova, C. Perfluoroalkyl substances are associated with elevated blood pressure and hypertension in highly exposed young adults. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birukov, A.; Andersen, L.B.; Andersen, M.S.; Nielsen, J.H.; Nielsen, F.; Kyhl, H.B.; Jørgensen, J.S.; Grandjean, P.; Dechend, R.; Jensen, T.K. Exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances and blood pressure in pregnancy among 1436 women from the Odense Child Cohort. Environ. Int. 2021, 151, 106442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Ye, T.; Jing, D.; Wei, K.; Ge, Y.; Bei, X.; Qi, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Association between exposure to per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances and levels of lipid profile based on human studies. Rev. Environ. Health 2025, 40, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odediran, A.; Bollen, K.; Obeng-Gyasi, E. Association of PFAS and Metals with Cardiovascular Disease Risk: Exploring the Mediating Effect of Diet. Environments 2025, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Zeng, X.; Lin, S.; Bloom, M.S.; Han, F.; Xiao, X.; Wang, H.; Matala, R.; Li, X.; Qu, Y. Gestational exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances and congenital heart defects: A nested case-control pilot study. Environ. Int. 2021, 154, 106567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domazet, S.L.; Jensen, T.K.; Wedderkopp, N.; Nielsen, F.; Andersen, L.B.; Grøntved, A. Exposure to perfluoroalkylated substances (PFAS) in relation to fitness, physical activity, and adipokine levels in childhood: The european youth heart study. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda-Kohmo, K.; Hutcheson, R.; Innes, K.E.; Conway, B.N. Perfluoroalkyl substances are inversely associated with coronary heart disease in adults with diabetes. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2019, 33, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarevic, N.; Smurthwaite, K.; Trevenar, S.; D’Este, C.; Batterham, P.; Lane, J.; Armstrong, B.; Lucas, R.; Clements, A.; Banwell, C. PFAS Health Study Component Three: Cross-Sectional Survey of Self-Reported Physical and Mental Health Outcomes and Associations with Blood Serum PFAS December 2021. Available online: https://nceph.anu.edu.au/files/PFAS%20Health%20Study%20Cross-sectional%20Survey%20Report_Dec2021.pdf? (accessed on 27 July 2025).
- Schillemans, T.; Donat-Vargas, C.; Lindh, C.H.; de Faire, U.; Wolk, A.; Leander, K.; Åkesson, A. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances and risk of myocardial infarction and stroke: A nested case–control study in Sweden. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 037007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutcheson, R.; Innes, K.; Conway, B. Perfluoroalkyl substances and likelihood of stroke in persons with and without diabetes. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2020, 17, 1479164119892223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosgood, S.A.; Nicholson, M.L. The role of perfluorocarbon in organ preservation. Transplantation 2010, 89, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, L.C.; Lin, H.-C.; Zhou, Y.-H.; Wright, F.A.; Gombar, V.K.; Sedykh, A.; Shah, R.R.; Chiu, W.A.; Rusyn, I. Characterizing PFAS hazards and risks: A human population-based in vitro cardiotoxicity assessment strategy. Hum. Genom. 2024, 18, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arredondo Eve, A.; Tunc, E.; Mehta, D.; Yoo, J.Y.; Yilmaz, H.E.; Emren, S.V.; Akçay, F.A.; Madak Erdogan, Z. PFAS and their association with the increased risk of cardiovascular disease in postmenopausal women. Toxicol. Sci. 2024, 200, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porfirio, K.; Yadav, P.; Dangudubiyyam, S.V.; Hofmann, A.; Mishra, J.S.; Kumar, S. Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Exposure Induces Cardiovascular Dysfunction in Female Rats: Role of Ovaries. Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 8, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, C.; Zhao, B.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Proteomic and cardiac dysregulation by representative perfluoroalkyl acids of different chemical speciation during early embryogenesis of zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 172000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstutz, V.; Mircheva, A.; Cengo, A.; Dubois, L.; Sijm, D.; Vrolijk, M. A subcellular study on reactive oxygen species generation by PFAS in HepG2 cells. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 21914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, A.; Shan, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wan, J.; Ning, P.; Hong, C.; Tian, H. Hepatotoxicity induced in rats by chronic exposure to F–53B, an emerging replacement of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS). Environ. Pollut. 2024, 346, 123544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-Y.; Xu, L.-L.; Zhong, M.-T.; Chen, Y.-K.; Lai, M.-Q.; Wang, Q.; Xie, X.-L. Gestational GenX and PFOA exposures induce hepatotoxicity, metabolic pathway, and microbiome shifts in weanling mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 168059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Shao, J.; Jia, D.; Sun, W. Immunotoxicity of legacy and alternative per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances on zebrafish larvae. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 358, 124511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkey, A.B.; Mead, M.; Natarajan, S.; Gondal, A.; Jarrett, O.; Levin, E.D. Embryonic exposure to PFAS causes long-term, compound-specific behavioral alterations in zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2023, 97, 107165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ng, C. Absorption, distribution, and toxicity of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the brain: A review. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2021, 23, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, O.; Zimmer, K.E.; Hudecova, A.M.; Hansen, K.E.; Khezri, A.; Berntsen, H.F.; Berg, V.; Lyche, J.L.; Mandal, S.; Duale, N. Maternal exposure to a human based mixture of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) affect gene expression related to brain function in mice offspring hippocampus. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierozan, P.; Karlsson, O. Differential susceptibility of rat primary neurons and neural stem cells to PFOS and PFOA toxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 349, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nisio, A.; Pannella, M.; Vogiatzis, S.; Sut, S.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Santa Rocca, M.; Antonini, A.; Porzionato, A.; De Caro, R.; Bortolozzi, M. Impairment of human dopaminergic neurons at different developmental stages by perfluoro-octanoic acid (PFOA) and differential human brain areas accumulation of perfluoroalkyl chemicals. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallgren, S.; Viberg, H. Postnatal exposure to PFOS, but not PBDE 99, disturb dopaminergic gene transcription in the mouse CNS. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 41, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foguth, R.; Sepúlveda, M.S.; Cannon, J. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) neurotoxicity in sentinel and non-traditional laboratory model systems: Potential utility in predicting adverse outcomes in human health. Toxics 2020, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaballah, S.; Swank, A.; Sobus, J.R.; Howey, X.M.; Schmid, J.; Catron, T.; McCord, J.; Hines, E.; Strynar, M.; Tal, T. Evaluation of developmental toxicity, developmental neurotoxicity, and tissue dose in zebrafish exposed to GenX and other PFAS. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 047005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, X.; Yang, M.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, T.; Sun, Y. Maternal PFBS exposure during gestation and lactation results in cognitive impairment in rat offspring. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2025, 37, 2475955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Bonilla, K.M.; Aga, D.S.; Lee, J.; König, M.; Qin, W.; Cristobal, J.R.; Atilla-Gokcumen, G.E.; Escher, B.I. Neurotoxic Effects of Mixtures of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) at Environmental and Human Blood Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 16774–16784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xie, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, X.; Sánchez, O.F.; Rochet, J.-C.; Freeman, J.L.; Yuan, C. Developmental neurotoxicity of PFOA exposure on hiPSC-derived cortical neurons. Environ. Int. 2024, 190, 108914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiako, P.C.; Ayisire, S.O.; Sayes, C.M. Impact of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorobutanoic acid (PFBA) on oxidative stress and metabolic biomarkers in human neuronal cells (SH-SY5Y). Environ. Int. 2024, 190, 108864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Shi, H.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Y. Prenatal PFAS exposure, gut microbiota dysbiosis, and neurobehavioral development in childhood. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Lai, H.; Tu, W. Comparative chronic toxicities of PFOS and its novel alternatives on the immune system associated with intestinal microbiota dysbiosis in adult zebrafish. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ma, M.; Qi, W.; Wang, D.; Han, Y.; Ji, X.; Zhu, K.; Li, N. In Vitro Multibiomarker Approaches for Assessing the Immunotoxicity of Certain Sections in Yangtze River. ACS EST Water 2022, 2, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodlief, T.; Vance, S.; Hu, Q.; DeWitt, J. Immunotoxicity of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances: Insights into short-chain PFAS exposure. Toxics 2021, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shane, H.L.; Baur, R.; Lukomska, E.; Weatherly, L.; Anderson, S.E. Immunotoxicity and allergenic potential induced by topical application of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in a murine model. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 111114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Guise, S.; Levin, M. Suppression of Th2 cytokines as a potential mechanism for reduced antibody response following PFOA exposure in female B6C3F1 mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 351, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, C.A.; Ward, C.; Hu, Q.; Vance, S.; Higgins, C.P.; DeWitt, J.C. Immunotoxicity of an electrochemically fluorinated aqueous film-forming foam. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 178, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lai, H.; Wang, Q.; Martínez, R.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Deng, M.; Tu, W. Immunotoxicity of F53B, an alternative to PFOS, on zebrafish (Danio rerio) at different early life stages. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Shen, L.; Ye, X.; Zhou, D.; He, Y.; Zhang, H. Mechanism of immunosuppression in zebrafish (Danio rerio) spleen induced by environmentally relevant concentrations of perfluorooctanoic acid. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillette, T.; McCord, J.; Guillette, M.; Polera, M.; Rachels, K.T.; Morgeson, C.; Kotlarz, N.; Knappe, D.R.; Reading, B.J.; Strynar, M. Elevated levels of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in Cape Fear River Striped Bass (Morone saxatilis) are associated with biomarkers of altered immune and liver function. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillette, T.; Jackson, T.W.; Guillette, M.; McCord, J.; Belcher, S.M. Blood concentrations of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances are associated with autoimmune-like effects in American alligators from Wilmington, North Carolina. Front. Toxicol. 2022, 4, 1010185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birgersson, L.; Jouve, J.; Jönsson, E.; Asker, N.; Andreasson, F.; Golovko, O.; Ahrens, L.; Sturve, J. Thyroid function and immune status in perch (Perca fluviatilis) from lakes contaminated with PFASs or PCBs. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, K.E.; Zell-Baran, L.M.; DeWitt, J.C.; Brindley, S.; McDonough, C.A.; Higgins, C.P.; Adgate, J.L.; Starling, A.P. Cross-sectional associations between serum PFASs and inflammatory biomarkers in a population exposed to AFFF-contaminated drinking water. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2022, 240, 113905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Espinosa, M.-J.; Carrizosa, C.; Luster, M.I.; Margolick, J.B.; Costa, O.; Leonardi, G.S.; Fletcher, T. Perfluoroalkyl substances and immune cell counts in adults from the Mid-Ohio Valley (USA). Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihovic, S.; Lind, L.; Larsson, A.; Lind, P.M. Plasma perfluoroalkyls are associated with decreased levels of proteomic inflammatory markers in a cross-sectional study of an elderly population. Environ. Int. 2020, 145, 106099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika, D.; Rovira, J.; Sabuz, Ó.; Balaguer, J.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L.; Kumar, V. Framework for risk assessment of PFAS utilizing experimental studies and in-silico models. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinete, N.; Hauser-Davis, R.A. Drinking water pollutants may affect the immune system: Concerns regarding COVID-19 health effects. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, P.; Timmermann, C.A.G.; Kruse, M.; Nielsen, F.; Vinholt, P.J.; Boding, L.; Heilmann, C.; Mølbak, K. Severity of COVID-19 at elevated exposure to perfluorinated alkylates. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Holst, H.; Nayak, P.; Dembek, Z.; Buehler, S.; Echeverria, D.; Fallacara, D.; John, L. Perfluoroalkyl substances exposure and immunity, allergic response, infection, and asthma in children: Review of epidemiologic studies. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iulini, M.; Bettinsoli, V.; Maddalon, A.; Galbiati, V.; Janssen, A.W.; Beekmann, K.; Russo, G.; Pappalardo, F.; Fragki, S.; Paini, A. In vitro approaches to investigate the effect of chemicals on antibody production: The case study of PFASs. Arch. Toxicol. 2025, 99, 2075–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, E.; Marques, E.; Agudelo Areiza, J.; Modaresi, S.M.S.; Slitt, A. Exposure to a PFOA, PFOS and PFHxS mixture during gestation and lactation alters the liver proteome in offspring of cd-1 mice. Toxics 2024, 12, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Abdallah, F.M.; Chen, X.; Rajkovic, A. Current knowledge of individual and combined toxicities of aflatoxin B1 and fumonisin B1 in vitro. Toxins 2023, 15, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, S.D.; Benson, D.B.; Xie, Z.-R.; Wang, J.-S.; Tang, L. Utilization of Artificial Intelligence Coupled with a High-Throughput, High-Content Platform in the Exploration of Neurodevelopmental Toxicity of Individual and Combined PFAS. J. Xenobiotics 2025, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iulini, M. Toward Sustainable Chemical Substances: Development of Novel Approach Methodologies to Study Immunotoxicity of PFAS. 2025. Available online: https://air.unimi.it/handle/2434/1154000? (accessed on 27 July 2025).
- Wang, N.; Dong, G.; Qiao, R.; Yin, X.; Lin, S. Bringing Artificial Intelligence (AI) into environmental toxicology studies: A perspective of AI-enabled Zebrafish high-throughput screening. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 9487–9499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Kang, J.; Gao, X.; Lan, Y.; Li, M. Towards a Better Understanding of the Human Health Risk of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Using Organoid Models. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Model Type | System | Application | Example Compounds Studied | Key References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In vitro | HepG2 cells | Mechanistic insight into ROS production; apoptosis | PFOS, GenX, and PFBS | A |
| In vivo (rodents) | Mouse/Rat | Systemic toxicity; liver/kidney effects | PFOA, PFOS, and GenX | B |
| In vivo (zebrafish) | Zebrafish embryos | Developmental and immune effects and neurotoxicity | PFOS, F-53B, and OBS | C |
| PFAS | Organ | Mechanisms/Modes of Action | Key Pathways/Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFOS, PFOA | Liver | Cellular injury, ROS-independent cytotoxicity, DNA damage, and apoptosis | Activation of PPARα, CAR; downregulation of NRF2 | A |
| GenX | Liver | Mediated through oxidative stress and dysregulation of fatty acid metabolism | Induce hepatocellular hypertrophy and lipid accumulation | B |
| PFOS, PFOA | Kidney | Decreased GFR, associated with CKD and RCC | Serum concentrations linked to renal cell carcinoma risk | C |
| PFNA, PFDA, PFOS | Kidney | Reduced eGFR significantly | Impaired renal function | D |
| PFOS, PFOA | Cardiovascular system | Platelet dysfunction, dyslipidemia, and altered blood pressure regulation | Increased platelet activation; elevated cholesterol; mixed results on blood pressure | E |
| PFHxS, PFHxA | Brain | Neurotoxic effects, increased ROS, and cholinergic signaling modulation | Dopaminergic degeneration | F |
| GenX, PFBS | Brain | Induce neuroinflammatory markers, including elevated IL-6 and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) | Disruption of dopamine regulation | G |
| PFOS | Immune system | Altered Th1/Th2 and pro-inflammatory cytokine levels and keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) stimulation | Spleen and thymus weight decreases and liver weight increases, along with changes in splenic B-cell numbers | H |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martano, P.; Mahdi, S.; Zhou, T.; Barazandegan, Y.; Iha, R.; Do, H.; Burken, J.; Nam, P.; Yang, Q.; Mu, R. Visceral, Neural, and Immunotoxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Mini Review. Toxics 2025, 13, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080658
Martano P, Mahdi S, Zhou T, Barazandegan Y, Iha R, Do H, Burken J, Nam P, Yang Q, Mu R. Visceral, Neural, and Immunotoxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Mini Review. Toxics. 2025; 13(8):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080658
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartano, Pietro, Samira Mahdi, Tong Zhou, Yasmin Barazandegan, Rebecca Iha, Hannah Do, Joel Burken, Paul Nam, Qingbo Yang, and Ruipu Mu. 2025. "Visceral, Neural, and Immunotoxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Mini Review" Toxics 13, no. 8: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080658
APA StyleMartano, P., Mahdi, S., Zhou, T., Barazandegan, Y., Iha, R., Do, H., Burken, J., Nam, P., Yang, Q., & Mu, R. (2025). Visceral, Neural, and Immunotoxicity of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: A Mini Review. Toxics, 13(8), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13080658





_Yang.png)



