Simultaneous Decontamination for Ammonia Nitrogen and Phosphate Efficiently by Crystal Morphology MgO-Coated Functional Biochar Derived from Sludge and Sunflower Stalk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material Pretreatment and Co-Pyrolysis Method
2.2. Analysis and Characterization of Material
2.3. Adsorption Experiment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
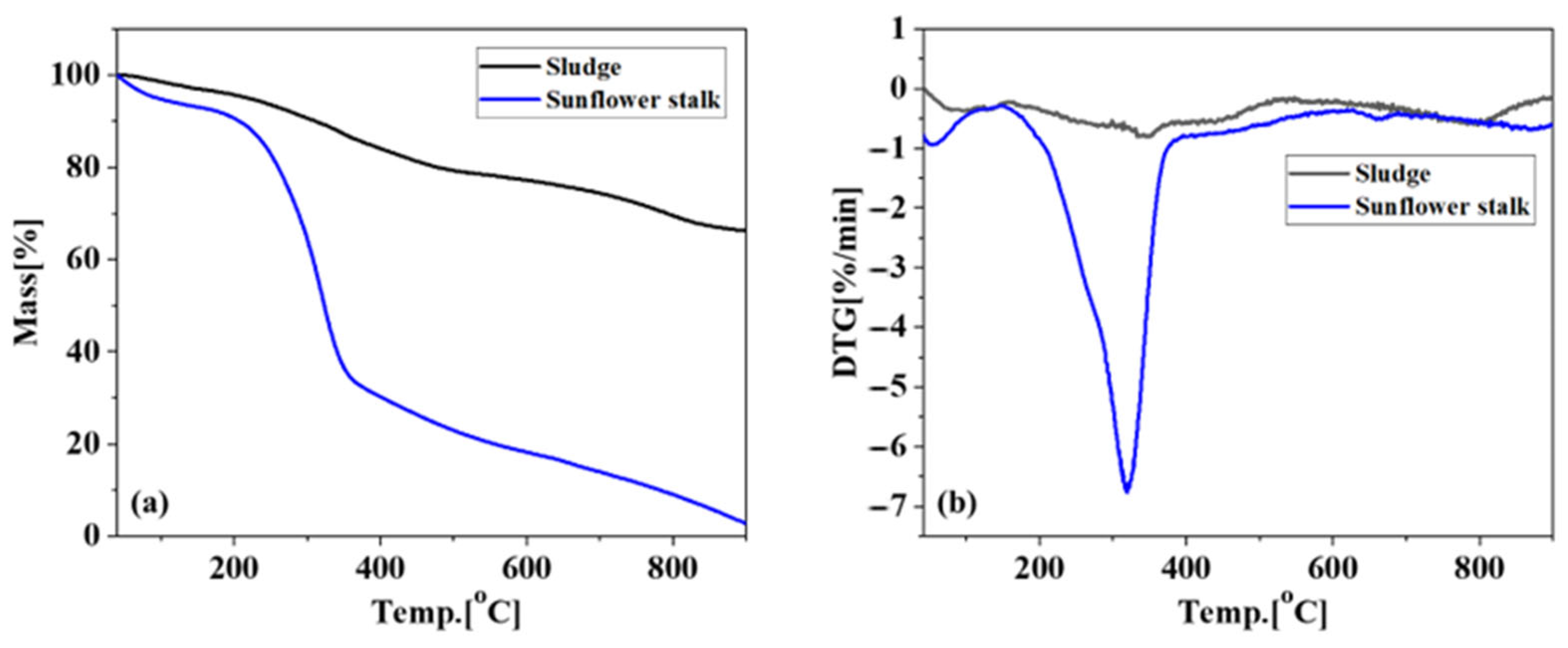
3.1. Analysis of Basic Physicochemical Properties of Raw Materials
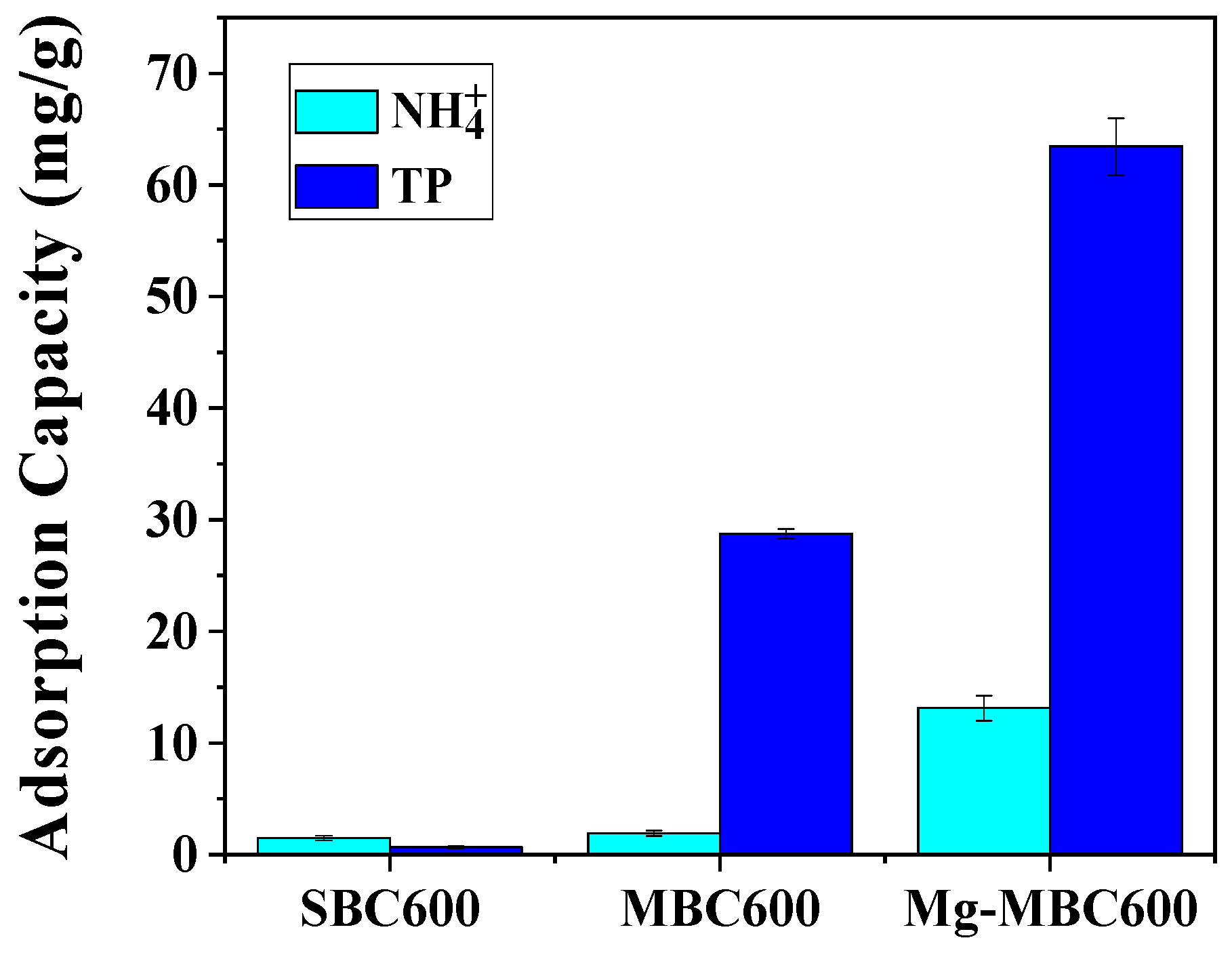
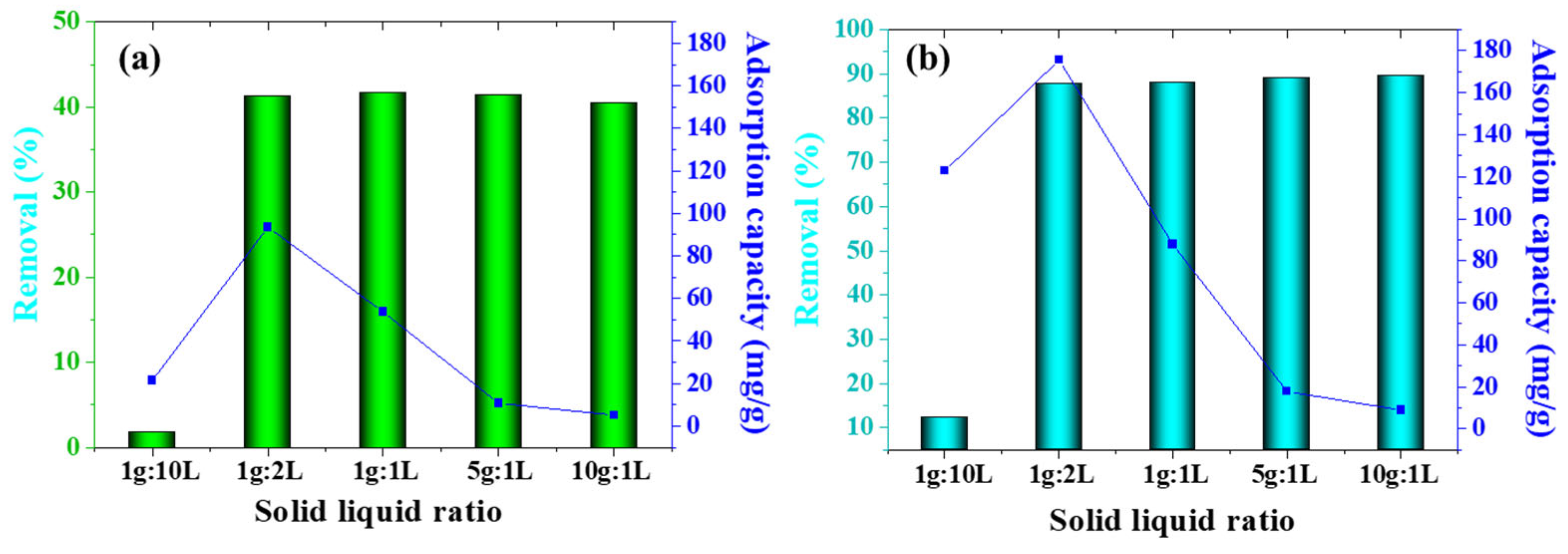
3.2. Effect of Preparation Conditions of Magnesium-Modified Biochar on Nitrogen and Phosphorus Adsorption Capacity
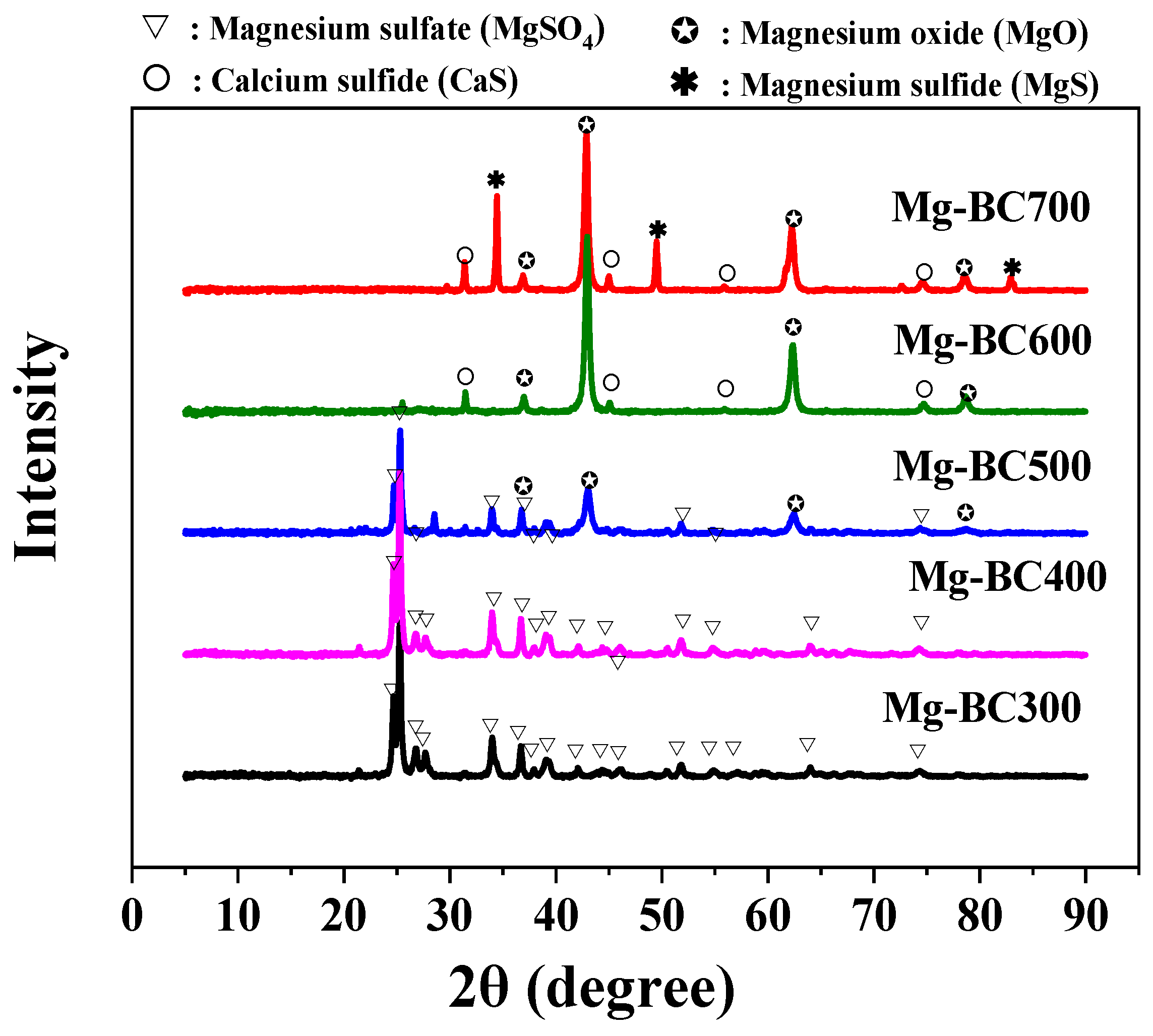
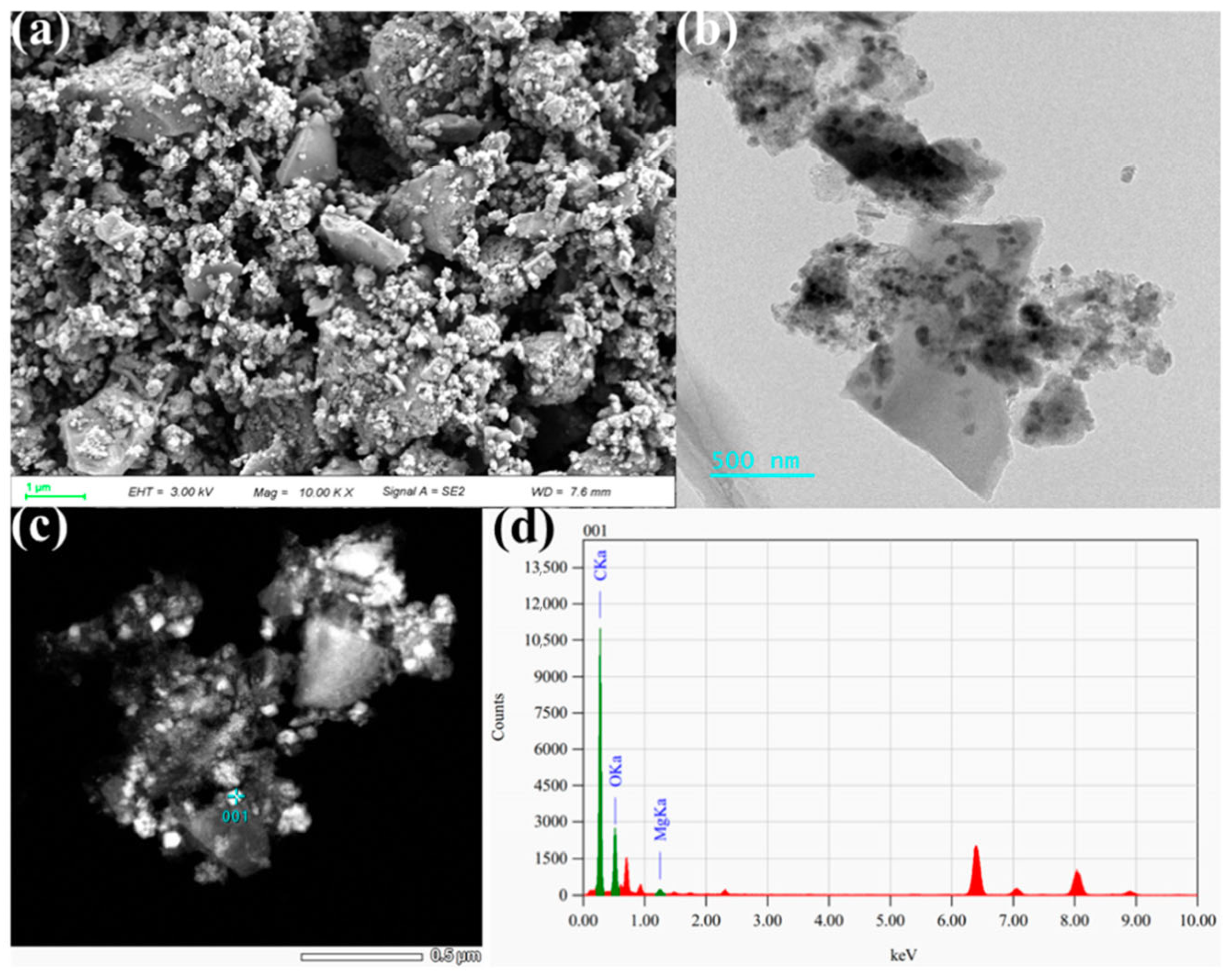
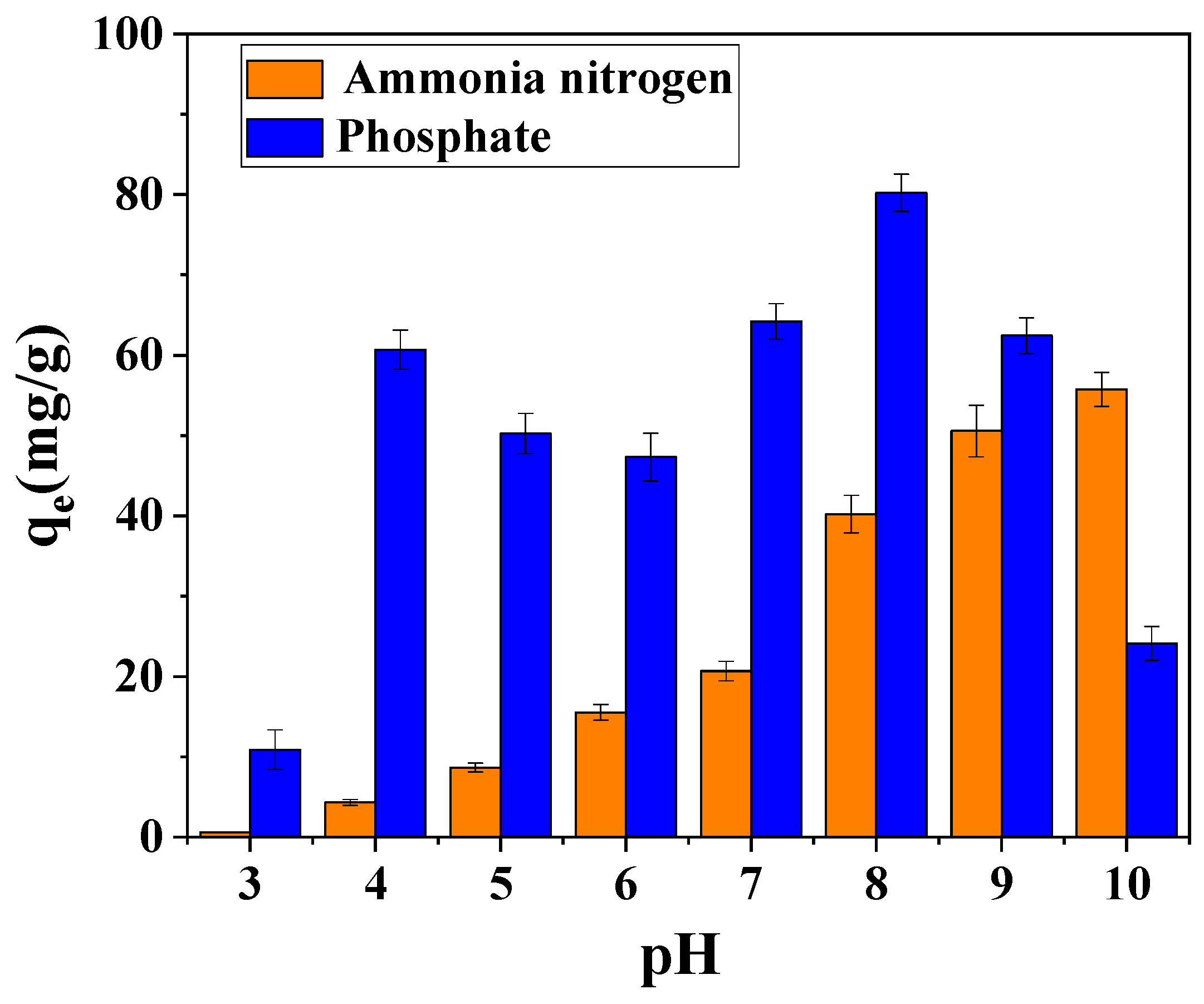
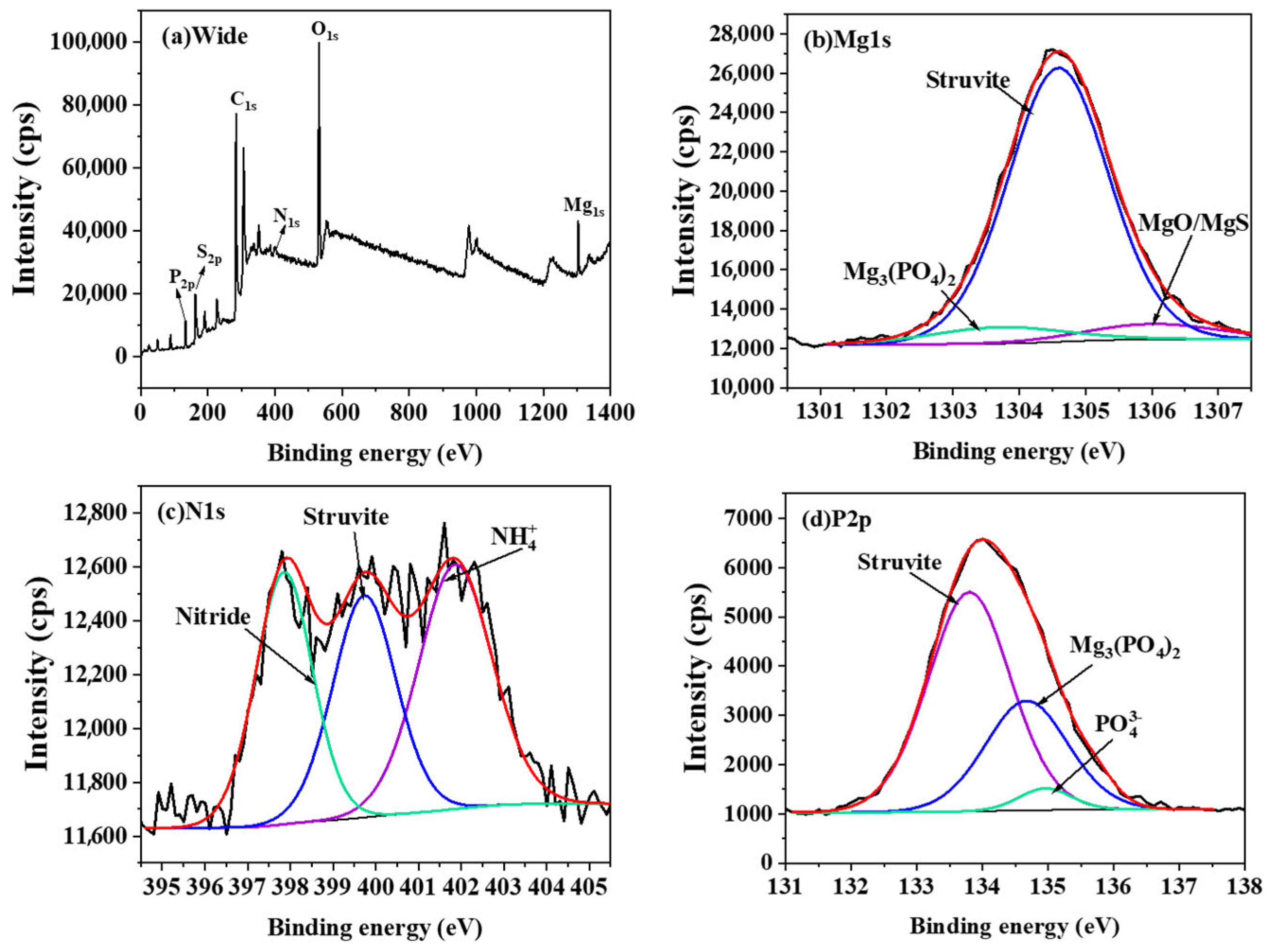
3.3. Factors and Mechanisms Affecting Adsorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geletu, T.T. Lake Eutrophication: Control of Phytoplankton Overgrowth and Invasive Aquatic Weeds. Lakes Reserv. 2023, 28, e12425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Leavitt, P.R.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. Anthropogenic Eutrophication of Shallow Lakes: Is It Occasional? Water Res. 2022, 221, 118728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.; Deng, J.; Shi, K.; Wang, J.; Brookes, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Paerl, H.W.; Wu, L. Extreme Climate Anomalies Enhancing Cyanobacterial Blooms in Eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR029371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yu, S.; Shi, C.; Li, C. Research Progress of Simultaneous Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal Adsorbents in Wastewater Treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Feng, J.; Sun, F. Efficient Simultaneous Phosphate and Ammonia Adsorption Using Magnesium-Modified Biochar Beads and Their Recovery Performance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Hassan, M.; Zhang, X. Biochar Coupled with Multiple Technologies for the Removal of Nitrogen and Phosphorus from Water: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, K.; Drużyński, S.; Kiełkowska, U.; Bielicka, A.; Gluzińska, J. Application of Sulphate and Magnesium Enriched Waste Rapeseed Cake Biochar for Recovery of Cu(II) and Zn(II) from Industrial Wastewater Generated in Sulphuric Acid Plants. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 216, 106014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yu, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. The Fate of Heavy Metals and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal in Pyrolysis Coupling with Acid Washing Treatment for Sewage Sludge. Toxics 2023, 11, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.; Zhang, R.; Ngo, H.H.; He, X.; Ma, J.; Nan, J.; Li, G. Life Cycle Assessment of Sewage Sludge Treatment and Disposal Based on Nutrient and Energy Recovery: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.; Amutio, M.; Lopez, G.; Bilbao, J.; Olazar, M. Fast Co-Pyrolysis of Sewage Sludge and Lignocellulosic Biomass in a Conical Spouted Bed Reactor. Fuel 2015, 159, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shan, R.; Jiang, L.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Chen, Y. A Review on the Migration and Transformation of Heavy Metals in the Process of Sludge Pyrolysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 185, 106452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Datta, S.; Bhatia, D.; Dhiman, J.; Samuel, J.; Prasad, R.; Singh, J. A Sustainable Paradigm of Sewage Sludge Biochar: Valorization, Opportunities, Challenges and Future Prospects. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Fu, J.; Ao, W.; Ali Siyal, A.; Zhou, C.; Liu, C.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, J.; et al. Co-Pyrolysis of Sewage Sludge and Lignocellulosic Biomass: Synergistic Effects on Products Characteristics and Kinetics. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 268, 116061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, B.A.; O’Boyle, M.; Li, L.Y. Co-Pyrolysis of Sewage Sludge with Lignocellulosic and Algal Biomass for Sustainable Liquid and Gaseous Fuel Production: A Life Cycle Assessment and Techno-Economic Analysis. Appl. Energy 2023, 346, 121318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, B.; Hallajisani, A.; Tavakoli, O. Super-Effective Biochar Adsorbents from Co-Pyrolysis of Rice Husk and Sewage Sludge: Adsorption Performance, Advanced Regeneration, and Economic Analysis. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2025, 29, 102046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Yu, P.; Chen, C. Evaluating Biochar for Adsorption of Ammonium Nitrogen in Wastewater:Insights into Modifications and Mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2025, 277, 121615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizmur, T.; Fresno, T.; Akgül, G.; Frost, H.; Moreno-Jiménez, E. Biochar Modification to Enhance Sorption of Inorganics from Water. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wu, R.; Pang, X.; Yu, C.; Jian, X. Adsorption of Phosphorus in Water by Metal-Modified Large-Size Biochar: Realizing the Recovery and Recycling of Phosphorus. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 36, 101279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, D.; Ma, L.; Dai, Q.; Yang, R.; Ao, R. Magnesium Modified Algae Biochar for Phosphorus Adsorption: Synthesis, Experimental Analysis, DFT Calculations and Regeneration. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 71, 107169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buss, W.; Bogush, A.; Ignatyev, K.; Mašek, O. Unlocking the Fertilizer Potential of Waste-Derived Biochar. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 12295–12303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, K.; Vijayakumar, S. Biochar—A Sustainable Soil Conditioner for Improving Soil Health, Crop Production and Environment under Changing Climate: A Review. Front. Soil Sci. 2024, 4, 1376159. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Chi, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Influence of Pyrolysis Temperature on Characteristics and Environmental Risk of Heavy Metals in Pyrolyzed Biochar Made from Hydrothermally Treated Sewage Sludge. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Pan, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zou, X.; Wang, Y. Low-Cost Ca/Mg Co-Modified Biochar for Effective Phosphorus Recovery: Adsorption Mechanisms, Resourceful Utilization, and Life Cycle Assessment. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 502, 157993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yu, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y. A Novel Strategy of Tannery Sludge Disposal—Converting into Biochar and Reusing for Cr(VI) Removal from Tannery Wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 138, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chang, V.W.-C.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. Co-Pyrolysis of Sewage Sludge and Organic Fractions of Municipal Solid Waste: Synergistic Effects on Biochar Properties and the Environmental Risk of Heavy Metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Z. Application of Mg–Al-Modified Biochar for Simultaneous Removal of Ammonium, Nitrate, and Phosphate from Eutrophic Water. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lin, K.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Yu, J.; Cao, S.; Zhang, D.; Xu, L.; Parikh, S.J.; Ok, Y.S. Removal of Phosphate from Water by Paper Mill Sludge Biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Wu, B.; Su, L.; Gao, X.; Chai, X.; Dai, X. Development of Nano-CaO2-Coated Clinoptilolite for Enhanced Phosphorus Adsorption and Simultaneous Removal of COD and Nitrogen from Sewage. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanassra, I.W.; Mckay, G.; Kochkodan, V.; Ali Atieh, M.; Al-Ansari, T. A State of the Art Review on Phosphate Removal from Water by Biochars. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-G.; Tsang, Y.F.; Baek, K. Removal of Ammonium, Phosphate, and Sulfonamide Antibiotics Using Alum Sludge and Low-Grade Charcoal Pellets. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Guo, X. Investigation on Mechanism of Phosphate Removal on Carbonized Sludge Adsorbent. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 64, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-B.; Nguyen, T.-K.-T.; Chen, W.-H.; Chen, C.-W.; Bui, X.-T.; Patel, A.K.; Dong, C.-D. Hydrothermal and Pyrolytic Conversion of Sunflower Seed Husk into Novel Porous Biochar for Efficient Adsorption of Tetracycline. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 373, 128711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizito, S.; Wu, S.; Kipkemoi Kirui, W.; Lei, M.; Lu, Q.; Bah, H.; Dong, R. Evaluation of Slow Pyrolyzed Wood and Rice Husks Biochar for Adsorption of Ammonium Nitrogen from Piggery Manure Anaerobic Digestate Slurry. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Lin, F.; Dou, X.; Zheng, M.; Tan, W.; Wang, C. Recovery of Ammonium and Phosphate from Urine as Value-Added Fertilizer Using Wood Waste Biochar Loaded with Magnesium Oxides. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanfan, L.; Yungen, L.; Yan, W.; Silin, Y.; Rong, M. Preparation of Structured Biochar, Its Adsorption Capacity of N and P and Its Characterization. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 2443–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Zhang, X.; Hua Zhang, A.; Guo, F.; Yang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Ying, G.; Zhang, J. Concurrent Removal of Phosphate and Ammonium from Wastewater for Utilization Using Mg-Doped Biochar/Bentonite Composite Beads. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 285, 120399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, K.; Tian, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, F. Comparative Study on Characteristics and Mechanism of Phosphate Adsorption on Mg/Al Modified Biochar. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, N.; Wang, M.; Yang, S.; Wang, W.; Jin, P. Evaluation of the Adsorption of Ammonium-Nitrogen and Phosphate on a Granular Composite Adsorbent Derived from Zeolite. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 17632–17643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, D.; Tian, H.; Yang, H. Simultaneous Adsorption of Ammonia and Phosphate Using Ferric Sulfate Modified Carbon/Zeolite Composite from Coal Gasification Slag. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, C.A.; Fletcher, L.A.; Singh, S.; Anyikude, K.U.; Ross, A.B. Phosphate and Ammonium Sorption Capacity of Biochar and Hydrochar from Different Wastes. Chemosphere 2016, 145, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.-P.; Ni, Z.-Y.; Xiong, Z.-Z.; Cheng, L.-H.; Xu, X.-H. Phosphate and Ammonium Adsorption of the Modified Biochar Based on Phragmites Australis after Phytoremediation. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 8326–8335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Liu, M.; Ren, H. Biochar Produced from the Co-Pyrolysis of Sewage Sludge and Walnut Shell for Ammonium and Phosphate Adsorption from Water. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Long, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X.-M.; Lu, M.; Huang, L.-Z. Phosphorus and Nitrogen Recovery from Wastewater by Ceramsite: Adsorption Mechanism, Plant Cultivation and Sustainability Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chen, X.L.; Zhou, C.H.; Yang, H.M.; Ji, S.F.; Tong, D.S.; Zhong, Z.K.; Yu, W.H.; Chu, M.Q. Environmental-Friendly Montmorillonite-Biochar Composites: Facile Production and Tunable Adsorption-Release of Ammonium and Phosphate. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 156, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Chang, B.; Tang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, S.; Chang, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, C.; Hu, F.; et al. Co-Adsorption Performance and Mechanism of Ammonium and Phosphate by Iron-Modified Biochar in Water. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 67, 106209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Proximate Analysis/% | Ultimate Analysis/% | BET (m2/g) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mad | Aad | Vad | FCad | Cad | Had | Nad | Oad * | Sad | H/Cad | ||
| Sunflower Stalk | 5.81 | 3.55 | 84.4 | 6.24 | 47.04 | 5.02 | 0.29 | 31.72 | 0.33 | 1.28 | 26.87 |
| Sludge | 5.21 | 63.74 | 35.07 | 1.19 | 15.44 | 3.25 | 1.62 | 14.14 | 0.55 | 2.53 | 17.47 |
| Sample Name | Elemental Composition (wt%) | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Size (nm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | N | Mg | ||||
| Sewage peat | 10.63 | 1.26 | 0.72 | 1.32 | 49.62 | 0.1685 | 14.87 |
| Co-pyrolysis carbon | 46.57 | 1.36 | 1.72 | 0.87 | 124.36 | 0.1764 | 4.23 |
| Magnesium-loaded modified biochar | 43.26 | 1.32 | 1.66 | 9.86 | 156.08 | 0.1829 | 3.67 |
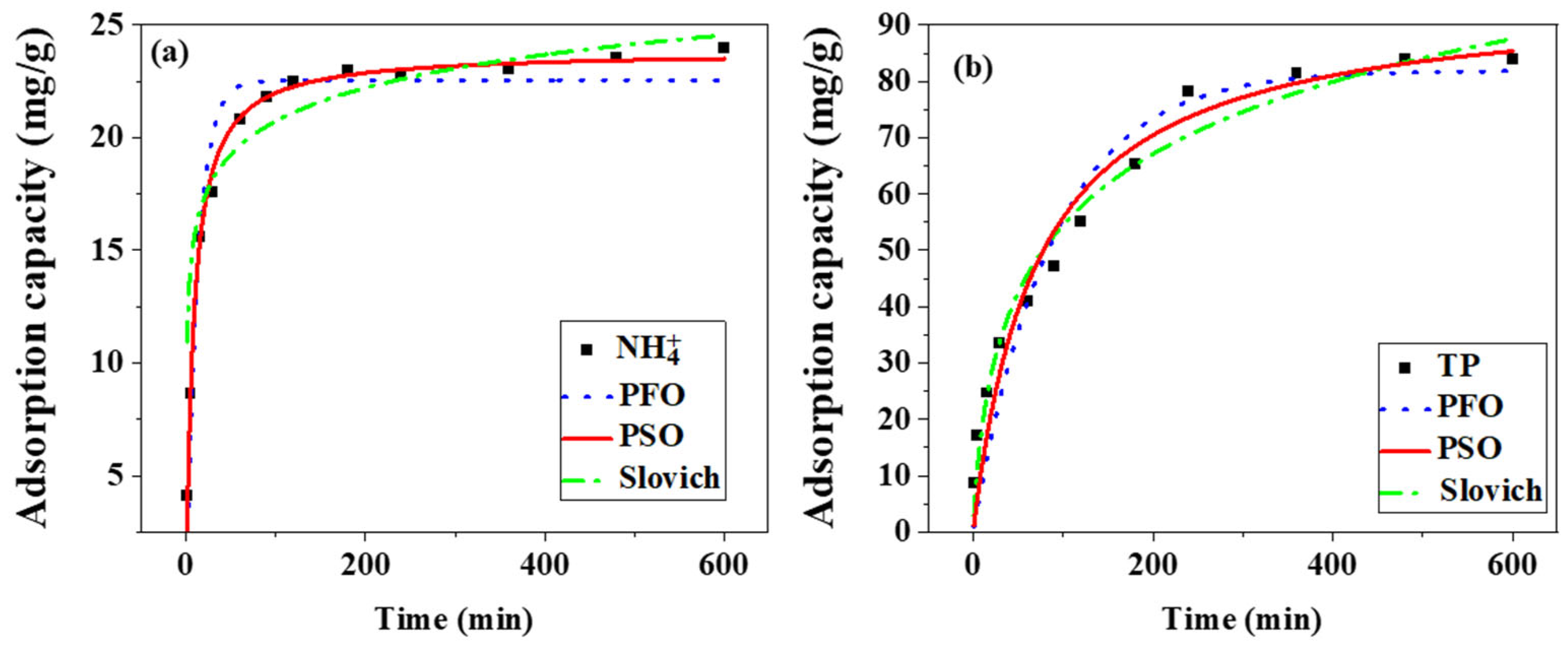
| Sample | Adsorbate | Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | Elovich | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | qe | R2 | k2 | qe | R2 | α | β | R2 | ||
| Mg-MBC | NH4+ | 0.0756 | 22.55 | 0.9469 | 0.005 | 23.84 | 0.9901 | 363.08 | 0.4698 | 0.7956 |
| Mg-MBC | TP | 0.0114 | 81.91 | 0.9224 | 0.001 | 95.45 | 0.9844 | 3.1758 | 0.05 | 0.9716 |
| Sample Name | Adsorbate | Langmuir | Freundlich | Langmuir–Freundlich | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL | qm | R2 | KF | n | R2 | k | n | qm | R2 | ||
| Mg-MBC600 | Ammonia nitrogen | 0.1048 | 52.56 | 0.9359 | 17.7376 | 4.5171 | 0.9133 | 0.0452 | 0.6496 | 47.17 | 0.9567 |
| Total phosphorus | 0.006 | 110.29 | 0.9845 | 6.3103 | 2.3826 | 0.9703 | 0.001 | 0.6987 | 91.09 | 0.9971 | |
| Precursor | Modification Agent | pH | qe (mg NH4+/g) | qe (mg TP/g) | Kinetic Model | Adsorbent Model | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn stalk | Magnesium | 9–11 | 177.25 | 253.95 (PO43−) | Pseudo-second order | Langmuir–Freundlich | [5] |
| Macrophyte cattails and sludge | HDPE | 10 | 111.96 | 107.72 (PO43−) | Pseudo-second order | Langmuir | [34] |
| Peanut shell and purified bentonite | MgCl2 CaCl2 | 7 | 39.5 | 132.2 (PO43−) | Pseudo-second order | Langmuir–Freundlich | [37] |
| Corn cob | AlCl3·6H2O | 5–6 | - | 44.79 (PO43−) | Pseudo-second order | Langmuir | [38] |
| Zeolite powders | NaCl | 6–7 | 12.0 | 9.3 (PO43−) | Pseudo-second order | Langmuir | [39] |
| Coal gasification slag | NaOH | 6–8 | 7.44 | 6.94 (PO43−) | Pseudo-second order | Langmuir | [40] |
| Oak wood and greenhouse waste; anaerobically waste | Ethanol ammonium acetate | 6–9 | 146.4 | 30 (PO43−) | Pseudo-second order | Langmuir–Freundlich | [41] |
| Municipal waste | MgCl2 | 7–9 | 32.01 | 109.58 (PO43−) | Pseudo-second order | Langmuir–Freundlich | [42] |
| Municipal sewage sludge and walnut shell | Material ratio | 7–9 | 22.85 | 303.49 (PO43−) | Pseudo-second order | Langmuir–Freundlich | [43] |
| Sewage sludge fly ash and clay ceramsite | NaOH/NaCl LaCl3/NaOH | 6–8 | 12.52 | 0.93 (PO43−) | Pseudo-second order | Langmuir | [18] |
| Bamboo powder and montmorillonite | 7 | 12.52 | 105.28 (PO43−) | Pseudo-first order | Langmuir | [44] | |
| Wheat straw, apple branches and kiwi branches | HCl FeCl3 | 7 | 22.98 | 28.10 (PO43−) | Pseudo-second order | Langmuir | [45] |
| Sludge and sunflower stalk | MgO | 3–9 | 84.92 | 182.27 | Pseudo-second order | Langmuir–Freundlich | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y. Simultaneous Decontamination for Ammonia Nitrogen and Phosphate Efficiently by Crystal Morphology MgO-Coated Functional Biochar Derived from Sludge and Sunflower Stalk. Toxics 2025, 13, 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070577
Li Z, Huang J, Zhang W, Yu H, Wang Y. Simultaneous Decontamination for Ammonia Nitrogen and Phosphate Efficiently by Crystal Morphology MgO-Coated Functional Biochar Derived from Sludge and Sunflower Stalk. Toxics. 2025; 13(7):577. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070577
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhiwei, Jingxin Huang, Weizhen Zhang, Hao Yu, and Yin Wang. 2025. "Simultaneous Decontamination for Ammonia Nitrogen and Phosphate Efficiently by Crystal Morphology MgO-Coated Functional Biochar Derived from Sludge and Sunflower Stalk" Toxics 13, no. 7: 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070577
APA StyleLi, Z., Huang, J., Zhang, W., Yu, H., & Wang, Y. (2025). Simultaneous Decontamination for Ammonia Nitrogen and Phosphate Efficiently by Crystal Morphology MgO-Coated Functional Biochar Derived from Sludge and Sunflower Stalk. Toxics, 13(7), 577. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13070577






