The Impact of Boron Carbide Nanoparticle (B4C-NPs) Toxicity on Caenorhabditis elegans Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Boron Carbide Nanoparticles
2.2. Reagents and Raw Materials
2.3. Chunking and Bleaching of C. elegans
2.4. Nanoparticle Exposure
2.5. Growth, Reproductive, Lifespan, and Lethality Assays of C. elegans
2.6. Locomotion Assay
2.7. Gene Expression Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Toxicological Effects of B4C Nanoparticles on Growth, Lethality, and Lifespan in C. elegans
3.2. B4C-NPs Impair Locomotion and Progeny Production in C. elegans
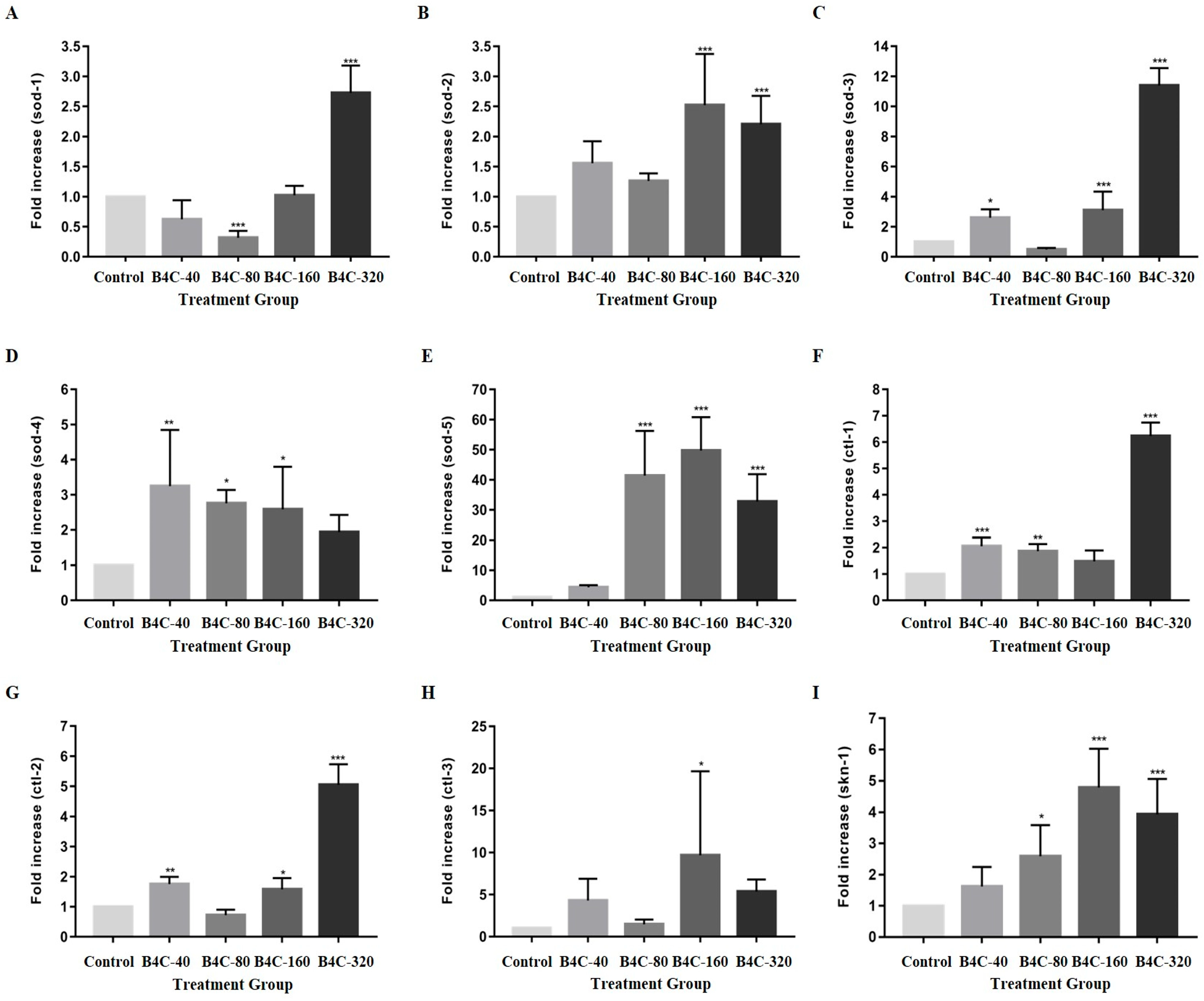
3.3. Impact of B4C-NPs on Oxidative Stress Genes in C. elegans
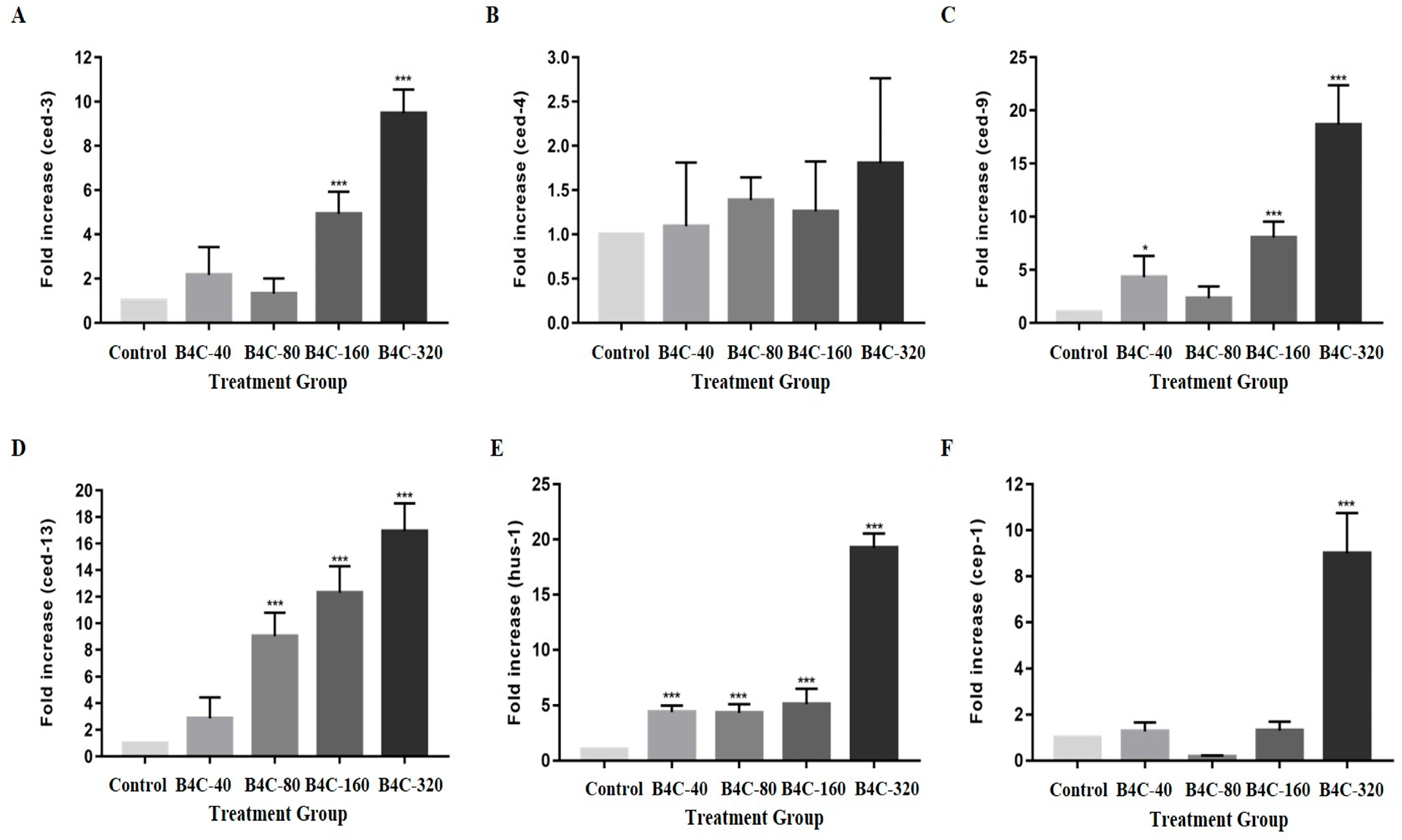
3.4. B4C-NPs Induce Apoptosis and DNA Damage Responses in C. elegans
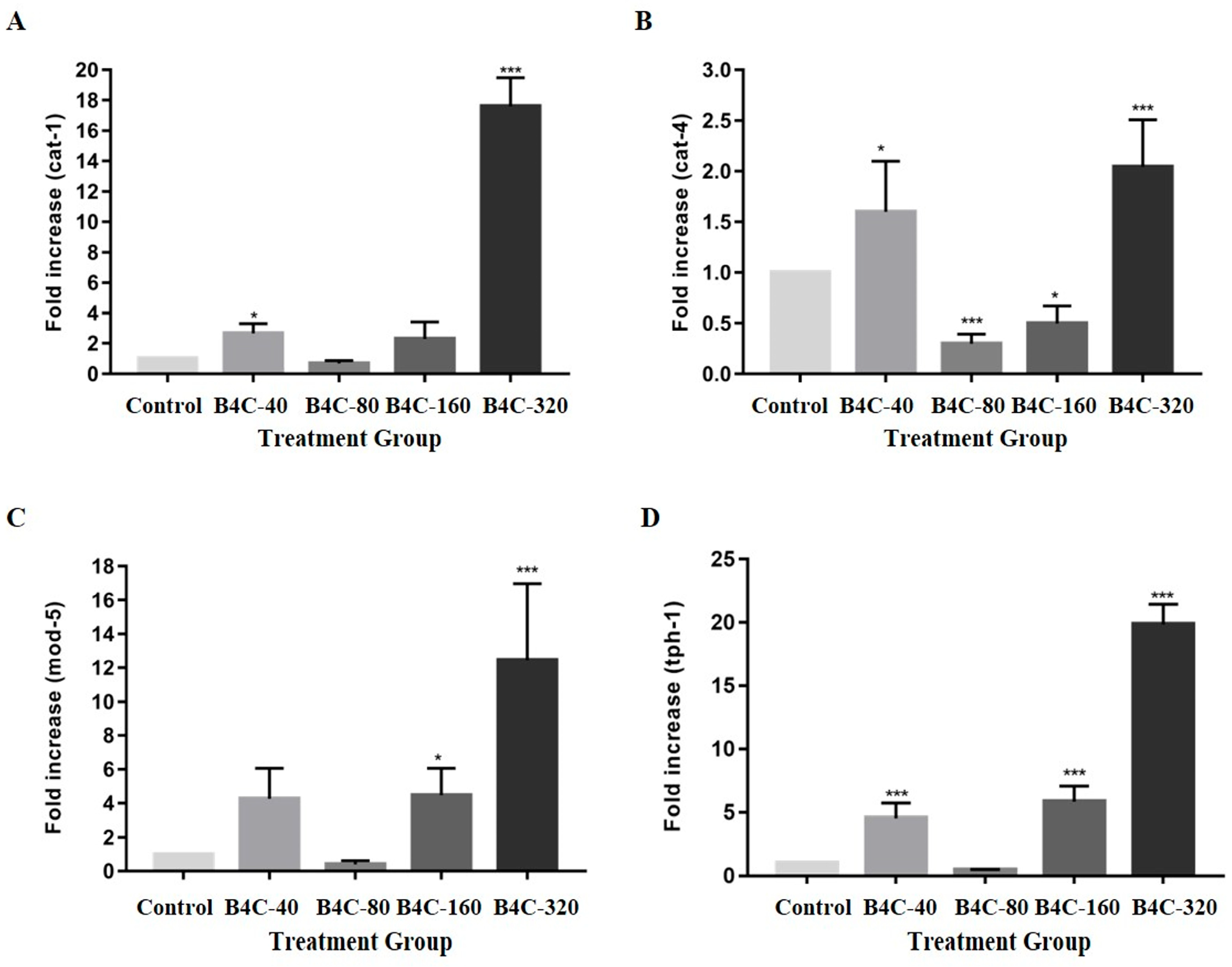
3.5. Effects of B4C-NPs on Neurotransmitter Synthesis-Related Gene Expression in C. elegans
3.6. Influence of B4C-NPs on Metal Detoxification Genes in C. elegans
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Avcıoğlu, S.; Buldu, M.; Kaya, F.; Üstündağ, C.B.; Kam, E.; Menceloğlu, Y.Z.; Kaptan, H.Y.; Kaya, C. Processing and properties of boron carbide (B4C) reinforced LDPE composites for radiation shielding. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamd, S.S.; Ramizy, A.; Ismail, R.A. Preparation of novel B4C nanostructure/Si photodetectors by laser ablation in liquid. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozień, D.; Żeliszewska, P.; Szermer-Olearnik, B.; Adamczyk, Z.; Wróblewska, A.; Szczygieł, A.; Węgierek-Ciura, K.; Mierzejewska, J.; Pajtasz-Piasecka, E.; Tokarski, T.; et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Boron Carbide Nanoparticles as Potential Boron-Rich Therapeutic Carriers. Materials 2023, 16, 6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitali, A.; Demichelis, M.P.; Di Martino, G.; Postuma, I.; Bortolussi, S.; Falqui, A.; Milanese, C.; Ferrara, C.; Sommi, P.; Anselmi-Tamburini, U. Synthesis and Characterization of Gd-Functionalized B4C Nanoparticles for BNCT Applications. Life 2023, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumah, E.A.; Fopa, R.D.; Harati, S.; Boadu, P.; Zohoori, F.V.; Pak, T. Human and environmental impacts of nanoparticles: A scoping review of the current literature. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, L.; Ju, Z.; Skonieczna, M.; Zhou, P.K.; Huang, R. Nanoparticles-induced potential toxicity on human health: Applications, toxicity mechanisms, and evaluation models. MedComm 2023, 4, e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkez, H.; Arslan, M.E.; Sönmez, E.; Geyikoğlu, F.; Açıkyıldız, M.; Tatar, A. Microarray assisted toxicological investigations of boron carbide nanoparticles on human primary alveolar epithelial cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 300, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delong, R.K.; Hurst, M.N.; Aryal, S.; Inchun, N.K. Unique Boron Carbide Nanoparticle Nanobio Interface: Effects on Protein-RNA Interactions and 3-D Spheroid Metastatic Phenotype. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 2097–2103. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, M.-C.; Tsai, M.-H.; Que, D.E.; Bongo, S.J.; Hsu, W.-L.; Tayo, L.L.; Chao, H.-R.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lin, S.-L.; Gou, Y.-Y.; et al. Fine Particulate Matter-Induced Toxic Effects in an Animal Model of Caenorhabditis elegans. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.-C.; Huang, K.-L.; Avelino, J.L.; Tayo, L.L.; Lin, C.-C.; Tsai, M.-H.; Lin, S.-L.; Mansor, W.N.W.; Su, C.-K.; Huang, S.-T. Toxic Assessment of Heavily Traffic-Related Fine Particulate Matter Using an In-Vivo Wild-Type Caenorhabditis elegans Model. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1974–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.H.; Hou, W.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Chang, Y.T.; Chao, H.R. The Impact of Background-Level Carboxylated Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWCNTs-COOH) on Induced Toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans and Human Cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.-H.; Tsai, M.-H.; Huang, S.-T.; Lee, J.-D.; Hsiao, T.-C.; Wan Mansor, W.N.; Chao, H.-R. Traffic-Related-Air-Pollutant PM2.5 Caused Toxicity on Caenorhabditis elegans with Cotreatment of High-Dose Glucose and Tempeh. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2023, 23, 220340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, D.E.; Hou, W.-C.; Yap Ang, M.B.M.; Lin, C.-C. Toxic Effects of Hydroxyl- and Amine-functionalized Silica Nanoparticles (SiO2 and NH2-SiO2 NPs) on Caenorhabditis elegans. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1987–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-H.; Chao, H.-R.; Jiang, J.-J.; Su, Y.-H.; Cortez, M.-s.P.; Tayo, L.L.; Lu, I.C.; Hsieh, H.; Lin, C.-C.; Lin, S.-L.; et al. Toxicity of Low-Dose Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles in an In-Vivo Wild Type of Caenorhabditis elegans Model. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Xu, H.; Liang, X.; Tang, M. Caenorhabditis elegans as a complete model organism for biosafety assessments of nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 708–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manimaran, P.; Chen, S.-M.; Aldossari, S.A.; Rajaji, U.; Hung, K.-Y. Elevated temperature fabrication of copper sulfide nanosphere implemented boron carbide nanocomposite for hyper-sensitive detection of sulfadiazine in water and urine samples. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 692, 137503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, T.K.; Steinbaugh, M.J.; Hourihan, J.M.; Ewald, C.Y.; Isik, M. SKN-1/Nrf, stress responses, and aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; St Clair, D.K. Regulation of superoxide dismutase genes: Implications in disease. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tullet, J.M.A.; Green, J.W.; Au, C.; Benedetto, A.; Thompson, M.A.; Clark, E.; Gilliat, A.F.; Young, A.; Schmeisser, K.; Gems, D. The SKN-1/Nrf2 transcription factor can protect against oxidative stress and increase lifespan in C. elegans by distinct mechanisms. Aging Cell 2017, 16, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Raamsdonk, J.M.; Hekimi, S. Deletion of the mitochondrial superoxide dismutase sod-2 extends lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betteridge, D.J. What is oxidative stress? Metabolism 2000, 49, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnaiyan, A.M.; O’Rourke, K.; Lane, B.R.; Dixit, V.M. Interaction of CED-4 with CED-3 and CED-9: A molecular framework for cell death. Science 1997, 275, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.D.; Gray, C.F.; Song, L.; Nechushtai, R.; Gumienny, T.L.; Mittler, R.; Padilla, P.A. The cisd gene family regulates physiological germline apoptosis through ced-13 and the canonical cell death pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Horvitz, H.R. Caenorhabditis elegans CED-9 protein is a bifunctional cell-death inhibitor. Nature 1997, 390, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Shaham, S.; Ledoux, S.; Ellis, H.M.; Horvitz, H.R. The C. elegans cell death gene ced-3 encodes a protein similar to mammalian interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. Cell 1993, 75, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, K.; Strasser, A.; Kayagaki, N.; Dixit, V.M. Cell death. Cell 2024, 187, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Tariq, M.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Neurotoxicity of nonylphenol exposure on Caenorhabditis elegans induced by reactive oxidative species and disturbance synthesis of serotonin. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerr, J.S.; Frisby, D.L.; Gaskin, J.; Duke, A.; Asermely, K.; Huddleston, D.; Eiden, L.E.; Rand, J.B. The cat-1 gene of Caenorhabditis elegans encodes a vesicular monoamine transporter required for specific monoamine-dependent behaviors. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, R.; Sawin, E.R.; Trent, C.; Horvitz, H.R. Mutations in the Caenorhabditis elegans Serotonin Reuptake Transporter MOD-5 Reveal Serotonin-Dependent and -Independent Activities of Fluoxetine. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 5871–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, J.Y.; Victor, M.; Loer, C.; Shi, Y.; Ruvkun, G. Food and metabolic signalling defects in a Caenorhabditis elegans serotonin-synthesis mutant. Nature 2000, 403, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, J.Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Ruvkun, G. The C. elegans POU-domain transcription factor UNC-86 regulates the tph-1 tryptophan hydroxylase gene and neurite outgrowth in specific serotonergic neurons. Development 2002, 129, 3901–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Vogt, M.C.; Fox, B.W.; Wrobel, C.J.J.; Fajardo Palomino, D.; Curtis, B.J.; Zhang, B.; Le, H.H.; Tauffenberger, A.; Hobert, O.; et al. Parallel pathways for serotonin biosynthesis and metabolism in C. elegans. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2023, 19, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.; Gray, J.A.; Roth, B.L. The expanded biology of serotonin. Annu. Rev. Med. 2009, 60, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.M.; Alshagga, M.; Kong, C.; Alshawsh, M.A.; Alshehade, S.A.; Pan, Y. CYP35 family in Caenorhabditis elegans biological processes: Fatty acid synthesis, xenobiotic metabolism, and stress responses. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 3163–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moilanen, L.H.; Fukushige, T.; Freedman, J.H. Regulation of Metallothionein Gene Transcription: Identification of Upstream Regulatory Elements and Transcription Factors Responsible for Cell-Specific Expression of the Metallothionein Genes from Caenorhabditis Elegans. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 29655–29665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.Y.; Illera, P.A.; Kukhtar, D.; Benseny-Cases, N.; Cerón, J.; Álvarez, J.; Fonteriz, R.I.; Montero, M.; Laromaine, A. Arrhythmic Effects Evaluated on Caenorhabditis elegans: The Case of Polypyrrole Nanoparticles. Acs Nano 2023, 17, 17273–17284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocheleau, S.; Arbour, M.; Elias, M.; Sunahara, G.I.; Masson, L. Toxicogenomic effects of nano- and bulk-TiO2 particles in the soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.T.; Lu, J.H.; Jualo, S.M.; Tayo, L.L.; Mansor, W.N.; Lai, Y.C.; Wang, C.L.; Chao, H.R. Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) Nanoparticle Toxicity in a Caenorhabditis elegans Model. Toxics 2023, 11, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashock, M.J.; Zanon, T.; Kappell, A.D.; Petrella, L.N.; Andersen, E.C.; Hristova, K.R. Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Impact Several Toxicological Endpoints and Cause Neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, S.K.; Montoro Bustos, A.R.; Peterson, A.W.; Reipa, V.; Scanlan, L.D.; Hosbas Coskun, S.; Cho, T.J.; Johnson, M.E.; Hackley, V.A.; Nelson, B.C.; et al. Agglomeration of Escherichia coli with Positively Charged Nanoparticles Can Lead to Artifacts in a Standard Caenorhabditis elegans Toxicity Assay. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5968–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Yi, C.-X. Cell type-targeting nanoparticles in treating central nervous system diseases: Challenges and hopes. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2023, 12, 20230158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat Razavi, Z.; Sina Alizadeh, S.; Sadat Razavi, F.; Souri, M.; Soltani, M. Advancing neurological disorders therapies: Organic nanoparticles as a key to blood-brain barrier penetration. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 670, 125186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyumentseva, A.; Khilazheva, E.; Petrova, V.; Stolyar, S. Effects of iron oxide nanoparticles on the gene expression profiles of cerebral endotheliocytes and astrocytes. Toxicol. Vitr. 2024, 98, 105829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Qu, M.; Rui, Q.; Wang, D. Combinational effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and nanopolystyrene particles at environmentally relevant concentrations on nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; You, X.; Zhu, T.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Yu, H.; Qian, B. Silica nanoparticles enhance germ cell apoptosis by inducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 45, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.; Singh, M.; Mayes, E.L.H.; Martinez, A.; Shutthanandan, V.; Bansal, V.; Singh, S.; Karakoti, A.S. Ligand-mediated reversal of the oxidation state dependent ROS scavenging and enzyme mimicking activity of ceria nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 13973–13976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Lenz, K.A.; Gao, X.; Li, S.; Wallis, L.K. Comparative toxicity of a food additive TiO2, a bulk TiO2, and a nano-sized P25 to a model organism the nematode C. elegans. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 3556–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ye, X.; Xiong, Z.; Ihsan, A.; Ares, I.; Martínez, M.; Lopez-Torres, B.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Anadón, A.; Wang, X.; et al. Cancer Metabolism: The Role of ROS in DNA Damage and Induction of Apoptosis in Cancer Cells. Metabolites 2023, 13, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumienny, T.L.; Lambie, E.; Hartwieg, E.; Horvitz, H.R.; Hengartner, M.O. Genetic control of programmed cell death in the Caenorhabditis elegans hermaphrodite germline. Development 1999, 126, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, D.; Liang, Y.; Luo, X. Evaluating the adverse effects and mechanisms of nanomaterial exposure on longevity of C. elegans: A literature meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis of multi-transcriptome data. Environ. Res. 2024, 247, 118106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, X.; Lin, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, C.; Wang, D. Serotonin control of thermotaxis memory behavior in nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, J.-Y.; Park, Y.-K.; Park, K.; Choi, J. Ecotoxicological investigation of CeO2 and TiO2 nanoparticles on the soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans using gene expression, growth, fertility, and survival as endpoints. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 29, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andric, A.; Niederwanger, M.; Albertini, E.; Jansen-Dürr, P.; Stürzenbaum, S.R.; Dallinger, R.; Pedrini-Martha, V.; Weiss, A.K.H. A multi-domain snail metallothionein increases cadmium resistance and fitness in Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.; Haas, K.L.; Freedman, J.H. Role of MTL-1, MTL-2, and CDR-1 in mediating cadmium sensitivity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 128, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, M.W.; Sørensen, P.G.; Björkdahl, O.; Jensen, M.R.; Gundersen, H.J.; Bjørnholm, T. Preparation and characterization of Boron carbide nanoparticles for use as a novel agent in T cell-guided boron neutron capture therapy. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2006, 64, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, M.W.; Björkdahl, O.; Sørensen, P.G.; Hansen, T.; Jensen, M.R.; Gundersen, H.J.; Bjørnholm, T. Functionalization and cellular uptake of boron carbide nanoparticles. The first step toward T cell-guided boron neutron capture therapy. Bioconjug Chem. 2006, 17, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, R.K.; Mitchell, J.A.; Morris, R.T.; Comer, J.; Hurst, M.N.; Ghosh, K.; Wanekaya, A.; Mudge, M.; Schaeffer, A.; Washington, L.L.; et al. Enzyme and Cancer Cell Selectivity of Nanoparticles: Inhibition of 3D Metastatic Phenotype and Experimental Melanoma by Zinc Oxide. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 13, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.E.; Comer, J.; Kim, M.J.; Marroquin, S.; Murthy, V.; Ramani, M.; Hopke, T.G.; McCall, J.; Choi, S.O.; DeLong, R.K. Comparative functional dynamics studies on the enzyme nano-bio interface. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 4523–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozień, D.; Szermer-Olearnik, B.; Rapak, A.; Szczygieł, A.; Anger-Góra, N.; Boratyński, J.; Pajtasz-Piasecka, E.; Bućko, M.M.; Pędzich, Z. Boron-Rich Boron Carbide Nanoparticles as a Carrier in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy: Their Influence on Tumor and Immune Phagocytic Cells. Materials 2021, 14, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Reina, G.; Kang, H.G.; Chen, X.; Zou, Y.; Ishikawa, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Komatsu, N. Polyglycerol Functionalized (10) B Enriched Boron Carbide Nanoparticle as an Effective Bimodal Anticancer Nanosensitizer for Boron Neutron Capture and Photothermal Therapies. Small 2022, 18, e2204044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróblewska, A.; Szermer-Olearnik, B.; Szczygieł, A.; Węgierek-Ciura, K.; Mierzejewska, J.; Kozień, D.; Żeliszewska, P.; Kruszakin, R.; Migdał, P.; Pędzich, Z.; et al. Macrophages as carriers of boron carbide nanoparticles dedicated to boron neutron capture therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, K.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, T. Boron carbide nanoparticles for boron neutron capture therapy. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 10717–10730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene Code | Forward Primer (5′ to 3′) | Reverse Primer (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| C. elegans | ||
| skn-1 | GGACGTCAACAGCAGACTCA | GAGAGCACGTTGATGACGAA |
| sod-1 | TCAGGTCTCCAACGCGATTT | ACCGGGAGTAAGTCCCTTGA |
| sod-2 | GAGGCGGTCTCCAAAGGAAA | CGCTCTTAATTGCGGTGAGC |
| sod-3 | CTCCAAGCACACTCTCCCAG | TCCCTTTCGAAACAGCCTCG |
| sod-4 | GACGCGGTACTTCAGACCAA | CTGGAGGAAGGGATGCTGTC |
| sod-5 | CCGATAAGGTGGTCAGCCTC | CAAAGACTCCTCGGCCTTGT |
| ctl-1 | GTGTCGTTCATGCCAAGGGAG | TGGATTGCGTCACGAATGAAG |
| ctl-2 | TCCCAGATGGGTACCGTCAT | GGTCCGAAGAGGCAAGTTGA |
| ctl-3 | ATGCCAATGCTTCCCCACAT | GCAGGTGGGGTTCCTGATTT |
| cat-1 | CGGTAGAAACTGAAGAACCTG | AGGCATAGTGTAGCCGATTC |
| cat-4 | TCGGAGAAGACATCAATCG | GCTCACAAAGGGAGAACATT |
| mod-5 | ATTATTCAAGCCTATGTTCCAA | GAGATGAGATTCCGACAGT |
| tph-1 | CTGCCGATTCTCCAGTAAAA | ACTACCCTCAACGGCATGTT |
| cyp35a2 | TCGATTTGTGGATGACTGG | AATGGATGCATGACGTTGAA |
| mtl--1 | AGTGCGGAGACAAATGTGAATGC | AGCAGTTCCCTGGTGTTGATGG |
| mtl-2 | TTGTTCCTGCAACACCGGAA | GTTGGCACACTTGCATCCTC |
| ced-3 | GGAGCTTGCTAGAGAGGAACA | TCAGCAAGTCCTTCGTGTCC |
| ced-4 | GCTGATGCTAAAAAGCGAAGA | CGTTGCTGGATTTCCACTGC |
| ced-9 | AGTGATGCTCAGGACTTGCC | AGCCTTGGCTCTTCCCAATC |
| ced-13 | ACACTTTCTCCCGCTGTTGT | TCAGAGTCAAACTCGTCGCA |
| hus-1 | CGGCGGACACTGTTATCTGA | AATTGACGGCCTGGAGTACG |
| cep-1 | AGAATACCCGATTCGCAGGAC | TCGCCATTGCCCAGTATTCC |
| actin | AGAAGAGCACCCAGTCCTCC | GAAGCGTAGAGGGAGAGGAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.-T.; Bulaon, E.P.; Yang, K.-J.; Taw, A.; Tayo, L.L.; Hsieh, P.-H.; Tsai, J.-H.; Lu, J.-H.; Jiang, J.-J.; Wu, H.-H.; et al. The Impact of Boron Carbide Nanoparticle (B4C-NPs) Toxicity on Caenorhabditis elegans Models. Toxics 2025, 13, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060492
Huang S-T, Bulaon EP, Yang K-J, Taw A, Tayo LL, Hsieh P-H, Tsai J-H, Lu J-H, Jiang J-J, Wu H-H, et al. The Impact of Boron Carbide Nanoparticle (B4C-NPs) Toxicity on Caenorhabditis elegans Models. Toxics. 2025; 13(6):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060492
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Sen-Ting, Erin P. Bulaon, Kai-Jie Yang, Adriana Taw, Lemmuel L. Tayo, Ping-Heng Hsieh, Jen-Hsiung Tsai, Jian-He Lu, Jheng-Jie Jiang, Hsing-Hsien Wu, and et al. 2025. "The Impact of Boron Carbide Nanoparticle (B4C-NPs) Toxicity on Caenorhabditis elegans Models" Toxics 13, no. 6: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060492
APA StyleHuang, S.-T., Bulaon, E. P., Yang, K.-J., Taw, A., Tayo, L. L., Hsieh, P.-H., Tsai, J.-H., Lu, J.-H., Jiang, J.-J., Wu, H.-H., & Chao, H.-R. (2025). The Impact of Boron Carbide Nanoparticle (B4C-NPs) Toxicity on Caenorhabditis elegans Models. Toxics, 13(6), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060492







