Vegan Red: A Safer Alternative to Synthetic Food Dyes?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Red Food Dye Solutions
2.2. Embryo Growth
2.3. Embryo Treatment
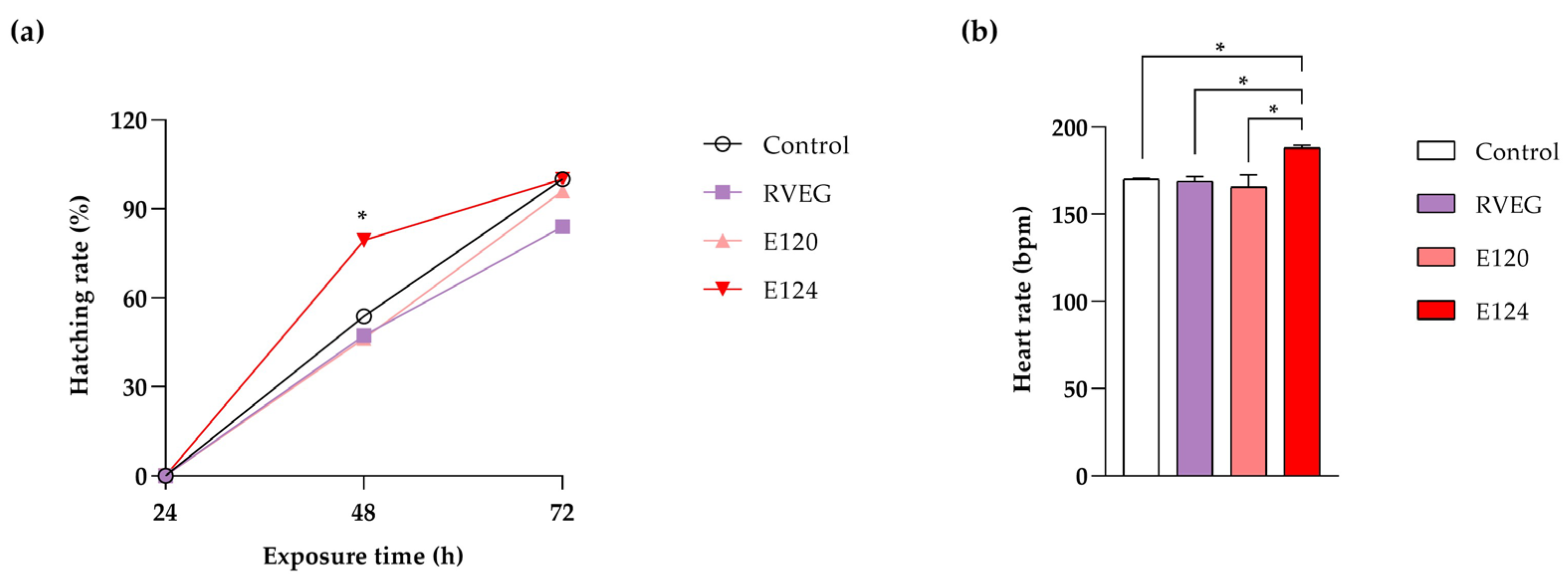
2.4. Hatching and Heart Rate Analyses
2.5. Behavioural Analyses
2.5.1. Spontaneous Embryonic Movements
2.5.2. Motility Test at 72 h
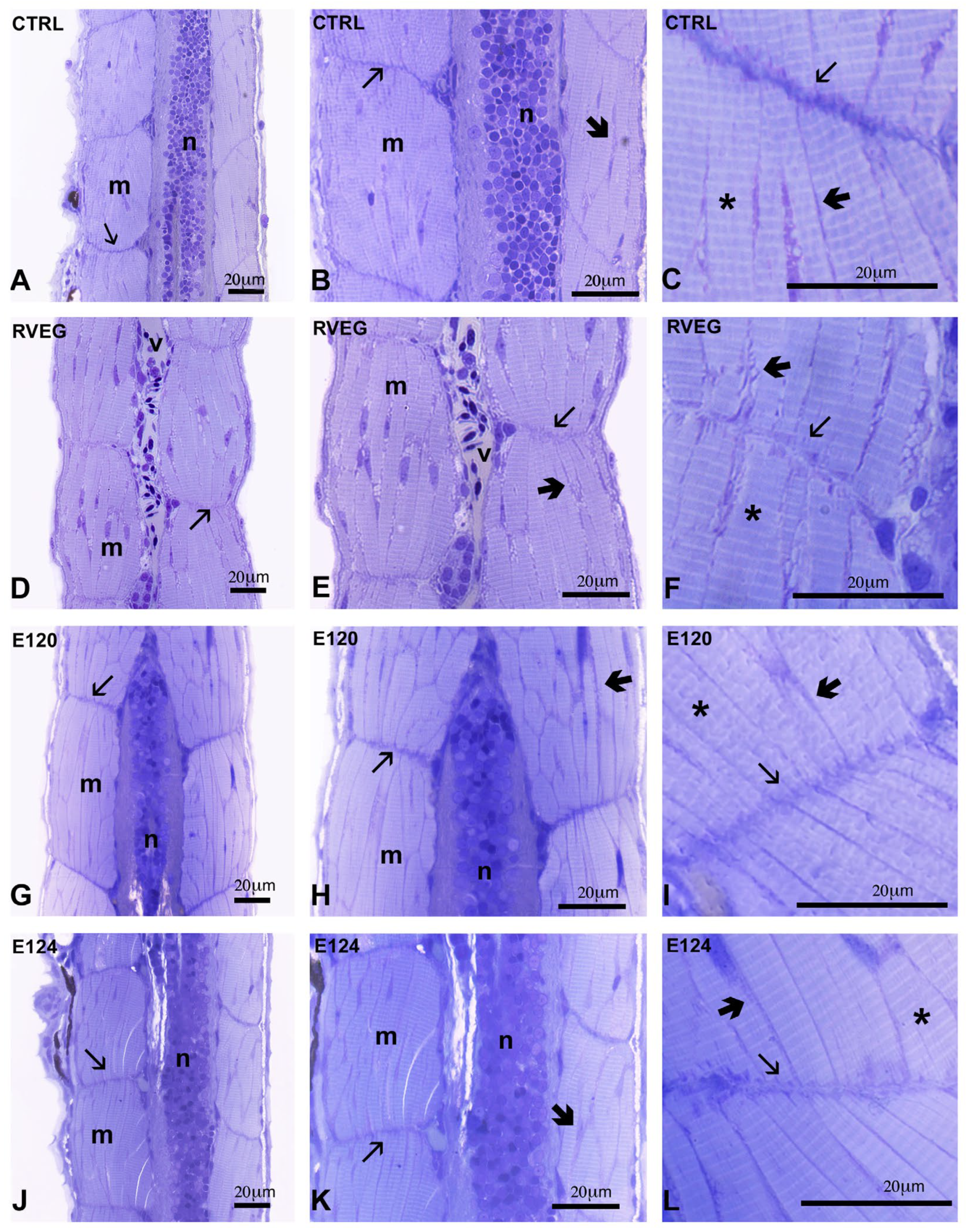
2.6. Histological Analyses
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Toxicity Parameters
3.2. Behavioural Tests
3.2.1. Assessment of Spontaneous Embryonic Movements
3.2.2. Evaluation of Swimming Performance
3.3. Histological Analysis of Skeletal Muscle
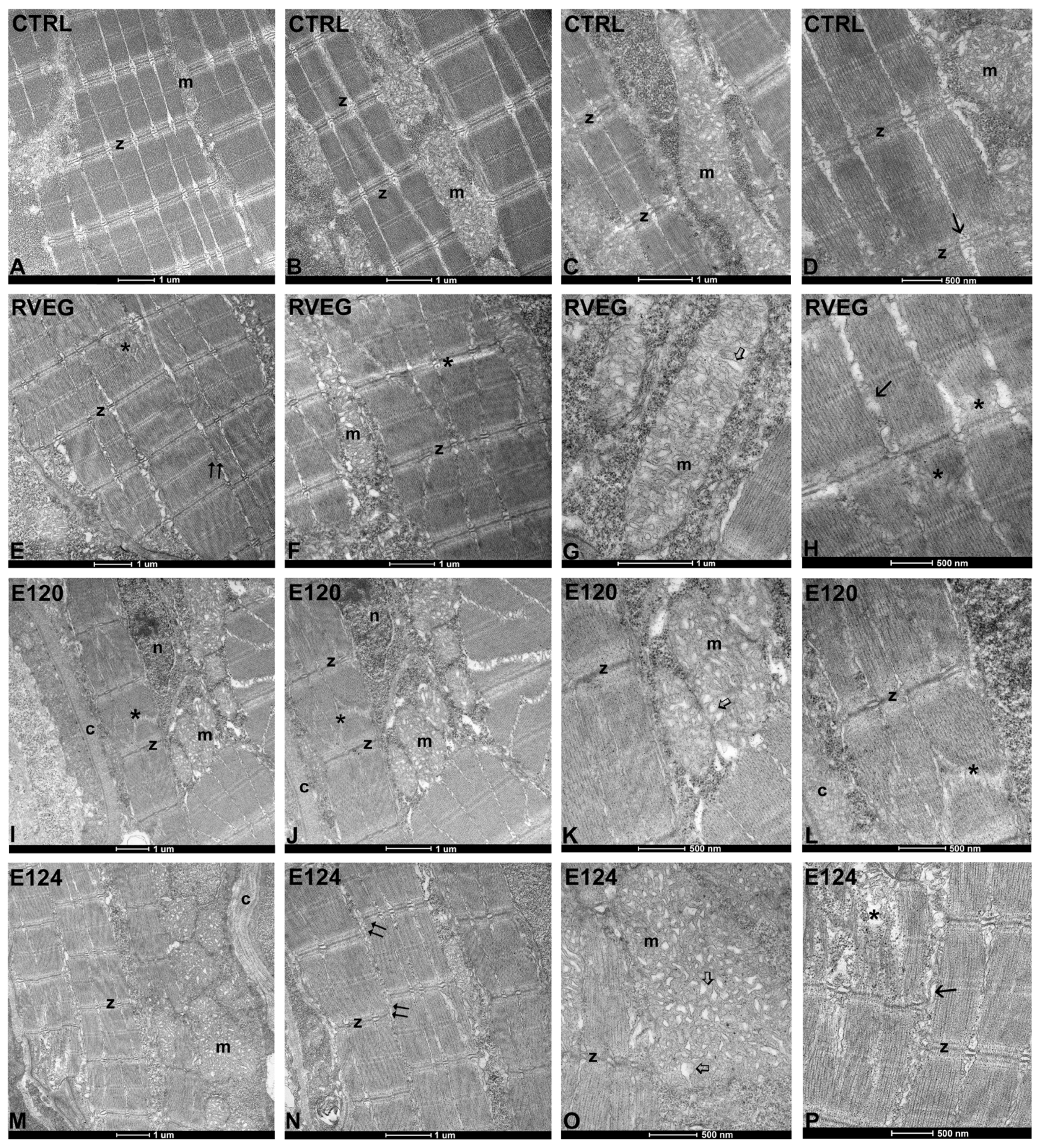
3.4. Ultrastructure of Skeletal Muscle
3.5. Analysis of Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kobylewski, S.; Jacobson, M.F. Toxicology of Food Dyes. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health 2012, 18, 220–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damotharan, K.; Sudhakaran, G.; Ramu, M.; Krishnan, M.; Arockiaraj, J. Biochemical Processes Mediating Neurotoxicity Induced by Synthetic Food Dyes: A Review of Current Evidence. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 143295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingue, S.; Mindang, E.L.N.; Awounfack, F.C.; Kalgonbe, A.Y.; Kada, M.M.; Njamen, D.; Ndinteh, D.T. Oral Administration of Tartrazine (E102) Accelerates the Incidence and the Development of 7, 12-Dimethylbenz (A) Anthracene (DMBA)-Induced Breast Cancer in Rats. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eagle, K. ADHD Impacted by Sulfotransferase (SULT1A) Inhibition from Artificial Food Colours and Plant-Based Foods. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 135, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husunet, M.T.; Mısırlı, R.Ç.; Istıflı, E.S.; Ila, H.B. Investigation of the Genotoxic Effects of Patent Blue V (E131) in Human Peripheral Lymphocytes and in Silico Molecular Docking. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 45, 1780–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, A.; Abdulkarim, S. Toxicological Study and Quantitative Determination of Allura Red (E129) Dye Additive in Some Food Beverages Consumed in Katsina Metropolis, Nigeria. FUDMA J. Sci. 2024, 8, 228–232. [Google Scholar]
- Schweiggert, R.M. Perspective on the ongoing Replacement of Artificial and Animal-Based Dyes with Alternative Natural Pigments in Foods and Beverages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3074–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rhim, J.W. Anthocyanin Food Colorant and its Application in Ph-Responsive Color Change Indicator Films. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2297–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, F.R.; Mendonça, J.N.; Moraes, L.A.; de Oliveira, G.A.; Gravato, C.; Soares, A.M.; de Oliveira, D.P. Toxicological and Behavioural Responses as a Tool to Assess the Effects of Natural and Synthetic Dyes on Zebrafish Early Life. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, C.M.; Simoniello, P.; Arena, C.; Capriello, T.; Panzuto, R.; Vitale, E.; Agnisola, C.; Tizzano, M.; Avallone, B.; Ferrandino, I. Effects of Four Food Dyes on Development of Three Model Species, Cucumis Sativus, Artemia Salina and Danio Rerio: Assessment of Potential Risk for the Environment. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avallone, B.; Arena, C.; Simoniello, P.; Di Lorenzo, M.; Vitale, E.; Capriello, T.; Ferrandino, I.; Raggio, A.; Sasso, M.; Napolitano, G.; et al. Comparative Toxicity of Vegan Red, E124, and E120 Food Dyes on Three Rapidly Proliferating Model Systems. Environments 2022, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, G.; Motta, C.M.; Agnisola, C.; Venditti, P.; Fasciolo, G.; Ferrandino, I.; Capriello, T.; Vitale, E.; Costanzo, G.; Avallone, B.; et al. Commercial Red Food Dyes Preparations Modulate the Oxidative State in Three Model Organisms (Cucumis sativus, Artemia salina, and Danio rerio). Environments 2022, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenberg, S.; Lewkowski, O.; Erler, S. Dyeing but not Dying: Colourful Dyes as a Non-Lethal Method of Food Labelling for in Vitro-Reared Honey Bee (Apis Mellifera) Larvae. J. Insect Physiol. 2019, 113, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Rubio, M.A.; Hernández-García, S.; García-Carmona, F.; Gandía-Herrero, F. Consumption of Commonly Used Artificial Food Dyes Increases Activity and Oxidative Stress in the Animal Model Caenorhabditis elegans. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriello, T.; Visone, I.M.; Motta, C.M.; Ferrandino, I. Adverse Effects of E150d on Zebrafish Development. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 147, 111877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J.S.; Al-Temeemy, A.A.; Isted, H.; Spencer, J.W.; Sneddon, L.U. Assessment of behaviour in groups of zebrafish (Danio rerio) using an intelligent software monitoring tool, the chromatic fish analyser. J. Neurosci. Methods 2019, 328, 108433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orger, M.B.; de Polavieja, G.G. Zebrafish Behaviour: Opportunities and Challenges. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 40, 125–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Deng, P.; Li, G.; Liu, H.; Zuo, J.; Cui, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Yao, J.; Peng, X.; et al. Neurotoxicity of Combined Exposure to the Heavy Metals (Pb and As) in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxics 2024, 12, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; Zhou, J.L.; Li, J.; Li, C.Q.; Wu, L.R. Developmental neurotoxicity and toxic mechanisms induced by olaquindox in zebrafish. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petel Légaré, V.; Rampal, C.J.; Gurberg, T.J.; Aaltonen, M.J.; Janer, A.; Zinman, L.; Shoubridge, E.A.; Armstrong, G.A. Loss of Mitochondrial Chchd10 or Chchd2 in Zebrafish Leads to an ALS-Like Phenotype and Complex I Deficiency Independent of The Mitochondrial Integrated Stress Response. Dev. Neurobiol. 2023, 83, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Saraswathy, V.M.; Xiang, L.; Fürthauer, M. Notch-mediated inhibition of neurogenesis is required for zebrafish spinal cord morphogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Row, R.H.; Tsotras, S.R.; Goto, H.; Martin, B.L. The Zebrafish Tailbud Contains Two Independent Populations of Midline Progenitor Cells That Maintain Long-Term Germ Layer Plasticity and Differentiate in Response to Local Signaling Cues. Development 2016, 143, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacGrogan, D.; Münch, J.; de la Pompa, J.L. Notch and Interacting Signalling Pathways in Cardiac Development, Disease, and Regeneration. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 685–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Pietra, A.; Fasciolo, G.; Lucariello, D.; Motta, C.M.; Venditti, P.; Ferrandino, I. Polystyrene Microplastics Effects on Zebrafish Embryological Development: Comparison of Two Different Sizes. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 106, 104371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book: A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). 2000. Available online: http://zfin.org/zf_info/zfbook/zfbk.html (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Monaco, A.; Capriello, T.; Grimaldi, M.C.; Schiano, V.; Ferrandino, I. Neurodegeneration in Zebrafish Embryos and Adults After Cadmium Exposure. Eur. J. Histochem. 2017, 61, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cresci, A.; De Rosa, R.; Agnisola, C. Assessing the Influence of Personality on Sensitivity to Magnetic Fields in Zebrafish. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 145, 59229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogliano, C.; Carotenuto, R.; Rusciano, G.; Sasso, A.; Motta, C.M.; Agnisola, C.; Avallone, B. Structural and Functional Damage to the Retina and Skeletal Muscle in Xenopus Laevis Embryos Exposed to the Commonly Used Psychotropic Benzodiazepine Delorazepam. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 102, 104235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Pietra, A.; Imperatore, R.; Coccia, E.; Mobilio, T.; Ferrandino, I.; Paolucci, M. Comparative Study of Condensed and Hydrolysable Tannins during the Early Stages of Zebrafish Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A New Mathematical Model for Relative Quantification in Real-Time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Horgan, G.W.; Dempfle, L. Relative Expression Software Tool (REST©) for Group-Wise Comparison and Statistical Analysis of Relative Expression Results in Real-Time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, M.; von der Ohe, P.C.; Gräff, T.; Kühnen, U.; Hebel, J.; Heid, C.; Kundy, L.; Kuttler, J.; Moroff, F.M.; Schlösinger, A.F.; et al. Heart rate as an early warning parameter and proxy for subsequent mortality in Danio rerio embryos exposed to ionisable substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, V.; Pancharatna, K. Food colourant Sunset Yellow (E110) intervenes in the developmental profile of zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Appl. Toxicol. 2019, 39, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Xiao, X.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; He, J. Tea and Its Components Prevent Cancer: A Review of the Redox-Related Mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Liu, H.-C.; Ou, W.-B.; Eilers, G.; Zhou, S.-M.; Meng, F.-G.; Li, C.-Q.; Li, Y.Q. Toxicity Induced by Basic Violet 14, Direct Red 28 and Acid Red 26 in Zebrafish Larvae. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, S.G.; Yuzbasioglu, D.; Avuloglu-Yilmaz, E.; Unal, F. Do The Azo Food Colorings Carmoisine and Ponceau 4R Have a Genotoxic Potential? Toxicol. Res. 2025, 14, tfaf033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana Marques, G.; do Anjos Sousa, J.J.; Peron, A.P. Action of Ponceau 4R (E-124) Food Dye on Root Meristematic Cells of Allium cepa L. Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2015, 37, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragato, C.; Pistocchi, A.; Bellipanni, G.; Confalonieri, S.; Balciuniene, J.; Monastra, F.M.; Gaudenzi, G. Zebrafish dnm1a Gene Plays a Role in the Formation of Axons and Synapses in the Nervous Tissue. J. Neurosci. Res. 2023, 101, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Re-Evaluation of Cochineal, Carminic Acid, Carmines (E 120) as a Food Additive. EFSA J. 2016, 14, 4288. [Google Scholar]
- Darroch, H.; Astin, J.W.; Hall, C.J. Microinjection of β-glucan Into Larval Zebrafish (Danio rerio) for the Assessment of a Trained-Like Immunity Phenotype. Bio-Protoc. 2023, 13, e4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosetti, F.; Chiuminatto, U.; Mazzucco, E.; Calabrese, G.; Gennaro, M.C.; Marengo, E. Identification of Photodegradation Products of Allura Red AC (E129) in a Beverage by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Quadrupole-Time-Of-flight Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 746, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant, K.E.; Sinno, P.P.; Jacobs, H.M.; Timme-Laragy, A.R. Nrf2a Modulates the Embryonic Antioxidant Response to Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid (PFOS) in the Zebrafish, Danio rerio. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 198, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stackley, K.D.; Beeson, C.C.; Rahn, J.J.; Chan, S.S.L. Bioenergetic Profiling of Zebrafish Embryonic Development. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rescan, P.Y. Development of myofibres and associated connective tissues in fish axial muscle: Recent insights and future perspectives. Differentiation 2019, 106, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Listrat, A.; Lebret, B.; Louveau, I.; Astruc, T.; Bonnet, M.; Lefaucheur, L.; Picard, B.; Bugeon, J. How Muscle Structure and Composition Influence Meat and Flesh Quality. Sci. World J. 2016, 2016, 3182746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, I.; Wang, L.; Hu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Zhou, J. GFAP (Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein)-Positive Progenitor Cells Contribute to the Development of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells and Endothelial Cells—Brief Report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, U.; Kern, H. Severely Atrophic Human Muscle Fibres with Nuclear Misplacement Survive Many Years of Permanent Denervation. Eur. J. Transl. Myol. 2016, 26, 5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuca-Nassr, G.N.; Vitzel, K.F.; Mancilla-Solorza, E.; Márquez, J.L. Sarcomere Structure: The Importance of Desmin Protein in Muscle Atrophy. Int. J. Morphol. 2018, 36, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.E.; Tokuyama, T.; Anzai, T.; Chanthra, N.; Uosaki, H. Sarcomere Maturation: Function Acquisition, Molecular Mechanism, and Interplay with Other Organelles. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2022, 377, 20210325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.H.; Liu, F.J.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Cheng, J.X.; Fan, M.; Wu, H.T. Notch1 Gain of Function in Skeletal Muscles Leads to Neuromuscular Junction Formation Defects and Neonatal Death. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2018, 24, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Franco, D.; Kalra, R.; Draper, I.; Pacak, C.A.; Asakura, A.; Kang, P.B. The Notch Signaling Pathway in Skeletal Muscle Health and Disease. Muscle Nerve 2022, 66, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ježek, P.; Jabůrek, M.; Holendová, B.; Engstová, H.; Dlasková, A. Mitochondrial Cristae Morphology Reflecting Metabolism, Superoxide Formation, Redox Homeostasis, and Pathology. Antiox. Redox Signal. 2023, 39, 635–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlach, J.; Pireddu, P.; Zhang, X.; Wetzel, S.; Mennuni, M.; Milenkovic, D.; Nolte, H.; Filograna, R. The CHCHD2-CHCHD10 Protein Complex is Modulated by Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Alters Lipid Homeostasis in the Mouse Brain. bioRxiv 2024. bioRxiv:2024.09.10.612325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wruss, J.; Waldenberger, G.; Huemer, S.; Uygun, P.; Lanzerstorfer, P.; Müller, U.; Höglinger, O.; Weghuber, J. Compositional Characteristics of Commercial Beetroot Products and Beetroot Juice Prepared from Seven Beetroot Varieties Grown in Upper Austria. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 42, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, N.; Mei, X.; Zu, Y.; Li, Z.; Qin, L.; Li, B. Effects of lime and oxalic acid on antioxidant enzymes and active components of Panax notoginseng under cadmium stress. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhong, Z.Y.; Wang, H.B.; Wang, H.J.; Wu, D.M. Effects of Oxalic Acid on Arsenic Uptake and the Physiological Responses of Hydrilla Verticillata Exposed to Different Forms of Arsenic. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 100, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Symbol | Primers | Accession No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actin1 | β-actin | F | CGAGCAGGAGATGGGAACC | NM_131031.1 |
| R | CAACGGAAACGCTCATTGC | |||
| Glial fibrillary acidic protein | gfap | F | GCTCTGAGACAAGCGAAGCA | NM_131373.2 |
| R | CACGGAGAGATTCCAGGTTCA | |||
| Coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain | chchd2 | F | TGTCGGACACACAATAGGTCAC | NM_200767.1 |
| R | CATATGAACATGGGTTCTGCTG | |||
| Notch receptor 1a | notch1a | F | ACATCACCCTTCCAGCAGTC | NM_131441.1 |
| R | AGGCTTCCCTAAACCCTGAA | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fogliano, C.; La Pietra, A.; Motta, C.M.; Mobilio, T.; Capriello, T.; Sasso, M.; Avallone, B.; Ferrandino, I. Vegan Red: A Safer Alternative to Synthetic Food Dyes? Toxics 2025, 13, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060447
Fogliano C, La Pietra A, Motta CM, Mobilio T, Capriello T, Sasso M, Avallone B, Ferrandino I. Vegan Red: A Safer Alternative to Synthetic Food Dyes? Toxics. 2025; 13(6):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060447
Chicago/Turabian StyleFogliano, Chiara, Alessandra La Pietra, Chiara Maria Motta, Teresa Mobilio, Teresa Capriello, Margherita Sasso, Bice Avallone, and Ida Ferrandino. 2025. "Vegan Red: A Safer Alternative to Synthetic Food Dyes?" Toxics 13, no. 6: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060447
APA StyleFogliano, C., La Pietra, A., Motta, C. M., Mobilio, T., Capriello, T., Sasso, M., Avallone, B., & Ferrandino, I. (2025). Vegan Red: A Safer Alternative to Synthetic Food Dyes? Toxics, 13(6), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13060447










