Pulmonary Toxicity of Long, Thick MWCNT and Very Long, Thin Carboxylated MWCNT Aerosols Following 28 Days Whole-Body Exposure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
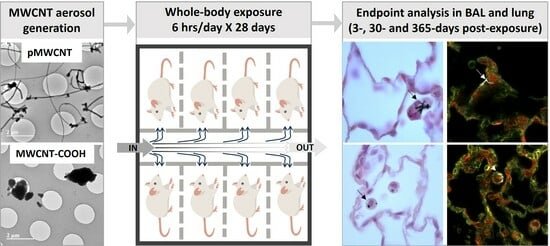
2.2. In Vivo Exposure Study
2.3. Whole-Body Exposure System
2.4. Aerosolisation of MWCNTs
2.5. Characterisation of MWCNT Aerosols
2.6. Deposited Dose Estimation
2.7. Bronchoalveolar Lavage and Lung Tissue Collection
2.8. Bronchoalveolar Lavage Analysis
2.9. RNA Extraction from Lung Tissues
2.10. Transcriptomic Analysis
2.11. Selected Cytokine Expression
2.12. Immunofluorescence on Lung Tissue Sections
2.13. Histopathology
2.14. Enhanced Dark-Field Microscopy
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
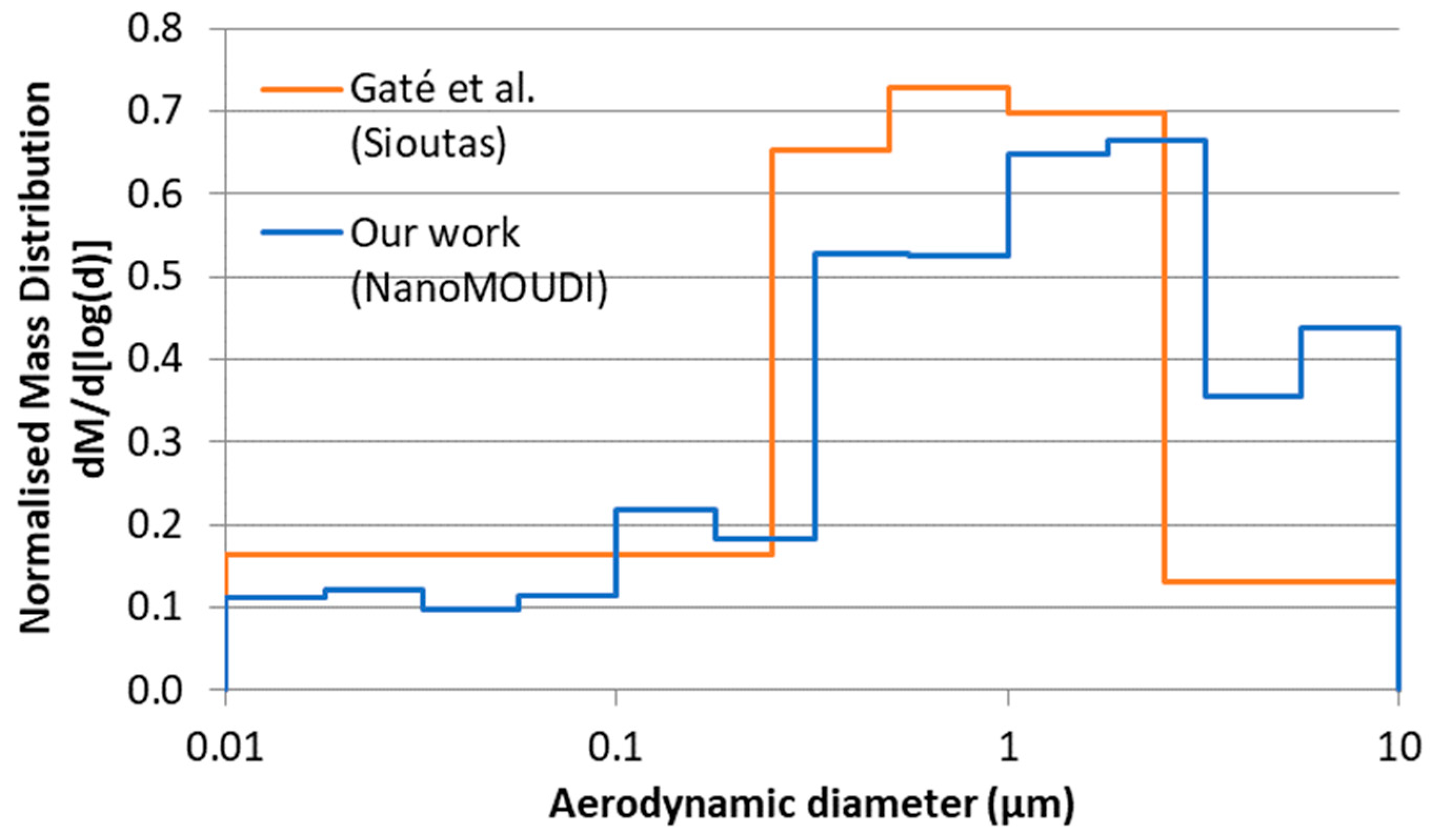
3.1. Aerosol Characterisation and Deposited Doses
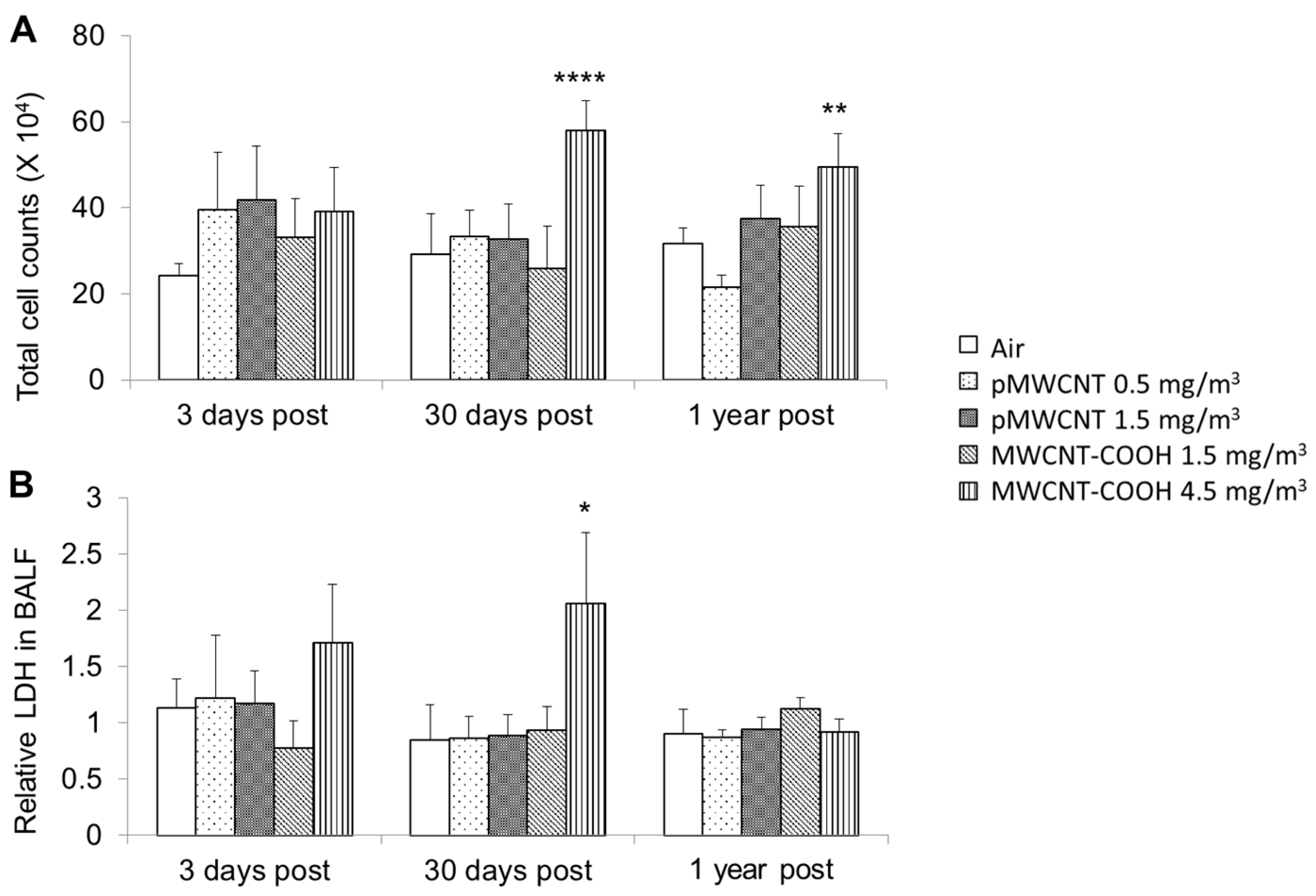
3.2. Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Cytology and Biochemistry
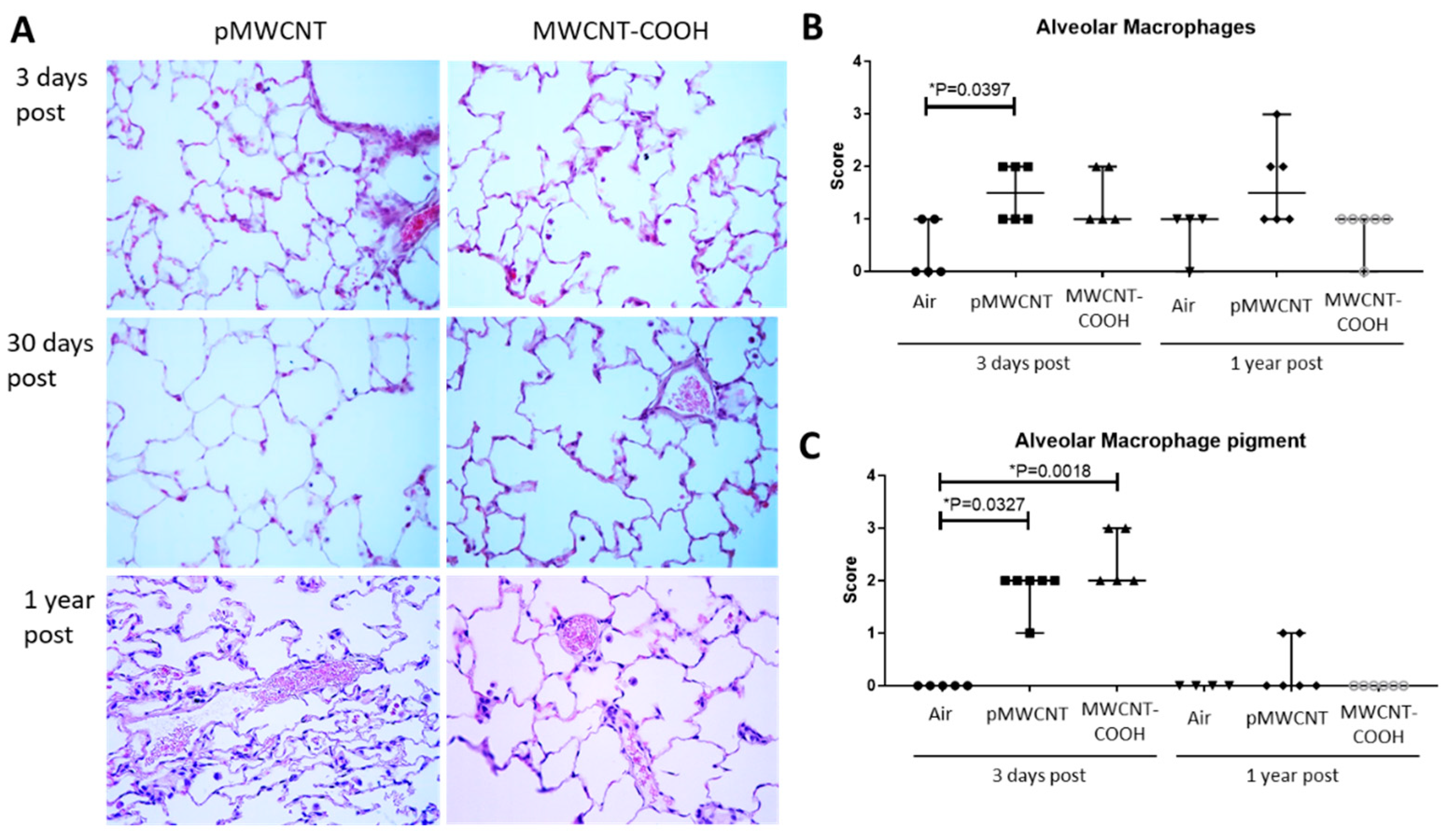
3.3. Histopathological Analysis
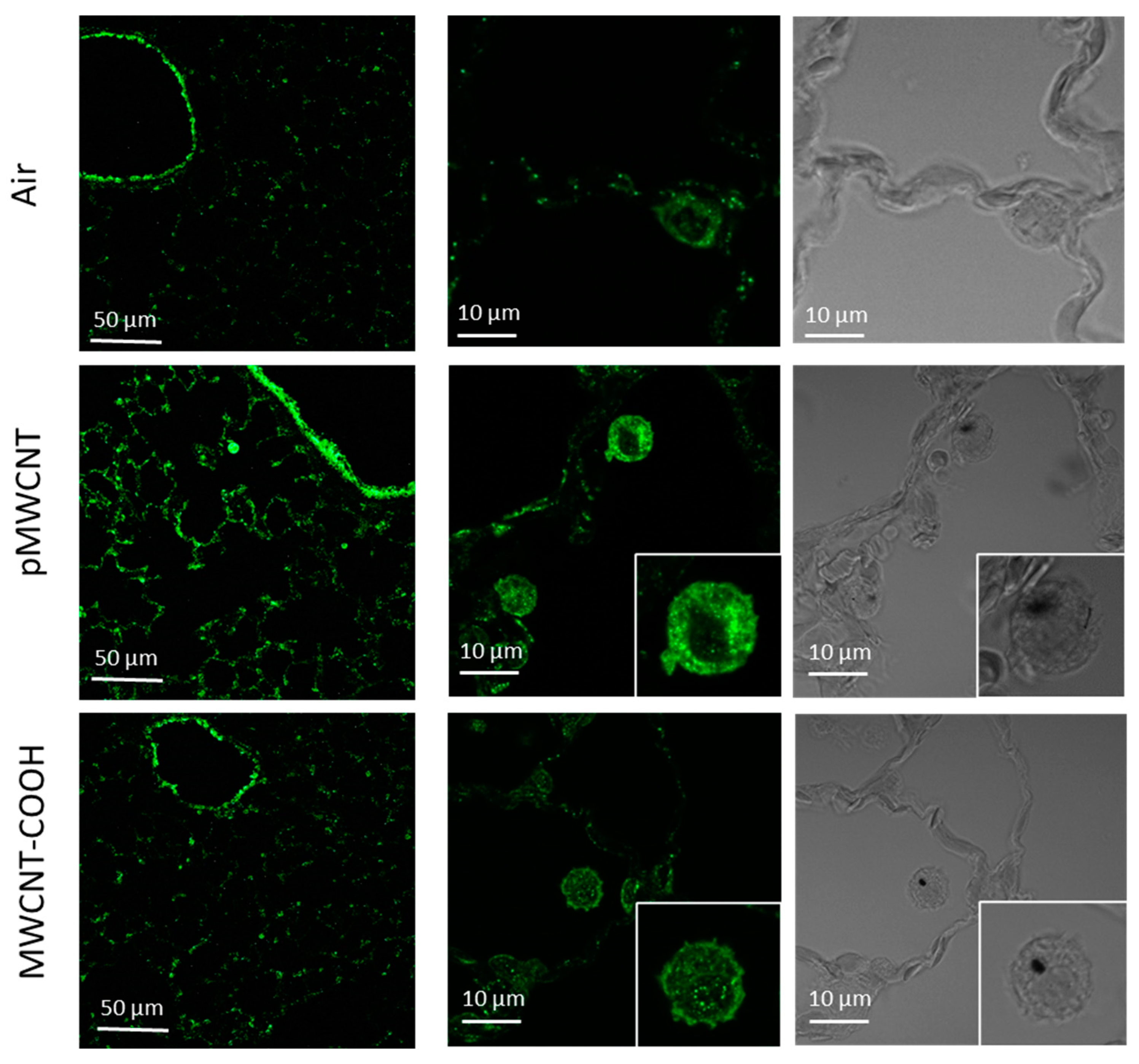
3.4. Pulmonary Distribution of Deposited MWCNTs and Biopersistence
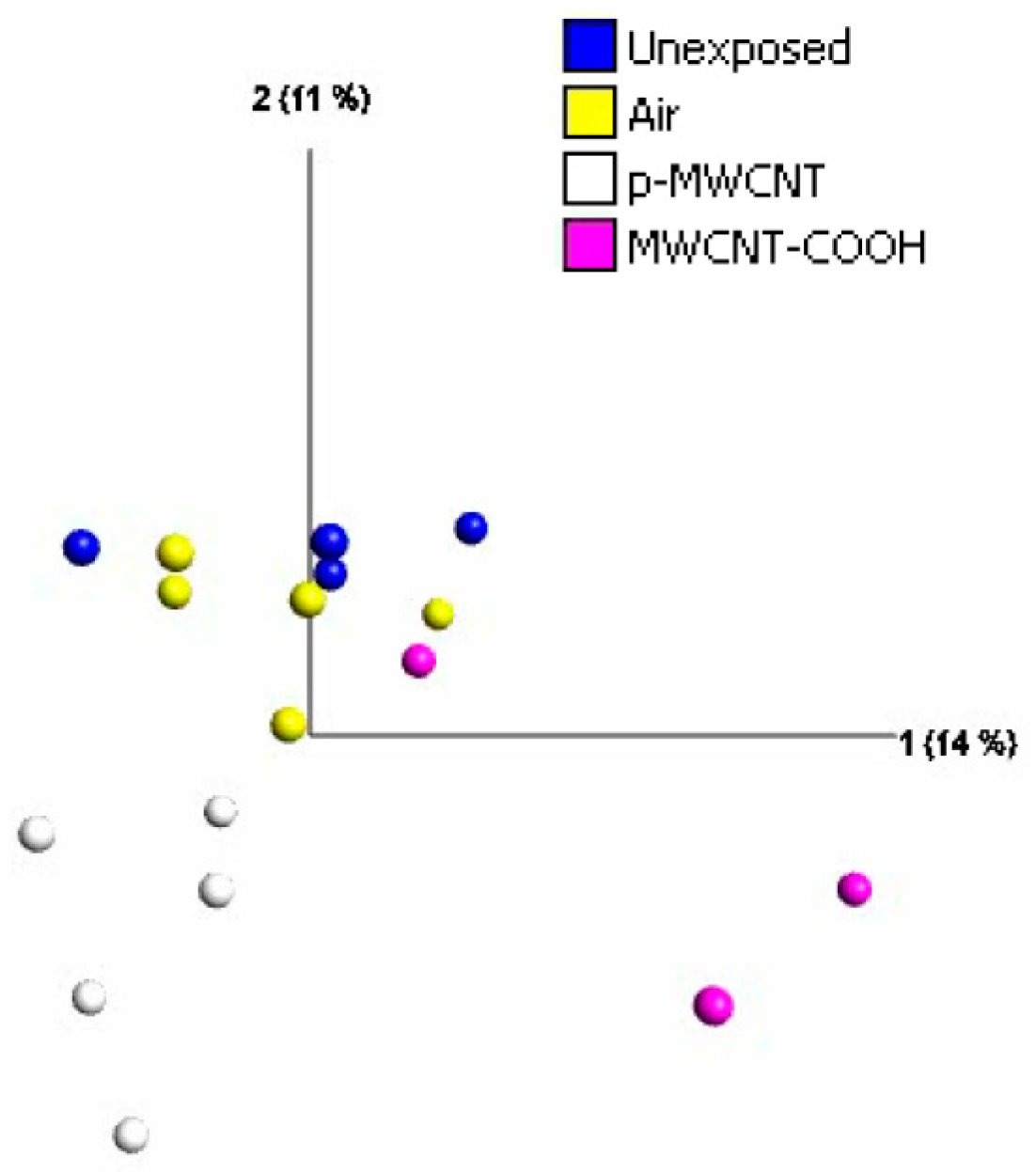
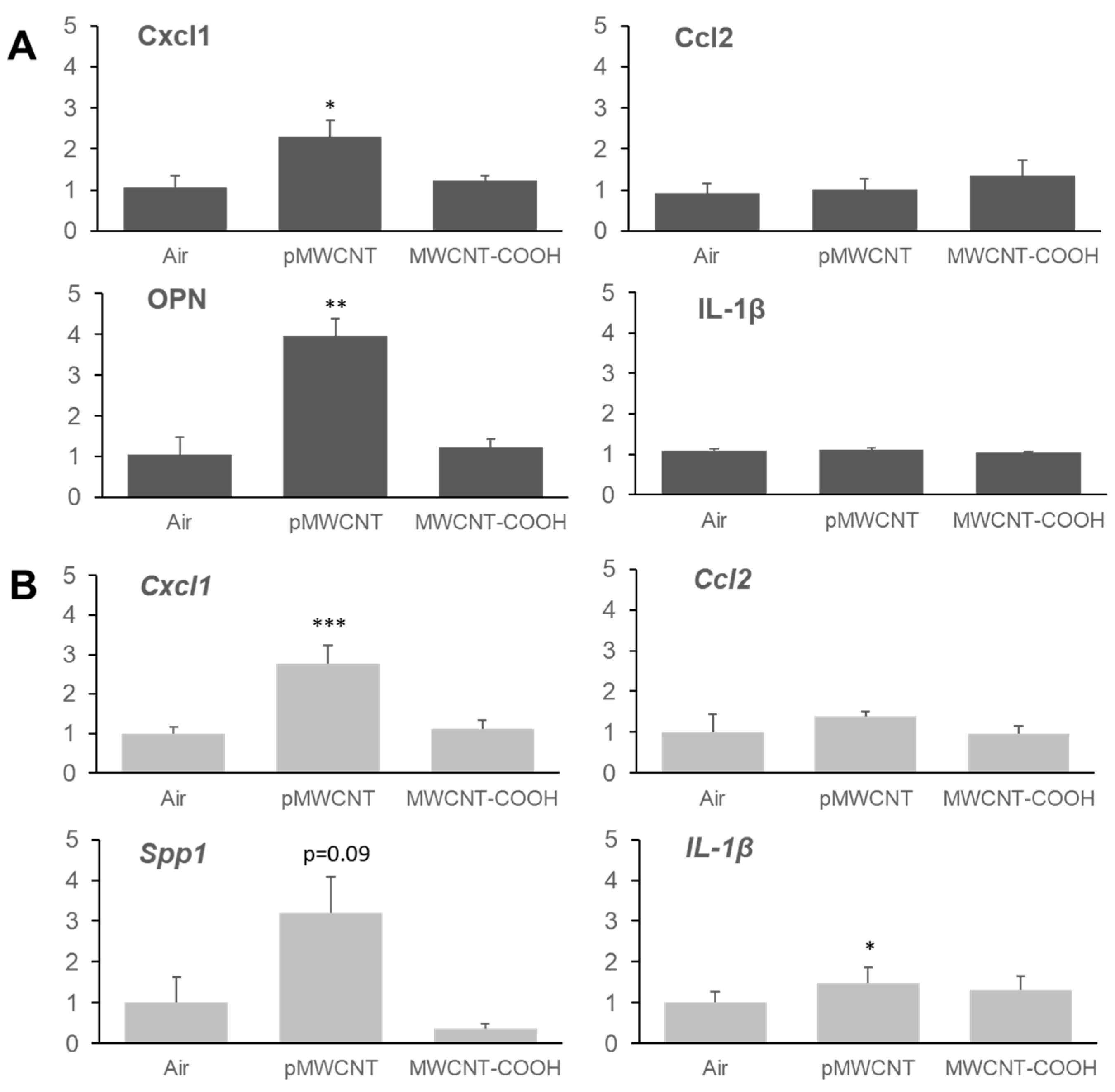
3.5. Transcriptomic Profiles of the Lung, Selected Cytokines, and Immunofluorescent Staining for Osteopontin
4. Discussion
4.1. Pulmonary Toxicity of MWCNT-COOH and pMWCNT Aerosols
4.2. Comparison of the Toxicity of Lung Deposited MWCNT-COOH and pMWCNT
4.3. Comparison of Whole-Body and Nose-Only Exposure Studies of pMWCNT (NM-401)
4.4. MWCNT-COOH and pMWCNT Have Different Effects on Global Gene Expression and Selected Cytokines
4.5. Lung Fibrogenic Effects Induced by CNTs and the Relevance of Osteopontin
4.6. Lung Clearance
4.7. Relevance of MWCNT Exposures
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APS | Aerodynamic particle sizer |
| AR | Aspect ratio |
| BAL | Bronchoalveolar lavage |
| BALF | Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid |
| CF | Carbon nanofibre |
| CMAD | Count median aerodynamic diameter |
| CNT | Carbon nanotubes |
| CPC | Condensation particle counter |
| DEG | Differentially expressed gene |
| GSD | Geometric standard deviation |
| H&E | Hematoxylin&Eosin |
| HARN | High aspect ratio nanomaterial |
| IATA | Integrated approach to testing and assessment |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| MMAD | Mass median aerodynamic diameter |
| MWCNT | Multi-walled carbon nanotube |
| NOAEL | No observed adverse effect level |
| OPN | Osteopontin |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| SWCNT | Single-walled carbon nanotube |
| TB | Tracheobronchial |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| TP | Total protein |
Appendix A
| MWCNT | Effective Density (g/cm3) | H Fraction | TB Fraction | P Fraction | Thoracic Deposition (µg) | Pulmonary Deposition (µg) | Pulmonary Deposition (cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pMWCNT | 0.032 * | 0.268 | 0.042 | 0.0001 | 109.2 (1.0) + | 6.1 (1.0) + | 1.1 |
| 0.36 | 0.267 | 0.034 | 0.011 | 115.6 (1.1) + | 33.3 (5.5) + | 6.0 | |
| 1.0 | 0.271 | 0.027 | 0.018 | 117.8 (1.1) + | 46.4 (7.6) + | 8.4 | |
| MWCNT-COOH | 0.071 * | 0.385 | 0.020 | 0.014 | 101.5 (1.0) + | 41.5 (1.0) + | 207.6 |
| 0.4 | 0.400 | 0.016 | 0.010 | 76.2 (0.8) + | 28.7 (0.7) + | 143.7 | |
| 0.8 | 0.404 | 0.015 | 0.007 | 65.7 (0.6) + | 21.2 (0.5) + | 105.9 |
| MWCNT | Aspect Ratio | H Fraction | TB Fraction | P Fraction | Thoracic Deposition (µg) | Pulmonary Deposition (µg) | Pulmonary Deposition (cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pMWCNT | 1 | 0.429 | 0.033 | 0.022 | 144.2 (1.3) + | 62.7 (10.3) + | 11.3 |
| 8 | 0.290 | 0.051 | 0.017 | 177.3 (1.6) + | 52.2 (8.6) + | 9.4 | |
| 15 | 0.280 | 0.050 | 0.003 | 138.7 (1.3) + | 22.5 (3.7) + | 4.1 | |
| 30 * | 0.268 | 0.042 | 0.0001 | 109.2 (1.0) + | 6.1 (1.0) + | 1.1 | |
| 60 | 0.257 | 0.034 | <0.0001 | 89.1 (0.8) + | 0.7 (0.1) + | 0.1 | |
| MWCNT-COOH | 1 | 0.657 | 0.037 | 0.021 | 171.5 (1.7) + | 69.1 (1.7) + | 345.3 |
| 4 * | 0.385 | 0.020 | 0.014 | 101.5 (1.0) + | 41.5 (1.0) + | 207.6 | |
| 8 | 0.346 | 0.014 | 0.005 | 57.0 (0.6) + | 17.3 (0.4) + | 86.7 |
| MWCNT | Breathing Mode and Frequency | Thoracic Mass Deposition (µg) | Pulmonary Mass Deposition (µg) | Pulmonary Surface Area Deposition (cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pMWCNT AR = 30 ρeff = 0.032 g/cm3 | Nose-only—166/min $ | 91.5 (0.8) + | 5.5 (0.9) + | 1.0 |
| Whole-body—116.4/min $,* | 109.2 (1.0) + | 6.1 (1.0) + | 1.1 | |
| Whole-body—93.12/min % | 115.0 (1.1) + | 6.1 (1.0) + | 1.1 | |
| MWCNT-COOH AR = 4 ρeff = 0.071 g/cm3 | Nose-only—166/min $ | 69.7 (0.7) + | 26.0 (0.6) + | 268.2 |
| Whole-body—116.4/min $* | 101.5 (1.0) + | 41.5 (1.0) + | 207.6 | |
| Whole-body—93.12/min % | 122.2 (1.2) + | 53.6 (1.3) + | 129.8 |
References
- Pang, J.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Yang, F.; Liu, H.; Zhou, W.; Rümmeli, M.H.; Cuniberti, G. Applications of Carbon Nanotubes in the Internet of Things Era. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.; Flahaut, E.; Golzio, M. Overview of Carbon Nanotubes for Biomedical Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, L.; de Perrot, M.; Zhao, X. Carbon Nanotubes: A Summary of Beneficial and Dangerous Aspects of an Increasingly Popular Group of Nanomaterials. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 693814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdörster, G.; Castranova, V.; Asgharian, B.; Sayre, P. Inhalation Exposure to Carbon Nanotubes (CNT) and Carbon Nanofibers (CNF): Methodology and Dosimetry. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2015, 18, 121–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, N.; Izumi, H.; Morimoto, Y. Review of toxicity studies of carbon nanotubes. J. Occup. Health 2017, 59, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacurari, M.; Lowe, K.; Tchounwou, P.B.; Kafoury, R. A Review on the Respiratory System Toxicity of Carbon Nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojo, M.; Maeno, A.; Sakamoto, Y.; Ohnuki, A.; Tada, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ikushima, K.; Inaba, R.; Suzuki, J.; Taquahashi, Y.; et al. Two-year intermittent exposure of a multiwalled carbon nanotube by intratracheal instillation induces lung tumors and pleural mesotheliomas in F344 rats. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, L.A.; Gao, J.; Wal, R.V.; Gigliotti, A.; Burchiel, S.W.; McDonald, J.D. Pulmonary and systemic immune response to inhaled multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 100, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.; Hirohashi, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Ogami, A.; Horie, M.; Oyabu, T.; Myojo, T.; Hashiba, M.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Kambara, T.; et al. Pulmonary toxicity of well-dispersed single-wall carbon nanotubes after inhalation. Nanotoxicology 2012, 6, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Berlo, D.; Wilhelmi, V.; Boots, A.W.; Hullmann, M.; Kuhlbusch, T.A.J.; Bast, A.; Schins, R.P.F.; Albrecht, C. Apoptotic, inflammatory, and fibrogenic effects of two different types of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in mouse lung. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1725–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Nie, H.; Gao, X.; Yang, J.; Pu, J.; Chen, Z.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Jia, G. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition involved in pulmonary fibrosis induced by multi-walled carbon nanotubes via TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 226, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Nie, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ge, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Bai, R.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Mediate Macrophage Activation and Promote Pulmonary Fibrosis Through TGF-β/Smad Signaling Pathway. Small 2013, 9, 3799–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vietti, G.; Ibouraadaten, S.; Palmai-Pallag, M.; Yakoub, Y.; Bailly, C.; Fenoglio, I.; Marbaix, E.; Lison, D.; van den Brule, S. Towards predicting the lung fibrogenic activity of nanomaterials: Experimental validation of an in vitro fibroblast proliferation assay. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Alexander, D.B.; Futakuchi, M.; Numano, T.; Fukamachi, K.; Suzui, M.; Omori, T.; Kanno, J.; Hirose, A.; Tsuda, H. Size- and shape-dependent pleural translocation, deposition, fibrogenesis, and mesothelial proliferation by multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, D.M.; Alexander, W.T.; Numano, T.; Ahmed, O.H.M.; Gunasekaran, S.; Alexander, D.B.; Abdelgied, M.; El-Gazzar, A.M.; Takase, H.; Xu, J.; et al. Comparative carcinogenicity study of a thick, straight-type and a thin, tangled-type multi-walled carbon nanotube administered by intra-tracheal instillation in the rat. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, K.; Kodali, V.; Yanamala, N.; Birch, M.E.; Cena, L.; Casuccio, G.; Bunker, K.; Lersch, T.L.; Evans, D.E.; Stefaniak, A.; et al. Physicochemical characterization and genotoxicity of the broad class of carbon nanotubes and nanofibers used or produced in U.S. facilities. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, S.S.; Jackson, P.; Kling, K.; Knudsen, K.B.; Skaug, V.; Kyjovska, Z.O.; Thomsen, B.L.; Clausen, P.A.; Atluri, R.; Berthing, T.; et al. Multi-walled carbon nanotube physicochemical properties predict pulmonary inflammation and genotoxicity. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, K.B.; Berthing, T.; Jackson, P.; Poulsen, S.S.; Mortensen, A.; Jacobsen, N.R.; Skaug, V.; Szarek, J.; Hougaard, K.S.; Wolff, H.; et al. Physicochemical predictors of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube–induced pulmonary histopathology and toxicity one year after pulmonary deposition of 11 different Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in mice. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadrup, N.; Knudsen, K.B.; Carriere, M.; Mayne-L’Hermite, M.; Bobyk, L.; Allard, S.; Miserque, F.; Pibaleau, B.; Pinault, M.; Wallin, H.; et al. Safe-by-design strategies for lowering the genotoxicity and pulmonary inflammation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes: Reduction of length and the introduction of COOH groups. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 103702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solorio-Rodriguez, S.A.; Williams, A.; Poulsen, S.S.; Knudsen, K.B.; Jensen, K.A.; Clausen, P.A.; Danielsen, P.H.; Wallin, H.; Vogel, U.; Halappanavar, S. Single-Walled vs. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Influence of Physico-Chemical Properties on Toxicogenomics Responses in Mouse Lungs. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsen, P.H.; Poulsen, S.S.; Knudsen, K.B.; Clausen, P.A.; Jensen, K.A.; Wallin, H.; Vogel, U. Physicochemical properties of 26 carbon nanotubes as predictors for pulmonary inflammation and acute phase response in mice following intratracheal lung exposure. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 107, 104413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaté, L.; Knudsen, K.B.; Seidel, C.; Berthing, T.; Chézeau, L.; Jacobsen, N.R.; Valentino, S.; Wallin, H.; Bau, S.; Wolff, H.; et al. Pulmonary toxicity of two different multi-walled carbon nanotubes in rat: Comparison between intratracheal instillation and inhalation exposure. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 375, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, C.; Zhernovkov, V.; Cassidy, H.; Kholodenko, B.; Matallanas, D.; Cosnier, F.; Gaté, L. Inhaled multi-walled carbon nanotubes differently modulate global gene and protein expression in rat lungs. Nanotoxicology 2021, 15, 238–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, K.; Murphy, F.A.; Duffin, R.; Poland, C.A. Asbestos, carbon nanotubes and the pleural mesothelium: A review of the hypothesis regarding the role of long fibre retention in the parietal pleura, inflammation and mesothelioma. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H.; Okazaki, Y.; Chew, S.H.; Misawa, N.; Yamashita, Y.; Akatsuka, S.; Ishihara, T.; Yamashita, K.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Yasui, H.; et al. Diameter and rigidity of multiwalled carbon nanotubes are critical factors in mesothelial injury and carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E1330–E1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, F.; Dekkers, S.; Braakhuis, H.; Ma-Hock, L.; Johnston, H.; Janer, G.; di Cristo, L.; Sabella, S.; Jacobsen, N.R.; Oomen, A.G.; et al. An integrated approach to testing and assessment of high aspect ratio nanomaterials and its application for grouping based on a common mesothelioma hazard. NanoImpact 2021, 22, 100314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, F.; Jacobsen, N.R.; Di Ianni, E.; Johnston, H.; Braakhuis, H.; Peijnenburg, W.; Oomen, A.; Fernandes, T.; Stone, V. Grouping MWCNTs based on their similar potential to cause pulmonary hazard after inhalation: A case-study. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgharian, B.; Anjilvel, S. A multiple-path model of fiber deposition in the rat lung. Toxicol. Sci. 1998, 44, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joint Research Centre: Institute for Health and Consumer Protection; Rasmussen, K.; Mast, J.; De Temmerman, P.; Verleysen, E.; Waegeneers, N.; Van Steen, F.; Pizzolon, J.; De Temmerman, L.; Van Doren, E.; et al. Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes, NM-400, NM-401, NM-402, NM-403, Characterisation and Physico-Chemical Properties; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- McKinney, W.; Chen, B.; Frazer, D. Computer controlled multi-walled carbon nanotube inhalation exposure system. Inhal. Toxicol. 2009, 21, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.D.; Buckley, A.J.; Smith, R. Estimates of carbon nanotube deposition in the lung: Improving quality and robustness. Inhal. Toxicol. 2020, 32, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsiedel, R.; Ma-Hock, L.; Hofmann, T.; Wiemann, M.; Strauss, V.; Treumann, S.; Wohlleben, W.; Gröters, S.; Wiench, K.; van Ravenzwaay, B. Application of short-term inhalation studies to assess the inhalation toxicity of nanomaterials. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xie, X. Change trends of organ weight background data in sprague dawley rats at different ages. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 26, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.A.; Yang, H.S.; Lee, J.; Kwon, S.; Jung, K.J.; Heo, J.D.; Cho, K.H.; Song, C.W.; Lee, K. Standardization of bronchoalveolar lavage method based on suction frequency number and lavage fraction number using rats. Toxicol. Res. 2010, 26, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Ma, Q. Osteopontin enhances multi-walled carbon nanotube-triggered lung fibrosis by promoting TGF-β1 activation and myofibroblast differentiation. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2017, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Haefner, V.; Yildirim, A.; Adler, H.; Stoeger, T. Carbonaceous particle exposure triggered accumulation of Osteopontin/SPP1+ macrophages contributes to emphysema development. MedComm 2025, 6, e70061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.; Hirohashi, M.; Ogami, A.; Oyabu, T.; Myojo, T.; Todoroki, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Hashiba, M.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Lee, B.W.; et al. Pulmonary toxicity of well-dispersed multi-wall carbon nanotubes following inhalation and intratracheal instillation. Nanotoxicology 2012, 6, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Sung, J.H.; Choi, B.G.; Ryu, H.Y.; Song, K.S.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Hwang, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, G.H.; et al. In vivo genotoxicity evaluation of lung cells from Fischer 344 rats following 28 days of inhalation exposure to MWCNTs, plus 28 days and 90 days post-exposure. Inhal. Toxicol. 2014, 26, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Jo, M.S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, T.G.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, B.W.; Kim, H.P.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, H.S.; Ahn, K.; et al. 28-Day inhalation toxicity study with evaluation of lung deposition and retention of tangled multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Nanotoxicology 2020, 14, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, T.; Umeda, Y.; Ohnishi, M.; Kondo, H.; Takeuchi, T.; Aiso, S.; Nishizawa, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Fukushima, S. Thirteen-week study of toxicity of fiber-like multi-walled carbon nanotubes with whole-body inhalation exposure in rats. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma-Hock, L.; Treumann, S.; Strauss, V.; Brill, S.; Luizi, F.; Mertler, M.; Wiench, K.; Gamer, A.O.; van Ravenzwaay, B.; Landsiedel, R. Inhalation toxicity of multiwall carbon nanotubes in rats exposed for 3 months. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 112, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauluhn, J. Subchronic 13-week inhalation exposure of rats to multiwalled carbon nanotubes: Toxic effects are determined by density of agglomerate structures, not fibrillar structures. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 113, 226–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 412: Subacute Inhalation Toxicity: 28-Day Study. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Test No. 413: Subchronic Inhalation Toxicity: 90-day Study. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Devoy, J.; Al-Abed, S.; Cerdan, B.; Cho, W.S.; Dubuc, D.; Flahaut, E.; Grenier, K.; Grossmann, S.; Gulumian, M.; Jeong, J.; et al. Analysis of carbon nanotube levels in organic matter: An inter-laboratory comparison to determine best practice. Nanotoxicology 2024, 18, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.J.; Flores-Cervantes, D.X.; Bucheli, T.D.; Elliott, L.C.C.; Fagan, J.A.; Gogos, A.; Hanna, S.; Kägi, R.; Mansfield, E.; Bustos, A.R.M.; et al. Quantification of Carbon Nanotubes in Environmental Matrices: Current Capabilities, Case Studies, and Future Prospects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4587–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, O.; Stoeger, T. Surface area is the biologically most effective dose metric for acute nanoparticle toxicity in the lung. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 99, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosnier, F.; Seidel, C.; Valentino, S.; Schmid, O.; Bau, S.; Vogel, U.; Devoy, J.; Gaté, L. Retained particle surface area dose drives inflammation in rat lungs following acute, subacute, and subchronic inhalation of nanomaterials. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Wang, X.; Ji, Z.; Sun, B.; Zhang, H.; Chang, C.H.; Lin, S.; Meng, H.; Liao, Y.-P.; Wang, M.; et al. Surface Charge and Cellular Processing of Covalently Functionalized Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Determine Pulmonary Toxicity. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2352–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, T.M.; Wolfarth, M.W.; Andrew, M.; Hubbs, A.; Friend, S.; Chen, T.H.; Porter, D.W.; Wu, N.; Yang, F.; Hamilton, R.F.; et al. Effect of multi-walled carbon nanotube surface modification on bioactivity in the C57BL/6 mouse model. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, K.S.; Taylor-Just, A.J.; Ihrie, M.D.; Shipkowski, K.A.; Thompson, E.A.; Dandley, E.C.; Parsons, G.N.; Bonner, J.C. STAT1-dependent and -independent pulmonary allergic and fibrogenic responses in mice after exposure to tangled versus rod-like multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2017, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydman, E.M.; Ilves, M.; Vanhala, E.; Vippola, M.; Lehto, M.; Kinaret, P.A.; Pylkkänen, L.; Happo, M.; Hirvonen, M.R.; Greco, D.; et al. A Single Aspiration of Rod-like Carbon Nanotubes Induces Asbestos-like Pulmonary Inflammation Mediated in Part by the IL-1 Receptor. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 147, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCarlo, P.F.; Slowik, J.G.; Worsnop, D.R.; Davidovits, P.; Jimenez, J.L. Particle Morphology and Density Characterization by Combined Mobility and Aerodynamic Diameter Measurements. Part 1: Theory. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1185–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, B.K.; Kulkarni, P. Measurement of Transport Properties of Aerosolized Nanomaterials. J. Aerosol Sci. 2015, 90, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Bahk, Y.K.; Chen, S.-C.; Pui, D.Y.H. Characteristics of airborne fractal-like agglomerates of carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2015, 93, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménache, M.G.; Miller, F.J.; Raabe, O.G. Particle inhalability curves for humans and small laboratory animals. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 1995, 39, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, F.J.; Asgharian, B.; Schroeter, J.D.; Price, O.; Corley, R.A.; Einstein, D.R.; Jacob, R.E.; Cox, T.C.; Kabilan, S.; Bentley, T. Respiratory tract lung geometry and dosimetry model for male Sprague-Dawley rats. Inhal. Toxicol. 2014, 26, 524–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyabu, T.; Morimoto, Y.; Izumi, H.; Yoshiura, Y.; Tomonaga, T.; Lee, B.W.; Okada, T.; Myojo, T.; Shimada, M.; Kubo, M.; et al. Comparison between whole-body inhalation and nose-only inhalation on the deposition and health effects of nanoparticles. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2016, 21, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.C.; Snipes, M.B.; Eidson, A.F.; Hobbs, C.H.; Henry, M.C. Comparative Evaluation of Nose-Only Versus Whole-Body Inhalation Exposures for Rats—Aerosol Characteristics and Lung Deposition. Inhal. Toxicol. 1990, 2, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagiello, K.; Halappanavar, S.; Rybińska-Fryca, A.; Willliams, A.; Vogel, U.; Puzyn, T. Transcriptomics-Based and AOP-Informed Structure-Activity Relationships to Predict Pulmonary Pathology Induced by Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Small 2021, 17, e2003465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merugu, S.; Jagiello, K.; Gajewicz-Skretna, A.; Halappanavar, S.; Willliams, A.; Vogel, U.; Puzyn, T. The Impact of Carbon Nanotube Properties on Lung Pathologies and Atherosclerosis Through Acute Inflammation: A New AOP-Anchored in Silico NAM. Small 2025, 21, e2501185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, T.M.; Umbright, C.M.; Mustafa, G.M.; Roberts, J.R.; Orandle, M.S.; Cumpston, J.L.; McKinney, W.G.; Boots, T.; Kashon, M.L.; Joseph, P. Pulmonary toxicity and gene expression changes in response to whole-body inhalation exposure to multi-walled carbon nanotubes in rats. Inhal. Toxicol. 2022, 34, 200–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Fukuda, M.; Endoh, S.; Maru, J.; Kato, H.; Nakamura, A.; Shinohara, N.; Uchino, K.; Honda, K. Size effects of single-walled carbon nanotubes on in vivo and in vitro pulmonary toxicity. Inhal. Toxicol. 2015, 27, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, A.P.; Ganapathy, S.; Palla, V.R.; Murthy, P.B.; Ramaprabhu, S.; Devasena, T. One time nose-only inhalation of MWCNTs: Exploring the mechanism of toxicity by intermittent sacrifice in Wistar rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, R.R.; Scabilloni, J.F.; Hubbs, A.F.; Battelli, L.A.; McKinney, W.; Friend, S.; Wolfarth, M.G.; Andrew, M.; Castranova, V.; Porter, D.W. Distribution and fibrotic response following inhalation exposure to multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.W.; Hubbs, A.F.; Chen, B.T.; McKinney, W.; Mercer, R.R.; Wolfarth, M.G.; Battelli, L.; Wu, N.; Sriram, K.; Leonard, S.; et al. Acute pulmonary dose-responses to inhaled multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Nanotoxicology 2013, 7, 1179–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryman-Rasmussen, J.P.; Cesta, M.F.; Brody, A.R.; Shipley-Phillips, J.K.; Everitt, J.I.; Tewksbury, E.W.; Moss, O.R.; Wong, B.A.; Dodd, D.E.; Andersen, M.E.; et al. Inhaled carbon nanotubes reach the subpleural tissue in mice. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryman-Rasmussen, J.P.; Tewksbury, E.W.; Moss, O.R.; Cesta, M.F.; Wong, B.A.; Bonner, J.C. Inhaled multiwalled carbon nanotubes potentiate airway fibrosis in murine allergic asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2009, 40, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvedova, A.A.; Kisin, E.; Murray, A.R.; Johnson, V.J.; Gorelik, O.; Arepalli, S.; Hubbs, A.F.; Mercer, R.R.; Keohavong, P.; Sussman, N.; et al. Inhalation vs. aspiration of single-walled carbon nanotubes in C57BL/6 mice: Inflammation, fibrosis, oxidative stress, and mutagenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008, 295, L552–L565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shvedova, A.A.; Yanamala, N.; Kisin, E.R.; Tkach, A.V.; Murray, A.R.; Hubbs, A.; Chirila, M.M.; Keohavong, P.; Sycheva, L.P.; Kagan, V.E.; et al. Long-term effects of carbon containing engineered nanomaterials and asbestos in the lung: One year postexposure comparisons. Am. J. Physiol. Lung. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L170–L182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treumann, S.; Ma-Hock, L.; Gröters, S.; Landsiedel, R.; van Ravenzwaay, B. Additional histopathologic examination of the lungs from a 3-month inhalation toxicity study with multiwall carbon nanotubes in rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 134, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Ma, Q. Type 2 Immune Mechanisms in Carbon Nanotube-Induced Lung Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliullin, T.O.; Kisin, E.R.; Murray, A.R.; Yanamala, N.; Shurin, M.R.; Gutkin, D.W.; Fatkhutdinova, L.M.; Kagan, V.E.; Shvedova, A.A. Mediation of the single-walled carbon nanotubes induced pulmonary fibrogenic response by osteopontin and TGF-β1. Exp. Lung Res. 2017, 43, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Ma, Q. TIMP1 promotes multi-walled carbon nanotube-induced lung fibrosis by stimulating fibroblast activation and proliferation. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Buckley, A.; Marczylo, T.; Seiffert, J.; Römer, I.; Warren, J.; Hodgson, A.; Chung, K.F.; Gant, T.W.; Smith, R.; et al. The small airway epithelium as a target for the adverse pulmonary effects of silver nanoparticle inhalation. Nanotoxicology 2018, 12, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Robertson, S.; Weber, R.J.M.; Buckley, A.; Warren, J.; Hodgson, A.; Rappoport, J.Z.; Ignatyev, K.; Meldrum, K.; Römer, I.; et al. Pulmonary toxicity of inhaled nano-sized cerium oxide aerosols in Sprague-Dawley rats. Nanotoxicology 2019, 13, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermudez, E.; Mangum, J.B.; Wong, B.A.; Asgharian, B.; Hext, P.M.; Warheit, D.B.; Everitt, J.I. Pulmonary responses of mice, rats, and hamsters to subchronic inhalation of ultrafine titanium dioxide particles. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 77, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, A.; Gelein, R.; Finkelstein, J.N.; Driscoll, K.E.; Harkema, J.; Oberdörster, G. Effects of subchronically inhaled carbon black in three species. I. Retention kinetics, lung inflammation, and histopathology. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 88, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, J.; Wohlleben, W.; Ma-Hock, L.; Strauss, V.; Gröters, S.; Küttler, K.; Wiench, K.; Herden, C.; Oberdörster, G.; van Ravenzwaay, B.; et al. Time course of lung retention and toxicity of inhaled particles: Short-term exposure to nano-Ceria. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 2033–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinger-Ziegelbauer, H.; Pauluhn, J. Pulmonary toxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (Baytubes®) relative to α-quartz following a single 6h inhalation exposure of rats and a 3 months post-exposure period. Toxicology 2009, 266, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuempel, E.D.; O’Flaherty, E.J.; Stayner, L.T.; Smith, R.J.; Green, F.H.; Vallyathan, V. A biomathematical model of particle clearance and retention in the lungs of coal miners. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2001, 34, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoratto, D.; Bailey, M.R.; Marsh, J.W. Modelling particle retention in the alveolar-interstitial region of the human lungs. J. Radiol. Prot. 2010, 30, 491–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debia, M.; Bakhiyi, B.; Ostiguy, C.; Verbeek, J.H.; Brouwer, D.H.; Murashov, V. A Systematic Review of Reported Exposure to Engineered Nanomaterials. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2016, 60, 916–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahm, M.M.; Schubauer-Berigan, M.K.; Evans, D.E.; Birch, M.E.; Bertke, S.; Beard, J.D.; Erdely, A.; Fernback, J.E.; Mercer, R.R.; Grinshpun, S.A. Exposure assessments for a cross-sectional epidemiologic study of US carbon nanotube and nanofiber workers. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIOSH. Current Intelligence Bulletin 65: Occupational Exposure to Carbon Nanotubes and Nanofibers; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, NIOSH: Cinncinnatic, OH, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Guseva Canu, I.; Bateson, T.F.; Bouvard, V.; Debia, M.; Dion, C.; Savolainen, K.; Yu, I.J. Human exposure to carbon-based fibrous nanomaterials: A review. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2016, 219, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, B.K.; Birch, M.E. Aerosolization and characterization of carbon nanotube and nanofiber materials: Relationship between aerosol properties and bulk density. J. Aerosol Sci. 2019, 127, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carley, D.W.; Berecek, K.; Videnovic, A.; Radulovacki, M. Sleep-disordered respiration in phenotypically normotensive, genetically hypertensive rats. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, R.; Liao, K.S.; Hamrahi, H.; Horner, R.L. Circadian rhythms and sleep have additive effects on respiration in the rat. J. Physiol. 2001, 536 Pt 1, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
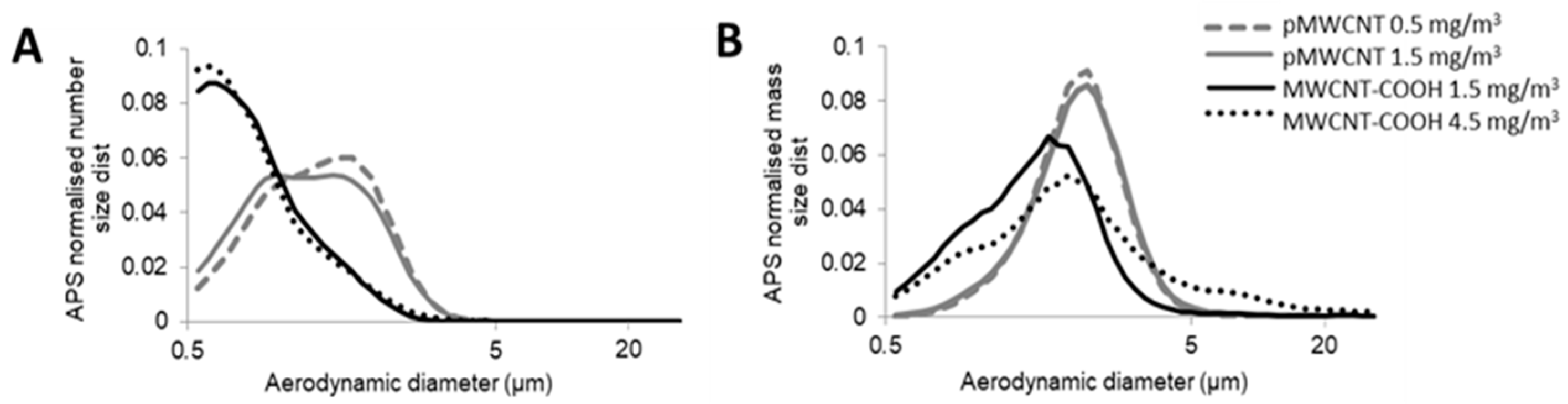


| MWCNT | Diameter (nm) | Length (µm) | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | COOH (%wt) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pMWCNT (a) | 67 ± 24 | 4.0 ± 2.3 | 18 | NA * |
| MWCNT-COOH (b) | <8 | 10–30 | 500 | 3.86 |
| MWCNT | Target Conc. (mg/m3) | Gravimetric Mass Conc. (mg/m3) | APS | CPC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMAD (µm) | GSD (CMAD) | MMAD (µm) | GSD (MMAD) | No. Conc. (particles/cm3) | No. Conc. (particles/cm3) | |||
| pMWCNT | 0.5 | 0.54 ± 0.04 | 0.80 ± 0.01 | 1.44 | 1.57 ± 0.07 | 1.65 | 190 ± 13 | 673 ± 79 |
| 1.5 | 1.50 ± 0.45 | 0.79 ± 0.02 | 1.48 | 2.01 ± 0.34 | 1.95 | 469 ± 106 | 1520 ± 328 | |
| MWCNT-COOH | 1.5 | 1.71 ± 0.23 | 1.35 ± 0.02 | 1.52 | 2.15 ± 0.03 | 1.45 | 187 ± 17 | 195 ± 21 |
| 4.5 | 4.48 ± 1.09 | 1.24 ± 0.05 | 1.55 | 2.17 ± 0.06 | 1.51 | 537 ± 107 | 392 ± 69 | |
| MWCNT | Effective Density (g/cm3) | Target Conc. (mg/m3) | Deposition Fraction | Thoracic Deposition (µg) | Pulmonary Deposition (µg) | Pulmonary Surface Area Deposition (cm2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | TB | P | ||||||
| pMWCNT | 0.032 | 0.5 (Low) | 0.349 | 0.057 | 0.0004 | 54.2 | 3.0 | 0.5 |
| 1.5 (Medium) | 0.268 | 0.042 | 0.0001 | 109.2 | 6.1 | 1.1 | ||
| MWCNT-COOH | 0.071 | 1.5 (Medium) | 0.385 | 0.020 | 0.014 | 101.5 | 41.5 | 207.6 |
| 4.5 (High) | 0.381 | 0.021 | 0.016 | 288.1 | 119.0 | 595.2 | ||
| Time | Material | Histopathological Characteristic * | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alv Oed | Alv M | M Pig | Alv Fibr | Br CC Prolif | Br Loss Cilia | Int Oed | Int Fibr | ||
| 3 days | Air (n = 5) | 0.00 | 0.40 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| pMWCNT (n = 6) | 0.00 | 1.50 | 1.83 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| MWCNT-COOH (n = 5) | 0.00 | 1.40 | 2.40 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| 1 year | Air (n = 4) | 0.00 | 0.75 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| pMWCNT (n = 6) | 0.00 | 1.67 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| MWCNT-COOH (n = 6) | 0.00 | 0.83 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Exposure | Effective Density (g/cm3) | Mass Conc. (mg/m3) | MMAD (µm) | Deposition Fraction | T Deposition (µg) | P Deposition (µg) | P Deposition (cm2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | TB | P | |||||||
| Whole-body * | 0.032 | 0.54 ± 0.04 | 1.57 | 0.349 | 0.057 | 0.0004 | 54 | 3.0 | 0.5 |
| 1.50 ± 0.45 | 2.01 | 0.268 | 0.042 | 0.0001 | 109 | 6.1 | 1.1 | ||
| Nose-only # | 0.36 | 0.54 ± 0.11 | 0.79 | 0.318 | 0.095 | 0.045 | 279 | 90 | 16 |
| 1.49 ± 0.24 | 0.79 | 0.304 | 0.119 | 0.060 | 709 | 239 | 43 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, C.; Wright, M.D.; Buckley, A.; Laycock, A.; Berthing, T.; Vogel, U.; Cosnier, F.; Gaté, L.; Leonard, M.O.; Smith, R. Pulmonary Toxicity of Long, Thick MWCNT and Very Long, Thin Carboxylated MWCNT Aerosols Following 28 Days Whole-Body Exposure. Toxics 2025, 13, 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050401
Guo C, Wright MD, Buckley A, Laycock A, Berthing T, Vogel U, Cosnier F, Gaté L, Leonard MO, Smith R. Pulmonary Toxicity of Long, Thick MWCNT and Very Long, Thin Carboxylated MWCNT Aerosols Following 28 Days Whole-Body Exposure. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050401
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Chang, Matthew D. Wright, Alison Buckley, Adam Laycock, Trine Berthing, Ulla Vogel, Frédéric Cosnier, Laurent Gaté, Martin O. Leonard, and Rachel Smith. 2025. "Pulmonary Toxicity of Long, Thick MWCNT and Very Long, Thin Carboxylated MWCNT Aerosols Following 28 Days Whole-Body Exposure" Toxics 13, no. 5: 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050401
APA StyleGuo, C., Wright, M. D., Buckley, A., Laycock, A., Berthing, T., Vogel, U., Cosnier, F., Gaté, L., Leonard, M. O., & Smith, R. (2025). Pulmonary Toxicity of Long, Thick MWCNT and Very Long, Thin Carboxylated MWCNT Aerosols Following 28 Days Whole-Body Exposure. Toxics, 13(5), 401. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050401