Dietary Exposure to Food Contaminants of Pregnant Women in Northern Spain and Possible Effects on Fetal Anthropometric Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Nutritional Information and Estimation of Contaminants
2.3. Data Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
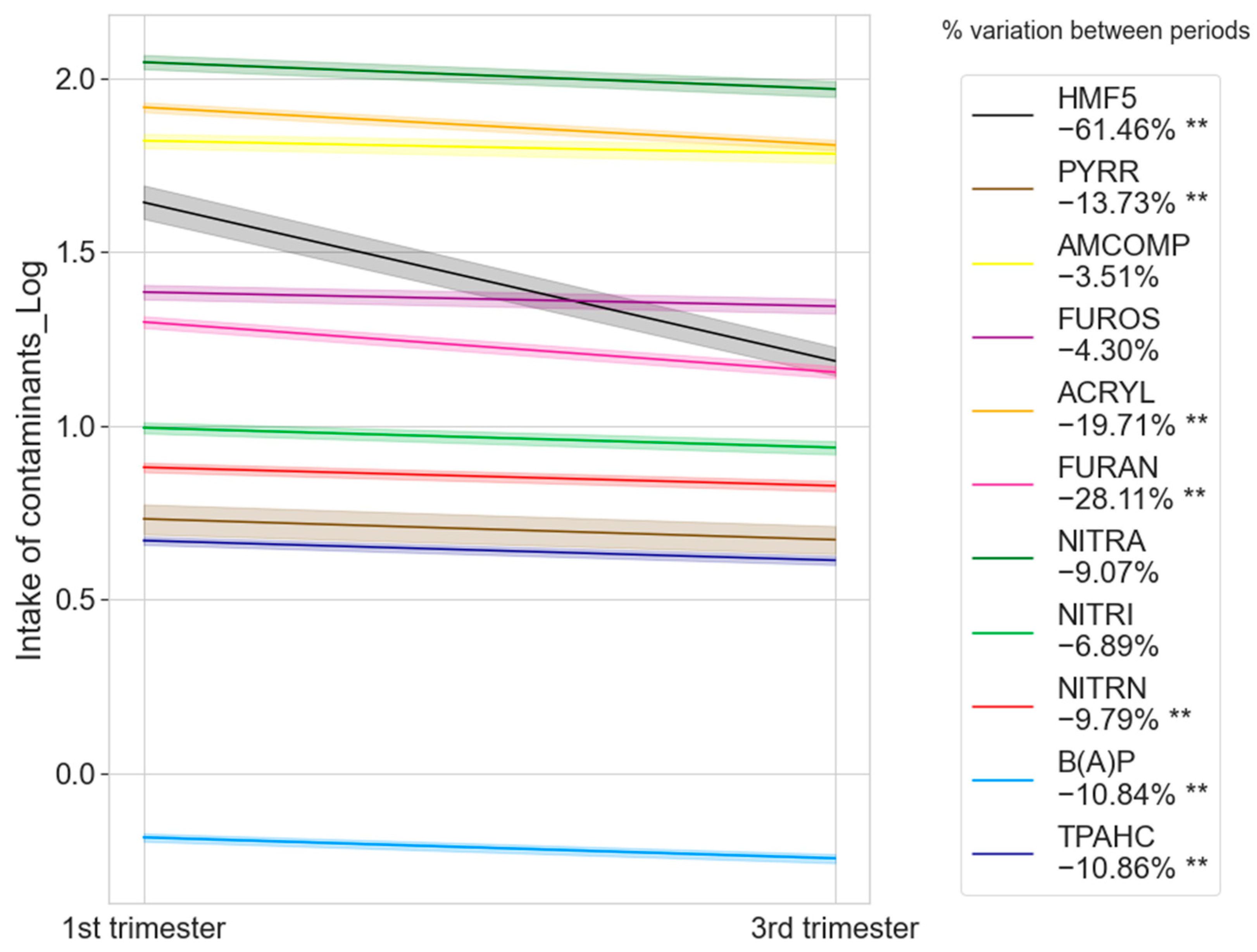
3.2. Distribution of Contaminant Intake by Food Group and Trimester of Pregnancy
3.3. Contaminant Intake and Exposure: Association with Fetal Anthropometric Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Intake and Exposure to Food Contaminants and Their Relationship with Maternal and Fetal Health
4.2. Strategies to Mitigate Exposure to Food Contaminants in Pregnant Women
4.3. Limitations and Strengths of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alabduljabbar, S.; Zaidan, S.A.; Lakshmanan, A.P.; Terranegra, A. Personalized Nutrition Approach in Pregnancy and Early Life to Tackle Childhood and Adult Non-Communicable Diseases. Life 2021, 11, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO; IFAD; UNICEF; WFP; WHO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2019: Safeguarding Against Economic Slowdowns and Downturns; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019; Volume 2019, ISBN 92-5-131570-1. [Google Scholar]
- Heidkamp, R.A.; Piwoz, E.; Gillespie, S.; Keats, E.C.; D’Alimonte, M.R.; Menon, P.; Das, J.K.; Flory, A.; Clift, J.W.; Ruel, M.T.; et al. Mobilising Evidence, Data, and Resources to Achieve Global Maternal and Child Undernutrition Targets and the Sustainable Development Goals: An Agenda for Action. Lancet 2021, 397, 1400–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations University; World Health Organization. Human Energy Requirements: Report of a Joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation: Rome, 17–24 October 2001; Food & Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2004; Volume 1, ISBN 92-5-105212-3. [Google Scholar]
- Lillford, P.; Hermansson, A.-M. Global Missions and the Critical Needs of Food Science and Technology. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbi, M.F.; Hasan, M.; Kovács, S. Food Security and Transition towards Sustainability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovarich, S.; Ciacci, A.; Baldin, R.; Roncaglioni, A.; Mostrag, A.; Tarkhov, A.; Carnesecchi, E.; Gibin, D.; Di Piazza, G.; Pasinato, L.; et al. OpenFoodTox: EFSA’s Chemical Hazards Database 2022; EFSA: Palma, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Talari, G.; Cummins, E.; McNamara, C.; O’Brien, J. State of the Art Review of Big Data and Web-Based Decision Support Systems (DSS) for Food Safety Risk Assessment with Respect to Climate Change. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 126, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa-Nogueira, D.; Muros, J.J.; Navajas-Porras, B.; Delgado-Osorio, A.; Pérez-Burillo, S.; Pastoriza, S.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á. Development of a Food Composition Database of Different Food Contaminants CONT11 and Estimation of Dietary Exposure in Children of Southern Spain. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 177, 113843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Andrade, C.; Morales, F.J.; Seiquer, I.; Navarro, M.P. Maillard Reaction Products Profile and Intake from Spanish Typical Dishes. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulin, M.; Bemrah, N.; Nougadère, A.; Volatier, J.; Sirot, V.; Leblanc, J. Assessment of Infant Exposure to Food Chemicals: The French Total Diet Study Design. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2014, 31, 1226–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, R.M.; Beaver, L.; Prater, M.C.; Hord, N.G. Dietary Nitrate and Nitrite Concentrations in Food Patterns and Dietary Supplements. Nutr. Today 2020, 55, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.; Jo, C.-H.; Choi, J.-D. Korea Total Diet Study-Based Risk Assessment on Contaminants Formed During Manufacture, Preparation and Storage of Food. J. Food Hyg. Saf. 2021, 36, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirot, V.; Rivière, G.; Leconte, S.; Vin, K.; Traore, T.; Jean, J.; Carne, G.; Gorecki, S.; Veyrand, B.; Marchand, P. French Infant Total Diet Study: Dietary Exposure to Heat-Induced Compounds (Acrylamide, Furan and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons) and Associated Health Risks. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 130, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Liu, A.H.; Blekkenhorst, L.C.; Bondonno, N.P.; Sim, M.; Woodman, R.J.; Croft, K.D.; Lewis, J.R.; Hodgson, J.M.; Bondonno, C.P. Development of a Food Composition Database for Assessing Nitrate and Nitrite Intake from Animal-based Foods. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, 2100272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan-Hon-Tong, A.; Charles, M.-A.; Forhan, A.; Heude, B.; Sirot, V. Exposure to Food Contaminants during Pregnancy. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Salles, T.; Von Stedingk, H.; Granum, B.; Gützkow, K.B.; Rydberg, P.; Törnqvist, M.; Mendez, M.A.; Brunborg, G.; Brantsæter, A.L.; Meltzer, H.M.; et al. Dietary Acrylamide Intake during Pregnancy and Fetal Growth—Results from the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study (MoBa). Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadawathagedara, M.; Tong, A.C.H.; Heude, B.; Forhan, A.; Charles, M.-A.; Sirot, V.; Botton, J. Eden Mother-Child Cohort Study Group Dietary Acrylamide Intake during Pregnancy and Anthropometry at Birth in the French EDEN Mother-Child Cohort Study. Environ. Res. 2016, 149, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaycıoğlu, Z.; Erim, F.B. Nitrate and Nitrites in Foods: Worldwide Regional Distribution in View of Their Risks and Benefits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7205–7222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, D.K.; Leem, J.-H.; Kim, H.-C.; Lee, J.-Y.; Park, M.-S.; Jung, D.-Y.; Ko, J.K.; Ha, M.; Kim, Y.; Hong, Y.-C.; et al. Impact of Prenatal Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Maternal Diet on Birth Outcomes: A Birth Cohort Study in Korea. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 2562–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.-Y.; Wu, P.-R.; Guo, Y. Urinary Metabolites of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Pregnant Women and Their Association with a Biomarker of Oxidative Stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 27281–27290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM) Scientific Opinion on Acrylamide in Food. Efsa J. 2015, 13, 4104. [Google Scholar]
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; World Health Organization. Safety Evaluation of Certain Contaminants in Food: Prepared by the Seventy-Second Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; ISBN 92-4-166063-5. [Google Scholar]
- Rannou, C.; Laroque, D.; Renault, E.; Prost, C.; Sérot, T. Mitigation Strategies of Acrylamide, Furans, Heterocyclic Amines and Browning during the Maillard Reaction in Foods. Food Res. Int. 2016, 90, 154–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrish, J.; Yeatman, H.; Williamson, M. Midwives and Nutrition Education during Pregnancy: A Literature Review. Women Birth 2014, 27, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, J.; Waller, A.; Cameron, E.; Hure, A.; Sanson-Fisher, R. Diet during Pregnancy: Women’s Knowledge of and Adherence to Food Safety Guidelines. Aust. N. Z. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2017, 57, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dello Russo, M.; Russo, P.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á.; Hinojosa-Nogueira, D.; Pérez-Burillo, S.; De La Cueva, S.P.; Rohn, S.; Fatouros, A.; Douros, K.; González-Vigil, V.; et al. The Stance4Health Project: Evaluating a Smart Personalised Nutrition Service for Gut Microbiota Modulation in Normal- and Overweight Adults and Children with Obesity, Gluten-Related Disorders or Allergy/Intolerance to Cow’s Milk. Foods 2022, 11, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Onis, M.; Habicht, J.-P. Anthropometric Reference Data for International Use: Recommendations from a World Health Organization Expert Committee. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvander, C.; Högberg, U.; Ekéus, C. The Influence of Fetal Head Circumference on Labor Outcome: A Population-based Register Study. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2012, 91, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenção, L.F.d.P.; de Paula, N.C.; Cardoso, M.A.; Santos, P.R.; de Oliveira, I.R.C.; Fonseca, F.L.A.; da Veiga, G.L.; Alves, B.d.C.A.; Graciano, M.M.d.C.; Pereira-Dourado, S.M. Biochemical Markers and Anthropometric Profile of Children Enrolled in Public Daycare Centers. J. Pediatr. 2022, 98, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Physical Status: The Use of and Interpretation of Anthropometry, Report of a WHO Expert Committee; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995; ISBN 92-4-120854-6. [Google Scholar]
- Formisano, A.; Russo, M.D.; Russo, P.; Siani, A.; Hinojosa-Nogueira, D.; Navajas-Porras, B.; Toledano-Marín, Á.; Pastoriza, S.; Blasco, T.; Lerma-Aguilera, A.; et al. Development and Validation of a Self-Administered Semiquantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire Focused on Gut Microbiota: The Stance4Health-FFQ. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa-Nogueira, D.; Pérez-Burillo, S.; Navajas-Porras, B.; Ortiz-Viso, B.; De La Cueva, S.P.; Lauria, F.; Fatouros, A.; Priftis, K.N.; González-Vigil, V.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á. Development of an Unified Food Composition Database for the European Project “Stance4Health”. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotemori, A.; Ishihara, J.; Nakadate, M.; Sawada, N.; Iwasaki, M.; Sobue, T.; Tsugane, S. Validity of a Self-Administered Food Frequency Questionnaire for the Estimation of Acrylamide Intake in the Japanese Population: The JPHC FFQ Validation Study. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 28, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadoran, Z.; Mirmiran, P.; Azizi, F.; Ghasemi, A. Nitrate-Rich Dietary Supplementation during Pregnancy: The Pros and Cons. Pregnancy Hypertens 2018, 11, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Salles, T.; Mendez, M.A.; Meltzer, H.M.; Alexander, J.; Haugen, M. Dietary Benzo (a) Pyrene Intake during Pregnancy and Birth Weight: Associations Modified by Vitamin C Intakes in the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study (MoBa). Environ. Int. 2013, 60, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadawathagedara, M.; Botton, J.; de Lauzon-Guillain, B.; Meltzer, H.M.; Alexander, J.; Brantsaeter, A.L.; Haugen, M.; Papadopoulou, E. Dietary Acrylamide Intake during Pregnancy and Postnatal Growth and Obesity: Results from the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study (MoBa). Environ. Int. 2018, 113, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.H.; Jones, R.R.; Brender, J.D.; De Kok, T.M.; Weyer, P.J.; Nolan, B.T.; Villanueva, C.M.; Van Breda, S.G. Drinking Water Nitrate and Human Health: An Updated Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastoriza de la Cueva, S.; Álvarez, J.; Végvári, Á.; Montilla-Gómez, J.; Cruz-López, O.; Delgado-Andrade, C.; Rufián-Henares, J.A. Relationship between HMF Intake and SMF Formation in Vivo: An Animal and Human Study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Andrade, C.; Seiquer, I.; Navarro, M.P.; Morales, F.J. Maillard Reaction Indicators in Diets Usually Consumed by Adolescent Population. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, A.; Kühne, Y.; Henle, T.O. Studies on Absorption and Elimination of Dietary Maillard Reaction Products. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1043, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santonicola, S.; Mercogliano, R. Occurrence and Production of Furan in Commercial Foods. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2016, 28, 155. [Google Scholar]
- Ekhator, O.C.; Udowelle, N.A.; Igbiri, S.; Asomugha, R.N.; Frazzoli, C.; Orisakwe, O.E. Street Foods Exacerbate Effects of the Environmental Burden of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Nigeria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 5529–5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorell, I.; Perelló, G.; Martí-Cid, R.; Castell, V.; Llobet, J.M.; Domingo, J.L. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) in Foods and Estimated PAH Intake by the Population of Catalonia, Spain: Temporal Trend. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadoran, Z.; Ghasemi, A.; Mirmiran, P.; Mehrabi, Y.; Azizi, F.; Hadaegh, F. Estimation and Validation of Dietary Nitrate and Nitrite Intake in Iranian Population. Iran. J. Public Health 2019, 48, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hord, N.G.; Tang, Y.; Bryan, N.S. Food Sources of Nitrates and Nitrites: The Physiologic Context for Potential Health Benefits. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.; Arcot, J.; Lee, N.A. Nitrate and Nitrite Quantification from Cured Meat and Vegetables and Their Estimated Dietary Intake in Australians. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Thresher, A.; Ponting, D.J. Utilisation of Parametric Methods to Improve Percentile-Based Estimates for the Carcinogenic Potency of Nitrosamines. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 121, 104875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drwal, E.; Rak, A.; Gregoraszczuk, E.L. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs)—Action on Placental Function and Health Risks in Future Life of Newborns. Toxicology 2019, 411, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Wu, W.; Cui, S.; Li, H.; Feng, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Effects of Benzo [a] Pyrene-DNA Adducts, Dietary Vitamins, Folate, and Carotene Intakes on Preterm Birth: A Nested Case–Control Study from the Birth Cohort in China. Environ. Health 2022, 21, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anese, M.; Manzocco, L.; Calligaris, S.; Nicoli, M.C. Industrially Applicable Strategies for Mitigating Acrylamide, Furan, and 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural in Food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 10209–10214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Update on Furan Levels in Food from Monitoring Years 2004–2010 and Exposure Assessment. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2347. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Tracking Contaminants in Food; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Capuano, E.; Fogliano, V. Acrylamide and 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF): A Review on Metabolism, Toxicity, Occurrence in Food and Mitigation Strategies. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwowska, M.; Kononiuk, A. Nitrates/Nitrites in Food—Risk for Nitrosative Stress and Benefits. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesías, M.; Sáez-Escudero, L.; Morales, F.J.; Delgado-Andrade, C. Occurrence of Furosine and Hydroxymethylfurfural in Breakfast Cereals. Evolution of the Spanish Market from 2006 to 2018. Foods 2019, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przygodzka, M.; Zieliński, H.; Ciesarová, Z.; Kukurová, K.; Lamparski, G. Study on Sensory Quality, Antioxidant Properties, and Maillard Reaction Products Formation in Rye-Buckwheat Cakes Enhanced with Selected Spices. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 418639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, Y.-J.; Her, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.-G.; Kim, M.Y.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, C.; Yoon, H.-J.; Lee, K.-G. Furan in Thermally Processed Foods-a Review. Toxicol. Res. 2015, 31, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas-Lorenzo, G.; Morales, F.J. Estimation of Dietary Intake of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural and Related Substances from Coffee to Spanish Population. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husøy, T.; Haugen, M.; Murkovic, M.; Jöbstl, D.; Stølen, L.; Bjellaas, T.; Rønningborg, C.; Glatt, H.; Alexander, J. Dietary Exposure to 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural from Norwegian Food and Correlations with Urine Metabolites of Short-Term Exposure. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 3697–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufian-Henares, J.; De la Cueva, S. Assessment of Hydroxymethylfurfural Intake in the Spanish Diet. Food Addit. Contam. 2008, 25, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellwig, M.; Kühn, L.; Henle, T. Individual Maillard Reaction Products as Indicators of Heat Treatment of Pasta—A Survey of Commercial Products. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 72, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotopoulou, S.; Zampelas, A.; Magriplis, E. Dietary Nitrate and Nitrite and Human Health: A Narrative Review by Intake Source. Nutr. Rev. 2022, 80, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, J.L.; Nadal, M. Human Dietary Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: A Review of the Scientific Literature. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 86, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazeni, M.; Heidari, Z.; Golipour, S.; Ghaisari, L.; Sillanpää, M.; Ebrahimi, A. Dietary Intake and Health Risk Assessment of Nitrate, Nitrite, and Nitrosamines: A Bayesian Analysis and Monte Carlo Simulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 45568–45580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polachova, A.; Gramblicka, T.; Parizek, O.; Sram, R.J.; Stupak, M.; Hajslova, J.; Pulkrabova, J. Estimation of Human Exposure to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Based on the Dietary and Outdoor Atmospheric Monitoring in the Czech Republic. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 108977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Blekkenhorst, L.C.; Bondonno, N.P.; Sim, M.; Woodman, R.J.; Croft, K.D.; Lewis, J.R.; Hodgson, J.M.; Bondonno, C.P. A Food Composition Database for Assessing Nitrate Intake from Plant-Based Foods. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Food-Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. EFSA J. 2008, 6, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheyney, M.; Moreno-Black, G. Nutritional Counseling in Midwifery and Obstetric Practice. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2010, 49, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucy, B.; Ingram, J.; Tonks, R.; Taylor, C. Provision of Information by Midwives for Pregnant Women in England on Guidance on Foods/Drinks to Avoid or Limit 2022. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2023, 23, 152. [Google Scholar]
- Olloqui-Mundet, M.J.; Cavia, M.M.; Alonso-Torre, S.R.; Carrillo, C. Nutritional Education in the Midwife’s Consultation Room. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecorguillé, M.; Camier, A.; Kadawathagedara, M. Weight Changes, Nutritional Intake, Food Contaminants, and Supplements in Women of Childbearing Age, Including Pregnant Women: Guidelines for Interventions during the Perinatal Period from the French National College of Midwives. J. Midwifery Womens Health 2022, 67 (Suppl. S1), S135–S148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidou, S.; Cascio, C.; Gilsenan, M.B. European Food Safety Authority Open Access Tools to Estimate Dietary Exposure to Food Chemicals. Environ. Int. 2021, 149, 106357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogias, C.; Kogias, D.; Kasmiridou, A.; Biagki, T.; Zouganeli, S.; Moriki, D.; Sardeli, O.; Chaloutsi, D.; Rufián-Henares, J.; Hinojosa-Nogueira, D.; et al. Repeatability and Validity Regarding Food Groups, Energy, and Macro-Nutrients Intake of a Semi-Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire for Children: The Stance4Health-FFQ. J Clin. Case Rep. Med. Images Health Sci. 2024, 7, 1306. [Google Scholar]


| Characteristic | %, Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Maternal Characteristics | |
| Maternal age | 34.9 ± 5.7 |
| Weight (Kg) | 68.2 ± 14.7 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.7 ± 5.6 |
| Energy intake | 2419 ± 386 |
| Infant Characteristics | |
| Infant sex (male/female) | 46.4%/53.6% |
| Gestational age (weeks) | 39.2 ± 1.92 |
| Birth weight (g) | 3277 ± 508 |
| Height of the newborns (cm) | 50.3 ± 2.68 |
| Head circumference (cm) | 34.1 ± 1.23 |
| Contaminants | Mean ± SD Intake (*/day) | Mean ± SD Exposure (*/kg body weight/day) |
|---|---|---|
| HMF5 (mg) | 64 ± 72.7 | 0.94 ± 1.06 |
| PYRR (mg) | 12.4 ± 7.7 | 0.18 ± 0.12 |
| AMCOMP (mg) | 67.4 ± 48.5 | 1.1 ± 0.69 |
| FUROS (mg) | 23.4 ± 15.8 | 0.3 ± 0.22 |
| ACRYL (µg) | 70.3 ± 42.4 | 1.08 ± 0.7 |
| FURAN (µg) | 14.5 ± 7.8 | 0.22 ± 0.1 |
| NITRA (mg) | 139 ± 67 | 2.08 ± 0.97 |
| NITRI (mg) | 11.3 ± 5.5 | 0.15 ± 0.07 |
| NITRN (µg) | 6.57 ± 3.04 | 0.10 ± 0.04 |
| B(A)P (µg) | 0.64 ± 0.17 | 0.04 ± 0.006 |
| TPAHC (µg) | 4.7 ± 1.1 | 0.07 ± 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hinojosa-Nogueira, D.; Bahamonde, J.R.; Aguilera-Nieto, M.; Navajas-Porras, B.; González-Vigil, V.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á.; Pastoriza de la Cueva, S. Dietary Exposure to Food Contaminants of Pregnant Women in Northern Spain and Possible Effects on Fetal Anthropometric Parameters. Toxics 2025, 13, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050399
Hinojosa-Nogueira D, Bahamonde JR, Aguilera-Nieto M, Navajas-Porras B, González-Vigil V, Rufián-Henares JÁ, Pastoriza de la Cueva S. Dietary Exposure to Food Contaminants of Pregnant Women in Northern Spain and Possible Effects on Fetal Anthropometric Parameters. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050399
Chicago/Turabian StyleHinojosa-Nogueira, Daniel, José Ramón Bahamonde, Marta Aguilera-Nieto, Beatriz Navajas-Porras, Verónica González-Vigil, José Ángel Rufián-Henares, and Silvia Pastoriza de la Cueva. 2025. "Dietary Exposure to Food Contaminants of Pregnant Women in Northern Spain and Possible Effects on Fetal Anthropometric Parameters" Toxics 13, no. 5: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050399
APA StyleHinojosa-Nogueira, D., Bahamonde, J. R., Aguilera-Nieto, M., Navajas-Porras, B., González-Vigil, V., Rufián-Henares, J. Á., & Pastoriza de la Cueva, S. (2025). Dietary Exposure to Food Contaminants of Pregnant Women in Northern Spain and Possible Effects on Fetal Anthropometric Parameters. Toxics, 13(5), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050399