Impact of Pesticide Exposure on High-Frequency Auditory Thresholds and Cochlear Function in Young People Residing near Agricultural Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
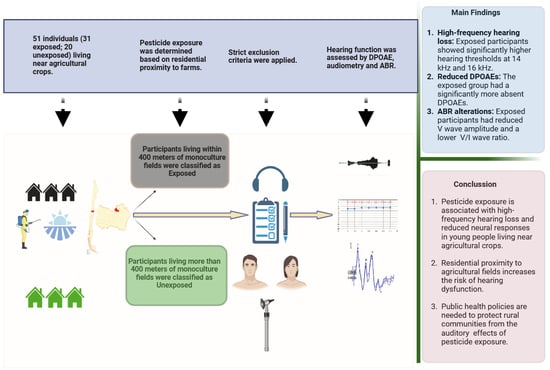
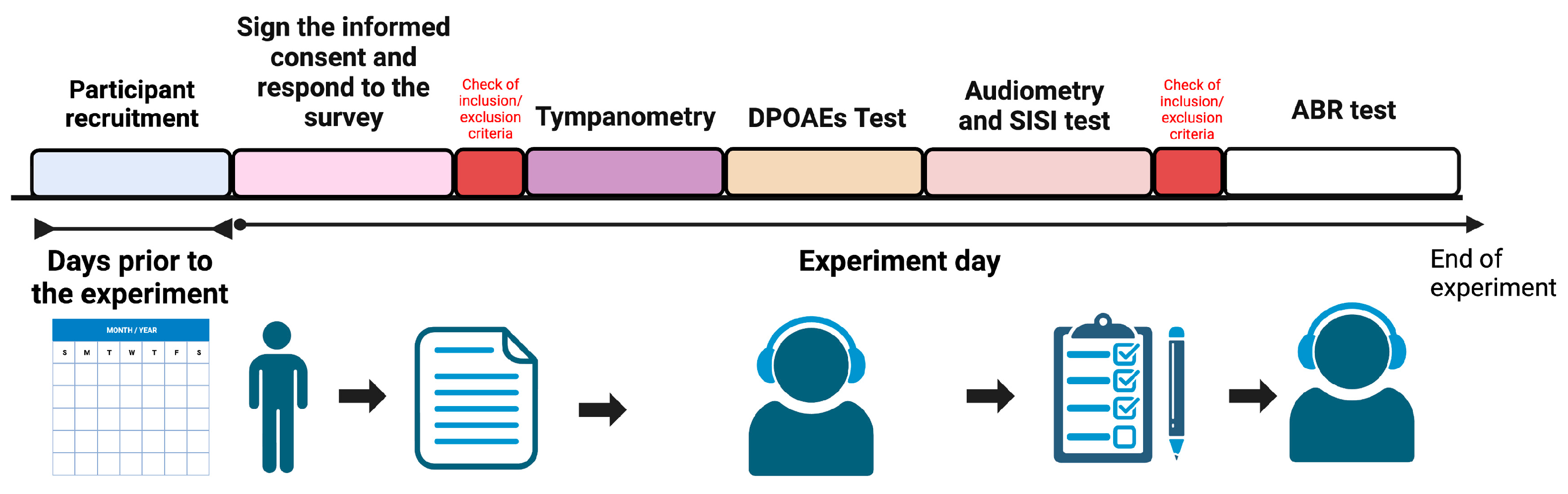
2.1. Subjects
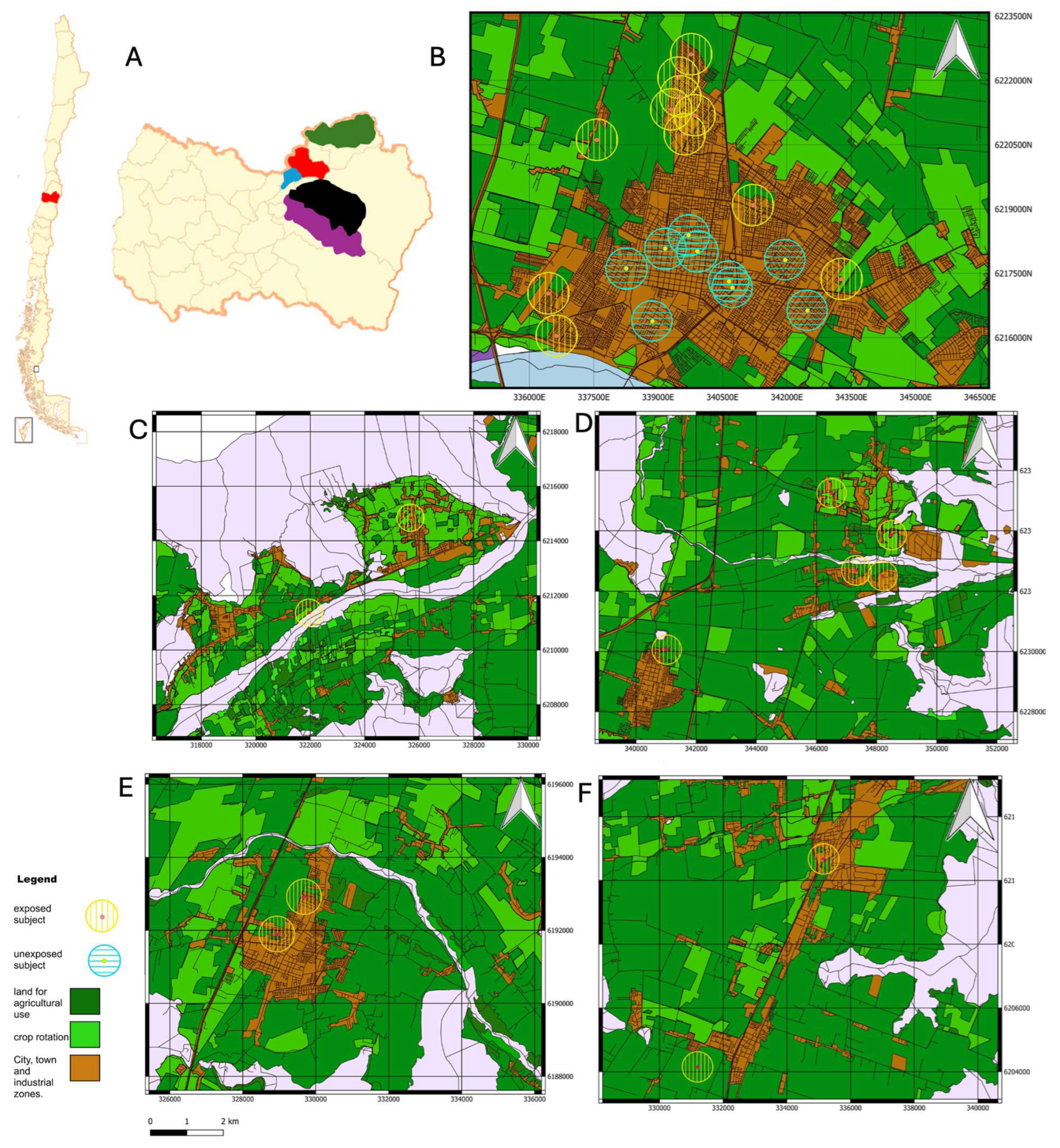
2.2. Experimental Groups and Pesticide Exposition
2.3. Hearing Assessment
2.3.1. Audiogram Thresholds
2.3.2. Distortion Product Otoacoustic Emissions (DPOAEs)
2.3.3. Auditory Brainstem Responses
2.3.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Conventional Audiometry, High-Frequency Hearing Thresholds, and SISI Test
3.2. Otoacoustic Emissions
3.3. Impact of Pesticide Exposure on Auditory Brainstem Evoked Potentials (ABR)
4. Discussion
4.1. High-Frequency Thresholds, Speech Disturbance in Noise, and Pesticide Exposure
4.2. Does Exposure to Pesticides Impair the Outer Hair Cell Functions?
4.3. Electrophysiological Auditory Response and Exposure to Pesticides
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| OP | Organophosphates |
| IHCs | Inner Hair Cells |
| OHCs | Outer Hair Cells |
| ABRs | Auditory Brainstem Responses |
| DPOAEs | Distortion Product Otoacoustic Emissions |
| GIS | Geographic Information System |
| PTA | Pure-Tone Average |
| SISI | Short Increment Sensitivity Index |
| SPL | Sound Pressure Level |
| E | E (group) |
| UE | UE (group) |
| RE | Right Ear |
| LE | Left Ear |
| GDP | Gross Domestic Product |
| SEM | Standard Error of the Mean |
| dB | Decibel |
| kHz | Kilohertz |
| Hz | Hertz |
| μV | Microvolts |
References
- Chadha, S.; Kamenov, K.; Cieza, A. The World Report on Hearing, 2021. Bull World Health Organ 2021, 99, 242-242A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesse, G. Innenohrschwerhörigkeit: Teil I: Prävalenz, Diagnostik Und Ätiologie. Laryngorhinootologie 2016, 95, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjdoost, F.; Ghaffari, M.-E.; Azimi, F.; Mohammadi, A.; Fouladi-Fard, R.; Fiore, M. Association between Air Pollution and Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss (SSHL): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos, M.J.; Fuente, A. The Adverse Effects of Heavy Metals with and without Noise Exposure on the Human Peripheral and Central Auditory System: A Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2016, 13, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terreros, G.; Cifuentes-Cabello, C.; D’Espessailles, A.; Munoz, F. Impact of Pesticide Exposure on Auditory Health: Mechanisms, Efferent System Disruption, and Public Health Implications. Toxicology 2025, 512, 154071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, R.G.; Steenland, K.; Jenkins, B.; Chrislip, D.; Russo, J. Chronic Neurologic Sequelae to Cholinesterase Inhibition among Agricultural Pesticide Applicators. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1995, 50, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körbes, D.; da Silveira, A.F.; Hyppolito, M.Â.; Munaro, G. Organophosphate-Related Ototoxicity: Description of the Vestibulocochlear System Ultrastructural Aspects of Guinea Pigs. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 76, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshammer, H.; Khan, A.W.; Wallner, P.; Poteser, M.; Kundi, M.; Hutter, H.-P. Validity of Reported Indicators of Pesticide Exposure and Relevance for Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Effects on Buccal Cells. Mutagenesis 2019, 34, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutter, H.-P.; Poteser, M.; Lemmerer, K.; Wallner, P.; Kundi, M.; Moshammer, H.; Weitensfelder, L. Health Symptoms Related to Pesticide Use in Farmers and Laborers of Ecological and Conventional Banana Plantations in Ecuador. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshammer, H.; Poteser, M.; Hutter, H.-P. More Pesticides—Less Children? Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2020, 132, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, C.S. Organic Phosphate Insecticide Poisoning. Am. J. Med. 1958, 24, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.M.; Hoppin, J.A.; Alavanja, M.C.R.; Blair, A.; Sandler, D.P.; Kamel, F. Hearing Loss among Licensed Pesticide Applicators in the Agricultural Health Study. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2008, 50, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, P.M.; Sircar, K.D.; Tarabar, S.; Galusha, D.; Slade, M.D. Hearing Loss in Migrant Agricultural Workers. J. Agromed. 2005, 10, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dundar, M.A.; Derin, S.; Aricigil, M.; Eryilmaz, M.A. Sudden Bilateral Hearing Loss after Organophosphate Inhalation. Turk. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 16, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, H.L.; Morini, R.G.; Cardoso, A.C.V. Avaliação Audiológica Em Trabalhadores Expostos a Ruído e Praguicida. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 76, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, C.F.; Brandão, M.F.A. Efeitos Dos Agrotóxicos No Sistema Auditivo Dos Trabalhadores Rurais. Cad Inf Prev Acid 1998, 19, 218. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, M.J.; May, J.J. Noise and Chemical Induced Hearing Loss. J. Agromed. 2005, 10, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash Krishnan Muthaiah, V.; Ding, D.; Salvi, R.; Roth, J.A. Carbaryl-Induced Ototoxicity in Rat Postnatal Cochlear Organotypic Cultures. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 956–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobarinas, E.; Salvi, R.; Ding, D. Selective Inner Hair Cell Dysfunction in Chinchillas Impairs Hearing-in-Noise in the Absence of Outer Hair Cell Loss. JARO 2016, 17, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawa, S.G.; Liberman, M.C. Adding Insult to Injury: Cochlear Nerve Degeneration after “Temporary” Noise-Induced Hearing Loss. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14077–14085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, R.J.; Ding, D.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.-Y. A Review of the Effects of Selective Inner Hair Cell Lesions on Distortion Product Otoacoustic Emissions, Cochlear Function and Auditory Evoked Potentials. Noise Health 2000, 2, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Helleman, H.W.; Dreschler, W.A. Overall versus Individual Changes for Otoacoustic Emissions and Audiometry in a Noise-Exposed Cohort. Int. J. Audiol. 2012, 51, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plack, C.J.; Barker, D.; Prendergast, G. Perceptual Consequences of “Hidden” Hearing Loss. Trends Hear. 2014, 18, 2331216514550621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobarinas, E.; Salvi, R.; Ding, D. Insensitivity of the Audiogram to Carboplatin Induced Inner Hair Cell Loss in Chinchillas. Hear. Res. 2013, 302, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maison, S.F.; Usubuchi, H.; Liberman, M.C. Efferent Feedback Minimizes Cochlear Neuropathy from Moderate Noise Exposure. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 5542–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, P.; Fritz, J.B.; Shamma, S.A. Rapid Spectrotemporal Plasticity in Primary Auditory Cortex during Behavior. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 4396–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liliana Yáñez Barrios Región Del Libertador Bernardo O’Higgins. 2021.
- Fenske, R.A.; Lu, C.; Barr, D.; Needham, L. Children’s exposure to chlorpyrifos and parathion in an agricultural community in central Washington State. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servicio Agrícola Ganadero (SAG). Declaración de Ventas de Plaguicidas de Uso Agrícola Año 2019; Servicio Agrícola Ganadero (SAG): Santiago, Chile, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gatto, M.P.; Fioretti, M.; Fabrizi, G.; Gherardi, M.; Strafella, E.; Santarelli, L. Effects of Potential Neurotoxic Pesticides on Hearing Loss: A Review. Neurotoxicology 2014, 42, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Tang, X. Exploring the Association of Organochlorine Pesticides Exposure and Hearing Impairment in United States Adults. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, C.F.; Augusto, L.G.d.S.; Morata, T.C. Saúde Auditiva de Trabalhadores Expostos a Ruído e Inseticidas. Rev. Saude Publica 2003, 37, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, H.G.; Lee, J.A.; Liu, Y.F.; Endriukaitis, L.; Isaac, J.L.; Bullington, W.M. Drug-Induced Ototoxicity: A Comprehensive Review and Reference Guide. Pharmacotherapy 2020, 40, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobarinas, E.; Spankovich, C.; Prell, C.G. Le Evidence of “Hidden Hearing Loss” Following Noise Exposures That Produce Robust TTS and ABR Wave-I Amplitude Reductions. Hear. Res. 2017, 349, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.J.; An, Y.-H.; Kim, D.H.; Yoon, J.E.; Yoon, J.H. Comparisons of Auditory Brainstem Response and Sound Level Tolerance in Tinnitus Ears and Non-Tinnitus Ears in Unilateral Tinnitus Patients with Normal Audiograms. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkler, A.D.; da Silveira, A.F.; Munaro, G.; Zanrosso, C.D. Otoproteção Em Cobaias Expostas a Agrotóxico e Ginkgo Biloba. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 78, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reischl, P.; Van Gelder, G.A.; Karas, G.G. Auditory Detection Behavior in Parathion-Treated Squirrel Monkeys (Saimiri Sciureus). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1975, 34, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zou, H. Research Progress on Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Diabetic Retinopathy. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcarás, P.A.d.S.; Zeigelboim, B.S.; Corazza, M.C.A.; Lüders, D.; Marques, J.M.; Lacerda, A.B.M. de Findings on the Central Auditory Functions of Endemic Disease Control Agents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, T.R.R.; Dourado, S.S.F.; Lima, L.V.; Antoniolli, Â.R. The Hearing of Rural Workers Exposed to Noise and Pesticides. Noise Health 2018, 20, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veuillet, E.; Collet, L.; Duclaux, R. Effect of Contralateral Acoustic Stimulation on Active Cochlear Micromechanical Properties in Human Subjects: Dependence on Stimulus Variables. J. Neurophysiol. 1991, 65, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korres, G.S.; Balatsouras, D.G.; Tzagaroulakis, A.; Kandiloros, D.; Ferekidou, E.; Korres, S. Distortion Product Otoacoustic Emissions in an Industrial Setting. Noise Health 2009, 11, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhiria, C.; Vergara, R.C.; Martín, S.S.; Leiva, A.; Marcenaro, B.; Martinez, M.; Delgado, C.; Delano, P.H. Cingulate Cortex Atrophy Is Associated with Hearing Loss in Presbycusis with Cochlear Amplifier Dysfunction. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturza, J.; Silver, M.K.; Xu, L.; Li, M.; Mai, X.; Xia, Y.; Shao, J.; Lozoff, B.; Meeker, J. Prenatal Exposure to Multiple Pesticides Is Associated with Auditory Brainstem Response at 9 months in a Cohort Study of Chinese Infants. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassanayake, T.; Gawarammana, I.B.; Weerasinghe, V.; Dissanayake, P.S.; Pragaash, S.; Dawson, A.; Senanayake, N. Auditory Event-Related Potential Changes in Chronic Occupational Exposure to Organophosphate Pesticides. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.M.; Baker, J.M.; Hyland, C.; Rodríguez-Zamora, M.G.; Rojas-Valverde, D.; Winkler, M.S.; Staudacher, P.; Palzes, V.A.; Gutiérrez-Vargas, R.; Lindh, C.; et al. Pesticide Exposure and Cortical Brain Activation among Farmworkers in Costa Rica. Neurotoxicology 2022, 93, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaette, R.; McAlpine, D. Tinnitus with a Normal Audiogram: Physiological Evidence for Hidden Hearing Loss and Computational Model. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 13452–13457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y. A Review on the Ethical Issues in Neurotechnology. Theor. Nat. Sci. 2023, 4, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, J.L.; Dunn, C.; Gaspari, R.J. Central Respiratory Failure during Acute Organophosphate Poisoning. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2013, 189, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, R.; Delgado-Téllez, E.; Cuadra, R.; Tórres, E.; Keifer, M.; Almendárez, J.; Miranda, J.; El-Fawal, H.A.N.; Wolff, M.; Simpson, D.; et al. Organophosphate Neuropathy Due to Methamidophos: Biochemical and Neurophysiological Markers. Arch. Toxicol. 1999, 73, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magomedov, K.E.; Zeynalov, R.Z.; Suleymanov, S.I.; Tataeva, S.D.; Magomedova, V.S. Calculation of Lipophilicity of Organophosphate Pesticides Using Density Functional Theory. Membranes 2022, 12, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatorre, R.J.; Belin, P. Spectral and Temporal Processing in Human Auditory Cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2001, 11, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tervaniemi, M.; Hugdahl, K. Lateralization of Auditory-Cortex Functions. Brain Res. Rev. 2003, 43, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durante, A.S.; Carvallo, R.M.M. Contralateral Suppression of Otoacoustic Emissions in Neonates: Supresión Contralateral de Las Emisiones Otoacüsticas En Recién Nacidos. Int. J. Audiol. 2002, 41, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalfa, S.; Collet, L. Functional Asymmetry of Medial Olivocochlear System in Humans. Towards a Peripheral Auditory Lateralization. Neuroreport 1996, 7, 993–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Jiang, H.; Salvi, R.J. Mechanisms of Rapid Sensory Hair-Cell Death Following Co-Administration of Gentamicin and Ethacrynic Acid. Hear. Res. 2010, 259, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ding, D.; Salvi, R.J. Functional Reorganization in Chinchilla Inferior Colliculus Associated with Chronic and Acute Cochlear Damage. Hear. Res. 2002, 168, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, L.; Delano, P.H. Efferent System. 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Terreros, G.; Delano, P.H. Corticofugal Modulation of Peripheral Auditory Responses. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, D.N.; Seltzer, B.; Petrides, M.; Cipolloni, P.B. Auditory System. In Cerebral Cortex: Architecture, Connections, and the Dual Origin Concept; Oxford Academic: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | Exposed (n = 31) | Unexposed (n = 20) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean years (SD) | 25.94 (6.45) | 28.2 (5.34) | 0.152 (a) |
| Sex, n (%) | 0.107 (b) | ||
| Male | 10 (32.26) | 11 (55) | |
| Female | 21 (67.74) | 9 (45) | |
| Mother’s educational level, n (%) | 0.127 (b) | ||
| None | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | |
| Elementary school | 1 (3.23) | 1 (5) | |
| High school | 11 (35.48) | 12 (60) | |
| College or more | 19 (61.29) | 6 (30) | |
| Economic perception, n (%) | 0.502 (b) | ||
| High | 13 (41.94) | 11 (55) | |
| Medium | 16 (51.61) | 7 (35) | |
| Low | 2 (6.45) | 2 (10) | |
| Alcohol intake, n (%) | 17 (54.84) | 12 (60) | 0.716 (b) |
| Smoking, n (%) | 7 (22.58) | 6 (30) | 0.553 (b) |
| Distance in meters from home to any crop, mean (SD) | 281.23 (371.19) | 2872.89 (3367.88) | <0.0001 * (c) |
| Frequency (kHz) | Left Ear Exposed | Left Ear Unexposed | Left Ear p-Value | Right Ear Exposed | Right Ear Unexposed | Right Ear p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.15 | 7.903 ± 4.614 | 8.500 ± 6.902 | >0.99 | 8.387 ± 5.383 | 7.250 ± 4.993 | >0.99 |
| 0.25 | 6.129 ± 6.546 | 8.000 ± 7.327 | >0.99 | 7.419 ± 6.308 | 7.250 ± 8.347 | >0.99 |
| 0.5 | 7.097 ± 6.554 | 6.750 ± 7.482 | >0.99 | 7.419 ± 6.174 | 8.500 ± 6.802 | >0.99 |
| 1 | 6.613 ± 4.161 | 6.500 ± 5.155 | >0.99 | 7.258 ± 5.138 | 6.500 ± 5.405 | >0.99 |
| 2 | 4.839 ± 6.890 | 5.250 ± 6.781 | >0.99 | 5.000 ± 4.830 | 6.000 ± 7.182 | >0.99 |
| 3 | 6.290 ± 5.472 | 6.500 ± 9.333 | >0.99 | 7.419 ± 6.816 | 7.250 ± 7.518 | >0.99 |
| 4 | 4.677 ± 7.631 | 7.500 ± 9.389 | >0.99 | 5.000 ± 6.708 | 4.750 ± 7.691 | >0.99 |
| 6 | 8.065 ± 9.633 | 7.000 ± 6.156 | >0.99 | 4.516 ± 5.966 | 6.750 ± 6.340 | >0.99 |
| 8 | 10.645 ± 7.931 | 9.250 ± 6.935 | >0.99 | 10.323 ± 8.557 | 10.750 ± 5.684 | >0.99 |
| 9 | 9.516 ± 9.518 | 8.250 ± 7.304 | >0.99 | 11.774 ± 8.221 | 9.750 ± 6.781 | >0.99 |
| 10 | 10.968 ± 9.951 | 7.500 ± 7.164 | >0.99 | 10.161 ± 8.415 | 9.500 ± 8.095 | >0.99 |
| 11.2 | 12.903 ± 11.956 | 8.250 ± 8.926 | >0.99 | 9.548 ± 9.999 | 8.750 ± 8.091 | >0.99 |
| 12.5 | 10.323 ± 13.162 | 4.250 ± 10.422 | 0.42 | 10.000 ± 12.845 | 8.750 ± 10.497 | >0.99 |
| 14 | 16.613 ± 16.451 | 7.750 ± 11.059 | 0.02 * | 15.000 ± 16.683 | 10.250 ± 11.410 | 0.97 |
| 16 | 21.897 ± 19.658 | 11.250 ± 13.943 | 0.002 ** | 16.607 ± 18.056 | 12.000 ± 12.397 | >0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munoz, F.; Aedo-Sanchez, C.; Paredes-Aravena, F.; Aguilar-Vidal, E.; Jilberto-Vergara, P.; Terreros, G. Impact of Pesticide Exposure on High-Frequency Auditory Thresholds and Cochlear Function in Young People Residing near Agricultural Areas. Toxics 2025, 13, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050375
Munoz F, Aedo-Sanchez C, Paredes-Aravena F, Aguilar-Vidal E, Jilberto-Vergara P, Terreros G. Impact of Pesticide Exposure on High-Frequency Auditory Thresholds and Cochlear Function in Young People Residing near Agricultural Areas. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050375
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunoz, Felipe, Cristian Aedo-Sanchez, Felipe Paredes-Aravena, Enzo Aguilar-Vidal, Pedro Jilberto-Vergara, and Gonzalo Terreros. 2025. "Impact of Pesticide Exposure on High-Frequency Auditory Thresholds and Cochlear Function in Young People Residing near Agricultural Areas" Toxics 13, no. 5: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050375
APA StyleMunoz, F., Aedo-Sanchez, C., Paredes-Aravena, F., Aguilar-Vidal, E., Jilberto-Vergara, P., & Terreros, G. (2025). Impact of Pesticide Exposure on High-Frequency Auditory Thresholds and Cochlear Function in Young People Residing near Agricultural Areas. Toxics, 13(5), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050375