Nanoplastics Elicit Stage-Specific Physiological, Biochemical, and Gut Microbiome Responses in a Freshwater Mussel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials of PS-NPs
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Characterization of PS-NPs
2.4. Ultrastructural Morphology Analysis of Intestinal Tract
2.5. Physiological and Biochemical Parameters
2.5.1. Oxidative Stress Markers and Total Protein Content
2.5.2. Physiological Metabolic Indexes at the Individual Level
2.6. Gut Microbiota DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
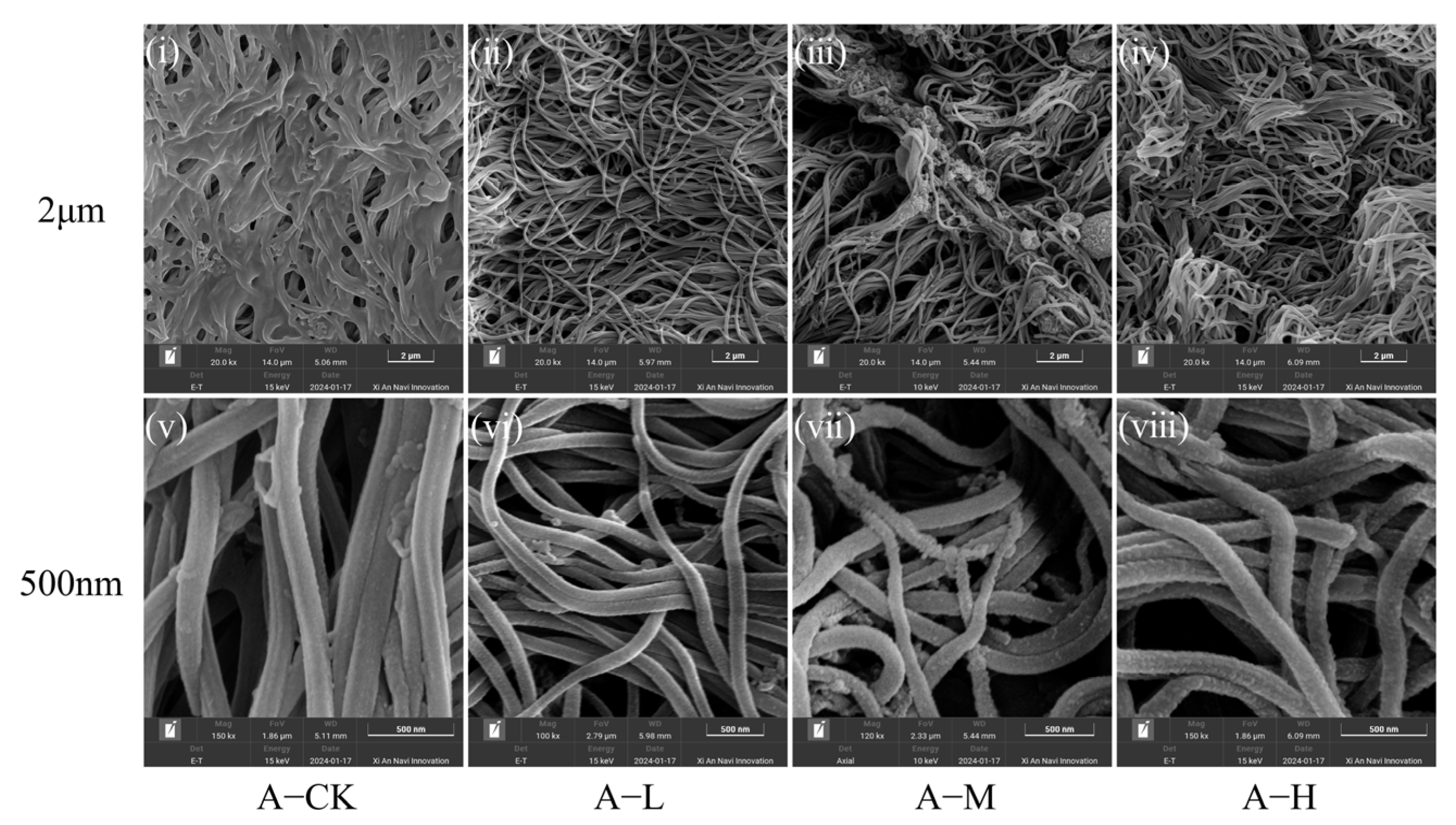
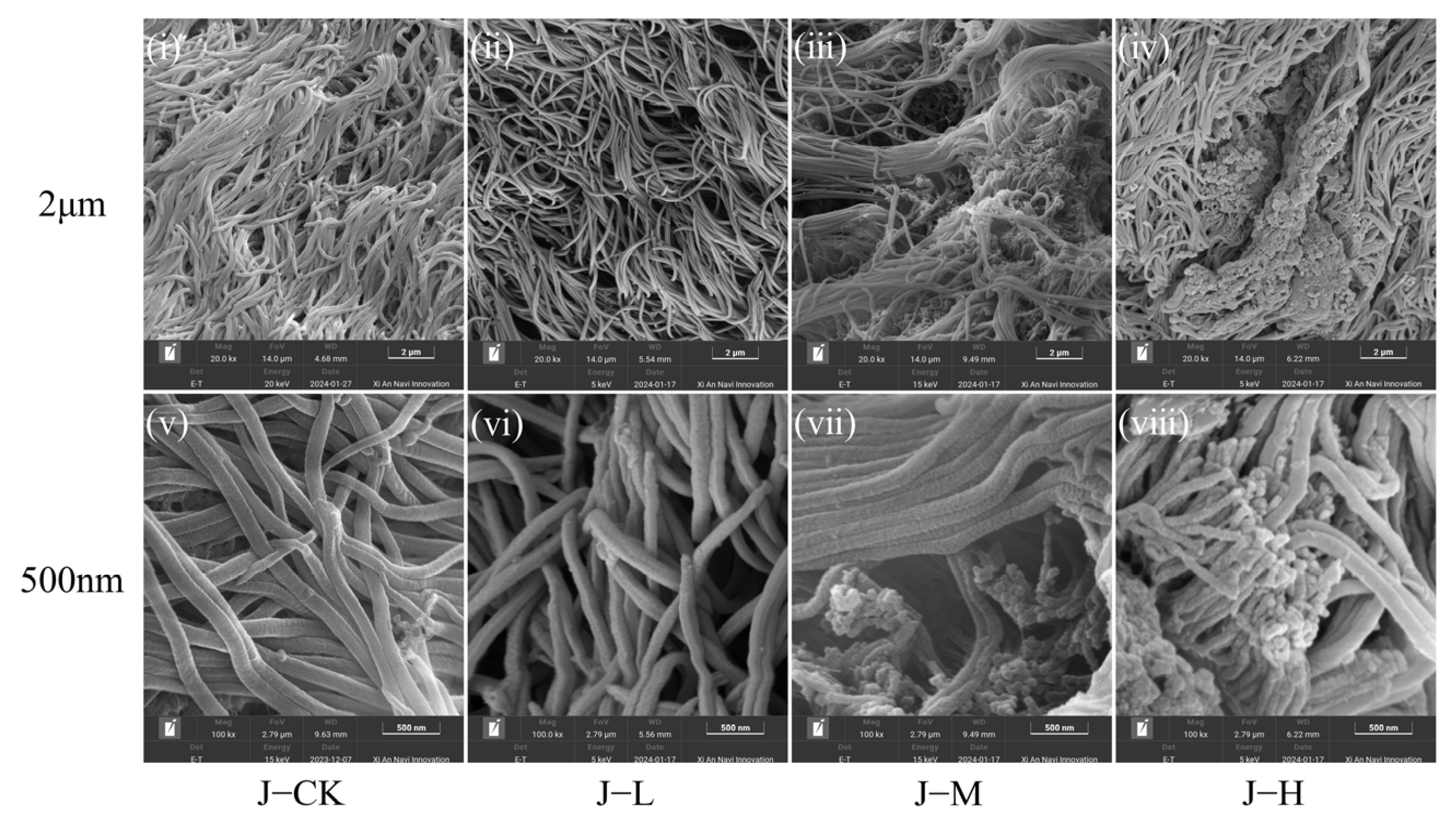
3.1. Effects of PS-NPs on Intestinal Tissue
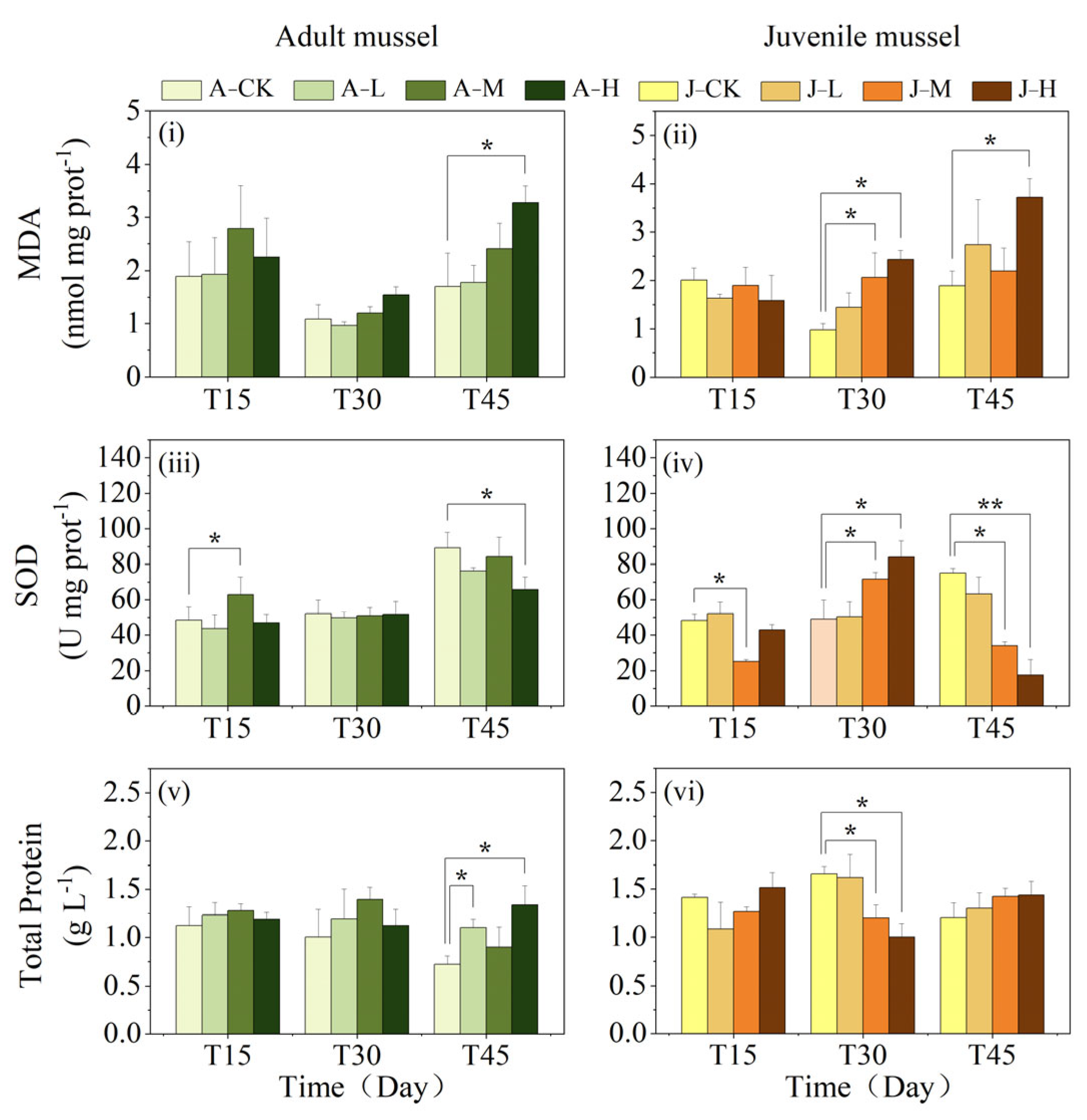
3.2. Effects of PS-NPs on Oxidative Stress Response and Total Protein
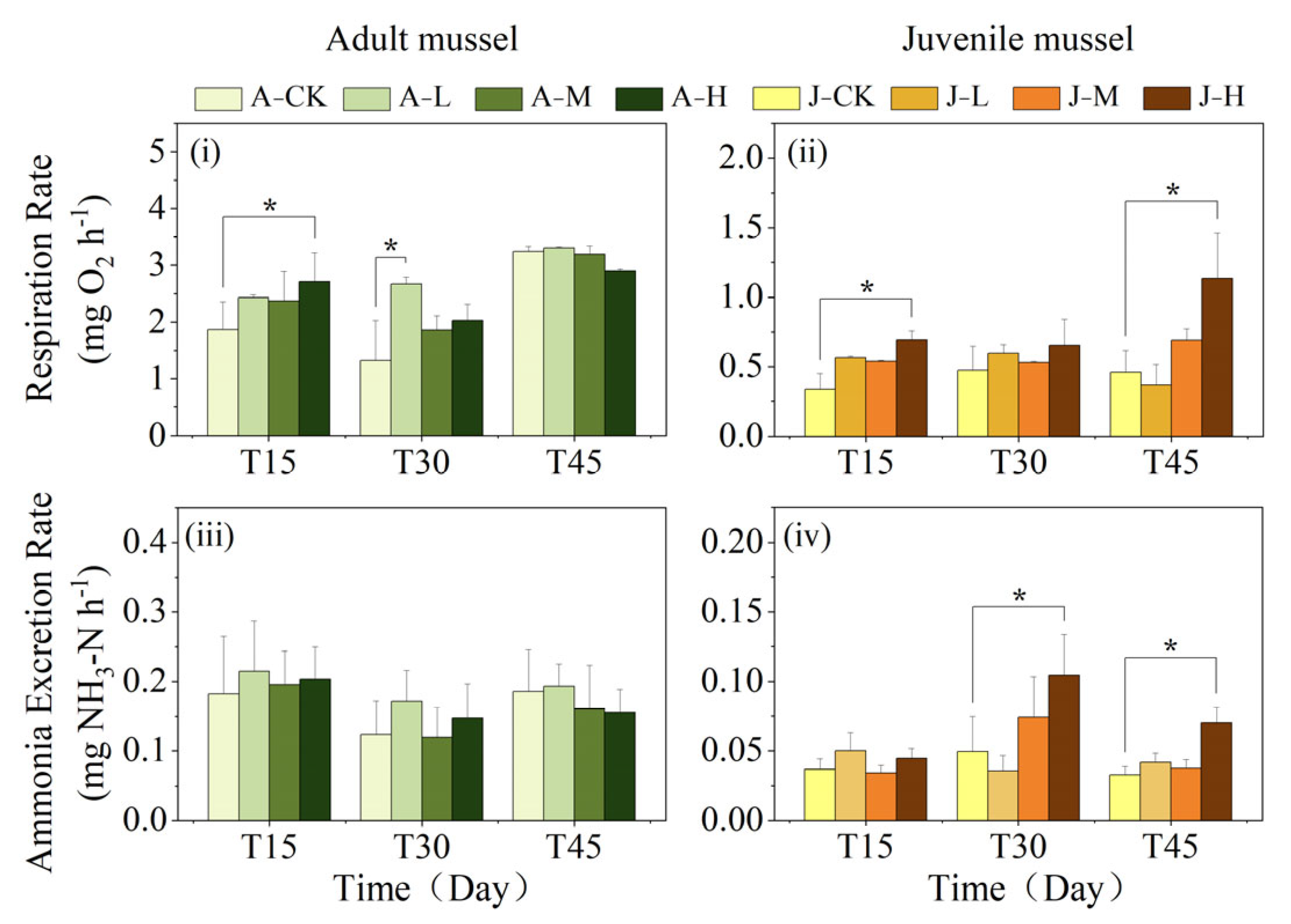
3.3. Effects of PS-NPs on Physiological Metabolism at the Individual Level
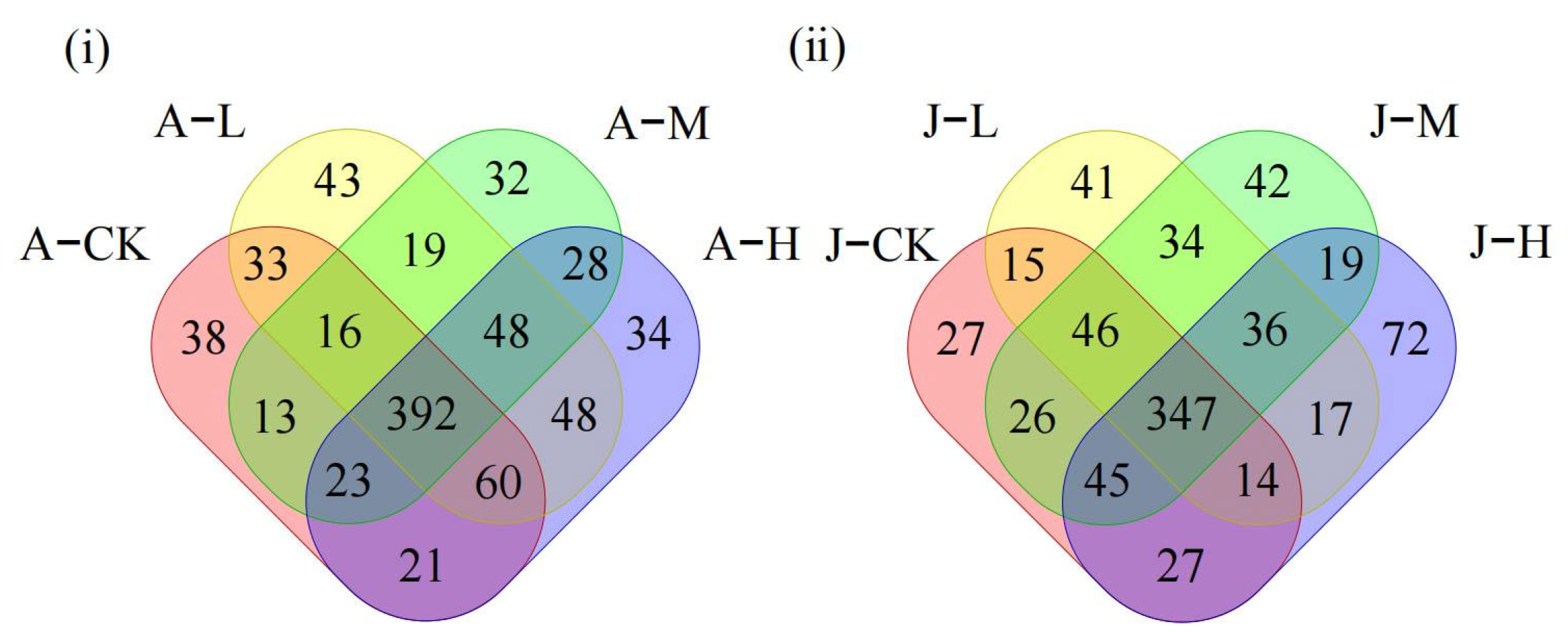
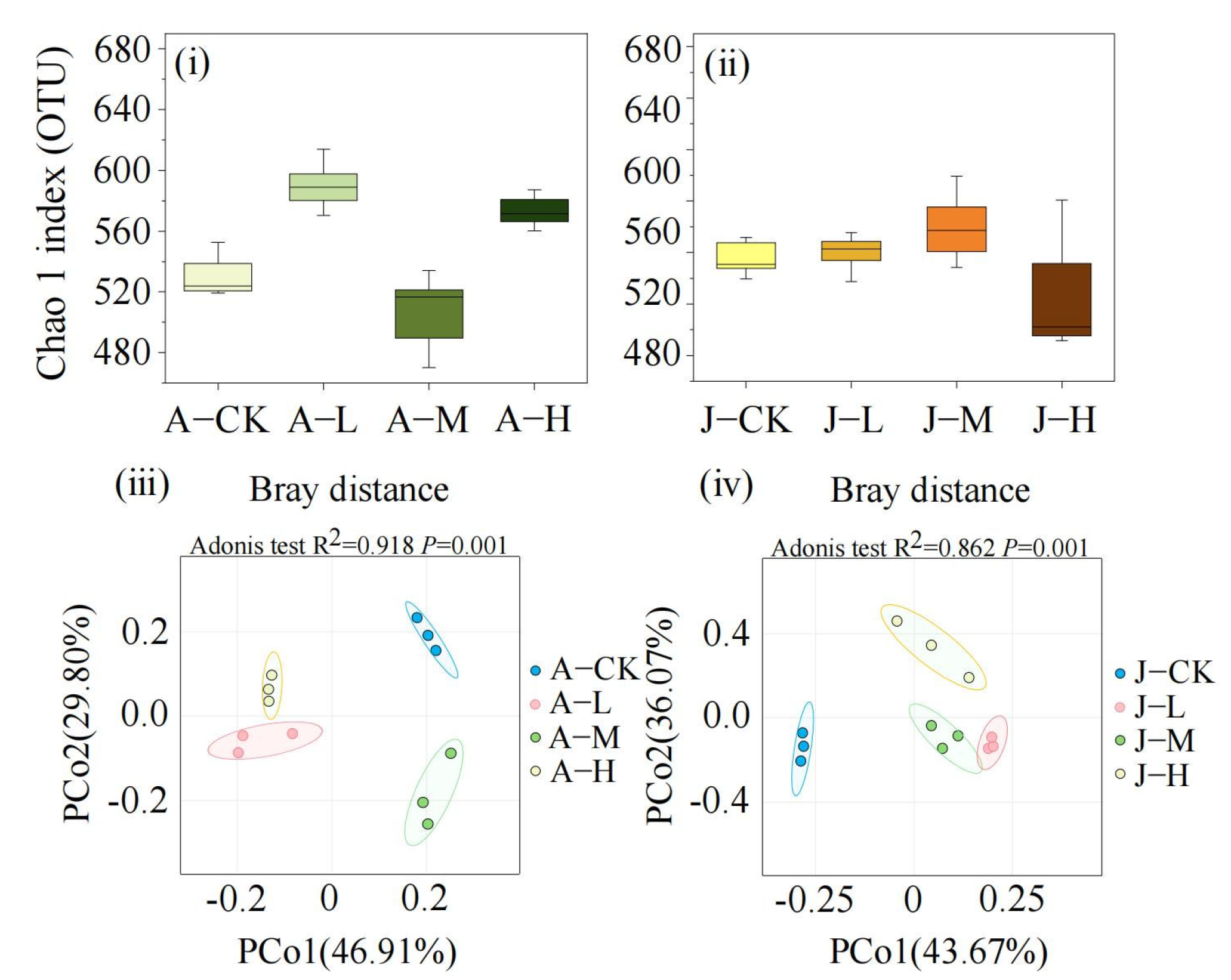
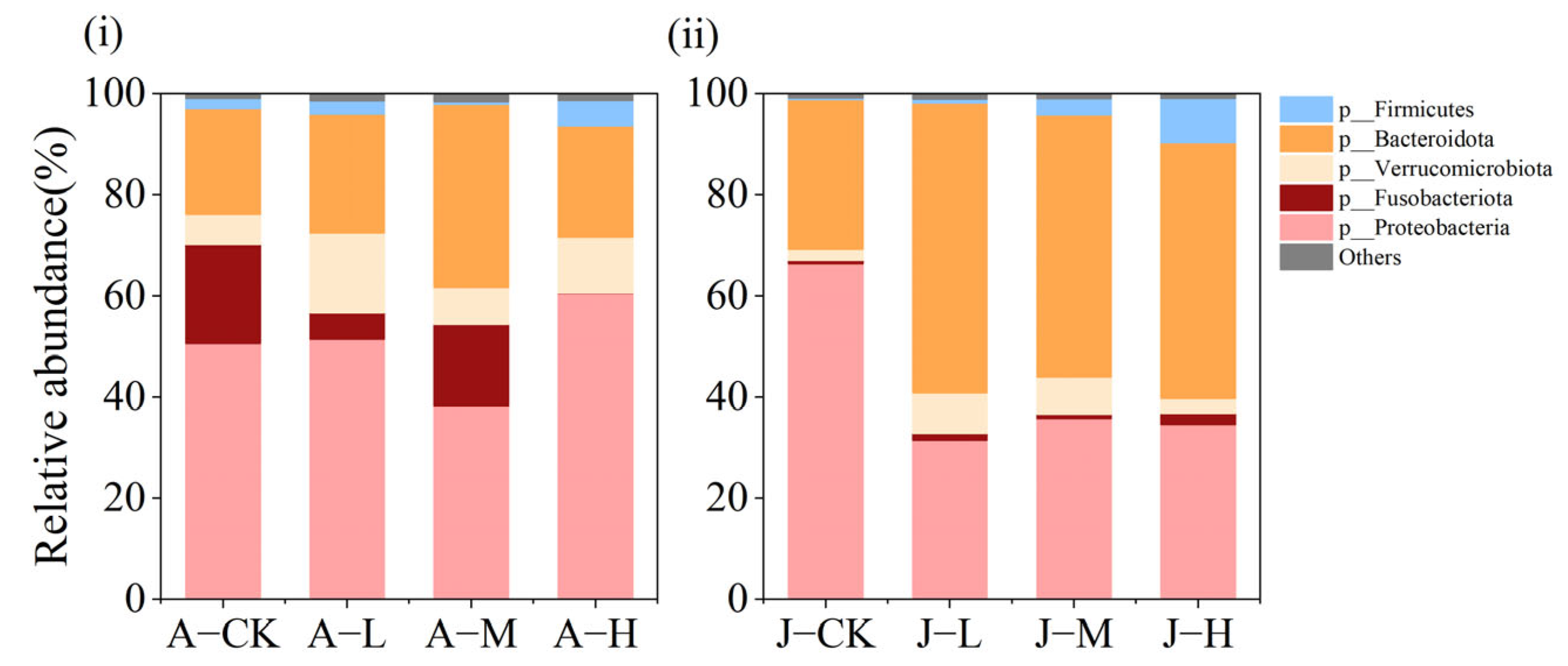
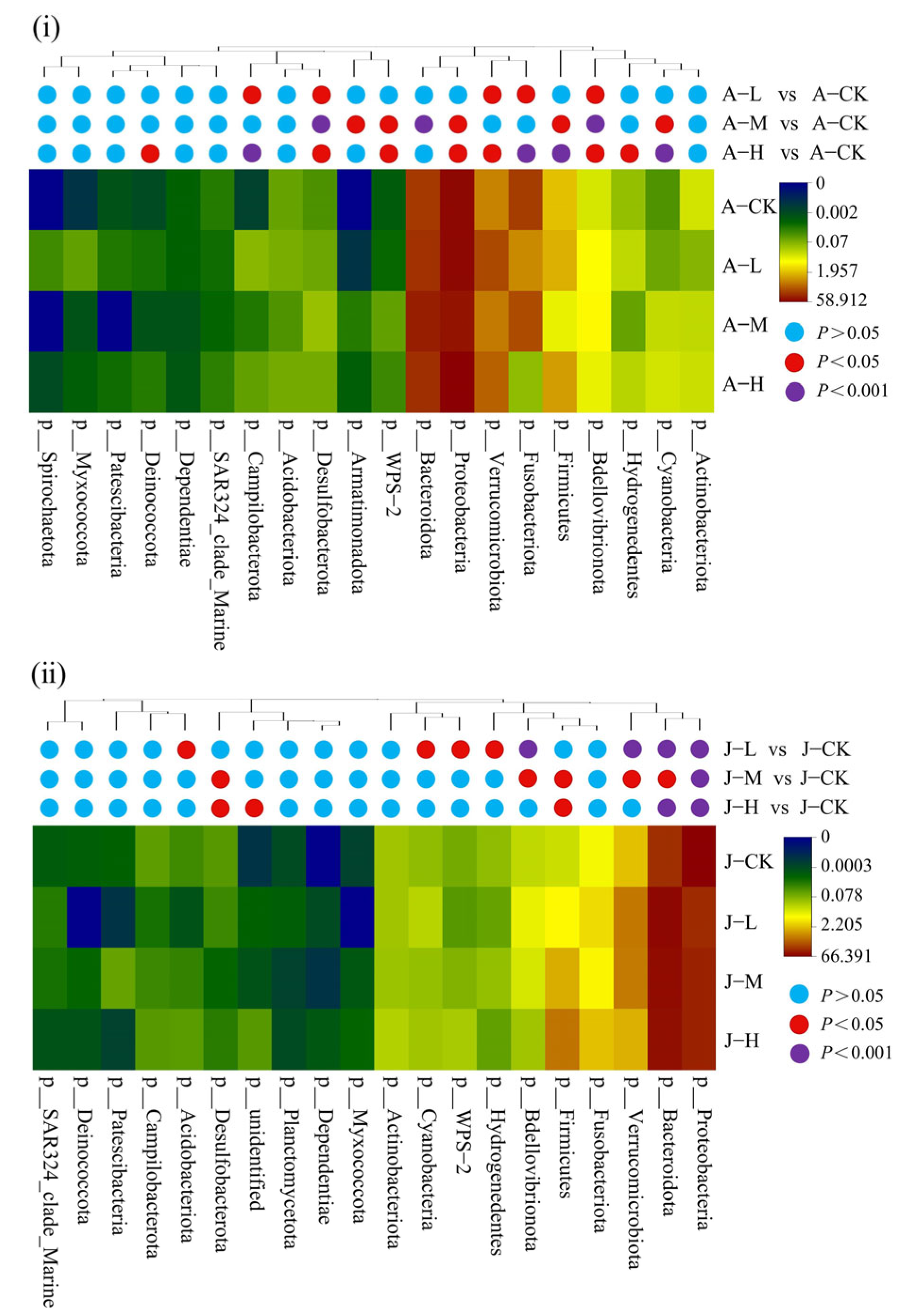
3.4. Effects of PS-NPs on Gut Microbiota
3.4.1. Effects of PS-NPs on Gut Microbiota Diversity
3.4.2. Effects of PS-NPs on Gut Microbiota Composition
4. Discussion
4.1. PS-NP Exposure Injured C. plicata Intestinal Tissue
4.2. Exposure to PS-NPs Induced C. plicata’s Oxidative Stress Responses
4.3. Exposure to PS-NPs Affected C. plicata’s Physiological Metabolism
4.4. Exposure to PS-NPs Disturbed Gut Microbiota
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Archambault, J.M. Contaminant-Related Ecosystem Functions and Services of Freshwater Mussels (Unionidae) and Public Views on Nature’s Contributions to Water Quality. Ph.D. Thesis, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Na, Y.K.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, J.H.; Kwak, I.S. Biological accessibility to algae control through measurement of filtration rate of three freshwater bivalves. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2021, 54, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, X.; Xiong, B.; Su, S.; Wu, Z.; Yao, W. Ecological efficiency of the mussel Hyriopsis cumingii (Lea, 1852) on particulate organic matter filtering, algal controlling and water quality regulation. Water 2021, 13, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, C.C. Ecosystem services provided by freshwater mussels. Hydrobiologia 2017, 810, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Yu, J.; Li, K.; Guan, B.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, Z. Effects of cyanobacterial blooms on submerged macrophytes alleviated by the native Chinese bivalve Hyriopsis cumingii: A mesocosm experiment study. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, C.C.; Hakenkamp, C.C. The functional role of burrowing bivalves in freshwater ecosystems. Freshw. Biol. 2008, 46, 1431–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Tang, Y. Effects of Anodonta woodiana on water quality improvement in restoration of eutrophic shallow lakes. J. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 1610–1615. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Strayer, D.L. Understanding how nutrient cycles and freshwater mussels (Unionoida) affect one another. Hydrobiologia 2014, 735, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, C.C.; Nichols, S.J.; Spooner, D.E. Community and food web ecology of freshwater mussels. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2008, 27, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, R.; Zanatta, D.T.; Lopes-Lima, M.; Gonçalves, D.V.; Bogan, A.E.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, X. Systematics, distribution, biology, and conservation of freshwater mussels (Bivalvia: Unionida) in China. Aquat. Conserv. 2022, 32, 859–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsaleheen, O.T.M. Reproduction Biology and Environmental Threats for Freshwater Mussels (Bivalvia: Unionidae). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.G.; Li, J.L. Biodiversity and conservation of freshwater mollusks. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2004, 28, 440–444. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelo, R.T.; Cringan, M.S.; Chamberlain, D.L.; Stahl, A.J.; Haslouer, S.G.; Goodrich, C.A. Residual effects of lead and zinc mining on freshwater mussels in the Spring River Basin (Kansas, Missouri, and Oklahoma, USA). Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 384, 467–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.N.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Yang, J.X. Effect of eutrophication on molluscan community composition in the Lake Dianchi (China, Yunnan). Limnologica 2011, 41, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, W.G.; Bergeron, C.M.; Archambault, J.M.; Jones, J.W.; Beaty, B.; Lazaro, P.R.; Shea, D.; Callihan, J.L.; Rogers, J.J. Understanding the influence of multiple pollutant stressors on the decline of freshwater mussels in a biodiversity hotspot. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 144757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhani, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gibson, C.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M.; Fang, C. Identification and visualisation of microplastics/nanoplastics by Raman imaging (i): Down to 100 nm. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendra, M.; Sparaventi, E.; Novoa, B.; Figueras, A. An overview of the internalization and effects of microplastics and nanoplastics as pollutants of emerging concern in bivalves. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 142024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjani, M.H.; Sharifinia, M.; Mohammadi, A.R. The impact of microplastics on bivalve mollusks: A bibliometric and scientific review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 194, 115271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, R.; Ranasinghe, P.; Jayasundara, N.; Di Giulio, R.T. Nanoplastics in aquatic environments: Impacts on aquatic species and interactions with environmental factors and pollutants. Toxics 2022, 10, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Feng, C.; Wu, Y.; Guo, X. Impacts of nanoplastics on bivalve: Fluorescence tracing of organ accumulation, oxidative stress and damage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auguste, M.; Lasa, A.; Balbi, T.; Pallavicini, A.; Vezzulli, L.; Canesi, L. Impact of nanoplastics on hemolymph immune parameters and microbiota composition in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 159, 105017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Miao, A.; Liao, Y.; Pan, K. Effects of nanoplastics on clam Ruditapes philippinarum at environmentally realistic concentrations: Toxicokinetics, toxicity, and gut microbiota. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 456, 131647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rist, S.; Baun, A.; Almeda, R.; Hartmann, N.B. Ingestion and effects of micro-and nanoplastics in blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) larvae. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Wang, W.X. Differential cascading cellular and subcellular toxicity induced by two sizes of nanoplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sui, Q.; Sun, X.; Zhu, L.; Booth, A.M.; Chen, B.; Qu, K.; Xia, B. Polystyrene nanoplastics affected the nutritional quality of Chlamys farreri through disturbing the function of gills and physiological metabolism: Comparison with microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 910, 168457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, C.; Mahé, P.; Latchere, O.; Catrouillet, C.; Gigault, J.; Métais, I.; Châtel, A. Effect of size continuum from nanoplastics to microplastics on marine mussel Mytilus edulis: Comparison in vitro/in vivo exposure scenarios. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 264, 109512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, C.C.; Hoellein, T.J. Bivalve impacts in freshwater and marine ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2018, 49, 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materić, D.; Peacock, M.; Dean, J.; Futter, M.; Maximov, T.; Moldan, F.; Röckmann, T.; Holzinger, R. Presence of nanoplastics in rural and remote surface waters. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 054036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Liu, S.; Liao, H.; Yue, Q.; Wang, J. Environmental nanoplastics quantification by pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in the Pearl River, China: First insights into spatiotemporal distributions, compositions, sources and risks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Xue, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, D.; Kolandhasamy, P.; Li, D.; Shi, H. Microplastics in taihu lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besseling, E.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.; Foekema, E.M.; Koelmans, A.A. Quantifying ecological risks of aquatic micro- and nanoplastic. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 49, 32–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Nor, N.H.M.; Hermsen, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.M.; De France, J. Microplastics in freshwaters and drinking water: Critical review and assessment of data quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Billey, L.O.; Shelver, W.L. Uptake and toxicity of polystyrene micro/nanoplastics in gastric cells: Effects of particle size and surface functionalization. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.L.; Rodrigues, C.C.; Oliveira, M.; Rocha, T.L. Microbiome: A forgotten target of environmental micro(nano)plastics? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, J.M.; Bebianno, M.J. Nanoplastics impact on marine biota: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasee, B.A. Histological and Ultrastructural Studies of Larval and Juvenile Lampsilis (Bivalvia) from the Upper Mississippi River. Ph.D. Thesis, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Dimock, R.V., Jr.; Wright, A.H. Sensitivity of juvenile freshwater mussels to hypoxic, thermal and acid stress. J. Elisha Mitchell Sci. Soc. 1993, 109, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Cao, Y.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, X. Comparative analysis of gut microbiota diversity in endangered, economical, and common freshwater mussels using 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 12015–12023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Han, R.; Cao, Y.; Hua, W.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pang, X.; Wei, C. Interactions between gut microbiota, host genetics and diet relevant to development of metabolic syndromes in mice. ISME J. 2010, 4, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhaes, J.G.; Tattoli, I.; Girardin, S.E. The intestinal epithelial barrier: How to distinguish between the microbial flora and pathogens. Semin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirt, N.; Body-Malapel, M. Immunotoxicity and intestinal effects of nano-and microplastics: A review of the literature. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klishko, O.K.; Lopes-Lima, M.; Froufe, E.; Bogan, A.E.; Abakumova, V.Y. Systematics and distribution of Cristaria plicata (Bivalvia, Unionidae) from the Russian Far East. ZooKeys 2016, 580, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Patnaik, B.B.; Wang, T.H.; Kang, S.W.; Hwang, H.J.; Park, S.Y.; Park, E.B.; Chung, J.M.; Song, D.K.; Kim, C.; Kim, S.; et al. Sequencing, De Novo Assembly, and Annotation of the Transcriptome of the Endangered Freshwater Pearl Bivalve, Cristaria plicata, Provides Novel Insights into Functional Genes and Marker Discovery. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magni, S.; Parolini, M.; Della Torre, C.; de Oliveira, L.F.; Catani, M.; Guzzinati, R.; Cavazzini, A.; Binelli, A. Multi-biomarker investigation to assess toxicity induced by two antidepressants on Dreissena polymorpha. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.F.; Wei, Q.S. On gonad development and reproduction cycle of the Cristaria Plicate in the south lake of Wuhan. J. Huazhong Agr. Univ. 1993, 12, 190–196. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.G.; Li, R.Z. Histological and scanning electron microscopic observations on the gill of Cristaria plicata. J. Fish. Chin. 2002, 26, 301–304. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kong, C.; Pan, T.; Chen, X.; Junaid, M.; Liao, H.; Gao, D.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics and PCB77 induced oxidative stress, histopathological damage and intestinal microbiota disruption in white hard clam Meretrix lyrata. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Lin, D.; Shang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Lu, W.; Huang, X.; Ning, K.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. CO2-induced pH reduction increases physiological toxicity of nano-TiO2 in the mussel Mytilus coruscus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kobert, K.; Flouri, T.; Stamatakis, A. PEAR: A fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Jing, Y.; Yang, M.; Du, L.; Gao, F.; Gong, H.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in male patients with chronic traumatic complete spinal cord injury. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Xu, B.; Chen, H.; Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, M.; Xia, S.; Wu, S. Gut toxicity of polystyrene microplastics and polychlorinated biphenyls to Eisenia fetida: Single and co-exposure effects with a focus on links between gut bacteria and bacterial translocation stemming from gut barrier damage. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, B.; Su, F.Y.; Zhang, C.D.; Guo, S.J. Histological study on the digestive system of Cristaria plicata (Leach). J. Anhui Agr. Sci. 2010, 38, 3496–3498. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brate, I.L.N.; Blazquez, M.; Brooks, S.J.; Thomas, K.V. Weathering impacts the uptake of polyethylene microparticles from toothpaste in Mediterranean mussels (M. galloprovincialis). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Ge, L.; Zhang, J.; Xue, J.; Gonzalez-Gil, G.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Li, Z. Systemic effects of nanoplastics on multi-organ at the environmentally relevant dose: The insights in physiological, histological, and oxidative damages. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, G.; Purvaja, R.; Anandavelu, I.; Robin, R.S.; Ramesh, R. Accumulation and ecotoxicological risk of weathered polyethylene (wPE) microplastics on green mussel (Perna viridis). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman Ringwood, A. Bivalves as biological sieves: Bioreactivity pathways of microplastics and nanoplastics. Biol. Bull. 2021, 241, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thubagere, A.; Reinhard, B.M. Nanoparticle-induced apoptosis propagates through hydrogen-peroxide-mediated bystander killing: Insights from a human intestinal epithelium in vitro model. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3611–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Homsi, M.; Ducroc, R.; Claustre, J.; Jourdan, G.; Gertler, A.; Estienne, M.; Bado, A.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Plaisancie, P. Leptin modulates the expression of secreted and membrane-associated mucins in colonic epithelial cells by targeting PKC, PI3K, and MAPK pathways. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 293, G365–G373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Feng, C.; Pang, W.; Tian, C.; Zhao, Y. Nanoplastic-Induced Genotoxicity and Intestinal Damage in Freshwater Benthic Clams (Corbicula fluminea): Comparison with Microplastics. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 9469–9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Cai, Y.; Kong, L.; Zhou, M.; Sun, D.; Guo, X.; Li, W.; Mai, Y.; Wang, X. Effects of polystyrene nanoplastics on the amino acid composition of Asian Clam (Corbicula fluminea). LWT 2024, 198, 115998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Zuo, J.; Pan, M.; Nie, H.; Shen, J.; Yang, Q.; Hung, T.C.; Li, G. The presence of polystyrene nanoplastics enhances the MCLR uptake in zebrafish leading to the exacerbation of oxidative liver damage. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Ren, J.; Liu, J. Effects of benzo(k)fluoranthene exposure on the biomarkers of scallop Chlamys farreri. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 141, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; He, T.; Farrar, S.; Ji, L.; Liu, T.; Ma, X. Antioxidants maintain cellular redox homeostasis by elimination of reactive oxygen species. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 532–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridovich, I. Superoxide dismutases: An adaptation to a paramagnetic gas. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 7761–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, D.; Huang, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y. Effects of nanoplastics on antioxidant and immune enzyme activities and related gene expression in juvenile Macrobrachium nipponense. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhong, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Gu, H.; Huang, W.; Fang, J.K.; Shi, H.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y. Physiological effects of plastic particles on mussels are mediated by food presence. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasuri, K.; Zhang, L.; Keller, J.N. Oxidative stress, neurodegeneration, and the balance of protein degradation and protein synthesis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedier, S.; Yalcinkaya, S.K.; Bostanci, D. Exposure to polypropylene microplastics via diet and water induces oxidative stress in Cyprinus carpio. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 259, 106540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaei, M.; Forouzanfar, M.; Jafarinia, M. Toxic effects of polyethylene microplastics on transcriptional changes, biochemical response, and oxidative stress in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 261, 109423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, W.G.; Bringolf, R.B.; Buchwalter, D.B.; Newton, T.J.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Wang, N.; Augspurger, T.; Dwyer, F.J.; Barnhart, M.C.; Neves, R.J.; et al. Differential exposure, duration, and sensitivity of unionoidean bivalve life stages to environmental contaminants. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2008, 27, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Hardesty, D.K.; Ivey, C.D.; Kunz, J.L.; May, T.W.; Dwyer, F.J.; Roberts, A.D.; Augspurger, T.; Kane, C.M. Acute toxicity of copper, ammonia, and chlorine to glochidia and juveniles of freshwater mussels (Unionidae). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 2036–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, I.M.; Frederich, M.; Bagwe, R.; Lannig, G.; Sukhotin, A.A. Energy homeostasis as an integrative tool for assessing limits of environmental stress tolerance in aquatic invertebrates. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 79, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, J.; Melzner, F. Moderate seawater acidification does not elicit long-term metabolic depression in the blue mussel Mytilus edulis. Mar. Biol. 2010, 157, 2667–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosloo, D.; Vosloo, A. Response of cold-acclimated, farmed South African abalone (Haliotis midae) to short-term and long-term changes in temperature. J. Therm. Biol. 2010, 35, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chackal, R.; Eng, T.; Rodrigues, E.M.; Matthews, S.; Page-Lariviere, F.; Avery-Gomm, S.; Xu, E.G.; Tufenkji, N.; Hemmer, E.; Mennigen, J.A. Metabolic Consequences of Developmental Exposure to Polystyrene Nanoplastics, the Flame Retardant BDE-47 and Their Combination in Zebrafish. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 822111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajmalnik-Brown, R.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Kang, D.W.; DiBaise, J.K. Effects of Gut Microbes on Nutrient Absorption and Energy Regulation. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2012, 27, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yan, L.; Junaid, M.; Chen, X.; Liao, H.; Gao, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Impacts of polystyrene nanoplastics at the environmentally relevant and sub-lethal concentrations on the oxidative stress, immune responses, and gut microbiota to grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, R.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wolosker, M.B.; Zhu, Q.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y. Accumulation of different shapes of microplastics initiates intestinal injury and gut microbiota dysbiosis in the gut of zebrafish. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Chen, H.; He, S.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Yao, G.; Huang, Y.; Chen, R.; Xie, L.; et al. Subchronic toxicity of dietary sulfamethazine and nanoplastics in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma): Insights from the gut microbiota and intestinal oxidative status. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 226, 112820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koliada, A.; Syzenko, G.; Moseiko, V.; Budovska, L.; Puchkov, K.; Perederiy, V.; Gavalko, Y.; Dorofeyev, A.; Romanenko, M.; Tkach, S.; et al. Association between body mass index and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in an adult Ukrainian population. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The firmicutes/bacteroidetes ratio: A relevant marker of gut dysbiosis in obese patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, L.; Sokolova, I.; Shang, Y.; Huang, W.; Khor, W.; Fang, J.K.H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M. Effects of elevated temperature and different crystal structures of TiO2 nanoparticles on the gut microbiota of mussel Mytilus coruscus. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 199, 115979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Item | MDA | SOD | TP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | F | p | F | p | |
| age | 2.666 | 0.109 | 31.000 | <0.001 | 26.719 | <0.001 |
| concentration | 11.877 | <0.001 | 5.051 | 0.004 | 0.905 | 0.446 |
| duration | 27.086 | <0.001 | 37.708 | <0.001 | 1.877 | 0.164 |
| age × concentration | 1.026 | 0.389 | 8.252 | <0.001 | 4.541 | 0.012 |
| age × duration | 8.123 | 0.001 | 61.866 | <0.001 | 1.689 | 0.196 |
| concentration × duration | 3.914 | 0.003 | 21.267 | <0.001 | 4.418 | 0.007 |
| age × duration × concentration | 2.016 | 0.082 | 13.754 | <0.001 | 4.773 | 0.007 |
| Item | RR | AER | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | F | p | |
| age | 592.723 | <0.001 | 132.785 | <0.001 |
| concentration | 5.371 | 0.006 | 1.17 | 0.331 |
| duration | 27.696 | <0.001 | 1.249 | 0.296 |
| age × concentration | 1.977 | 0.144 | 1.782 | 0.163 |
| age × duration | 21.076 | <0.001 | 5.148 | 0.009 |
| concentration × duration | 0.982 | 0.459 | 0.323 | 0.922 |
| age × duration × concentration | 2.045 | 0.099 | 0.898 | 0.504 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Wan, L.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, H.; Liao, M.; Cuthbert, R.N. Nanoplastics Elicit Stage-Specific Physiological, Biochemical, and Gut Microbiome Responses in a Freshwater Mussel. Toxics 2025, 13, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050374
Chi Y, Zhang H, Gao J, Wan L, Jiao Y, Wang H, Liao M, Cuthbert RN. Nanoplastics Elicit Stage-Specific Physiological, Biochemical, and Gut Microbiome Responses in a Freshwater Mussel. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050374
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Yangli, Hui Zhang, Jian Gao, Liang Wan, Yiying Jiao, Heyun Wang, Mingjun Liao, and Ross N. Cuthbert. 2025. "Nanoplastics Elicit Stage-Specific Physiological, Biochemical, and Gut Microbiome Responses in a Freshwater Mussel" Toxics 13, no. 5: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050374
APA StyleChi, Y., Zhang, H., Gao, J., Wan, L., Jiao, Y., Wang, H., Liao, M., & Cuthbert, R. N. (2025). Nanoplastics Elicit Stage-Specific Physiological, Biochemical, and Gut Microbiome Responses in a Freshwater Mussel. Toxics, 13(5), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050374






