Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Aggravated the Developmental Neurotoxicity of Ammonia Nitrogen on Zebrafish Embryos
Highlights
- n-TiO₂ acts as a carrier, significantly enhancing the bioaccumulation of total ammonia nitrogen in zebrafish larvae.
- Co-exposure to n-TiO₂ and TAN exacerbates neurodevelopmental toxicity, leading to severe locomotor deficiencies.
- Aggravated neurotoxicity is driven by multi-mechanistic synergy involving oxidative stress, neuronal apoptosis, and the disruption of cholinergic and dopaminergic systems.
- This work underscores the potential neurotoxic threat posed by complex pollutant interactions in aquatic ecosystems.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Characterization of n-TiO2 Suspension
2.3. Exposure of Embryos
2.4. TAN Levels in Zebrafish Larvae
2.5. Detection of Locomotor Behaviour in Zebrafish Larvae
2.6. Oxidative Stress Analysis
2.7. Acridine Orange (AO) Staining
2.8. Detection of Caspase Enzyme Activity
2.9. Detection of Dopamine Levels
2.10. Determination of AChE Activity
2.11. Gene Expression
2.12. Transcriptomics Sequencing
2.13. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
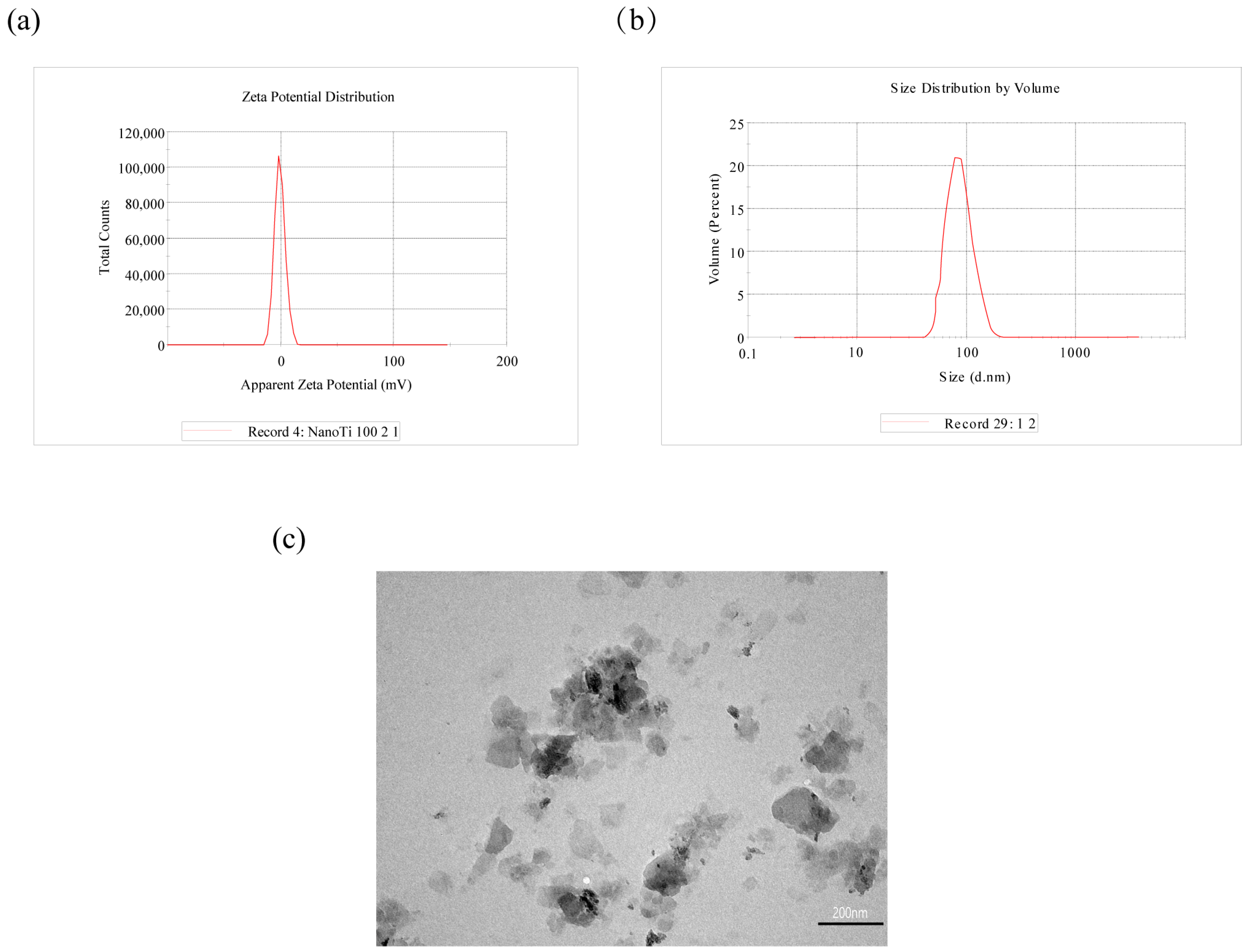
3.1. n-TiO2 Characterisation
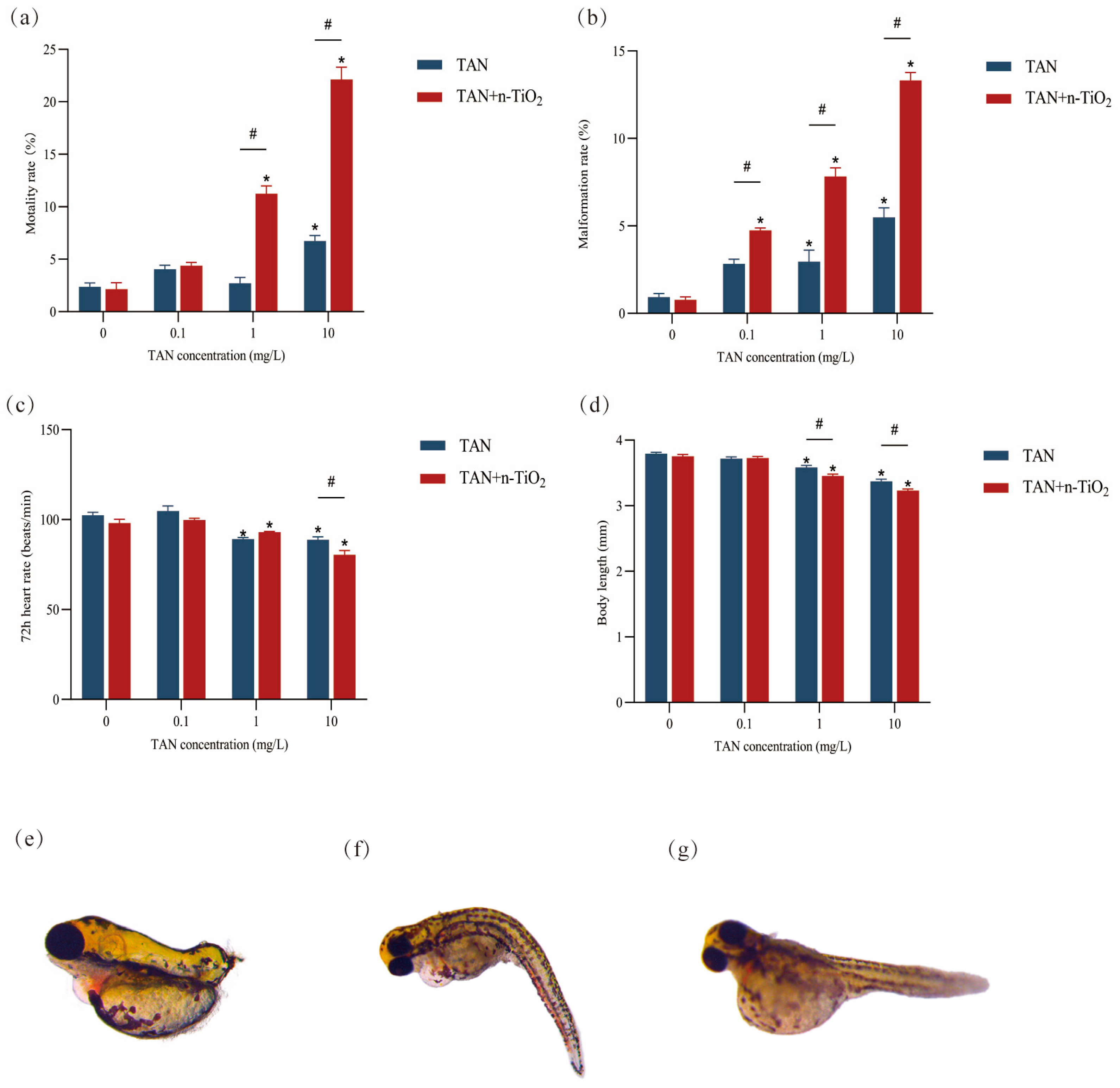
3.2. Developmental Toxicity
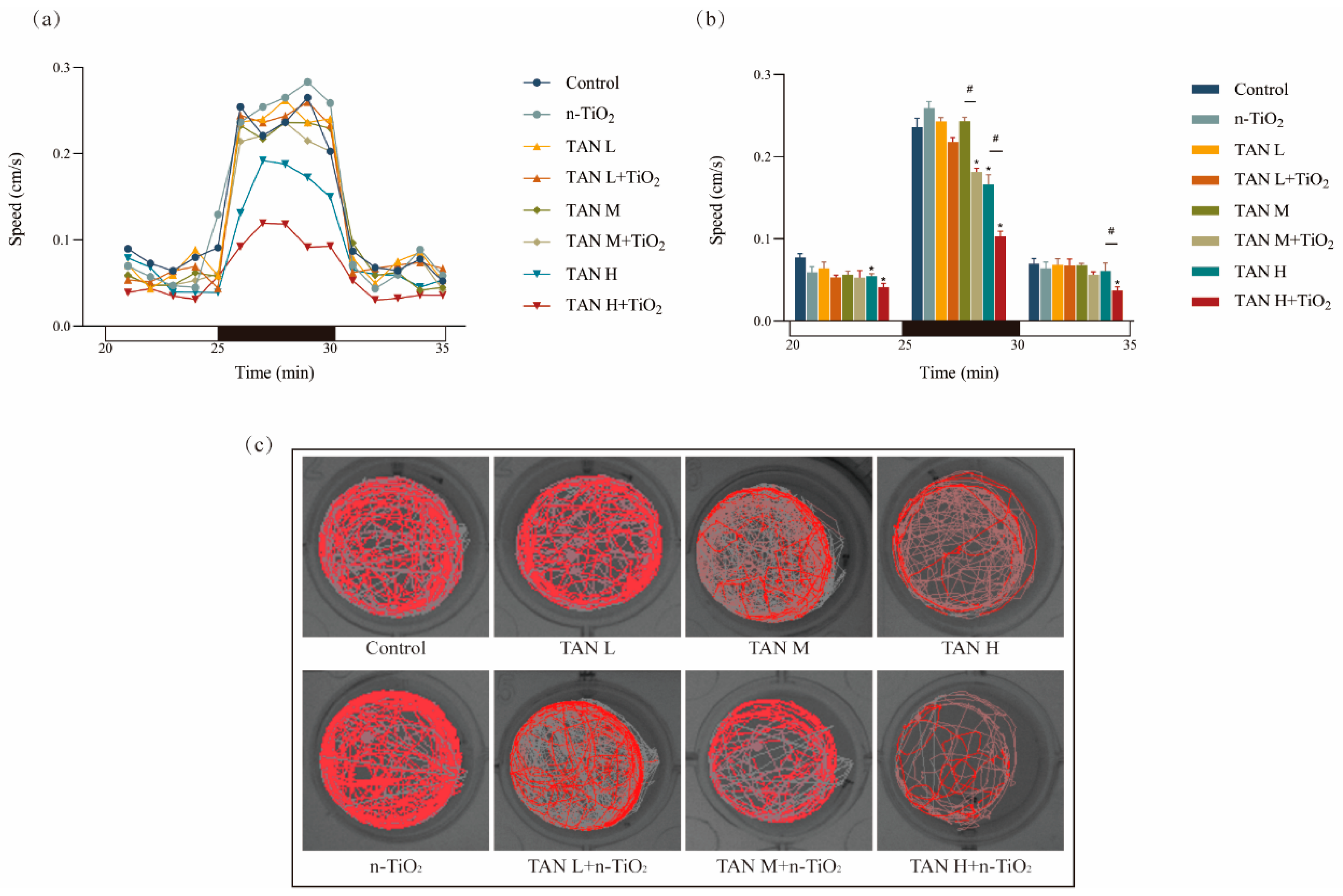
3.3. Behavioural Detection
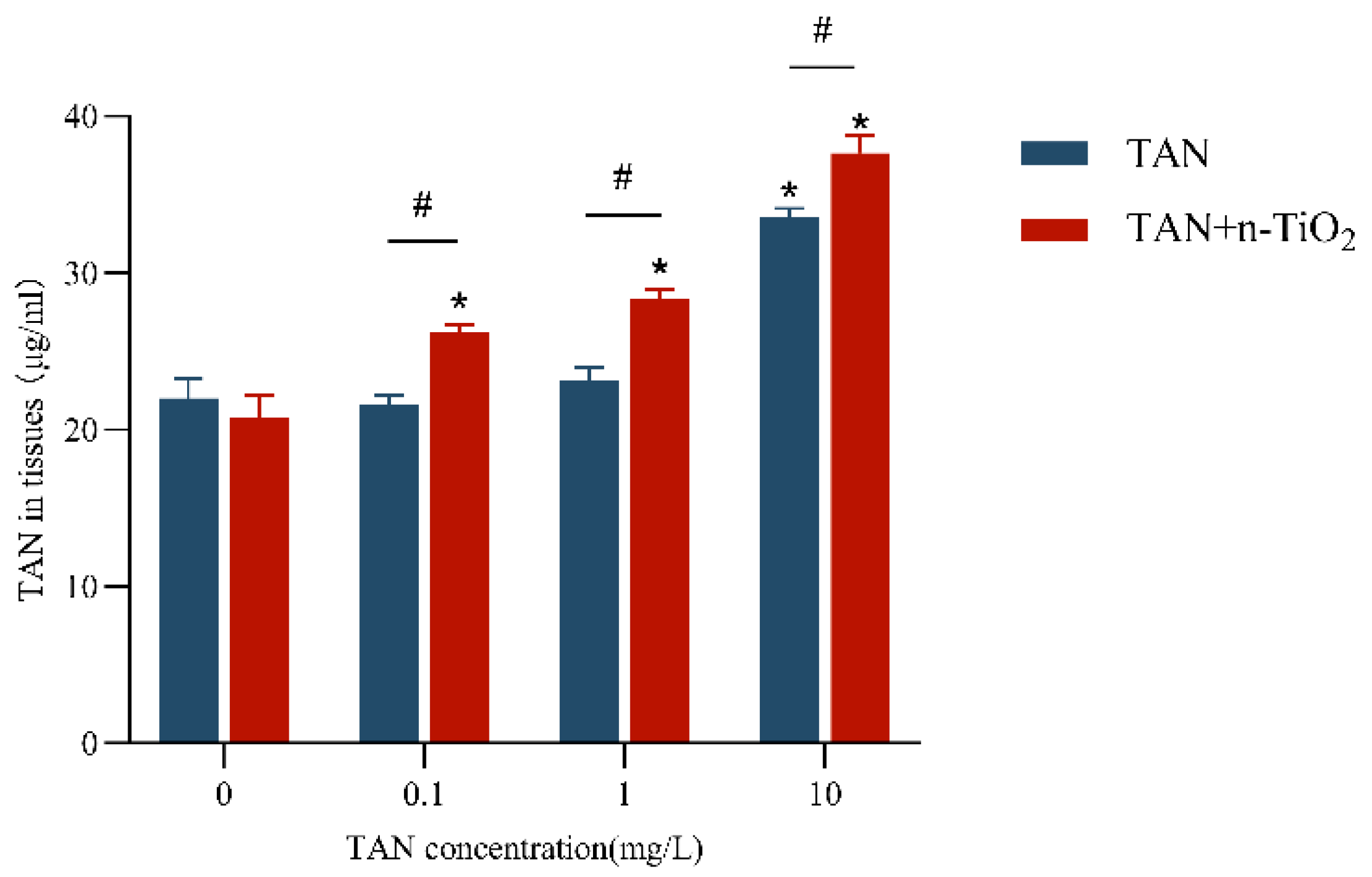
3.4. TAN Content in Zebrafish Larvae
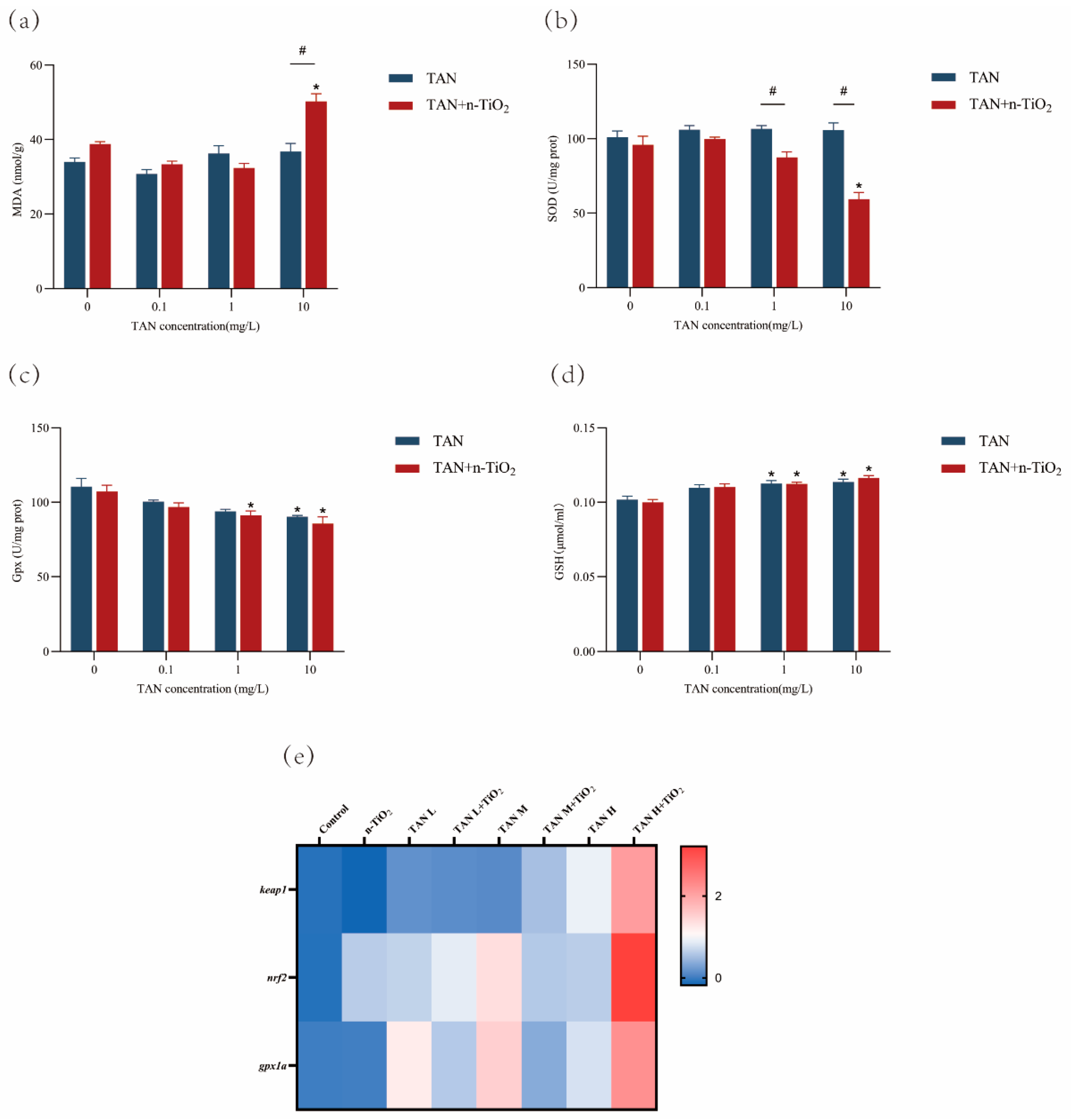
3.5. Measurement of Oxidative Stress
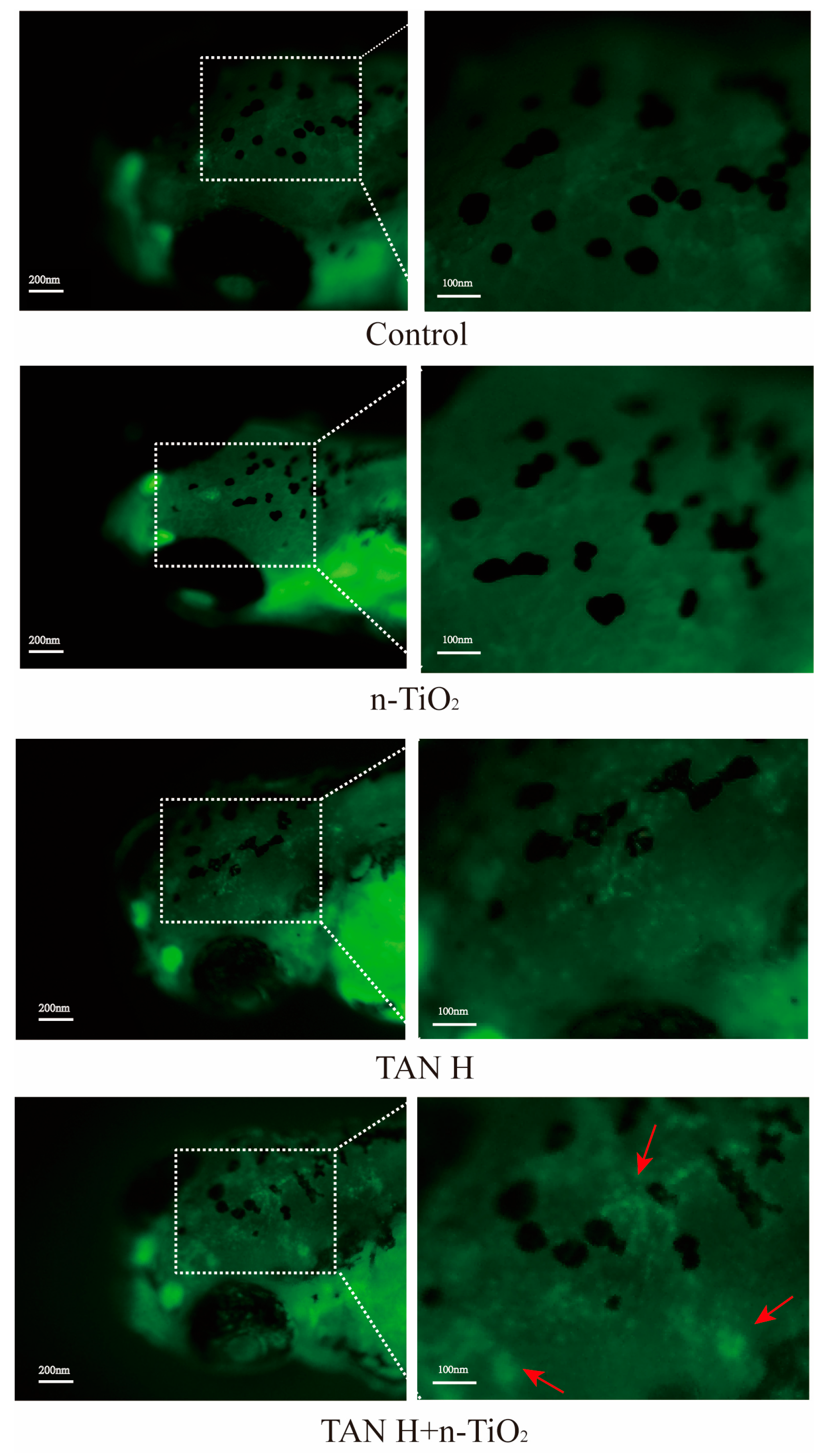
3.6. AO Staining
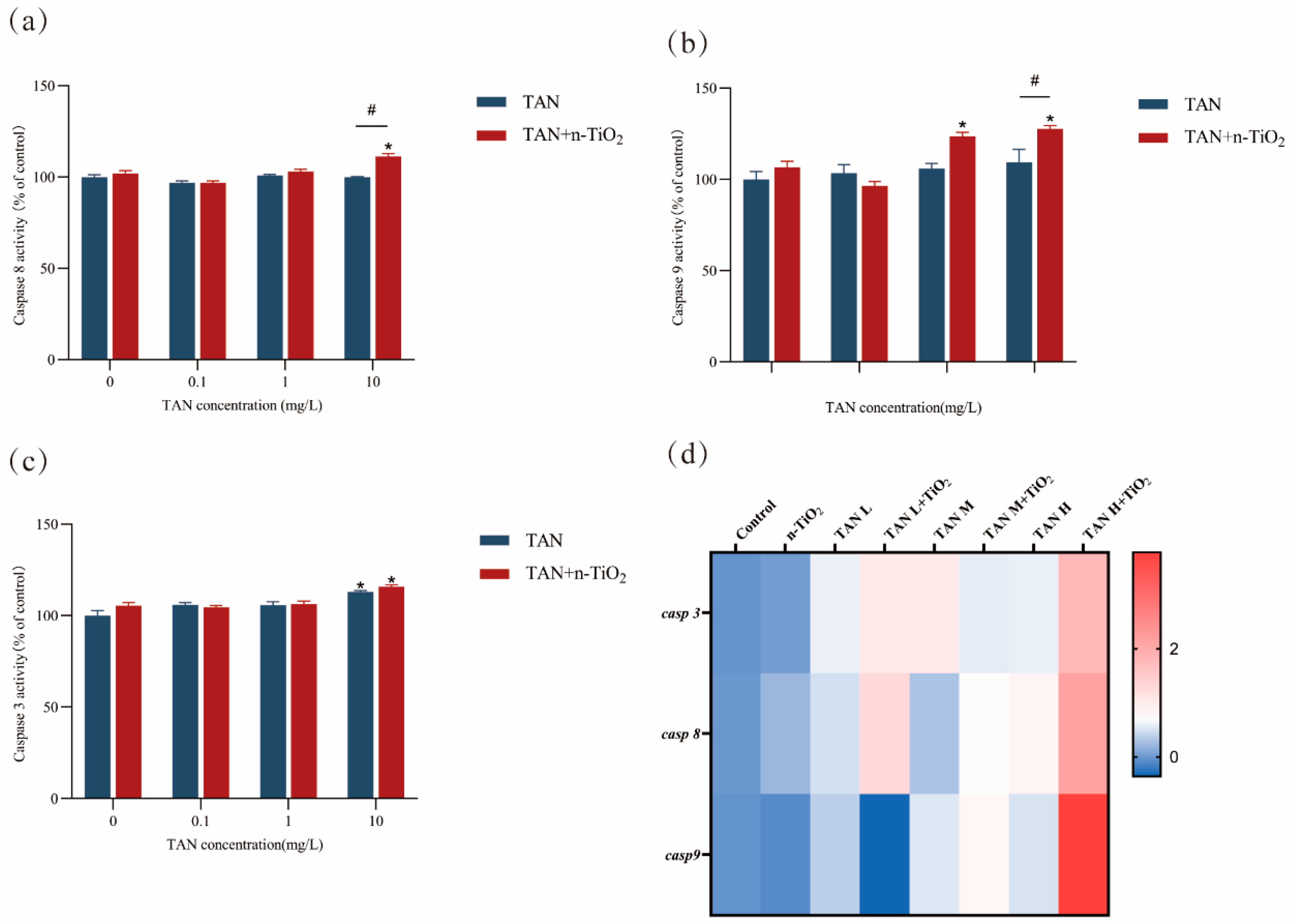
3.7. Result of Caspase Enzyme Activity
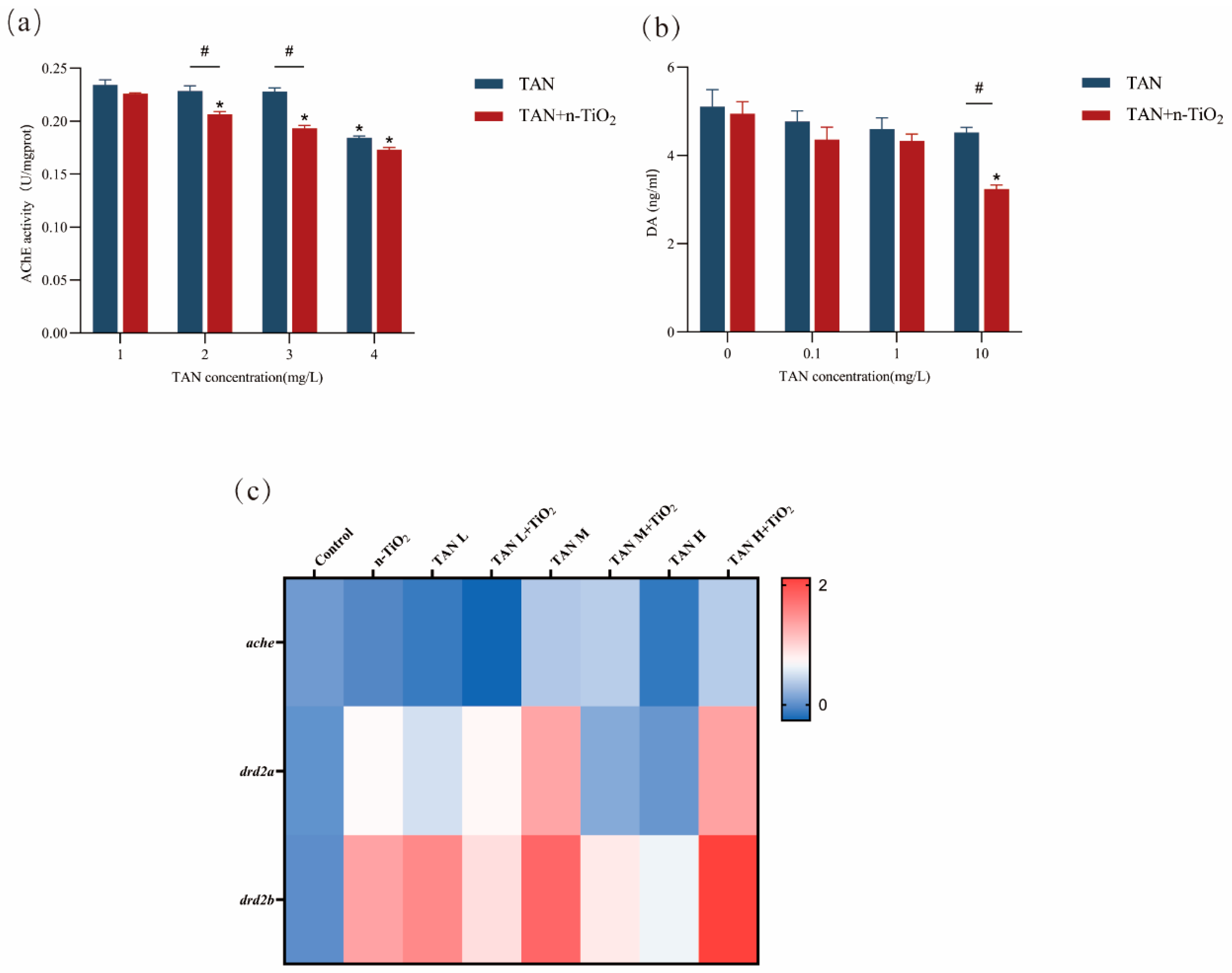
3.8. Determination of AChE Activity and DA Content
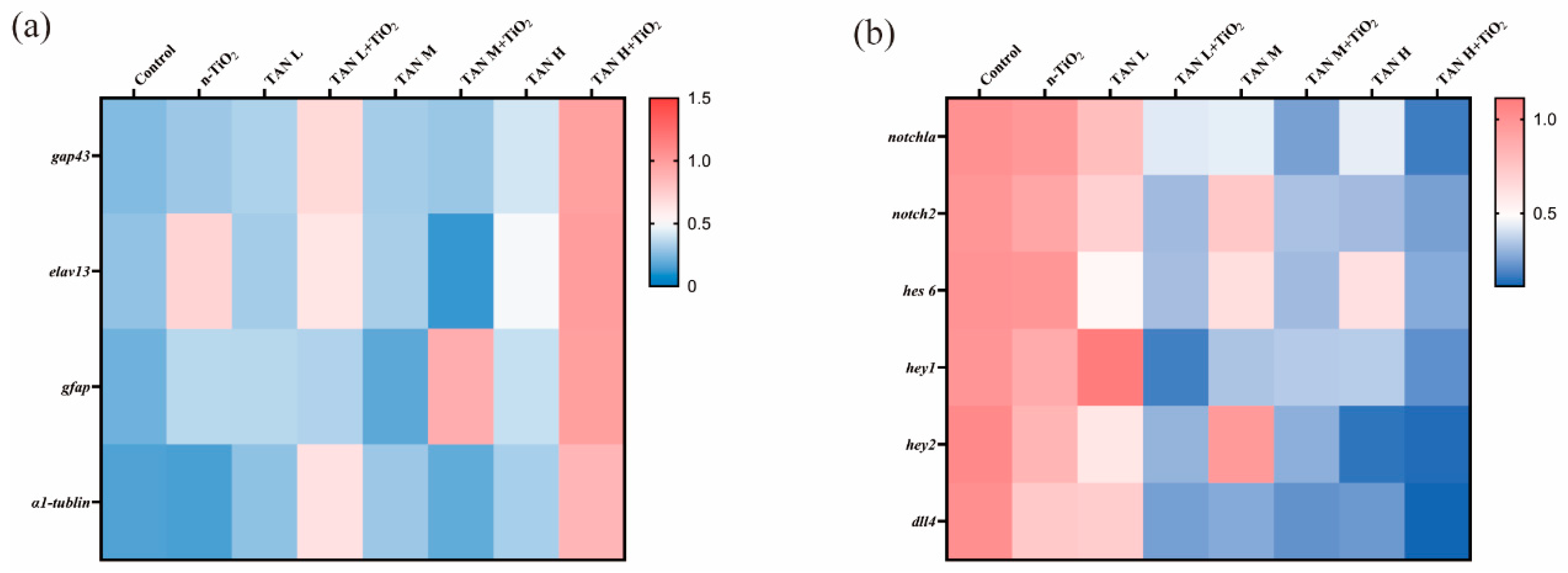
3.9. Result of Gene Expression
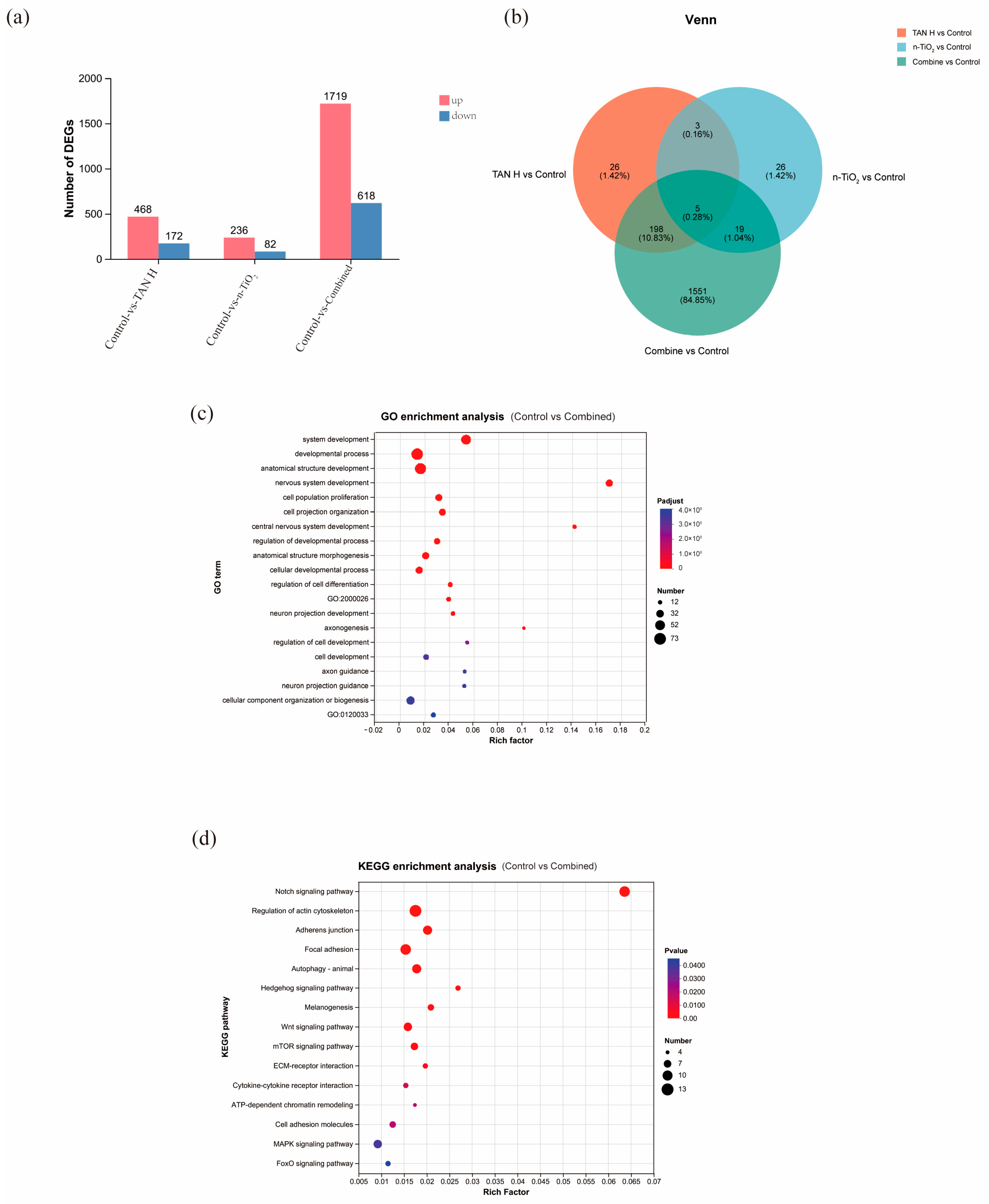
3.10. Transcriptomic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, C.H.; Ma, H.L.; Su, Y.L.; Deng, Y.Q.; Feng, J.; Xie, J.W.; Chen, X.L.; Guo, Z.X. Ammonia toxicity in the mud crab (Scylla paramamosain): The mechanistic insight from physiology to transcriptome analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 179, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snelder, T.H.; Whitehead, A.L.; Fraser, C.; Larned, S.T.; Schallenberg, M. Nitrogen loads to New Zealand aquatic receiving environments: Comparison with regulatory criteria. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2020, 54, 527–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, M.; Wu, H.; Yang, H.; Zhao, J.; Lv, J. Gill damage and neurotoxicity of ammonia nitrogen on the clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Ecotoxicology 2017, 26, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.D.; Chen, Q.; Ding, D.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, W.; Xia, F.; Li, M.; Jing Wei Chen, Y.; Deng, S. Derivation of human health and odor risk control values for soil ammonia nitrogen by incorporating solid-liquid partitioning, ammonium/ammonia equilibrium: A case study of a retired nitrogen fertilizer site in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 273, 116133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Cai, T.; Klümper, U.; Luo, L.; Zhu, Y.; He, Y. Novel multi-drug-resistant yeast efficiently removed ammonia nitrogen from antibiotic-contaminated aquaculture water. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2025, 203, 106111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.N.; Chen, J.; Cui, L.; Li, W.; Gao, X.Y.; Liu, Z.T. Water quality criteria of total ammonia nitrogen (TAN) and un-ionized ammonia (NH3-N) and their ecological risk in the Liao River, China. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, D.J.; Tsui, T.K.N. Ammonia toxicity in fish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 45, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Ouyang, K.; Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Li, L. The impact of ammonia and microcystin-LR on neurobehavior and glutamate/gamma-aminobutyric acid balance in female zebrafish (Danio rerio): ROS and inflammation as key pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 920, 170914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.Y.; Horng, J.L.; Cheng, C.A.; Chang, C.Y.; Cherng, B.W.; Liu, S.T.; Chou, M.Y. Sublethal ammonia induces alterations of emotions, cognition, and social behaviors in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 244, 114058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandoliya, R.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, V.; Joshi, R.; Sivanesan, I. Titanium dioxide nanoparticle: A comprehensive review on synthesis, applications and toxicity. Plants 2024, 13, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, M.; Wang, B. Health effects of exposure to nano-TiO2: A meta-analysis of experimental studies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, M.Q.; Wang, Z.Y.; Cao, X.S.; Xing, B.S. Engineered nanomaterials in the environment: Are they safe? Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 1443–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, F.; Sonderer, T.; Scholz, R.W.; Nowack, B. Modeled environmental concentrations of engineered nanomaterials (TiO2, ZnO, Ag, CNT, Fullerenes) for different regions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9216–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.W.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, P.; Li, W.W.; Wang, J.X.; Huang, C.J.; Wang, X.F.; Lin, K.F.; Zhou, B.S. Bioconcentration and metabolism of BDE-209 in the presence oftitanium dioxidenanoparticles and impact on the thyroid endocrine system and neuronal developmentin zebrafish larvae. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakir, M.; Abad-Alvaro, I.; Laborda, F.; Slaveykova, V.I. Comparative assessment of uptake and effects of TiO2 and CeO2 nanoparticles in Algae using advanced single-entity analytical techniques. Aquat. Toxicol. 2025, 286, 107430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Yan, W.; Liu, C.; Hung, T.C.; Li, G.Y. Co-exposure with titanium dioxide nanoparticles exacerbates MCLR-induced brain injury in zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Dai, L.; Liu, C.; Sun, Q.; Yu, L. Nano-TiO2 aggravates bioaccumulation and developmental neurotoxicity of triphenyl phosphate in zebrafish larvae. Chemosphere 2022, 287 Pt 3, 132161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, M.; Navas, J.M.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Barata, C. Oxidative stress effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticle aggregates in zebrafish embryos. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihtisham, M.; Noori, A.; Yadav, S.; Sarraf, M.; Kumari, P.; Brestic, M.; Imran, M.; Jiang, F.; Yan, X.; Rastogi, A. Silver nanoparticle’s toxicological effects and phytoremediation. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, U.D.; Srinivasan, M.R. Zebrafish: An Animal Model in Biomedical Research. In Animal Models in Research; Vijayakumar Sreelatha, H., Patel, S., Nagarajan, P., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.M.; Liu, J.H.; Shu, L.H.; Chen, C.H. Anti-oxidative responses of zebrafish (Danio rerio) gill, liver and brain tissues upon acute cold shock. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 187, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmeester, H.; Hollman, P.C.H.; Peters, R.J.B. Potential Health Impact of Environmentally Released Micro- and Nanoplastics in the Human Food Production Chain: Experiences from Nanotoxicology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8932–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.A.; Kozal, J.S.; Jayasundara, N.; Massarsky, A.; Trevisan, R.; Geitner, N.; Wiesner, M.; Levin, E.D.; Di Giulio, R.T. Uptake, tissue distribution, and toxicity of polystyrene nanoparticles in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 194, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouke, K.E.; He, Z.; Loring, M.D.; Naumann, E.A. Neural circuits underlying divergent visuomotor strategies of zebrafish and Danionella cerebrum. Curr. Biol. 2025, 35, 2457–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Ge, F.; Han, Z.; Li, J. Analysis of behavior trajectory based on deep learning in ammonia environment for fish. Sensors 2020, 20, 4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, D.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, H.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Jia, J.; Liu, H.; Luan, N.; Liu, X. Polystyrene nanomicroplastics aggravate ammonia-induced neurotoxic effects in zebrafish embryos. Toxics 2024, 12, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, J.K.; Trangadia, B.J.; Patel, U.D.; Patel, H.B.; Kalaria, V.A.; Kathiriya, J.B. Neurotoxicity of 4-nonylphenol in adult zebrafish: Evaluation of behaviour, oxidative stress parameters and histopathology of brain. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.N.; Ma, J.S.; Qi, Q.; Xu, M.J.; Xu, R.Y. Effects of ammonia exposure on anxiety behavior, oxidative stress and inflammation in guppy (Poecilia reticulate). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 265, 109539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gubory, K.H. Environmental pollutants and lifestyle factors induce oxidative stress and poor prenatal development. Reprod. BioMed. Online 2014, 29, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggins, J.N.; Pratt, D.A.; Voehler, M.; Daniels, J.S.; Marnett, L.J. Kinetics and mechanism of the General-Acid-Catalyzed Ring-Closure of the Malondialdehyde-DNA Adduct, N2-(3-Oxo-1-propenyl)deoxyguanosine (N2OPdG-), to 3-(2’-Deoxy-β-d-erythro-pentofuranosyl)pyrimido[1,2-α]purin-10(3H)-one (M1dG). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10571–10581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.A.; López-Sánchez, R.C.; Rendón-Ramírez, A. Lipids and Oxidative Stress Associated with Ethanol-Induced Neurological Damage. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 1543809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohé, L.; Toppo, S.; Orian, L. The glutathione peroxidase family: Discoveries and mechanism. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 187, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Pop, A. The role of antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajadimajd, S.; Khazaei, M. Oxidative Stress and Cancer: The Role of Nrf2. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2018, 18, 538–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyimah, E.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, M.; Xu, H.; Mensah, J.K.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gyimah, G.N.W. Oxidative stress and apoptosis in Bisphenol AF-induced neurotoxicity in zebrafish embryos. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 2273–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, S. Apoptosis and clearance of apoptotic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 489–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.H.; Yang, F.F.; Ling, R.Z.; Liao, S.A.; Miao, Y.T.; Ye, C.X.; Wang, A.L. Effects of ammonia exposure on apoptosis, oxidative stress and immune response in pufferfish (Takifugu obscurus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 164, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brentnall, M.; Rodriguez-Menocal, L.; De Guevara, R.L.; Cepero, E.; Boise, L.H. Caspase9, Caspase 3 and Caspase 7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.Y.; Cheng, C.A.; Liu, S.T.; Horng, J.L. Investigation of ammonia-induced lethal toxicity toward ion regulation in zebrafish embryos. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 276, 109807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behra, M.; Cousin, X.; Bertrand, C.; Vonesch, J.L.; Biellmann, D.; Chatonnet, A.; Strähle, U. Acetylcholinesterase is required for neuronal and muscular development in the zebrafish embryo. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyano, P.; Flores, A.; García, J.; García, J.M.; Anadon, M.J.; Frejo, M.T.; Sola, E.; Pelayo, A.; Del Pino, J. Bisphenol A single and repeated treatment increases HDAC2, leading to cholinergic neurotransmission dysfunction and SN56 cholinergic apoptotic cell death through AChE variants overexpression and NGF/TrkA/P75NTR signaling disruption. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 157, 112614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaasinen, V.; Vahlberg, T.; Stoessl, A.J.; Strafella, A.P.; Antonini, A. Dopamine Receptors in Parkinson’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Imaging Studies. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradner, J.M.; Suragh, T.A.; Wilson, W.W.; Lazo, C.R.; Stout, K.A.; Kim, H.M.; Wang, M.Z.; Walker, D.I.; Pennell, K.D.; Richardson, J.R.; et al. Exposure to the polybrominated diphenyl ether mixture DE-71 damages the nigrostriatal dopamine system: Role of dopamine handling in neurotoxicity. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 241, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, J. Dopamine: Opening the door of movement. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alm, H.; Kultima, K.; Scholz, B.; Nilsson, A.; Andrén, P.E.; Fex-Svenningsen, Å.; Dencker, L.; Stigson, M. Exposure to brominated flame retardant PBDE-99 affects cytoskeletal protein expression in the neonatal mouse cerebral cortex. NeuroToxicology 2008, 29, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udvadia, A.J.; Köster, R.W.; Skene, J.H.P. GAP-43 promoter elements in transgenic zebrafish reveal a difference in signals for axon growth during CNS development and regeneration. Development 2001, 128, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brösamle, C.; Halpern, M.E. Characterization of myelination in the developing zebrafish. Glia 2002, 39, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Shen, W.; Zhang, B.; Meng, A. The genetic program of oocytes can be modified in vivo in the zebrafish ovary. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 10, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; He, X.; Tian, C.; Meng, A. Two GC-rich boxes in huC promoter play distinct roles in controlling its neuronal specific expression in zebrafish embryos. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 342, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, M.; Messing, A. Regulation of GFAP Expression. ASN Neuro 2021, 13, 1759091420981206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tykhomyrov, A.A.; Pavlova, A.S.; Nedzvetsky, V.S. Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP): On the 45th Anniversary of Its Discovery. Neurophysiology 2016, 48, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dong, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Dechlorane Plus exposure on axonal growth, musculature and motor behavior in embryo-larval zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Jia, Y.; Dai, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Yu, L. Tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate disrupts axonal growth, cholinergic system and motor behavior in early life zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 192, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, Z.; Li, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, H. Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway is strongly implicated in cadmium-induced developmental neurotoxicity and neuroinflammation: Clues from zebrafish neurobehavior and in vivo neuroimaging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, I.; Keyser, C.; Zhang, Z.; Rosolia, B.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Zukin, R.S.; Yan, J. Epigenetic regulation of autophagy in neuroinflammation and synaptic plasticity. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1322842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.S.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, J.; Cha, G.-H.; Song, J.G. Autophagy Modulators and Neuroinflammation. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 955–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Fan, M.; Chu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Rahman, S.U.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, D.; Feng, S.; Li, Y.; et al. Deoxynivalenol induces toxicity and apoptosis in piglet hippocampal nerve cells via the MAPK signaling pathway. Toxicon 2018, 155, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Lin, W.; Long, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, K.; Chu, Q. Notch signaling pathway: Architecture, disease, and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2022, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebel, C.; Lendahl, U. Notch signaling in development, tissue homeostasis, and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 1235–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, F.; Wan, M.; Liu, J.; Huang, L.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Ding, X.; Liao, X.; et al. Pamiparib induces neurodevelopmental defects and cerebral haemorrhage in zebrafish embryos via inhibiting notch signalling. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 6652–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, M.; Yu, J.; Yang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Shi, F.; Zou, X.; Zha, J.; et al. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Aggravated the Developmental Neurotoxicity of Ammonia Nitrogen on Zebrafish Embryos. Toxics 2025, 13, 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121031
Lyu M, Yu J, Yang Q, Shen Y, Liu H, Wang X, Liu X, Shi F, Zou X, Zha J, et al. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Aggravated the Developmental Neurotoxicity of Ammonia Nitrogen on Zebrafish Embryos. Toxics. 2025; 13(12):1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121031
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Minglei, Jiaqian Yu, Qing Yang, Yi Shen, Haoling Liu, Xuanjie Wang, Xiaolin Liu, Fang Shi, Xi Zou, Jinmiao Zha, and et al. 2025. "Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Aggravated the Developmental Neurotoxicity of Ammonia Nitrogen on Zebrafish Embryos" Toxics 13, no. 12: 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121031
APA StyleLyu, M., Yu, J., Yang, Q., Shen, Y., Liu, H., Wang, X., Liu, X., Shi, F., Zou, X., Zha, J., Li, G., & Ma, X. (2025). Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Aggravated the Developmental Neurotoxicity of Ammonia Nitrogen on Zebrafish Embryos. Toxics, 13(12), 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121031




