Toxicological Evaluation and Antimicrobial Activity of a Natural Thymol–Eucalyptol-Based Mixture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Toxicity Assay
2.3.1. In Chicken
2.3.2. In Model Organisms Artemia salina
2.3.3. In Model Organisms Daphnia magna
2.4. Griess Assay
2.5. TBARS Assay
2.6. Antioxidative Assay
2.7. Biochemical Assay
2.8. Histopathological Study
2.9. Hematology Study
2.10. Hematology Study
2.11. Antimicrobial Activity In Vitro
- ISO 4833-2:2013 [44], Microbiology of the food chain — Horizontal method for the enumeration of microorganisms — Part 2: Colony count at 30 °C by the surface plating technique. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- ISO 16649-1: 2018 [44], Microbiology of the food chain — Horizontal method for the enumeration of beta-glucuronidase-positive Escherichia coli — Part 1: Colony-count technique at 44 °C using membranes and 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl beta-D-glucuronide. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- ISO 15213-2:2023 [44], Microbiology of the food chain — Horizontal method for the detection and enumeration of Clostridium spp. — Part 2: Enumeration of Clostridium perfringens by colony-count technique. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- ISO 6579-1: 2017 [44], Microbiology of the food chain — Horizontal method for the detection, enumeration and serotyping of Salmonella — Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- The results obtained were expressed in bacterial colony-forming units per gram (CFU g−1), and as percentages of reduction (%).
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
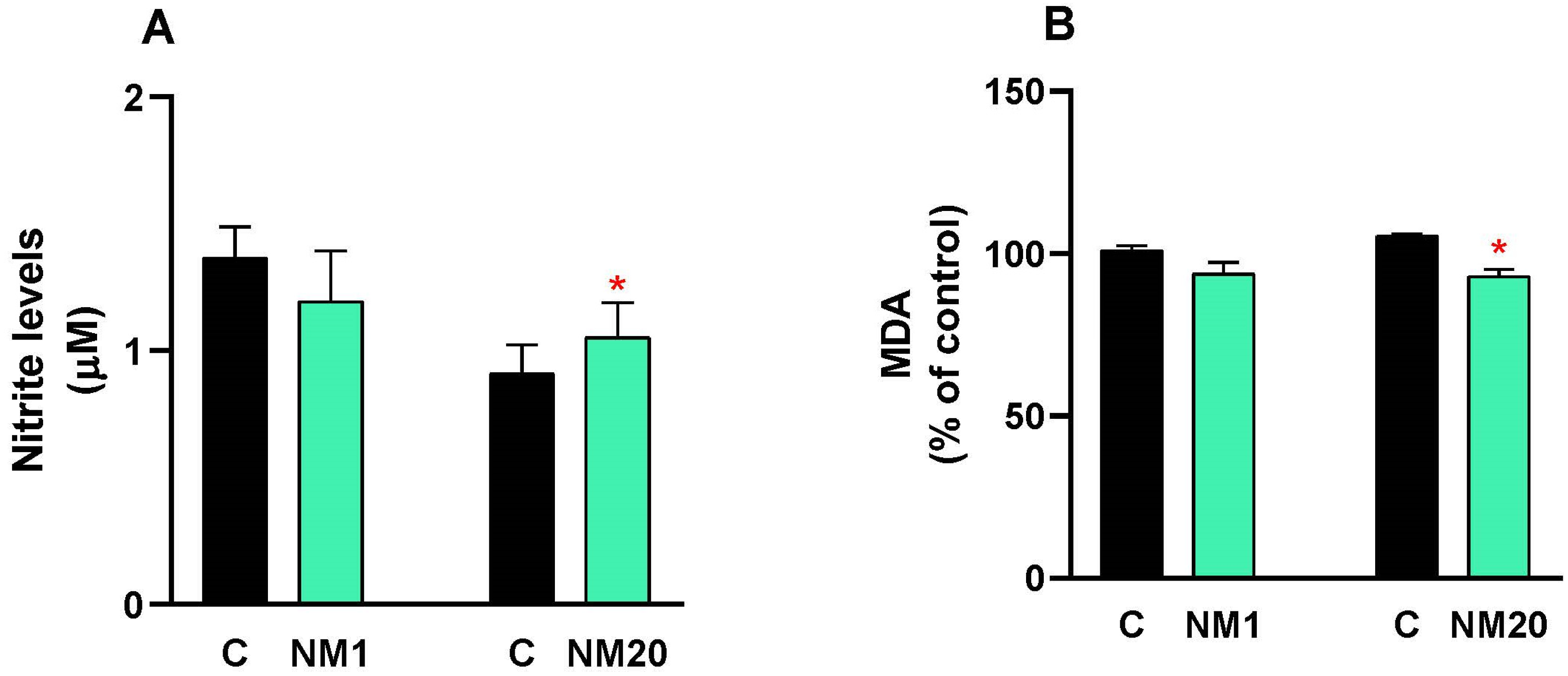
3.1. Oxidative Stress
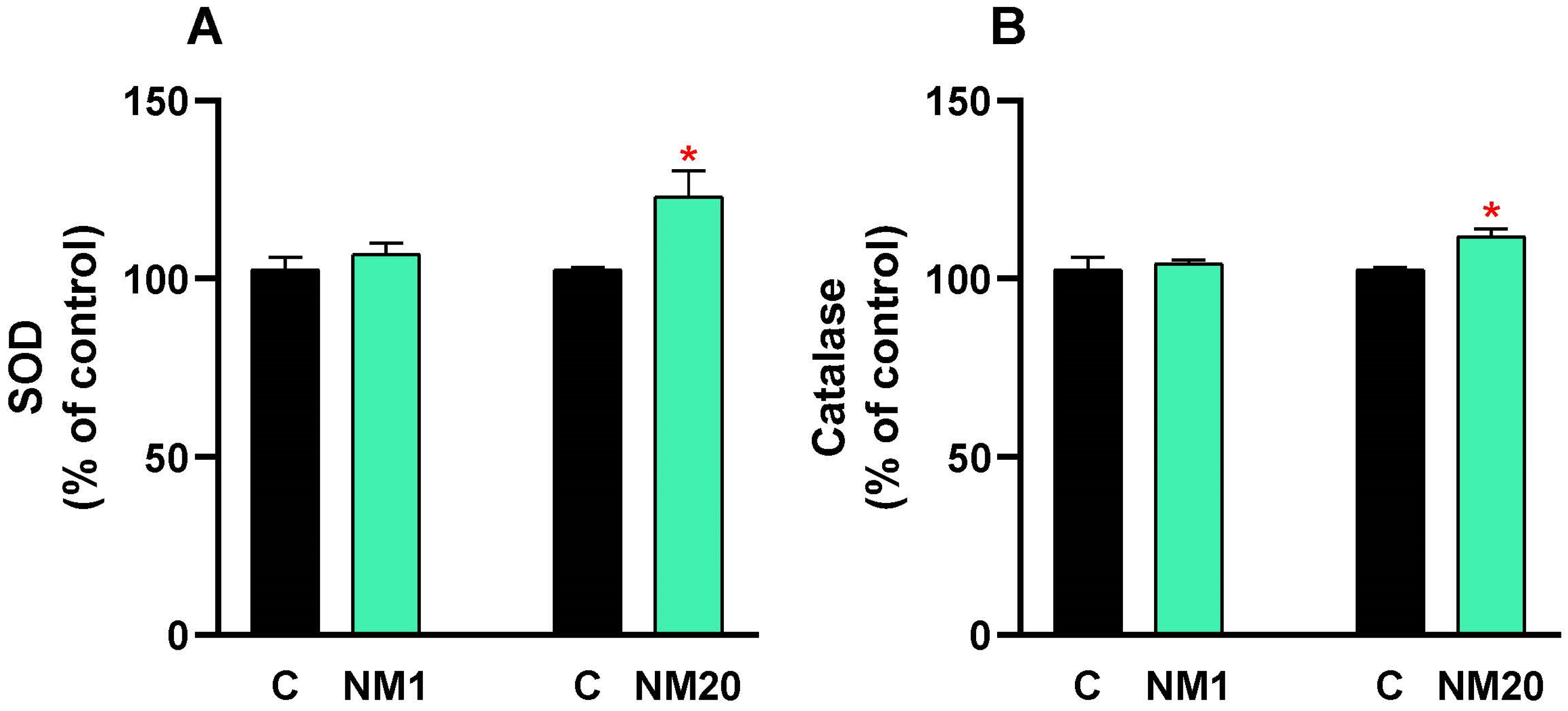
3.2. Antioxidative Assay
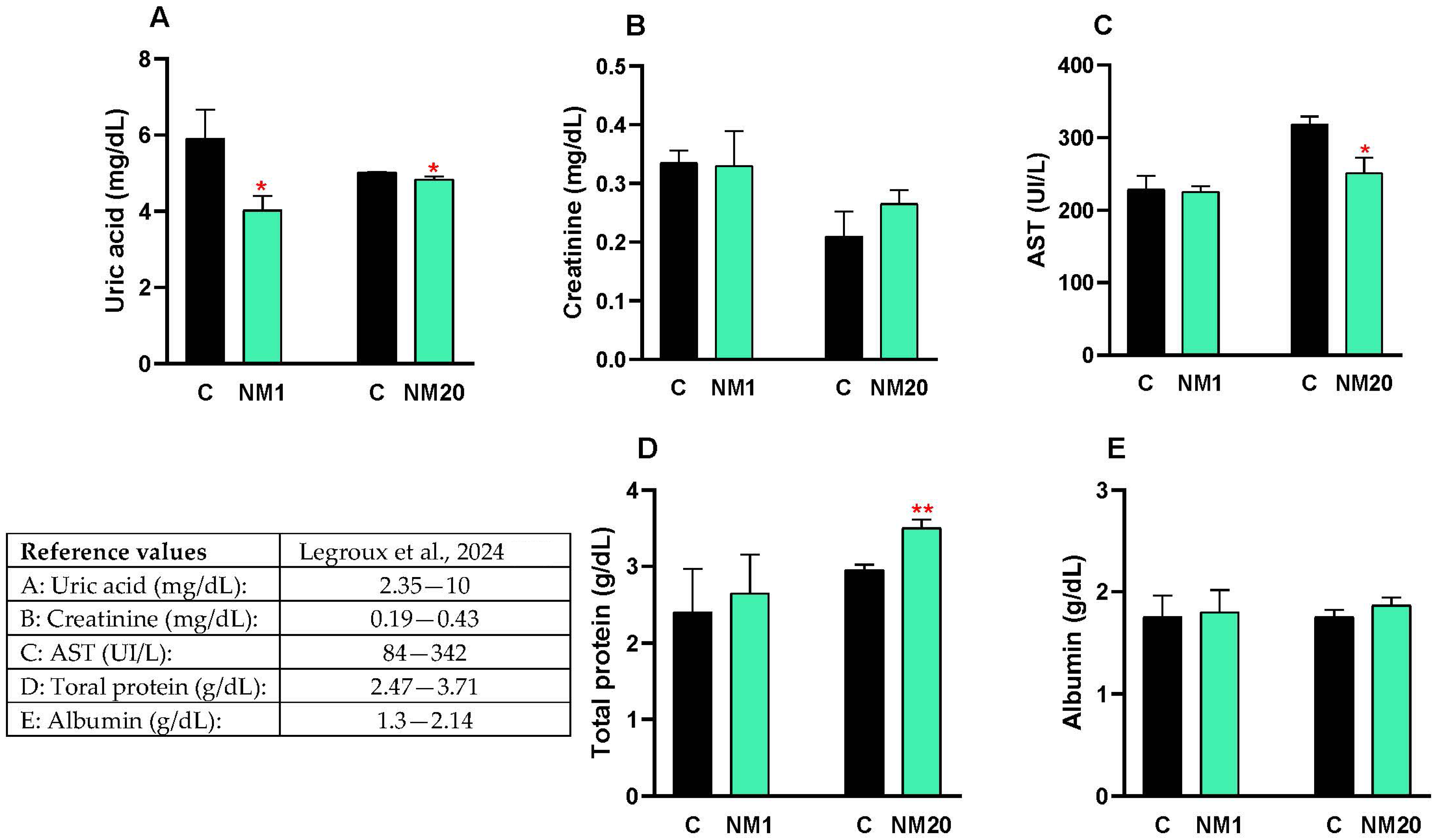
3.3. Biochemical Assay
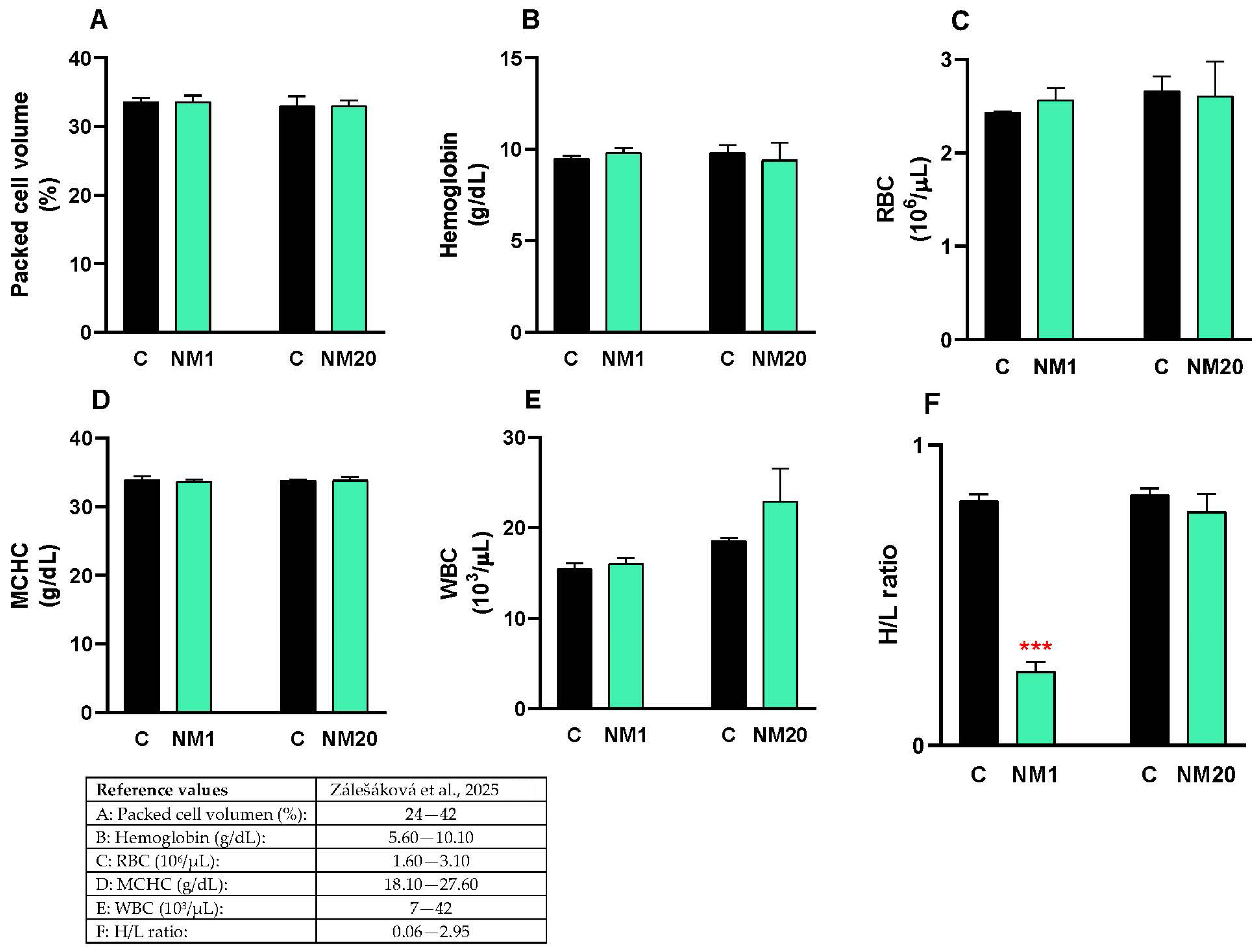
3.4. Hematology Study
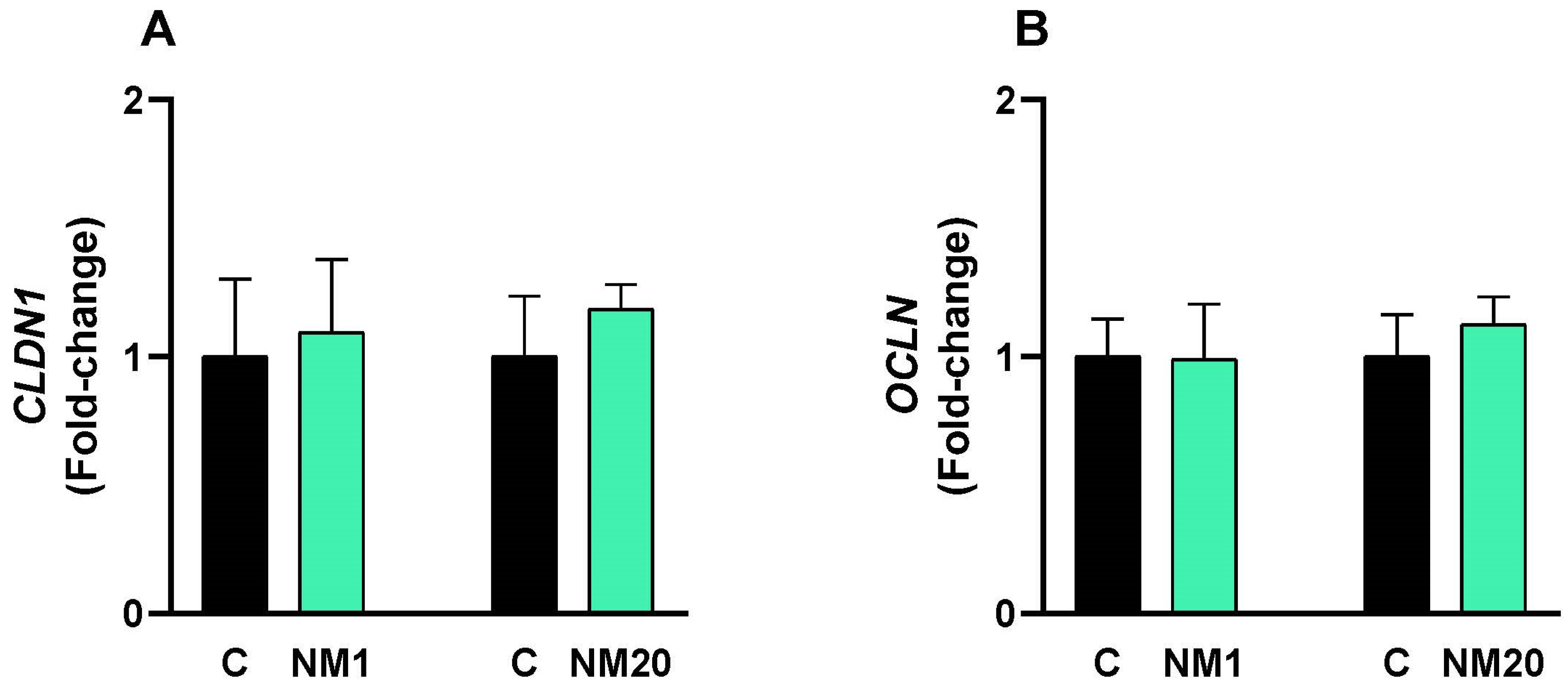
3.5. qPCR Assay
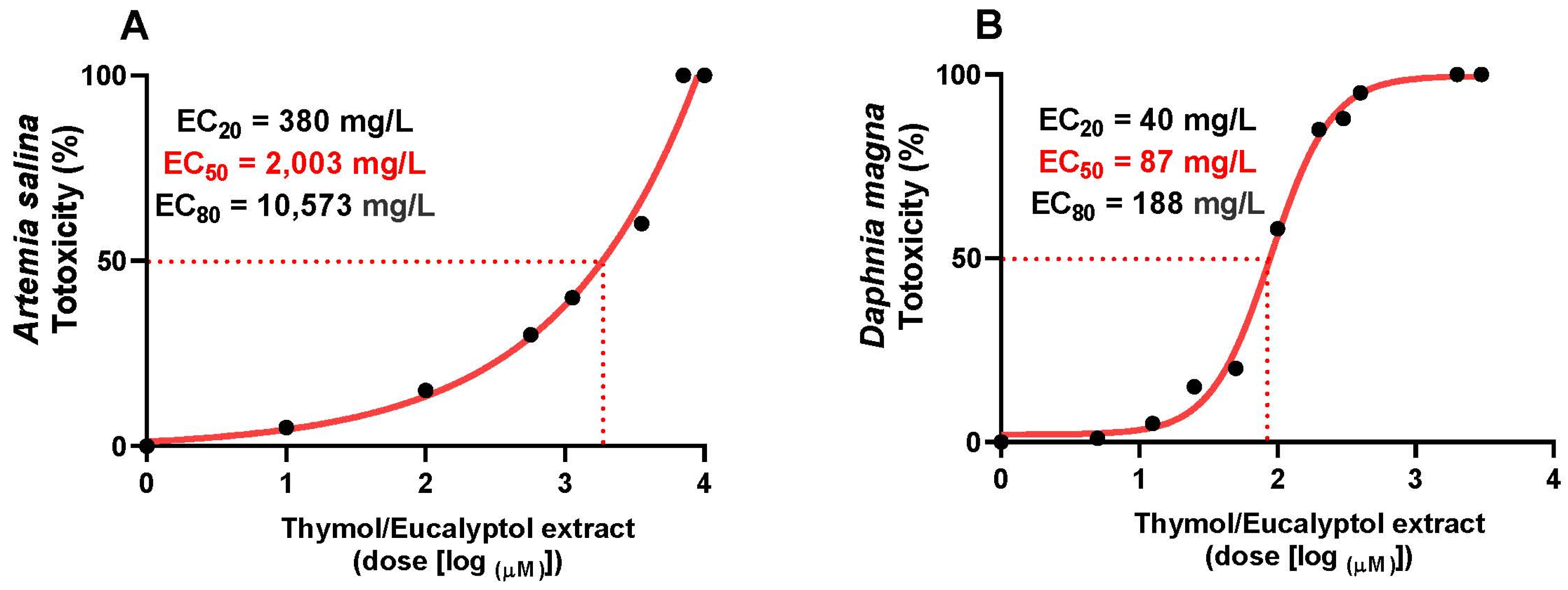
3.6. Toxicity Study in Artemia salina and Daphnia magna
3.7. Antimicrobial Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu-Wu, J.W.F.; Guadamuz-Mayorga, C.; Oviedo-Cerdas, D.; Zamora, W.J. Antibiotic Resistance and Food Safety: Perspectives on New Technologies and Molecules for Microbial Control in the Food Industry. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashempour-Baltork, F.; Hosseini, H.; Shojaee-Aliabadi, S.; Torbati, M.; Alizadeh, A.M.; Alizadeh, M. Drug Resistance and the Prevention Strategies in Food Borne Bacteria: An Update Review. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Tian, C.; Huang, Z.; Malakar, P.K.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, Y. Meta-Analysis for the Global Prevalence of Foodborne Pathogens Exhibiting Antibiotic Resistance and Biofilm Formation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 906490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karanth, S.; Feng, S.; Patra, D.; Pradhan, A.K. Linking Microbial Contamination to Food Spoilage and Food Waste: The Role of Smart Packaging, Spoilage Risk Assessments, and Date Labeling. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1198124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, N.; Waheed, A.; Motwani, S. Synthetic and Natural Antimicrobials as Control against Food Borne Pathogens: A Review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshome, E.; Forsido, S.F.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V.; Olika Keyata, E. Potentials of Natural Preservatives to Enhance Food Safety and Shelf Life: A Review. Sci. World J. 2022, 2022, 9901018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyldgaard, M.; Mygind, T.; Meyer, R.L. Essential Oils in Food Preservation: Mode of Action, Synergies, and Interactions with Food Matrix Components. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angane, M.; Swift, S.; Huang, K.; Butts, C.A.; Quek, S.Y. Essential Oils and Their Major Components: An Updated Review on Antimicrobial Activities, Mechanism of Action and Their Potential Application in the Food Industry. Foods 2022, 11, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, A.; Prasad, J.; Das, S.; Dwivedy, A.K. Essential Oils and Their Application in Food Safety. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 653420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagoor Meeran, M.F.; Javed, H.; Al Taee, H.; Azimullah, S.; Ojha, S.K. Pharmacological Properties and Molecular Mechanisms of Thymol: Prospects for Its Therapeutic Potential and Pharmaceutical Development. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouhan, S.; Sharma, K.; Guleria, S. Antimicrobial Activity of Some Essential Oils—Present Status and Future Perspectives. Medicines 2017, 4, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Langa, E.; Valenzuela, A.; Ballestero, D.; Pino-Otín, M.R. Synergistic Activity of Thymol with Commercial Antibiotics against Critical and High WHO Priority Pathogenic Bacteria. Plants 2023, 12, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khwaza, V.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Antibacterial Activity of Selected Essential Oil Components and Their Derivatives: A Review. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksic Sabo, V.; Knezevic, P. Antimicrobial Activity of Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehn. Plant Extracts and Essential Oils: A Review. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 132, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatori, E.S.; Morgan, L.V.; Ferrarini, S.; Zilli, G.A.L.; Rosina, A.; Almeida, M.O.P.; Hackbart, H.C.S.; Rezende, R.S.; Albeny-Simões, D.; Oliveira, J.V.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Effects of Eucalyptus spp. Essential Oils: A Potential Valuable Use for an Industry Byproduct. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2023, 2023, 2582698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoch, C.C.; Petry, J.; Griesbaum, L.; Weiser, T.; Werner, K.; Ploch, M.; Verschoor, A.; Multhoff, G.; Bashiri Dezfouli, A.; Wollenberg, B. 1,8-Cineole (Eucalyptol): A Versatile Phytochemical with Therapeutic Applications across Multiple Diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengin, H.; Baysal, A.H. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activity of Essential Oil Terpenes against Pathogenic and Spoilage-Forming Bacteria and Cell Structure-Activity Relationships Evaluated by SEM Microscopy. Molecules 2014, 19, 17773–17798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mączka, W.; Duda-Madej, A.; Górny, A.; Grabarczyk, M.; Wińska, K. Can Eucalyptol Replace Antibiotics? Molecules 2021, 26, 4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merghni, A.; Belmamoun, A.R.; Urcan, A.C.; Bobiş, O.; Lassoued, M.A. 1,8-Cineol (Eucalyptol) Disrupts Membrane Integrity and Induces Oxidative Stress in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antioxidant 2023, 12, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Pruthi, V.; Poluri, K.M. Mechanistic Insights into Candida Biofilm Eradication Potential of Eucalyptol. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.S.; Xue, J.Z.; Qi, Y.; Muhammad, I.; Wang, H.; Li, X.Y.; Luo, Y.J.; Zhu, D.M.; Gao, Y.H.; Kong, L.C.; et al. Citric Acid Confers Broad Antibiotic Tolerance through Alteration of Bacterial Metabolism and Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.C.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Nguyen, K.T.; Yang, J. Study on the Antimicrobial Properties of Citrate-Based Biodegradable Polymers. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2014, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burel, C.; Kala, A.; Purevdorj-Gage, L. Impact of pH on Citric Acid Antimicrobial Activity against Gram-Negative Bacteria. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 72, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnwal, A.; Malik, T. Exploring the Untapped Potential of Naturally Occurring Antimicrobial Compounds: Novel Advancements in Food Preservation for Enhanced Safety and Sustainability. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1307210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, L.; Tapia-Rodríguez, M.R.; Baruzzi, F.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F. Plant Antimicrobials for Food Quality and Safety: Recent Views and Future Challenges. Foods 2023, 12, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jiang, S.; Jia, W.; Guo, T.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Yao, Z. Natural Antimicrobials from Plants: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Food Chem. 2024, 432, 137231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanović, Z.D.; Bošnjak-Neumüller, J.; Pajić-Lijaković, I.; Raj, J.; Vasiljević, M. Essential Oils as Feed Additives—Future Perspectives. Molecules 2018, 23, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori Tamburlin, I.; Roux, E.; Feuillée, M.; Labbé, J.; Aussaguès, Y.; El Fadle, F.E.; Fraboul, F.; Bouvier, G. Toxicological Safety Assessment of Essential Oils Used as Food Supplements to Establish Safe Oral Recommended Doses. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 157, 112603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Tashkin, D.P.; Luo, M.Z.; Zhang, J.Y. Chronic Toxicity of Inhaled Thymol in Lungs and Respiratory Tracts in Mouse Model. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2019, 7, e00516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negi, P.S. Plant Extracts for the Control of Bacterial Growth: Efficacy, Stability and Safety Issues for Food Application. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 156, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, D.; Abdu, P.A.; Mamman, M.; Jolayemi, K.O.; Yusuf, P.O.; Andamin, A.D. Research Note: Evaluation of Acute Oral Toxicity of Povidone-Iodine in Cockerels Using the Up-and-Down Procedure. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 205: Avian Dietary Toxicity Test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 223: Avian Acute Oral Toxicity Test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, B.S.; Carvalho, F.D.; Guilhermino, L.M.; Van Stappen, G. Use of the Genus Artemia in Ecotoxicity Testing. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 202: Daphnia sp. Acute Immobilisation Test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, L.C.; Wagner, D.A.; Glogowski, J.; Skipper, P.L.; Wishnok, J.S.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Analysis of Nitrate, Nitrite, and [15N]Nitrate in Biological Fluids. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 126, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placer, Z.A.; Cushman, L.L.; Johnson, B.C. Estimation of Product of Lipid Peroxidation (Malonyl Dialdehyde) in Biochemical Systems. Anal. Biochem. 1966, 16, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, T.W. Exotic Animal Hematology and Cytology, 4th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2015; p. 402. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, P.; Boardman, W.; Raidal, S. Atlas of Clinical Avian Hematology; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2009; p. 184. [Google Scholar]
- Natt, M.P.; Herrick, C.H.A. A New Blood Diluent for Counting the Erythrocytes and Leucocytes of the Chicken. Poult. Sci. 1952, 31, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, E.; Moreno, J.; Merino, S.; Sanz, J.J.; Arriero, E. Haematological Variables Are Good Predictors of Recruitment in Nestling Pied Flycatchers (Ficedula hypoleuca). Écoscience 2005, 12, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masello, J.F.; Choconi, R.G.; Helmer, M.; Kremberg, T.; Lubjuhn, T.; Quillfeldt, P. Do Leucocytes Reflect Condition in Nestling Burrowing Parrots Cyanoliseus patagonus in the Wild? Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2009, 152, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira-Mejía, B.; Calderon-Romero, R.; Ordaya-Fierro, J.; Medina, C.; Rodríguez, J.L.; Romero, A.; Dávila, R.; Ramos-Gonzalez, M. Impact of Exposure Duration to High-Altitude Hypoxia on Oxidative Homeostasis in Rat Brain Regions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2025; Available online: https://www.iso.org/search.html?PROD_isoorg_en%5Bquery%5D=Microbiology%20of%20the%20food%20chain%20horizontal%20method (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Legroux, D.; Kersten, L.; Barral, G.; Mauras, A.; Buronfosse, T.; Ramery, E. Evaluation of blood erythroid parameters in male broiler chickens (Ross 308) with the Sysmex XT-2000iV and Sysmex XN-1000V analyzers and determination of hematological reference intervals obtained with manual and instrumental methods. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2025, 54, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zálešáková, D.; Novotný, J.; Řiháček, M.; Horáková, L.; Mrkvicová, E.; Šťastník, O.; Pavlata, L. The blood biochemical parameters intervals and dynamics in modern broiler chickens. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2025, 29, 100465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, D.G.; Sganzerla, W.G.; da Silva, L.R.; Vieira, Y.G.S.; Almeida, A.R.; Dominguini, D.; Ceretta, L.; Pinheiro, A.C.; Bertoldi, F.C.; Becker, D.; et al. Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Potential of Eucalyptus Essential Oil-Based Nanoemulsions for Mouthwashes Application. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, S.; Chang, Y.; Imm, J.Y. Synergistic antimicrobial effect and mode of action of palmarosa oil-loaded nanoemulsion and citric acid against Pectobacterium carotovorum. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 32, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahari, A.; Khosravi-Darani, K. Hurdle technology using enzymes and essential oil to remove biofilm and increase the effectiveness of this process with the microencapsulation method. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 8483–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechmechani, S.; Khelissa, S.; Gharsallaoui, A.; Omari, K.E.; Hamze, M.; Chihib, N.E. Hurdle technology using encapsulated enzymes and essential oils to fight bacterial biofilms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 2311–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances Used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP). Scientific Opinion on the Safety and Efficacy of Formaldehyde as a Feed Hygiene Substance in Feed for Pigs and Poultry. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, J.; Ou, J.; Ou, S. Toxicity of Formaldehyde, and Its Role in the Formation of Harmful and Aromatic Compounds during Food Processing. Food Chem. X 2025, 25, 102225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, D.L.; Cavicchioli, A.; Puglieri, T.S. Indoors Lead Corrosion: Reassessing the Role of Formaldehyde. Vib. Spectrosc. 2010, 54, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollmann, A.; Kaulfers, P.M. Formaldehyde-Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Identification of Resistance Genes by DNA-Hybridization. Zentralblatt Hyg. Umweltmed. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Med. 1991, 191, 449–456. [Google Scholar]
- Vilas-Boas, A.A.; Pintado, M.; Oliveira, A.L.S. Natural Bioactive Compounds from Food Waste: Toxicity and Safety Concerns. Foods 2021, 10, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surai, P.F.; Kochish, I.I.; Fisinin, V.I.; Kidd, M.T. Antioxidant Defence Systems and Oxidative Stress in Poultry Biology: An Update. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coudert, E.; Baéza, E.; Chartrin, P.; Jimenez, J.; Cailleau-Audouin, E.; Bordeau, T.; Berri, C. Slow and Fast-Growing Chickens Use Different Antioxidant Pathways to Maintain Their Redox Balance during Postnatal Growth. Animals 2023, 13, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa Rao, B.; Chandrasekaran, C.V.; Srikanth, H.S.; Sasikumar, M.; Edwin Jothie, R.; Haseena, B.; Bharathi, B.; Selvam, R.; Prashanth, D. Mutagenicity and Acute Oral Toxicity Test for Herbal Poultry Feed Supplements. J. Toxicol. 2018, 9412167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP); Bampidis, V.; Azimonti, G.; Bastos, M.L.; Christensen, H.; Dusemund, B.; Durjava, M.; Kouba, M.; López-Alonso, M.; López Puente, S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of a feed additive consisting of a preparation of essential oils of thyme and star anise, and quillaja bark powder (BIOSTRONG® 510 all natural) for all poultry species (Delacon Biotechnik GmbH). EFSA J. 2023, 21, e07955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierżant, K.; Piksa, E.; Konkol, D.; Lewandowska, K.; Asghar, M.U. Performance and antioxidant traits of broiler chickens fed with diets containing rapeseed or flaxseed oil and optimized quercetin. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvedaki, I.; Pappas, A.C.; Surai, P.F.; Zoidis, E. Nutrigenomics of Natural Antioxidants in Broilers. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Xing, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, F. Oxidative stress impairs the meat quality of broiler by damaging mitochondrial function, affecting calcium metabolism and leading to ferroptosis. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 35, 1616–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, J.; Melkman-Zehavi, T.; Reicher, N.; Braun, U.; Inhuber, V.; Mabjeesh, S.J.; Halevy, O.; Uni, Z. Supply and demand of creatine and glycogen in broiler chicken embryos. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1079638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo Ghanima, M.M.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Al-Otaibi, A.M.; Nasr, S.; Almohmadi, N.H.; Taha, A.E.; Jaremko, M.; El-Kasrawy, N.I. Growth performance, liver and kidney functions, blood hormonal profile, and economic efficiency of broilers fed different levels of threonine supplementation during feed restriction. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesser, G.L.S.; Avila, A.S.; Broch, J.; Souza, C.; Polese, C.; Kaufmann, C.; Eyng, C.; Savaris, V.D.L.; Junior, N.R.; Bruno, L.D.G.; et al. Performance, metabolism, and meat quality of broilers fed dry brewery residue. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2022, 54, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalia, A.M.; Loh, T.C.; Sazili, A.Q.; Samsudin, A.A. Influence of bacterial organic selenium on blood parameters, immune response, selenium retention and intestinal morphology of broiler chickens. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righi, F.; Pitino, R.; Manuelian, C.L.; Simoni, M.; Quarantelli, A.; De Marchi, M.; Tsiplakou, E. Plant Feed Additives as Natural Alternatives to the Use of Synthetic Antioxidant Vitamins on Poultry Performances, Health, and Oxidative Status: A Review of the Literature in the Last 20 Years. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, W.B.; Siegel, H.S. Evaluation of the heterophil/lymphocyte ratio as a measure of stress in chickens. Avian Dis. 1983, 27, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Murrani, W.K.; Kassab, A.; al-Sam, H.Z.; al-Athari, A.M. Heterophil/lymphocyte ratio as a selection criterion for heat resistance in domestic fowls. Br. Poult. Sci. 1997, 38, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.G.; Gomez-Raya, L.; Torres, O.; Cigarroa-Vazquez, F.A.; Davila, S.G.; Rauw, W.M. Heterophil/lymphocyte response of local Spanish breeds of laying hens to cold stress, heat stress, and water restriction. J. Therm. Biol. 2023, 113, 103542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Buchholz, J.S.; Ruhnau, D.; Hess, C.; Aschenbach, J.R.; Hess, M.; Awad, W.A. Paracellular intestinal permeability of chickens induced by DON and/or C. jejuni is associated with alterations in tight junction mRNA expression. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 168, 105509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, W.A.; Hess, C.; Hess, M. Enteric Pathogens and Their Toxin-Induced Disruption of the Intestinal Barrier through Alteration of Tight Junctions in Chickens. Toxins 2017, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrì, A.; Stazi, A.V.; Di Delupis, G.D. Acute toxicity of furazolidone on Artemia salina, Daphnia magna, and Culex pipiens molestus larvae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1988, 16, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favilla, M.; Macchia, L.; Gallo, A.; Altomare, C. Toxicity assessment of metabolites of fungal biocontrol agents using two different (Artemia salina and Daphnia magna) invertebrate bioassays. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 1922–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, M.; Suzuki, N. Toxicities of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons for Aquatic Animals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavion, F.; Pelin, M.; Ponti, C.; Della Loggia, R.; Tubaro, A.; Sosa, S. Ecotoxicological Impact of the Marine Toxin Palytoxin on the Micro-Crustacean Artemia franciscana. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmani, M.H.; Garzegar, S.; Ehrampoush, M.H.; Askarishahi, M. Predicting anionic surfactant toxicity to Daphnia magna in aquatic environment: A green approach for evaluation of EC50 values. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 50731–50746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Target Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | 5′-ACTTTGGCATTGTGGAGGGT-3′ | 5′-GGACGCTGGGATGATGTTCT-3′ |
| Claudin 1 (CLD1) | 5′-AGCCTGGCTTAACTGAGTGT-3′ | 5′-TGCTAGCCGTTGTAGCTGTA-3′ |
| Occludin (OCL) | 5′-GTCTGTGGGTTCCTCATC-3′ | 5′-CCAGTAGATGTTGGCTTTG-3′ |
| Microbiocide | Time Exposure | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 7 Days | ||||||
| CFU g−1 | S.D. | MR (%) | CFU g−1 | S.D. | MR (%) | ||
| E. coli | BN (0.5 L/T) | 6.5 × 104 *a | 1.0 × 103 | 96 | 3.3 × 104 *b | 2.2 × 103 | 98 |
| F-PA (2 L/T) | 2.7 × 104 *a | 0.7 × 103 | 98 | 0.6 × 104 *b | 0.2 × 103 | 99 | |
| Control (-) | 1.5 × 106 a | 5.3 × 104 | - | 1.7 × 106 a | 2.5 × 104 | - | |
| C. perfringens | BN (0.5 L/T) | 8.31 × 104 *a | 2.5 × 103 | 93 | 1.3 × 104 *b | 1.4 × 103 | 99 |
| F-PA (2 L/T) | 5.7 × 104 *a | 2.5 × 103 | 95 | 0.7 × 104 *b | 0.1 × 103 | 99 | |
| Control (-) | 1.2 × 106 a | 3.6 × 104 | - | 1.2 × 106 a | 2.5 × 104 | - | |
| Salmonella sp. | BN (0.5 L/T) | 7.3 × 104 *a | 1.8 × 103 | 94 | 2.6 × 104 *b | 0.4 × 103 | 98 |
| F-PA (2 L/T) | 2.4 × 104 *a | 0.3 × 103 | 97 | 0.1 × 104 *b | 1.0 × 103 | 99 | |
| Control (-) | 1.1 × 106 a | 5.0 × 104 | - | 1.2 × 106 a | 4.1 × 104 | - | |
| P. aeruginosa | BN (0.5 L/T) | 6.2 × 104 *a | 2.5 × 103 | 95 | 4.1 × 104 *b | 1.5 × 103 | 97 |
| F-PA (2 L/T) | 3.0 × 104 *a | 2.5 × 103 | 97 | 1.4 × 104 *b | 0.3 × 103 | 99 | |
| Control (-) | 1.1 × 106 a | 2.0 × 104 | - | 1.2 × 106 a | 4.1 × 104 | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lira-Mejía, B.; Barrios-Arpi, L.; Villaorduña, C.; Ancajima, T.; Rodríguez, J.-L.; Romero, A.; Puicón, V.; Patiño, H. Toxicological Evaluation and Antimicrobial Activity of a Natural Thymol–Eucalyptol-Based Mixture. Toxics 2025, 13, 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100875
Lira-Mejía B, Barrios-Arpi L, Villaorduña C, Ancajima T, Rodríguez J-L, Romero A, Puicón V, Patiño H. Toxicological Evaluation and Antimicrobial Activity of a Natural Thymol–Eucalyptol-Based Mixture. Toxics. 2025; 13(10):875. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100875
Chicago/Turabian StyleLira-Mejía, Boris, Luis Barrios-Arpi, Carlos Villaorduña, Tatiana Ancajima, José-Luis Rodríguez, Alejandro Romero, Víctor Puicón, and Hugo Patiño. 2025. "Toxicological Evaluation and Antimicrobial Activity of a Natural Thymol–Eucalyptol-Based Mixture" Toxics 13, no. 10: 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100875
APA StyleLira-Mejía, B., Barrios-Arpi, L., Villaorduña, C., Ancajima, T., Rodríguez, J.-L., Romero, A., Puicón, V., & Patiño, H. (2025). Toxicological Evaluation and Antimicrobial Activity of a Natural Thymol–Eucalyptol-Based Mixture. Toxics, 13(10), 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100875







