Development of an Improved Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria-Based Ecotoxicity Test for Simple and Rapid On-Site Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SOB Strain and Cultivation
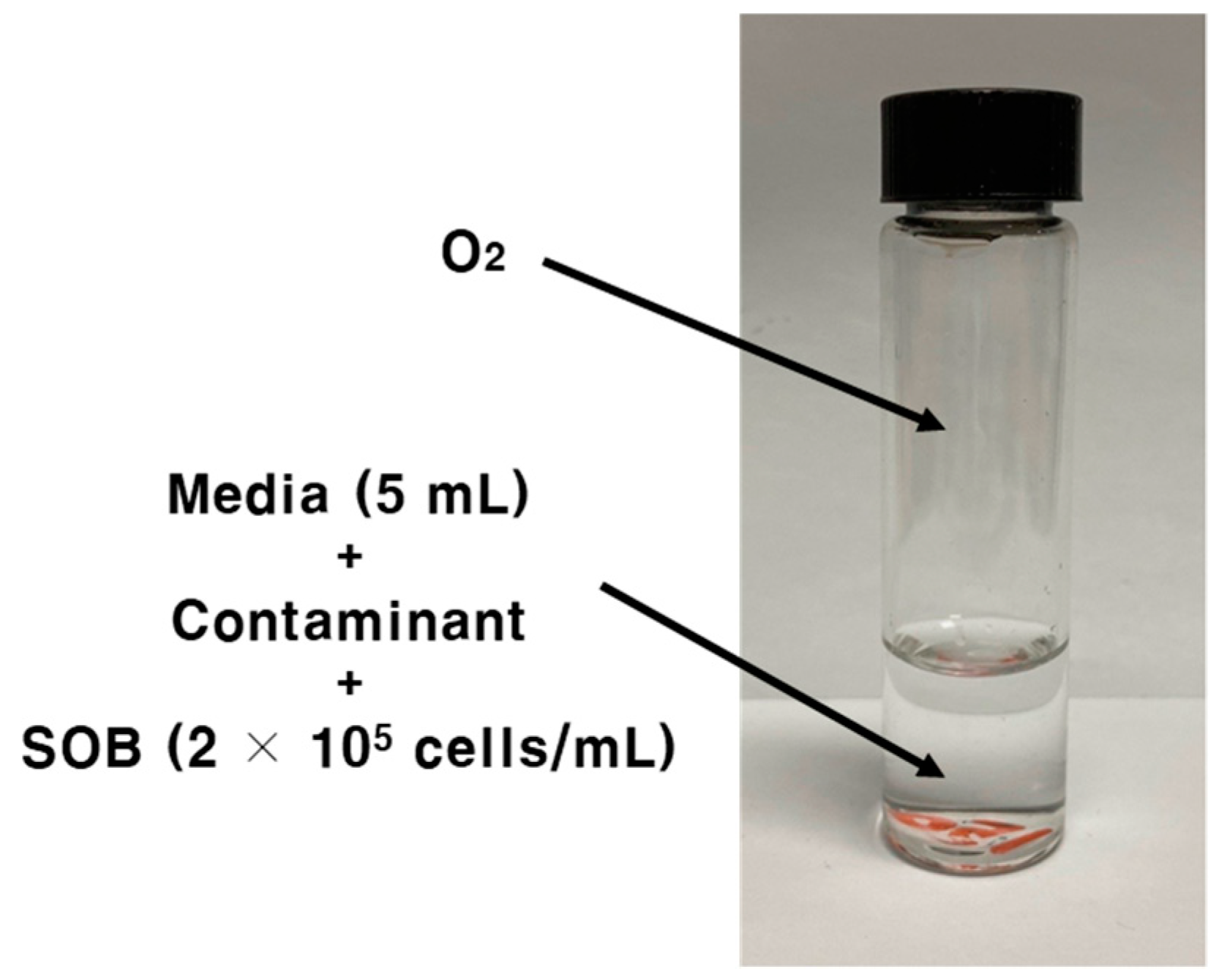
2.2. SOB Toxicity Test and Optimization of Test Conditions
2.3. Chemicals and Laboratory Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization for Test Conditions of SOB Toxicity Kit
3.2. Comparisons of SOB Toxicity Test Results between the Current Optimal and Earlier Techniques
3.3. Advantages of SOB Toxicity Tests
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Environmental Agency (UK). Chemicals: Challenges for the Water Environment. 2021. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/chemicals-challenges-for-the-water-environment (accessed on 22 February 2023).
- Van Ginkel, S.W.; Hassan, S.H.A.; Oh, S.-E. Detecting endocrine disrupting compounds in water using sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, H.; Park, M.; Jang, A.; Kim, S.; Oh, S.-E. A simple and rapid algal assay kit to assess toxicity of heavy metal-contaminated water. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemirycz, E.; Nichthauser, J.; Staniszewska, M.; Nałęcz-Jawecki, G.; Bolałek, J. The Microtox® biological test: Application in toxicity evaluation of surface waters and sediments in Poland. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2007, 36, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Sharma, B.; Singh, P.; Dobhal, R. Water Quality Assessment in Terms of Water Quality Index. Am. J. Water Resour. 2013, 1, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.-J.; Park, Y.-S. Biological early warning system based on the responses of aquatic organisms to disturbances: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 466–467, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanian, N.; Ali, S.H.B.; Homayoonfard, M.; Ali, N.J.; Rehan, M.; Sadef, Y.; Nizami, A.S. Analysis of Physiochemical Parameters to Evaluate the Drinking Water Quality in the State of Perak, Malaysia. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 716125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brayner, R.; Couté, A.; Livage, J.; Perrette, C.; Sicard, C. Micro-algal biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 581–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.H.A.; Van Ginkel, S.W.; Oh, S.-E. Effect of organics and alkalinity on the sulfur oxidizing bacteria (SOB) biosensor. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunjan, D.; Gargi, B. Toxicity tests to check water quality. Int. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 4, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Hernando, M.D.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; Tauler, R.; Barceló, D. Toxicity assays applied to wastewater treatment. Talanta 2005, 65, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wezel, A.; Mons, M.; van Delft, W. New methods to monitor emerging chemicals in the drinkingwater production chain. J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Barik, S.K.; Ayyappan, S.; Mohapatra, B. Fish bioassays for evaluation of raw and bioremediated dairy effluent. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 72, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sponza, D.T. Incorporation of Toxicity Tests into the Turkish Industrial Discharge Monitoring Systems. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 43, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.-C.; Park, K.-J.; Ihm, H.-S.; Park, J.-E.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kang, I.; Lee, K.-H.; Jahng, D.; Lee, D.-H.; Kim, S.-J. A novel continuous toxicity test system using a luminously modified freshwater bacterium. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 20, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-Santos, M.; Soares, A.M.; Ribeiro, R. An in situ bioassay for freshwater environments with the microalga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 59, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, C.; Alañon, P.; Gutierrez-Alonso, S.; Riva, M.C.; Fernández, C.; Tarazona, J.V. A Daphnia magna feeding bioassay as a cost effective and ecological relevant sublethal toxicity test for Environmental Risk Assessment of toxic effluents. Sci. Total. Environ. 2008, 405, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, P.; Palma, V.L.; Matos, C.; Fernandes, R.M.; Bohn, A.; Soares, A.; Barbosa, I. Effects of atrazine and endosulfan sulphate on the ecdysteroid system of Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2008, 74, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.D. Acute toxicity of copper in flow-through system with suspended particles. Environ. Eng. Res. 2001, 6, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.H.; Oh, S.E. Improved detection of toxic chemicals by Photobacterium phosphoreum using modified Boss medium. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2010, 101, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-E.; Hassan, S.H.A.; Van Ginkel, S.W. A novel biosensor for detecting toxicity in water using sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 154, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, K.; Robertson, D.; Hudson, S.; Teasdale, P.R.; Welsh, D.T.; John, R. A sensitive, rapid ferricyanide-mediated toxicity bioassay developed using Escherichia coli. Talanta 2010, 82, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.H.A.; Van Ginkel, S.W.; Hussein, M.A.M.; Abskharon, R.; Oh, S.-E. Toxicity assessment using different bioassays and microbial biosensors. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, Y.; Kobata, T.; Nakaoka, C. A simple and easy method for the monitoring of environmental pollutants using oligotrophic bacteria. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 32, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.C.; Park, K.S.; Kim, S.D.; Gu, M.B. Evaluation of a high throughput toxicity biosensor and comparison with a Daphnia magna bioassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 18, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eilersen, A.M.; Arvin, E.; Henze, M. Monitoring toxicity of industrial wastewater and specific chemicals to a green alga, nitrifying bacteria and an aquatic bacterium. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 50, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tencaliec, A.M.; Laschi, S.; Magearu, V.; Mascini, M. A comparison study between a disposable electrochemical DNA biosensor and a Vibrio fischeri-based luminescent sensor for the detection of toxicants in water samples. Talanta 2006, 69, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatev, R.; Magnin, J.-P.; Ozil, P.; Stoytcheva, M. Bacterial sensors based on Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans: Part I. Fe2+ and S2O32− determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.H.; Van Ginkel, S.W.; Kim, S.-M.; Yoon, S.-H.; Joo, J.-H.; Shin, B.-S.; Jeon, B.-H.; Bae, W.; Oh, S.-E. Isolation and characterization of Acidithiobacillus caldus from a sulfur-oxidizing bacterial biosensor and its role in detection of toxic chemicals. J. Microbiol. Methods 2010, 82, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ginkel, S.W.; Hassan, S.H.A.; Ok, Y.S.; Yang, J.E.; Kim, Y.-S.; Oh, S.-E. Detecting Oxidized Contaminants in Water Using Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3739–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, A.; Shin, B.-S.; Oh, S.-E. Effect of different air flow rate on operation of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (SOB) biosensor. Geosystem Eng. 2015, 18, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qambrani, N.A.; Hwang, J.-H.; Oh, S.-E. Comparison of chromium III and VI toxicities in water using sulfur-oxidizing bacterial bioassays. Chemosphere 2016, 160, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Oh, S.-E. Toxicity assessment of selected heavy metals in water using a seven-chambered sulfur-oxidizing bacterial (SOB) bioassay reactor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, H.; Hwang, J.-H.; Hassan, S.H.; Joo, J.H.; Hur, J.H.; Chon, K.; Jeon, B.-H.; Song, Y.-C.; Chae, K.-J.; Oh, S.-E. Rapid detection of heavy metal-induced toxicity in water using a fed-batch sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (SOB) bioreactor. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 161, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, H.; Kim, S.; Oh, S.-E. Evaluation of joint toxicity of BTEX mixtures using sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, K.; Rana, N.; Singh, B. Chapter 10—Applications of sulfur oxidizing bacteria. Physiol. Biotechnol. Asp. Extrem. 2020, 2020, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, M.T.; Martinko, J.M.; Parker, J. Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 10th ed.; Prentice Hall/Pearson Education: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Eom, H.S.; Ashun, E.; Toor, U.A.; Oh, S.-E. A solid-phase direct contact bioassay using sulfur-oxidizing bacteria (SOB) to evaluate toxicity of soil contaminated with heavy metals. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 305, 127510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B.; Macvicar, J.H.; Rolfe, S. A new solid medium for the isolation and enumeration of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and acidophilic heterotrophic bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 1987, 7, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duquesne, K.; Lebrun, S.; Casiot, C.; Bruneel, O.; Personné, J.-C.; Leblanc, M.; Elbaz-Poulichet, F.; Morin, G.; Bonnefoy, V. Immobilization of Arsenite and Ferric Iron by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Its Relevance to Acid Mine Drainage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 6165–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Shrivastava, A.K. Role of initial cell density of algal bioassay of toxic chemicals. J. Basic Microbiol. 2015, 56, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-H.; Kao, W.-C.; Tsai, K.-P.; Chen, C.-Y. A novel algal toxicity testing technique for assessing the toxicity of both metallic and organic toxicants. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1869–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaggi, A.R.C.; Aulakh, M.S.; Sharma, R. Temperature effects on soil organic sulphur mineralization and elemental sulphur oxidation in subtropical soils of varying pH. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 1999, 54, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-H.; Stöven, K.; Haneklaus, S.; Singh, B.R.; Schnug, E. Elemental Sulfur Oxidation by Thiobacillus spp. and Aerobic Heterotrophic Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.H.A.; Van Ginkel, S.W.; Oh, S.-E. Detection of Cr6+ by the Sulfur Oxidizing Bacteria Biosensor: Effect of Different Physical Factors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7844–7848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Coillie, R.; Couture, P.; Schoenert, R.; Thellen, C. Mise au Point d’une ‘Evaluation Rapide de Latoxicit’e Originale des Effluents et de Leurs Composantes al’Aide d’Algues; Environnement Canada, Service de laProtection de 1′Environnement: Quebec, PQ, Canada, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Blaise, C.; Legault, R.; Bermingham, N.; Van Coillie, R.; Vasseur, P. A simple microplate algal assay technique for aquatic toxicity assessment. Environ. Toxicol. 1986, 1, 261–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalzell, D.J.B.; Alte, S.; Aspichueta, E.; de la Sota, A.; Etxebarria, J.; Gutierrez, M.; Hoffmann, C.C.; Sales, D.; Obst, U.; Christofi, N. A comparison of five rapid direct toxicity assessment methods to determine toxicity of pollutants to activated sludge. Chemosphere 2002, 47, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudłak, B.; Wolska, L.; Namieśnik, J. Determination of EC50 toxicity data of selected heavy metals toward Heterocypris incongruens and their comparison to “direct-contact” and microbiotests. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 174, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaniran, A.O.; Balgobind, A.; Pillay, B. Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Soil: Impact on Microbial Biodegradation of Organic Compounds and Possible Improvement Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10197–10228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitton, G.; Garland, E.; Kong, I.; Morel, J.L.; Koopman, B. A direct solid-phase assay specific for heavy metal toxicity. I. methodology. J. Soil Contam. 1996, 5, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 11348; Water quality—Determination of the inhibitory effets of water samples on the light emission of Vibrio fischeri. (Luminscent bacteria tests). International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
| Initial Cell Density (Cells/mL) | Incubating Temperature (℃) | Mixing Intensity (rpm) | EC50 (μg/L) | CV (%) | Initial Cell Density (Cells/mL) | Incubating Temperature (°C) | Mixing Intensity (rpm) | EC50 (μg/L) | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 105 | 27 | 70 | 90.7 | 12.1 | 5 × 105 | 27 | 70 | 115.7 | 4.3 |
| 100 | 84.7 | 12.5 | 100 | 99.3 | 5.0 | ||||
| 120 | 44.7 | 12.3 | 120 | 56.4 | 4.5 | ||||
| 150 | 48.3 | 11.4 | 150 | 64.7 | 4.7 | ||||
| 32 | 70 | 92.0 | 9.7 | 32 | 70 | 124.0 | 2.4 | ||
| 100 | 85.3 | 8.3 | 100 | 114.1 | 2.6 | ||||
| 120 | 44.0 | 9.1 | 120 | 58.0 | 3.0 | ||||
| 150 | 44.7 | 8.5 | 150 | 62.3 | 4.0 | ||||
| 37 | 70 | 143.0 | 10.3 | 37 | 70 | 155.0 | 3.2 | ||
| 100 | 115.3 | 10.3 | 100 | 133.3 | 3.0 | ||||
| 120 | 57.3 | 11.3 | 120 | 72.3 | 3.5 | ||||
| 150 | 60.0 | 10.0 | 150 | 69.7 | 4.4 | ||||
| 42 | 70 | 154.3 | 10.1 | 42 | 70 | 174.7 | 2.3 | ||
| 100 | 124.7 | 10.2 | 100 | 147.0 | 2.4 | ||||
| 120 | 75.1 | 11.9 | 120 | 86.3 | 5.7 | ||||
| 150 | 72.3 | 10.2 | 150 | 88.0 | 5.0 | ||||
| 2 × 105 | 27 | 70 | 93.3 | 4.3 | 106 | 27 | 70 | 142.3 | 3.3 |
| 100 | 84.0 | 3.1 | 100 | 126.7 | 2.5 | ||||
| 120 | 44.7 | 4.6 | 120 | 67.7 | 2.3 | ||||
| 150 | 46.1 | 3.8 | 150 | 74.7 | 5.1 | ||||
| 32 | 70 | 96.3 | 2.2 | 32 | 70 | 146.0 | 3.1 | ||
| 100 | 88.3 | 2.8 | 100 | 130.3 | 1.9 | ||||
| 120 | 38.0 | 2.6 | 120 | 70.7 | 2.9 | ||||
| 150 | 44.3 | 2.6 | 150 | 72.3 | 2.1 | ||||
| 37 | 70 | 144.7 | 3.8 | 37 | 70 | 160.0 | 1.7 | ||
| 100 | 120.3 | 2.1 | 100 | 145.7 | 4.0 | ||||
| 120 | 60.3 | 2.5 | 120 | 82.0 | 3.7 | ||||
| 150 | 62.1 | 3.2 | 150 | 79.7 | 1.9 | ||||
| 42 | 70 | 165.3 | 2.4 | 42 | 70 | 187.0 | 2.8 | ||
| 100 | 133.7 | 4.3 | 100 | 159.1 | 4.7 | ||||
| 120 | 78.3 | 2.7 | 120 | 92.7 | 1.2 | ||||
| 150 | 76.0 | 4.7 | 150 | 94.0 | 4.6 |
| Earlier SOB Tests | Current SOB Tests | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contaminant | Processing Time (h) | EC50 (mg/L) | CV (%) | Reference | Processing Time (h) | EC50 (mg/L) | CV (%) | |
| Heavy metal | Ag2+ | 2 | 1.76–3.62 | - | Gurung et al. (2015) [31]; Ahmed et al. (2018) [33] | 0.5 | 0.195 | 3.1 |
| As3+ | 2 | 0.2 | 11.5 | Eom et al. (2019) [34] | 0.5 | 0.047 | 4.5 | |
| CN− | 2 | 4.9 | 12.7 | Eom et al. (2019) [34] | 0.5 | 0.676 | 3.3 | |
| Cr6+ | 2 | 1.17–2.7 | 10.5 | Qambrani et al. (2016) [32]; Ahmed et al. (2018) [33]; Eom et al. (2019) [34] | 0.5 | 0.456 | 3.0 | |
| Cu2+ | 2 | 5 | - | Ahmed et al. (2018) [33] | 0.5 | 0.860 | 2.4 | |
| Hg2+ | 2 | 0.21–0.92 | 8.7 | Ahmed et al. (2018) [33]; Eom et al. (2019) [34] | 0.5 | 0.038 | 2.6 | |
| Zn2+ | 2 | 1.55 | - | Ahmed et al. (2018) [33] | 0.5 | 0.692 | 3.4 | |
| Petrochemical | Benzene | 24 | 166.1 | 9.8 | Eom et al. (2023) [35] | 0.5 | 35.849 | 4.6 |
| Toluene | 24 | 94.4 | 9.5 | Eom et al. (2023) [35] | 0.5 | 20.575 | 3.8 | |
| Ethylbenzene | 24 | 38.9 | 9.7 | Eom et al. (2023) [35] | 0.5 | 4.038 | 4.1 | |
| p-Xylenes | 24 | 34.3 | 8.6 | Eom et al. (2023) [35] | 0.5 | 3.803 | 2.4 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eom, H. Development of an Improved Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria-Based Ecotoxicity Test for Simple and Rapid On-Site Application. Toxics 2023, 11, 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040352
Eom H. Development of an Improved Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria-Based Ecotoxicity Test for Simple and Rapid On-Site Application. Toxics. 2023; 11(4):352. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040352
Chicago/Turabian StyleEom, Heonseop. 2023. "Development of an Improved Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria-Based Ecotoxicity Test for Simple and Rapid On-Site Application" Toxics 11, no. 4: 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040352
APA StyleEom, H. (2023). Development of an Improved Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria-Based Ecotoxicity Test for Simple and Rapid On-Site Application. Toxics, 11(4), 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040352






