Source Apportionment and Model Applicability of Heavy Metal Pollution in Farmland Soil Based on Three Receptor Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.3. Source Apportionment Models
2.3.1. Absolute Principal Component Scores–Multivariate Linear Regression (APCS-MLR)
2.3.2. UNMIX Model
2.3.3. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF)
2.4. Potential Ecological Risk Index
2.5. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Statistical Analysis of Heavy Metals in Soil
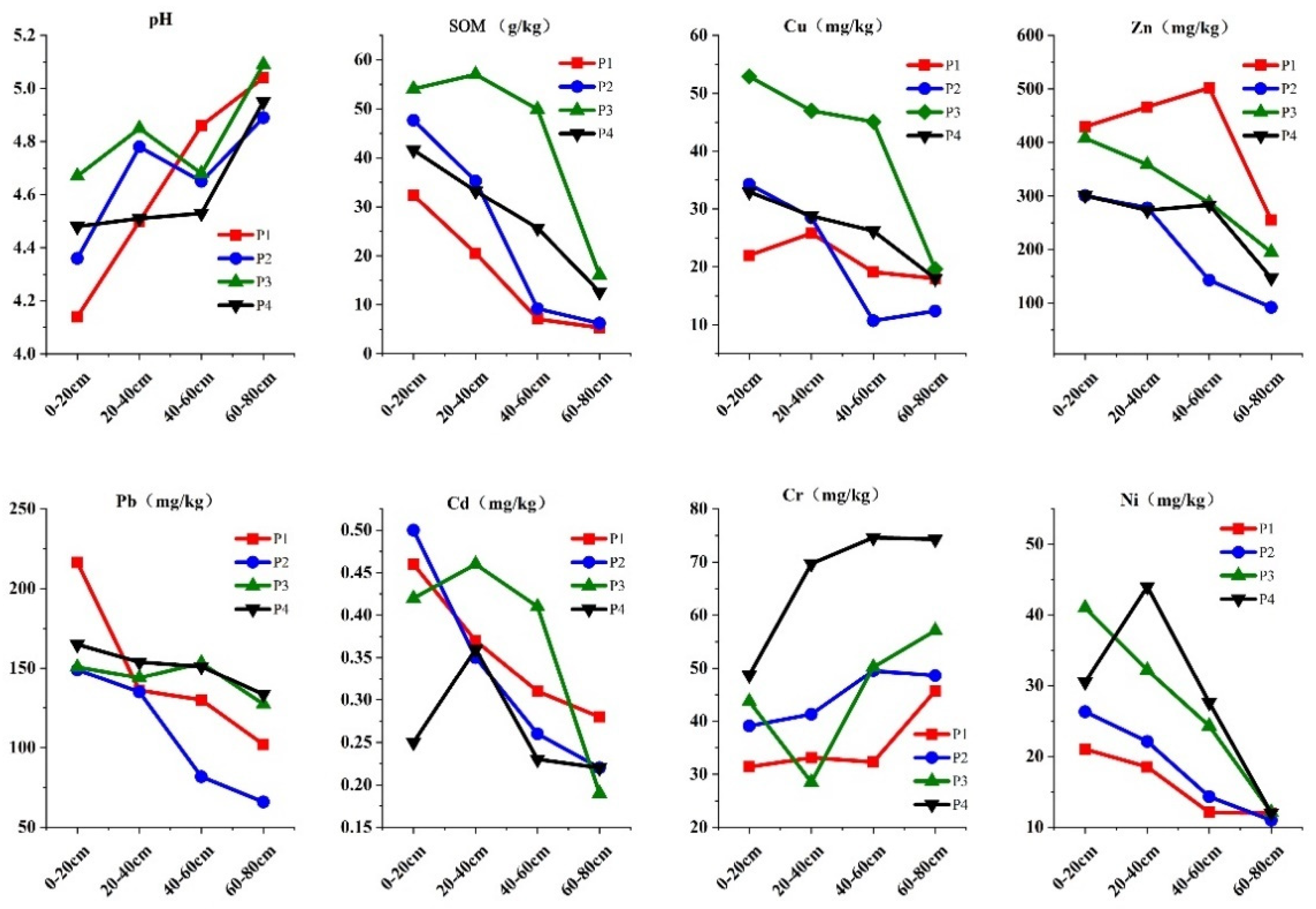
3.2. Heavy Metal Content in Soil Profile
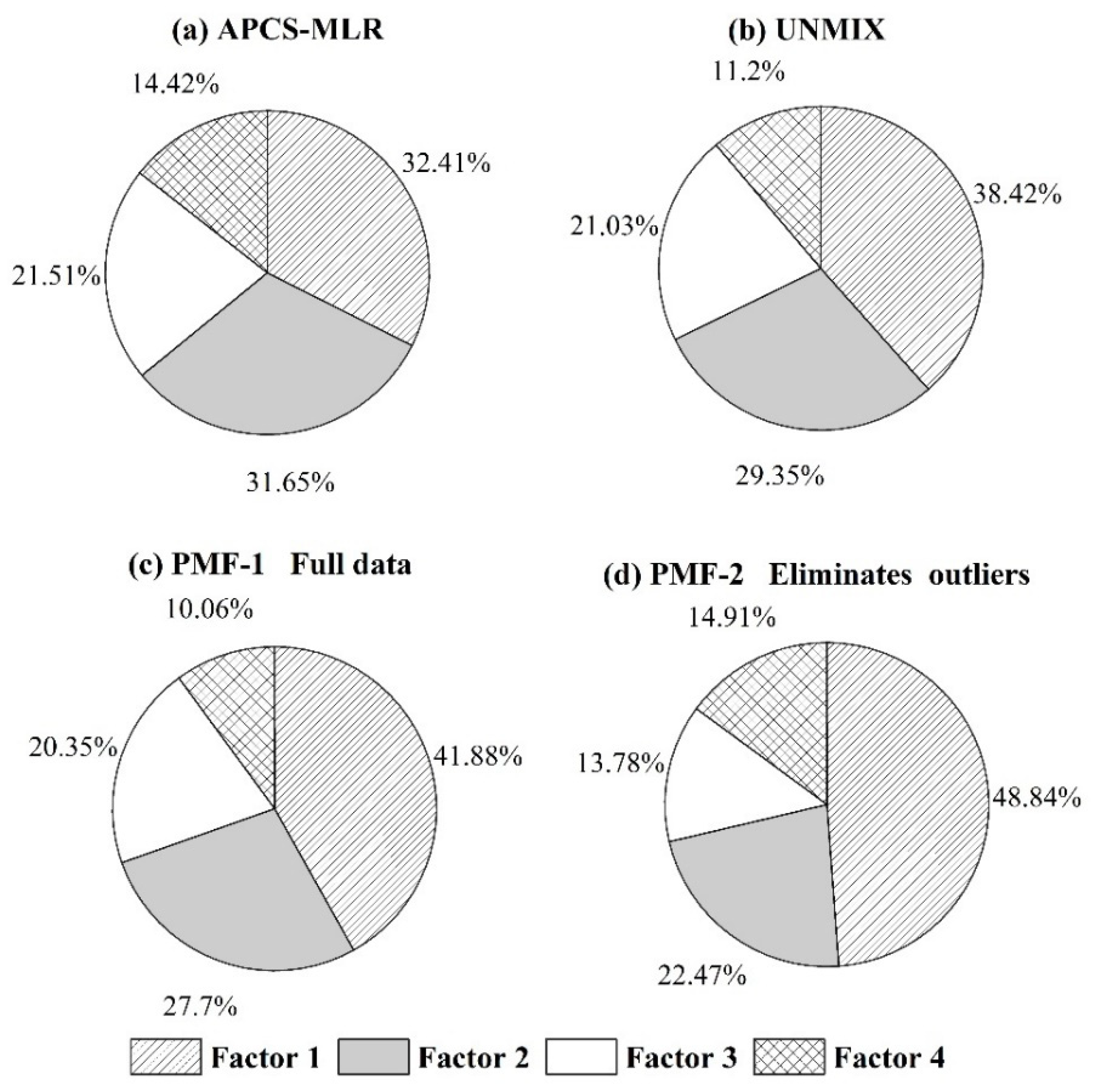
3.3. Results of Three Models
3.4. Source Apportionment of Heavy Metals in Soil
3.5. Source Contribution Analysis
3.6. Evaluation of Potential Ecological Risk Index
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drobnik, T.; Greiner, L.; Keller, A.; Grêt-Regamey, A. Soil quality indicators–from soil functions to ecosystem services. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Christakos, G.; Guo, M.; Xiao, L.; Huang, W. Space-time quantitative source apportionment of soil heavy metal concentration increments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Shi, J.; Dahlgren, R.A. Heavy metal sources identification and sampling uncertainty analysis in a field-scale vegetable soil of Hangzhou, China. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabukdhara, M.; Nema, A.K. Heavy metals assessment in urban soil around industrial clusters in Ghaziabad, India: Probabilistic health risk approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 87, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Huang, J.; Zeng, G.; Gu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Tang, B.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Shi, L. Exploiting extracellular polymeric substances (eps) controlling strategies for performance enhancement of biological wastewater treatments: An overview. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xia, B.; Fan, C.; Zhao, P.; Shen, S. Human health risk from soil heavy metal contamination under different land uses near Dabaoshan mine, southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 417–418, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Wang, F.; Xu, C.; Pan, N.; Lin, J.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Y.; Luo, H. Source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil based on PMF: A case study in Hexi corridor, northwest China. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, T.; Wu, C.; He, Z.; Japenga, J.; Deng, M.; Yang, X. An integrated approach to assess heavy metal source apportionment in peri-urban agricultural soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Ma, J.; Wu, X.; Ju, T.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Gong, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhao, L.; et al. Inventories of heavy metal inputs and outputs to and from agricultural soils: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Guo, D.; Liu, K.; Meng, H.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, F.; Zhu, G. Levels, sources, and spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils from a typical coal industrial city of Tangshan, China. Catena 2019, 175, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Xiaoyong, L.; Xiulan, Y.; Ganghui, Z.; Dong, M. Evaluation of heavy metal and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons accumulation in plants from typical industrial sites: Potential candidate in phytoremediation for co-contamination. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 12494–12504. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Deng, M.; Wu, S.; Japenga, J.; Li, T.; Yang, X.; He, Z. A modified receptor model for source apportionment of heavy metal pollution in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 354, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavković, L.; Škrbić, B.; Miljević, N.; Onjia, A. Principal component analysis of trace elements in industrial soils. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2004, 2, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Jia, G.; Sheli, C.; Jing, C.; Linfu, X.; Qingwei, Z. Source identification of eight heavy metals in grassland soils by multivariate analysis from the Baicheng-Songyuan area, Jilin province, northeast China. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.-s.; Yu, S.; Li, X.-d. Distribution, availability, and sources of trace metals in different particle size fractions of urban soils in Hong Kong: Implications for assessing the risk to human health. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, X.; Peng, P.; Bai, J. Combination of unmix and positive matrix factorization model identifying contributions to carcinogenicity and mutagenicity for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons sources in Liaohe delta reed wetland soils, China. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Fang, W.; Shafi, M.; Wu, D.; Li, Y.; Zhong, B.; Ma, J.; Liu, D. Source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soil with application of APCS-MLR model: A pilot study for restoration of farmland in Shaoxing city Zhejiang, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, I.; Abdugheni, A.; Qingdong, S.; Suhong, L.; Li, H. Quantitatively assessing the risks and possible sources of toxic metals in soil from an arid, coal-dependent industrial region in NW China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 212, 106505. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Tang, Z.; Kong, M.; Chen, X.; Zhou, C.; Huang, K.; Wang, Z. Tracing the potential pollution sources of the coastal water in Hong Kong with statistical models combining APCS-MLR. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 245, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogundele, L.T.; Owoade, O.K.; Olise, F.S.; Hopke, P.K. Source identification and apportionment of pm2.5 and pm2.5-10 in iron and steel scrap smelting factory environment using PMF, PCFA and UNMIX receptor models. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, F.; Zhou, J.; Schauer, J.J. A hybrid source apportionment strategy using positive matrix factorization (PMF) and molecular marker chemical mass balance (MM-CMB) models. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Chen, H.; Song, L.; Yao, Z.; Meng, F.; Teng, Y. Characterization and source apportionment of heavy metals in the sediments of lake tai (China) and its surrounding soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Peng, W.; Cheng, C. Source estimating of heavy metals in shallow groundwater based on unmix model: A case study. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 45, 756–762. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, L.; Chan, L.Y.; Bi, X.; Guo, H.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Q.; Wang, X.; Peng, P.a.; Sheng, G. Effect of cloud-to-ground lightning and meteorological conditions on surface nox and o3 in Hong Kong. Atmos. Res. 2016, 182, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 142, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, R.C. Multivariate receptor modeling by n-dimensional edge detection. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2003, 65, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Shi, X.; Lu, X.; Li, X. Pollution assessment and source apportionment of trace metals in urban topsoil of Xi’an city in northwest China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 77, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.-H.; Cai, L.-M.; Wen, H.-H.; Hu, G.-C.; Chen, L.-G.; Luo, J. An integrated approach to quantifying ecological and human health risks from different sources of soil heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J. Multivariate receptor models and robust Geostatistics to estimate source apportionment of heavy metals in soils. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.-L.; Zhi, Y.-Y.; Yang, L.-P.; Shi, J.-C.; Zeng, L.-Z.; Wu, L.-S. Positive matrix factorization as source apportionment of soil lead and cadmium around a battery plant (Changxing county, China). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7698–7707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Duan, J.; Ma, Y.; He, K.; Cheng, Y.; Deng, S.-X.; Huang, Y.-L.; Si-Tu, S.-P. Long-term trends of chemical characteristics and sources of fine particle in Foshan city, pearl river delta: 2008–2014. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.K.; Sharma, A.; Saxena, M.; Choudhary, N.; Masiwal, R.; Mandal, T.K.; Sharma, C. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of aerosol at an urban area of central Delhi, India. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, J.; Li, L.; Min, X.; Luo, Y. Pollution, ecological-health risks, and sources of heavy metals in soil of the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, G.; Zheng, W. Soil geochemical baseline and environmental background values of agricultural regions in Zhejiang province. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2007, 23, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, D.; Zhang, C.; Carton, O.T. Geostatistical analyses and hazard assessment on soil lead in silver mines area, Ireland. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 127, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, A.; Paramá, R. Spatial variability of soil elements in two plant communities of NW Spain. Geoderma 2007, 139, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, T.; Zhu, Q.; Zeng, M.; Shen, J.; Shi, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F.; Vries, W.D. Impacts of nitrogen fertilizer type and application rate on soil acidification rate under a wheat-maize double cropping system. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.-X.; Li, L.-Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.-K.; Sun, X.-B.; Xu, X.-B.; Jiang, D.-A. Organic carbon stock in topsoil of Jiangsu province, China, and the recent trend of carbon sequestration. J. Environ. Sci. 2004, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.L.; Minasny, B.; Wang, H.L.; Zhao, Y.G.; Zhang, G.L.; Wu, Y.J. Spatiotemporal modelling of soil organic matter changes in Jiangsu, China between 1980 and 2006 using inla-spde. Geoderma 2021, 384, 114808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diacono, M.; Montemurro, F. Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. Sustain. Agric. 2011, 2, 761–786. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; He, M.; Han, W.; Gu, Y. Analysis and assessment on heavy metal sources in the coastal soils developed from alluvial deposits using multivariate statistical methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Peng, S.; Mao, X.; Li, F.; Guo, S.; Shi, L.; Shi, Y.; Yu, H.; Zeng, G.-M. Source apportionment and spatial and quantitative ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from a typical Chinese agricultural county. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 126, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orescanin, V.; Barisic, D.; Mikelic, L.; Lovrencic, I.; Rubcic, M.; Rozmaric-Macefat, M.; Lulic, S. Environmental contamination assessment of the surroundings of the ex-sibenik’s ferro-manganese smelter, Croatia. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2004, 39, 2493–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragović, R.; Gajić, B.; Dragović, S.; Đorđević, M.; Đorđević, M.; Mihailović, N.; Onjia, A. Assessment of the impact of geographical factors on the spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils around the steel production facility in Smederevo (Serbia). J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 84, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.; Wang, J.; Qin, X.; Wang, K.; Han, P.; Zhang, S. Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and origin of heavy metals in the agricultural soils in Shunyi, Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 425, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Peng, C. Regional accumulation characteristics of cadmium in vegetables: Influencing factors, transfer model and indication of soil threshold content. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigalke, M.; Ulrich, A.; Rehmus, A.; Keller, A. Accumulation of cadmium and uranium in arable soils in Switzerland. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Mu, H.-y.; Fu, P.-n.; Wan, Y.-n.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.-f. Accumulation of potentially toxic elements in agricultural soil and scenario analysis of cadmium inputs by fertilization: A case study in Quzhou county. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 269, 110797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Lv, J. Identifying quantitative sources and spatial distributions of potentially toxic elements in soils by using three receptor models and sequential indicator simulation. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Guo, D.; Ali, A.; Mi, S.; Liu, T.; Ren, C.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z. Accumulation, ecological-health risks assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in paddy soils: A case study in Hanzhong, Shaanxi, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chang, Q.; Liu, J.; Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Kooistra, L. Identification of soil heavy metal sources and improvement in spatial mapping based on soil spectral information: A case study in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smichowski, P.; Gomez, D.; Frazzoli, C.; Caroli, S. Traffic-related elements in airborne particulate matter. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2008, 43, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.-M.; Wang, Q.-S.; Wen, H.-H.; Luo, J.; Wang, S. Heavy metals in agricultural soils from a typical township in Guangdong province, China: Occurrences and spatial distribution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Uría, A.; López-Mateo, C.; Roca, E.; Fernández-Marcos, M.L. Source identification of heavy metals in pastureland by multivariate analysis in NW Spain. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Xu, Z.; Ren, M.; Guo, Q.; Hu, X.; Hu, G.; Wan, H.; Peng, P. Source identification of eight hazardous heavy metals in agricultural soils of Huizhou, Guangdong province, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 78, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, S.; Wu, S.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Combining emission inventory and isotope ratio analyses for quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter/ Element | Min | Max | Mean | SD a | CV b(%) | Background of Zhejiang c | Screening Value d | Standard Exceeding Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 3.94 | 5.37 | 4.74 | 0.29 | 6.21 | —— | —— | —— |
| SOM e | 16.76 | 66.06 | 41.65 | 9.52 | 22.85 | —— | —— | —— |
| Cu | 10.80 | 57.00 | 30.26 | 8.39 | 27.72 | 17.6 | 50.00 | 3.96 |
| Zn | 141.40 | 532.20 | 271.50 | 71.71 | 26.41 | 70.6 | 200.00 | 86.14 |
| Pb | 59.50 | 361.60 | 151.41 | 58.30 | 38.50 | 23.7 | 80.00 | 97.03 |
| Cd | 0.11 | 0.95 | 0.37 | 0.15 | 40.17 | 0.07 | 0.30 | 70.30 |
| Cr | 17.30 | 159.00 | 47.81 | 10.05 | 21.03 | 52.9 | 250.00 | 0.00 |
| Ni | 6.99 | 71.60 | 39.07 | 15.25 | 39.03 | 24.60 | 60.00 | 0.99 |
| Point | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth | Clay | Silt | Sand | Clay | Silt | Sand | Clay | Silt | Sand | Clay | Silt | Sand |
| 0–20 cm | 8.5 | 55.6 | 35.9 | 6.2 | 52.8 | 41 | 8.2 | 46.7 | 45.1 | 11.3 | 46.8 | 41.9 |
| 20–40 cm | 10.2 | 52.4 | 37.4 | 8.5 | 50.4 | 41.1 | 5.3 | 43.1 | 51.6 | 13.6 | 54.2 | 32.2 |
| 40–60 cm | 32.5 | 43.7 | 23.8 | 27.6 | 41.5 | 30.9 | 15.6 | 35.4 | 49.3 | 28.2 | 45.7 | 26.1 |
| 60–80 cm | 35.3 | 45.2 | 19.5 | 32.4 | 43.2 | 24.4 | 24.8 | 38.4 | 36.8 | 22.4 | 38.4 | 39.2 |
| Element | APCS-MLR | UNMIX | PMF-1 Full Data | PMF-2 Eliminated Outliers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | 0.785 | 0.880 | 0.984 | 0.994 |
| Zn | 0.820 | 0.876 | 0.402 | 0.448 |
| Pb | 0.924 | 0.948 | 0.119 | 0.213 |
| Cd | 0.895 | 0.914 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Cr | 0.983 | 0.999 | 0.403 | 0.610 |
| Ni | 0.906 | 0.917 | 0.998 | 0.995 |
| Parameter/Element | pH | SOM | Cu | Zn | Pb | Cd | Cr | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1.000 | |||||||
| SOM | −0.228 * | 1.000 | ||||||
| Cu | −0.020 | 0.430 ** | 1.000 | |||||
| Zn | −0.225 * | 0.437 ** | 0.422 ** | 1.000 | ||||
| Pb | −0.030 | 0.130 | 0.346 ** | 0.405 ** | 1.000 | |||
| Cd | −0.190 | 0.487 ** | 0.170 | 0.546 ** | 0.060 | 1.000 | ||
| Cr | 0.130 | 0.090 | 0.308 ** | −0.080 | 0.010 | −0.236 * | 1.000 | |
| Ni | 0.020 | 0.395 ** | 0.567 ** | 0.277 ** | 0.090 | 0.266 ** | 0.204 * | 1.000 |
| Statistics | RI | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Zn | Pb | Cd | Cr | Ni | ||
| Min | 3.07 | 2.00 | 12.55 | 47.14 | 0.65 | 2.57 | 92.37 |
| Max | 16.19 | 7.54 | 76.29 | 407.14 | 9.79 | 26.32 | 489.68 |
| Mean | 8.60 | 3.85 | 31.94 | 160.01 | 2.56 | 10.69 | 217.65 |
| SD | 2.37 | 1.01 | 12.24 | 63.96 | 1.24 | 3.38 | 67.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, J.; Lanwang, K.; Liao, S.; Zhong, B.; Chen, Z.; Ye, Z.; Liu, D. Source Apportionment and Model Applicability of Heavy Metal Pollution in Farmland Soil Based on Three Receptor Models. Toxics 2023, 11, 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11030265
Ma J, Lanwang K, Liao S, Zhong B, Chen Z, Ye Z, Liu D. Source Apportionment and Model Applicability of Heavy Metal Pollution in Farmland Soil Based on Three Receptor Models. Toxics. 2023; 11(3):265. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11030265
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Jiawei, Kaining Lanwang, Shiyan Liao, Bin Zhong, Zhenhua Chen, Zhengqian Ye, and Dan Liu. 2023. "Source Apportionment and Model Applicability of Heavy Metal Pollution in Farmland Soil Based on Three Receptor Models" Toxics 11, no. 3: 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11030265
APA StyleMa, J., Lanwang, K., Liao, S., Zhong, B., Chen, Z., Ye, Z., & Liu, D. (2023). Source Apportionment and Model Applicability of Heavy Metal Pollution in Farmland Soil Based on Three Receptor Models. Toxics, 11(3), 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11030265





