Abstract
Cosmetic residues have been found in water resources, especially trace elements of precursors, couplers, and pigments of hair dyes, which are indiscriminately disposed of in the sewage system. These contaminants are persistent, bioactive, and bioaccumulative, and may pose risks to living beings. Thus, the present study assessed the ecotoxicity of two types of effluents generated in beauty salons after the hair dyeing process. The toxicity of effluent derived from capillary washing with water, shampoo, and conditioner (complete effluent—CE) and effluent not associated with these products (dye effluent—DE) was evaluated by tests carried out with the aquatic organisms Artemia salina, Daphnia similis, and Danio rerio. The bioindicators were exposed to pure samples and different dilutions of both effluents. The results showed toxicity in D. similis (CE50 of 3.43% and 0.54% for CE and DE, respectively); A. salina (LC50 8.327% and 3.874% for CE and DE, respectively); and D. rerio (LC50 of 4.25–4.59% and 7.33–8.18% for CE and DE, respectively). Given these results, we can infer that hair dyes, even at low concentrations, have a high toxic potential for aquatic biota, as they induced deleterious effects in all tested bioindicators.
1. Introduction
The aquatic environment is highly complex, characterized by diverse ecosystems such as rivers, lakes, estuaries, seas, and oceans [1]. However, this classification is simplistic, because these ecosystems are dynamic structures with specific characteristics [2]. When pollutants are released into the environment, they can disperse inside a distinct compartment, such as soil, water, and air, and be transported among them. Despite fabrication processes that generate distinct effluents, generally, cosmetics are released as domestic sewage, bypass the conventional wastewater treatment system (when present), and reach different receiving waters, such as freshwater bodies, and then marine environments [3]. During the movement of a contaminant, several interactions between abiotic and biotic factors occur, reaching exposed organisms. Once it enters into the biota, bioaccumulation becomes an impairment factor for living beings, and through the trophic chain, biomagnification worsens the scenario [4,5].
The integrity of aquatic ecosystems has been disturbed by anthropogenic activities, derived from changes in lifestyle, social context, agriculture, industry, and technological advances [6]. The changes in these environments happen directly or indirectly, and their ecotoxicological damage is unpredictable and of high complexity [7]. Hüttl et al. [7] also highlight that the maintenance of environmental quality will only be possible if interdisciplinary studies are implemented, which include a multifaceted view of the complexity of the environmental problem.
Regarding water sustainability, there is also a concern about establishing a water ethics program, with proposals for the conduct of rigid decisions, especially for natural environments that are little or not fully known [7]. This call for a new water ethics policy is also based on concerns about the increased degradation of water systems [7,8], To attend to the concept of “one health” (the decompartmentalization of human, animal, and ecosystem health) and reveal unknown impacts, the interlocution among different study areas should be strengthened, such as environmental chemistry, human toxicology, and ecotoxicology [9].
In recent years, some studies of aquatic ecosystems have shown the presence of traces of dyes, precursors, and couplers, whose origin would be from the process of hair dyeing [10]. The effluents generated in beauty salons are, in most cases, directly disposed of into the environment or incorporated into the urban sewer system. The characteristics of this effluent are much closer to industrial than to domestic effluent [5]. However, as the conventional system used in sewage treatment plants is not completely efficient for the removal of this pollutant, many cosmetic products remain in surface waters [5,11].
As an example, the work of Yurtsever [12] describes how glitter particles from some cosmetics are found in the environment, first in sewage sludge, then in rivers (water and sediment), and finally in oceans. Hair dyes also constitute a serious environmental threat, and their effluents must be investigated.
The indiscriminate disposal of toxic agents in the environment can be characterized as a risk factor for the survival of organisms [13,14], in a more intensive way for aquatic species whose entire life cycles can be assumed to be aqueous [15]. Considering the current high consumption of hair dyes and the dyeing process, beauty salons generate a large volume of complex effluents (with compounds belonging to groups of preservatives, humectants, organic solvents, surfactant oils, and also with dyes based on heavy metals, such as lead, cadmium, chromium, and arsenic) [16,17].
Studies of water quality and the polluting load of effluents are usually done by physicochemical analyses [18]. However, this type of evaluation is very limited, as the analyses are insufficient to estimate the real toxic potential of a given contaminant [19,20]. On the other hand, ecotoxicological studies allow the meticulous assessment of the toxicity of both effluents and their receiving bodies. These tests are performed with aquatic bioindicators of high sensitivity, whose patterns of effects may reflect the possible damages on other biological categories [21]. Bioindicators are tools widely used by environmental regulatory bodies [18] to identify effects on the aquatic biota of inland, estuarine, and marine waters, and can be used both in laboratory and field conditions [22].
With these tests, it is also possible to establish permissible limits for different substances, as well as to evaluate the impact of complex mixtures on the aquatic organisms of the receiving bodies [19]. According to Domingues and Bertoletti [23], when conducting ecotoxicological tests on aquatic organisms, it is important to use taxonomic groups that are representative of the ecosystem. Also, it is recommended to use organisms from different trophic levels to get an idea of the natural sensitivity variability of organisms in the ecosystem under consideration.
Given the health and environmental problems related to hair dyes, it is essential to conduct studies that help in understanding the interaction of these compounds with the aquatic biota, as well as the possible damage that these contaminants may induce in living beings in general. In the present study, by in vivo tests, the toxicity and embryotoxicity of two types of effluents generated in the hair dyeing process were evaluated on three bioindicators of various trophic levels: Artemia salina, Daphnia similis, and Danio rerio.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Obtaining, Storing, and Determining Effluent Samples
To perform the tests, effluents generated from the hair dyeing process were collected from a beauty salon (city of Rio Claro, São Paulo, Brazil). Two types of effluents were collected under the authorization of the owner of the establishment and its customers: (1) effluent derived from the freshly dyed hair washed using water, shampoo, and conditioner (complete effluent—CE); and (2) effluent composed of wash water and only the dye removed from the hair (dye effluent—DE), i.e., without shampoo and conditioner. Brown hair dye was applied to the hair according to the manufacturer’s instructions, for 40 min. Then, a complete wash was done (removal of excessive dye by washing with water, shampoo, and conditioner), generating CE. Following the same protocol of the dyeing process on another person, the washing was performed only with tap water (until the complete removal of the dye that was not fixed to the hair), generating DE. To remove possible impurities, such as hair strands, the samples were filtered by qualitative filter paper (80 g/m2) and stored, separately, in properly identified polypropylene carboys (20 L capacity—much more effluent was discarded). To avoid the degradation of the components of the effluents until the assembly of the tests, samples were stored in a freezer (−10 °C).
2.2. Treatments
The bioassays were performed with both types of effluents (DE and CE), followed by their respective control tests. The bioassays performed with A. salina and D. rerio were developed with the same concentrations/dilutions of DE and CE, as follows: pure sample (100%) and dilutions of 3.125, 6.25, 12.50, 25.00, and 50.00%. The bioassays with D. similis were performed with pure sample (100%) and dilutions of the effluents (1.00, 3.00, 3.125, 6.25, 12.50, 25.00, and 50.00%). For DE and CE EC50 determination, 0.5 and 5.0% treatments were added, respectively, for test validation.
2.3. Bioassays
2.3.1. Test Method with Artemia salina
The bioassays of acute ecotoxicity with Artemia salina followed the guideline of ABNT NBR 16530/2016 [24]. For greater reliability of the results obtained in the test, larvae (nauplii) were obtained from the hatching of selected and vacuum-packed cysts (Artemia salina RN®, Natal, Brazil) acquired in an aquarium store. The cysts and nauplii were maintained in optimal conditions of hatching and growth (25.0 ± 2.0 °C, salinity around 3.2%, and slightly alkaline pH ~8.0).
The experiment was carried out in a glass aquarium of 19 × 10 × 15 cm dimensions, with one of the walls covered by aluminum foil. The volume of the aquarium was separated into two parts by a partition plate, uniformly perforated (~2 mm in diameter, spaced by 4 mm). The aquarium received 500 mL of reconstituted water (synthetic seawater), prepared by dissolving commercial sea salt (Blue Treasure Reef Sea®, Qingdao Sea-Salt Aquarium Technology Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China) in distilled water, according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
The aquarium was accommodated in a biological oxygen demand (BOD) incubator with the temperature controlled at 25.0 ± 2.0 °C, constant aeration, and lighting. One of the parts of the aquarium received constant illumination (aquarium wall without aluminum foil cover), i.e., it was exposed to a fluorescent lamp of 15 W. The other part, covered with aluminum foil, and therefore without lighting (dark), received 0.3 g/L of A. salina cysts. The light/dark system of the aquarium was prepared to attract the newly hatched larvae to the light side, forcing them to cross the partition (through the holes) due to the positive phototropism they have, standardizing the organisms used in the test. Incubation was carried out for a period of 48 h.
After the incubation period, the A. salina nauplii were separated and exposed to different effluent dilutions (described in Section 2.2) for 48 h in a static system. Test tubes received 10 individuals and 10 mL of sample, and each treatment was organized in quadruplicate. Through the lethality results, the LC50 of the samples of each effluent was determined, characterizing the concentration responsible for causing death in 50% of the organisms.
The exposure of the organisms was accompanied by a negative control (NC), performed only with reconstituted water. In addition, the sensitivity of the bioindicator was ensured by exposure to a reference substance, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS—0.625, 1.25, 2.5, 5.0, 10.0, and 20.0 mg/L), solubilized in reconstituted water.
2.3.2. Test Method with Daphnia similis
The acute toxicity bioassays carried out with the microcrustacean Daphnia similis followed the guideline ABNT NBR 12713/2016 [25]. The individuals of D. similis used in the experiment were obtained from cultures maintained in the Water Toxicity Laboratory, from the Department of General and Applied Biology, São Paulo State University (UNESP), Rio Claro, Brazil. The cultures were maintained following the technical standards recommended by ABNT NBR 12713/2016 [25].
To assess the toxicity of the effluents, a total of five neonates, aged between 6 and 24 h, were exposed to 10 mL of the samples in treatments organized in quadruplicate. Different concentrations of the samples were evaluated (according to Section 2.2), accompanied by a negative control (NC), consisting only of diluted water (culture water of the organisms—hardness 40 mg/L to 48 mg/L and pH in the range of 7.2 to 7.6) [25]. The test tubes containing the organisms were kept in a BOD incubator at 20 ± 2 °C, in the dark, without feeding, for 48 h. At the end of the exposure period, the toxicity of the effluents was evaluated by the number of mobile and immobile organisms (lethality parameter).
2.3.3. FET Test
Zebrafish Maintenance and Spawning
The procedures for the care and use of animals were approved by the Ethiculture, and spawning and test procedures were conducted according to OECD guidelines (OECD No. 236, Commission, 2013) [26], in the Zebrafish Animal Laboratory located at UNIPEX—Experimental Research Unit of Botucatu Medical School, UNESP, Brazil, approved by CEUA n° 1392/2021.
Adult male and female zebrafish (Danio rerio) were kept separately in a recirculating aquaculture system containing mechanical biological filtration and disinfection. The temperature was 26.0 ± 1.0 °C in a 14 h light/10 h dark cycle. Water hardness was approximately 150 mg CaCO3/L and pH was 6.8 to 8.5. The dissolved oxygen concentration was above 6.0 mg/L. Fish were fed with Artemia salina three times daily. Sexually mature male and female zebrafish were transferred into a spawning tank separated by a partition and placed in a dark and quiet environment (2 males:1 female), and breeding began with the presence of light the following day. Approximately 35 min after spawning, fertilized eggs were collected and selected with an inverted microscope (Motic®, AE2000). Viable eggs were selected for the embryotoxicity test.
Fish Embryo Exposure Assays
The Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) test (OECD No. 236, Commission, 2013) [26] was performed in independent replicates with 24-well plates (SPL Life Sciences), one embryo per well. The experimental design consisted of four treatments with different dilutions for each effluent (DE and CE): 3.125, 6.25, and 12.5%; a negative control (NC) (reconstituted water—ISO-7346); and a positive control (4.0 mg/L 3,4-dichloroaniline). In the NC, 24 embryos were exposed to the ISO-7346 water. On the other plates, 20 eggs were exposed to each different dilution for each effluent (DE and CE), and four eggs in ISO-7346 water were the internal NC. For each effluent, three replicates were used (n = 3).
Embryonic development was evaluated at 8, 24, 48, 72, 96, 120, and 144 h post-fertilization (hpf) with an inverted microscope (AE2000, Motic®, Barcelona, Spain). Mortality was recorded daily according to lethality observations: coagulation of embryos, lack of somite formation, non-detachment of the tail, and lack of heartbeat. Microphotographs (24 and 144 hpf) were recorded with an Olympus MVX10 magnifier. Images were processed with Fiji-ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA). The LC50 (median lethal concentration—for embryo-lethality) was determined at 24, 96, and 144 hpf for DE and CE, and it was determined whether there was a significant difference in these values between the effluents. For DE LC50 determination, a 0.5% treatment was added for test validation.
2.4. Physicochemical Analysis
Water samples were measured after collection using the Horiba multiparameter probe (Multi Water Quality Checker U-50 Series, Kyoto, Japan). The parameters evaluated by the probe were: temperature, pH, conductivity, turbidity, dissolved oxygen, total dissolved solids, and salinity.
2.5. Spectrophotometric Analysis
The evaluation of the remaining concentration of hair dye in the effluents studied (DE and CE) was performed using UV-visible spectrophotometry (UV-5100, Global Trade Technology®, Jaboticabal, Brazil). For this, a standard solution was prepared with the commercial mixture at 12.0 g/L, the same used in the hair coloring process to obtain the effluents. Then, the absorbance reading was performed by spectrophotometry, using the external calibration method, to identify the wavelength of maximum light absorption by the mixture. The wavelength corresponding to maximum light absorption occurred at 290 nm. Thus, absorbance readings of the standard solution and different dilutions of the same mixture (0.6, 1.2, 2.4, 4.8, 6.0, and 12.0 g/L) were performed to obtain the standard curve by linear regression. After making the standard curve, an aliquot of each effluent was subjected to centrifugation for 4 min at 484× g (Centrifuge 80-2B, Centribio®, São Paulo, Brazil), to remove possible impurities, and read at 290 nm. Thus, based on the absorbances obtained, the concentration of the capillary dye mixture of each effluent was determined using the equation of linear regression [27,28,29].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
For D. rerio data, the median lethal concentrations of the effluents DE and CE were estimated using the GW-Basic 3.0 Software, according to the “Trimmed Spearman Karber” statistical method [30]. Differences in LC50 values were determined using Student’s t-test. The data obtained in this study were submitted for analysis of variance (one-way ANOVA). Shapiro-Wilk and Levene tests respectively verified the subjects of normality and homogeneity of the variances of the residues. When significant differences between treatments were detected (p < 0.05), Tukey’s a posteriori test was used. In the case of non-parametric data, the Kruskal-Wallis test was used, followed by the multiple comparison test as an a posteriori test [31].
The determinations of LC50 (A. salina) and EC50 (D. similis) were performed by the “Trimmed Spearman Karber” method, as described in ABNT NBR 16530/2016 and ABNT NBR 12713/2016, respectively [24,25].
3. Results
3.1. Artemia salina
The mortality of the bioindicator A. salina for the different dilutions of DE and CE is shown in Table 1. The results indicate mortality of 100% for concentrations of 25, 50 and 100% for both effluents and higher mean percentages for non-lethal DE concentrations. The estimated mean values for LC50 were statistically determined as 3.874% for DE and 8.327% for CE.

Table 1.
Mean mortality of Artemia salina during the 48-h exposure to different concentrations of DE and CE.
3.2. Daphnia similis
The mean mortality of D. similis exposed to the different dilutions of DE and CE effluents are shown in Table 2. The results indicate mortality of 100% for concentrations of 3.00, 3.125, 6.25, 12.50, 50.00, and 100.00% of the DE. The treatment performed with CE also induced mortality of 100% for the same concentrations, except for 3.00%. The mean EC50 values were statistically determined as 0.54% for DE and 3.43% for CE.

Table 2.
Mean mortality of Daphnia similis for 48 h exposure to different concentrations of DE and CE.
3.3. FET Test
The LC50 for 24 hpf for zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos exposed to DE was 7.33% (95% confidence interval: 6.25–8.65%) and to CE was 4.59% (95% confidence interval: 3.94–5.36%). At the end of the 144-h post-fertilization exposure, the LC50 was 8.18% (95% confidence interval: 7.13–9.4%) for DE and 4.25% (95% confidence interval: 3.67–4.93%,) for CE. The results of LC50 showed significant differences for all times of exposure (24, 96, and 144 hpf) between DE and CE (Table 3). Embryonic coagulation was the most observed lethal endpoint in DE and CE treatments (Figure 1). High mortality was verified at 24 hpf in the effluents at concentrations ≥6.25% (Figure 1a,b; examples of mortality are shown in Figure 1c). The data obtained showed that CE exposure is more toxic than exposure to DE for zebrafish embryo-larval development.

Table 3.
Results of LC50 after exposure to DE and CE during different periods (24, 96, and 144 hpf).
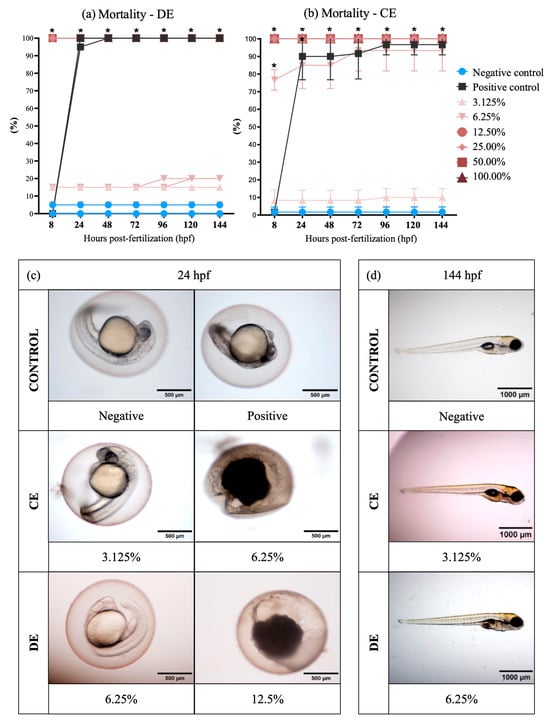
Figure 1.
Mortality in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. (a,b) Graphic representation of zebrafish embryo and larvae mortality, expressed by the proportion of coagulated eggs and absence of heartbeats per effluent, concentration, and exposure time. The negative control corresponds to the healthy embryos not exposed to effluents. Significant mortality of exposed zebrafish (p ≤ 0.05) relative to the control is identified with (*). Prepared with GraphPad Prism 5.01 software. (c) Micrographs showing zebrafish mortality: at the 6.125% dilution compared to negative control and the 3.125% dilution in the associated effluent (CE); and at the 12.5% dilution compared to the negative control and the 6.25% dilution in the non-associated effluent (DE) (2× magnification on MVX10 microscope, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). Photographs are representative (n = 3) and were taken at 24 hpf. (d) Micrographs showing zebrafish survival from dilutions of 3.125% in the associated effluent (CE) and 6.25% in the non-associated effluent (DE) at the end of the exposure (1.6× magnification on Olympus MVX10 microscope). Photographs are representative (n = 3) and were taken at 144 hpf.
The survivor embryos in CE treatments showed no malformations significantly up to 144 hpf (Figure 1d), but some results showed pericardial and yolk sac edema in embryos of DE treatments (Figure 2). The highest percentage of malformations was present at 48 h. After 120 h, the edema disappeared, showing an adaptive response of the embryo.
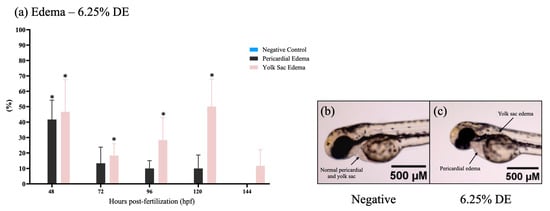
Figure 2.
Pericardial and yolk sac edema in zebrafish (Danio rerio). (a) Graphic representation of pericardial edema rate and yolk sac edema rate in zebrafish larvae expressed by the incidence of this effect by DE dilution 6.25%, and exposure time. The negative control corresponds to the healthy embryos not exposed to effluents. The incidence of exposed zebrafish was significant if (p ≤ 0.05) relative to the control, as identified with (*). Prepared with GraphPad Prism 5.01 software. (b) Micrograph of the absence of pericardial edema and yolk sac edema in the negative control. (c) Micrograph showing the presence of pericardial edema and yolk sac edema in zebrafish exposed to DE (non-associated) effluent at 6.25% dilution (1.6× magnification on Olympus MVX10 microscope). Photographs are representative (n = 3) and were taken at 72 hpf.
3.4. Physicochemical Analysis
The results of the physicochemical analyses of the DE and CE samples, obtained with the multiparameter probe (Table 4), showed differences in turbidity, for CE, and in dissolved oxygen and turbidity for DE, when compared with two Brazilian laws established by the National Environment Council (Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente—CONAMA—n° 357/2005 e n° 430/2011) [32,33] and an international document from the European Union concerning urban wastewater treatment (Council Directive nº 91/271/EEC of 21 May 1991; EUR-LEX, 1991) [34].

Table 4.
Results of physicochemical analyses of DE and CE samples, obtained with the multiparameter probe.
3.5. Spectrophotometric Analysis
The absorbance measured for DE was 0.192, and that for CE was 0.342. Thus, the concentration of the hair dye mixture was determined by the analytical curve (Figure 3), resulting in values of 1.505 g/L for CE and 0.895 g/L for DE.
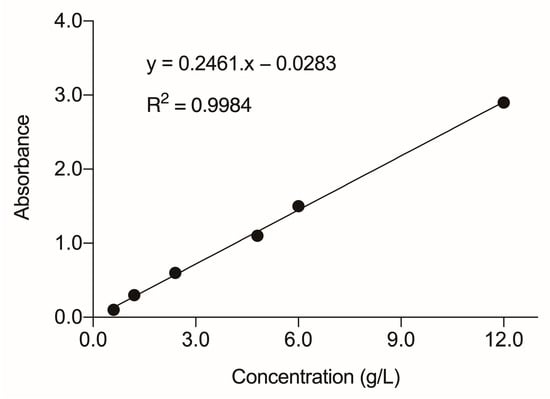
Figure 3.
Standard curve for hair dye mixture obtained by linear regression. Readings were performed at 290 nm, the most suitable wavelength for maximum light absorption.
4. Discussion
The assessment of the polluting loads of the studied effluents (DE and CE) was performed by physicochemical characterization, measured by a multiparameter probe. In this analysis, the parameters of pH, temperature, conductivity, dissolved oxygen, total soluble solids, turbidity, and salinity were considered. These parameters obeyed Resolution No. 357/2005 of CONAMA, which classifies Brazilian freshwater bodies into different categories, according to the water quality standards [32].
Another legislation used was Resolution No. 430/2011 of this same Brazilian council, which provides conditions, parameters, and standards for the discharge of effluents into water bodies [33]. According to the few reference parameters of this resolution, it is noted that the DE and CE presented temperature, pH, and salinity within the acceptable range. In addition to these Brazilian legislations used to classify the effluents studied here, the European Union Council Directive No. 91/271/EEC [34] was also considered to evaluate the quality of the effluents, regarding the requirements recommended at the international level.
The pH measured for both effluents (6.19 and 5.14 for DE and CE, respectively) is within the standards defined by Resolution 357/2005 [32] and by Resolution 430/2011 [33], which determines a pH range for effluents between 5.0 and 9.0. The determination of this pH range is due to the water quality safety policy because values below 5.0 or above 9.0 can cause a decrease in cellular activity, making survival impossible for aquatic organisms [32,33]. The pH is considered an important variable of water quality, as it influences several biological and chemical processes. Changes in pH can affect the survival of aquatic organisms as they have pH-dependent metabolic activities [35]. According to Omer [36], most aquatic organisms are already adapted to a specific pH and changes can impair their survival; a pH below 3.0 is commonly fatal. Also, this author highlights that pH affects the solubility of other chemicals in water, which endangers the exposed biota. The maintenance of the recommended values for this parameter is essential, as preserving the water quality also directly meets two of the goals established by the UN 2030 Agenda (goals 6 and 14) [37] and the water ethics policy [7,8].
According to the Annual Inland Water Quality Report in the State of São Paulo [38], Brazil, conductivity can be considered the numerical expression of the capacity of water to conduct electric current. That is, considering a freshwater environment, the conductivity value expresses the quantity of salt in the water, representing an indirect measure of pollutant concentration. Conductivity also acts as an indication of changes in water bodies, because this parameter tends to be constant when there is no anthropic interference in the environment [39].
Although there is no legislation that defines effluent conductivity limits, impacted environments are those that have conductivity levels higher than 100 μS/cm [40]. The DE and CE samples presented conductivity values higher than 100 μS/cm (391.0 and 204.0 μS/cm, respectively). Therefore, because this parameter is considered an indirect measure of the concentration of pollutants [40], it can be inferred that effluents contaminated with hair dye can compromise the water quality of their receiving water bodies.
Rodrigues et al. [41] suggest that the amounts of dye that are fixed in the hair may vary according to the type of dyed hair, a fact that could generate variation in the composition of the effluents of the hair washes. Considering this concern, in the present study a spectrophotometric analysis was performed to quantify the presence of brown hair dye in each of the effluents evaluated. In this analysis, a higher concentration of dye was observed in the CE (1.505 g/L) than in the DE (0.895 g/L), which can be explained by the use of shampoo during hair washing. Professional shampoos have ingredients in extremely concentrated forms or special anionic or cationic detergents, capable of removing the residues of chemicals applied in the hair coloring process [42].
Another physicochemical parameter considered in the present study was turbidity. This parameter scores the presence of solid particles in suspension [43]. However, although the parameters turbidity and total solids are associated with each other, they are not absolutely equivalent [44]. In the analysis performed with the studied effluents, both presented high turbidity values (369 NTU and 173 NTU for DE and CE, respectively) for Class 2 rivers, compared to the recommended value of ≤100 NTU (Resolution No. 357/2005). High turbidity values tend to compromise light scattering, which affects the process of photosynthesis and, consequently, the functioning of aquatic ecosystems [45].
Nkansah et al. [46] attribute the high turbidity of salon effluents to the cosmetics components, such as volatile organic compounds, methacrylates, phthalates, sulfates, parabens, and formaldehyde. The authors also highlight that the turbidity derived specifically from hair dyeing processes is related to the excess of emulsifiers, composed of precursor agents, couplers, and oxidants. The altered turbidity results of the DE and CE corroborate the pH and conductivity data, thus reaffirming the polluting potential of hair dyes for aquatic environments.
According to Article 18 of the V Decree No. 8468/1976 [47], effluents from any polluting source can only be released into water resources, directly or indirectly, if they present dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration greater than 5.0 mg/L. The DO value of CE (5.60 mg/L) was very close to the reference value mentioned above, whereas DE presented a value considerably lower (2.37 mg/L) than recommended by Brazilian law. This low concentration of DO is worrisome because this parameter is a limiting factor for the maintenance of aquatic life, as well as for the processes of self-purification of natural aquatic systems [48,49,50]. Oxygen is necessary for aerobic organisms [36], so its depletion impairs the physiological processes and metabolic rate of aquatic species [51]. These data corroborate the records for pH, conductivity, and turbidity, confirming, once again, the concern of releasing these effluents directly into water bodies.
The effluents analyzed presented characteristics that can compromise the receiving water body, especially if released without treatment and in low-flow rivers. However, as the composition of salon effluents may vary according to the hair coloring process and the use of additional products, traditional physicochemical analyses serve only to identify and quantify the present compounds, but not to evaluate the biological effects and their potential risk [52,53]. Thus, physicochemical analyses are important as auxiliary information to ecotoxicity tests.
Aquatic ecotoxicity analyses should be done in a multifaceted way, with bioindicators of distinct taxonomic groups and different trophic levels [23]. The analyses should also consider the variability of the organisms’ sensitivity and the possible impacts on the ecosystem. The species Daphnia similis, Artemia salina, and Danio rerio have been successfully applied in this type of evaluation, so they were used as bioindicators of this study.
The species D. similis is a freshwater microcrustacean (order Cladocera), also known as a water flea. It is a species widely used in ecotoxicity tests because of its place in the aquatic trophic chain as an important food source for fish [54,55,56]. The organism has a relatively short life cycle, is easy to grow in the laboratory, and, due to its small size, requires low volumes of samples to perform the tests. In addition, it is an organism that presents high sensitivity to several aquatic contaminants [57,58,59].
The assays developed with D. similis showed a high sensitivity to both samples (DE EC50 = 0.54%; CE EC50 = 3.43%), with DE being more toxic than CE for this species. Associating these EC50 results with the physicochemical profile, it is possible to link the higher toxicity of DE with the higher turbidity (369 NTU), higher conductivity (391.0 μS/cm), and lower DO concentration (2.37 mg/L) of this effluent. These results corroborate the data of Melo et al. [53,60], who also reported higher acute toxicity to D. similis when exposed to effluents from the hair products industry, whose turbidity ranged from 313 to 5000 NTU.
Another microcrustacean used in the ecotoxicity evaluations of this study was A. salina. This saltwater microcrustacean is widely used as live food for small fish, which are the main representatives of secondary consumers in the food chains of marine environments [61,62]. This species of the order Anostraca is considered a good indicator of toxicity due to its short life cycle (2 to 4 months); high sensitivity to toxic substances; small size (8 to 12 mm for adults); high adaptability to various test conditions; low cost and rapid response test; and availability of commercial cysts that can be stored and used for long periods [63,64,65,66,67]. Based on the results presented here, this bioindicator showed a higher ecotoxicity for DE (LC50 = 3.874%) when compared to CE (LC50 = 8.327%). Although the results obtained in this evaluation with A. salina were, in general, similar to those of D. similis, the latter was more sensitive. Studies conducted in joint trials with Daphnia sp. and Artemia sp. by de Vega et al. [68] and Favilla et al. [69] also showed higher sensitivity in Daphnia sp. However, the direct comparison of the sensitivity of both species should be performed with great caution because there is a difference in the complexity of these test organisms.
Fish can also be used as bioindicators of toxicity tests. Among the most used fish species in ecotoxicology is D. rerio, popularly known as zebrafish [70,71,72]. Zebrafish have characteristics that make them an excellent vertebrate animal model for toxicity assessment, such as small size; easy maintenance; high reproductive rate; easily observable and quantifiable behavior; and having about 70% genetic homology with mammals [73,74,75].
The bioassays with D. rerio performed in this study showed higher toxicity to CE compared to DE. We also observed an increase in toxicity after 144 h of exposure to both effluents (DE: 24 hpf − LC50 = 6.59%; 96 hpf − LC50 = 6.59%; 144 hpf − LC50 = 6.37% and CE: 24 hpf − LC50 = 4.93%; 96 hpf − LC50 = 3.90%; 144 hpf − LC50 = 3.90%). Generally, TiO2-NP is used in cosmetic products, mainly in the production of pigments [76,77], so the toxicity observed in this assay may be associated with the presence of these compounds in the studied hair dye (see the cosmetics ingredients in Supplementary Material Table S1). There is now a growing concern about the harmful effects of these nanoparticles, due to their ability to associate with colloids naturally present in the aquatic environment [77].
In this context, the greater toxicity presented by the CE can be attributed to the association of TiO2-NP with the organic matter of this effluent, since it presents, in addition to the components of the dye, ingredients of the shampoo and conditioner. Thus, it is possible to infer that the association of TiO2-NP with the components from shampoo and conditioner increases the toxicological potential of CE. According to Vale et al. [78], TiO2-NP can interact with molecules of the biotic and abiotic environment of natural systems, generating effects that remain unknown. Adam et al. [79] warn that the reactivity of TiO2-NP with other elements is one of the most important processes to understand and predict how these particles are transported in the environment and what could be their potential effects on organisms. According to the study developed by Zhu et al. [62], exposure to TiO2-NP resulted in toxic effects on embryos and larvae of D. rerio, which corroborates the information and discussions of the present study.
Egg mortality was another endpoint evaluated, and the egg coagulation process was evident after 144 hpf of exposure to DE (12.5%) and CE (3.125 and 6.25%). Some studies reinforce that the toxicity of dyes may be a result of the action of TiO2-NP. According to Chen [80] and Clemente et al. [81], TiO2-NP tend to adhere to the chorion of the egg, forming a white and black outer layer. This event was also observed in this study (Figure 1c), more intensely for CE exposure. This uncommon structure may have caused the coagulation of the eggs and the embryonic development disruption, observed in the highest concentrations of both effluents.
There is evidence that TiO2-NP can adhere to the chorion of the embryo, being absorbed and evenly distributed across the tissues of the fish, without any tissue specificity [82]. Also, some studies cite that TiO2-NP toxicity would be caused by dyspnea and hypoxia, resulting from their adsorption to the surfaces of respiratory organs and subsequent tissue damage [83,84].
The increase in toxicity, which occurred in a time-dependent manner for both effluents, can also be attributed to the interaction of TiO2-NP and chorion. Ma and Diamond [85] suggest that this interaction may interfere with the oxygen transport process and that waste products may generate reactive oxygen species (ROS). Among the possible changes in redox balance, TiO2-NP may accelerate the production of hydroxyl radical (·OH), through the reactions of Fenton and Haber–Weiss, because it is based on a transition metal. TiO2-NP can also dissociate into cations, promoting competition with enzymatic factors for the allosteric site of superoxide dismutase, causing its inhibition [86,87]. Thus, it is estimated that the production of ROS, over the exposure time, may cause an oxidative disturbance and, consequently, potentiate the toxicity of both DE and CE.
In addition, edema of the pericardium and yolk sac was observed after 72 hpf when exposed to 6.25% of DE. According to the literature, edema is characterized as an abnormal accumulation of fluid in any tissue of the body [88]. The appearance of pericardial edema may be associated with cardiac dysfunction, acting as an indicator of osmotic or metabolic dysfunction, which is often correlated with the extravasation of endothelial vessels [89,90].
Verma et al. [91] found morphological and anatomical changes in zebrafish when the animals were treated with lower (50 µg mL−1) and higher (250 μg mL−1) concentrations of TiO2. In addition, the authors also observed the presence of abnormalities, such as deformation of the chorion and yolk sac at 48 hpf, whereas flexed tails, notochord malformation, and abnormal heart development were identified at 96 hpf. These effects were related to the accumulation of TiO2-NP in the different tissues of the animals [91]. In their review work, Roberto and Christofoletti [92] point out additional studies regarding the possible effects of TiO2-NP on chordate animals, such as D. rerio, Pimephales promelas, and Xenopus laevis.
Therefore, the endpoints adopted in the environmental toxicity tests presented in this work clearly demonstrate that the effluents containing hair dyes induced significant losses in the three test organisms. Although the effects varied among the bioindicators, the effluents containing capillary dyes acted on multiple targets, which suggests that they could compromise the population dynamics of aquatic ecosystems.
5. Conclusions
Considering all of the results reported here, we can conclude that the effluents generated in beauty salons after the use of hair dye (in this case, the brown color), associated or not with shampoo and conditioner, present high toxic potential concerning the aquatic biota as they induced deleterious effects to all studied organisms (Daphnia similis, Artemia salina, and Danio rerio).
Among the species used in the present study, D. similis was the one with the highest sensitivity, followed by A. salina and D. rerio. Although it was possible to determine and differentiate the toxic sensitivities of each indicator, the tests performed with D. rerio allowed a slightly better understanding of the effects of hair dye effluents. However, additional studies are still needed to elucidate the possible mechanisms of action of these compounds on each of the organisms tested.
The ecotoxicological evaluation proposed here was developed through tests performed with organisms of different taxonomic groups and trophic levels, to simulate, in a simplified way, the impacts that hairdressing salon effluents promote in aquatic ecosystems when released into the environment. Our results are corroborated by other toxicity studies performed with hair dyes, so it can be concluded that this class of effluent must receive specific prior treatment before being discarded in the environment. This study also provides support and highlights the need to create water ethics policies, especially concerning emerging contaminants from cosmetics, whose disposal is not yet regulated.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/toxics11110911/s1, Table S1: Components of brown hair dye, shampoo and hair conditioner.
Author Contributions
L.C.G.: Conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, writing—original draft preparation, visualization. M.M.R.: Conceptualization, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision. P.V.L.P.: Methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation. C.V.: Methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation. A.F.C.d.S.: Methodology, validation. V.J.A.d.O.: Methodology, validation. M.C.C.N.: Methodology, validation, formal analysis. L.C.P.: Conceptualization, writing—review and editing, project administration, supervision, resources, funding acquisition. D.d.F.d.A.: Conceptualization, methodology, resources. M.A.M.-M.: Conceptualization, writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration, resources, funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by CNPq—National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, Project PP n306062/2019-4.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee CEUA of UNESP, Brazil (protocol code n° 1392/2021 of 31 August 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sieber, G.; Beisser, D.; Bock, C.; Boenigk, J. Protistan and fungal diversity in soils and freshwater lakes are substantially different. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Tiwari, A.; Kaushik, R.; Iqbal, H.M.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Diatoms recovery from wastewater: Overview from an ecological and economic perspective. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 39, 101705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ashokkumar, V.; Amobonye, A.; Bhattacharjee, G.; Sirohi, R.; Singh, V.; Flora, G.; Kumar, V.; Pillai, S.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Current research trends on cosmetic microplastic pollution and its impacts on the ecosystem: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 320, 121106. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, A.; Naz, A.; Maiti, S.K. Distribution, speciation, and bioaccumulation of potentially toxic elements in the grey mangroves at Indian Sundarbans, in relation to vessel movements. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 189, 106042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin-Crini, N.; Lichtfouse, E.; Liu, G.; Balaram, V.; Ribeiro, A.R.L.; Lu, Z.; Stock, F.; Carmona, E.; Teixeira, M.R.; Picos-Corrales, L.A.; et al. Worldwide cases of water pollution by emerging contaminants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2311–2338. [Google Scholar]
- Coronado-Apodaca, K.G.; González-Meza, G.M.; Aguayo-Acosta, A.; Araújo, R.G.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, R.B.; Oyervides-Muñoz, M.A.; Martínez-Ruiz, M.; Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Barceló, D.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; et al. Immobilized Enzyme-based Novel Biosensing System for Recognition of Toxic Elements in the Aqueous Environment. Top. Catal. 2023, 66, 606–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüttl, R.F.; Bens, O.; Bismuth, C.; Hoechstetter, S.; Frede, H.-G.; Kümpel, H.-J. Introduction: A Critical Appraisal of Major Water Engineering Projects and the Need for Interdisciplinary Approaches. In Society-Water-Technology: A Critical Appraisal of Major Water Engineering Projects; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A. Ethical issues in water use and sustainability. Area 2006, 38, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.T.; Ågerstrand, M.; Brooks, B.W.; Allen, J.; Bertram, M.G.; Brodin, T.; Dang, Z.; Duquesne, S.; Sahm, R.; Hoffmann, F.; et al. The Role of Behavioral Ecotoxicology in Environmental Protection. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5620–5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, R.M.; Morel, O.J.X. The Coloration of Human Hair. In The Coloration of Wool and other Keratin Fibres; Lewis, D.M., Rippon, J.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 357–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arman, N.Z.; Salmiati, S.; Aris, A.; Salim, M.R.; Nazifa, T.H.; Muhamad, M.S.; Marpongahtun, M. A Review on Emerging Pollutants in the Water Environment: Existences, Health Effects and Treatment Processes. Water 2021, 13, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurtsever, M. Glitters as a Source of Primary Microplastics: An Approach to Environmental Responsibility and Ethics. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2019, 32, 459–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Mehmood, S.; Iqbal, H.M.N. The Beast of Beauty: Environmental and Health Concerns of Toxic Components in Cosmetics. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, F.; Qureshi, I.Z.; Ali, M. Histopathological changes in the kidney of common carp, Cyprinus carpio, following nitrate exposure. J. Res. 2004, 15, 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.X. Incorporating exposure into aquatic toxicological studies: An imperative. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 105, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavithra, K.G.; Jaikumar, V. Removal of colorants from wastewater: A review on sources and treatment strategies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 75, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maifadi, S.; Mhlanga, S.D.; Nxumalo, E.N.; Motsa, M.M.; Kuvarega, A.T. Carbon nanotube embedded ultrafiltration membranes for the treatment of rapid granular multimedia prefiltered beauty hair salon and municipal wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 267, 118618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freddi, L.A.; Américo-Pinheiro, J.H.P. Ecotoxicidade de Efluentes Para Organismos Aquáticos. Rev. Científica ANAP Bras. 2017, 10, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagatto, P.A. Ecotoxicologia Aquática: Princípios e Aplicações. In Proceedings of the 2015: IV Seminário sobre Ecotoxicologia, São José do Barreto, Macaé, RJ, Brazil, 10–12 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues-Chaparro, T.R.; Cleto- Pires, E.C. Toxicity evaluation as a tool to assess the performance of an anaerobic immobilized biomass reactor. Dyna 2010, 77, 284–291. [Google Scholar]
- De Paiva Magalhães, D.; Da, A.; Filho, S.F. A ecotoxicologia como ferramenta no biomonitoramento de ecossistemas aquáticos a ecotoxicologia como ferramenta no biomonitoramento de ecossistemas aquáticos. Oecol. Bras. 2008, 12, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, T.F.G.; de Ferreira, K.S.; Rojas, I.E.B.; Pompêo, M. Aspectos da Ecotoxicidade em Ambientes Aquáticos; Instituto de Biociências da USP: São Paulo, Brazil, 2022; 274p. [Google Scholar]
- Domingues, D.F.; Bertoletti, E. Seleção, Manutenção e Cultivo de Organismos Aquáticos. In Ecotoxicologia Aquática—Princípios e Aplicações; Editora Rima: São Carlos, Brazil, 2006; pp. 153–184. [Google Scholar]
- ABNT—Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. NBR 16530. Ecotoxicologia Aquática—Toxicidade Aguda—Método de Ensaio Com Artemia sp. (Crustacea, Brachiopoda); ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- ABNT—Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. NBR 12713. Ecotoxicologia Aquática—Toxicidade Aguda—Método de Ensaio Com Daphnia sp. (Crustacea, Cladocera); ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2: Effects on Biotic Systems Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test; Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 2013; Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-236-fish-embryo-acute-toxicity-fet-test_9789264203709-en (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Rocha, F.R.P.; Teixeira, L.S.G. Estratégias Para Aumento de Sensibilidade em Espectrofotometria UV-VIS. Química Nova 2004, 27, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holler, F.J.; Skoog, D.A.; Crouch, S.R.; Pasquini, C.J.; Rohwedder, J.J.R. Princípios de Análise Instrumental, 6th ed.; Bookman: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Canassa, T.A.; Lamonato, A.L.; Ribeiro, A.V. Utilização da Lei de Lambert-Beer Para Determinação da Concentração de Soluções. J. Exp. Tech. Instrum. 2018, 1, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, M.A.; Russo, R.C.; Thurston, R.V. Trimmed Spearman-Karber Method for Estimating Median Lethal Concentrations in Toxicity Bioassays. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1977, 11, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of Embryonic Development of the Zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CONAMA—Conselho Nacional de Meio Ambiente. Dispõe Sobre a Classificação Dos Corpos de Água e Diretrizes Ambientais Para Seu Enquadramento, Bem Como Estabelece as Condições e Padrões de Lançamentos de Efluentes. Resoluções no 357, de 17 de março de 2005. Available online: https://www.mpf.mp.br/atuacao-tematica/ccr4/dados-da-atuacao/projetos/qualidade-da-agua/legislacao/resolucoes/resolucao-conama-no-357-de-17-de-marco-de-2005/at_download/file (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- CONAMA—Conselho Nacional de Meio Ambiente CONAMA No 430 de 13 de maio de 2011. Diário Oficial da União. Republica Federativa do Brasil, P.E.B.D. 16 mai. 2011, Ed. 2011. Available online: https://conexaoagua.mpf.mp.br/arquivos/legislacao/resolucoes/resolucao-conama-430-2011.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- EUR-LEX; Council of the European Communities. Council Directive of 21 May 1991 Concerning Urban Waste Water Treatment (91/271/EEC); Official Journal of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Osibanjo, O.; Daso, A.P.; Gbadebo, A.M. The impact of industries on surface water quality of River Ona and River Alaro in Oluyole Industrial Estate, Ibadan, Nigeria. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 696–702. [Google Scholar]
- Omer, N.H. Water Quality Parameters. In Water Quality—Science, Assessments and Policy; Summers, J.K., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- ONU—Organização das Nações Unidas. Take Action for the Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals (accessed on 26 July 2023).
- CETESB. Companhia Ambiental do Estado de São Paulo Qualidade Das Águas Interiores No Estado de São Paulo. Apêndice C—Significado Ambiental e Sanitário Das Variáveis de Qualidade Das Águas e Dos Sedimentos e Metodologias Analíticas e de Amostragem 2021. Available online: https://cetesb.sp.gov.br/aguas-interiores/wp-content/uploads/sites/12/2022/11/Apendice-C-Significado-ambiental-e-sanitario-das-variaveis-de-qualidade-das-aguas-e-dos-sedimentos-e-metodologias-analiticas-e-de-amostragem.pdf (accessed on 26 July 2023).
- Maciel, M.A.M.; Dos Reis, S.M.; Ramalho, H.M.M. Águas Potáveis: Padrões de Qualidade, Metodologias Experimentais e Técnicas de Purificação; Amplla Editora: Campina Grande, Brazil, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Abreu, C.H.M.; Cunha, A.C. Qualidade Da Água e Índice Trófico em Rio de Ecossistema Tropical Sob Impacto Ambiental. Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2016, 22, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.C.; Oliveira, J.T.; Pires, M.J.R.; Bernardes, A.M.H. A Estudo Da Oxidação Fotoquímica em Efluentes Líquidos Gerados em Salões de Beleza. In Simpósio Internacional de Qualidade Ambiental; ABES-RS: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2016; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- D’Souza, P.; Rathi, S.K. Shampoo and Conditioners: What a Dermatologist Should Know? Indian J. Dermatol. 2015, 60, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameen, H.A. Spring Water Quality Assessment Using Water Quality Index in Villages of Barwari Bala, Duhok, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRASIL, Ministério da Saúde; Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde. Vigilância e Controle da Qualidade da Água Para Consumo Humano; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2006.
- Health Canada. Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality: Guideline Technical Document—Turbidity; Water, Air and Climate Change Bureau, Healthy 105 Environments and Consumer Safety Branch, Health Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2012.
- Nkansah, M.A.; Opoku, F.; Ephraim, J.H.; Wemegah, D.D.; Tetteh, L.P.M. Characterization of Beauty Salon Wastewater from Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi, Ghana, and Its Surrounding Communities. Environ. Health Insights 2016, 10, EHI-S40360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SÃO PAULO Decreto No 10.755, de 22 de Novembro de 1977. Dispõe Sobre o Enquadramento Dos Corpos Receptores Na Classificação Prevista No Decreto No 8.468, de 08 de Setembro de 1976 e Dá Providências Correlatas; Diário Oficial do Estado de São Paulo, Ed.; Caderno Executivo, n. 221: São Paulo, Brazil, 1976. Available online: https://www.al.sp.gov.br/repositorio/legislacao/decreto/1977/decreto-10755-22.11.1977.html (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Oliveira, G.H.; Pinto, A.L.; Pereira, G.A. Avaliação da eficiência da utilização do oxigênio dissolvido como principal indicador da qualidade das águas superficiais da bacia do córrego bom jardim, Brasilândia/MS. Rev. Geomae 2010, 1, 69–82. [Google Scholar]
- Queiroz, J.F.; Boeira, R.C. Boas Práticas de Manejo Para Manter Concentrações Adequadas de Oxigênio Dissolvido em Viveiros de Piscicultura; Embrapa Meio Ambiente: Jaguariúna, Brazil, 2016; Available online: https://ainfo.cnptia.embrapa.br/digital/bitstream/item/172486/1/2017CT03.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- CETESB—Companhia Ambiental do Estado de São Paulo. Matéria Orgânica e Nutrientes; São Paulo. 2019. Available online: https://cetesb.sp.gov.br/mortandade-peixes/alteracoes-fisicas-e-quimicas/materiaorganica-e-nutrientes/#targetText=A%20mat%C3%A9ria%20org%C3%A2nica%20sofre%20um,do%20oxig%C3%AAnio%20presente%20no%20meio.&targetText=O%20processo%20de%20enriquecimento%20das,vinhoto%2C%20acarretando%20graves%20problemas%20ambientais (accessed on 14 June 2023).
- Ferreira, A.L.G.; Loureiro, S.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Toxicity prediction of binary combinations of cadmium, carbendazim and low dissolved oxygen on Daphnia magna. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 89, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdigón-Melón, J.A.; Carbajo, J.B.; Petre, A.L.; Rosal, R.; García-Calvo, E. Coagulation–Fenton Coupled Treatment for Ecotoxicity Reduction in Highly Polluted Industrial Wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, E.D.; Mounteer, A.H.; Leão, L.H. de S.; Bahia, R.C.B.; Campos, I.M.F. Toxicity Identification Evaluation of Cosmetics Industry Wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knie, J.L.W.; Lopes, E.W.B. Testes Ecotoxicológicos: Métodos, Técnicas e Aplicações; FATMA/GTZ: Florianópolis, Brazil, 2004; 289p. [Google Scholar]
- Personne, E.; Loubet, B.; Herrmann, B.; Mattsson, M.; Schjoerring, J.K.; Nemitz, E.; Sutton, M.A.; Cellier, P. SURFATM-NH3: A Model Combining the Surface Energy Balance and Bi-Directional Exchanges of Ammonia Applied at the Field Scale. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 1371–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, S.L.; Cáceres, C.E.; Rogers, D.C. Cladocera and Other Branchiopoda. In Ecology and Classification of North American Freshwater Invertebrates; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 773–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteeg, D.J.; Stalmans, M.; Dyer, S.D.; Janssen, C. Ceriodaphnia and Daphnia: A Comparison of Their Sensitivity to Xenobiotics and Utility as a Test Species. Chemosphere 1997, 34, 869–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radix, P.; Léonard, M.; Papantoniou, C.; Roman, G.; Saouter, E.; Gallotti-Schmitt, S.; Thiébaud, H.; Vasseur, P. Comparison of Brachionus Calyciflorus 2-d and Microtox® Chronic 22-h Tests with Daphnia magna 21-d Test for the Chronic Toxicity Assessment of Chemicals. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 2178–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, C. Química Ambiental, 2nd ed.; Bookman: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2002; 622p. [Google Scholar]
- De Melo, E.D.; Mounteer, A.; Reis, E.; Costa, E.; Vilete, A. Screening of Physicochemical Treatment Processes for Reducing Toxicity of Hair Care Products Wastewaters. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 212, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, J.M.; Bomm, M.D.; Pereira, N.F.G.; Garcez, W.S.; Boaventura, M.A.D. Estudo Fitoquímico de Unonopsis Lindmanii—Annonaceae, Biomonitorado Pelo Ensaio de Toxicidade Sobre a Artemia salina Leach. Química Nova 1998, 21, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhu, L.; Duan, Z.; Qi, R.; Li, Y.; Lang, Y. Comparative Toxicity of Several Metal Oxide Nanoparticle Aqueous Suspensions to Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Early Developmental Stage. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2008, 43, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, P.; Benova, K.; Vitek, J. Alternative Biotest on Artemia franciscana. In Ecotoxicology, 1st ed.; Begum, G., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Mu, J.; Han, J.; Gu, X. An Improved Brine Shrimp Larvae Lethality Microwell Test Method. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2011, 22, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, A.C.; Piovezan, M. Bioensaio Toxicológico Utilizando Artemia salina: Fatores Envolvidos Em Sua Eficácia. Instituto Federal de Santa Catarina. 2015. Available online: http://docente.ifsc.edu.br/michael.nunes/MaterialDidatico/Analises%20Quimicas/TCC%20II/TCC%202015%202/Ariele.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Libralato, G.; Prato, E.; Migliore, L.; Cicero, A.M.; Manfra, L. A Review of Toxicity Testing Protocols and Endpoints with Artemia Spp. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntungwe, N.E.; Domínguez-Martín, E.M.; Roberto, A.; Tavares, J.; Isca, V.M.S.; Pereira, P.; Cebola, M.-J.; Rijo, P. Artemia Species: An Important Tool to Screen General Toxicity Samples. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 2892–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, A.C.S.; Cruz-Alcalde, A.; Mazón, C.S.; Diaz-Cruz, M.S. Nano-TiO2 Phototoxicity in Fresh and Seawater: Daphnia magna and Artemia Sp. as Proxies. Water 2020, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favilla, M.; Macchia, L.; Gallo, A.; Altomare, C. Toxicity assessment of metabolites of fungal biocontrol agents using two different (Artemia salina and Daphnia magna) invertebrate bioassays. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 1922–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, R.; Gerlach, G.; Lawrence, C.; Smith, C. The Behaviour and Ecology of the Zebrafish, Danio rerio. Biol. Rev. 2008, 83, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Costa, A.; Shepherd, I.T. Zebrafish Development and Genetics: Introducing Undergraduates to Developmental Biology and Genetics in a Large Introductory Laboratory Class. Zebrafish 2009, 6, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluru, N. Epigenetic Effects of Environmental Chemicals: Insights from Zebrafish. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2017, 6, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kari, G.; Rodeck, U.; Dicker, A.P. Zebrafish: An Emerging Model System for Human Disease and Drug Discovery. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 82, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieschke, G.J.; Currie, P.D. Animal Models of Human Disease: Zebrafish Swim into View. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The Zebrafish Reference Genome Sequence and Its Relationship to the Human Genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, F.; Perales-Perez, O.J.; Hwang, S.; Román, F. Antimicrobial Nanomaterials as Water Disinfectant: Applications, Limitations and Future Perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.N. Do Nanoparticles Present Ecotoxicological Risks for the Health of the Aquatic Environment? Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, G.; Mehennaoui, K.; Cambier, S.; Libralato, G.; Jomini, S.; Domingos, R.F. Manufactured Nanoparticles in the Aquatic Environment-Biochemical Responses on Freshwater Organisms: A Critical Overview. Aquatic. Toxicol. 2016, 170, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, V.; Loyaux-Lawniczak, S.; Labille, J.; Galindo, C.; del Nero, M.; Gangloff, S.; Weber, T.; Quaranta, G. Aggregation Behaviour of TiO2 Nanoparticles in Natural River Water. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2016, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G. Electrochemical Technologies in Wastewater Treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 38, 11–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, Z.; Castro, V.L.S.S.; Moura, M.A.M.; Jonsson, C.M.; Fraceto, L.F. Toxicity Assessment of TiO2 Nanoparticles in Zebrafish Embryos under Different Exposure Conditions. Aquatic. Toxicol. 2014, 147, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Ilan, O.; Louis, K.M.; Yang, S.P.; Pedersen, J.A.; Hamers, R.J.; Peterson, R.E.; Heideman, W. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Produce Phototoxicity in the Developing Zebrafish. Nanotoxicology 2012, 6, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.; Fang, T.; Yu, L.; Sima, X.; Zhu, W. Effects of Nano-Scale TiO2, ZnO and Their Bulk Counterparts on Zebrafish: Acute Toxicity, Oxidative Stress and Oxidative Damage. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, D.; Al-Bairuty, G.A.; Henry, T.B.; Handy, R.D. Critical Comparison of Intravenous Injection of TiO2 Nanoparticles with Waterborne and Dietary Exposures Concludes Minimal Environmentally-Relevant Toxicity in Juvenile Rainbow Trout Oncorhynchus Mykiss. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Diamond, S.A. Phototoxicity of TiO2 Nanoparticles to Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Is Dependent on Life Stage. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 2139–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercal, B.; Gurer-Orhan, B.; Nukhet Aykin-Burns, B. Toxic Metals and Oxidative Stress Part I: Mechanisms Involved in Metal-Induced Oxidative Damage. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2005, 1, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, R.R. Leukocytes and Oxidative Stress: Dilemma for Sperm Function and Male Fertility. Asian J. Androl. 2011, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Hua, L.; Zhang, D.; Hu, T.; Ge, Z.L. Maternal Periodontal Disease and Risk of Preeclampsia: A Meta-Analysis. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol.—Med. Sci. 2014, 34, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejana, E.; Tournier-Lasserve, E.; Weinstein, B.M. The Control of Vascular Integrity by Endothelial Cell Junctions: Molecular Basis and Pathological Implications. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallare, A.V.; Schirling, M.; Luckenbach, T.; Köhler, H.R.; Triebskorn, R. Combined Effects of Temperature and Cadmium on Developmental Parameters and Biomarker Responses in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. J. Therm. Biol. 2005, 30, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.K.; Jha, E.; Panda, P.K.; Mukherjee, M.; Thirumurugan, A.; Makkar, H.; Das, B.; Parashar, S.K.S.; Suar, M. Mechanistic Insight into ROS and Neutral Lipid Alteration Induced Toxicity in the Human Model with Fins (Danio rerio) by Industrially Synthesized Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Toxicol. Res. 2018, 7, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, M.M.; Christofoletti, C.A.; Roberto, M.M.; Christofoletti, C.A. How to Assess Nanomaterial Toxicity? An Environmental and Human Health Approach. In Nanomaterials—Toxicity, Human Health and Environment; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).