Assessment of Genotoxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Mosquito as Test Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Dose
2.2. Determination of LD20 of ZnO NPs for Mosquito C. quinquefasciatus
2.3. Treatment of Larvae with the Selected Dose
2.4. Preparation of Chromosomal Slides
2.5. Sperm Head Assay
2.6. Dominant Lethal Test
3. Results
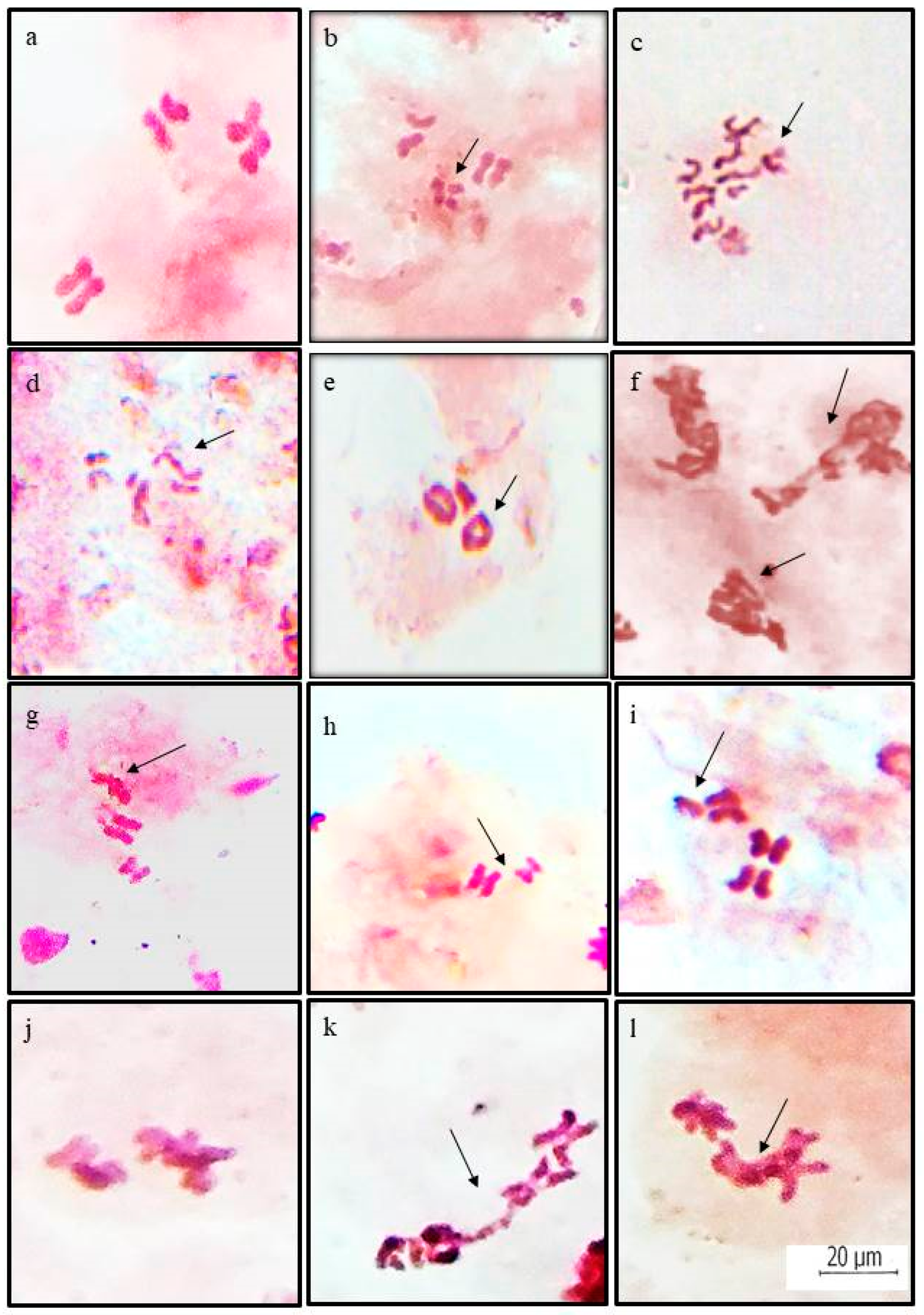
3.1. Chromosomal Aberrations
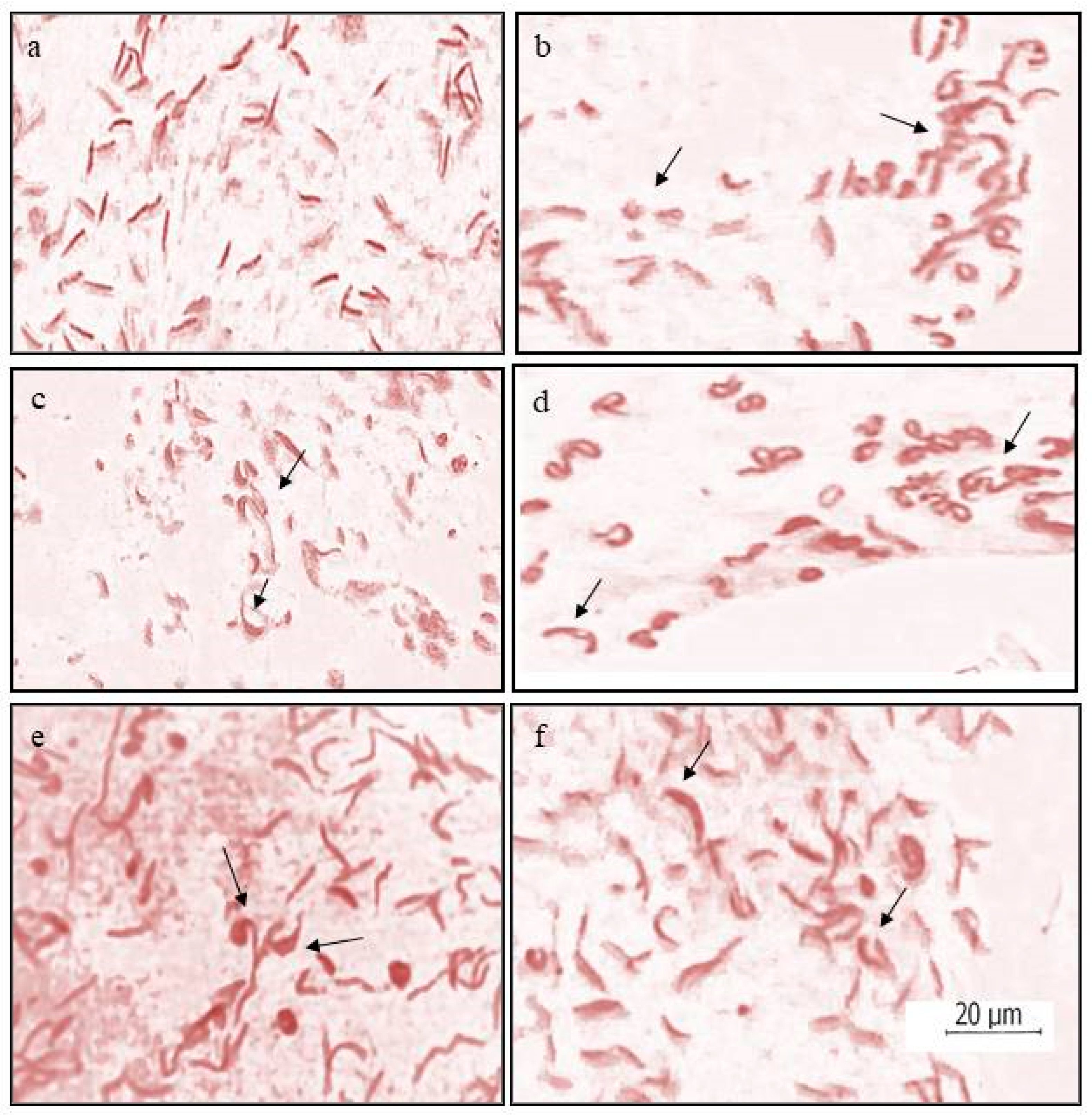
3.2. Sperm Head Assay
3.3. Dominant Lethal Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wahab, R.; Mishra, A.; Yun, S.I.; Kim, Y.S.; Shin, H.S. Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles prepared via non-hydrolytic solution route. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.J.; Li, H.; Zhang, T.; Song, B.; Wang, X.; Gu, Z. Recent Advances in ZnO Nanomaterial-Mediated Biological Applications and Action Mechanisms. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.D.; Stotland, M.; Ellis, J.I. The safety of nanosized particles in titanium dioxide and zinc oxide based sunscreens. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009, 61, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin Sevinç, B.; Hanley, L. Antibacterial activity of dental composites containing zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 94, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espitia, P.J.P.; Soares, N.D.F.F.; Dos Reis Coimbra, J.S.; De Andrade, N.J.; Cruz, R.S.; Medeiros, E.A.A. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, antimicrobial activity and food packaging applications. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 1447–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, H.; Darroudi, M. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: Biological synthesis and biomedical applications. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmanullah, M.Z.; Inayat, N.; Majeed, A. Application of nanoparticles in agriculture as fertilizers and pesticides: Challenges and opportunities. In New Frontiers in Stress Management for Durable Agriculture; Rakshit, A., Singh, H.B., Singh, A.K., Singh, U.S., Fraceto, L., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 281–293. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Pi, J.; Cai, J. The advancing of zinc oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raha, S.; Ahmaruzzaman, M. ZnO nanostructured materials and their potential applications: Progress, challenges and perspectives. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 1868–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, M. Low power and stable resistive switching in graphene oxide-based RRAM embedded with ZnO nanoparticles for nonvolatile memory applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 17545–17557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, S.; Basciu, I.; Vocciante, M.; Ferretti, M. Experimental and physico-chemical comparison of ZnO nanoparticles’ activity for photocatalytic applications in wastewater treatment. Catalysts 2021, 11, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishnav, J.; Subha, V.; Kirubanandan, S.; Arulmozhi, M.; Renganathan, S. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Celosia argentea and its characterization. J. Optoelectron. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 9, 59–71. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, Y.; Guan, J. Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for cancer therapy. Smart Mater. Med. 2020, 1, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.A.; Das, J.; Sil, P.C. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: A comprehensive review on its synthesis, anticancer and drug delivery applications as well as health risks. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 286, 102317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowack, B.; Bucheli, T.D. Occurrence, behavior and effects of nanoparticles in the environment. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.W.; Li, M.; Cui, Y.B.; Li, D.S.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.Y. Toxicological effects of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles in soil on earthworm Eisenia fetida. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, S.; Rocco, A.; Carotenuto, R.; Picione, F.D.L.; Miglietta, M.L.; Rametta, G.; Francia, D.I. Investigation of ZnO nanoparticles’ ecotoxicological effects towards different soil organisms. Environ.Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohynek, G.J.; Antignac, E.; Re, T.; Toutain, H. Safety assessment of personal care products/cosmetics and their ingredients. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 243, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmond, M.J.; McCall, M.J. Zinc oxide nanoparticles in modern sunscreens: An analysis of potential exposure and hazard. Nanotoxicology 2010, 4, 15–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iavicoli, I.; Leso, V.; Beezhold, D.H.; Shvedova, A.A. Nanotechnology in agriculture: Opportunities, toxicological implications, and occupational risks. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 329, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebi, A.R.; Khorsandi, L.; Moridian, M. The effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on mouse spermatogenesis. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2013, 30, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, A.; Karimi, F.; Fatahian, S.; Yazdani, F. Effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on renal function in mice. Int. J. Biosci. 2014, 5, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.Q.; Xu, M.; Rong, Q.; Jin, R.W.; Liu, Q.J.; Li, Y. The effect of ZnO nanoparticles on liver function in rats. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 4275–4285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pati, R.; Das, I.; Mehta, R.K.; Sahu, R.; Sonawane, A. Zinc-oxide nanoparticles exhibit genotoxic, clastogenic, cytotoxic and actin depolymerization effects by inducing oxidative stress responses in macrophages and adult mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 150, 454–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahdar, A.; Hajinezhad, M.R.; Bilal, M.; Askari, F.; Kyzas, G.Z. Behavioral effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the brain of rats. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 119, 108131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, L.K.; Lyon, D.Y.; Alvarez, P.J. Comparative eco-toxicity of nanoscale TiO2, SiO2, and ZnO water suspensions. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3527–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, D.; Fang, T.; Yu, L.; Sima, X.; Zhu, W. Effects of nano-scale TiO2, ZnO and their bulk counterparts on zebrafish: Acute toxicity, oxidative stress and oxidative damage. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.M.; Behal, A.; Sushkova, S.N.; Mandzhieva, S.; Singh, R.; Movsesyan, H.S. Effects of zinc-oxide nanoparticles on soil, plants, animals and soil organisms: A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2018, 9, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Peijnenburg, W.J. Toxicity of mixtures of zinc oxide and graphene oxide nanoparticles to aquatic organisms of different trophic level: Particles outperform dissolved ions. Nanotoxicology 2018, 12, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stałanowska, K.; Szablińska-Piernik, J.; Okorski, A.; Lahuta, L.B. Zinc oxide nanoparticles affect early seedlings’ growth and polar metabolite profiles of pea (Pisum sativum L.) and wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Kim, R.O.; Yoon, S.; Kim, W.K. Developmental toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to zebrafish (Danio rerio): A transcriptomic analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, A.R.; Rebelo, S.; Pereira, M.D.L. The impact of zinc oxide nanoparticles on male (in) fertility. Materials 2020, 13, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.P.; Sobti, R.C.; Chaudhry, A.; Gill, R.K.; Ahluwalia, K.K. Mutagenic potential of a substituted urea herbicide, Monuron. Cytologia 1987, 52, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sharma, G.P.; Sobti, R.C.; Chaudhry, A.; Ahluwalia, K.K. Genotoxicity of two heavy metal compounds-lead acetate and mercuric chloride in the mosquito, Anopheles stephensi Liston (Culicidae: Diptera). Cytologia 1988, 53, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.P.; Sobti, R.C.; Chaudhry, A.; Ahluwalia, K.K. Chromosome aberrations and dominant lethals in Culex fatigans due to mercuric chloride. Cytobios 1989, 59, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, G.P.; Chaudhry, A.; Ahluwalia, K.K. Genotoxic effect of three N-oxidized derivatives of o-toluidine on the germ cells of a mosquito, Culex fatigans (Culicidae: Diptera). Res. Bull. Panjab Univ. Sci. 1989, 40, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ahluwalia, K.K.; Chaudhry, S. Genotoxic potential of mercuric nitrate in Culex quinquefasciatus. Res. Bull. Panjab Univ. 1999, 49, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ahluwalia, K.K. Mutagenic potential of nickel nitrate in mosquito Culex fatigans. In Perspectives and Trends, Science Technology and Environment; Ahluwalia, A.S., Gaur, R., Eds.; Panjab University: Chandigarh, India, 2014; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Marwaha, L. In vivo genotoxicity evaluation of carbaryl pesticides using polytene chromosomes of Anopheles culicifacies (Diptera: Culicidae). Toxicol. Int. 2016, 23, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, D.J. A statistical treatment of the sigmoid response curve. In Probit Analysis, 3rd ed.; Finney, D.J., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1971; p. 333. [Google Scholar]
- Crozier, R. An acetic acid dissociation, air-drying technique for insect chromosomes, with aceto-lactic orcein staining. Stain Technol. 1968, 43, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdolenova, Z.; Collins, A.; Kumar, A.; Dhawan, A.; Stone, V.; Dusinska, M. Mechanisms of genotoxicity. A review of in vitro and in vivo studies with engineered nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 233–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Khan, S.S.; Pakrashi, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Cytogenetic and genotoxic effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on root cells of Allium cepa. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Sinha, S.; Jothiramajayam, M.; Jana, A.; Nag, A.; Mukherjee, A. Cyto-genotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by zinc oxide nanoparticle in human lymphocyte cells in vitro and Swiss albino male mice in vivo. Food Chem.Toxicol. 2016, 97, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastav, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Prakash, J.; Singh, D.; Jagdale, P.; Shankar, J.; Kumar, M. Genotoxicity evaluation of zinc oxide nanoparticles in Swiss mice after oral administration using chromosomal aberration, micronuclei, semen analysis, and RAPD profile. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2017, 33, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ickrath, P.; Wagner, M.; Scherzad, A.; Gehrke, T.; Burghartz, M.; Hagen, R.; Hackenberg, S. Time-dependent toxic and genotoxic effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles after long-term and repetitive exposure to human mesenchymal stem cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gümüş, D.; Berber, A.A.; Ada, K.; Aksoy, H. In vitro genotoxic effects of ZnO nanomaterials in human peripheral lymphocytes. Cytotechnology 2014, 66, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Naqvi, A.H.; Ahmad, M. Comparative study of the cytotoxic and genotoxic potentials of zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, A.G.C.; do Amaral, D.F.; Benvindo-Souza, M.; Rocha, T.L.; Silva, D.D.M. Genotoxic and mutagenic effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles and zinc chloride on tadpoles of Lithobates catesbeianus (Anura: Ranidae). Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaymurat, T.; Gu, J.; Xu, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y. Phytotoxic and genotoxic effects of ZnO nanoparticles on garlic (Allium sativum L.): A morphological study. Nanotoxicology 2012, 6, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, M.S.; Elamawi, R.M. Evaluation of phytotoxicity, cytotoxicity, and genotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles in Vicia faba. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18972–18984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borboa, L.; De la Torre, C. The genotoxicity of Zn (II) and Cd (II) in Allium cepa root meristematic cells. New Phytol. 1996, 134, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Lucas, B.; Schrand, A.; Murdock, R.C.; Lee, T.; Schlager, J.J.; Hofmann, M.C. Silver nanoparticles disrupt GDNF/Fyn kinase signaling in spermatogonial stem cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 116, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borm, P.J.; Kreyling, W. Toxicological hazards of inhaled nanoparticles–potential implications for drug delivery. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2004, 4, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, B.; Hong, W.; Chen, L.; Yao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H. ZnO nanoparticles induced male reproductive toxicity based on the effects on the endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling pathway. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2019, 11, 9563–9576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S. Retention of particles in Caenohabditis elegans after exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2014, 3, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Brayner, R.; Ferrari-Iliou, R.; Brivois, N.; Djediat, S.; Benedetti, M.F.; Fievet, F. Toxicological impact studies based on Escherichia coli bacteria in ultrafine ZnO nanoparticles colloidal medium. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S. Zinc oxide nanoparticles impacts: Cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, developmental toxicity, and neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2019, 29, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Singh, P.; Pandey, A.K.; Dhawan, A. Induction of oxidative stress, DNA damage and apoptosis in mouse liver after sub-acute oral exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2012, 745, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Tang, C.; Lin, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, T.; Lan, W.; Cheng, R.; Lin, Y.; Chang, H.; Jeng, J. Toxic mechanisms of Roth801, canals, microparticles and nanoparticles of ZnO on MG-63 osteoblasts. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2021, 119, 111635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, H.A.; Swanson, J. Toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles in mammalian cells. J. Environ. Sci. Health A. 2006, 41, 2699–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Shukla, R.K.; Saxena, N.; Parmar, D.; Das, M.; Dhawan, A. DNA damaging potential of zinc oxide nanoparticles in human epidermal cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 185, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, S.; Oliviero, M.; Miglietta, M.; Rametta, G.; Manzo, S. Genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of ZnO nanoparticles for Dunaliella tertiolecta and comparison with SiO2 and TiO2 effects at population growth inhibition levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.T.; Yong, L.Q.; Hande, M.P.; Ong, C.N.; Yu, L.E.; Bay, B.H.; Baeg, G.H. Zinc oxide nanoparticles exhibit cytotoxicity and genotoxicity through oxidative stress responses in human lung fibroblasts and Drosophila melanogaster. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1621–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Cheng, S.; Singh, S. Oxidative stress-mediated genotoxic effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on Deinococcus radiodurans. 3 Biotech. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, J.; Felder, E.; Tahir, M.N.; Kaltbeitzel, A.; Heinrich, U.R.; Brochhausen, C.; Brieger, J. Genotoxic effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2015, 19, 8931–8938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, T.J.; Wick, P.; Manser, P.; Spohn, P.; Grass, R.N.; Limbach, L.K.; Stark, W.J. In vitro cytotoxicity of oxide nanoparticles: Comparison to asbestos, silica, and the effect of particle solubility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4374–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimercati, L.; Cavone, D.; Caputi, A.; De Maria, L.; Tria, M.; Prato, E.; Ferri, G.M. Nanoparticles: An experimental study of zinc nanoparticles toxicity on marine crustaceans. General overview on the health implications in humans. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kononenko, V.; Repar, N.; Marušič, N.; Drašler, B.; Romih, T.; Hočevar, S.; Drobne, D. Comparative in vitro genotoxicity study of ZnO nanoparticles, ZnO macroparticles and ZnCl2 to MDCK kidney cells: Size matters. Vitr. Toxicol. 2017, 40, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Mashayekhi, H.; Xing, B. Bacterial toxicity comparison between nano—and micro-scaled oxide particles. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona, E.R.; Inostroza, B.C.; Rubio, L.; Marcos, R. Genotoxic and oxidative stress potential of nanosized and bulk zinc oxide particles in Drosophila melanogaster. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2016, 32, 1987–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
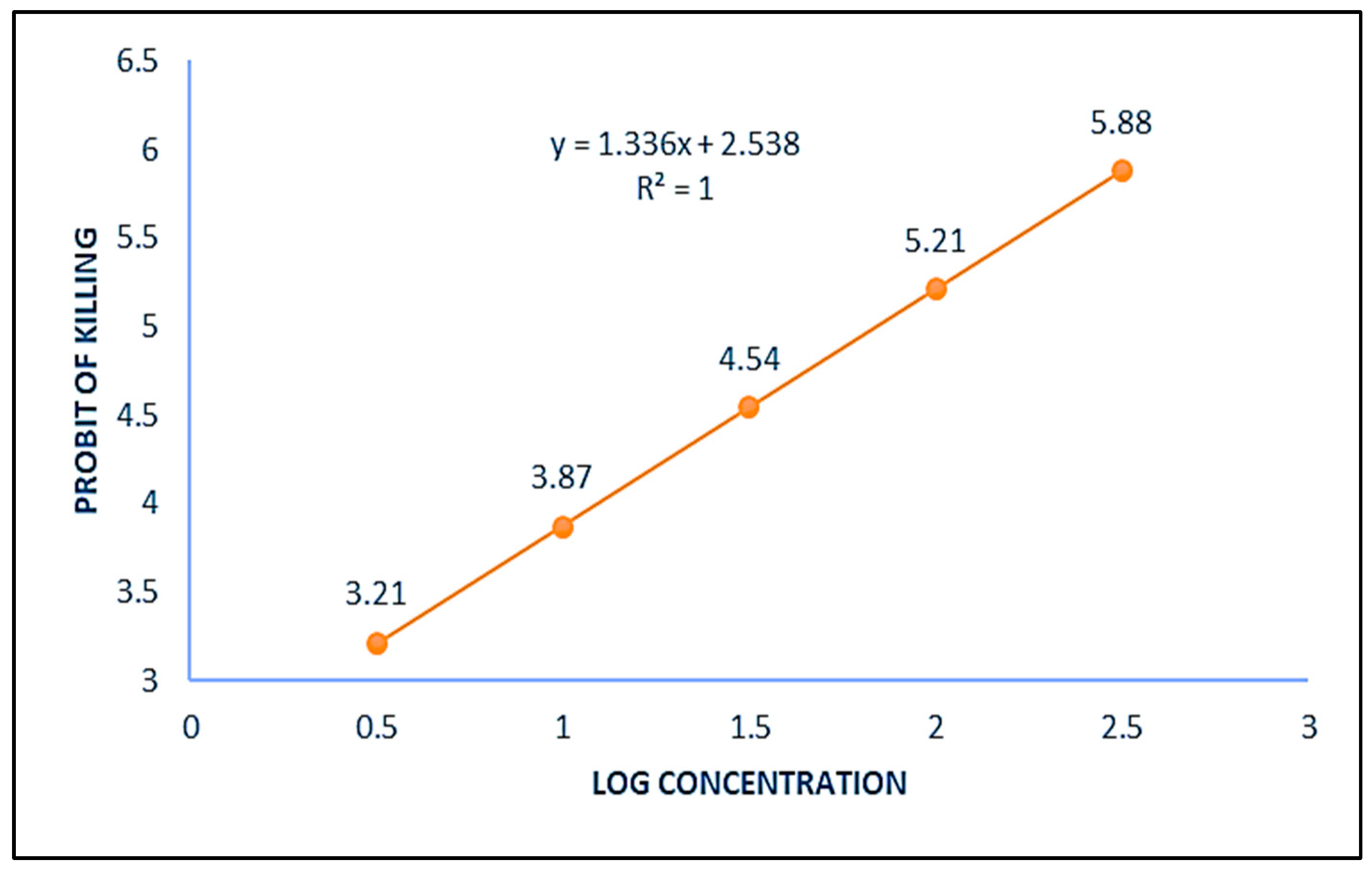

| S. No. | Dose/Concentration (µg/mL) | No of Larvae Treated (n) | No of Insect Killed (r) | Percent Mortality (r/n × 100) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10,000 | 40 | 34 | 85 |
| 2 | 1000 | 40 | 30 | 75 |
| 3 | 100 | 40 | 31 | 77.5 |
| 4 | 10 | 40 | 13 | 32.5 |
| 5 | 1 | 40 | 12 | 30 |
| 6 | Control | 40 | 2 | 5 |
| Treatment | Chromosomal Aberrations * | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structural Aberrations (S) | Numerical Aberrations (N) | Total Structural Aberrations | Total Numerical Aberrations | Total Aberrations | ||||||||
| Aneuploids | ||||||||||||
| Breaks | Fragments | Translocations | Clumped Chromosomes | Terminal fusions | (2n − 1) | (2n − 2) | (2n + 1) | (2n + 2) | S | N | S + N | |
| ZnO NPs | 3.68 ± 0.78 | 3.33 ± 0.83 | 4.08 ± 1.16 | 8.33 ± 1.10 | 2.41 ± 0.72 | 1.16 ± 0.65 | 1.58 ± 0.33 | 1.16 ± 1.16 | 1.91 ± 0.33 | 21.83 ± 3.04 | 5.81 ± 1.16 | 27.64 ± 3.33 |
| Control | 0.76 ± 0.76 | 0.83 ± 0.41 | 0.83 ± 0.41 | 1.91 ± 0.33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.41 ± 0.41 | 0 | 4.33 ± 0.41 | 0.41 ± 0.41 | 4.74 ± 0.72 |
| Treatment | Sperm Head Abnormalities * | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sickle Shaped | Oval | Triangular | Vacuolated | Total | |
| ZnO NPs | 10.20 ± 1.95 | 0.99 ± 0.19 | 0.22 ± 0.05 | 0.22 ± 0.05 | 11.63 ± 1.99 |
| Control | 0.88 ± 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.93 ± 0.11 |
| Treatment | Replicates | Total Eggs/Egg Raft | Unhatched Eggs | % of Unhatched Eggs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1 | 315 | 7 | 2.22 |
| 2 | 287 | 3 | 1.04 | |
| 3 | 301 | 4 | 1.32 | |
| ZnO NPs | 1 | 178 | 22 | 12.35 |
| 2 | 141 | 17 | 12.05 | |
| 3 | 239 | 34 | 14.22 |
| Treatment | No. of Egg Rafts Counted | % Age Frequency of Unhatched Eggs (Mean ± S.E.) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 3 | 1.53 ± 0.366 |
| ZnO NPs | 3 | 12.87 ± 0.679 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahluwalia, K.K.; Thakur, K.; Ahluwalia, A.S.; Hashem, A.; Avila-Quezada, G.D.; Abd_Allah, E.F.; Thakur, N. Assessment of Genotoxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Mosquito as Test Model. Toxics 2023, 11, 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110887
Ahluwalia KK, Thakur K, Ahluwalia AS, Hashem A, Avila-Quezada GD, Abd_Allah EF, Thakur N. Assessment of Genotoxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Mosquito as Test Model. Toxics. 2023; 11(11):887. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110887
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhluwalia, Kanwaljit Kaur, Kritika Thakur, Amrik Singh Ahluwalia, Abeer Hashem, Graciela Dolores Avila-Quezada, Elsayed Fathi Abd_Allah, and Neelam Thakur. 2023. "Assessment of Genotoxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Mosquito as Test Model" Toxics 11, no. 11: 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110887
APA StyleAhluwalia, K. K., Thakur, K., Ahluwalia, A. S., Hashem, A., Avila-Quezada, G. D., Abd_Allah, E. F., & Thakur, N. (2023). Assessment of Genotoxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Mosquito as Test Model. Toxics, 11(11), 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110887







