The Patterns of Migration of Potentially Toxic Elements from Coal Mining Subsidence Areas and Associated Soils to Waterlogged Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.2. Assessment of Trace Metal Pollution in Sediment
2.3. Sediment Quality Guidelines (SQGs)
2.4. Ecological Risk Assessment
2.5. Human Health Risk Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Differences in PTE Content among the Five Water Areas with Coal Mining Subsidence
3.2. Ecological Risk Assessment
3.3. Health Risk Assessment
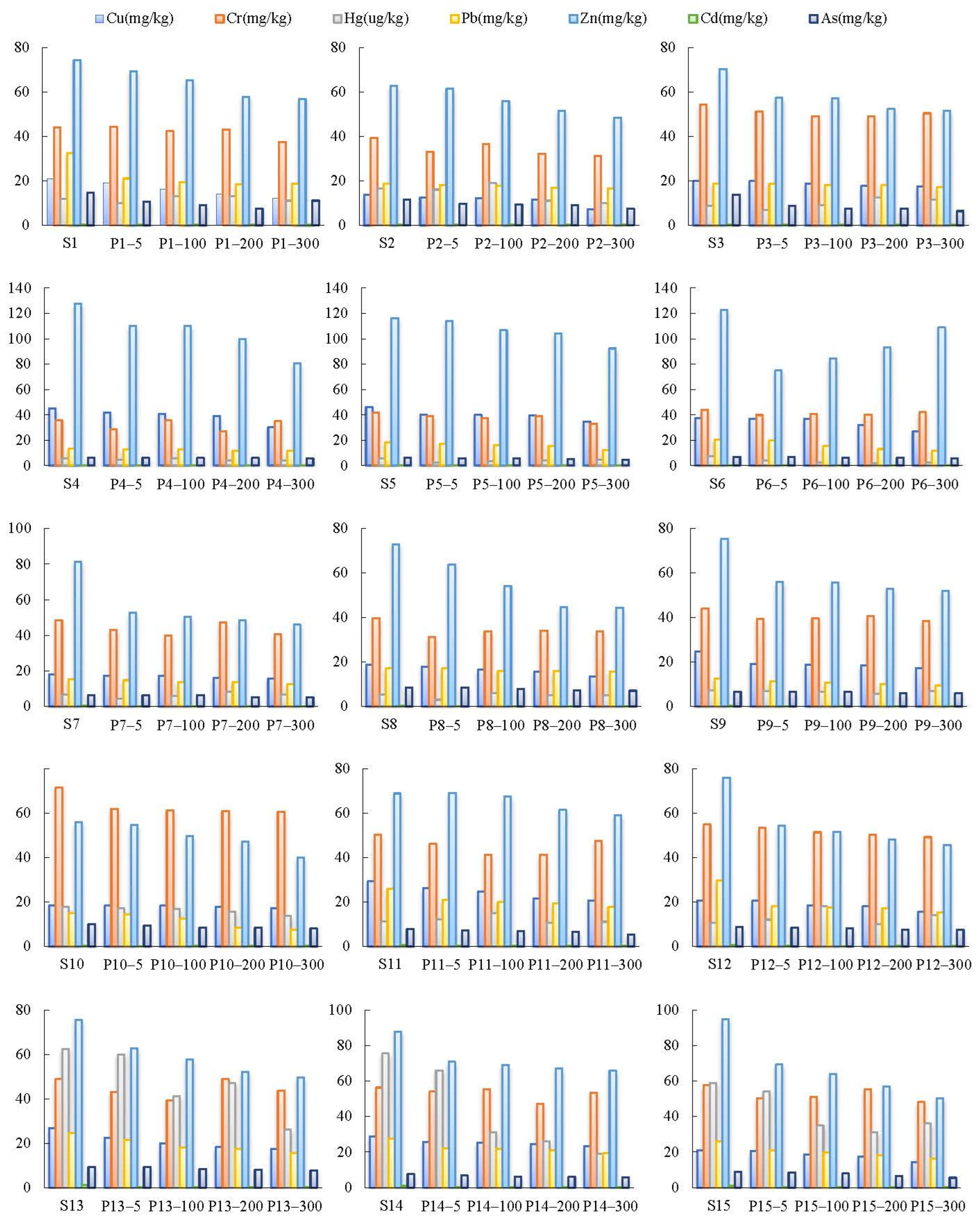
3.4. Variation Trends of Soil PTEs at Different Distances
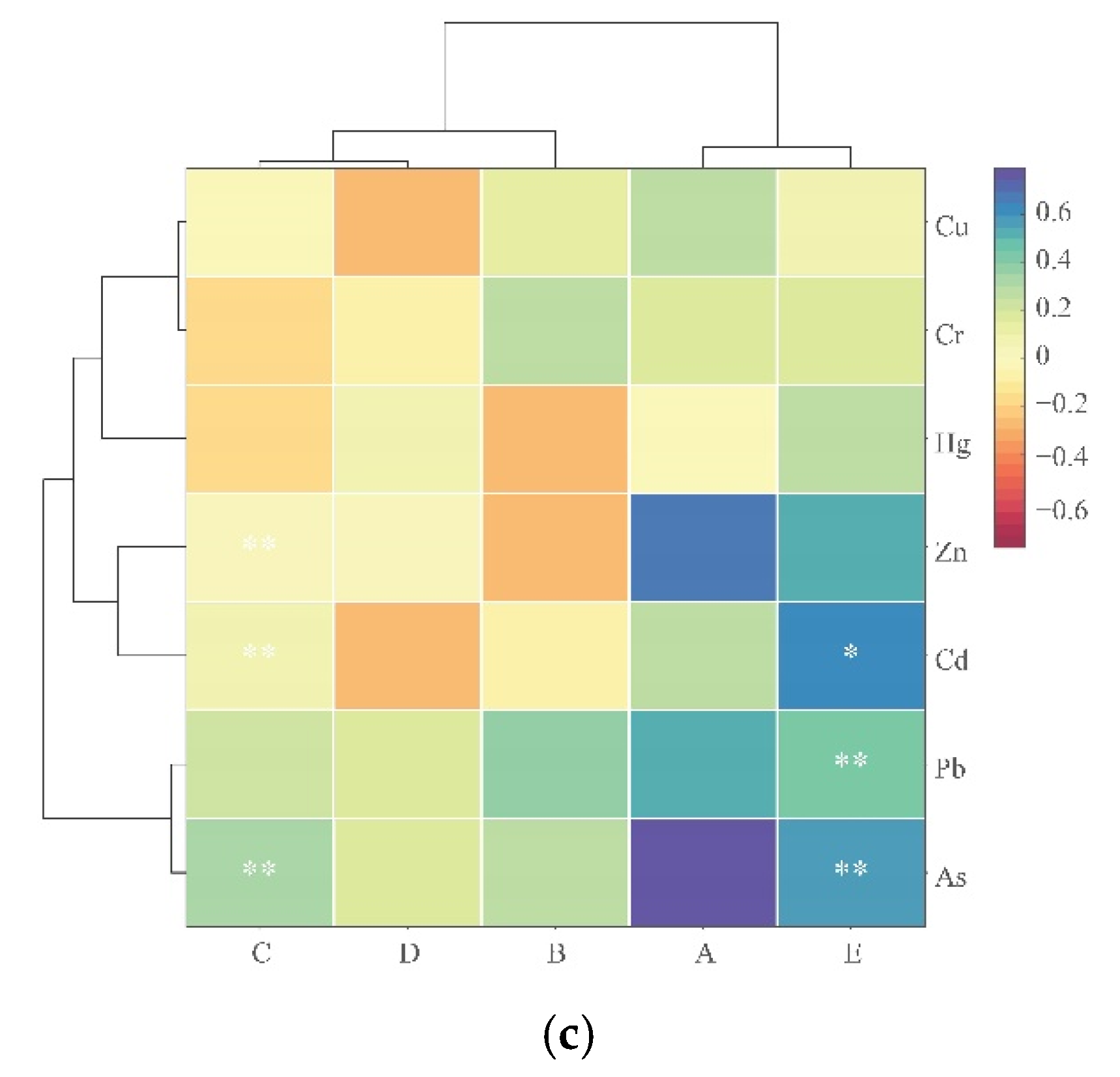
3.5. Analysis of the Correlation between PTE Content and Distance, SOC, and pH
4. Discussion
4.1. Developing as Landscaped Wetlands, Fish Farming, Fish–Photovoltaic Complementary Wetland, and Photovoltaic Wetlands Can All Help Reduce the Comprehensive PTE Pollution in Waterlogged Areas with Coal Mining Subsidence
4.2. Cu Showed Clear Diffusion Patterns
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, W.; Xu, R.; Li, X.; Min, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Li, J. Soil reconstruction and heavy metal pollution risk in reclaimed cultivated land with coal gangue filling in mining areas. Catena 2023, 228, 107147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Bian, Z.; Dong, J.; Hao, M.; Qu, J. Comparing the variation and influencing factors of CO2 emission from subsidence waterbodies under different restoration modes in coal mining area. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 116936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ning, Z.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, P.; Sun, R.; Yang, X.; Liu, H. A novel calculation method of subsidence waterlogging spatial information based on remote sensing techniques and surface subsidence prediction. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 335, 130366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Qu, X.; Xie, K. Eutrophication and nutrient limitation in the aquatic zones around Huainan coal mine subsidence areas, Anhui, China. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Xiao, W. Optimization of concurrent mining and reclamation plans for single coal seam: A case study in northern Anhui, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Liu, G. Distribution and potential ecological risk of heavy metals accumulated in subsidence lakes formed in the Huainan Coalfield, China. Environ. Forensics 2017, 18, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Chen, G. Characteristics of Water Pollution and Evaluation of Water Quality in Subsidence Water Bodies in Huainan Coal Mining Areas, China. J. Chem. 2022, 2022, 2857700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defera, J.; Wogi, L.; Mishra, B.B. Assessment of Physicochemical Properties of Soil under Different Land Use Types at Wuye Gose Sub-Watershed, North Shoa Zone of Oromia Region, Ethiopia. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2019, 3, 34–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelaki, A.; Dionysidis, A.; Sihag, P.; Golia, E.E. Assessment of Contamination Management Caused by Copper and Zinc Cations Leaching and Their Impact on the Hydraulic Properties of a Sandy and a Loamy Clay Soil. Land 2022, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Biggs, A.J.W.; Marchuk, A.; Bennett, J.M. Effect of Irrigation Water pH on Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity and Electrokinetic Properties of Acidic, Neutral, and Alkaline Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2019, 83, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Chu, Z.X.; Yu, X.K.; Fan, T.Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.M.; Xu, X.P.; Zhen, Q.; Cheng, X.J.; et al. Influence of Solar Photovoltaic System on the Concentration and Environmental Risks of Heavy Metals in Subsidence Pond Water from Coal Mining Area: A Case Study from Huainan Subsidence Pond. Water 2022, 14, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, C.; Sun, Q.; Xiao, W.; Cao, G.; Li, H.; Yan, L.; Zhang, B. Simulating the hydrologic cycle in coal mining subsidence areas with a distributed hydrologic model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Su, L.J.; Chen, X.X.; Liu, C.F.; Sun, A.G. A boundary model of terrain reconstruction in a coal-mining subsidence waterlogged area. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Gao, X.; Jiang, J.; Yang, L.; Li, Y. Characteristic Analysis of Water Quality Variation and Fish Impact Study of Fish-Lighting Complementary Photovoltaic Power Station. Energies 2020, 13, 4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, Q.; Yan, J. Optimal resource utilization and ecological restoration of aquatic zones in the coal mining subsidence areas of the Huaibei Plain in Anhui Province, China. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 4019–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Baskoro, M.S.; Kusbuiyanto, A. Evaluation of photo voltaic generating system performance for fishing light application. Fish. Sci. 2000, 66, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lakra, K.C.; Mistri, A.; Banerjee, T.K.; Lal, B. Analyses of the health status, risk assessment and recovery response of the nutritionally important catfish Clarias batrachus reared in coal mine effluent-fed pond water: A biochemical, haematological and histopathological investigation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 47462–47487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.; Xu, Q.; Lyu, H.; Kong, J.; Wang, X.; Shen, B.; Bi, Y. Sediment and residual feed from aquaculture water bodies threaten aquatic environmental ecosystem: Interactions among algae, heavy metals, and nutrients. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Sonne, C.; Chen, X.; Yue, X.; Gu, H.; Lam, S.S.; Peng, W. Phytosphere purification of urban domestic wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 336, 122417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.E.; Bathrellos, G.D.; Skilodimou, H.D.; Gamvroula, D.E. Land Suitability Mapping Using Geochemical and Spatial Analysis Methods. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makri, P.; Stathopoulou, E.; Hermides, D.; Kontakiotis, G.; Zarkogiannis, S.D.; Skilodimou, H.D.; Bathrellos, G.D.; Antonarakou, A.; Scoullos, M. The Environmental Impact of a Complex Hydrogeological System on Hydrocarbon-Pollutants’ Natural Attenuation: The Case of the Coastal Aquifers in Eleusis, West Attica, Greece. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.E.; Bathrellos, G.D.; Skilodimou, H.D.; Gamvroula, D.E. Spatial Distribution and Evaluation of Arsenic and Zinc Content in the Soil of a Karst Landscape. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Gao, X.; Wei, P.; Gao, B.; Lin, C.; Hao, F. A review of diffuse pollution modeling and associated implications for watershed management in China. J. Soils Sed. 2017, 17, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, N.; Eqani, S.A.M.A.S.; Maria, A.S.; Alessandra, C.; Ali, N.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Tanveer, Z.I.; Bokhari, H. Geo-accumulation and enrichment of trace metals in sediments and their associated risks in the Chenab River, Pakistan. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 165, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Hu, Z.; Yang, P. Levels and ecological risk of heavy metals in the surface sediments of tidal flats along the North Jiangsu coast, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 170, 112663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surenbaatar, U.; Lee, S.; Kwon, J.Y.; Lim, H.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Hong, Y.S. Bioaccumulation of Lead, Cadmium, and Arsenic in a Mining Area and Its Associated Health Effects. Toxics 2023, 11, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Zhao, H.; Li, G.; Qu, J. Assessment of potentially toxic pollutants and urban livability in a typical resource-based city, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18640–18649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, B.; Xue, N.; Li, F.; Seip, H.M.; Cong, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, B.; Han, B.; Li, H. Ecological risks and potential sources of heavy metals in agricultural soils from Huanghuai Plain, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T 1377-2007; Determination of pH in Soil. Chinese Academy of Agricultural Quality Standards and Testing Technology Institute: Beijing, China, 2007.
- HJ 615-2011; Soil-Determination of Organic Carbon-Potassium Dichromate Oxidation Spectrphotometric Method. Dalian Municipal Environmental Monitoring Center: Dalian, China, 2011.
- HJ 803-2016; Soil and Sediment-Determination of Aqua Regia Extracts of 12 Metal Elements-Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Ministry of Environmental Protection: Beijing, China, 2016.
- HJ 923-2017; Soil and Sediment—Determination of Total Mercury—Catalytic Pyrolysis-Cold Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Salam, R.; Islam, M.S.; Khan, R.; Rahman, M.S.; Pal, S.C.; Ali, M.M.; Idris, A.M.; et al. Potentially toxic elemental contamination in Wainivesi River, Fiji impacted by gold-mining activities using chemometric tools and SOM analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 42742–42767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.D.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Berger, T.A. Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Bai, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Lu, Q.; Jia, J. Heavy metal contamination in soils from freshwater wetlands to salt marshes in the Yellow River Estuary, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Mostefa, B.; Bernard, A.; Olivier, R. Levels and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of fishing grounds along Algerian coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 136, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Dong, Z.; Yang, B.; Zeng, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, J.; Wu, S.; Shao, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. Spatial distribution, source identification, and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metal in surface sediments from river-reservoir system in the Feiyun river basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perumal, K.; Antony, J.; Muthuramalingam, S. Heavy metal pollutants and their spatial distribution in surface sediments from Thondi coast, Palk Bay, South India. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Han, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, R.; Xia, L.; Fan, Y. Assessment of Soil-Heavy Metal Pollution and the Health Risks in a Mining Area from Southern Shaanxi Province, China. Toxics 2022, 10, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, A.; Raju, N.J.; Madhav, S.; Khan, A.H. Trace elements contamination in groundwater and associated human health risk in the industrial region of southern Sonbhadra, Uttar Pradesh, India. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 3373–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, H.; Yang, Q.; Lu, X.; Wang, H.; Gu, Q.; Martin, J.D. Spatial distribution, contamination characteristics and ecological-health risk assessment of toxic heavy metals in soils near a smelting area. Environ. Res. 2023, 222, 115328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ge, S.; Liu, J.; Iqbal, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, R.; Ruan, X.; Wang, Y. Spatial Distribution and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal(oid)s Contamination in Topsoil around a Lead and Zinc Smelter in Henan Province, Central China. Toxics 2023, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.S.; Ma, Z.W.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Bi, J.; Huang, L. Human exposure pathways of heavy metals in a lead-zinc mining area, Jiangsu Province, China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmani-Ghabeshi, S.; Palomo-Marin, M.R.; Bernalte, E.; Rueda-Holgado, F.; Miro-Rodriguez, C.; Cereceda-Balic, F.; Fadic, X.; Vidal, V.; Funes, M.; Pinilla Gil, E. Spatial gradient of human health risk from exposure to trace elements and radioactive pollutants in soils at the Puchuncaví-Ventanas industrial complex, Chile. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatelopoulou, A.; Dasopoulou, M.; Bairachtari, K.; Karavoltsos, S.; Sakellari, A.; Maggos, T. Contamination and potential risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (pahs) and heavy metals in house settled dust collected from residences of young children. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; Mclennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution: An Examination of the Geochemical Record Preserved in Sedimentary Rocks; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- McLennan, S.M. Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2001, 2, 2000GC000109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Martin, J.A.; Ramos-Miras, J.J.; Boluda, R.; Gil, C. Spatial relations of heavy metals in arable and greenhouse soils of a Mediterranean environment region (Spain). Geoderma 2013, 200, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitimus, D.; Nedeff, V.; Mosnegutu, E.; Barsan, N.; Irimia, O.; Nedeff, F. Studies on the Accumulation, Translocation, and Enrichment Capacity of Soils and the Plant Species Phragmites Australis (Common Reed) with Heavy Metals. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, A.; Oka, M.; Fujii, Y.; Soda, S.; Ishigaki, T.; Machimura, T.; Ike, M. Removal of heavy metals from synthetic landfill leachate in lab-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Wang, B.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Wen, J.; Lu, G.; Zhu, C.; Zhou, Y. Heavy metals contamination and accumulation in submerged macrophytes in an urban river in China. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2018, 20, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canpolat, O.; Eroglu, M.; Coban, M.Z.; Dusukcan, M. Transfer factors and bioaccumulation of some heavy metals in muscle of a freshwater fish species: A human health concern. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2014, 23, 418–425. [Google Scholar]
- Yigit, S.; Altindag, A. Accumulation of heavy metals in the food web components of Burdur Lake, Turkey. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2002, 11, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Hong, C.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, Y. Long-distance mobilization of chromium(III) in soil associated with submicron Cr2O3. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciszewski, D.; Grygar, T.M. A Review of Flood-Related Storage and Remobilization of Heavy Metal Pollutants in River Systems. Water Air Soil Poll. 2016, 227, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaider, L.A.; Senn, D.B.; Estes, E.R.; Brabander, D.J.; Shine, J.P. Sources and fates of heavy metals in a mining-impacted stream: Temporal variability and the role of iron oxides. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z. Evaluation of heavy metal pollution and its ecological risk in one river reach of a gold mine in Inner Mongolia, Northern China. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 128, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
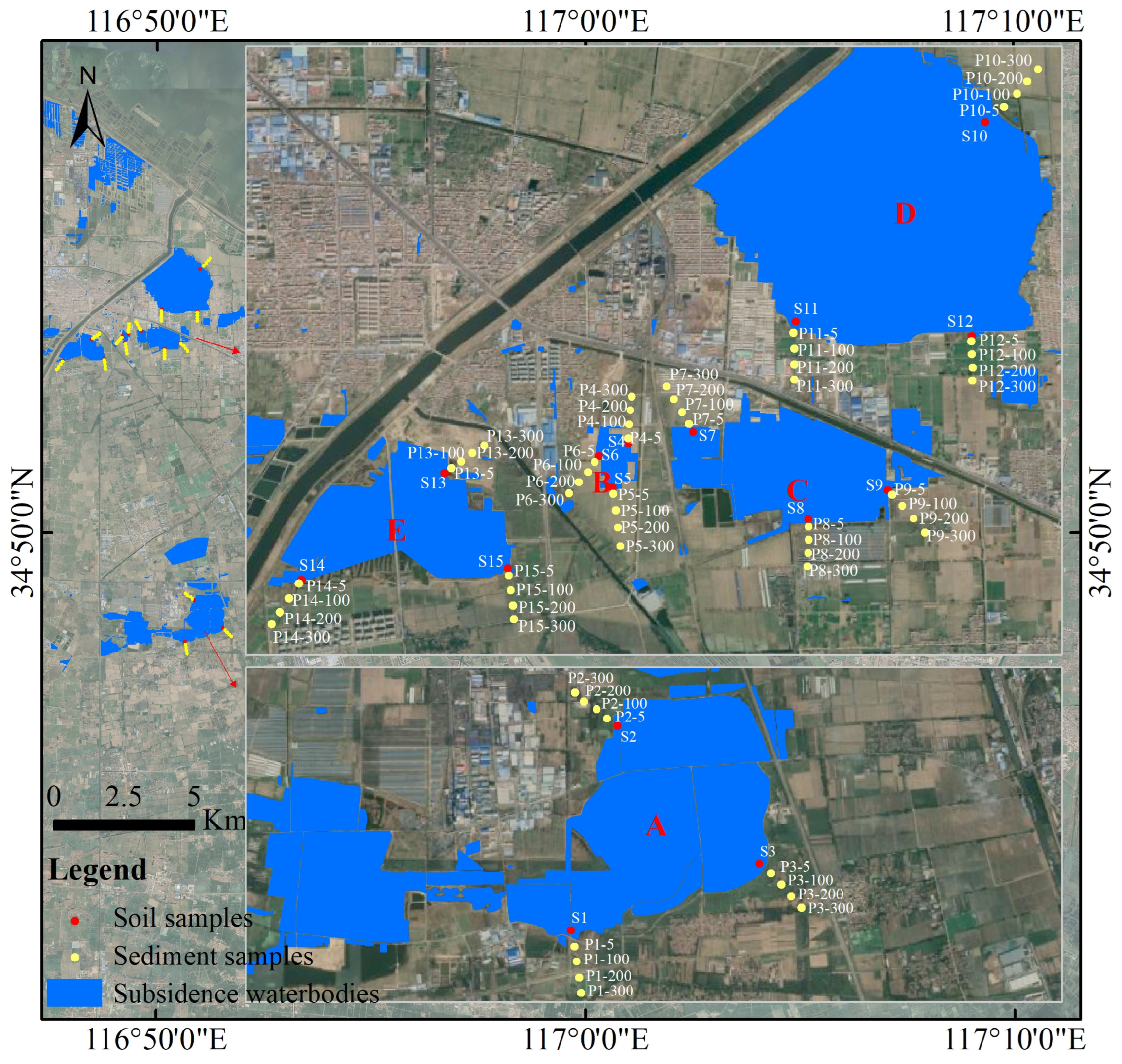
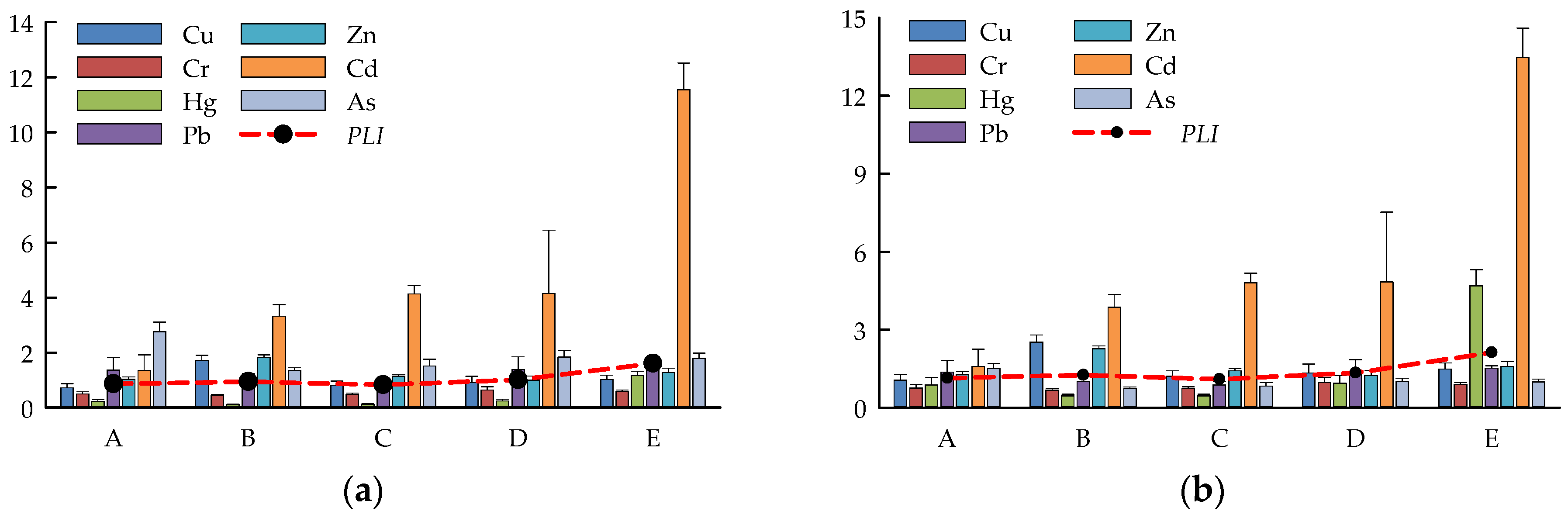
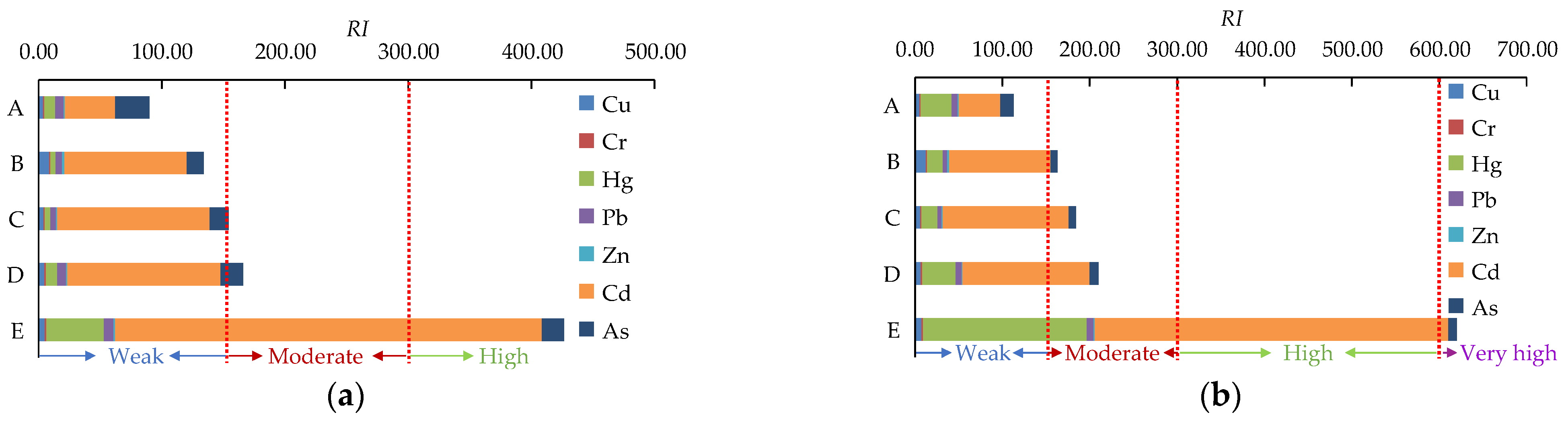




| RI | Ecological Risk Level | |
|---|---|---|
| ≤ 40 | RI ≤ 150 | Low |
| 40 < ≤ 80 | 150 < RI ≤ 300 | Moderate |
| 80 < ≤ 160 | 300 < RI ≤ 600 | High |
| 160 < ≤ 320 | 600 ≤ RI | Very high |
| 320 < | Extremely high |
| Cu | Cr | Hg | Pb | Zn | Cd | As | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | ug kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | |
| A | 18.09 ± 3.87 | 45.88 ± 7.7 | 12.35 ± 3.96 | 23.3 ± 7.88 | 69.12 ± 5.85 | 0.13 ± 0.06 | 13.27 ± 1.69 |
| B | 42.82 ± 4.83 | 40.53 ± 4.26 | 6.33 ± 0.95 | 17.27 ± 3.74 | 122.45 ± 5.77 | 0.33 ± 0.04 | 6.49 ± 0.48 |
| C | 20.57 ± 3.63 | 44.16 ± 4.34 | 6.45 ± 0.9 | 15.04 ± 2.27 | 76.6 ± 4.33 | 0.4 ± 0.03 | 7.26 ± 1.18 |
| D | 22.82 ± 5.76 | 58.87 ± 11.22 | 13.24 ± 4 | 23.55 ± 7.77 | 66.92 ± 10.22 | 0.41 ± 0.23 | 8.52 ± 1.17 |
| E | 25.39 ± 4.11 | 54.29 ± 4.65 | 65.64 ± 8.67 | 26.02 ± 1.57 | 86.09 ± 9.75 | 1.13 ± 0.09 | 8.57 ± 0.93 |
| UCG [47,48] | 25 | 92 | 56 | 17 | 67 | 0.098 | 4.8 |
| Background values | 17 | 60 | 14 | 17 | 54 | 0.084 | 8.7 |
| TEL | 18.7 | 52.3 | 170 | 30.2 | 124 | 0.68 | 7.2 |
| PEL | 108.2 | 160.4 | 170 | 112.2 | 271 | 4.2 | 41.6 |
| Cu-HQ | Cr-HQ | Hg-HQ | Pb-HQ | Zn-HQ | Cd-HQ | As-HQ | HI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children | |||||||||
| A | mean | 3.72 × 10−3 | 2.51 × 10−4 | 6.34 × 10−4 | 1.37 | 1.89 × 10−3 | 3.65 × 10−5 | 6.54 × 10−2 | 1.44 |
| sd | 7.95 × 10−4 | 4.22 × 10−5 | 2.03 × 10−4 | 4.63 × 10−1 | 1.60 × 10−4 | 1.51 × 10−5 | 8.34 × 10−3 | 0.00 | |
| B | mean | 8.80 × 10−3 | 2.22 × 10−4 | 3.25 × 10−4 | 1.01 | 3.35 × 10−3 | 8.91 × 10−5 | 3.20 × 10−2 | 1.06 |
| sd | 9.92 × 10−4 | 2.34 × 10−5 | 4.87 × 10−5 | 2.19 × 10−1 | 1.58 × 10−4 | 1.12 × 10−5 | 2.36 × 10−3 | 0 | |
| C | mean | 4.23 × 10−3 | 2.42 × 10−4 | 3.31 × 10−4 | 8.83 × 10−1 | 2.10 × 10−3 | 1.11 × 10−4 | 3.58 × 10−2 | 9.26 × 10−1 |
| sd | 7.46 × 10−4 | 2.38 × 10−5 | 4.63 × 10−5 | 1.33 × 10−1 | 1.19 × 10−4 | 8.42 × 10−6 | 5.81 × 10−3 | 0.00 | |
| D | mean | 4.69 × 10−3 | 3.23 × 10−4 | 6.80 × 10−4 | 1.38 | 1.83 × 10−3 | 1.11 × 10−4 | 4.35 × 10−2 | 1.43 |
| sd | 1.18 × 10−3 | 6.15 × 10−5 | 2.06 × 10−4 | 4.56 × 10−1 | 2.80 × 10−4 | 6.17 × 10−5 | 5.77 × 10−3 | 0.00 | |
| E | mean | 5.22 × 10−3 | 2.97 × 10−4 | 3.37 × 10−3 | 1.53 | 2.36 × 10−3 | 3.10 × 10−4 | 4.23 × 10−2 | 1.58 |
| sd | 8.44 × 10−4 | 2.55 × 10−5 | 4.45 × 10−4 | 9.19 × 10−2 | 2.67 × 10−4 | 2.60 × 10−5 | 4.57 × 10−3 | 0.00 | |
| Adults | |||||||||
| A | mean | 3.98 × 10−4 | 2.69 × 10−5 | 6.80 × 10−5 | 1.47 × 10−1 | 2.03 × 10−4 | 3.91 × 10−6 | 7.01 × 10−3 | 1.54 × 10−1 |
| sd | 8.52 × 10−5 | 4.52 × 10−6 | 2.18 × 10−5 | 4.96 × 10−2 | 1.72 × 10−5 | 1.62 × 10−6 | 8.94 × 10−4 | 0.00 | |
| B | mean | 9.43 × 10−4 | 2.38 × 10−5 | 3.49 × 10−5 | 1.09 × 10−1 | 3.59 × 10−4 | 9.54 × 10−6 | 3.43 × 10−3 | 1.13 × 10−1 |
| sd | 1.06 × 10−4 | 2.50 × 10−6 | 5.22 × 10−6 | 2.35 × 10−2 | 1.69 × 10−5 | 1.20 × 10−6 | 2.52 × 10−4 | 0.00 | |
| C | mean | 4.53 × 10−4 | 2.59 × 10−5 | 3.55 × 10−5 | 9.46 × 10−2 | 2.25 × 10−4 | 1.19 × 10−5 | 3.83 × 10−3 | 9.92 × 10−2 |
| sd | 7.99 × 10−5 | 2.55 × 10−6 | 4.96 × 10−6 | 1.43 × 10−2 | 1.27 × 10−5 | 9.02 × 10−7 | 6.22 × 10−4 | 0.00 | |
| D | mean | 5.02 × 10−4 | 3.46 × 10−5 | 7.29 × 10−5 | 1.48 × 10−1 | 1.96 × 10−4 | 1.19 × 10−5 | 4.66 × 10−3 | 1.54 × 10−1 |
| sd | 1.27 × 10−4 | 6.59 × 10−6 | 2.20 × 10−5 | 4.89 × 10−2 | 3.00 × 10−5 | 6.61 × 10−6 | 6.18 × 10−4 | 0.00 | |
| E | mean | 5.59 × 10−4 | 3.19 × 10−5 | 3.61 × 10−4 | 1.64 × 10−1 | 2.53 × 10−4 | 3.32 × 10−5 | 4.53 × 10−3 | 1.69 × 10−1 |
| sd | 9.05 × 10−5 | 2.73 × 10−6 | 2.77 × 10−5 | 9.84 × 10−3 | 2.86 × 10−5 | 2.78 × 10−6 | 4.89 × 10−4 | 0.00 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, M.; Dong, J.; Qu, J.; Hao, M. The Patterns of Migration of Potentially Toxic Elements from Coal Mining Subsidence Areas and Associated Soils to Waterlogged Areas. Toxics 2023, 11, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110888
Tan M, Dong J, Qu J, Hao M. The Patterns of Migration of Potentially Toxic Elements from Coal Mining Subsidence Areas and Associated Soils to Waterlogged Areas. Toxics. 2023; 11(11):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110888
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Min, Jihong Dong, Junfeng Qu, and Ming Hao. 2023. "The Patterns of Migration of Potentially Toxic Elements from Coal Mining Subsidence Areas and Associated Soils to Waterlogged Areas" Toxics 11, no. 11: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110888
APA StyleTan, M., Dong, J., Qu, J., & Hao, M. (2023). The Patterns of Migration of Potentially Toxic Elements from Coal Mining Subsidence Areas and Associated Soils to Waterlogged Areas. Toxics, 11(11), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110888






