Abstract
Inflammation leads to porcine tight junction disruption of small intestinal epithelial cells, resulting in intestinal dysfunction. Herein, we established lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced in-vivo and in-vitro inflammatory models. The results revealed that LPS induced tight junction disruption in IPEC-J2 cells by downregulating tight-junction-related protein zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), occludin and claudin-1 expression, while ginsenoside Rg1 rescued such inhibition and abrogated the upregulated expression of phosphorylation p38 MAPK. The p38 MAPK inhibitor (SB203580) showed a similar effect with Rg1 and attenuated the LPS-induced inhibition of ZO-1, occludin and claudin-1 expression, which is consistent with the reduced expression of NLRP3 inflammasome and IL-1β. Furthermore, the specific inhibitors of NLRP3 and IL-1β result in increased expression of tight-junction-related protein, demonstrating that p38 MAPK signaling was associated with Rg1 suppression of tight junction disruption. Besides, LPS treatment decreased the expression of ZO-1, occludin and claudin-1 through p38 MAPK signaling, and caused abnormal morphological changes in murine ileum. Meanwhile, Rg1 attenuated the decreased expression of ZO-1, occludin and claudin-1 and partially alleviated LPS-induced morphological changes in murine ileum. In summary, these findings characterized a novel mechanism by which Rg1 alleviates LPS-induced intestinal tight junction disruption by inhibiting the p38 MAPK-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome pathway.
1. Introduction
Intestinal dysfunction is a critical problem in pork production and can be caused by several factors, including weaning, bacterial or viral infections, and tight junction disruption [1]. One of the most important components of the intestinal barrier is the intestinal tight junction, which functions together with the mucous gel layer and mucosal immune system to provide a physical barrier to the diffusion of pathogens and toxins into the circulatory system from the luminal environment. [2,3]. A number of reports have documented that intestinal dysfunction due to the disruption of tight junctions can cause various intestinal illnesses, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), celiac disease [4] and sepsis [5] in pigs, causing huge economic losses to the global porcine industry. As a consequence, the restoration of tight junctions in the intestine is critical to the recovery of intestinal function.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a class of endotoxins produced by Gram-negative bacteria. LPS is toxic to humans and stimulates several cytokines associated with inflammation. It is believed to be involved in the pathogenesis of numerous disorders, such as endotoxemia/sepsis, multiorgan injuries and liver damage, etc. [6,7]. Previously, it has been demonstrated that LPS was found to induce the intestinal inflammation and destruction of tight junctions [8]. It is, therefore, of great significance to investigate the molecular mechanisms involved in LPS-induced intestinal toxicity. It is well known that p38 MAPK, an important intracellular signal transduction system, is associated with trauma [9], infection [10] and inflammation [11]. Several physiological and pathological responses in mammalian intestines are mediated by the p38 MAPK signaling pathway, such as ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury caused by inflammation [12], intestinal disturbances, and oxidative stress [13]. However, the involvement of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway in the disruption of inflammation-mediated tight junctions is still unclear. The NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasomes are among the protein complexes in the cytosol, which play an important role in microbial infections and in regulating the immune, metabolic and mucosal systems. [14]. The NLRP3 inflammasome complex consists of the sensor NLRP3, the adaptor-apoptosis-associated speck-like protein and the effector protein-caspase-1 [15]. Activated caspase-1 cleaves substrates, such as pro-IL-1β, to produce IL-1β with biological activity that stimulates inflammation in intestinal epithelial cells [16]. Researchers reported that inflammatory factors can further damage tight junctions in the digestive tract, thus, contributing to the development or deterioration of intestinal diseases [17]. Therefore, it is crucial to investigate active pharmaceutical agents that may prevent intestinal dysfunction.
Ginseng is widely used in traditional Chinese medicine due to its antitumor and anti-inflammatory properties [18,19], which are attributed, primarily, to ginsenosides [20]. Among them, ginsenoside Rg1 (hereinafter referred to as Rg1) is the most active and abundant steroidal saponin, with a similar structure to those of other steroidal hormones [21]. Rg1 has many pharmacological effects, such as antitumor, immuno-modulatory and anti-inflammatory activity [22,23]. A recent study indicated that Rg1 reverses IL-1β-mediated downregulation in macrophages associated with the disruption of tight junction proteins [24]. Based on the above-mentioned concerns, this study explored the protective effect of Rg1 on the LPS-induced disruption of tight junctions in IPEC-J2 cells and its underlying mechanisms. Meanwhile, we have also demonstrated that Rg1 regulates intestinal tight junctions and decreases LPS-induced intestinal tight junctions in mice, thus, providing new insights into Rg1’s role in the recovery of intestinal dysfunctions.
2. Materials and Methods
LPS, Rg1, MCC950, IL-1Ra and SB 203580 were purchased from MedChemExpress (Shanghai, China). Rg1 and LPS were purchased from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
Specific pathogen-free (SPF) 6-week-old female KM mice (Laboratory Animal Center of South China Agricultural University, China) were kept in single cages under a 12 h light/dark cycle, at temperature (20–25°C) and humidity (40–70%). The animals were provided ad libitum access to food and water for 7 days. Before the experiment, the animals were fasted for 12 h. All the experimental protocols were approved by the Animal Protection and Use Committee of South China Agricultural University.
Thirty-two mice were randomly divided into four groups (eight mice per group). Group 1 was the vehicle control group in which the mice were administered with normal saline intraperitoneally (i.p.). Group 2 was the LPS group in which the mice were i.p. injected with LPS at a dose of 10 mg/kg without Rg1 treatment. Groups 3 and 4 were the treatment groups in which the mice were i.p injected with LPS for three consecutive days at a dose of 10 mg/kg per day, and after daily injection, Rg1 was orally administered at a dose of 10 and 20 mg/kg, respectively. At 24 h after the last administration, all the mice were sacrificed after being anesthetized by i.p. injection with pentobarbital (50 mg/kg), and their ileum samples were collected for further analyses.
PEC-J2 cells (Tongpai Biotechnology Co., LTD, Shanghai, China) were cultured in DMEM/F--12 medium (Gibco, Shanghai, China) with 10% FBS (Gibco, Shanghai, China) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin (Invitrogen, Shanghai, China) at 37°C and 5% CO2. When being cultured to four to eight generations, the cells were seeded in six-well plates (5 × 105 cells/well) and cultured for 24 h, and then treated with LPS (at a final concentration of 0.5, 1 and 2 μg/mL) and/or Rg1(at a final concentration of 10 and 60 μM) at the indicated concentrations for 48 h.
Total RNA was extracted from the tissues and cells with TRIzol reagent (Solarbio, Beijing, China) and immediately reverse transcribed with a Prime Script RT Reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (TaKaRa, Dalian, China). qPCR was performed on the amplified cDNA with SYBR Green II PCR mix (TaKaRa) and a LightCycler 480 Realtime Detection System (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). The qPCR reactants consisted of 10 L 2 SYBR Green II PCR mix (TaKaRa), 25 μmol/L forward and reverse primers, 2 μL template, and ddH2O to a total volume of 20 μL. The thermocycler was set to 95 °C for 600 s, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s and 60 °C for 30 s. The melting curve was obtained from 65 to 95 °C, increasing by an increment of 0.5 °C every 5 s. The data were analyzed with the 2−ΔΔCt calculation method and β-actin as the internal reference. Table 1 lists the sequences of the forward and reverse primers used in this study.

Table 1.
Primers used for qRT-PCR.
The tissues and cells were collected and washed with ice-cold PBS, and then treated with ice-cold radioimmunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) lysis buffer containing 1 mm phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF). Western blotting analysis was performed as described previously. The primary antibodies were ZO-1 (1:3000 dilution; bs-1329R; Bioss), occludin (1:3000 dilution; bs-10011R; Bioss), claudin-1 (1:1000 dilution; bs-10008R; Bioss), phosphorylated p38 MAPK (α) (hereinafter referred to as p-p38) (1:1000 dilution; bs-0636R; Bioss), p38 MAPK (α) (1:1000 dilution; bsm-33423R; Bioss), NLRP3 (1:1000 dilution; bs-10021R; Bioss), IL-1β (1:1000 dilution; bs-0821R; Bioss) and β-actin (1:3000 dilution; bs-0061R; Bioss). HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit antibody (1:3000 dilution, bs-0295P-HRP; Bioss) was used as the secondary antibody. The bands were detected with ECL solution and signals were quantified with Image J software.
Ileum was fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin and embedded in paraffin. The paraffin was sectioned (5 μm thick) for hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining to observe the morphological structure. The sections were observed and photographed with the Olympus-DP73 optical microscope (Tokyo, Japan).
Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of means (SEM). All statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS 16.0 software (Chicago, IL, USA). Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVAs. A p value of less than 0.05 is considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different Concentrations of LPS on ZO-1, Occludin and Claudin-1 Expression in IPEC-J2 Cells
LPS is commonly used as an inflammatory-mimetic agent. We aimed to assess tight junction disruption induced by LPS-mediated inflammation in IPEC-J2 cells. We initially set three doses to determine the LPS concentration required to cause significant damage to the tight junctions of IPEC-J2 cells. The results showed that LPS at doses below 1 µg/mL for 48 h did not significantly reduce the expression of the tight junction proteins ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1 (p > 0.05) and 2 μg/mL LPS showed more obvious inhibitory effects on the expression of occludin (p < 0.01) (Figure 1A–D). In addition, discrete cell arrangement and more cell gaps were observed in IPEC-J2 treated with 2 μg/mL LPS (Figure 1E). These results indicated that LPS with a concentration of 2 μg/mL can induce obvious tight junction disruption of IPEC-J2 cells.
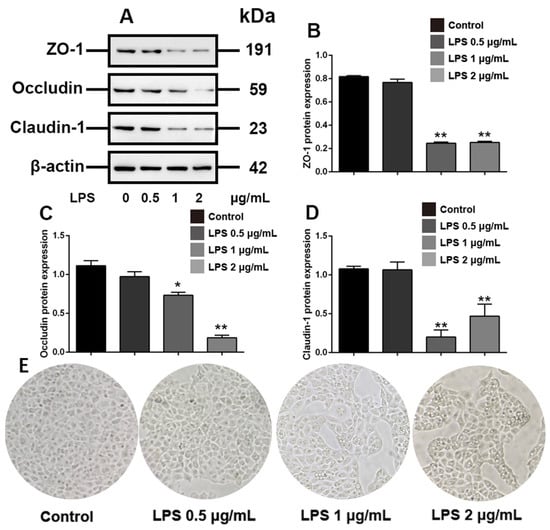
Figure 1.
LPS disrupts tight junctions in IPEC-J2 cells. IPEC-J2 cells were treated with vehicle or LPS at the indicated concentrations for 48 h. (A) Western blot analyses of tight-junction-related proteins; effect of LPS on ZO-1 (B), occludin (C) and claudin-1 (D) in IPEC-J2 cells; (E) morphology of IPEC-J2 (400 × total magnification). β-Actin was used as an internal control. Blots are representative of three independent experiments with densitometry showing the mean ± s.d. * p < 0.05 versus control and ** p < 0.01 versus control.
3.2. Rg1 Inhibited LPS-Induced Morphological Damage of Ipec-j2 Cells via Downregulating ZO-1, Occludin and Claudin-1 Expression
We subsequently investigated the effects of different doses of Rg1 on LPS-induced tight junction disruptions in IPEC-J2 cells. As shown in Figure 2, Rg1 at a dose of 10 and 60 μM significantly attenuated the inhibition of ZO-1, occludin and claudin-1 proteins’ expression (p < 0.05) and partially ameliorated LPS-induced morphological damage in IPEC-J2 cells. Taken together, these results demonstrated that Rg1 alleviates LPS-induced intestinal tight junction destruction in IPEC-J2 cells.
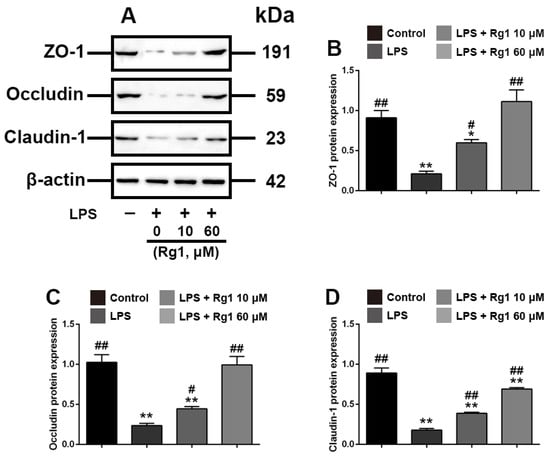
Figure 2.
Rg1 inhibits LPS-induced tight junction disruption in IPEC-J2 cells in vitro. IPEC-J2 cells were treated with vehicle, Rg1 or LPS at the indicated concentrations for 48 h. (A) Western blot analyses of tight-junction-related proteins; effect of Rg1 on ZO-1 (B), occludin (C) and claudin-1 (D) in IPEC-J2 cells. β-Actin was used as an invariant control for equal loading. Blots are representative of three independent experiments with densitometry, showing the mean ± s.d. * p < 0.05 versus control and ** p < 0.01 versus control. # p < 0.05 versus LPS and ## p < 0.01 versus LPS.
3.3. Rg1 Inhibits LPS-Induced Tight Junction Disruption in IPEC-J2 Cells by Interfering with P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway
We next explored the molecular events underlying the Rg1 inhibition of LPS-induced tight junction disruption in IPEC-J2 cells. p38 MAPK signaling has been demonstrated to have a key role in the tight junction of various tissues [25,26]. We herein found that the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK was upregulated in LPS-treated IPEC-J2 cells (Figure 3A). Rg1 reduced the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK dose dependently, indicating Rg1 interference with the p38 MAPK signaling in LPS-stimulated IPEC-J2 cells (Figure 3B). To evaluate whether p38 MAPK signaling activation is involved in Rg1-inhibited tight junction destruction in LPS-stimulated IPEC-J2 cells, SB203580, a p38 MAPK inhibitor, was used. As shown in Figure 3C, Rg1 effects under LPS treatment were similar to those observed when IPEC-J2 cells were exposed to SB203580, and the combined treatment of Rg1 and SB203580 decreased the expression of ZO-1, occludin and claudin-1. Hence, Rg1 inhibition of LPS-induced tight junction disruption in IPEC-J2 cells was associated with inhibition of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway in vitro.
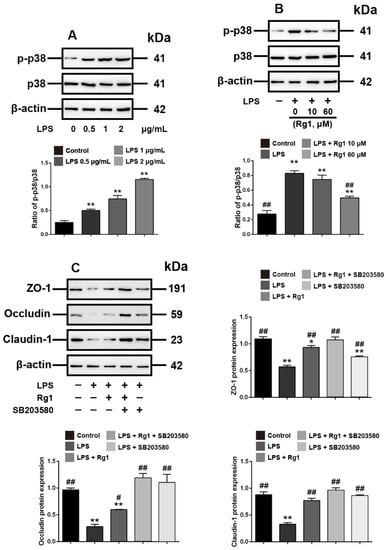
Figure 3.
Interference with p38 MAPK signaling is associated with Rg1 inhibition of LPS-induced tight junction disruption in IPEC-J2 cells in vitro. IPEC-J2 cells were treated with vehicle and LPS at the indicated concentrations for 48 h. (A) Western blot analyses of p38 MAPK signaling molecules. IPEC-J2 cells were treated with vehicle, LPS (2 μg/mL) and Rg1 at the indicated concentrations for 48 h; (B) Western blot analyses of p38 MAPK signaling molecules. IPEC-J2 cells were treated with vehicle, LPS (2 μg/mL), SB203580 (10 μM), and Rg1 (60 μM) for 48 h; (C) Western blot analyses of tight-junction-related proteins. β-Actin was used as an invariant control for equal loading. Blots are representative of three independent experiments with densitometry showing the mean ± s.d. * p < 0.05 versus control and ** p < 0.01 versus control. # p < 0.05 versus LPS and ## p < 0.01 versus LPS.
3.4. Rg1 Inhibits the mRNA and Protein Expression of NLRP3 and IL-1β through p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway
To verify that Rg1 reversed LPS-induced tight junction disruption through p38 MAPK signaling, we evaluated the effects of Rg1 and SB203580 on NLRP3 and IL-1β, which belong to the downstream proteins of p38 MAPK signaling, as demonstrated previously [27,28]. The Q-PCR and Western blot results showed (Figure 4) that LPS significantly enhanced the mRNA and protein expression of NLRP3 and IL-1β, while Rg1 treatment significantly reversed the increased expression (p < 0.01). We further used SB203580 to verify that the expression of NLRP3 and IL-1β is associated with p38 MAPK signaling, and the result showed that Rg1 had a similar effect with SB203580 in reducing the expression of NLRP3 and IL-1β by inhibiting p38 MAPK signaling.
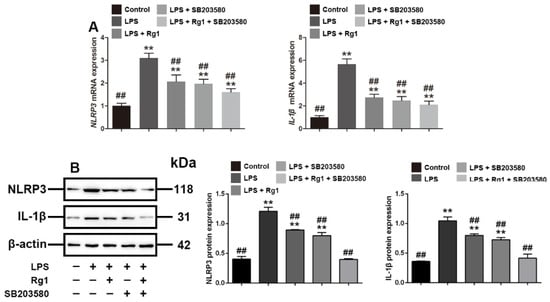
Figure 4.
Rg1 regulates NLRP3 and IL-1β through p38 MAPK signaling in IPEC-J2 cells treated with LPS in vitro. PEC-J2 cells were treated with vehicle, LPS (2 μg/mL), SB203580 (10 μM), and Rg1 (60 μM) for 48 h. (A) mRNA level analyses of NLRP3 and IL-1β; (B) Western blot analyses of NLRP3 and IL-1β. β-Actin was used as an invariant control for equal loading. Blots are representative of three independent experiments with densitometry showing the mean ± s.d. ** p < 0.01 versus control. ## p < 0.01 versus LPS.
3.5. Effects of MCC950 and IL-1Ra on Expression of ZO-1, Occludin, and Claudin-1 in LPS-Treated IPEC-J2 Cells
Subsequently, to examine the effects of the increased expression of NLRP3 and IL-1β on tight junctions, we investigated the effects of the specific inhibitors of NLRP3 and IL-1β, MCC950 and IL-1Ra, on the expression of ZO-1, occludin and claudin-1. The results showed that the MCC950 and IL-1Ra-mediated inhibition of both NLRP3 and IL-1β reversed the decreased expression of ZO-1, occludin and claudin-1 caused by LPS (p < 0.01) (Figure 5). Thus, these in-vitro data indicated that Rg1 inhibited tight junction disruption associated with LPS-caused intestinal dysfunction in IPEC-J2 cells.
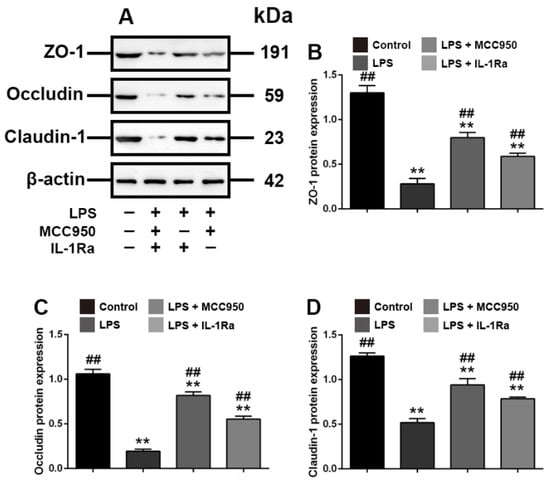
Figure 5.
Interference with NLRP3 and IL-1β is associated with tight junction in IPEC-J2 cells in vitro. PEC-J2 cells were treated with vehicle, LPS (2 μg/mL), MCC950 (10 μm) and IL-1Ra (10 ng/mL) for 48 h. Western blot analyses of tight-junction-related proteins. (A) Western blot analyses of tight-junction-related proteins; effect of LPS on ZO-1 (B), occludin (C) and claudin-1 (D) in IPEC-2 cells. β-Actin was used as an invariant control for equal loading. Blots are representative of three independent experiments with densitometry showing the mean ± s.d. ** p < 0.01 versus control. ## p < 0.01 versus LPS.
3.6. Rg1 Inhibits Tight Junction Disruption via P38 MAPK Signaling in Mice
The effects of Rg1 on tight junction disruption in intestinal dysfunction were examined in LPS-treated mice. Histological examination showed that Rg1 partially ameliorated the abnormal pathological changes in the small intestine (Figure 6A). In addition, Western blot analyses further showed that Rg1 dose dependently and partially reduced NLRP3, IL-1β expression and the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK in the experimental animals (Figure 6C), and restored the level of ZO-1, occludin and claudin-1 protein (Figure 6B), consistent with the results obtained in LPS-treated IPEC-J2 cells. Thus, it has been further confirmed that Rg1 protected the intestinal tight junctions associated with p38 MAPK-dependent NLRP3 signaling pathway in LPS-induced intestinal dysfunction.
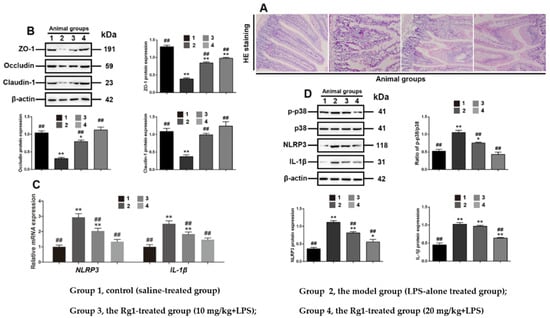
Figure 6.
Rg1 inhibits tight junction disruption associated with interference with p38 MAPK signaling in murine intestinal dysfunction caused by LPS. Experimental groups including Group 1, control (saline-treated group); Group 2, the model group (LPS-alone-treated group); Group 3, the Rg1-treated group (10 mg/kg + LPS); and Group 4, the Rg1-treated group (20 mg/kg + LPS). Ileum sections were stained with HE for histological assessment. (A) Representative views are shown (original magnification × 20); (B) Western blot analyses of tight-junction-related proteins. Western blot analyses of tight-junction-related proteins; (C) mRNA level analyses of NLRP3 and IL-1β; (D) Western blot analyses of p38 MAPK signaling-related proteins. β-Actin was used as an invariant control for equal loading. Blots are representative of three independent experiments with densitometry showing the mean ± s.d. * p < 0.05 versus control and ** p < 0.01 versus control. ## p < 0.01 versus LPS.
4. Discussion
Ginsenosides are considered as key constituents for ginseng function against several diseases, among which Rg1 has attracted much attention because of its antitumor, immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects [29,30,31]. In this study, we found that Rg1 can restore the tight junction dysfunction of porcine intestines by inhibiting NLRP3/IL-1β regulated by p38 MAPK signaling to some extent.
Tight junctions shape the continuous intercellular barrier, which acts as the first physical barrier against a variety of pathogens and maintains homeostasis in the gastrointestinal tract [32]. The functions of mammalian intestinal tight junctions are determined by several types of proteins, namely junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs), occludin and claudins, and other cytoplasmic tight junction proteins, including ZO-1 and claudins [33]. A recent study pointed out that intestinal barrier dysfunction was reflected by the downregulation of the expression of ZO-1, occludin and claudin-1, leading to hyperuricemia in mice [34,35]. Substantial experimental evidence also supports the observation that LPS serves as an important stimuli of tight junction disruption in a variety of cells, such as intestinal epithelial cells [36] and brain microvascular endothelial cells [37]. Herein, we established tight junction disruption, characterized by a decrease in the expression of tight-junction-related proteins ZO-1, occludin and claudin-1, in IPEC-J2 cells treated with LPS in culture, and the results are also supported by a recent study demonstrating that LPS stimulation led to tight junction disruption in porcine intestines [38].
Rg1 has many protective effects on animal intestinal health, such as alleviating experimental colitis [39], affecting the expression of apoptosis proteins [40] and ameliorating the homeostasis of intestinal flora [41]. In the present study, we confirmed that Rg1 restores the intestinal structure and function by upregulating tight-junction-related proteins ZO-1 occludin and claudin-1 in LPS-induced intestinal dysfunction. These findings are also in line with those of a recent study demonstrating that the integrity of intestinal morphology and tight junction were enhanced in the intestines by the supplementation of Rg1 in the diet of chickens, improving growth performance and intestinal health [42].
Once the tight-junction-protective properties of Rg1 were confirmed, we focused on elucidating the underlying molecular mechanism. According to a recent study, LPS inhibits tight junction expression by activating p38 MAPK in IPEC-J2 cells [38], and we further explored how Rg1 inhibits tight junction disruption focusing on p38 MAPK signaling. Our data showed that Rg1 significantly reduced the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK in LPS-treated IPEC-J2 cells, which might disrupt the downstream signal transduction. It was tested via the pharmacological inhibition of p38 MAPK caused by the specific inhibitor sb203580, investigating whether this interference was associated with the reversal of tight junction disruption in IPEC-J2 cells. SB203580 treatment rescued the expression of the tight-junction-related proteins (ZO-1, occludin and claudin-1) in LPS-treated IPEC-J2 cells. From these results, it has been suggested that the suppression of p-p38 MAPK might be involved in Rg1 inhibition of tight junction disruption.
NLRP3, one of the key regulators of the inflammatory response, mediates a variety of inflammation-associated diseases. It was reported that dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) treatment regulated the expression of NLRP3 by activating the p38 pathway, resulting in ulcerative colitis [43]; T. gondii-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation was strongly associated with the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK in human small intestinal epithelial cells [44]. It has been confirmed that Rg1 ameliorated aging-induced liver fibrosis by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome in mice [45]. Previous reports showed that SB203580 is a specific inhibitor of p38 MAPK, and widely used in mechanistic studies. It can be inferred that the testing compound plays a biological function by inhibiting p38 MAPK if the compound shows a similar inhibitory effect to SB203580 [46]. Similarly, our data showed that Rg1 inhibited the expression of NLRP3 and IL-1β in IPEC-J2 cells, and the effect was similar to that of SB203580, demonstrating that this inhibition is regulated by p38 MAPK, and this finding is in line with a previous study [47].
To further analyze whether NLRP3 and IL-1β are involved in intestinal tight junctions, we employed inhibitors of these two proteins, MCC950 and IL-1Ra, to IPEC-J2 cells, respectively. The results show that these two inhibitors partially blocked the inhibition of LPS on tight-junction-related proteins, namely ZO-1, occludin and claudin-1, indicating that tight junction was regulated by NLRP3 and IL-1β. Our in-vitro data provide evidence that Rg1 can restore the tight junction of NLRP3 and IL-1β, which is regulated by p38 MAPK to some extent. We also investigated whether Rg1 has any effects on tight junction disruption during intestinal dysfunction in mice induced by LPS. This could be helpful for verifying the role of maintaining tight junctions in the interventions for intestinal dysfunction. Our data showed that all the tested tight-junction-related proteins were significantly downregulated in mice with inflamed intestines, suggesting that tight junction disruption occurred. However, Rg1 treatment not only increased the expression of these markers, but also improved the intestinal histology (as demonstrated by hematoxylin–eosin staining). Examinations of p38 MAPK signaling in mice showed that the expressions of p-p38 MAPK, NLRP3 and IL-1β were inhibited by Rg1 treatment, which was consistent with the results obtained in LPS-treated IPEC-J2 cells, confirming the protective molecular mechanism of Rg1.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the data showed that Rg1 could inhibit intestinal tight junction disruption in LPS-treated IPEC-J2 cells and mice. Rg1 alleviated the increased expression of p38 MAPK-dependent NLRP3 and IL-1β expression and restored the protein expression of occludin, claudin-1 and ZO-1. These results provide evidence supporting the application of an NLRP3 inhibitor in the treatment of intestinal inflammation. Taken together, these results provided mechanistic insights and scientific evidence to support the use of Rg1 to prevent and treat intestinal tight junction disorders. However, further clinical studies are needed to investigate the protective effects of Rg1 on porcine intestinal inflammation and tight junctions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.K. and B.F.; methodology, J.K. and T.R.; software, Y.Z. (Yong Zhang); validation, J.K., Y.Z. (Yanhong Zhou) and C.Z.; formal analysis, J.K.; investigation, L.X.; resources, B.F.; data curation, J.K.; writing—original draft preparation, J.K.; writing—review and editing, B.F. and L.X.; supervision, B.F.; project administration, B.F.; funding acquisition, B.F. and L.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the 13th Five-year Plan for National Key Research, grant number 2016YFD0501308, and General Science and Technology Project of Beijing Municipal Education Commission, grant number KM202110020004.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of South China Agricultural University (protocol code 2019192. 30 December 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yi, D.; Liu, W.; Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, D.; Wu, T.; Ding, B.; Wu, G. Establishment of a porcine model of indomethacin-induced intestinal injury. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 2166–2176. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Hara, H. Role of flavonoids in intestinal tight junction regulation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.R. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M.; Madsen, K.; Spiller, R.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Verne, G.N. Intestinal barrier function in health and gastrointestinal disease. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liang, T.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhu, H.; Xiao, K. Necroptosis is active and contributes to intestinal injury in a piglet model with lipopolysaccharide challenge. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prima, V.; Wang, A.; Molina, G.; Wang, K.; Svetlov, S.I. Inhibition of LPS toxicity by hepatic argininosuccinate synthase (ASS): Novel roles for ASS in innate immune responses to bacterial infection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.C.; Chen, H.; Mochly-Rosen, D.; Li, Y.E.; Chen, M.H. The Role of Alcohol, LPS Toxicity, and ALDH2 in Dental Bony Defects. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo, S.; Grasa, L.; Arruebo, M.P.; Plaza, M.A.; Murillo, M.D. Inhibition of p38 MAPK improves intestinal disturbances and oxidative stress induced in a rabbit endotoxemia model. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.T.; Le, P.H.; Lin, C.J.; Chen, T.H.; Kuo, C.J.; Chiang, K.C.; Yeh, T.S. Mechanism of salutary effects of melatonin-mediated liver protection after trauma-hemorrhage: p38 MAPK-dependent iNOS/HIF-1α pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G427–G433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Sun, F.; Wang, L.; Gao, M.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yi, W.; Huang, Z.; et al. Virus-induced p38 MAPK activation facilitates viral infection. Theranostics 2020, 10, 12223–12240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K.; Han, J. The p38 signal transduction pathway: Activation and function. Cell. Signal. 2000, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Chen, Q.H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Liang, S.S.; Zhang, H.G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.K. Dexmedetomidine protects intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibiting p38 MAPK cascades. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2020, 115, 104444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Yin, L.; Li, J.Y.; Li, Q.; Shi, D.; Feng, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, W.D.; Wu, P.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Glutamate attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative damage and mRNA expression changes of tight junction and defensin proteins, inflammatory and apoptosis response signaling molecules in the intestine of fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 70, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinon, F.; Burns, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasome: A molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, L.; Martinon, F.; Burns, K.; McDermott, M.F.; Hawkins, P.N.; Tschopp, J. NALP3 forms an IL-1beta-processing inflammasome with increased activity in Muckle-Wells autoinflammatory disorder. Immunity 2004, 20, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.Y.; Tu, C.E.; Wang, S.C.; Hung, Y.L.; Su, C.C.; Fang, S.H.; Chen, C.S.; Liu, P.L.; Cheng, W.C.; Huang, Y.W.; et al. Corylin inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response and attenuates the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utech, M.; Mennigen, R.; Bruewer, M. Endocytosis and recycling of tight junction proteins in inflammation. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 484987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Yi, Y.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Role of ginsenosides, the main active components of Panax ginseng, in inflammatory responses and diseases. J. Ginseng. Res. 2017, 41, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Chu, S.; Li, L.; Chen, N.; Zhang, L. Ginsenoside Rg1 prevent and treat inflammatory diseases: A review. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 87, 106805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Wei, J.; Chunhua, M.; Danhong, Y.; Jianguo, Z.; Zongqi, C.; Jian-An, B. Protective effects of Ginsenoside Rg1 against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice through suppression of inflammation. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Ginsenoside Rg1 Protects Cardiomyocytes Against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury via Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling and Inhibition of JNK. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Fan, C.; Zhang, P.; Shen, J.; Yu, S.Y. Ginsenoside-Rg1 Rescues Stress-Induced Depression-Like Behaviors via Suppression of Oxidative Stress and Neural Inflammation in Rats. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 2325391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Cai, H.A.; Zhang, M.S.; Liao, R.Y.; Huang, X.; Hu, F.D. Ginsenoside Rg1 promoted the wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers via miR-489-3p/Sirt1 axis. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 147, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, K.; Duan, H.; Wang, W.; Zhao, S.; Khan, G.J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Thakur, K.; Fang, X.; Wu, C.; et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption and traumatic brain injury via attenuating macrophages derived exosomes miR-21 release. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 3493–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Gan, X.; Liu, X.; An, R. Calcium oxalate crystals induces tight junction disruption in distal renal tubular epithelial cells by activating ROS/Akt/p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Ren. Fail. 2017, 39, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, C.H.; Seok, J.S.; Petriello, M.C.; Han, S.G. Arsenic downregulates tight junction claudin proteins through p38 and NF-κB in intestinal epithelial cell line, HT-29. Toxicology 2017, 379, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Liang, S.; Mori, Y.; Han, R.; Sutterwala, F.S.; Qiao, L. TRPM2 links oxidative stress to NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhang, C.; Xing, Y.; Xue, G.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, F.; Wu, G.; Hu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Lu, A.; et al. Remodelling of the gut microbiota by hyperactive NLRP3 induces regulatory T cells to maintain homeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rastogi, V.; Santiago-Moreno, J.; Doré, S. Ginseng: A promising neuroprotective strategy in stroke. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 8, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, B.N.; Ji, M.G.; Kang, T.H. The efficacy of red ginseng in type 1 and type 2 diabetes in animals. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 593181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, E. Complementary/alternative medicine for hypertension: A mini-review. Wien Med. Wochenschr. 2005, 155, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T. Regulation of intestinal epithelial permeability by tight junctions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 631–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umeda, K.; Ikenouchi, J.; Katahira-Tayama, S.; Furuse, K.; Sasaki, H.; Nakayama, M.; Matsui, T.; Tsukita, S.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. ZO-1 and ZO-2 independently determine where claudins are polymerized in tight-junction strand formation. Cell 2006, 126, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Itallie, C.M.; Holmes, J.; Bridges, A.; Gookin, J.L.; Coccaro, M.R.; Proctor, W.; Colegio, O.R.; Anderson, J.M. The density of small tight junction pores varies among cell types and is increased by expression of claudin-2. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, C.; Yu, Y.; Tian, Z. Impaired intestinal barrier function in a mouse model of hyperuricemia. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 3292–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Deng, J.; Hu, X.; Zhou, S.; Wu, J.; Xiao, D.; Darko, K.O.; Huang, Y.; Tao, T.; Peng, M.; et al. Vitamin A inhibits the action of LPS on the intestinal epithelial barrier function and tight junction proteins. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zou, L.; Wang, H.; He, R.; Liu, K.; Zhu, H. RhoA/ROCK-2 Pathway Inhibition and Tight Junction Protein Upregulation by Catalpol Suppresses Lipopolysaccaride-Induced Disruption of Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability. Molecules 2018, 23, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Z.; Liu, L.; Tao, W.; Pei, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, M. Clostridium Tyrobutyricum Protect Intestinal Barrier Function from LPS-Induced Apoptosis via P38/JNK Signaling Pathway in IPEC-J2 Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 1779–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhong, Y.; Long, J.; Wu, T.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, H.; Ge, W.; Zhao, H.; Liu, D. Ginsenoside Rg1 relieves experimental colitis by regulating balanced differentiation of Tfh/Treg cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 100, 108133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Lu, J.; Jiao, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liang, Z.; Zheng, H. Ginsenoside Rg1 improves cognitive capability and affects the microbiota of large intestine of tree shrew model for Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Liu, X.K.; Kang, Z.P.; Wang, M.X.; Zhao, H.M.; Huang, J.Q.; Xiao, Q.P.; Liu, D.Y.; Zhong, Y.B. Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorated experimental colitis by regulating the balance of M1/M2 macrophage polarization and the homeostasis of intestinal flora. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 917, 174742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Xie, K.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Q.; He, X.; Zhang, H. Effects of Dietary Ginsenoside Rg1 Supplementation on Growth Performance, Gut Health, and Serum Immunity in Broiler Chickens. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 705279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.Y.; Fan, Y.M.; Ga, Y.; Zhang, Y.N.; Han, J.C.; Hao, Z.H. Shaoyao decoction attenuates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis, macrophage and NLRP3 inflammasome activation through the MKP1/NF-κB pathway. Phytomedicine 2021, 92, 153743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, J.Q.; Gao, F.F.; Wu, W.; Li, C.; Pan, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Huang, C.; Lee, S.H.; Quan, J.H.; et al. Expression profiles of NOD-like receptors and regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in Toxoplasma gondii-infected human small intestinal epithelial cells. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Han, Y.; Dong, X.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Li, W. Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates aging-induced liver fibrosis by inhibiting the NOX4/NLRP3 inflammasome in SAMP8 mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wu, Y.N.; Wang, H.; Ma, J.Y.; Zhai, S.S.; Duan, J. Dapk1 improves inflammation, oxidative stress and autophagy in LPS-induced acute lung injury via p38MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 120, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ren, W.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, L. Regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and macrophage pyroptosis by the p38 MAPK signaling pathway in a mouse model of acute lung injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 4399–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).