The Status and Research Progress of Cadmium Pollution in Rice- (Oryza sativa L.) and Wheat- (Triticum aestivum L.) Cropping Systems in China: A Critical Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Data Retrieval and Analysis
2.3. Risk Assessment
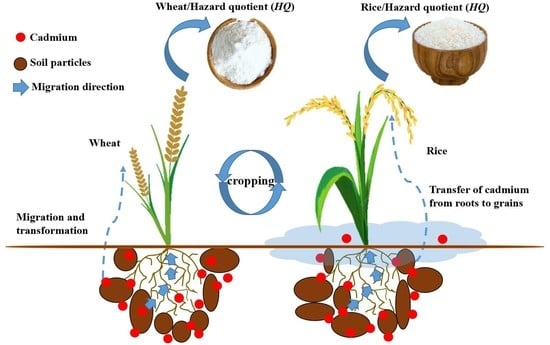
3. Cd Pollution in Rice and Wheat Cropping System
3.1. Cd Concentrations in Rice and Wheat Grain
3.2. Cd Hazard Quotients in Rice and Wheat
3.3. Cd in Rice-Wheat Cropping Field
4. Mechanism of Cd Pollution in Rice and Wheat Cropping System
4.1. Transport of Cd in Rice and Wheat Cropping System
4.2. Factors Affecting Transport of Cd in Soil
| Model | Grain | R2 | p | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YDTPA-Cd = 0.152 + 0.05Xsoil total Cd −0.029Xsoil pH + 0.006XSOM | rice/wheat | 0.53 | <0.01 | [173] |
| LogCdwg = 0.703 + 1.041LgCdsoil − 0.175pH | wheat | 0.783 | <0.01 | [174] |
| logCdwg = − 0.383 + 0.824logeCd | wheat | 0.375 | 0.01 | [175] |
| LogCdrg = 1.38 + 0.41LogCdsoil − 0.183pH − 0.09SOM | rice | 0.51 | <0.001 | [155] |
| Log(Cdrg) = − 0.369 − 0.068pH + 0.153logCdsoil | rice | 0.565 | <0.0001 | [176] |
| Log(103 Cdrg) = 3.301 + 0.534lgCdsoil − 0.211pH − 0.012SOM + 0.006CEC | rice | 0.448 | 0.000 | [177] |
5. Research Progress and Key Study Areas
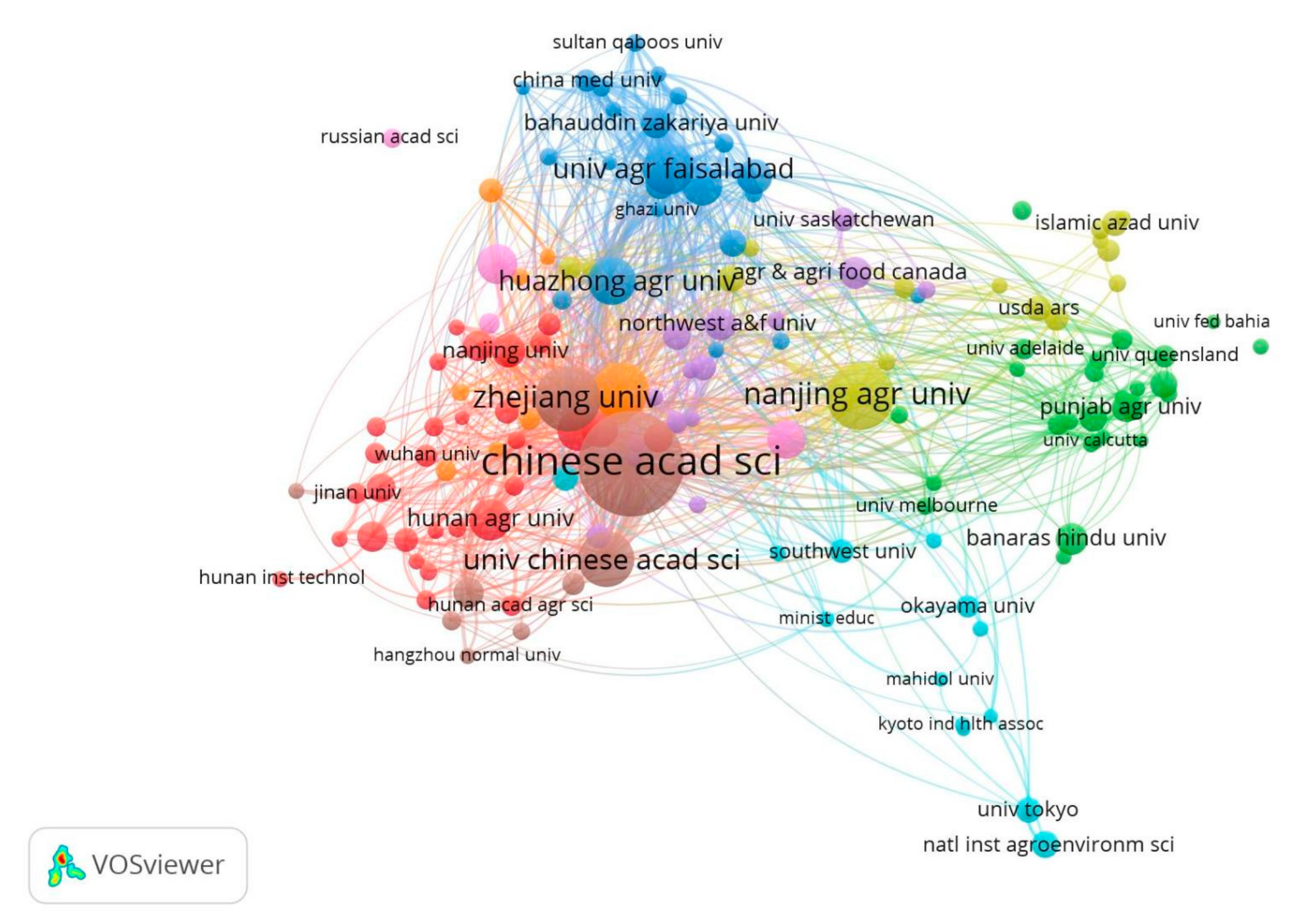
5.1. Analysis of Publication Sources, Discipline Categories, and Annual Trends
5.2. Research Prospects
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, Y.; Song, S.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.; Meng, J.; Sweetman, A.J.; Jenkins, A.; Ferrier, R.C.; Li, H.; Luo, W.; et al. Impacts of soil and water pollution on food safety and health risks in China. Environ. Int. 2015, 77, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Xiao, B.; Xiao, P.W.; Zhao, P.; Li, R.L.; Bibi, S. Research Progress on Heavy Metals Pollution in the Soil of Smelting Sites in China. Toxics 2022, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Kopittke, P.M.; McGrath, S.P.; Zhao, F.J. Cadmium transfer from soil to plants and its potential risk to human health. Nexus Soils Plants Anim. Hum. Health. 2017, 19, 138–147. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, M.; Wang, Y.; Huang, B.; Zhao, Y. Spatial uncertainty assessment of the environmental risk of soil copper using auxiliary portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometry data and soil pH. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.Q.; Yang, H.M.; Wang, M.; Sun, L.; Xu, Y.M.; Sun, G.H. Immobilization of soil Cd by sulfhydryl grafted palygorskite in wheat-rice rotation mode: A field-scale investigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 154156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satarug, S. Editorial to Special Issue Toxic Metals, Chronic Diseases and Related Cancers. Toxics 2022, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, H.P.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.J. Cadmium contamination in agricultural soils of China and the impact on food safety. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Hu, H.; Shaheen, S.M.; Zhong, H.; Tack, F.M.G. Speciation, transportation, and pathways of cadmium in soil-rice systems: A review on the environmental implications and remediation approaches for food safety. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Report on the National General Survey of Soil Contamination. 2014. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/govweb/foot/2014-04/17/content_2661768.htm (accessed on 17 April 2014).
- Xiao, J.; Yuan, X.; Li, J. Characteristics and transformation of heavy metal pollution in soil and rice of Yangtze River Delta Region. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2010, 11, 148–163. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Khan, S.; Khan, A.; Alam, M. Soil contamination with cadmium, consequences and remediation using organic amendments. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 1591–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, B.; Lin, Q.; Hamid, Y.; Sanaullah, M.; Di, L.; Khan, M.B.; He, Z.; Yang, X. Foliage application of selenium and silicon nanoparticles alleviates Cd and Pb toxicity in rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.X.; Gao, C.; Chen, C.; Zhang, W.W.; Huang, X.Y.; Zhao, F.J. Overexpression of rice OsHMA3 in wheat greatly decreases cadmium accumulation in wheat grains. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10100–10108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.P.; Zhao, Z.M.; Zhao, H.; Du, J.; Zhou, J. Toxic Metals in a Paddy Field System: A Review. Toxics 2022, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.P.; Ye, X.Z.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, W.D.; Wu, S.F.; Hu, J.; Gao, N.; Huang, M.J. Multi-Component Passivators Regulate Heavy Metal Accumulation in Paddy Soil and Rice: A Three-Site Field Experiment in South China. Toxics 2022, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järup, L.; Åkesson, A. Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Adrees, M.; Rizvi, H.; Rehman, M.Z.; Hannan, F.; Qayyum, M.F.; Hafeez, F. Cadmium stress in rice: Toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms and management: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17859–17879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Abbas, T.; Rehman, M.Z.; Hannan, F.; Keller, C.; Al-Wabel, M.I. Cadmium minimization in wheat: A critical review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 130, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H. Heavy metal contents, distribution, and prediction in a regional soil-wheat system. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.Z.; Khalid, H.; Akmal, F.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Qayyum, M.F.; Iqbal, M.; Khalid, M.U.; Azhar, M. Effect of limestone, lignite and biochar applied alone and combined on cadmium uptake in wheat and rice under rotation in an effluent irrigated field. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Huang, B.; Zhao, Y. Spatially nonstationary relationships between copper accumulation in rice grain and some related soil properties in paddy fields at a regional scale. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, G. Soil properties and cultivars determine heavy metal accumulation in rice grain and cultivars respond differently to Cd stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2019, 26, 14638–14648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, M.A.; James, B.; Chen, Y.H.; Ahmed Saqib, H.S.; Li, H.H.; Jayasuriya, P.; Guo, W. Uptake, translocation, and accumulation of Cd and its interaction with mineral nutrients (Fe, Zn, Ni, Ca, Mg) in upland rice. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ji, X.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lin, Z.; Xiao, S.; Peng, B.; Tan, C.; Zhang, X. Effect of a novel Ca-Si composite mineral on Cd bioavailability, transport and accumulation in paddy soil-rice system. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.S.; Chen, Y.; Fu, H.B.; Cui, Z.H.; Shi, L.; Wang, L.L.; Liu, Z.F. Health risk of heavy metals in food crops grown on reclaimed tidal flat soil in the Pearl River Estuary, China. J. Hazard Mater. 2012, 227–228, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.W.; Zeng, X.F.; Geng, M.S.; Chen, C.Y.; Cai, J.C.; Yu, X.M.; Hou, Y.Y.; Zhang, H. Health risks of heavy metals uptake by crops grown in a sewage irrigation area in China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Yuan, X.Y.; Chen, Y.; Ji, J.F.; Xi, B.B. Quantification of contributions from different sources on heavy metals accumulation in the paddy soil from Suzhou area. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2015, 35, 3269–3275. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.J.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.P.; Shi, Y.; Han, T.Q.; Ye, Y.Y.; Gong, N.; Sun, J.W.; Zhu, C. Different responses of low grain-Cd-accumulating and high grain-Cd accumulating rice cultivars to Cd stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 96, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Jiang, Q.; Xv, C.; Li, L.; Bu, S.; Shi, G. Comparative proteomics analysis of peanut roots reveals differential mechanisms of cadmium detoxification and translocation between two cultivars differing in cadmium accumulation. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Xu, C.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, Q. Heavy metal uptake in rice is regulated by pH-dependent iron plaque formation and the expression of the metal transporter genes. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 162, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Yadav, P.; Thukral, A.K.; Walia, A.; Bhardwaj, R. Co-application of 6-ketone type brassinosteroid and metal chelator alleviates cadmium toxicity in B. juncea L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; You, Y.; Shentu, J.L.; Weng, Y.N.; Wang, S.T.; Xu, Q.R.; Liu, H.J.; Du, S.T. Abscisic acid (ABA)-importing transporter 1 (AIT1) contributes to the inhibition of Cd accumulation via exogenous ABA application in Arabidopsis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudoreanu, L.; Phillips, C.J. Empirical models of cadmium accumulation in maize, rye grass and soya bean plants. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2004, 84, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, A.; Burritt, D.J.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Cao, D.; Tran, L.S.P. The CRISPR/Cas9 system and its applications in crop genome editing. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2019, 39, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Luna, J.; Silva-Silva, M.J.; Martinez-Vargas, S.; Mijangos-Ricardez, O.F.; Gon-zález-Chávez, M.C.; Solís-Domínguez, F.A.; Cuevas-Díaz, M.C. Magnetite nanoparticle (NP) uptake by wheat plants and its effect on cadmium and chromium toxicological behavior. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yourtchi, M.S.; Bayat, H.R. Effect of cadmium toxicity on growth, cadmium accumulation and macronutrient content of durum wheat (Dena CV.). Int. J. Agric. Crop Sci. 2013, 6, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Ci, D.; Jiang, D.; Dai, T.; Jing, Q.; Cao, W. Effects of cadmium on plant growth and physiological traits in contrast wheat recombinant inbred lines differing in cadmium tolerance. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Hu, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H. Comparative proteomic analysis of Cd-responsive proteins in wheat roots. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2011, 33, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, S.; Zhang, L.; Hou, W.; Yu, N. Effect of combined pollution of Cd and B[a]P on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics of wheat. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondor, O.K.; Szalai, G.; Kovács, V.; Janda, T.; Pál, M. Impact of UV-B on drought-or cadmium-induced changes in the fatty acid composition of membrane lipid fractions in wheat. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 108, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgher, M.; Khan, M.I.R.; Anjum, N.A.; Khan, N.A. Minimising toxicity of cadmium in plants-role of plant growth regulators. Protoplasma 2015, 252, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.Q.; Ye, S.C.; Hu, L.Y.; Hu, K.D.; Yan, H.; Li, W.J.; Jiao, H.; Zhang, H. Hydrogen sulfide promotes wheat grain germination under cadmium stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India B Biol. Sci. 2015, 86, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, N.; Ishioka, G.; Yanaka, M.; Takata, K.; Murakami, M. Effects of ammonium chloride fertilizer and its application stage on cadmium concentrations in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grain. Plant Prod. Sci. 2015, 18, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, Y.S.; Chang, S.X.; Gao, B.; Chung, H.J. SMART biochar technology-A shifting paradigm towards advanced materials and healthcare research. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2015, 4, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.T.; Asghar, H.N.; Saleem, M.; Khan, M.Y.; Zahir, Z.A. Synergistic effect of rhizobia and biochar on growth and physiology of maize. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greger, M.; Landberg, T. Novel field data on phytoextraction: Pre-cultivation with salix reduces cadmium in wheat grains. Int. J. Phytorem. 2015, 17, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, Z.; Wei, H. Microwave pretreatment can enhance tolerance of wheat seedlings to CdCl2 stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Reional Screening Level (RSL) Summary Table. 2016. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2016-06/documents/master_sl_table_run_may2016.pdf. (accessed on 1 June 2016).
- Zhuang, P.; McBride, M.B.; Xia, H.P.; Li, N.Y.; Lia, Z.A. Health risk from heavy metals via consumption of food crops in the vicinity of Dabaoshan mine, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meharg, A.A.; Norton, G.; Deacon, C.; Williams, P.; Adomako, E.E.; Price, A.; Zhu, Y.G.; Li, G.; Zhao, F.J.; McGrath, S.; et al. Variation in rice cadmium related to human exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5613–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.P.; Yang, X.P.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.X.; Li, M.; Zhao, F.J. Dietary cadmium intake from rice and vegetables and potential health risk: A case study in Xiangtan, southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustsson, A.; Uddh-Soderberg, T.; Filipsson, M.; Helmfrid, I.; Berglund, M.; Karlsson, H.; Hogmalm, J.; Karlsson, A.; Alriksson, S. Challenges in assessing the health risks of consuming vegetables in metal-contaminated environments. Environ. Int. 2018, n113, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, W.P.; Wang, M.E.; Li, Y.L.; Peng, C. Evaluating the potential health risk of toxic trace elements in vegetables: Accounting for variations in soil factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.M.; Rao, K.Q.; Kong, L.Z.; Yao, C.H.; Xiang, H.D.; Zhai, F.Y.; Ma, G.S.; Yang, X.G. A description on the Chinese national nutrition and health survey in 2002. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 26, 478. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.W. Enrichment Characteristic and Rsk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Rice (Oryza.sativa L.) from Suzhou Regions; Suzhou University of Science and Technology: Suzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L. Heavy Metal Distribution and Food Safety Risk Analysis and Simulation in Soil-Rice System in Northern Jiangsu Province; Nanjing Agricultural University: Nanjing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.B.; Huang, B.; Yang, Y.F.; Darilek, J.L.; Zhao, Y.C.; Sun, W.X.; Wang, Z.G. Heavy metal accumulation characteristics and risk assessment of rice grain in different regions of Suzhou City, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 659–665. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Liao, Q.L.; Xu, H.M.; Ren, J.H.; Chang, Q.; Zhu, B.W.; Li, M. General characteristics of heavy metals absorbed by rice and wheat seeds within topsoil of farmland. J. Geol. 2016, 44, 701–709. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Lin, Y.S.; Zhang, X.F.; Xu, Y.G.; Yu, F. Heavy metal pollution of the soils and wheat grains alongside the Shanghai-Nanjing Expressway. Rural Eco-Environ. 2005, 21, 50–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Jia, J.R.; Dai, B. Distribution of heavy metals in wheat in Jiangsu province. Cereal Food Ind. 2021, 28, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Wu, C.F.; Chen, Y. Concentrations of heavy metals in wheat grains and their potential health risk in the central region of Jiangsu. Environ. Monit. Manag. Technol. 2021, 29, 35–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, T.; Li, F.H.; Huang, L.; Qi, H.B.; Xie, F.; Liang, J.; Wang, A.Q. Research on content of harmful metals in wheat grain from different places in China. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2018, 16, 248–250. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.M.; Liao, Q.L.; Hua, M.; Gao, M.; Zhu, B.W.; Jin, Y. The evaluation of the heavy metal content in the Plough layer and crop in southern Jiangsu province. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 38, 248–250. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.D.; Dai, Q.G.; Xu, X.H.; Zhong, X.C.; Guo, B.W.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, H.C.; Xu, K.; Huo, Z.Y.; Wei, H.Y. Heavy metal contents and evaluation of farmland soil and wheat in typical area of Jiangsu Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 3487–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.T. Simulation Study on the Migration Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Soil-Wheat of Mining Area; China University of Mining and Technology: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L. The Pollution Characteristics of Heavy Metals on Wheat in Mining Area in North of Xuzhou; China University of Mining and Technology: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Liao, S.P.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.K.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.H.; Lu, J.W. Annual nutrient budget differences between oil-rice and wheat-rice rotation systems in the Yangtze River basin. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci. 2019, 25, 64–73. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Fan, Z.X.; Zhang, B.; Bi, Y.P. Study on cadmium pollution and remediation of soil in China. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2007, 6, 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.D.; Yuan, X.Y.; Wang, Y.M. Enrichment characteristics and risk prediction of heavy metals for rice grains growing in paddy soils with a high geological background. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2018, 37, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.Y.; Ma, J.W.; Liu, D.; Fu, W.J.; Ye, Z.Q. Survey and risk assessment of soil heavy metals in the main rice producing areas in Hangjiahu Plain. J. Zhejiang A F Univ. 2021, 38, 336–345. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.B.; Chu, X.Y.; Yin, H.Q.; Xu, M.X.; Huang, C.L.; Song, M.Y. Spatial variation of eight heavy metals in farmland soils and their accumulation in rice grains in Longyou pyrite mine, Zhejiang Province. Soils 2017, 49, 760–769. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.X. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Farmland Soil in Zhejiang Province; Wenzhou University: Wenzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.J.; Wang, H.L.; Li, X.C.; Zhang, Y.H.; Liu, J.; Li, D.Y. Pollution of heavy metals in typical crops of northern Henan Prov-ince and health risk assessment. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 23, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.F.; Tan, J.; Lei, D.E.; Tao, C.J.; Du, G.Q.; Liu, C. Characteristics and ecological security assessment of heavy metal on wheat and root soils along Huaihe river commercial grain base in Anhui Province. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 33, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.P.; Peng, K.L.; Zhou, M.H. Investigation and evaluation of heavy metal pollution in suburb an paddy soils. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2008, 16, 680–685. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, J.Z. Characteristics of Heavy Metal Pollution in Paddy Soils and Soil-Rice Heavy Metal Coupling Relationship in Typical Paddy Fields; Nanjing Agricultural University: Nanjing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.Y. Heavy Metal Pollution in Farmland Soil and Crops in a Mining Area in Hunan Province and Its Health Risk Assessment; Hunan Agricultural University: Nanjing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.L. Distribution Characteristics of Cadmium-Contaminated Paddy Soil-Rice Elements and Evaluation of Heavy Metal Pollution in Liling, Hunan Province; Chengdu University of Technology: Chengdu, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Tang, Z.M.; Zhang, M.; Liang, X.H.; Zhan, L. Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metal in soil-rice system in the Ganzhou area, Jiangxi Province. Geol. Bull. China. 2021, 40, 2149–2158. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.Y.; Wang, P.; Wu, X.C.; Li, Z.P.; Zhou, D.M. Effect of long-term fertilization experiment on concention of micronutrients heavy metals in soil and brown rice. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2009, 46, 281–288. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Y.S.; Shi, Z.H.; Yang, G.; Si, Y.Y.; Cheng, R. Status of heavy metal pollution in paddy soil and human health risk as-sess-ment of rice around phosphogypsum yard. J. Earth Environ. 2021, 12, 224–231. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Deng, L.J. Effects of heavy metals in the paddy soil in Sichuan province on rice grain. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2005, 24, 174–177. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. The Speciation and Bioavailability Study of Heavy Metals in Paddy Soils under the Rice-Wheat Cultivation Rotation; Sichuan Agricultural University: Ya’an, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, F.F. Effects of Swine Manure Application on Heavy Metals in Soils and Crops under Rice Wheat Rotation System; Sichuan Agri-cultural University: Ya’an, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Application Study on In-Situ Remediation of Safe Use Farmland Soil with Mild to Moderate Cd Contamination; Beijing Forestry University: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, T.Z.; Zhu, M.X.; Xiao, J. Characteristics of Migration and Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Soil-Rice System of Tianmen and Its Health Risk Assessment. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 45, 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Peng, M.M.; Xia, H. Investigation and Analysis of Wheat Quality in Hubei Province. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2017, 56, 4872–4874. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.S.; Li, X.; Wan, W.; Liu, K. Study on tracking and verification of heavy metal content in soil and rice in a typical area of Chongqing. Acta Agric. Jiangxi. 2020, 32, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, F. Heavy Metal Correlation between Soil and Grain Crops Characteristics and Pollution Assessment in Chongqing; South-west Agricultural University: Guangzhou, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.J.; Jin, C.Z.; Sun, C.; Liu, S.C.; Yao, H.H.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, J.P. The content and enrichment characteristics of heavy met-als in soil-rice system of paddy field in Minhang District, Shanghai. Acta Agric. Shanghai. 2020, 36, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Han, J.X.; Ma, J.H. Health risk assessment of wheat seeds heavy metals in the sewage irrigation area of Huafei River, Kaifeng City. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2008, 27, 2332–2337. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Wu, X.J.; Hui, R.Q.; Xia, X.; Chen, Z.J.; Yao, L.G.; Yang, J.J. Synergistic effects of Cd-loving Bacillus sp. N3 and iron oxides on immobilizing Cd and reducing wheat uptake of Cd. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 305, 119303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Chen, W.P.; Yang, Y. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and comprehensive risk evaluation of farmland across the eastern plain of Jiyuan city. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2020, 40, 2229–2236. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.C.; Fan, L.X.; Zhao, P.J.; Chen, L. Contamination status and evaluation of cadmium and chromium in wheat grain in typical areas of Shandong Province. J. Triticeae Crops. 2016, 36, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Li, M.; Wu, H. Spatial variation and evaluation of Pb and Cd in suburban farmland soils–a case study of Changsha city. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin. 2012, 21, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- He, P. Study on Safety Control Technology of Soil Cadmium at Typical Pollution Area in Southern China; Guizhou University: Gui-yang, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Wang, Y.B.N.; Mao, W.F.; Sui, H.X.; Yong, L.; Yang, D.J.; Jiang, D.G.; Zhang, L.; Gong, Y.Y. Dietary cadmium exposure assessment among the Chinese population. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. Cadmium dietary exposure in the European population. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; WHO. Evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants. Seventy-third Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Indian J. Med. Res. 2012, 135, 446–447. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, W.; Liu, Q.; Li, Q. Hazard and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution to Agricultural Products; South-West Agricultural University: Guangzhou, China, 2010; pp. 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.L.; Yang, X.E.; Stoffella, P.J. Trace elements in agroecosystems and impacts on the environment. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2005, 19, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inboonchuay, T.; Suddhiprakarn, A.; Kheoruenromne, I.; Anusontpornperm, S.; Gilkes, R.J. Amounts and associ ations of heavy metals in paddy soils of the Khorat basin, Thailand. Geoderma. Reg. 2016, 7, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.L.; He, T.B.; Liu, C.Q.; Lu, X.H. Effects of land use and parent materials on trace elements accumulation in topsoil. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Z.; Xiao, T.F.; Xiong, Y.; Ning, Z.P.; Shuang, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, L.; Chen, H.Y. Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils and crops from an area with a high geochemical background of cadmium, Southwestern China. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 2877–2884. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.H.; Peng, M.; Liu, F.; Guo, F.; Tang, S.Q.; Liu, X.J.; Zhou, Y.L.; Yang, K.; Li, K.; Yang, Z.; et al. Bioavailability, trans-loca-tion, and accumulation characteristic of heavy metals in a soil-crop system from a typical carbonate rock area in Guangxi. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 449–459. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Pang, R.; Wang, F. Safety assessment of rice planting in soil cadmium geological anomaly areas in Southwest Guang-xi. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.B.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.F.; Zhuo, X.X.; Guan, D.X.; Song, Y.X.; Guo, C.; Ji, J.F. Evaluation of various approaches to predict cadmium bioavailability to rice grown in soils with high geochemical background in the karst region, Southwestern China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Mining Development Report (Excerpt). Equip. Geotech. Eng. 2020, 21, 43–45.
- Navarro, M.C.; Pérez-Sirvent, C.; Martínez-Sánchez, V.J.; Tovar, P.J.; Bech, J. Abandoned mine sites as a source of contami-na-tion by heavy metals: A case study in a semi-arid zone. J. Geochem. Explor. 2008, 96, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S. The Pollution of Heavy Metal Elements Accumulation and Risk in Ore District; South China University of Technology: Guangzhou, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. Metal Contamination Evaluation, Eco-Toxicity and Microbial Remediation of Paddy Soil Located in e-Waste Recy-cling Area; Zhejiang University: Hangzhou, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Tao, S. The challenges and solutions for cadmium contaminated rice in China: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 515–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Mao, K.; Zhang, H.; Junaid, M.; Xu, N.; Rasool, A.; Feng, X.B.; Yang, Z.G. Comprehensive review of the basic chemical behaviours, sources, processes, and endpoints of trace element contamination in paddy soil-rice systems in rice-growing coun-tries. J. Hazard Mater. 2020, 397, 122720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Lee, S.S.; Zhang, M.; Tsang, Y.F.; Kim, K.H. Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and man-agement. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nziguheba, G.; Smolders, E. Inputs of trace elements in agricultural soils via phosphate fertilizers in European countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Chen, Y.L.; Weng, L.P.; Ma, J.; Ma, Y.L.; Li, Y.T.; Islam, M.S. Comparisons of heavy metal input inven tory in agri-cul-tural soils in north and south China: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Qiao, Y.H.; Su, D.C.; Jiang, R.F.; Rui, Y.K.; Li, H.F. Application of ICP-MS and AFS to de-tect-ing heavy metals in phosphorus fertilizers. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2013, 34, 1403–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Yang, Z.L.; Dai, M.W.; Diao, X.Y.; Dai, S.L.; Fang, T.; Dong, X.J. Input of cd from agriculture phosphate fertilizer ap-pli-cation in China during 2006-2016. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Ma, Y.B.; Zhang, S.Z.; Wei, D.P.; Zhu, Y.G. An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2524–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Adebayo, A.; Jia, J. Impacts of heavy metals and soil properties at a Nigerian e-waste site on soil micro bial com-mu-nity. J. Hazard Mater. 2018, 362, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, J.K.; Kumar, S. Informal e-waste recycling: Environmental risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in mandoli industrial area, Delhi, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Control Ser. 2014, 21, 7913–7928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.Q.; Yu, Y.; Wan, Y.A.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Z.; Qiao, Y.H.; Su, D.C.; Li, H.F. Effects of continuous fertilization on bioa-vail-ability and fractionation of cadmium in soil and its uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 215, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogusz, A.; Oleszczuk, P. Effect of biochar addition to sewage sludge on cadmium, copper and lead speciation in sewage sludge-amended soil. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakis, I.; Emmanouil, C.; Mitrakas, M.; Manakou, V.; Kungolos, A. Chemical and ecotoxicological assessment of sludge-based biosolids used for corn field fertilization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codling, E.E.; Jaja, N.; Adewunmi, W.; Evanylo, G.K. Residual Effects of Long-term Biosolids Application on Concentrations of Carbon, Cadmium, Copper, Lead and Zinc in Soils from Two Regions of the United States. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2021, 52, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, A.; Prasad, M.N.V. Iron- and manganese-assisted cadmium tolerance in Oryza sativa L.: Lowering of rhizotoxicity next to functional photosynthesis. Planta 2015, 241, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.R.; Kandeel, M.M.; Ghareeb, D.; Ghoneim, T.M.; Talha, N.I.; Alaoui-Sosse, B.; Aleya, L.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Wheat bi-ological responses to stress caused by cadmium, nickel and lead. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 706, 136013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsen, J. Measuring bioavailability: From a scientific approach to standard methods. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.; Yoon, J.K.; Kim, T.S.; Yang, J.E.; Owens, G.; Kim, K.R. Bioavailability of heavy metals in soils: Definitions and practical implementation–a critical review. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2015, 37, 1041–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Ishikawa, S.; Abe, T. Role of the node in controlling traffic of cadmium, zinc, and manganese in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 2729–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Han, L.; Chao, D. Ionomic and transcriptomic analysis provides new insight into the distribution and transport of cadmium and arsenic in rice. J. Hazard Mater. 2017, 331, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeniji, B.A.; Budimir-Hussey, M.T.; Macfie, S.M. Production of organic acids and adsorption of Cd on roots of durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var. durum). Acta Physiol. Plant. 2010, 32, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, A.; McLaren, R.G.; Speir, T.W.; Clucas, L.; Condron, L.M. Gradient differences in soil metal solubility and uptake by shoots and roots of wheat (T. aestivum). Biol. Fert. Soils 2014, 50, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Tian, R.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, H.; Pei, D.; Wang, X. Combined cadmium and elevated ozone affect concentrations of cad-mi-um and antioxidant systems in wheat under fully open-air conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Lv, J.; He, W.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.; Dai, Y. Major factors influencing cadmium uptake from the soil into wheat plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greger, M.; Landberg, T. Role of rhizosphere mechanisms in Cd uptake by various wheat cultivars. Plant Soil 2008, 312, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, A.S.; Eriksson, J.; Campbell, C.D.; Öborn, I. Soil amendment affects Cd uptake by wheat—Are we under estimating the risks from chloride inputs? Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 554, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, D.; Jiang, D.; Wollenweber, B.; Dai, T.; Jing, Q.; Cao, W. Cadmium stress in wheat seedlings: Growth, cadmium accumu-la-tion and photosynthesis. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2010, 32, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, J.J.; Welch, R.M.; Norvell, W.A.; Kochian, L.V. Characterization of cadmium uptake, translocation and stor age in near-isogenic lines of durum wheat that differ in grain cadmium concentration. New Phytol. 2006, 172, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, N.S.; Taylor, G.J. Cadmium uptake and translocation in seedlings of near isogenic lines of durum wheat that differ in grain cadmium accumulation. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Harris, N.S.; Taylor, G.J. Cadmium uptake and partitioning in durum wheat during grain filling. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riesen, O.; Feller, U. Redistribution of nickel, cobalt, manganese, zinc, and cadmium via the phloem in young and maturing wheat. J. Plant Nutr. 2005, 28, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Vliet, L.; Peterson, C.; Hale, B. Cd accumulation in roots and shoots of durum wheat: The roles of tran spiration rate and apoplastic bypass. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 2939–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Zhu, C.; Ren, Y.F.; Yan, Y.P.; Jiang, D. Genotypic variation in grain cadmium concentration of lowland rice. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2006, 169, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, A.; Yamaji, N.; Feng, M.J. Overexpression of OsHMA3 enhances Cd tolerance and expression of Zn trans porter genes in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 6013–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Liang, S.; Qiao, K.; Wang, F.H.; Zhang, Y.X.; Chai, T.Y. Co-expression of multiple heavy metal transport ers changes the translocation, accumulation, and potential oxidative stress of Cd and Zn in rice (Oryza sativa). J. Hazard Mater. 2019, 380, 120853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Huang, X.M.; Sun, L.M.; Li, S.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Cao, X.Y.; Wang, W.X.; Dai, Y.L. Screening stably low cadmium and mod-erately high micronutrients wheat cultivars under three different agricultural environments of China. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Du, B.Y.; Lu, B.X.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y. Effects of node restriction on cadmium accumulation in eight Chi-nese wheat (Triticum turgidum) cultivars. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.R.; Zhang, Q.F.; Fu, B.S.; Cai, S.; Wu, J.D.; Chen, Y. Differences of lead, cadmium and zinc accumulation among Chi-nese wheat mini-core collections germplasms and screening for low Pb, Cd and Zn accumulative cultivars in grains. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2017, 40, 393–399. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, K.; Wang, F.; Liang, S.; Wang, S.; Chai, T. New biofortification tool: Wheat Ta CNR5 enhances zinc and manganese tol-erance and increases zinc and manganese accumulation in rice grains. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 9877–9884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Miao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Gan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Dai, J. Roles of rhizospheric organic acids and microorgan isms in mer-cury accumulation and translocation to different winter wheat cultivars. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 258, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, G. Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 119, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, C.; Ma, L.Q. Concentration, pH, and surface charge effects on cadmium and lead sorption in three tropical soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.M. Sorption and lability of cadmium and lead in different soils from Egypt and Greece. Geoderma 2009, 153, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.Z.; Zhang, X.M.; Li, B.Z.; Wang, Y.J.; Guo, J.C. Distribution of Cd and Cu fractions in Chinese soils and their relation-ships with soil pH: A meta-analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicińska, A.; Pomykała, R.; Izquierdo Diaz, M. Changes in soil pH and mobility of heavy metals in contaminated soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, e13203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.P.; Song, Y.X.; Chen, L.X.; Ji, J.F.; Li, J.Z.; Yuan, X.Y.; Yang, Z.F.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L.; Theiss, F. Human health risks of heavy metals in paddy rice based on transfer characteristics of heavy metals from soil to rice. Catena 2019, 175, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, S.; Xu, M.; Gilles, C. Evolution characteristics and influence factors of acidification in paddy soil of Southern China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2015, 48, 4811–4817. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, J. The effects of clay, organic matter and time on adsorption and plant uptake of cadmium added to the soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1988, 40, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.P.; Mota, A.M.; Varennes, A.de; Pinto, F.C. Influence of organic matter on the uptake of cadmium, zinc, copper and iron by sorghum plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 326, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yuan, X.; Li, T.; Hu, S.; Ji, J.; Wang, C. Characteristics of heavy metal transfer and their influencing factors in dif-fer-ent soil crop systems of the industrialization region, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Ding, X. Biochar combined with phosphate fertilizer application reduces soil cadmium availability and cad-mium uptake of maize in Cd-contaminated soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 25925–25938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, N.; Saifullah, U.; Malhi, S.S.; Zia, H.M.; Naeem, A.; Bibi, S.; Farid, G. Role of mineral nutrition in minimizing cadmium accumulation by plants. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Yu, H.Y.; Li, F.B.; Fang, L.P.; Liu, C.P.; Huang, W.L.; Du, Y.M.; Peng, Y.M.; Xu, Q. Behaviors of heavy metal(loid)s in a cocontaminated alkaline paddy soil throughout the growth period of rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 136204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.; Singh, R.; Arora, N.K. Alleviation of heavy metal stress in plants and remediation of soil by rhizosphere mi-croor-ganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Pang, H.D.; He, L.Y.; Wang, Q.; Sheng, X.F. Cd immobilization and reduced tissue Cd accumulation of rice in the pres-ence of heavy metal-resistant bacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 138, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Guan, D.; Peart, M.R.; Chen, Y.J.; Li, Q.Q.; Dai, J. The influence of bioavailable heavy metals and microbial parameters of soil on the metal accumulation in rice grain. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanbakhsh, M.; Kowalchuk, G.A.; Jousset, A. Optimization of plant hormonal balance by microorganisms pre vents plant heavy metal accumulation. J. Hazard Mater. 2019, 379, 120787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etesami, H. Bacterial mediated alleviation of heavy metal stress and decreased accumulation of metals in plant tissues: Mech-anisms and future prospects. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.L.; Fu, G.H.; Song, Q.; Fan, C.W.; Liu, G.H. Characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal pollution of Triassic osmotic paddy soil in the Southwest of Guizhou province. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2020, 36, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Fathollahi, A.; Khasteganan, N.; Coupe, S.J.; Newman, A.P. A meta-analysis of metal biosorption by suspended bacteria from three phyla. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 129290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Tie, B.Q.; Li, Y.X.L.; Lei, M.; Wei, X.D.; Liu, X.L.; Du, H.H. Inoculation of soil with cadmium-resistant bacterium Delftia sp. B9 reduces cadmium accumulation in rice grains. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.K.; Chen, J.; Huang, B.; Zhao, Y.C. Exploring the spatially varying relationships between cadmium accu mulations and the main influential factors in the rice-wheat rotation system in a large-scale area. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, S.B.; Guo, X.Y.; Ning, R.Y. Influencing Factors of Cadmium Content in Wheat Grain: A Meta-analysis and De-cision Tree Analysis. Environ. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Jia, Z.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Chen, L.; Zou, M.M.; Li, Y.; Zhou, S.L. Heavy metal distribution, relationship and prediction in a wheat-rice rotation system. Geoderma 2019, 354, 113886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L. Effects of soil properties on crop Cd uptake and prediction of Cd concentration in grains. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2007, 26, 699–703. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.Y.; Liu, S.T.; Mi, C.H.; Hou, Y.L.; Wang, M.; Cai, Y.M. Statistical analysis of factors affecting Cd bioaccumulation in soil-rice grain system. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 1880–1888. [Google Scholar]
- Greger, M.; Löfstedt, M. Comparison of uptake and distribution of cadmium in different cultivars of bread and durum wheat. Crop Sci. 2004, 44, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarnejadi, A.R.; Homaee, M.; Sayyad, G.; Bybordi, M. Large scale spatial variability of accumulated cadmium in the wheat farm grains. Soil. Sediment Contam. 2011, 20, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, M.; Bakht, J.; Razuddin, R.; Hayat, Y.; Zhang, G.P. Genotypic difference in the inhibition of photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence by salinity and cadmium stresses in wheat. J. Plant Nutr. 2011, 34, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.L.; Liang, L.; Yang, H. Joint ecotoxicology of cadmium and metsulfuronmethyl in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 2939–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Cai, Z. Effect of soil HHCB on cadmium accumulation and phytotoxicity in wheat seedlings. Bull. Environ. Con-tam. Toxicol. 2015, 95, 272–277. [Google Scholar]
- Poghosyan, G.H.; Mukhaelyan, Z.H.; Vardevanyan, P.H. Influence of cadmium ions on growth and antioxidant system activity of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Seedlings. Int. J. Sci. Res. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 371–378. [Google Scholar]
- Tauqeer, H.M.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, Q.; Saeed, R.; Iftikhar, U.; Ahmad, R.; Farid, M.; Abbasi, G.H. Phytoreme diation of heavy metals by Alternanthera bettzickiana: Growth and physiological response. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Zhou, Q.X.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Y.Y. Effects of soil polycyclic musk and cadmium on pollutant uptake and biochemical responses of wheat (Triticum aestivum). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 59, 564–573. [Google Scholar]
- Gajewska, E.; SkŁodowska, M. Differential effect of equal copper, cadmium and nickel concentration on biochem ical reactions in wheat seedlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Mohr, R.M.; McLaren, D.L.; Grant, C.A. Grain cadmium and zinc concentrations in wheat as affected by genotypic variation and potassium chloride fertilization. Field Crops Res. 2011, 122, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, H.; Tosun, Y.K.; Ozturk, M. Effect of cadmium-zinc interactions on growth and Cd-Zn concentration in durum and bread wheats. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2012, 21, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Naeem, A.; Saifullah, S.; Rehman, M.Z.U.; Akhtar, T.; Ok, Y.S.; Rengel, Z. Genetic variation in cadmium accumula tion and toler-ance among wheat cultivars at the seedling stage. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plant Anal. 2016, 47, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Hu, N.; Yang, M.; Zhan, X.; Zhang, Z. Effects of different tillage and straw return on soil organic carbon in a rice-wheat rotation system. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


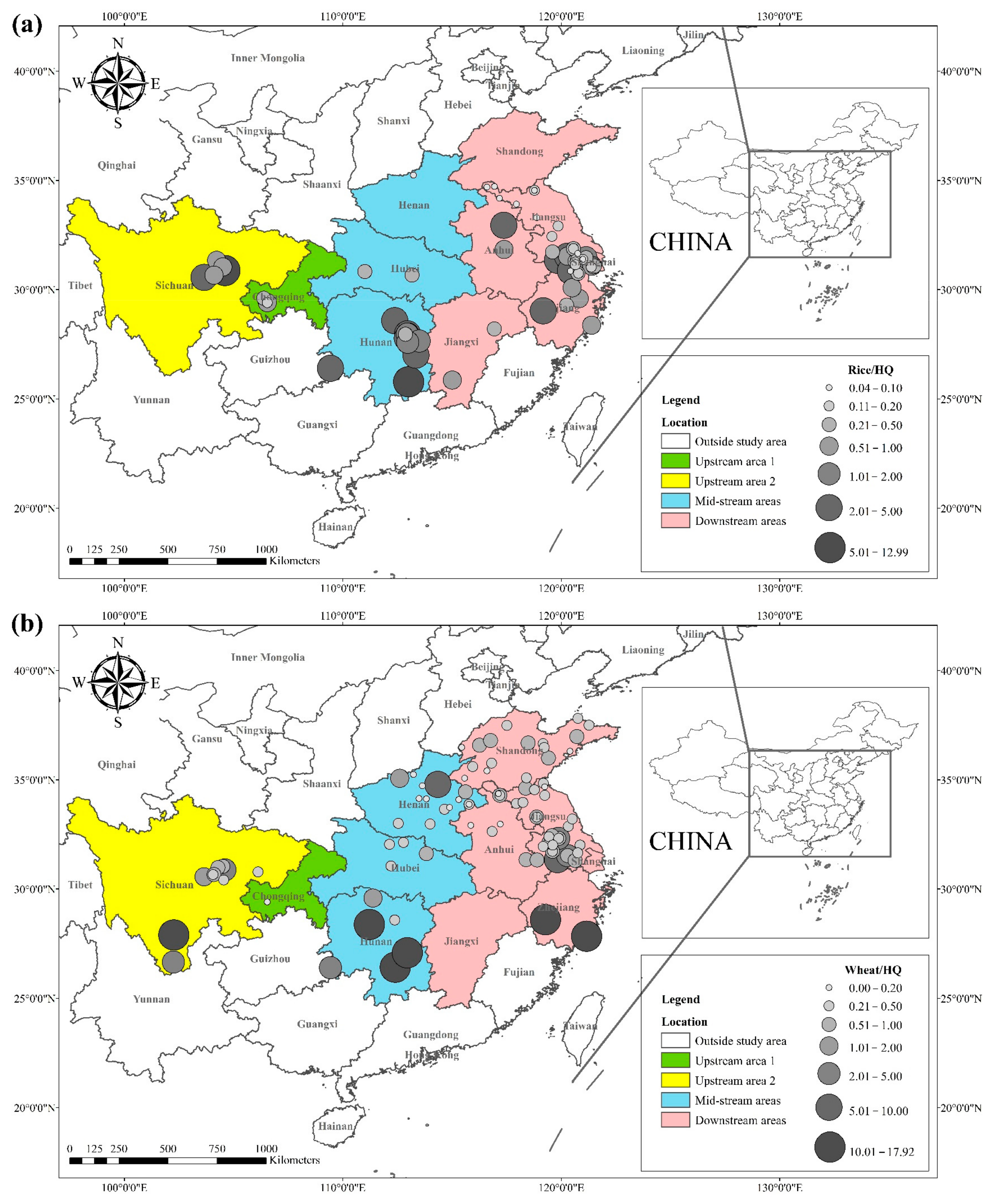

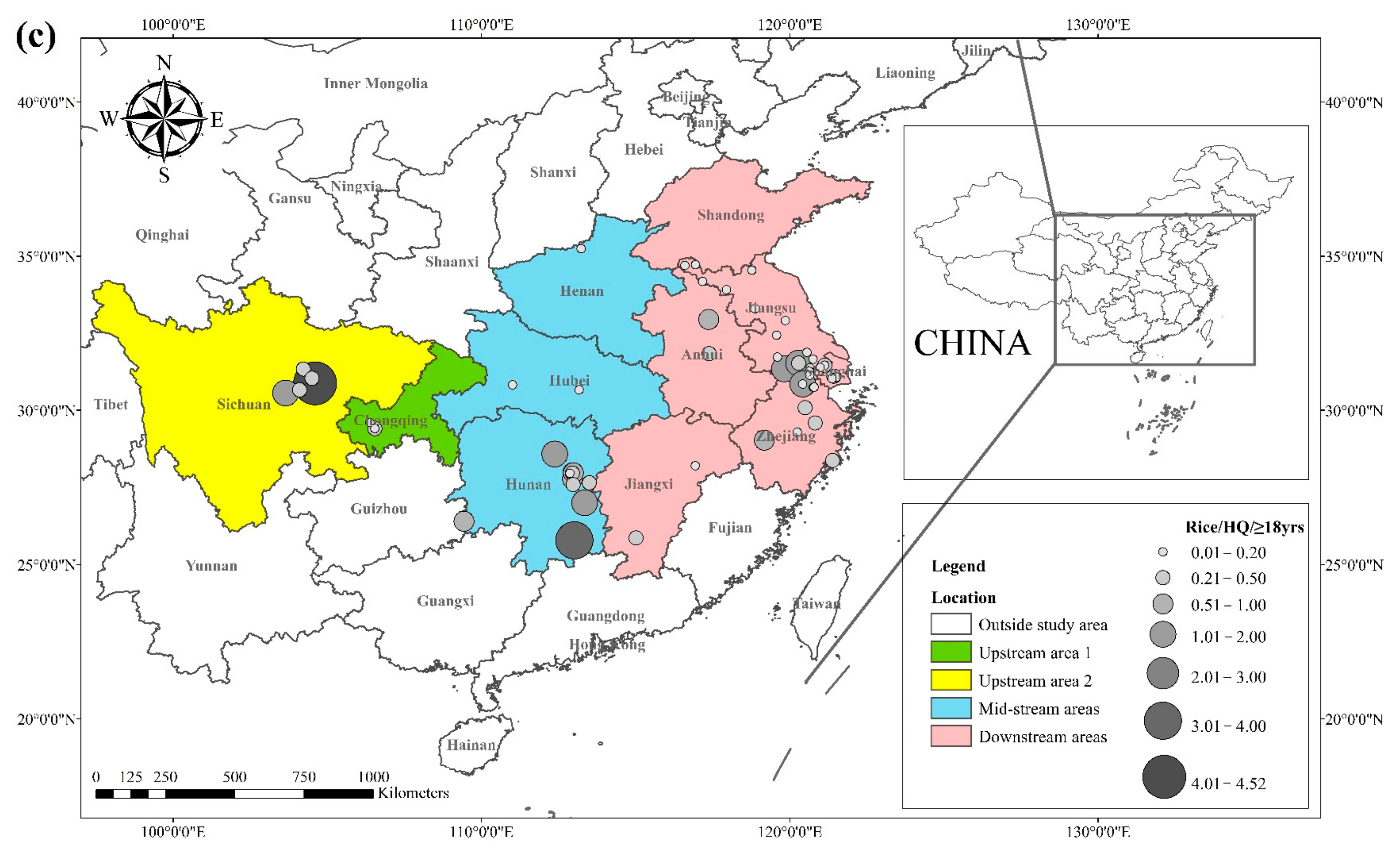


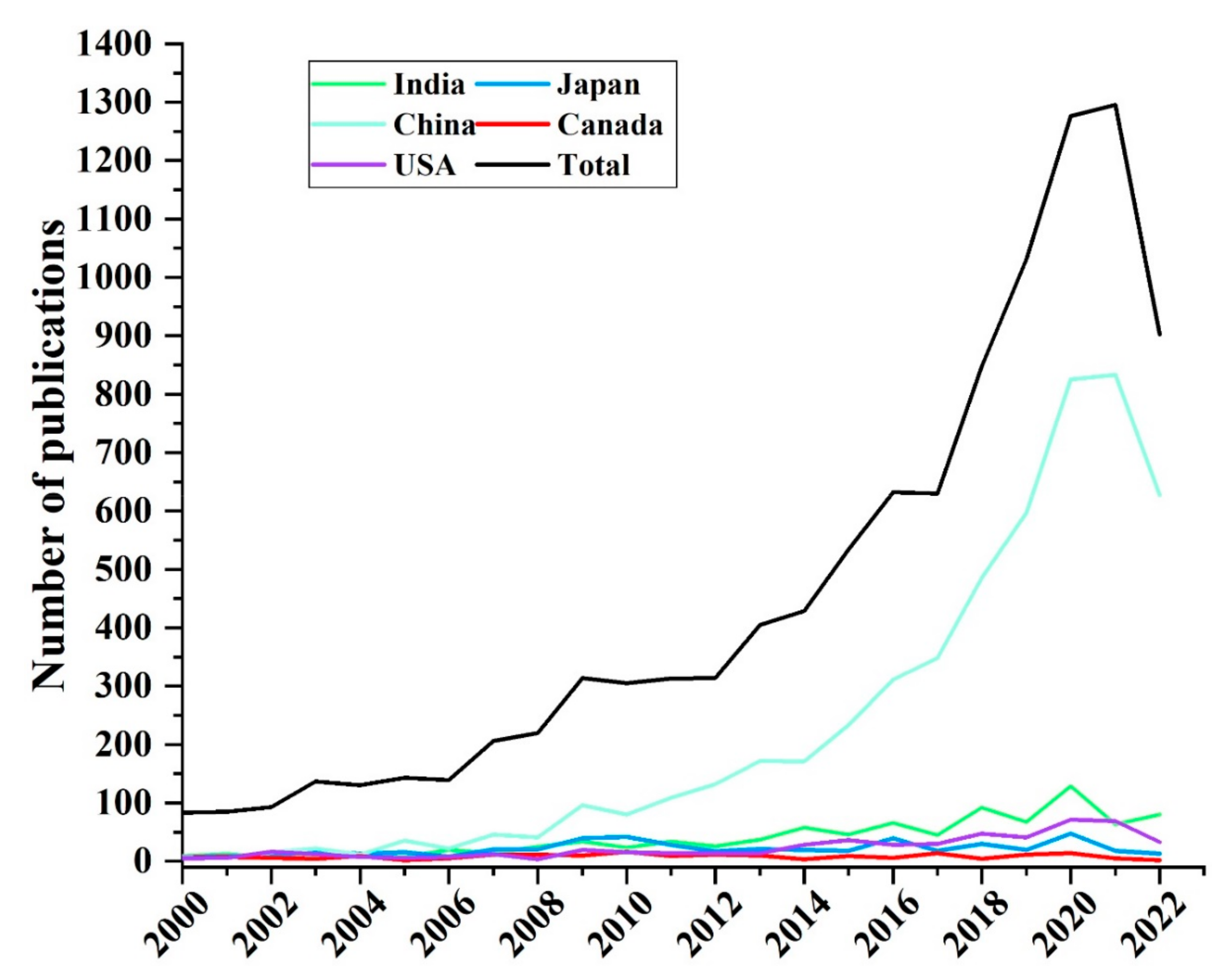
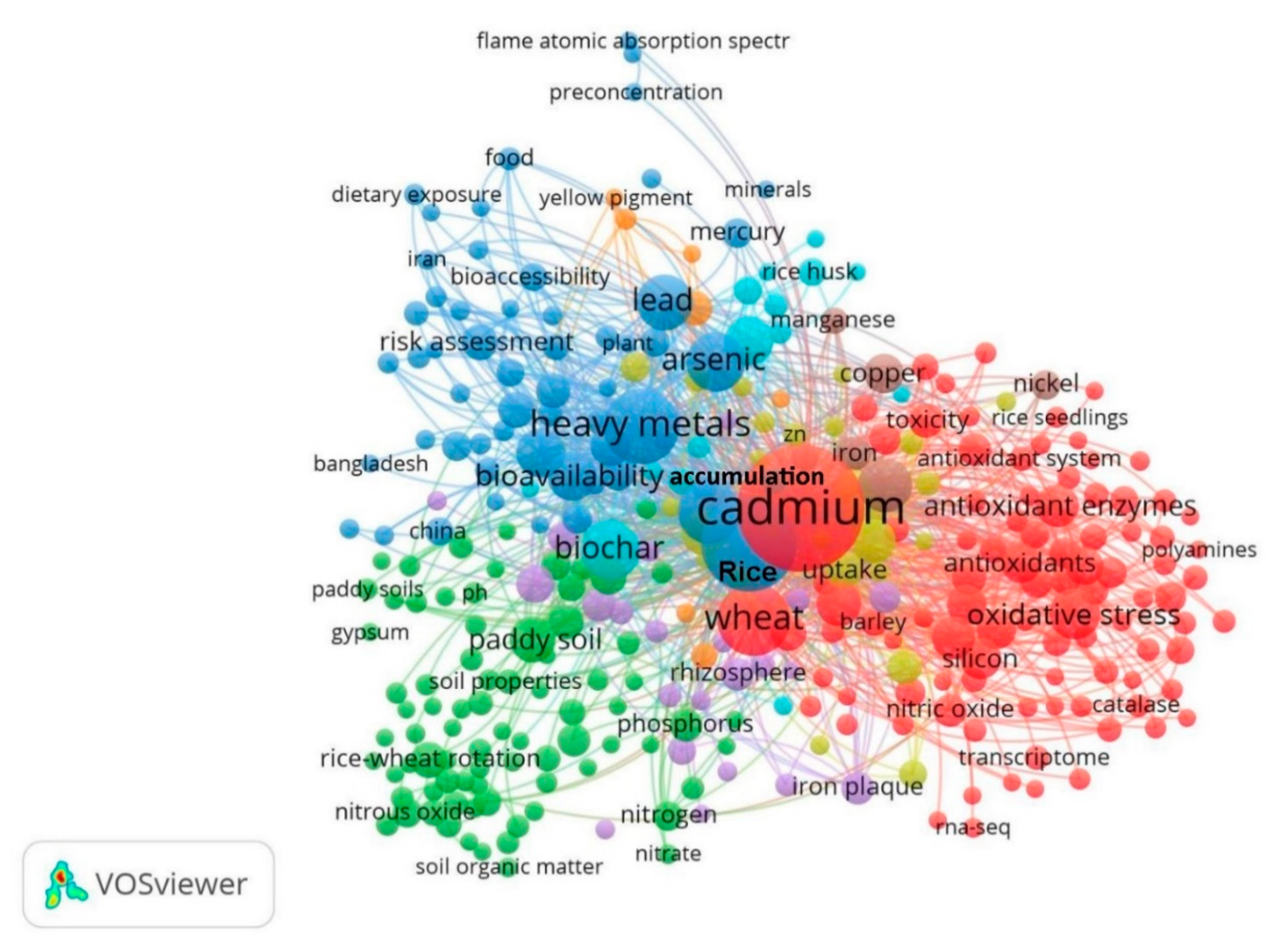
| Province | Mean/Ricecd (mg kg−1) | Range (mg kg−1) | Mean/Wheatcd (mg kg−1) | Range (mg kg−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jiangsu | 0.0532 ± 0.0204 | 0.0040~0.4190 | 0.1050 ± 0.0320 | 0.0150~0.8700 | [55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67] |
| Zhejiang | 0.1216 ± 0.0378 | 0.0200~0.3400 | 0.9010 ± 0.3361 | 0.0233~1.30 | [68,69,70,71,72] |
| Anhui | 0.0860 | 0.0860 | 0.0358 ± 0.0250 | 0.0358~0.0102 | [62,73,74] |
| Hunan | 0.4322 ± 0.1513 | 0.0420~1.415 | 0.8720 ± 0.3185 | 0.0400~1.57 | [62,71,74,75,76,77,78] |
| Jiangxi | 0.0605 ± 0.0185 | 0.0420~0.0790 | — | — | [79,80] |
| Sichuan | 0.4403 ± 0.2123 | 0.1100~1.4500 | 0.3448 ± 0.1896 | 0.0400~0.4400 | [5,68,81,82,83,84,85] |
| Hubei | 0.0460 | 0.0460 | 0.0533 ± 0.0233 | 0.0300~0.100 | [61,86,87] |
| Chongqing | 0.0462 ± 0.0143 | 0.0220~0.0870 | 0.0080 | 0.0080 | [88,89] |
| Shanghai | 0.0448 ± 0.0111 | 0.0190~0.0820 | — | — | [90] |
| Henan | 0.0046 | 0.0046 | 0.0482 ± 0.0174 | 0.0100~0.6300 | [62,73,91,92,93] |
| Shangdong | — | — | 0.0435 ± 0.0061 | 0.0100~0.0920 | [61,94] |
| Rank | Publication Sources | Number of Literature |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Environmental Science and Pollution Research | 425 |
| 2 | Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety | 339 |
| 3 | Science of the Total Environment | 297 |
| 4 | Chemosphere | 263 |
| 5 | Environmental Pollution | 238 |
| 6 | Journal of Hazardous Materials | 212 |
| 7 | Plant and Soil | 169 |
| 8 | Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis | 101 |
| 9 | Fields Crops Research | 93 |
| 10 | Scientific Reports | 87 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, D.; Li, X. The Status and Research Progress of Cadmium Pollution in Rice- (Oryza sativa L.) and Wheat- (Triticum aestivum L.) Cropping Systems in China: A Critical Review. Toxics 2022, 10, 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120794
Gao Y, Duan Z, Zhang L, Sun D, Li X. The Status and Research Progress of Cadmium Pollution in Rice- (Oryza sativa L.) and Wheat- (Triticum aestivum L.) Cropping Systems in China: A Critical Review. Toxics. 2022; 10(12):794. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120794
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yue, Zengqiang Duan, Lingxiao Zhang, Da Sun, and Xun Li. 2022. "The Status and Research Progress of Cadmium Pollution in Rice- (Oryza sativa L.) and Wheat- (Triticum aestivum L.) Cropping Systems in China: A Critical Review" Toxics 10, no. 12: 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120794
APA StyleGao, Y., Duan, Z., Zhang, L., Sun, D., & Li, X. (2022). The Status and Research Progress of Cadmium Pollution in Rice- (Oryza sativa L.) and Wheat- (Triticum aestivum L.) Cropping Systems in China: A Critical Review. Toxics, 10(12), 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120794