Transcriptomic Interaction between Young Fecal Transplantation and Perfluorobutanesulfonate in Aged Zebrafish Gonads
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
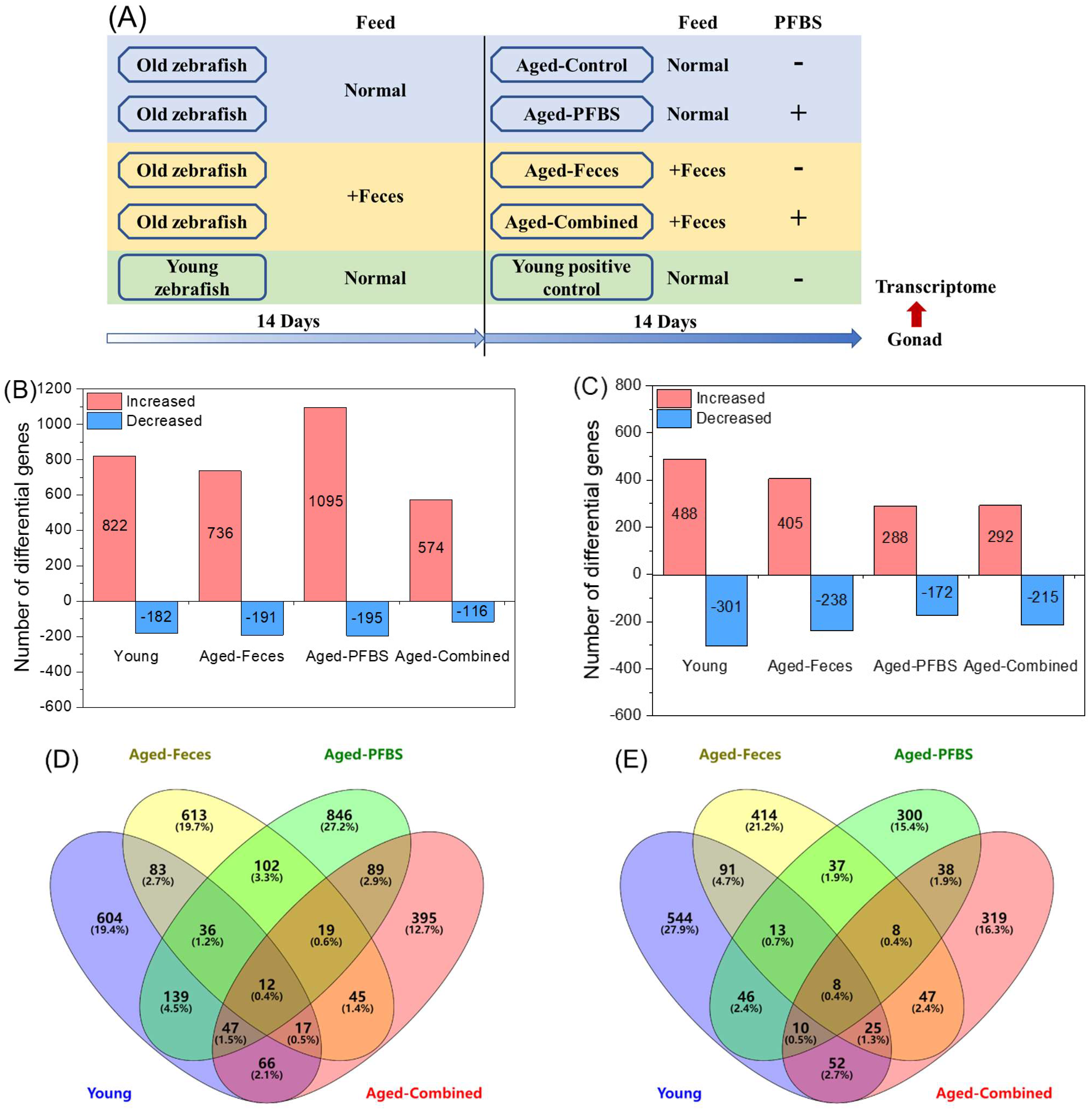
2.2. Fish Maintenance and Exposure
2.3. High-Throughput Transcriptomic Sequencing
2.3.1. Total RNA Isolation and Illumina Sequencing
2.3.2. Bioinformatics Analyses
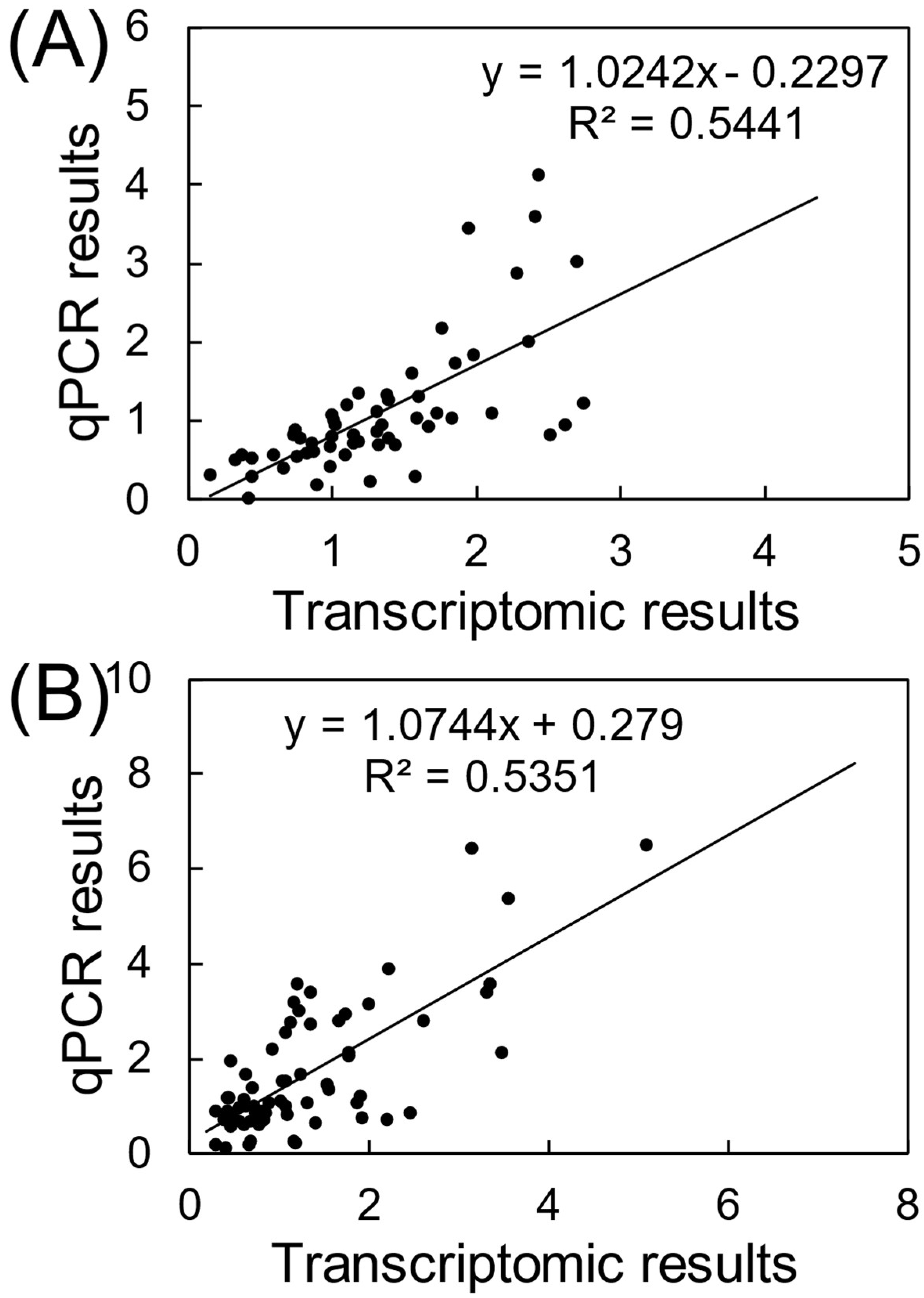
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Assays (qRT-PCR)
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
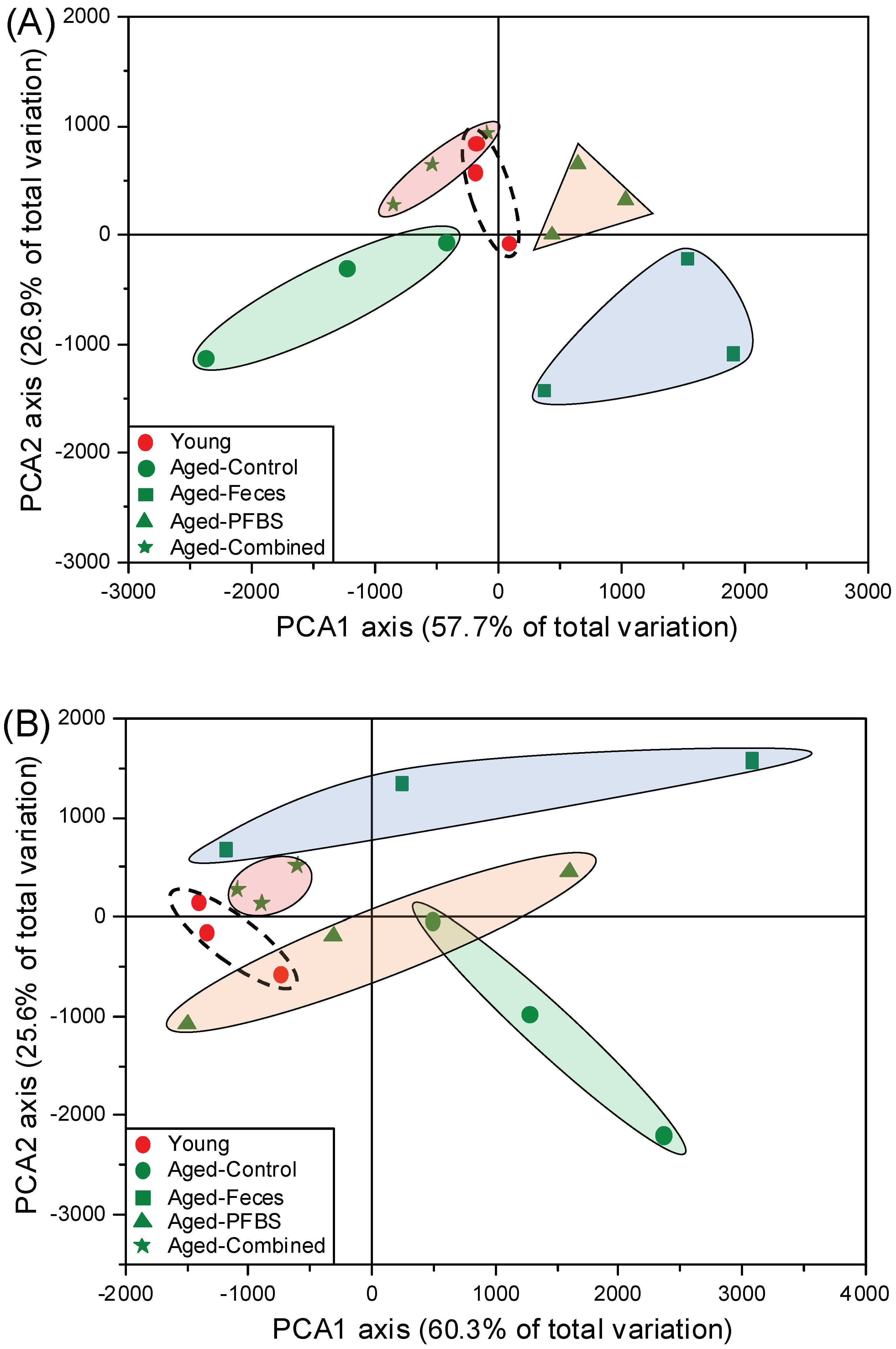
3.1. Transcriptomic Sequencing Quality
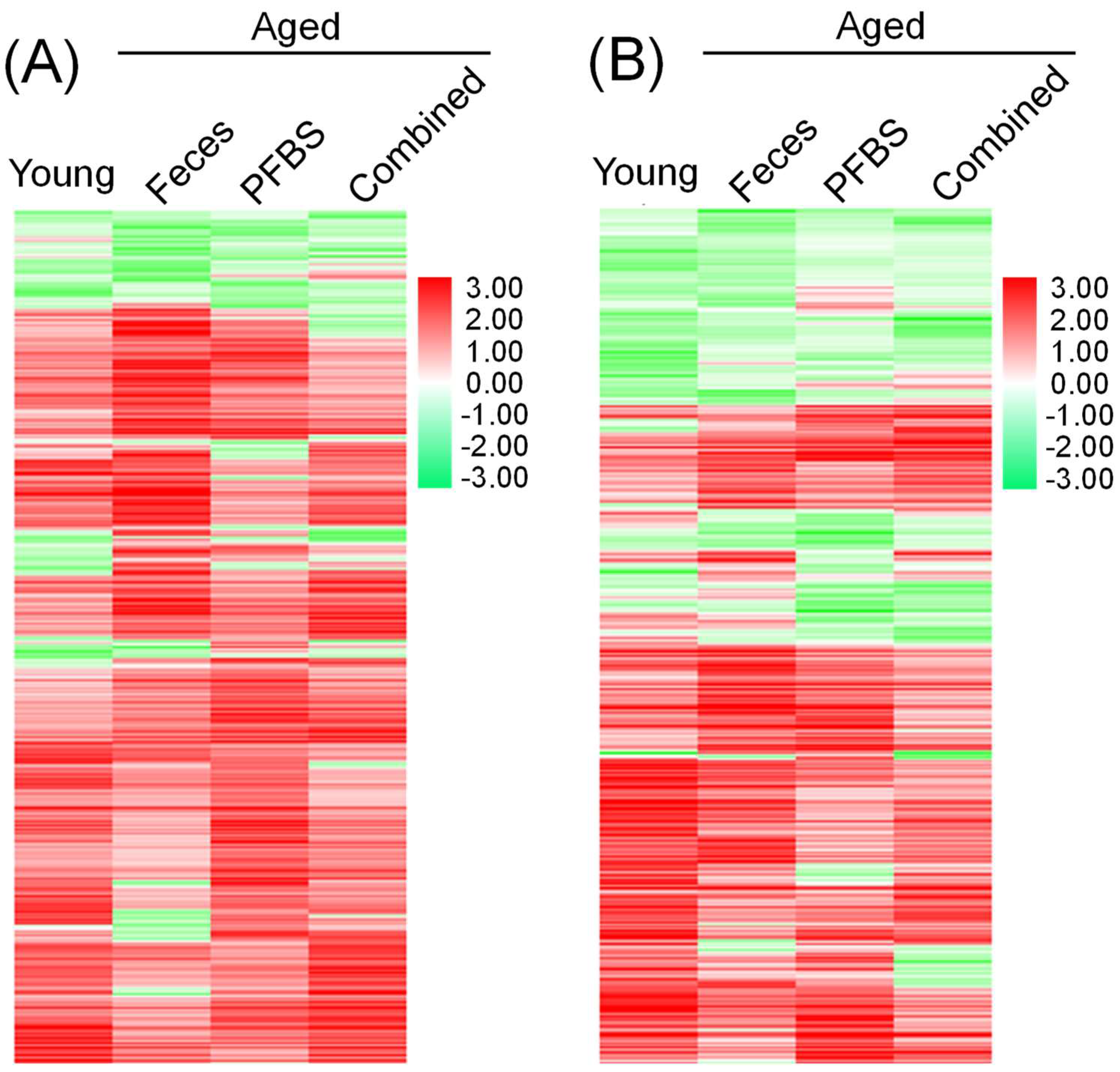
3.2. Summary of DEGs
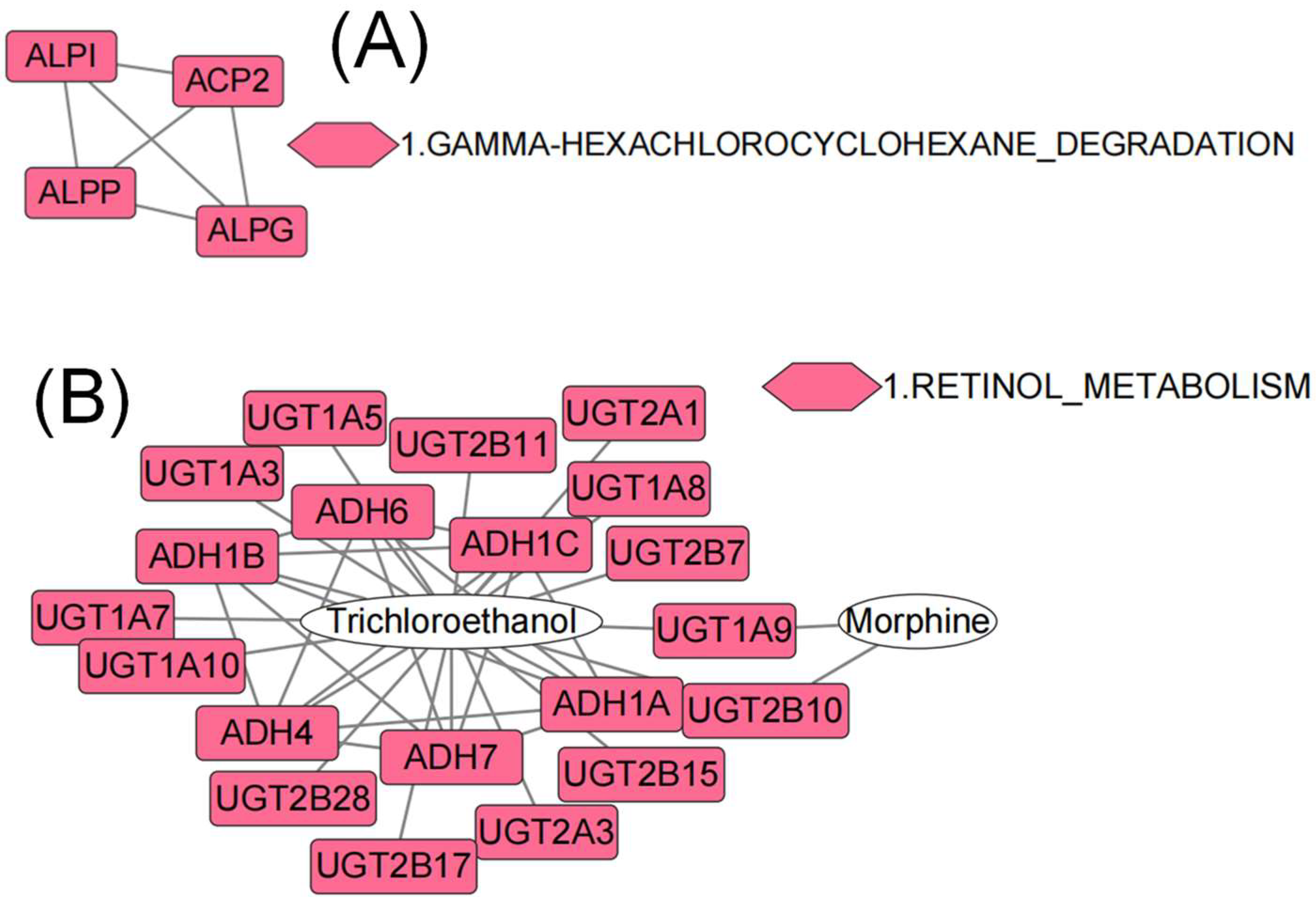
3.3. GO, KEGG, and PPI Analyses Based on DEGs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baldini, F.; Hertel, J.; Sandt, E.; Thinnes, C.C.; Neuberger-Castillo, L.; Pavelka, L.; Betsou, F.; Krüger, R.; Thiele, I.; on behalf of the NCER-PD Consortium; et al. Parkinson’s Disease-Associated Alterations of the Gut Microbiome Predict Disease-Relevant Changes in Metabolic Functions. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.; Lembo, A. Microbiome and Its Role in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haran, J.P.; McCormick, B.A. Aging, Frailty, and the Microbiome—How Dysbiosis Influences Human Aging and Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portune, K.J.; Benítez-Páez, A.; Del Pulgar, E.M.G.; Cerrudo, V.; Sanz, Y. Gut Microbiota, Diet, and Obesity-Related Disorders-The Good, the Bad, and the Future Challenges. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremaroli, V.; Bäckhed, F. Functional Interactions between the Gut Microbiota and Host Metabolism. Nature 2012, 489, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevaranjan, N.; Puchta, A.; Schulz, C.; Naidoo, A.; Szamosi, J.C.; Verschoor, C.P.; Loukov, D.; Schenck, L.P.; Jury, J.; Foley, K.P.; et al. Age-Associated Microbial Dysbiosis Promotes Intestinal Permeability, Systemic Inflammation, and Macrophage Dysfunction. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 455–466.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, M.; Biagi, E.; Brigidi, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; De Vos, W.M. Maintenance of a Healthy Trajectory of the Intestinal Microbiome during Aging: A Dietary Approach. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 136–137, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, J.C.; Ursell, L.K.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. The Impact of the Gut Microbiota on Human Health: An Integrative View. Cell 2012, 148, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagi, E.; Franceschi, C.; Rampelli, S.; Severgnini, M.; Ostan, R.; Turroni, S.; Consolandi, C.; Quercia, S.; Scurti, M.; Monti, D.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Extreme Longevity. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 1480–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Atarashi, K.; Plichta, D.R.; Arai, Y.; Sasajima, S.; Kearney, S.M.; Suda, W.; Takeshita, K.; Sasaki, T.; Okamoto, S.; et al. Novel Bile Acid Biosynthetic Pathways Are Enriched in the Microbiome of Centenarians. Nature 2021, 599, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badal, V.D.; Vaccariello, E.D.; Murray, E.R.; Yu, K.E.; Knight, R.; Jeste, D.V.; Nguyen, T.T. The Gut Microbiome, Aging, and Longevity: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, G.W.; Chang, S.-C.; Noker, P.E.; Gorman, G.S.; Ehresman, D.J.; Lieder, P.H.; Butenhoff, J.L. A Comparison of the Pharmacokinetics of Perfluorobutanesulfonate (PFBS) in Rats, Monkeys, and Humans. Toxicology 2009, 256, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsted, J.L.; Beach, S.A.; Gallagher, S.P.; Giesy, J.P. Acute and Chronic Effects of Perfluorobutane Sulfonate (PFBS) on the Mallard and Northern Bobwhite Quail. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 54, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.F.; Peldszus, S.; Anderson, W.B. Behaviour and Fate of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Drinking Water Treatment: A Review. Water Res. 2014, 50, 318–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Yu, W.-J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, Y.-H.; Dong, G.-H. Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Groundwater and Home-Produced Vegetables and Eggs around a Fluorochemical Industrial Park in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, R.; Jin, F.; Lou, H.; Mao, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J. Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Endometriosis-Related Infertility in Chinese Women. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lam, J.C.W.; Hu, C.; Tsui, M.M.P.; Wang, Q.; Giesy, J.P.; Lam, P.K.S. Perfluorobutanesulfonate Exposure Causes Durable and Transgenerational Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota in Marine Medaka. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liu, M.; Wan, T.; Tang, L.; Sun, B.; Zhou, B.; Lam, J.C.W.; Lam, P.K.S.; Chen, L. Disturbances in Microbial and Metabolic Communication across the Gut-Liver Axis Induced by a Dioxin-like Pollutant: An Integrated Metagenomics and Metabolomics Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Wang, S.; Dou, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Avula, U.; Hoxha, M.; Díaz, A.; McCracken, J.; et al. Air Pollution Exposure and Telomere Length in Highly Exposed Subjects in Beijing, China: A Repeated-Measure Study. Environ. Int. 2012, 48, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Sun, B.; Liu, M.; Yu, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L. Fecal Transplantation from Young Zebrafish Donors Efficiently Ameliorates the Lipid Metabolism Disorder of Aged Recipients Exposed to Perfluorobutanesulfonate. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Sun, B.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L. Disturbed Glucose Metabolism by Perfluorobutanesulfonate Pollutant and Benefit of Young Fecal Transplantation in Aged Zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Liu, M.; Tang, L.; Zhou, X.; Hu, C.; Chen, L. Variability in Fecal Metabolome Depending on Age, PFBS Pollutant, and Fecal Transplantation in Zebrafish: A Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Health. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 127, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Liu, M.; Sun, B.; Tang, L.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L. Young Fecal Transplantation Mitigates the Toxicity of Perfluorobutanesulfonate and Potently Refreshes the Reproductive Endocrine System in Aged Recipients. Environ. Int. 2022, 167, 107418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Petrof, E.O. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation: In Perspective. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2016, 9, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotz, C.; Zarrinpar, A. Treating Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome with Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2016, 89, 383–388. [Google Scholar]
- Mathis, D.; Benoist, C. The Influence of the Microbiota on Type-1 Diabetes: On the Threshold of a Leap Forward in Our Understanding: The Microbiota and Autoimmune Diabetes. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 245, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Liu, M.; Hu, C.; Zhou, B.; Lam, P.K.S.; Lam, J.C.W.; Chen, L. Binary Exposure to Hypoxia and Perfluorobutane Sulfonate Disturbs Sensory Perception and Chromatin Topography in Marine Medaka Embryos. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimand, J.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Kolberg, L.; Reisberg, S.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. G:Profiler—A Web Server for Functional Interpretation of Gene Lists (2016 Update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W83–W89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, H.; Au, D.W.T.; Lam, P.K.S.; Zhang, W.; Bajic, V.B.; Qiu, J.-W.; Qian, P.-Y. Hepatic Proteomic Responses in Marine Medaka (Oryzias melastigma) Chronically Exposed to Antifouling Compound Butenolide [5-Octylfuran-2(5H)-One] or 4,5-Dichloro-2-N-Octyl-4-Isothiazolin-3-One (DCOIT). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1851–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, A.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Lucarini, E.; Man, A.L.; Le Gall, G.; Branca, J.J.V.; Ghelardini, C.; Amedei, A.; Bertelli, E.; Regoli, M.; et al. Faecal Microbiota Transplant from Aged Donor Mice Affects Spatial Learning and Memory via Modulating Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity- and Neurotransmission-Related Proteins in Young Recipients. Microbiome 2020, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Dou, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, J. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation from Young Donor Mice Improves Ovarian Function in Aged Mice. J. Genet. Genom. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binyamin, S.S.; Hoque, M.d.R. Understanding the Drivers of Wearable Health Monitoring Technology: An Extension of the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, K.C.; Morales-Polanco, F.; van der Lienden, J.; Rainbolt, T.K.; Frydman, J. Ageing Exacerbates Ribosome Pausing to Disrupt Cotranslational Proteostasis. Nature 2022, 601, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, S.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Fang, J.-Y. Natural Compounds and Aging: Between Autophagy and Inflammasome. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 297293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohen, S.P.; Kralli, A.; Yamamoto, K.R. Hold ′em and Fold ′em: Chaperones and Signal Transduction. Science 1995, 268, 1303–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Siles, M.; Khan, T.M.; Duncan, S.H.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Garcia-Gil, L.J.; Flint, H.J. Cultured Representatives of Two Major Phylogroups of Human Colonic Faecalibacterium Prausnitzii Can Utilize Pectin, Uronic Acids, and Host-Derived Substrates for Growth. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Guidry, H.J.; Johnston, M.; Bohnert, K.A. A Fat-Promoting Botanical Extract From Artemisia Scoparia Exerts Geroprotective Effects on Caenorhabditis Elegans Life Span and Stress Resistance. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2022, 77, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babayev, E.; Duncan, F.E. Age-Associated Changes in Cumulus Cells and Follicular Fluid: The Local Oocyte Microenvironment as a Determinant of Gamete Quality. Biol. Reprod. 2022, 106, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, N.; Zhang, P.; Wu, W.; Fu, L. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Mitigates Bone Loss by Improving Gut Microbiome Composition and Gut Barrier Function in Aged Rats. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Qi, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, L.; Wen, S.; Liu, Y.; Tang, L. Association between Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and Gut Microbiota. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetel, M.J.; de Vries, G.J.; Melcangi, R.C.; Panzica, G.; O’Mahony, S.M. Steroids, Stress and the Gut Microbiome-Brain Axis. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2018, 30, e12548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.-H.; Park, Y.-H.; Sim, M.; Kim, S.-A.; Joung, H.; Shin, D.-M. Serum Level of Sex Steroid Hormone Is Associated with Diversity and Profiles of Human Gut Microbiome. Res. Microbiol. 2019, 170, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Lam, J.C.W.; Hu, C.; Tsui, M.M.P.; Lam, P.K.S.; Zhou, B. Perfluorobutanesulfonate Exposure Skews Sex Ratio in Fish and Transgenerationally Impairs Reproduction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8389–8397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.-H.; Jian, L.-Y.; Ce, L.; Ma, Y.; Xu, C.-C.; Gao, Y.-F.; Machaty, Z.; Luo, H.-L. Identification of Candidate Genes in Regulation of Spermatogenesis in Sheep Testis Following Dietary Vitamin E Supplementation. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2019, 205, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raverdeau, M.; Gely-Pernot, A.; Féret, B.; Dennefeld, C.; Benoit, G.; Davidson, I.; Chambon, P.; Mark, M.; Ghyselinck, N.B. Retinoic Acid Induces Sertoli Cell Paracrine Signals for Spermatogonia Differentiation but Cell Autonomously Drives Spermatocyte Meiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16582–16587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, J.G.; Milani, C.; de Giori, G.S.; Sesma, F.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Bacteria as Vitamin Suppliers to Their Host: A Gut Microbiota Perspective. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, E.I.; Mruk, D.D.; Cheng, C.Y. Regulation of Microtubule (MT)-Based Cytoskeleton in the Seminiferous Epithelium during Spermatogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 59, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Thompson, C.B. Metabolic Regulation of Cell Growth and Proliferation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, M.S.; Marciniak, C.; Eckel-Mahan, K.; McManus, M.; Crimi, M.; Waymire, K.; Lin, C.S.; Masubuchi, S.; Friend, N.; Koike, M.; et al. Heteroplasmy of Mouse MtDNA Is Genetically Unstable and Results in Altered Behavior and Cognition. Cell 2012, 151, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya-Soriano, M.J.; Taberner, E.; López-Béjar, M. Retinol Improves in Vitro Oocyte Nuclear Maturation under Heat Stress in Heifers. Zygote 2013, 21, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, M.; Ohshita, T.; Aoki, Y.; Sakaguchi, M. Plasma Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances, Vitamin A and Vitamin E Levels and Resumption of Postpartum Ovarian Activity in Dairy Cows: Plasma TBARS and Postpartum Ovulation. Anim. Sci. J. 2014, 85, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yu, K.; Huang, C.; Yu, L.; Zhu, B.; Lam, P.K.S.; Lam, J.C.W.; Zhou, B. Prenatal Transfer of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) Results in Developmental Neurotoxicity in Zebrafish Larvae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 9727–9734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogra, D.; Ahuja, S.; Kim, H.; Rasouli, S.; Stainier, D.; Reischauer, S. Opposite Effects of Activin Type 2 Receptor Ligands on Cardiomyocyte Proliferation during Development and Repair. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Niu, C.; Cheng, C. Igf3 Serves as A Mediator of Luteinizing Hormone in Zebrafish Ovulation. Biol. Reprod. 2018, 6, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ge, W. Developmental Profiles of Activin βA, βB, and Follistatin Expression in the Zebrafish Ovary: Evidence for Their Differential Roles during Sexual Maturation and Ovulatory Cycle. Biol. Reprod. 2004, 71, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, B.; Boger, M.; Bennewitz, K.; Sticht, C.; Kopf, S.; Morgenstern, J.; Fleming, T.; Hell, R.; Yuan, Z.; Nawroth, P.; et al. Elevated 4-Hydroxynonenal Induces Hyperglycaemia via Aldh3a1 Loss in Zebrafish and Associates with Diabetes Progression in Humans. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yin, Y.; Li, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, X.; et al. Gene Knockout of Nuclear Progesterone Receptor Provides Insights into the Regulation of Ovulation by LH Signaling in Zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, L.; Li, J.; Sun, B.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L. Transcriptomic Interaction between Young Fecal Transplantation and Perfluorobutanesulfonate in Aged Zebrafish Gonads. Toxics 2022, 10, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10110631
Tang L, Li J, Sun B, Bai Y, Zhou X, Chen L. Transcriptomic Interaction between Young Fecal Transplantation and Perfluorobutanesulfonate in Aged Zebrafish Gonads. Toxics. 2022; 10(11):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10110631
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Lizhu, Jing Li, Baili Sun, Yachen Bai, Xiangzhen Zhou, and Lianguo Chen. 2022. "Transcriptomic Interaction between Young Fecal Transplantation and Perfluorobutanesulfonate in Aged Zebrafish Gonads" Toxics 10, no. 11: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10110631
APA StyleTang, L., Li, J., Sun, B., Bai, Y., Zhou, X., & Chen, L. (2022). Transcriptomic Interaction between Young Fecal Transplantation and Perfluorobutanesulfonate in Aged Zebrafish Gonads. Toxics, 10(11), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10110631







