Inactivation of Aeromonas hydrophila and Vibrio parahaemolyticus by Curcumin-Mediated Photosensitization and Nanobubble-Ultrasonication Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Inoculum Preparation
2.2. Preparation of Curcumin Solutions
2.3. Light Irradiation of Bacteria
2.4. Photodynamic Inactivation in RAS-Aquaponics Water
2.5. Nanobubble Inactivation of Bacteria
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
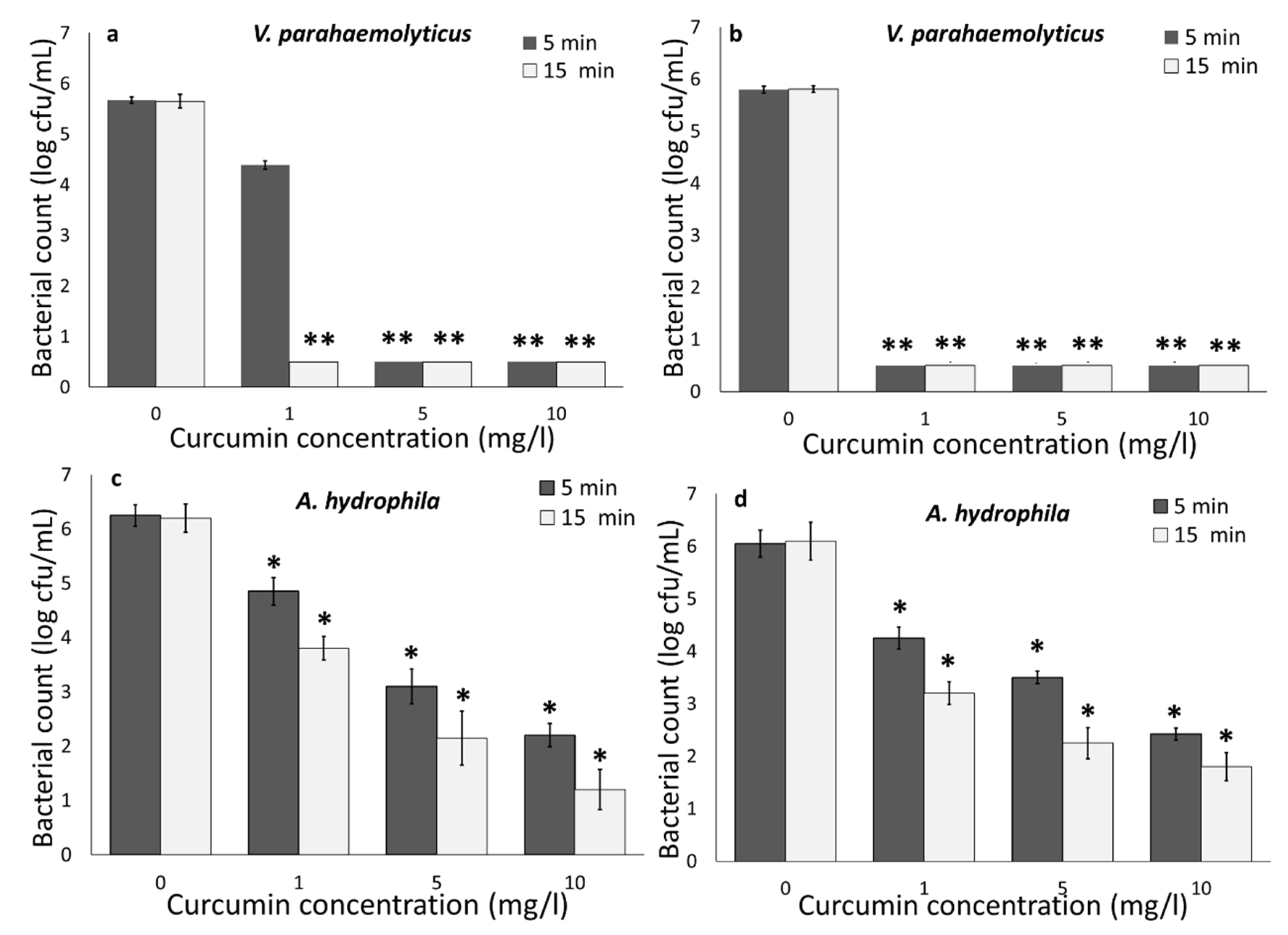
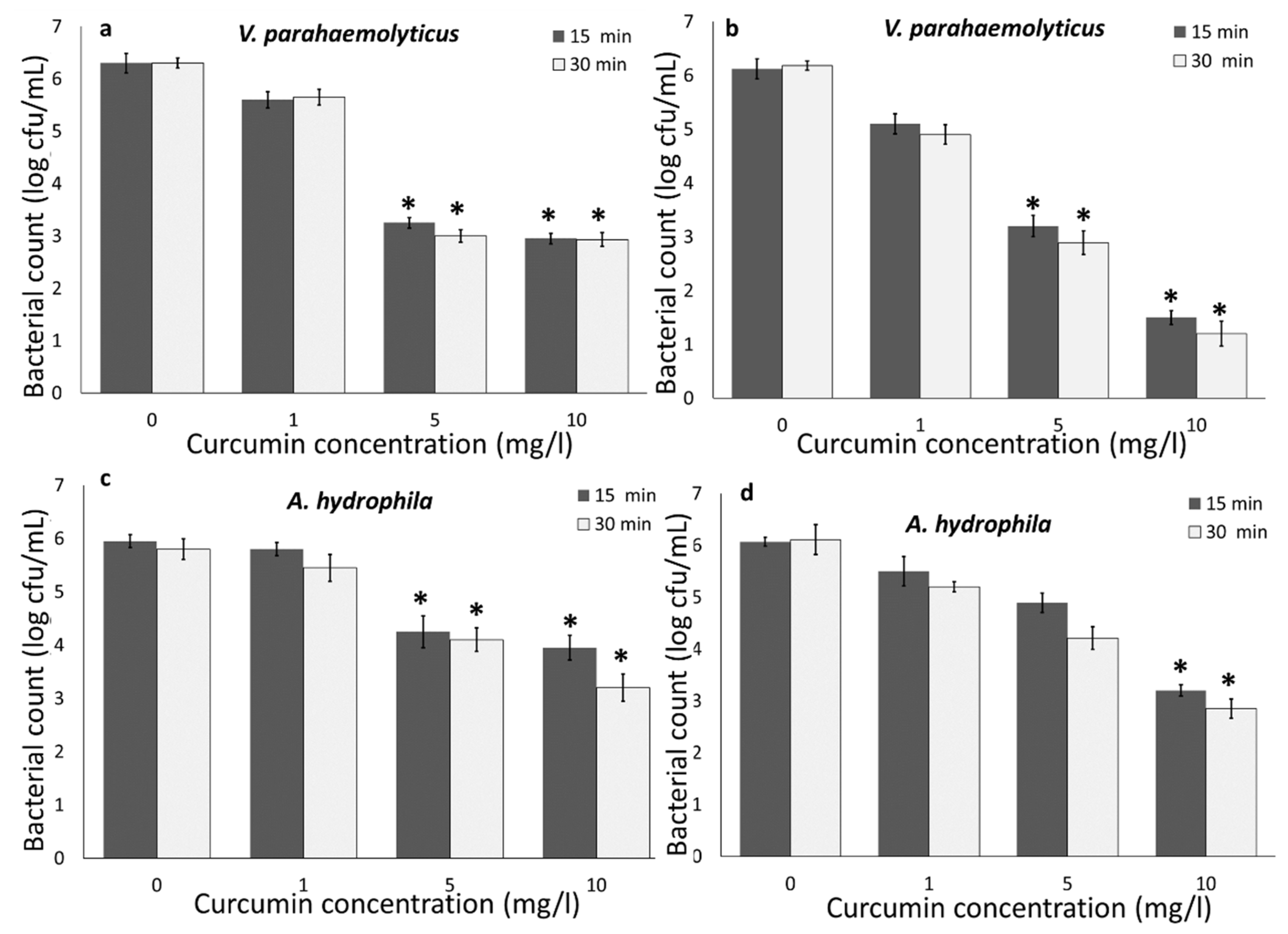
3.1. Photodynamic Bacterial Inactivation
3.1.1. Impact of Curcumin Concentration and Light Wavelength
3.1.2. Impact of Temperature
3.1.3. Bacterial Inactivation in RAS-Aquaponics Water
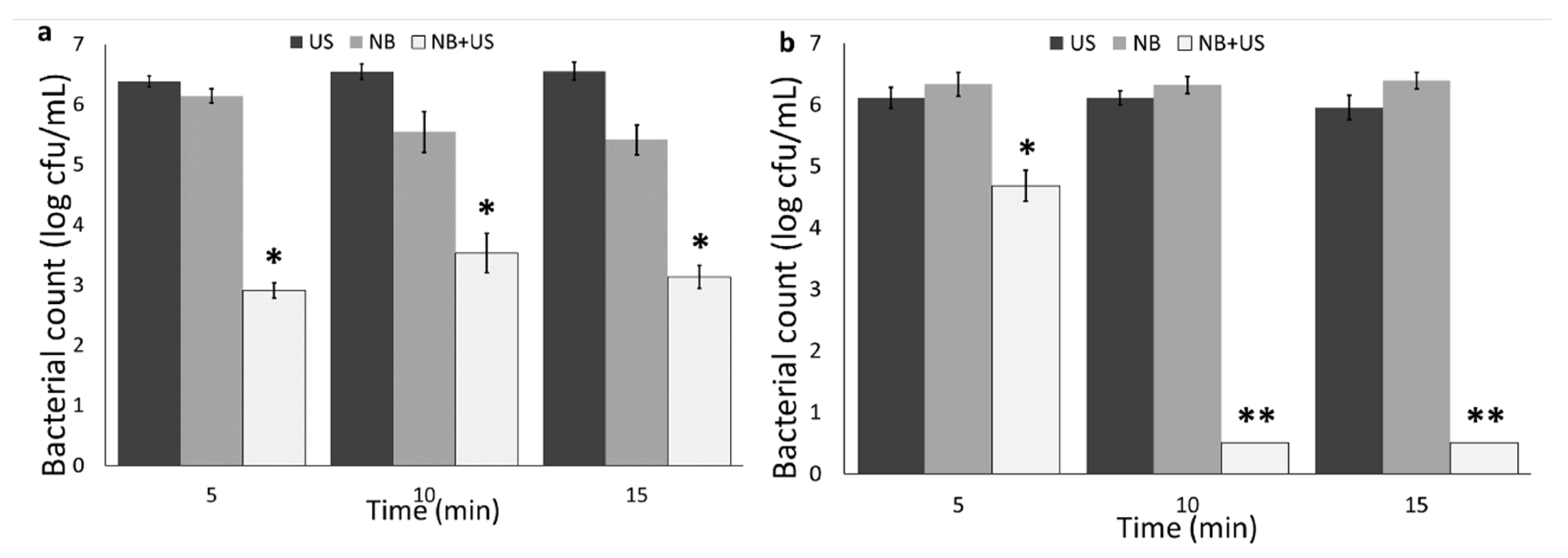
3.2. Nanobubble and Ultrasound Inactivation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics. Yearbook. 2019, p. 109. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/ca5495t/CA5495T.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Kumar, S.; Lekshmi, M.; Parvathi, A.; Nayak, B.B.; Varela, M.F. Antibiotic Resistance in Seafood Borne Pathogens. In Food Borne Pathogens and Antibiotic Resistance; Singh, O.V., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 397–416. [Google Scholar]
- Vivekanandhan, G.; Hatha, A.A.M.; Lakshmanaperumalsamy, P. Prevalence of Aeromonas hydrophila in fish and prawns from the seafood market of Coimbatore, South India. Food Microb. 2005, 22, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kledal, P.R.; Thorarinsdottir, R. Aquaponics: A commercial niche for sustainable modern aquaculture. In Sustainable Aquaculture; Hai, F.I., Visvanathan, C., Boopathy, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 173–190. [Google Scholar]
- Ovissipour, M.; Rasco, B.; Bledsoe, G.; Shiroodi, S. A Guide to the Aquaponics Food Safety Plan Development: Green Aquaponics LLC as a Model. 2019. Available online: https://vtechworks.lib.vt.edu/bitstream/handle/10919/88927/FST-302.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Oliveira, E.F.; Cossu, A.; Tikekar, R.V.; Nitin, N. Enhanced antimicrobial activity based on a synergistic combination of sublethal levels of stresses induced by UV-A light and organic acids. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, E.F.; Tikekar, R.; Nitin, N. Combination of aerosolized curcumin and UV-A light for the inactivation of bacteria on fresh produce surfaces. Food Res. Int. 2018, 114, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, E.F.; Tosati, J.V.; Tikekar, R.V.; Monteiro, A.R.; Nitin, N. Antimicrobial activity of curcumin in combination with light against Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Listeria innocua: Applications for fresh produce sanitation. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 137, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, Z.; Cao, B.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Xu, J.; Xue, C.; Tang, Q.J. The effect of a novel photodynamic activation method mediated by curcumin on oyster shelf life and quality. Food Res. Int. 2016, 87, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penha, C.B.; Bonin, E.; da Silva, A.F.; Hioka, N.; Zanqueta, É.B.; Nakamura, T.U.; Filho, B.A.A.; Campanerut-Sa, P.A.Z.; Mikcha, J.M.G. Photodynamic inactivation of foodborne and food spoilage bacteria by curcumin. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosati, J.V.; de Oliveira, E.F.; Oliveira, J.V.; Nitin, N.; Monteiro, A.R. Light-activated antimicrobial activity of turmeric residue edible coatings against cross-contamination of Listeria innocua on sausages. Food Control. 2018, 84, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Mou, H.; Xue, C.; Leung, A.W.; Xu, C.; Tang, Q.J. Photodynamic effect of curcumin on Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2016, 15, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafisi, S.; Adelzadeh, M.; Norouzi, Z.; Sarbolouki, M.N. Curcumin binding to DNA and RNA. DNA Cell Biol. 2009, 28, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, S.; Du, L.; Prasad, A.; Yadav, B.; Roopesh, M.S. Inactivation of Salmonella and quality changes in wheat flour after pulsed light-emitting diode (LED) treatments. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 121, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; An, H.; Alheshibri, M.; Liu, L.; Terpstra, P.M.; Liu, G.; Craig, V.S. Cleaning with bulk nanobubbles. Langmuir 2016, 32, 11203–11211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teirlinck, E.; Xiong, R.; Brans, T.; Forier, K.; Fraire, J.; Van Acker, H.; Matthijs, N.; Rycke, R.D.; De Smedt, S.C.; Coenye, T.; et al. Laser-induced vapour nanobubbles improve drug diffusion and efficiency in bacterial biofilms. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teirlinck, E.; Fraire, J.C.; Van Acker, H.; Wille, J.; Swimberghe, R.; Brans, T.; Xiong, R.; Meire, M.; De More, R.J.G.; De Smidt, S.C.; et al. Laser-induced vapor nanobubbles improve diffusion in biofilms of antimicrobial agents for wound care. Biofilm 2019, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, K.K.T.; Truong, T.; Wang, Y.; Bhandari, B. Nanobubbles: Fundamental characteristics and applications in food processing. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 95, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Longo, M.L.; Powell, R.L. Stability and rheological behavior of concentrated monodisperse food emulsifier coated microbubble suspensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 327, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Sun, D.W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Cheng, L. Effects of micro-nano bubbles on the nucleation and crystal growth of sucrose and maltodextrin solutions during ultrasound-assisted freezing process. LWT 2018, 92, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiroodi, S.; Schwarz, M.; Nitin, N.; Ovissipour, R. Efficacy of nanobubbles in removing biofilms formed by Escherichia coli O157:H7, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and Listeria innocua. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2020. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Wu, Z.; Craig, V.S. Cleaning of protein-coated surfaces using nanobubbles: An investigation using a quartz crystal microbalance. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 16748–16753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, H.; Dong, Y.; Mao, H.; Sun, J.; Chen, S.; Craig, V.S.J.; Hu, J. Cleaning using nanobubbles: Defouling by electrochemical generation of bubbles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 328, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimkhani, A.; Zhang, W.; Marhaba, T. Ceramic membrane defouling (cleaning) by air Nano Bubbles. Chemosphere 2016, 146, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakumo, S.; Arakawa, S.; Takahashi, M.; Kondo, K.; Mano, Y.; Izumi, Y. Effects of ozone nano-bubble water on periodontopathic bacteria and oral cells-in vitro studies. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2014, 15, 055003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushida, A.; Koyama, T.; Nakamoto, Y.; Narumi, T.; Sato, T.; Hasegawa, T. Antimicrobial effectiveness of ultra-fine ozone-rich bubble mixtures for fresh vegetables using an alternating flow. J. Food Eng. 2017, 206, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozima, H.; Mukai, Y.; Ransangan, J.; Senoo, S. Feasibility study of applications of micro-bubbles for aquaculture. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Coastal Oceanography and Sustainable Marina Aquaculture, Confluence and Synergy, Sabah, Malaysia, 2–4 May 2006; pp. 220–223. Available online: http://irep.iium.edu.my/11261/ (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Roh, H.J.; Kim, A.; Kang, G.S.; Kim, D.H. Photoinactivation of major bacterial pathogens in aquaculture. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ghate, V.; Kim, M.J.; Zhou, W.; Khoo, G.H.; Yuk, H.G. Antibacterial efficacy of 405, 460 and 520 nm light emitting diodes on Lactobacillus plantarum, Staphylococcus aureus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jori, G.; Fabris, C.; Soncin, M.; Ferro, S.; Coppellotti, O.; Dei, D.; Fantetti, L.; Chiti, G.; Roncucci, G. Photodynamic therapy in the treatment of microbial infections: Basic principles and perspective applications. Lasers Surg. Med. 2006, 38, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghate, V.S.; Ng, K.S.; Zhou, W.; Yang, H.; Khoo, G.H.; Yoon, W.B.; Yuk, H.G. Antibacterial effect of light emitting diodes of visible wavelengths on selected foodborne pathogens at different illumination temperatures. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 166, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kussovski, V.; Mantareva, V.; Angelov, I.; Orozova, P.; Wöhrle, D.; Schnurpfeil, G.; Borisova, E.; Avramov, L. Photodynamic inactivation of Aeromonas hydrophila by cationic phthalocyanines with different hydrophobicity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 294, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Tang, S.; Wu, Q.; Tian, J.; Riley, W.W.; Chen, Z. Inactivation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus by antimicrobial photodynamic technology using methylene blue. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajlouni, S.; Sibrani, H.; Premier, R.; Tomkins, B. Ultrasonication and fresh produce (Cos lettuce) preservation. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Wrenn, S.; Tikekar, R.; Nitin, N. Efficacy of decontamination and a reduced risk of cross-contamination during ultrasound-assisted washing of fresh produce. J. Food Eng. 2018, 224, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakeh, A.A.B.; Kloas, W.; Jung, R.; Ariav, R.A.; Knopf, K. Low frequency ultrasound and UV-C for elimination of pathogens in recirculating aquaculture systems. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demangeat, J.L. Gas nanobubbles and aqueous nanostructures: The crucial role of dynamization. Homeopathy 2015, 104, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, L.-F.; Pedersen, P.B. Hydrogen peroxide application to a commercial recirculating aquaculture system. Aqua. Eng. 2012, 46, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Xu, D.H.; Fu, Y.W.; Lin, D.J.; Zhou, S.Y.; Li, J.P. Antiparasitic efficacy of curcumin from Curcuma longa against Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in grass carp. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 236, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rafeeq, S.; Shiroodi, S.; Schwarz, M.H.; Nitin, N.; Ovissipour, R. Inactivation of Aeromonas hydrophila and Vibrio parahaemolyticus by Curcumin-Mediated Photosensitization and Nanobubble-Ultrasonication Approaches. Foods 2020, 9, 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9091306
Rafeeq S, Shiroodi S, Schwarz MH, Nitin N, Ovissipour R. Inactivation of Aeromonas hydrophila and Vibrio parahaemolyticus by Curcumin-Mediated Photosensitization and Nanobubble-Ultrasonication Approaches. Foods. 2020; 9(9):1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9091306
Chicago/Turabian StyleRafeeq, Shamil, Setareh Shiroodi, Michael H. Schwarz, Nitin Nitin, and Reza Ovissipour. 2020. "Inactivation of Aeromonas hydrophila and Vibrio parahaemolyticus by Curcumin-Mediated Photosensitization and Nanobubble-Ultrasonication Approaches" Foods 9, no. 9: 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9091306
APA StyleRafeeq, S., Shiroodi, S., Schwarz, M. H., Nitin, N., & Ovissipour, R. (2020). Inactivation of Aeromonas hydrophila and Vibrio parahaemolyticus by Curcumin-Mediated Photosensitization and Nanobubble-Ultrasonication Approaches. Foods, 9(9), 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9091306



