Unravelling Conformational Aspects of Milk Protein Structure—Contributions from Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
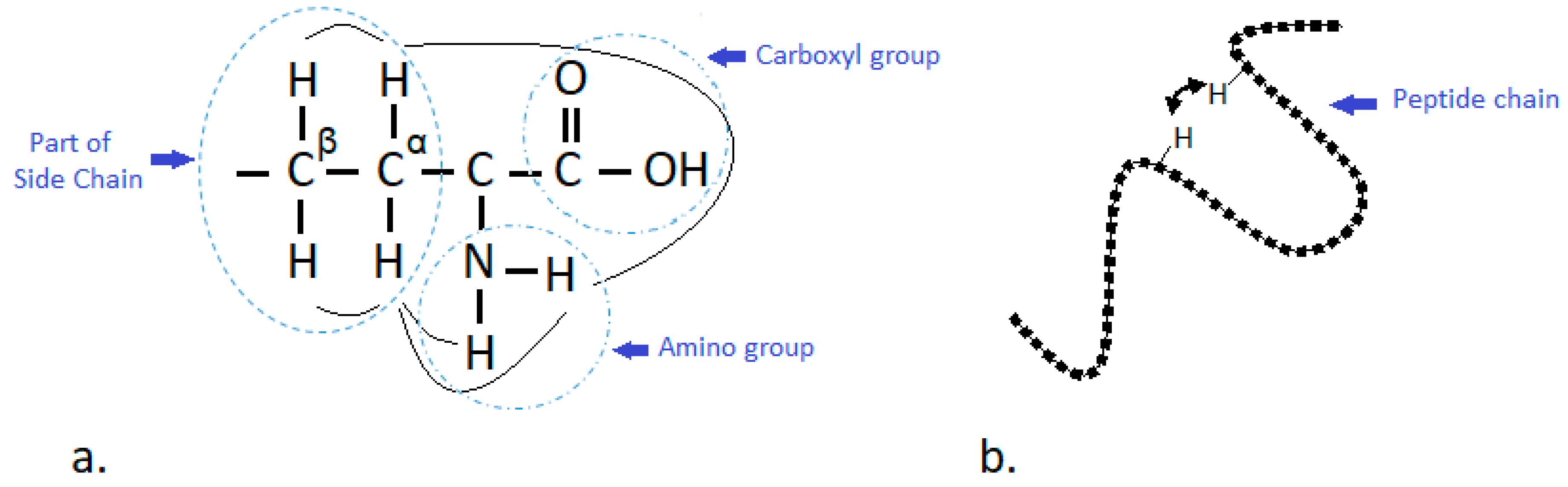
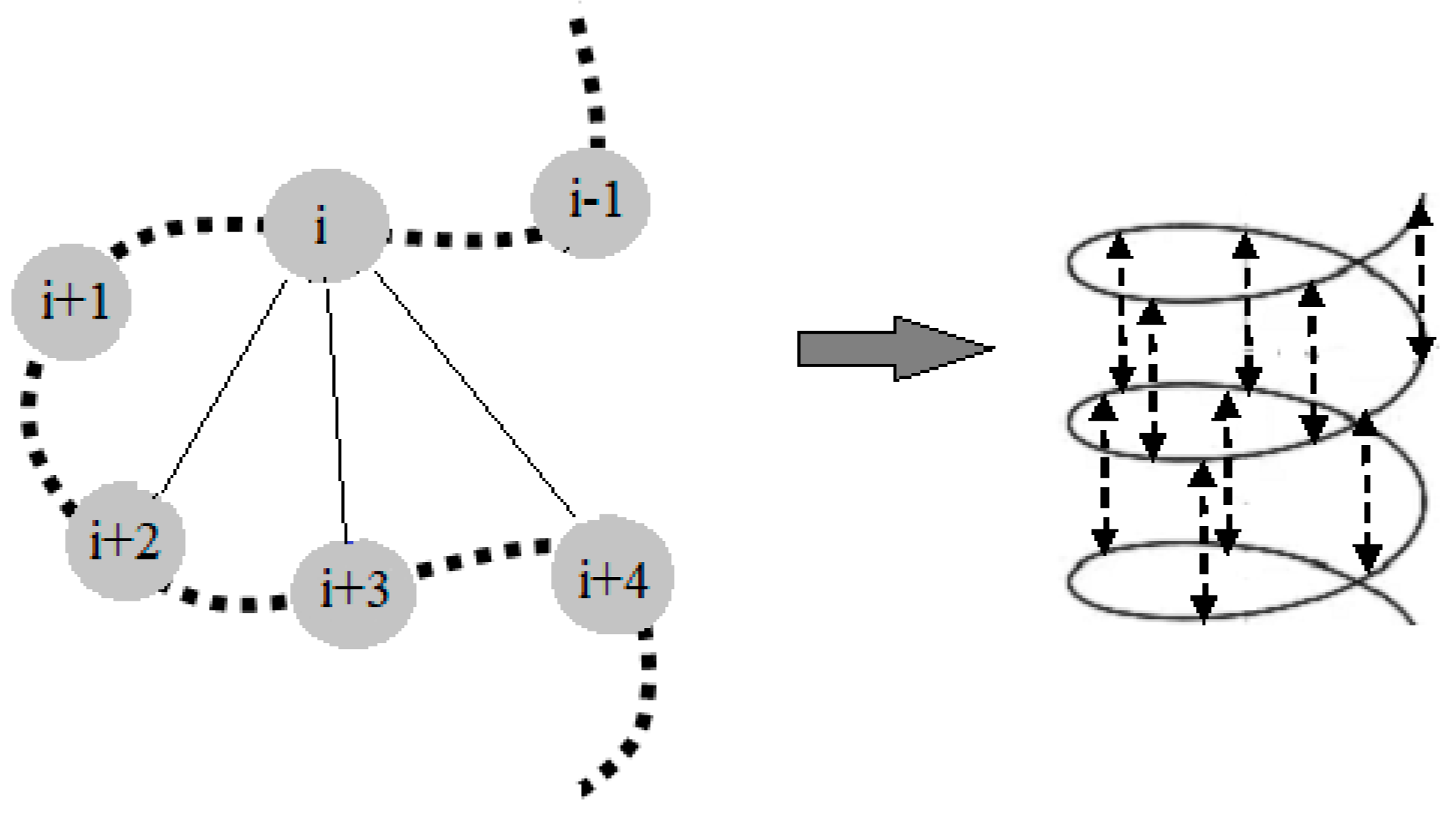
2. NMR Approach for Structural Elucidation of Proteins
- (1)
- For a backbone assignment, including 13Cβ nuclei, the best approach is full labelling of 15N, 2H and 13C samples obtained from D2O based growths. The measurements are performed on protein dispersed in H2O after 2H > 1H exchange;
- (2)
- For Leu, Ile δ1 and Val methyl groups and measurements of 3JCγCO scalar coupling and nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE) connectivity (NH-CH3; HN-HN distance), the most appropriate labelling procedure is considered to be linearized 13C spin system including ((U-15N,2H,13C), Leu, Val (13CH3, 12CD3), Ileδ1(13CH3));
- (3)
- A methyl labelling scheme similar to step 2, but including different carbon positions 12C ((U-15N,2H), Leu, Val (13CH3, 12CD3), Ileδ1 (13CH3)), should be used for measurements of 3JCγN coupling and NOE connectivity (CH3-CH3);
- (4)
- Methyl labelling as 13CHD2- labelled proteins for detecting methyl 13C relaxation rates.
3. NMR Studies on Structure of Milk Proteins
3.1. Whey Proteins
3.1.1. α-Lactalbumin
3.1.2. β-Lactoglobulin
3.2. Caseins
3.2.1. β-Casein
3.2.2. αs1-Casein
3.2.3. αs2-Casein
3.2.4. κ-Casein
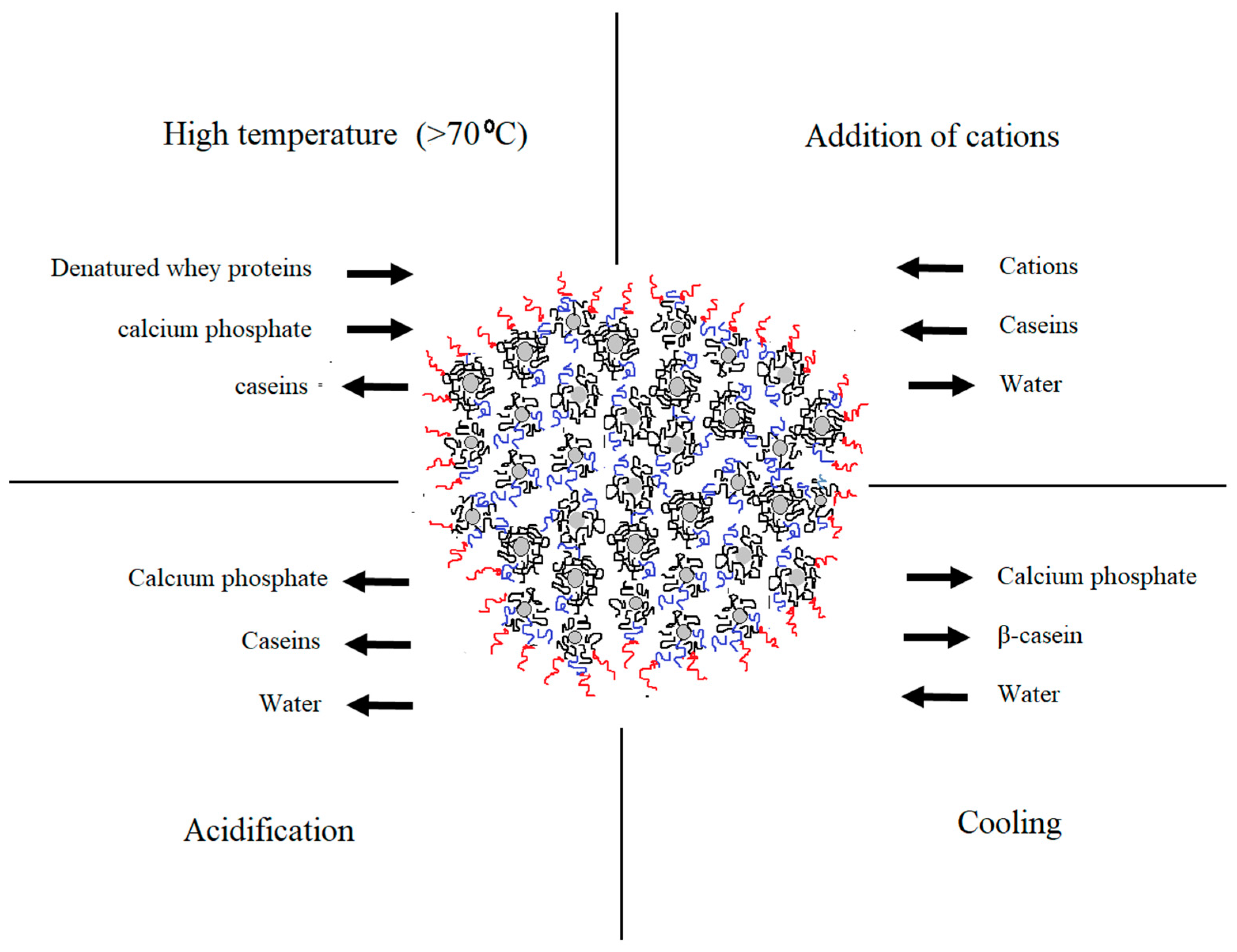
4. NMR Studies on Casein Micelles
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dalgleish, D.G.; Corredig, M. The structure of the casein micelle of milk and its changes during processing. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 3, 449–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, L.; Holt, C. The secondary structure of milk proteins and their biological function. J. Dairy Sci. 1993, 76, 3062–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forge, V.; Wijesinha, R.T.; Balbach, J.; Brew, K.; Robinson, C.V.; Redfield, C.; Dobson, C.M. Rapid collapse and slow structural reorganisation during the refolding of bovine α-lactalbumin. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 288, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrínová, S.; Smith, M.H.; Jameson, G.B.; Uhrín, D.; Sawyer, L.; Barlow, P.N. Structural changes accompanying pH-induced dissociation of the β-lactoglobulin dimer. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 3565–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, K.; Konuma, T.; Yagi, M.; Goto, Y. Structural dynamics and folding of β-lactoglobulin probed by heteronuclear NMR. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2009, 1790, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppertz, T. Chemistry of the caseins. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 135–160. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, D.G. On the structural models of bovine casein micelles—Review and possible improvements. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 2265–2272. [Google Scholar]
- De Kruif, C.G.; Huppertz, T.; Urban, V.S.; Petukhov, A.V. Casein micelles and their internal structure. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 171, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppertz, T.; Gazi, I.; Luyten, H.; Nieuwenhuijse, H.; Alting, A.; Schokker, E. Hydration of casein micelles and caseinates: Implications for casein micelle structure. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 74, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, D.S. Casein micelle structure and stability. In Milk Proteins; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 213–250. [Google Scholar]
- Gaucheron, F. The minerals of milk. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2005, 45, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creamer, K.L.; Berry, G.P.; Mills, O.E. Study of the dissociation of beta casein from the bovine casein micelle at low temperature. N. Z. J. Dairy Sci. Technol. 1977, 74, 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- Hyslop, D.B. Enzymatic coagulation of milk. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry—1 Proteins; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 839–878. [Google Scholar]
- Anema, S.G.; Li, Y. Association of denatured whey proteins with casein micelles in heated reconstituted skim milk and its effect on casein micelle size. J. Dairy Res. 2003, 70, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, D.T.; Brodkorb, C.A.; Kouaouci, R. Quantitation of proteins in milk and milk products. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 87–134. [Google Scholar]
- Plowman, J.E.; Creamer, L.K.; Liddell, M.J.; Cross, J.J. Solution conformation of a peptide corresponding to bovine κ-casein B residues 130–153 by circular dichroism spectroscopy and 1 H-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Dairy Res. 1997, 64, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinari, H.; Ragona, L.; Varani, L.; Musco, G.; Consonni, R.; Zetta, L.; Monaco, H.L. Partially folded structure of monomeric bovine β-lactoglobulin. FEBS Lett. 1996, 381, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragona, L.; Pusterla, F.; Zetta, L.; Monaco, H.L.; Molinari, H. Identification of a conserved hydrophobic cluster in partially folded bovine β-lactoglobulin at pH 2. Fold. Des. 1997, 2, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.M.; Jess, T.J.; Price, N.C. How to study proteins by circular dichroism. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Proteins Proteom. 2005, 1751, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, H.M., Jr.; Wickham, E.D.; Unruh, J.J.; Qi, P.X.; Hoagland, P.D. Secondary structural studies of bovine caseins: Temperature dependence of β-casein structure as analyzed by circular dichroism and FTIR spectroscopy and correlation with micellization. Food Hydrocoll. 2001, 15, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, T.; Subirade, M. Structural and interaction properties of β-Lactoglobulin as studied by FTIR spectroscopy. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 34, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, M.K.; Huppertz, T.; Vasiljevic, T. FTIR fingerprinting of structural changes of milk proteins induced by heat treatment, deamidation and dephosphorylation. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 80, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlow, S.; Cabral, J.H.M.; Cooper, R.; Flower, D.R.; Yewdall, S.J.; Polikarpov, I.; North, A.C.T.; Sawyer, L. Bovine β-lactoglobulin at 1.8 Å resolution—Still an enigmatic lipocalin. Structure 1997, 5, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, H.M.; Brown, E.M.; Malin, E.L. Higher order structures of the caseins: A paradox? In Advanced Dairy Chemistry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 161–184. [Google Scholar]
- Sakae, T.; Niki, R.; Kuwata, T.; Tanaka, I.; Hikichi, K. 1H NMR study of casein phosphopeptide (1–25): Assignment and conformation. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1991, 29, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Wahlgren, N.M.; Léonil, J.; Dejmek, P.; Drakenberg, T. Two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance study of the β-casein peptide 1–25: Resonance assignments and secondary structure. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1993, 1202, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, K.J.; Huq, N.L.; Bicknell, W.; Reynolds, E.C. Cation-dependent structural features of β-casein-(1–25). Biochem. J. 2001, 356, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cross, K.J.; Huq, N.L.; Stanton, D.P.; Sum, M.; Reynolds, E.C. NMR studies of a novel calcium, phosphate and fluoride delivery vehicle-αS1-casein (59–79) by stabilized amorphous calcium fluoride phosphate nanocomplexes. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5061–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, K.J.; Huq, N.L.; Reynolds, E.C. Casein phosphopeptide–amorphous calcium phosphate nanocomplexes: A structural model. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 4316–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laila, H.N.; Cross, K.J.; Reynolds, E.C. A 1H-NMR study of the casein phosphopeptide αs1-casein (59–79). Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1995, 1247, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huq, N.L.; Cross, K.J.; Reynolds, E.C. Nascent helix in the multiphosphorylated peptide αS2-casein (2–20). J. Pept. Sci. 2003, 9, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malin, E.L.; Alaimo, M.H.; Brown, E.M.; Aramini, J.M.; Germann, M.W.; Farrell, H.M.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; Fox, P.F. Solution structures of casein peptides: NMR, FTIR, CD, and molecular modeling studies of αs1-casein, 1–23. J. Protein Chem. 2001, 20, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plowman, J.E.; Smith, M.H.; Creamer, L.K.; Liddell, M.J.; Coddington, J.; Gibson, J.J.; Engelbretsen, D.R. Proton assignment and structural features of a peptide from the chymosin-sensitive region of bovine k-casein determined by 2D-NMR spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1994, 32, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, P.S.; Grieve, P.A.; Marschke, R.J.; Daly, N.L.; McGhie, E.; Craik, D.J.; Alewood, P.F. Chemical synthesis and structure elucidation of bovine κ-casein (1–44). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 340, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüthrich, K. NMR with proteins and nucleic acids. Europhys. News 1986, 17, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanelis, V.; Forman-Kay, J.D.; Kay, L.E. Multidimensional NMR methods for protein structure determination. Iubmb Life 2001, 52, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugarinov, V.; Kanelis, V.; Kay, L.E. Isotope labeling strategies for the study of high-molecular-weight proteins by solution NMR spectroscopy. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wüthrich, K. Protein structure determination in solution by NMR spectroscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 22059–22062. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cavanagh, J.; Fairbrother, W.J.; Palmer, A.G., III; Skelton, N.J. Protein NMR Spectroscopy: Principles and Practice; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bodenhausen, G.; Ruben, D.J. Natural abundance nitrogen-15 NMR by enhanced heteronuclear spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1980, 69, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, D.; Wüthrich, K. Application of phase sensitive two-dimensional correlated spectroscopy (COSY) for measurements of 1 H-1 H spin-spin coupling constants in proteins. In NMR in Structural Biology: A Collection of Papers by Kurt Wüthrich; World Scientific: Singapore, 1995; pp. 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Griesinger, C.; Otting, G.; Wüthrich, K.; Ernst, R.R. Clean TOCSY for proton spin system identification in macromolecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 7870–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüthrich, K.; Wider, G.; Wagner, G.; Braun, W. Sequential resonance assignments as a basis for determination of spatial protein structures by high resolution proteins nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Mol. Biol. 1982, 155, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüthrich, K.; Billeter, M.; Braun, W. Polypeptide secondary structure determination by nuclear magnetic resonance observation of short proton–proton distances. In NMR in Structural Biology: A Collection of Papers by Kurt Wüthrich; World Scientific: Singapore, 1995; pp. 218–243. [Google Scholar]
- Karplus, M. Contact electron-spin coupling of nuclear magnetic moments. J. Chem. Phys. 1959, 30, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, G.N. Stereochemistry of polypeptide chain configurations. J. Mol. Biol. 1963, 7, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariette, F. NMR relaxometry and imaging of dairy products. Mod. Magn. Reson. 2018, 1535–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brew, K. α-Lactalbumin. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry—1 Proteins; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 387–419. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeguchi, M.; Kuwajima, K.; Mitani, M.; Sugai, S. Evidence for identity between the equilibrium unfolding intermediate and a transient folding intermediate: A comparative study of the folding reactions of. alpha.-lactalbumin and lysozyme. Biochemistry 1986, 25, 6965–6972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada, C.M.; Schulman, B.A.; Froggatt, J.J.; Dobson, C.M.; Redfield, C. Local and global cooperativity in the human α-lactalbumin molten globule. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 338, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulman, B.A.; Kim, P.S.; Dobson, C.M.; Redfield, C. A residue-specific NMR view of the non-cooperative unfolding of a molten globule. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1997, 4, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrescu, A.T.; Evans, P.A.; Pitkeathly, M.; Baum, J.; Dobson, C.M. Structure and dynamics of the acid-denatured molten globule state of. alpha.-lactalbumin: A two-dimensional NMR study. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesinha-Bettoni, R.; Dobson, C.M.; Redfield, C. Comparison of the structural and dynamical properties of holo and apo bovine α-lactalbumin by NMR spectroscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 307, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, C.; Schulman, B.A.; Milhollen, M.A.; Kim, P.S.; Dobson, C.M. α-Lactalbumin forms a compact molten globule in the absence of disulfide bonds. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1999, 6, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramboarina, S.; Redfield, C. Structural characterisation of the human α-lactalbumin molten globule at high temperature. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 330, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrescu, A.T.; Broadhurst, R.W.; Wormald, C.; Chyan, C.; Baum, J.; Dobson, C.M. 1H-NMR assignments and local environments of aromatic residues in bovine, human and guinea pig variants of α-lactalbumin. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 210, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berliner, L.J.; Kaptein, R.; Koga, K.; Musci, G. NMR Studies of the Structure and Environment of the Milk Protein α-Lactalbumin. In NMR Applications in Biopolymers; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 231–253. [Google Scholar]
- Akio, S.; Ikeguchi, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Sugai, S. A synthetic peptide study on the molten globule of α-lactalbumin. J. Biochem. 1996, 119, 947–952. [Google Scholar]
- Kazuo, K.; Hoshino, M.; Era, S.; Batt, C.A.; Goto, Y. α→ β transition of β-lactoglobulin as evidenced by heteronuclear NMR. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 283, 731–739. [Google Scholar]
- Fogolari, F.; Ragona, L.; Zetta, L.; Romagnoli, S.; de Kruif, G.K.; Molinari, H. Monomeric bovine β-lactoglobulin adopts a β-barrel fold at pH 2. FEBS Lett. 1998, 436, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazuo, K.; Era, S.; Hoshino, M.; Forge, V.; Goto, Y.; Batt, C.A. Solution structure and dynamics of bovine β-lactoglobulin A. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 2541–2545. [Google Scholar]
- Belloque, J.; Smith, G.M. Thermal denaturation of β-lactoglobulin. A 1H NMR study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrinova, S.; Uhrín, D.; Denton, H.; Smith, M.; Sawyer, L.; Barlow, P.N. Complete assignment of 1 H, 13 C and 15 N chemical shifts for bovine β-lactoglobulin: Secondary structure and topology of the native state is retained in a partially unfolded form. J. Biomol. NMR 1998, 12, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belloque, J.; López-Fandiño, R.; Smith, G.M. A 1H-NMR study on the effect of high pressures on β-lactoglobulin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3906–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, K.; Goto, Y. Dynamics and mechanism of the Tanford transition of bovine β-lactoglobulin studied using heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 356, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazuo, K.; Li, H.; Yamada, H.; Batt, C.A.; Goto, Y.; Akasaka, K. High pressure NMR reveals a variety of fluctuating conformers in β-lactoglobulin. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar]
- Lübke, M.; Guichard, E.; Tromelin, A.; le Quéré, J.L. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic study of β-lactoglobulin interactions with two flavor compounds, γ-decalactone and β-ionone. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 7094–7099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazumasa, S.; Goto, Y. Principal component analysis of the pH-dependent conformational transitions of bovine β-lactoglobulin monitored by heteronuclear NMR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15346–15351. [Google Scholar]
- Kazumasa, S.; Yagi, M.; Konuma, T.; Takahashi, S.; Nishimura, C.; Goto, Y. Non-native α-helices in the initial folding intermediate facilitate the ordered assembly of the β-barrel in β-lactoglobulin. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 4799–4807. [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer, L.; Brownlow, S.; Polikarpov, I.; Wu, S. β-Lactoglobulin: Structural studies, biological clues. Int. Dairy J. 1998, 8, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, L. β-Lactoglobulin. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 211–259. [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella, J.E.; Whitehead, D.M. Proteins in whey: Chemical, physical, and functional properties. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1989; Volume 33, pp. 343–438. [Google Scholar]
- Kontopidis, G.; Holt, C.; Sawyer, L. Invited review: β-lactoglobulin: Binding properties, structure, and function. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, E.C. Anticariogenic complexes of amorphous calcium phosphate stabilized by casein phosphopeptides: A review. Spec. Care Dent. 1998, 18, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlgren, N.; Dejmek, M.P.; Drakenberg, T. Secondary structures in β-casein peptide 1–42: A two dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance study. J. Dairy Res. 1994, 61, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huq, N.L.; Cross, K.J.; Reynolds, E.C. Molecular modelling of the multiphosphorylated casein phosphopeptide [alpha] S1-casein (59–79) based on NMR constraints. J. Dairy Res. 2004, 71, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaimo, M.H.; Farrell, H.M., Jr.; Germann, M.W. Conformational analysis of the hydrophobic peptide αs1-casein (136–196). Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1999, 1431, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creamer, L.K.; Richardson, T.; Parry, D.A.D. Secondary structure of bovine αs1-and β-casein in solution. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1981, 211, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.R.B.; Malcolm, G.N.; McKenzie, H.A. On the isolation and conformation of bovine β-casein A1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1984, 6, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.X. Studies of casein micelle structure: The past and the present. Le Lait 2007, 87, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, E.C. Stabilized Calcium Phosphate Complexes. U.S. Patent 8,609,071, 17 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Haberkorn, R.A.; Ruben, D.J. A two-dimensional nuclear Overhauser experiment with pure absorption phase in four quadrants. J. Magn. Reson. 1982, 48, 286–292. [Google Scholar]
- Chazin, W.J.; Wright, P.E. A modified strategy for identification of 1H spin systems in proteins. Biopolym. Orig. Res. Biomol. 1987, 26, 973–977. [Google Scholar]
- Byler, D.M.; Farrell, H.M., Jr.; Susi, H. Raman spectroscopic study of casein structure. J. Dairy Sci. 1988, 71, 2622–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominique, M.; Ikura, M.; Tschudin, R.; Bax, A.D. Rapid recording of 2D NMR spectra without phase cycling. Application to the study of hydrogen exchange in proteins. J. Magn. Reson. 1989, 85, 393–399. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, J.K.; Huq, N.L.; He, H.; Stanton, D.P.; Lau, K.; Reynolds, E.C. Structural characterization of the anticariogenic casein phosphopeptide αS2-casein (46–70) complexed with amorphous calcium phosphate. Aust. Dent. J. 2007, 52, S10–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, M.; Rasmussen, L.K.; Petersen, T.E.; Nielsen, N.C. Colloidal calcium phosphates in casein micelles studied by slow-speed-spinning 31P magic angle spinning solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloque, J. High-resolution NMR of milk and milk proteins. In Modern Magnetic Resonance; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 1631–1635. [Google Scholar]
- Wahlgren, N.M.; Dejmek, P.; Drakenberg, T. A 43 Ca and 31 P NMR study of the calcium and phosphate equilibria in heated milk solutions. J. Dairy Res. 1990, 57, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Jordan, A.; Thomar, P.; Nicolai, T.; Dittmer, J. The effect of pH on the structure and phosphate mobility of casein micelles in aqueous solution. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Hiramatsu, K.; Ohba, T.; Tsutsumi, A. The liquid-state 31P-nuclear magnetic resonance study on microfiltrated milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 2357–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollema, H.S.; Brinkhuis, J.A. A 1 H-NMR study of bovine casein micelles; influence of pH, temperature and calcium ions on micellar structure. J. Dairy Res. 1989, 56, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiani, M.; Fenelon, M.; FitzGerald, R.J.; Kelly, P.M. Use of 31P NMR and FTIR to investigate key milk mineral equilibria and their interactions with micellar casein during heat treatment. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 81, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sa Peixoto, P.; Silva, J.V.C.; Laurent, G.; Schmutz, M.; Thomas, D.; Bouchoux, A.; Gesan-Guiziou, G. How high concentrations of proteins stabilize the amorphous state of calcium orthophosphate: A solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) study of the casein case. Langmuir 2017, 33, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindmarsh, J.P.; Watkinson, P. Experimental evidence for previously unclassified calcium phosphate structures in the casein micelle. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 6938–6948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumy, J.-J.; Guenot, P.; Sinbandhit, S.; Brulé, G. Study of calcium binding to phosphoserine residues of β-casein and its phosphopeptide (1–25) by 31 P NMR. J. Dairy Res. 1989, 56, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hekken, D.L.; Dudley, R.L. Analysis of Modified Whole Casein with Different Phosphorus Contents Using Phosphorus-31 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 2751–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaisgood, H.E. Chemistry of the caseins. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry—1 Proteins; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 139–201. [Google Scholar]
| Protein | NMR Methods Used | Additional Methods | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-LA | DQF-COSY, RELAY, NOESY | PCODNP | [56] |
| α-LA | DQF-COSY, NOESY, RELAY | [52] | |
| α-LA | DQF-COSY, TOCSY, NOESY, ROESY, presaturation | CD | [58] |
| α-LA | 3D: TOCSY-HSQC, NOESY-HSQC, TOCSY, NOESY | CD | [3] |
| α-LA | 3D: 15N-edited NOESY-HSQC, COSY | [53] | |
| β-LG | DQF-COSY, TOCSY, NOESY | CD | [17] |
| β-LG | DQF-COSY, TOCSY, NOESY | [18] | |
| β-LG | 13C, 15N-protein labelling | CD, X-ray scattering | [59] |
| 2D: 15N-HSQC, TOCSY | |||
| 3D: CBCA(CO)NH, HNCACB, HNCO, HN(CA)CO, HCCH-TOCSY, CCH-TOCSY, (Hβ)Cβ(CγCδ)Hδ Hβ(CβCγCδ)Hδ, 1H-1H-15N NOESY | |||
| β-LG | DQF-COSY, TOCSY, NOESY | Structure calculation (DYANA) | [60] |
| β-LG | 15N,13C-labelled proteins | [61] | |
| 2D: 1H-15N HSQC | |||
| 3D: CBCA(CO)NH, HNCACB, HBHA(CBCACO)NH, HBHA(CBCA)NH, HNCO, HN(CA)CO, H(C)(CO)NH-TOCSY, WATERGATE | |||
| β-LG | DQF-COSY, TOCSY, NOESY | Thermal analysis | [62] |
| β-LG | 13C, 15N-protein labelling | Structure calculation (DYANA, X-PLOR) | [63] |
| 3D: 1H-15N NOESY-HSQC, 13C NOESY-HSQC, HNHA, HNHB | |||
| β-LG | DQF-COSY, TOCSY, T1 and T2 relaxation studies | X-ray crystallography for modelling | [64] |
| β-LG | 15N,13C-labelled proteins | Structure calculation (ARIA extension of X-PLOR) | [4] |
| 3D: 13C- and 15N-edited NOESY-HSQC, HNHA, T1 and T2 15N relaxation times, WATERGATE | |||
| β-LG | 1H-15N NOESY-HSQC, 13C NOESY-HSQC | [65] | |
| β-LG | TOCSY, NOESY, WATERGATE | [66] | |
| β-LG | 15N, 13C double-labelled protein | CD | [67] |
| 3D: CBCA(CO)NH, HNCACB, HNCO, HNCACO, relaxation analysis | |||
| β-LG | 15N, 13C double-labelled protein | PCA | [68] |
| H/D Exchange experiments | |||
| 3D: CBCA(CO)NH, HNCACB, HNCO, HNCACO | |||
| β-LG | 1H−15N HSQC; H/D exchange; transverse relaxation (R2) | [69] | |
| 3D: HNCACB, CBCACONH, HNCO, HNCACO |
| Protein Fragments | NMR Methods | Additional Methods | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-CN f(1–25) | 2D: DQF-COSY, TOCSY, ROESY, NOESY | [25] | |
| β-CN f(1–25) | 2D: COSY, R-COSY, TOCSY, NOESY | [26] | |
| β-CN f(1–25) | 2D: DQF-COSY, TOCSY, NOESY, ROESY | [27] | |
| β-CN f(1–25) | 2D: DQF-COSY, TOCSY, NOESY, ROESY | Molecular modelling | [29] |
| αs1-CN f(59–79) | 2D: DQF-COSY, TOCSY, NOESY, ROESY | Molecular modelling | [30,76] |
| αs1-CN f(1–23) | 2D: TOCSY, NOESY, HSQC | FTIR, CD, Molecular modelling | [32] |
| αs1-CN f(59–79) | 2D: DQF-COSY, TOCSY, NOESY, WET, Presaturation | sLED, X-ray scattering | [28] |
| αs1-CN f(136–196) | 2D: DQF-COSY, TOCSY, NOESY, Presaturation | Far-UV CD, FTIR | [77] |
| αs2-CN f(2–20) | 2D: DQF-COSY, TOCSY, NOESY, WET, Presaturation | Molecular modelling | [31] |
| κ-CN f(98–111) | 2D: DQF-COSY, TOCSY, ROESY | [33] | |
| κ-CN f(130–153) | 2D: DQF-COSY, TOCSY, NOESY, ROESY, Presaturation | CD | [16] |
| κ-CN f(1–44) | 2D: DQF-COSY, TOCSY, NOESY | CD, Structure calculation (X-PLOR) | [34] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markoska, T.; Vasiljevic, T.; Huppertz, T. Unravelling Conformational Aspects of Milk Protein Structure—Contributions from Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies. Foods 2020, 9, 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081128
Markoska T, Vasiljevic T, Huppertz T. Unravelling Conformational Aspects of Milk Protein Structure—Contributions from Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies. Foods. 2020; 9(8):1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081128
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkoska, Tatijana, Todor Vasiljevic, and Thom Huppertz. 2020. "Unravelling Conformational Aspects of Milk Protein Structure—Contributions from Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies" Foods 9, no. 8: 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081128
APA StyleMarkoska, T., Vasiljevic, T., & Huppertz, T. (2020). Unravelling Conformational Aspects of Milk Protein Structure—Contributions from Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies. Foods, 9(8), 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081128





