Fibrinogen Increases Resveratrol Solubility and Prevents it from Oxidation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
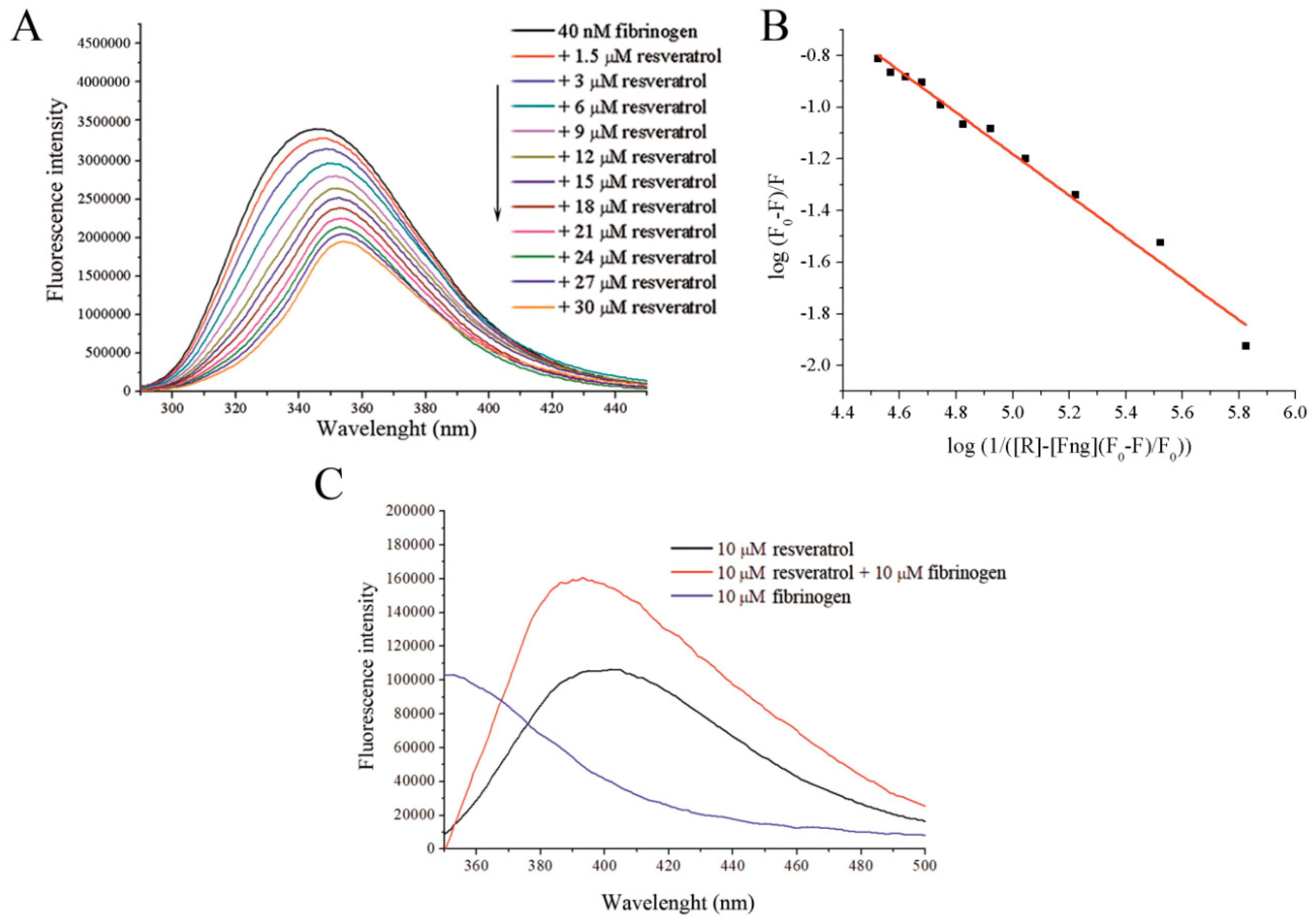
2.2. Spectrofluorometric Determination of the Fibrinogen/Resveratrol Affinity Constant
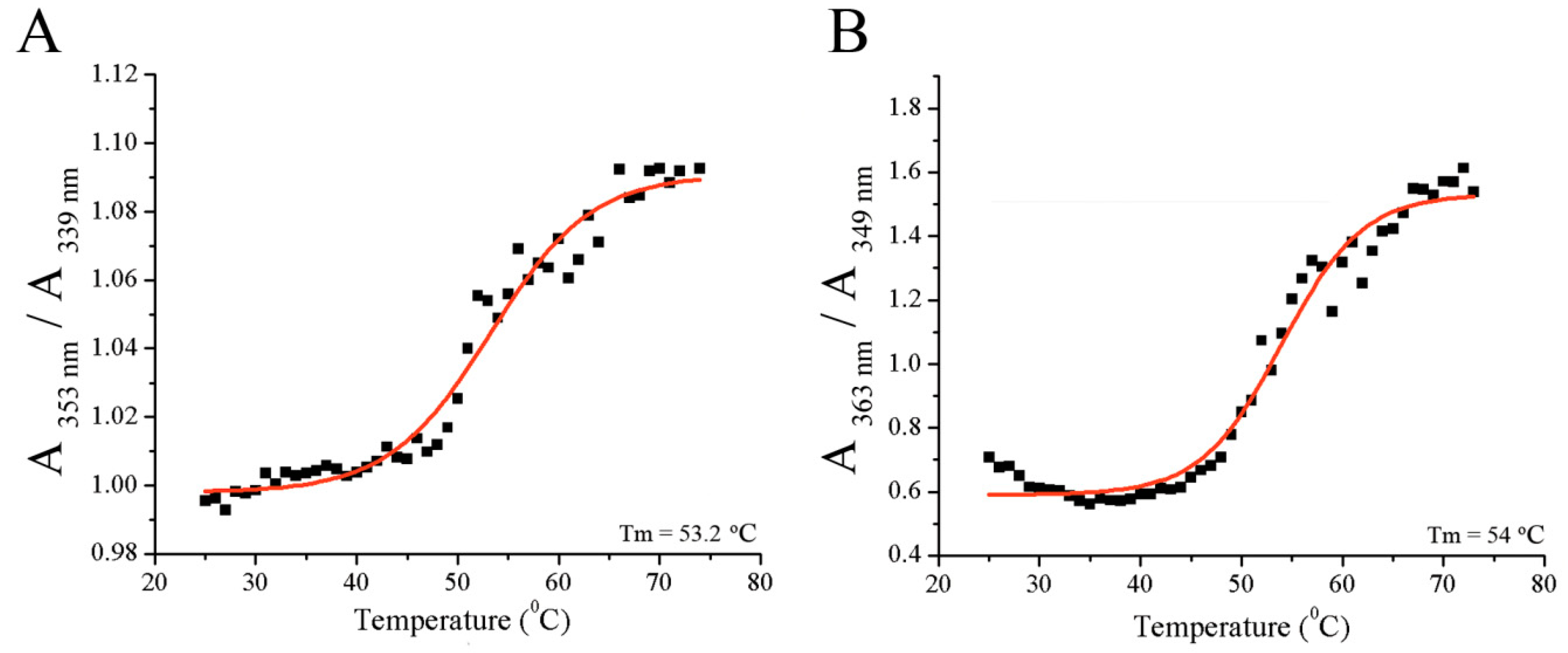
2.3. Determination of Temperature Stability of the Fibrinogen/Resveratrol Complex
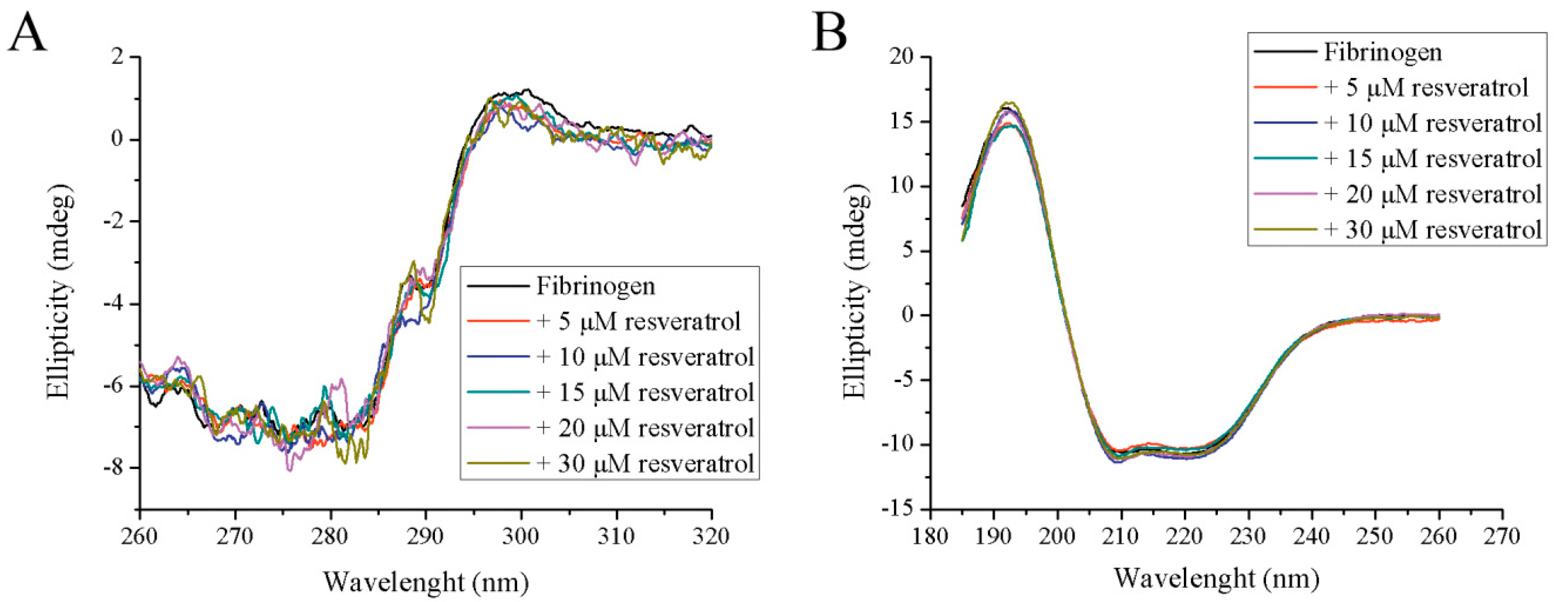
2.4. Analysis of Fibrinogen/Resveratrol Complex Formation Using Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy
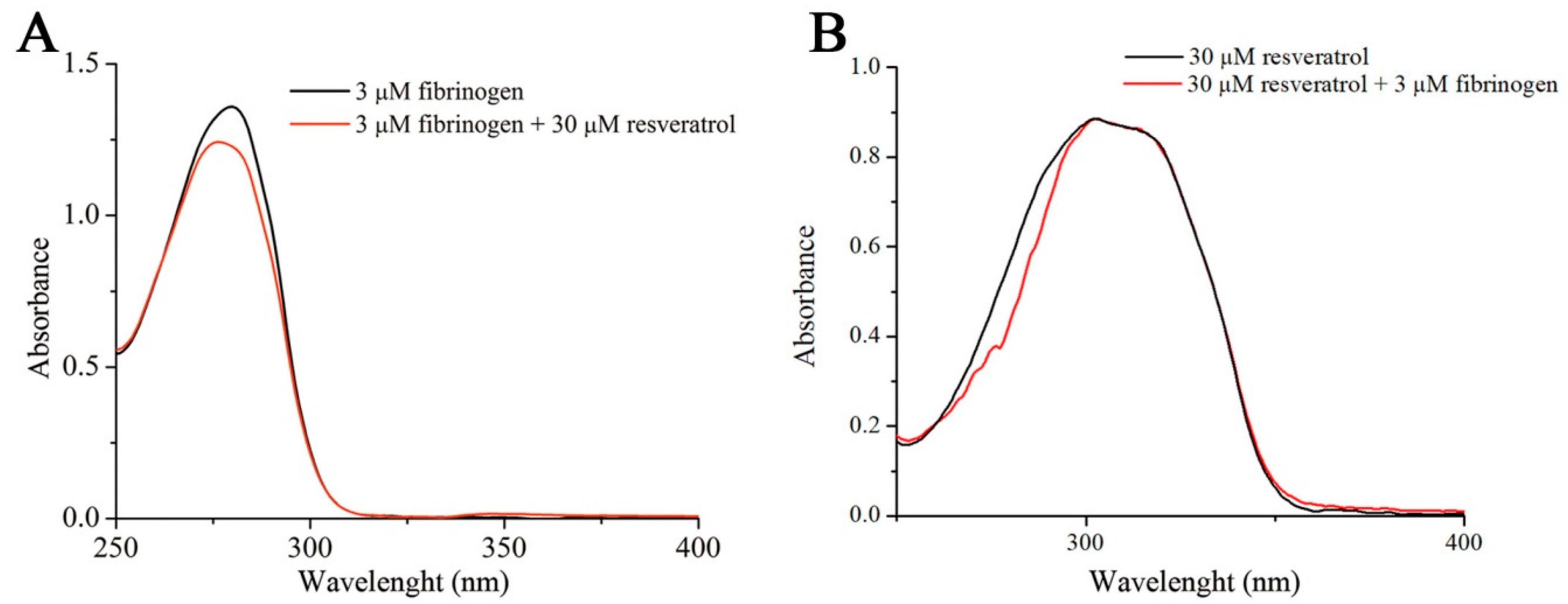
2.5. UV-VIS Analysis of Fibrinogen/Resveratrol Complex Formation
2.6. Effect of Fibrinogen on Resveratrol Solubility
2.7. Free Radical-Mediated Oxidation of Fibrinogen and Resveratrol
2.8. Total Reducing Power of Fibrinogen, Resveratrol, and Their Complex
2.9. Statistical Analysis of Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Binding Analysis of Fibrinogen and Resveratrol
3.2. Structural Analysis of Fibrinogen in Complex with Resveratrol
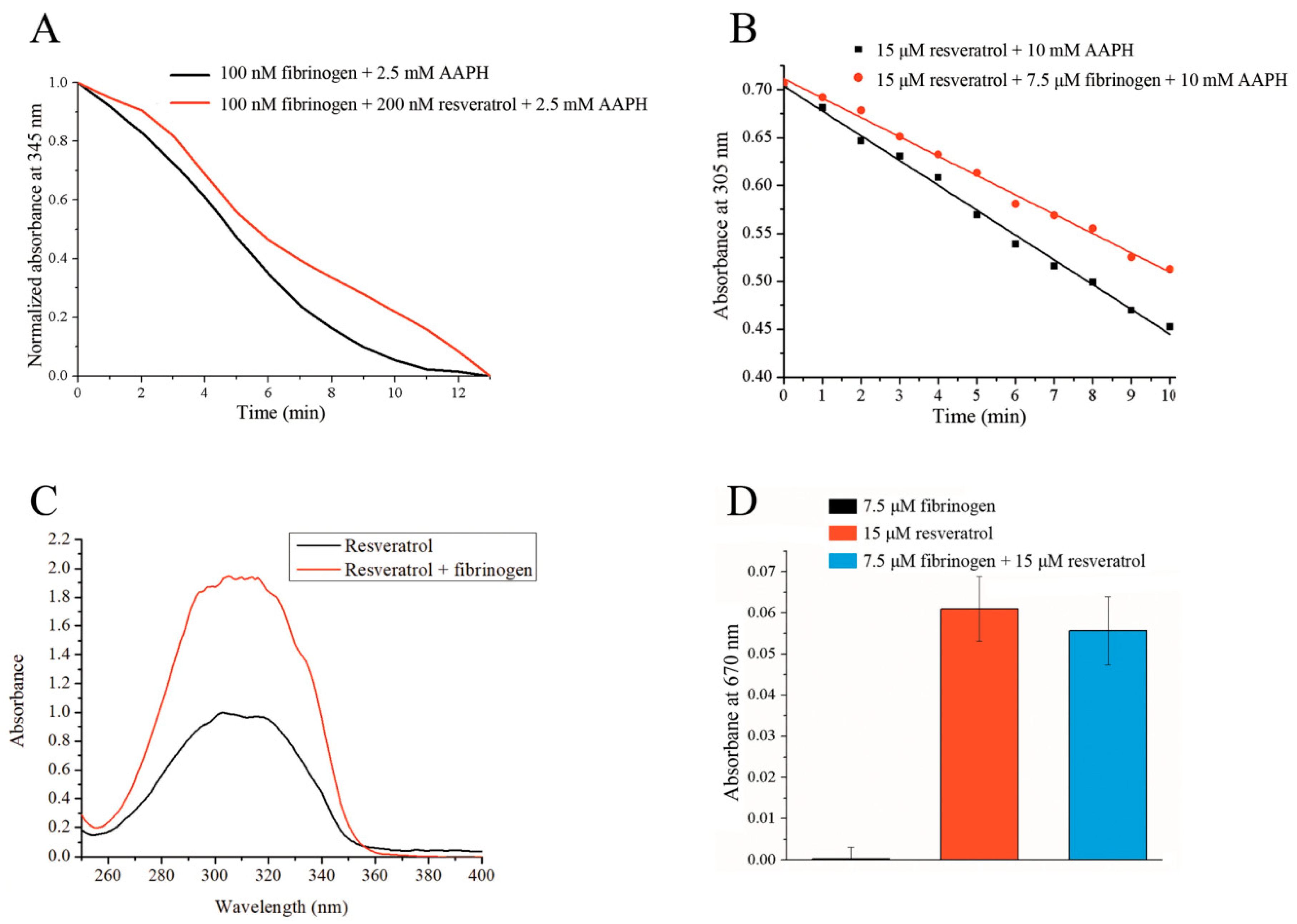
3.3. Anti-Oxidative Effects of Fibrinogen/Resveratrol Complex
3.4. Effect of Fibrinogen on Resveratrol Solubility
3.5. Reducing Ability of Fibrinogen/Resveratrol Complex
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Breuss, J.M.; Atanasov, A.G.; Uhrin, P. Resveratrol and its effects on the vascular system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, G.; Franchini, M.; Favaloro, E.J.; Targher, G. Moderate red wine consumption and cardiovascular disease risk: Beyond the French Paradox. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2010, 36, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, G.A.; Johnson, C.; Abajobir, A.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abera, S.F.; Abyu, G.; Ahmed, M.; Aksut, B.; Alam, T.; Alam, K.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of cardiovascular diseases for 10 causes, 1990 to 2015. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djoussé, L.; Lee, I.-M.; Buring, J.E.; Gaziano, J.M. Alcohol consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality in women: Potential mediating mechanisms. Circulation 2009, 120, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoliga, J.M.; Blanchard, O. Enhancing the delivery of resveratrol in humans: If low bioavailability is the problem, what is the solution? Molecules 2014, 19, 17154–17172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walle, T. Bioavailability of resveratrol. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1215, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosesson, M.W. Fibrinogen and fibrin structure and functions. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1894–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialkower, M.; McLiesh, H.; Manderson, C.A.; Tabor, R.F.; Garnier, G. Rapid paper diagnostic for plasma fibrinogen concentration. Analyst 2019, 144, 4848–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broos, K.; Feys, H.B.; De Meyer, S.F.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Deckmyn, H. Platelets at work in primary hemostasis. Blood Rev. 2011, 25, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, M.M.; Macrae, F.L.; Mcpherson, H.R.; Bridge, K.I.; Ajjan, R.A.; Ridger, V.C.; Connell, S.D.; Philippou, H.; Ari, R.A.S. Thrombin and fibrinogen γ, impact clot structure by marked effects on intra fi brillar structure and proto fi bril packing. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2019, 127, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisman, T.; Ariëns, R.A.S. Alterations in Fibrin Structure in Patients with Liver Diseases. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2016, 42, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligorijević, N.; Minić, S.; Robajac, D.; Nikolić, M.; Ćirković Veličković, T.; Nedić, O. Characterisation and the effects of bilirubin binding to human fibrinogen. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, R.; Barlow, S.; Boskou, D.; Castle, L.; Crebelli, R.; Dekant, W.; Engel, K.-H.; Forsythe, S.; Grunow, W.; Heinonen, M.; et al. Opinion of the Scientific Panel on food additives, flavourings, processing aids and materials in contact with food (AFC) related to use of an enzyme preparation based on thrombin:fibrinogen derived from cattle and/or pigs as a food additive for reconstituting food. EFSA J. 2005, 214, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bolognesi, C.; Castle, L.; Cravedi, J.-P.; Engel, K.-H.; Fowler, P.; Franz, R.; Grob, K.; Güertler, R.; Husoy, T.; Mennes, W.; et al. Scientific Opinion on thrombin from cattle (bovines) and pig’s blood. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarté, R. Ingredients in Meat Products, Properties, Functionality and Applications, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, N.K.; Lawrie, R.A. Functional aspects of blood plasma proteins. 11. Gelling properties. J. Food Technol. 1984, 19, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.; Weisel, J.W.; Ischiropoulos, H. Functional impact of oxidative post-translational modifications on fibrinogen and fibrin clots. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shacter, E.; Williams, J.A.; Lim, M.; Levine, R.L. Differential susceptibility of plasma proteins to oxidative modification: Examination by western blot immunoassay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1994, 17, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štikarová, J.; Kotlín, R.; Riedel, T.; Suttnar, J.; Pimková, K.; Chrastinová, L.; Dyr, J.E. The effect of reagents mimicking oxidative stress on fibrinogen function. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dai, X.F.; Huang, J.Y. Resveratrol Binding to Fibrinogen and its Biological Implication. Food Biophys. 2012, 7, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, L.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.A.; Subirade, M. Interaction of β-Lactoglobulin with resveratrol and its biological implications. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minic, S.; Stanic-Vucinic, D.; Radomirovic, M.; Radibratovic, M.; Milcic, M.; Nikolic, M.; Cirkovic Velickovic, T. Characterization and effects of binding of food-derived bioactive phycocyanobilin to bovine serum albumin. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisaidoobe, A.B.T.; Chung, S.J. Intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence in the detection and analysis of proteins: A focus on förster resonance energy transfer techniques. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22518–22538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munishkina, L.A.; Fink, A.L. Fluorescence as a method to reveal structures and membrane-interactions of amyloidogenic proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2007, 1768, 1862–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.; Maldonado-Valderrama, J.; Gunning, A.P.; Morris, V.J.; Ruso, J.M. Investigating the effect of an arterial hypertension drug on the structural properties of plasma protein. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 87, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani Gorji, E.; Rocchi, E.; Schleining, G.; Bender-Bojalil, D.; Furtmüller, P.G.; Piazza, L.; Iturri, J.J.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Characterization of resveratrol-milk protein interaction. J. Food Eng. 2015, 167, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuett, K.; Savvaidis, A.; Maxeiner, S.; Lysaja, K.; Jankowski, V.; Schirmer, S.H.; Dimkovic, N.; Boor, P.; Kaesler, N.; Dekker, F.W.; et al. Clot structure: A potent mortality risk factor in patients on hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1622–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becatti, M.; Emmi, G.; Silvestri, E.; Bruschi, G.; Ciucciarelli, L.; Squatrito, D.; Vaglio, A.; Taddei, N.; Abbate, R.; Emmi, L.; et al. Neutrophil Activation Promotes Fibrinogen Oxidation and Thrombus Formation in Behçet Disease. Circulation 2016, 133, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugenholtz, G.C.G.; Macrae, F.; Adelmeijer, J.; Dulfer, S.; Porte, R.J.; Lisman, T.; Ariëns, R.A.S. Procoagulant changes in fibrin clot structure in patients with cirrhosis are associated with oxidative modifications of fibrinogen. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, E.J.; Philippou, H.; Ariëns, R.A.S.; Grant, P.J. Molecular mechanisms involved in the resistance of fibrin to clot lysis by plasmin in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinowska, J.; Olas, B. Effect of resveratrol on hemostatic properties of human fibrinogen and plasma during model of hyperhomocysteinemia. Thromb. Res. 2010, 126, e379–e382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.Y.; Hsiao, G.; Liu, C.L.; Fong, T.H.; Lin, K.H.; Chou, D.S.; Sheu, J.R. Inhibitory mechanisms of resveratrol in platelet activation: Pivotal roles of p38 MAPK and NO/cyclic GMP. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 139, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, E.N.W.; Treskes, P.; Martin, S.F.; Manning, J.R.; Dunbar, D.R.; Rogers, S.M.; Le Bihan, T.; Lockman, K.A.; Morley, S.D.; Hayes, P.C.; et al. Fibrinogen production is enhanced in an in-vitro model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An isolated risk factor for cardiovascular events? Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, S.-J.; Liu, N.-C.; Ou, C.-C.; Bee, Y.-S.; Chen, S.-C.; Lin, H.-C.; Chan, J.Y.H. Resveratrol stimulates mitochondrial bioenergetics to protect retinal pigment epithelial cells from oxidative damage. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 6426–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widlund, A.L.; Baral, K.; Dalgaard, L.T.; Vang, O. Functional mitochondria are important for the effect of resveratrol. Molecules 2017, 22, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodotou, M.; Fokianos, K.; Moniatis, D.; Kadlenic, R.; Chrysikou, A.; Aristotelous, A.; Mouzouridou, A.; Diakides, J.; Stavrou, E. Effect of resveratrol on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Mishra, A.P.; Nigam, M.; Sener, B.; Kilic, M.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Martins, N.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Resveratrol: A double-edged sword in health benefits. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertacche, V.; Lorenzi, N.; Nava, D.; Pini, E.; Sinico, C. Host-guest interaction study of resveratrol with natural and modified cyclodextrins. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2006, 55, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojadinovic, M.; Radosavljevic, J.; Ognjenovic, J.; Vesic, J.; Prodic, I.; Stanic-Vucinic, D.; Cirkovic Velickovic, T. Binding affinity between dietary polyphenols and β-lactoglobulin negatively correlates with the protein susceptibility to digestion and total antioxidant activity of complexes formed. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gligorijević, N.; Radomirović, M.; Rajković, A.; Nedić, O.; Ćirković Veličković, T. Fibrinogen Increases Resveratrol Solubility and Prevents it from Oxidation. Foods 2020, 9, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9060780
Gligorijević N, Radomirović M, Rajković A, Nedić O, Ćirković Veličković T. Fibrinogen Increases Resveratrol Solubility and Prevents it from Oxidation. Foods. 2020; 9(6):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9060780
Chicago/Turabian StyleGligorijević, Nikola, Mirjana Radomirović, Andreja Rajković, Olgica Nedić, and Tanja Ćirković Veličković. 2020. "Fibrinogen Increases Resveratrol Solubility and Prevents it from Oxidation" Foods 9, no. 6: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9060780
APA StyleGligorijević, N., Radomirović, M., Rajković, A., Nedić, O., & Ćirković Veličković, T. (2020). Fibrinogen Increases Resveratrol Solubility and Prevents it from Oxidation. Foods, 9(6), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9060780






