Effect of Selenium Source and Level on Performance, Egg Quality, Egg Selenium Content, and Serum Biochemical Parameters in Laying Hens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Animal Assignment
2.2. Animal Management
2.3. Experimental Diets
3. Sampling and Analysis
3.1. Feed Sampling
3.2. Measurements of Performance
3.3. Blood Sample Collection
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Performance Indices
4.2. Egg Quality
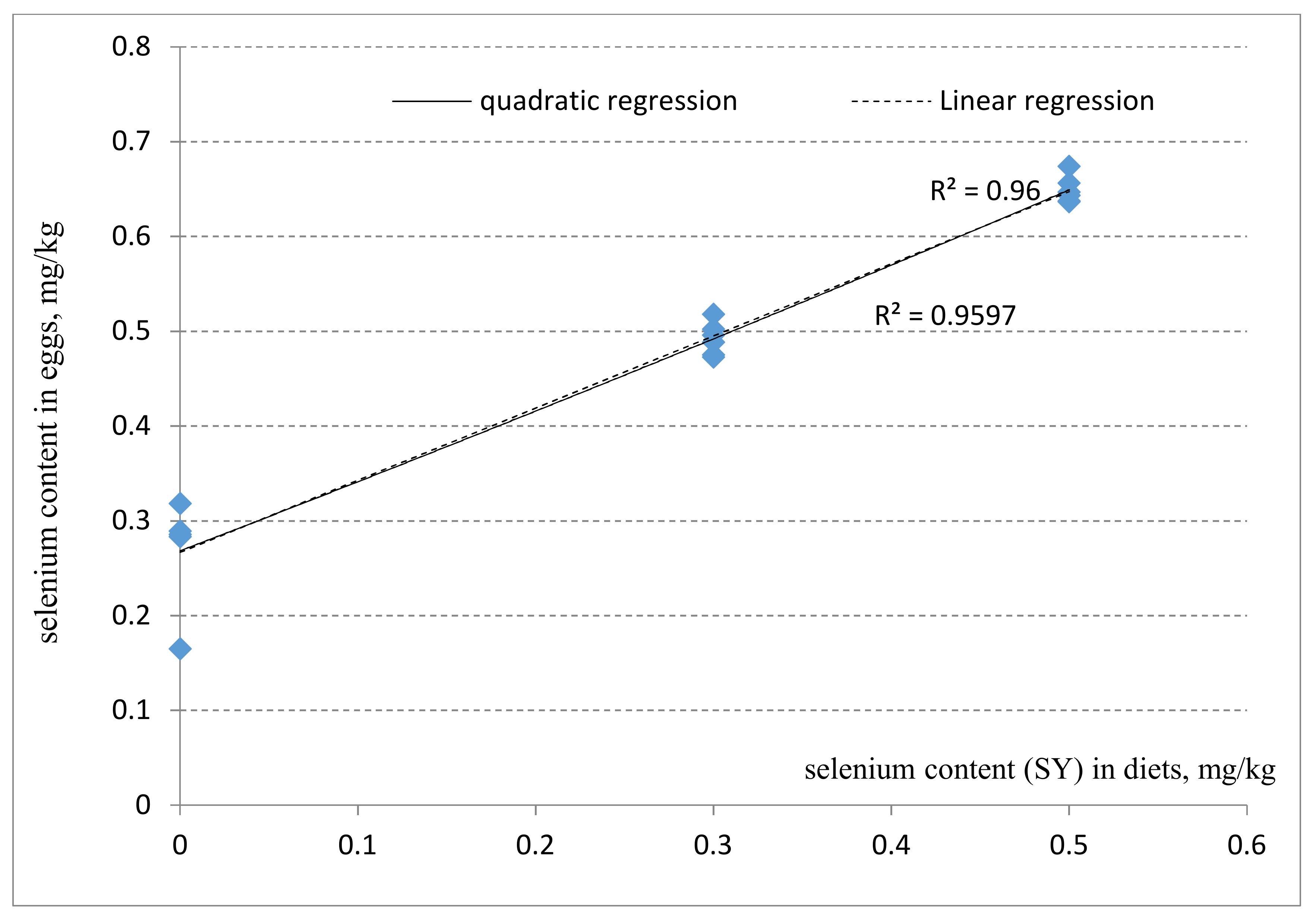
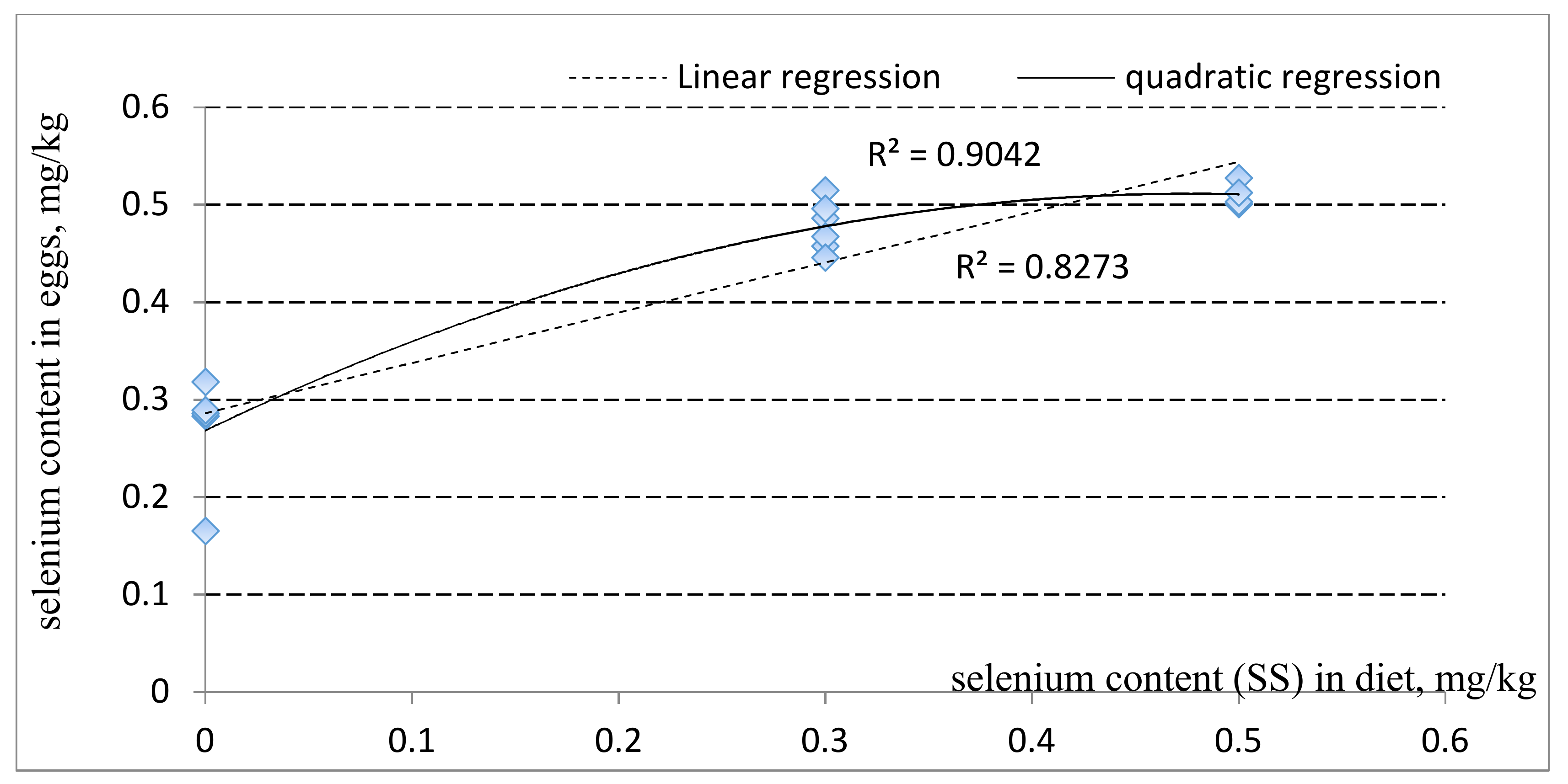
4.3. Selenium Concentrations in Egg Yolk
4.4. Serum Biochemistry
5. Discussion
5.1. Performance
5.2. Egg Quality
5.3. Selenium Content of Egg Yolk
5.4. Serum Biochemical Indices
6. Conclusions
Reference
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rotruck, J.T.; Pope, A.L.; Ganther, H.E.; Swanson, A.B.; Hafeman, D.G.; Hoekstra, W.G. Selenium: Biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science 2010, 179, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, L.R.; Karunasinghe, N.; Zhu, S.; Wang, A.H. Selenium and its’ role in the maintenance of genomic stability. Mutat. Res. 2012, 733, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spears, J.W.; Weiss, W.P. Role of antioxidants and trace elements in health and immunity of transition dairy cows. Vet. J. 2008, 176, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hefnawy, A.E.G.; Tórtora-Pérez, J.L. The importance of selenium and the effects of its deficiency in animal health. Small Rumin. Res. 2010, 89, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, D.H. The diverse role of selenium within seleno-proteins: A review. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1999, 99, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanguy, S.; Grauzam, S.; De Leiris, J.; Boucher, F. Impact of dietary selenium intake on cardiac health: Experimental approaches and human studies. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1106–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalska–Mosiej, M.; Socha, K.; Soroczyńska, J.; Karpińska, E.; Lazarczyk, B.; Borawska, M.H. Selenium, zinc, copper, and total antioxidant status in the serum of patients with chronic tonsillitis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 173, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, C.; Fraser, J.; Shekar, K.; Clarke, A.; Coombes, J.; Barnett, A.; Pearse, B.; Fung, L. Low preoperative selenium is associated with post-operative atrial fibrillation in patients having intermediate-risk coronary artery surgery. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, K.C.; Vieira, M.L.; Beltrame, R.L.; Cartum, J.; Alves, S.I.; Azzalis, L.A.; Junqueira, V.B.C.; Pereira, E.C.; Fonseca, F.L. Impact of selenium supplementation in neutropenia and immunoglobulin production in childhood cancer patients. J. Med. Food 2016, 19, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.G.; Nogueira, R.J.; Antonio de Azevedo and Hessel, G.; Barros-Filho, A.D.A.; Hessel, G. Selenium deficiency and the effects of supplementation on preterm infants. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2014, 32, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.G.B.O.N.; Nogueira, R.J.N.; Cozzolino, S.M.F.; Vasques, A.C.J.; Hessel, G. Influence of selenium supplementation on patients with inflammation: A pilot double blind randomized study. Nutrition 2017, 41, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi, F.; Shariatmadari, F.; Karimitorshizi, M.A.; Mohiti-Asli, M. Comparison of Different Selenium Sources and Vitamin E in Laying Hen Diet and Their Influences on Egg Selenium and Cholesterol Content, Quality and Oxidative Stability. Iran. J. Appl. Anim. Sci. 2017, 7, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Delezie, E.; Rovers, M.; Van der Aa, A.; Ruttens, A.; Wittocx, S.; Segers, L. Comparing responses to different selenium sources and dosages in laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 3083–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, Y.A.; Abdalah, A.A.; Zeweil, H.S.; Bovera, F.; El-Din, A.A.T.; Araft, M.A. Effect of inorganic or organic selenium supplementation on productive performance, egg quality and some physiological traits of dual-purpose breeding hens. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 55, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.J.; Qin, P.; Li, W.X.; Ma, Q.G.; Ji, C.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhao, L.H. Effect of sodium selenite and selenium yeast on performance, egg quality, antioxidant capacity, and selenium deposition of laying hens. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 3973–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utterback, P.L.; Parsons, C.M.; Yoon, I.; Butler, J. Effect of supplementing selenium yeast in diets of laying hens on egg selenium content. Poult. Sci. 2005, 84, 1900–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Yang, J.; Sun, Z.Z.; Zhang, R.H.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, K.C.; Xia, Y.; Huang, K.H.; Mao, D.N. Effect of Selenium Nanoparticles on Anti-Oxidative Level, Egg Production and Quality and Blood Parameter of Laying Hens Exposed to Deoxynivalenol. J. Anim. Res. Nutr. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Nutrient Requirements of Poultry, 9th ed.; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 16th ed.; Association of Official Analysis Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Joaquim, A.N.; Gelinas, A.; Krushevska Barnes, R.M. Determination of elements in biological and botanical materials by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission and mass spectrometry after extraction with a tertiary aminere agent. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1997, 12, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Gjorgovska, N.; Kiril, F.; Tosho, K. The effect of different levels of selenium in feed on egg production, egg quality and selenium content in yolk. Lucrări Ştiinţifice-Seria Zootehnie 2012, 57, 270–274. [Google Scholar]
- Leeson, S.; Namkung, H.; Caston, L.; Durosoy, S.; Schlegel, P. Comparison of selenium levels and sources and dietary fat quality in diets for broiler breeders and layer hens. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 2605–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, R.N.; Vieira, S.L.; Nascimento, P.C.; Pena, J.E.; Barros, R.; Torres, C.A. Selenium contents of eggs from broiler breeders supplemented with sodium selenite or zinc-l-selenium-methionine. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2009, 18, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, N.D. Organic Selenium in the Nutrition of Laying Hens: Effects on Egg Selenium Content, Egg Quality and Transfer to Developing Chick Embryos. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, R.L.; Lavergne, T.K.; Soutnher, L.L. Effect of inorganic versus organic selenium on hen production and egg selenium concentration. Poult. Sci. 2005, 84, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urso, U.R.A.; Dahlke, F.; Maiorka, A.; Bueno, I.J.M.; Schneider, A.F.; Surek, D.; Rocha, C. Vitamin E and selenium in broiler breeder diets: Effect on live performance, hatching process, and chick quality. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surai, P.F.; Fisinin, V.I. Selenium in poultry breeder nutrition: An update. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 191, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Y. Influence of dietary nano elemental selenium on growth performance, tissue selenium distribution, meat quality, and glutathione peroxidase activity in guangxi yellow chicken. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.H.; Li, Y.L.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, H.M.; Song, J.; Xia, M.S. Comparative effects of nano elemental selenium and sodium selenite on selenium retention in broiler chickens. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2012, 177, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnold, R.L.; Olson, O.E.; Carloson, C.W. Dietary selenium and arsenic additions and their effects on tissue and egg selenium. Poult. Sci. 1973, 52, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadai, L.; Radwan, T.A.; Salah Eldin, A.A. EL-Zaiat. Effect of Dietary Nano-Selenium Supplementation on Selenium Content and Oxidative Stability in Table Eggs and Productive Performance of Laying Hens. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2015, 14, 161–176. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.F.; Consatable, P.D.; Misk, N.A. Effect of feeding frequency and route of administration on abomasa luminal PH in dairy calve fed milk replacer. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 1502–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Nie, J.; Tan, B.E.; Dong, X.H.; Chi, S.Y. Effects of selenium source and selenium level on growth performance, liver and serum antioxidant indices and selenium content in tissues of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum). Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 27, 3699–3707. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S. Effects of selenium and vitamin e on nutrient apparent digestibility, nitrogen balance, energy metabolism and blood biochemical indices of beef cattle. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2013, 24, 2476–2484. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
| Ingredients | Content (%) | Nutrition level | Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 61.0 | ME, MJ/kg (2) | 11.12 |
| Soybean meal | 23.0 | CP, % | 15.90 |
| Limestone | 8.00 | Ca, % | 3.50 |
| Rapeseed meal | 3.00 | AP, % | 0.34 |
| Soybean oil | 1.00 | Lys, % | 0.84 |
| Premix (1) | 4.00 | Met, % | 0.33 |
| Parameters | Basal Diet | SY-L | SY-H | SS-L | SS-H | P-Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | L | S × L | ||||||
| ADFI, g/d | 114.58 ± 2.08 a | 114.73 ± 5.13 a | 114.39 ± 5.08 a | 116.05 ± 6.32 b | 114.43 ± 5.03 a | 0.106 | 0.438 | 0.023 |
| AEW, g | 55.47 ± 0.65 | 56.00 ± 2.68 | 55.47 ± 2.96 | 55.03 ± 2.48 | 55.22 ± 2.40 | 0.122 | 0.740 | 0.209 |
| FCR | 2.29 ± 0.04 | 2.24 ± 0.20 | 2.19 ± 0.14 | 2.30 ± 0.16 | 2.21 ± 0.09 | 0.075 | 0.716 | 0.366 |
| Laying Rate, % | 90.14 ± 0.99 a | 92.05 ± 6.84 b | 94.72 ± 5.06 c | 92.04 ± 5.23 b | 93.95 ± 3.71c | 0.679 | 0.022 | 0.525 |
| Soft or Cracked Eggs, % | 0.63 ± 0.32 b | 0.61 ± 0.99 b | 0.36 ± 0.49 a | 1.27 ± 1.43 c | 0.67 ± 0.76 b | 0.191 | 0.081 | 0.118 |
| Parameters | Basal Diet | SY-L | SY-H | SS-L | SS-H | P-Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | L | S × L | ||||||
| Egg shape index | 1.30 ± 0.03 | 1.31 ± 0.10 | 1.29 ± 0.03 | 1.31 ± 0.06 | 1.30 ± 0.04 | 0.982 | 0.374 | 0.189 |
| Eggshell thickness, mm | 0.50 ± 0.30 | 0.48 ± 0.03 | 0.49 ± 0.04 | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 0.48 ± 0.02 | 0.629 | 0.669 | 0.143 |
| Eggshell strength, kg/m2 | 5.27 ± 0.62 | 4.87 ± 0.87 | 4.89 ± 0.87 | 5.04 ± 1.02 | 4.94 ± 0.64 | 0.654 | 0.875 | 0.550 |
| Yolk weight, g | 15.60 ± 0.64 | 15.69 ± 0.54 | 15.84 ± 0.37 | 15.66 ± 0.85 | 15.74 ± 1.18 | 0.813 | 0.706 | 0.097 |
| Yolk index | 0.38 ± 0.04 | 0.39 ± 0.04 | 0.39 ± 0.04 | 0.41 ± 0.04 | 0.43 ± 0.02 | 0.281 | 0.144 | 0.102 |
| Albumen height, mm | 5.65 ± 0.36 | 5.88 ± 0.90 | 5.35 ± 0.81 | 5.53 ± 0.56 | 5.24 ± 1.12 | 0.058 | 0.437 | 0.539 |
| Haugh unit | 75.01 ± 2.87 | 75.62 ± 4.67 | 75.52 ± 4.02 | 75.34 ± 3.35 | 75.54 ± 3.97 | 0.913 | 0.973 | 0.973 |
| Parameters. | Basal Diet | SY-L | SY-H | SS-L | SS-H | P-Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | L | S × L | ||||||
| Se content, mg/kg | 0.2683 ± 0.0593 A | 0.4920 ± 0.0171 B | 0.6491 ± 0.0142 C | 0.4780 ± 0.0257 B | 0.5107 ± 0.0120 B | 0.009 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Parameters | Basal Diet | SY-L | SY-H | SS-L | SS-H | P-Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | L | S × L | ||||||
| ALB, g/L | 24.58 ± 1.74 | 25.80 ± 4.67 | 26.52 ± 4.28 | 24.08 ± 2.95 | 25.90 ± 2.38 | 0.453 | 0.410 | 0.712 |
| TP, mg/ml | 54.71 ± 3.13 | 58.17 ± 7.75 | 59.75 ± 5.71 | 55.56 ± 3.89 | 57.45 ± 3.32 | 0.302 | 0.144 | 0.450 |
| BUN, mmol/L | 5.32 ± 1.12 | 5.55 ± 0.66 | 5.75 ± 0.29 | 5.42 ± 1.24 | 5.35 ± 1.10 | 0.589 | 0.818 | 0.931 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Yu, Q.; Fang, C.; Chen, S.; Tang, X.; Ajuwon, K.M.; Fang, R. Effect of Selenium Source and Level on Performance, Egg Quality, Egg Selenium Content, and Serum Biochemical Parameters in Laying Hens. Foods 2020, 9, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010068
Liu H, Yu Q, Fang C, Chen S, Tang X, Ajuwon KM, Fang R. Effect of Selenium Source and Level on Performance, Egg Quality, Egg Selenium Content, and Serum Biochemical Parameters in Laying Hens. Foods. 2020; 9(1):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010068
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hu, Qifang Yu, Chengkun Fang, Sijia Chen, Xiaopeng Tang, Kolapo M. Ajuwon, and Rejun Fang. 2020. "Effect of Selenium Source and Level on Performance, Egg Quality, Egg Selenium Content, and Serum Biochemical Parameters in Laying Hens" Foods 9, no. 1: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010068
APA StyleLiu, H., Yu, Q., Fang, C., Chen, S., Tang, X., Ajuwon, K. M., & Fang, R. (2020). Effect of Selenium Source and Level on Performance, Egg Quality, Egg Selenium Content, and Serum Biochemical Parameters in Laying Hens. Foods, 9(1), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010068





