A Novel Chiral Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on β-CD Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots for Enantioselective Detection of D-Carnitine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
2.2. Preparation of GQDs and GQDs/β-CD
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
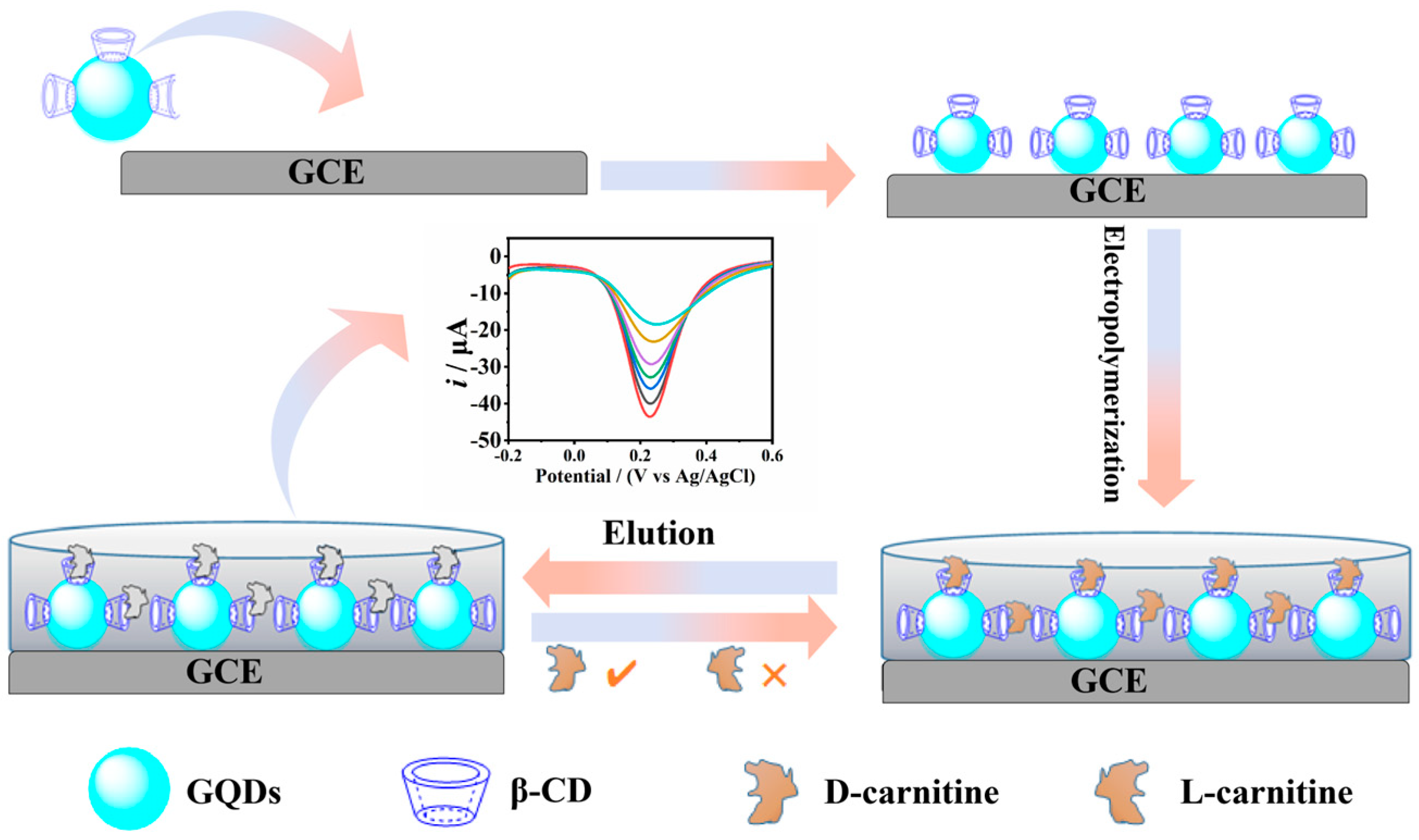
2.4. Sensors Fabrication
2.5. Preparation of Real Sample
3. Results
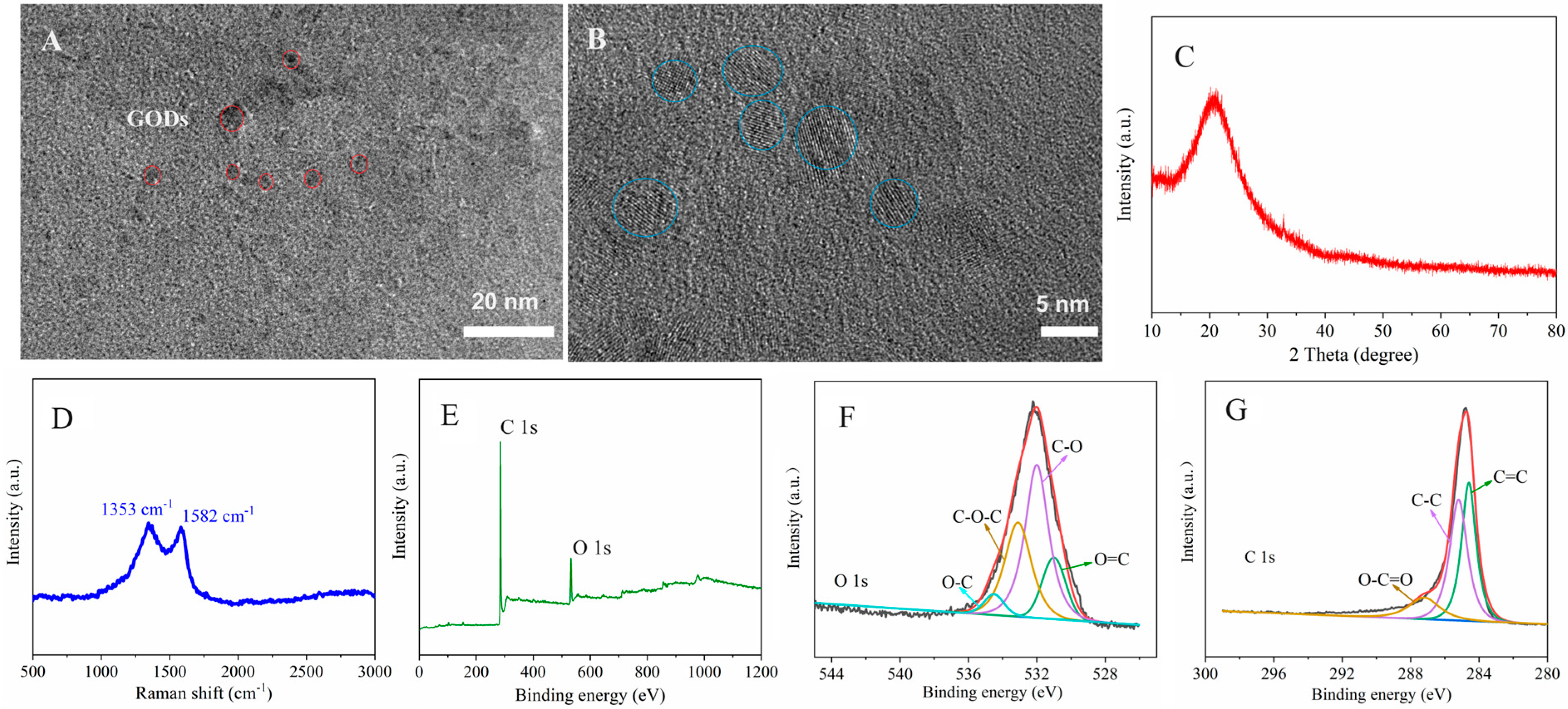
3.1. Material Characterization
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization of Sensors
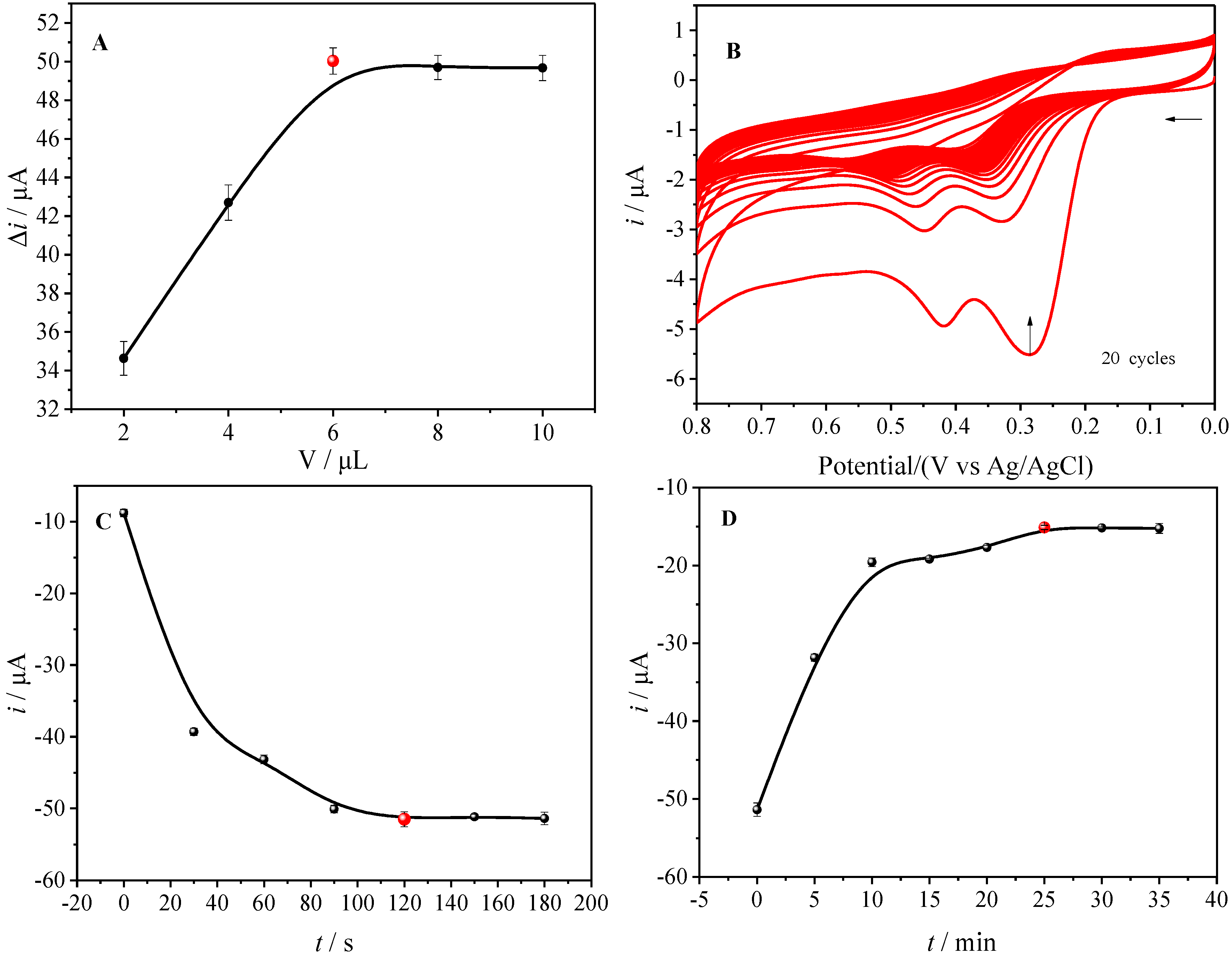
3.3. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
3.4. Analytical Performance
3.4.1. Selectivity
3.4.2. Anti-Interference Ability
3.4.3. Stability, Reproducibility, and Lifespan
3.4.4. Real Sample Detection
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Motazedian, N.; Ashari, A.; Dehdari Ebrahimi, N.; Sayadi, M.; Pourjafar, S.; Motazedian, N.; Khademi, V.; Shamsaeefar, A.; Eshraghian, A. Effects of L-carnitine on frailty status in patients with liver cirrhosis: A randomized-controlled trial. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e70148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carillo, M.R.; Bertapelle, C.; Scialò, F.; Siervo, M.; Spagnuolo, G.; Simeone, M.; Peluso, G.; Digilio, F.A. L-Carnitine in drosophila: A review. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xue, X.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, B.; Yin, Z.; Ou, G.; Zhou, Q. L-carnitine combined with traditional Chinese medicine for male infertility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gziut, T.; Thanacoody, R. L-carnitine for valproic acid-induced toxicity. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 91, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Li, K.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, D. Carnitine analysis in food and biological samples: Chromatography and mass spectrometry insights. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittain, E.L.; Lindsey, A.; Burke, K.; Agrawal, V.; Robbins, I.; Pugh, M.; Calcutt, M.W.; Mallugari, R.; West, J.; Nian, H.; et al. Carnitine consumption and effect of oral supplementation in human pulmonary arterial hypertension: A pilot study. Pulm. Circ. 2024, 14, e12425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uner, B.; Ergin, A.D.; Ansari, I.A.; Macit-Celebi, M.S.; Ansari, S.A.; Kahtani, H.M.A. Assessing the in vitro and in vivo performance of L-carnitine-loaded nanoparticles in combating obesity. Molecules 2023, 28, 7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, S.; Samiee, S.; Zarif, M.N.; Deyhim, M.R. l-carnitine modulates free mitochondrial DNA DAMPs and platelet storage lesions during storage of platelet concentrates. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2023, 55, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, R.; Lunetti, P.; Zara, V.; Ferramosca, A.; Marra, F.; Fiermonte, G.; Cappello, A.R.; De Leonardis, F.; Capobianco, L.; Dolce, V. Drosophila melanogaster mitochondrial carriers: Similarities and differences with the human carriers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Deng, W.; Cui, W.; Xie, Q.; Zhao, G.; Wu, X.; Dai, L.; Chen, D.; Yu, B. Analysis of amino acid and acyl carnitine profiles in maternal and fetal serum from preeclampsia patients. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020, 33, 2743–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Luo, K.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, J. Chiral molecular imprinted sensor for highly selective determination of D-carnitine in enantiomers via dsDNA-assisted conformation immobilization. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1136, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvutiene, J.; Prentice, U.; Ramanavicius, S.; Ramanavicius, A. Molecular imprinting technology for biomedical applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2024, 71, 108318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banan, K.; Niknam, S.; Ahmadi, M.; Tabasi, S.; Ghalkhani, M.; Adabi, M.; Ghorbani-Bidkoreph, F. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on carbon nanofibers for Amiodarone determination. Microchem. J. 2024, 200, 110365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Ren, S.; Zheng, Z. Construction of molecularly imprinted voltammetric sensor based on rGO/Ti3C2Tx for the selective determination of acetaminophen. Microchem. J. 2024, 199, 109909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Jamal, R.; Abdiryim, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, F.; Xu, F.; Cheng, Q.; Tang, X.; Fan, N. An ionic liquid-modified PEDOT/Ti3C2TX based molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for pico-molar sensitive detection of L-Tryptophan in milk. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 139114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Manna, K.; Dey, S.; Pal, S. Chemical modification of β-cyclodextrin towards hydrogel formation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 306, 120576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Wang, M.; Gong, W.; Wang, H.; Fan, H.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on α-Cyclodextrin inclusion complex and MXene modification for highly sensitive and selective detection of alkylresorcinols in whole wheat foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 10655–10664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Tang, L.; Teng, K.S.; Lau, S.P. Graphene quantum dots from chemistry to applications. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 10, 221–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, T.; Gooding, J.J.; Liu, J. Review of carbon and graphene quantum dots for sensing. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1732–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Gong, J.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, W.; Pu, K.; Liu, J.; Chen, P. Recent advances on graphene quantum dots: From chemistry and physics to applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, J.; Wang, T.; Li, L. Graphene quantum dots as nanoprobes for fluorescent detection of propofol in emulsions. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 181753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Zhu, Y.; Kong, Y.; Ma, J. Graphene quantum dots/β-cyclodextrin nanocomposites: A novel electrochemical chiral interface for tryptophan isomer recognition. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 60, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Ammari, R.H.; Ganash, A.A.; Salam, M.A. Electrochemical molecularly imprinted polymer based on zinc oxide/graphene/poly (o-phenylenediamine) for 4-chlorophenol detection. Synth. Met. 2019, 254, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeva-Andany, M.M.; Calvo-Castro, I.; Fernández-Fernández, C.; Donapetry-García, C.; Pedre-Piñeiro, A.M. Significance of l-carnitine for human health. IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 578–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, R.I.; Bokretsion, R.G.; van Staden, J.F.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Simultaneous determination of L-and D-carnitine using a sequential injection analysis/amperometric biosensors system. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 33, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Hernández, L.; Castro-Puyana, M.; García-Ruiz, C.; Crego, A.L.; Marina, M.L. Determination of L-and D-carnitine in dietary food supplements using capillary electrophoresis–tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Detection Method | Linear Range (mol/L) | Detection Limit (mol/L) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raman Spectroscopy | 1.0 × 10−6~1.0 × 10−3 | 1.0 × 10−6 | [24] |
| Amperometry Biosensor | 4.0 × 10−14~6.0 × 10−12 | 2.0 × 10−15 | [25] |
| Capillary Electrophoresis-Tandem Mass Spectrometry | 6.2 × 10−8~3.7 × 10−4 | 6.2 × 10−8 | [26] |
| MIPs/(GQDs/β-CD) Sensor | 1.0 × 10−12~1.0 × 10−9 | 2.35 × 10−13 | This work |
| Sample | Found (mol/L) | RSD% n = 5 | Added (mol/L) | Total Found (mol/L) | RSD% n = 5 | Recovery % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-Carnitine Coffee | 1.16 × 10−11 | 1.00 × 10−11 | 2.19 × 10−11 | 3.26 | 103.0 | |
| 3.42 | 2.00 × 10−11 | 3.13 × 10−11 | 2.64 | 98.5 | ||
| 3.00 × 10−11 | 4.21 × 10−10 | 2.37 | 101.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, F.; Qi, X.; Chen, Y.; Tang, K.; Fang, M.; Song, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L. A Novel Chiral Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on β-CD Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots for Enantioselective Detection of D-Carnitine. Foods 2025, 14, 1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091648
Yang F, Qi X, Chen Y, Tang K, Fang M, Song Y, Liu J, Zhang L. A Novel Chiral Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on β-CD Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots for Enantioselective Detection of D-Carnitine. Foods. 2025; 14(9):1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091648
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Feng, Xin Qi, Yan Chen, Kai Tang, Mengyang Fang, Yanwei Song, Jiufen Liu, and Lianming Zhang. 2025. "A Novel Chiral Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on β-CD Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots for Enantioselective Detection of D-Carnitine" Foods 14, no. 9: 1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091648
APA StyleYang, F., Qi, X., Chen, Y., Tang, K., Fang, M., Song, Y., Liu, J., & Zhang, L. (2025). A Novel Chiral Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor Based on β-CD Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots for Enantioselective Detection of D-Carnitine. Foods, 14(9), 1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091648





