Effects of Different Water Contents on the Quality Characteristics of Roasted Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Fillets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Equipment
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Sample Preparation
2.3.2. Color and Luster
2.3.3. Hardness and Shear Force
2.3.4. TBARS
2.3.5. TVB-N
- V1—volume of hydrochloric acid in the test solution;
- V2—hydrochloric acid volume in reagent blanks;
- m—sample weight;
- C—hydrochloric acid concentration;
- d—dilution factor.
2.3.6. Water Distribution
2.3.7. Electronic Nose Analysis
2.3.8. Electronic Tongue Analysis
2.3.9. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
- Ai—peak area of volatile flavor substance;
- CTMP—concentration of the internal standard;
- VTMP—volume of the internal standard;
- ATMP—peak area of the internal standard;
- M—quality of the fish sample.
2.3.10. Preparation and Determination of Myofibrillar Proteins
2.3.11. Sensory Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Color of Large Yellow Croaker Fillets with Different Water Contents After Roasting
3.2. Changes in Texture of Large Yellow Croaker Fillets with Different Water Content After Roasting
3.3. Changes in TBARS Content of Large Yellow Croaker Fillets with Different Water Contents After Roasting
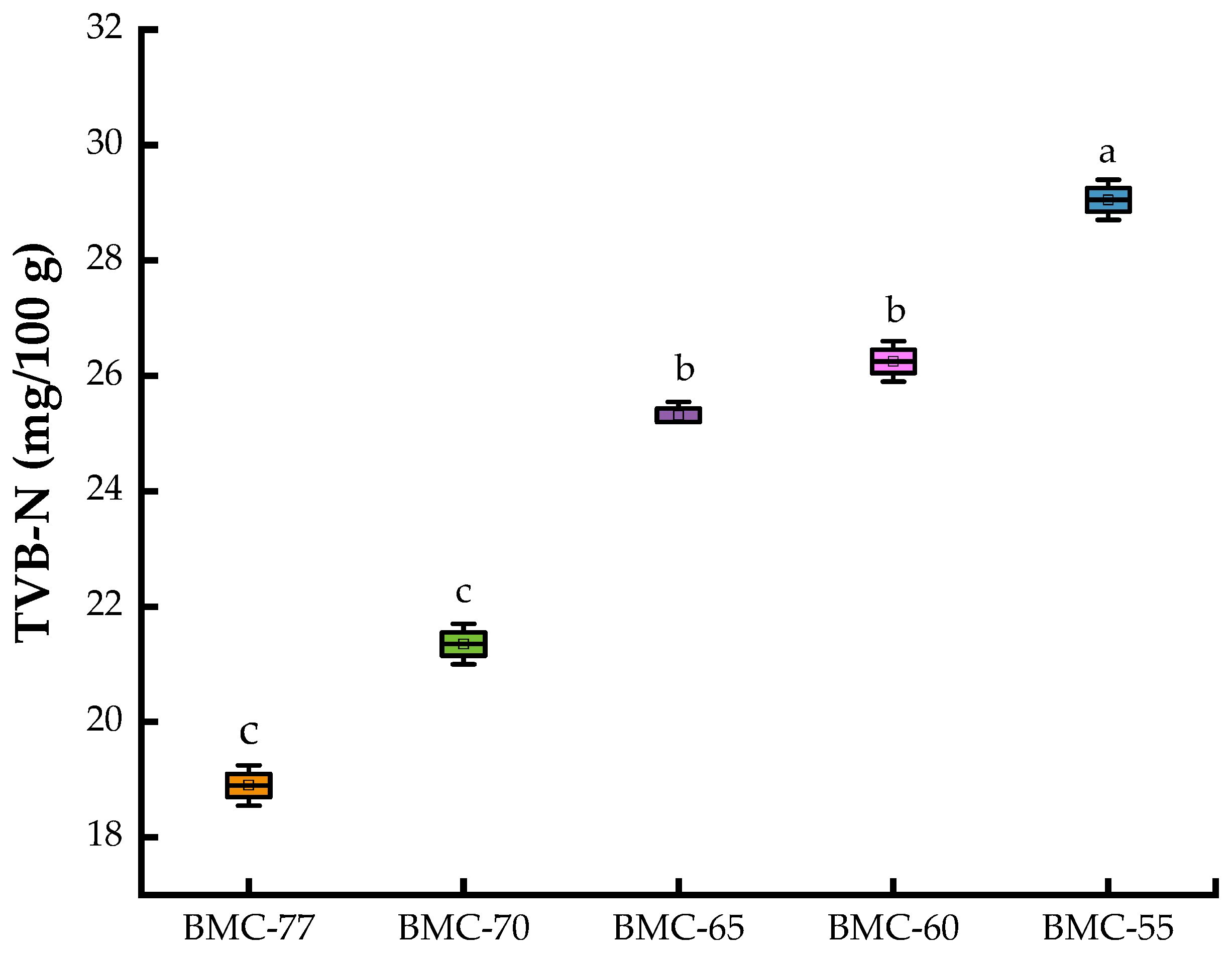
3.4. Changes in TVB-N Content of Large Yellow Croaker Fillets with Different Water Contents After Roasting
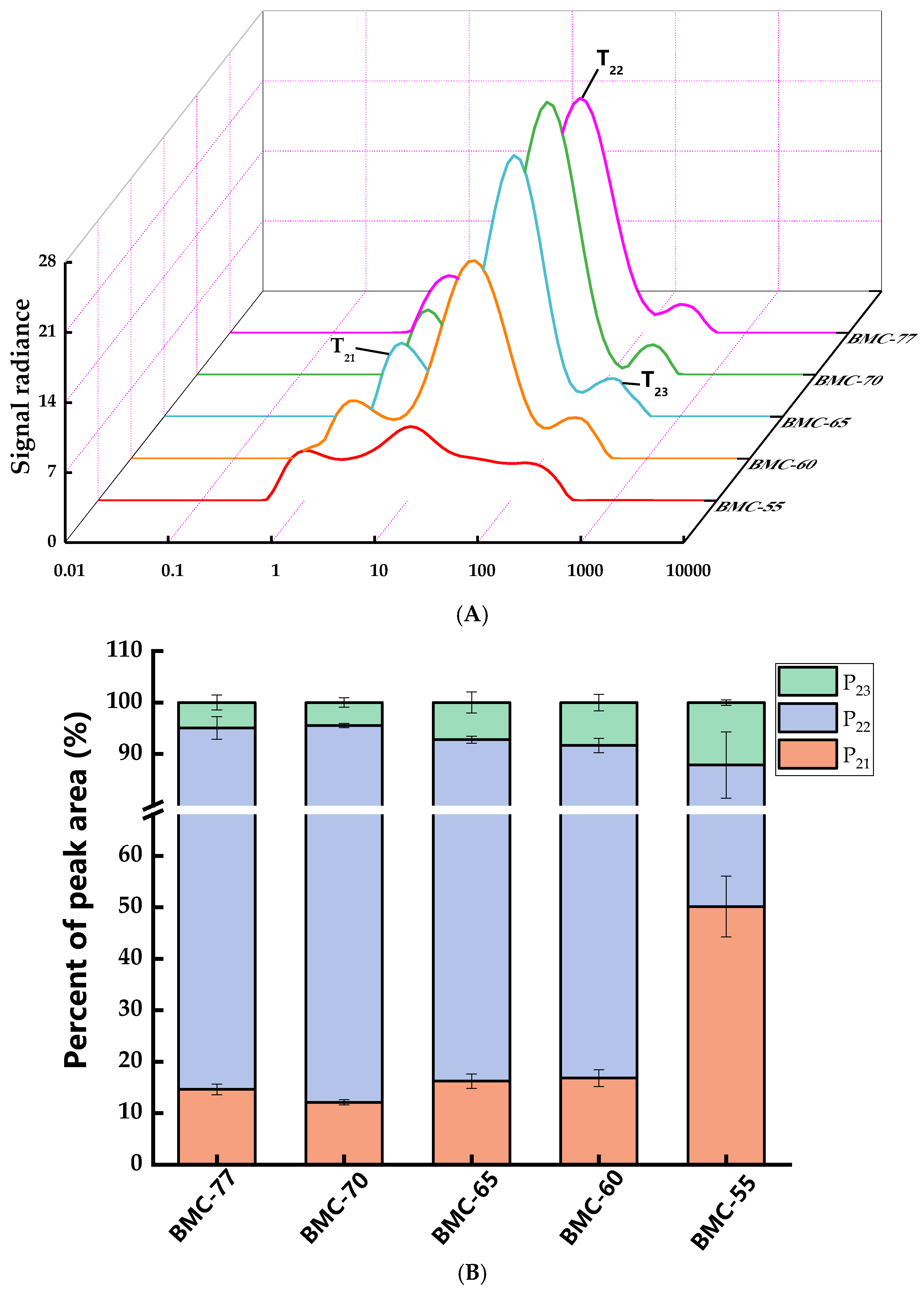
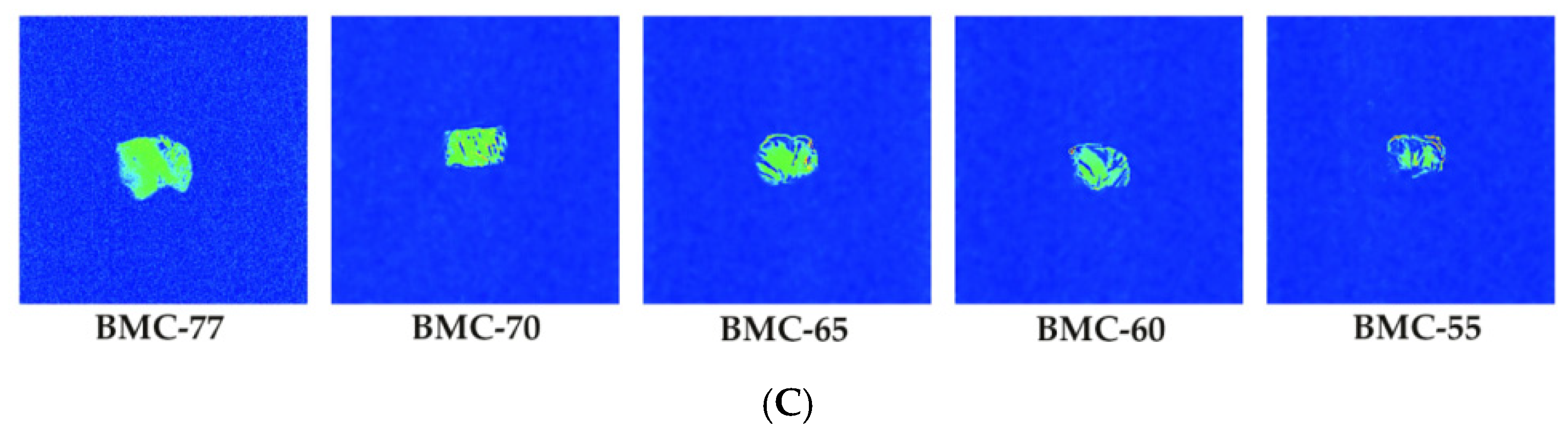
3.5. Influence of Different Water Content on Water Migration Pattern in Large Yellow Croaker Fillet After Roasting
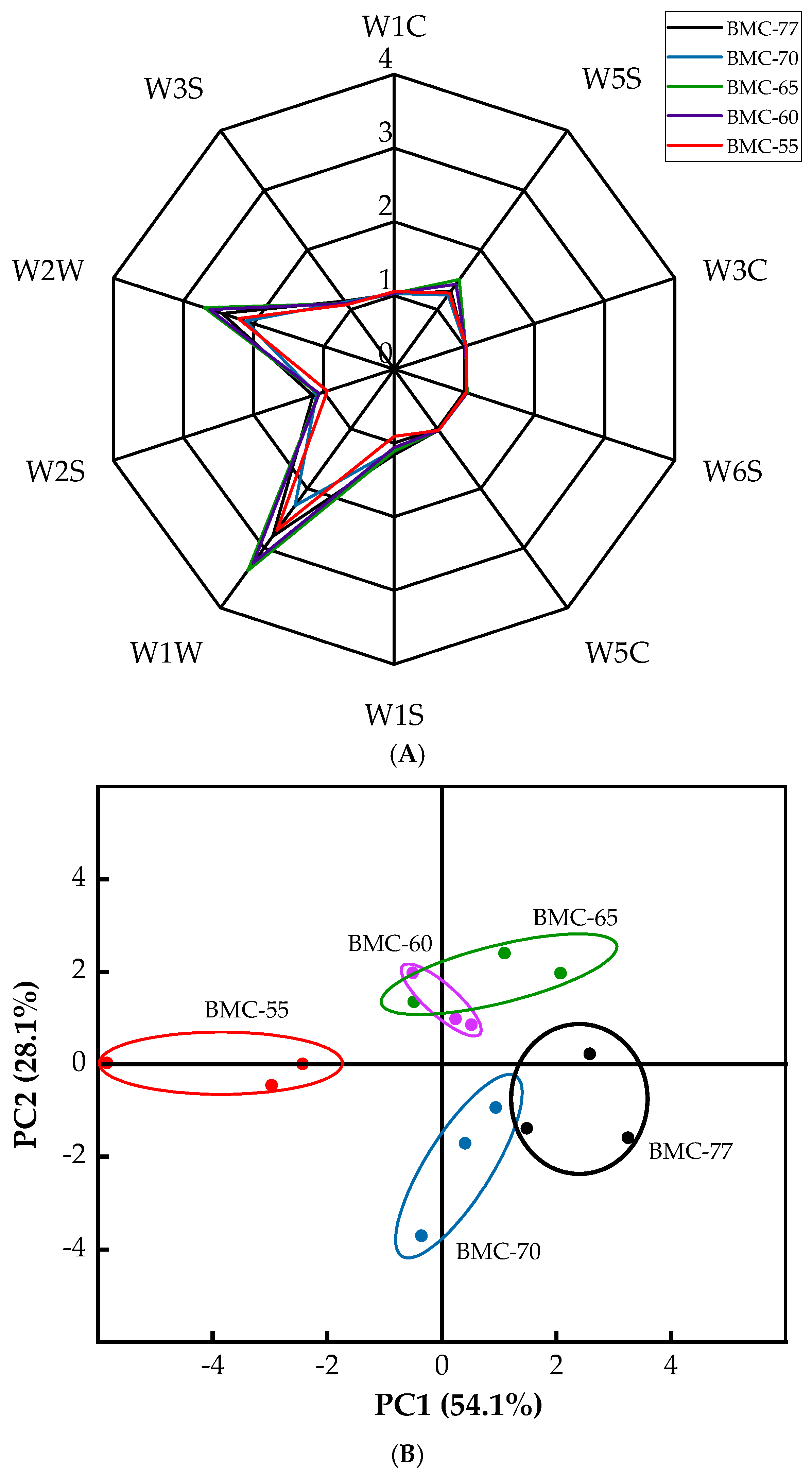
3.6. Electronic Nose Analysis Results for Large Yellow Croaker Fillets with Different Water Contents After Roasting
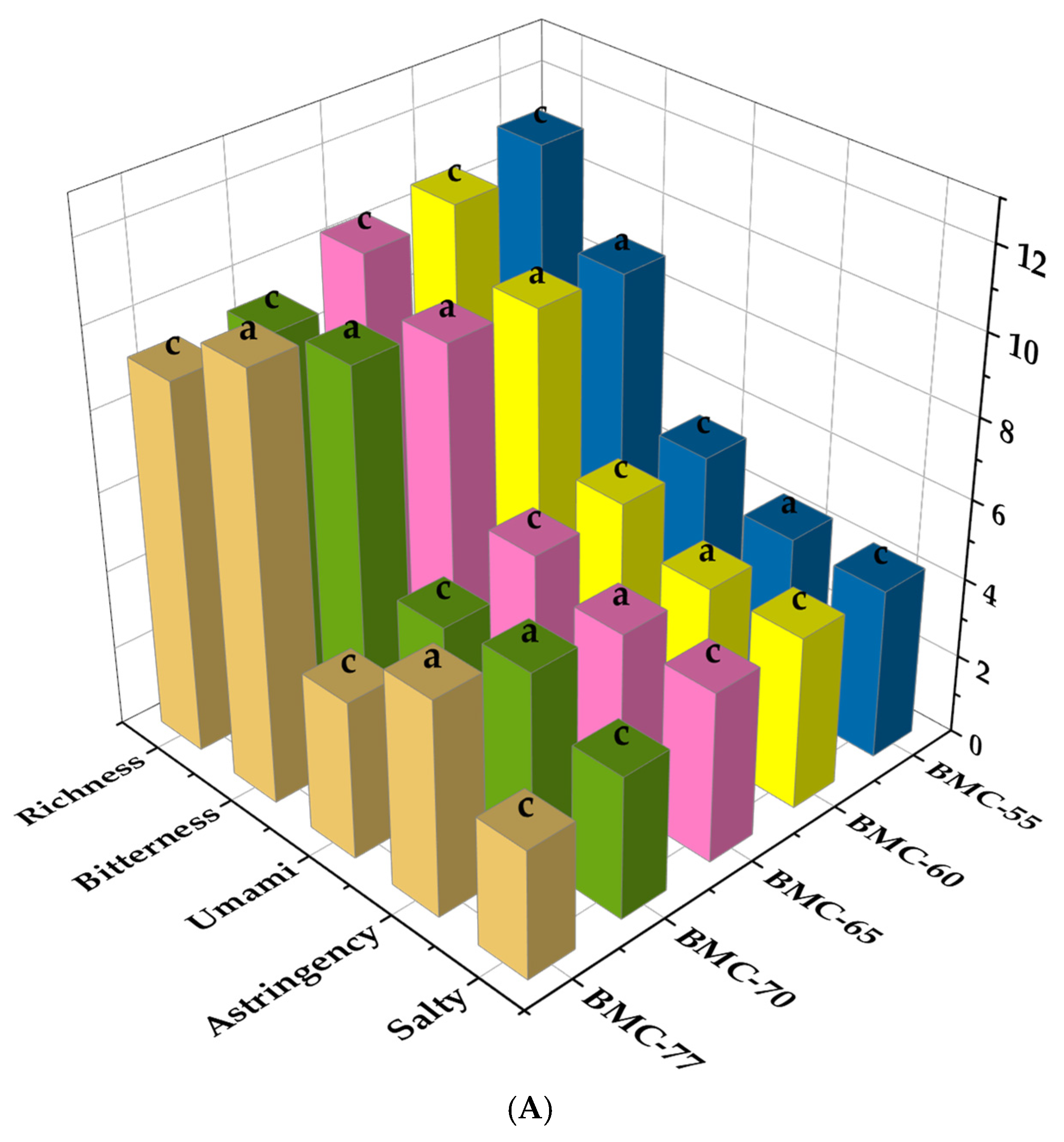
3.7. The Effect of Different Water Content on Electronic Tongue Analysis of Large Yellow Croaker Fillet After Roasting
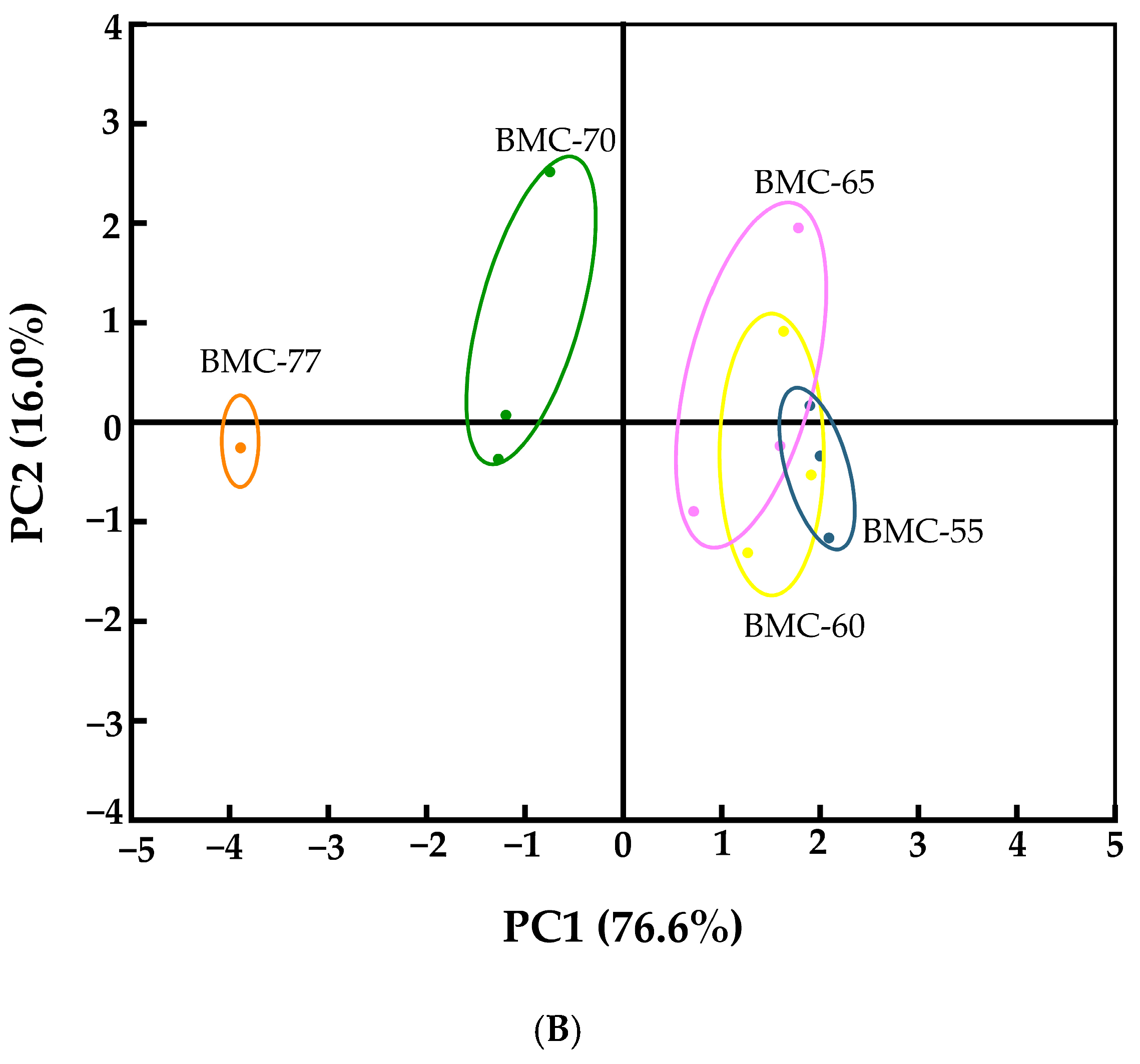
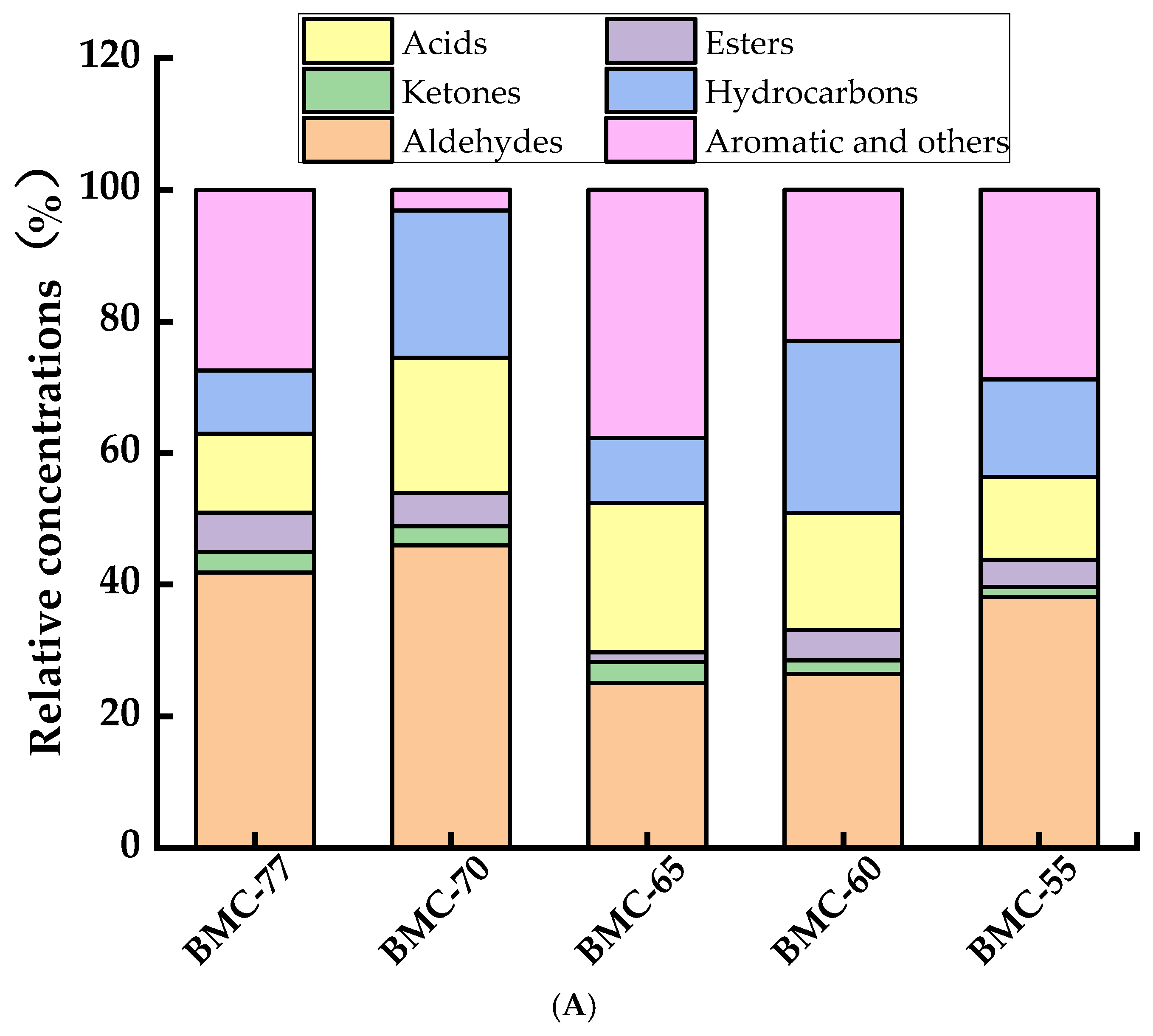
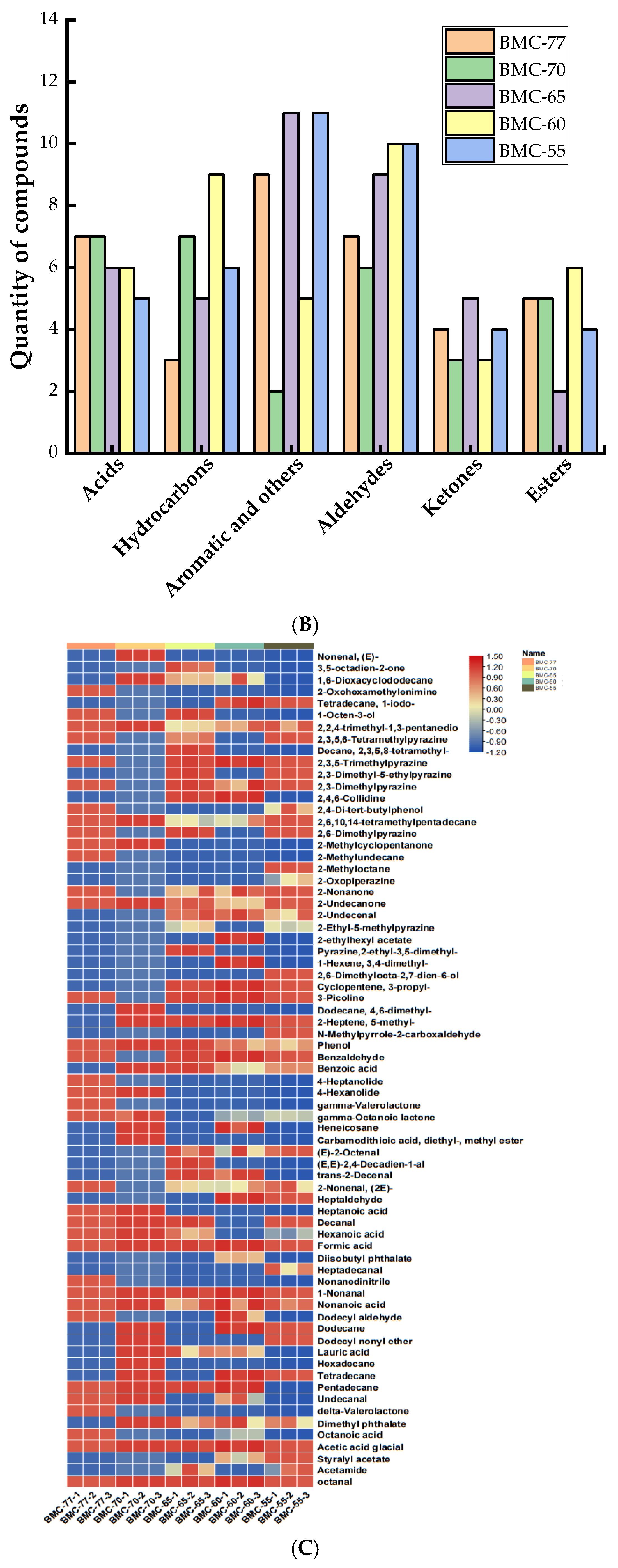
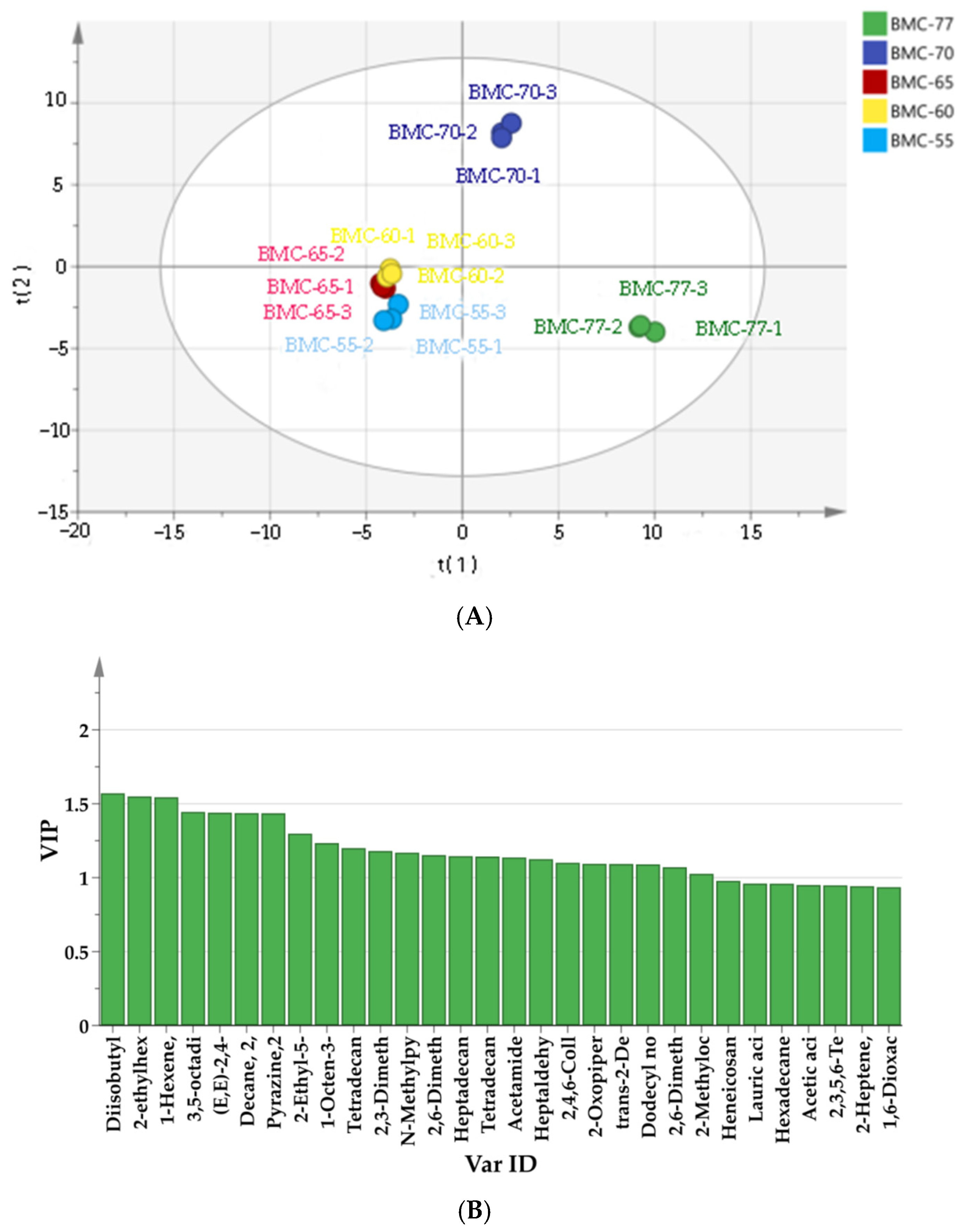
3.8. The Effect of Different Water Contents on Volatile Components of Large Yellow Croaker Fillets After Roasting
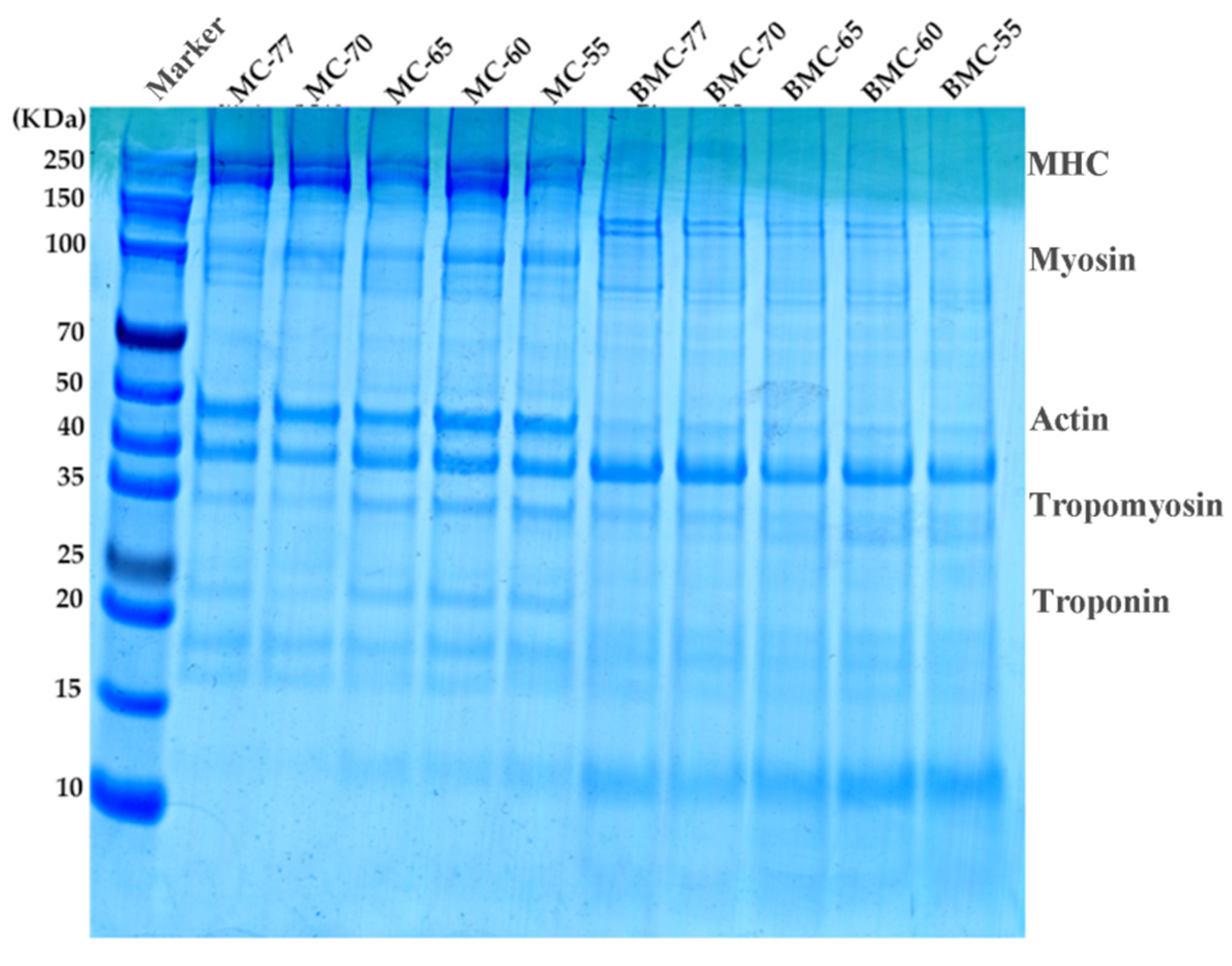
3.9. Effect of Water Content on Myofibrillar Proteins in Large Yellow Croaker Fillets After Roasting
3.10. Effect of Water Content on Sensory Evaluation of Roasted Large Yellow Croaker Fillets
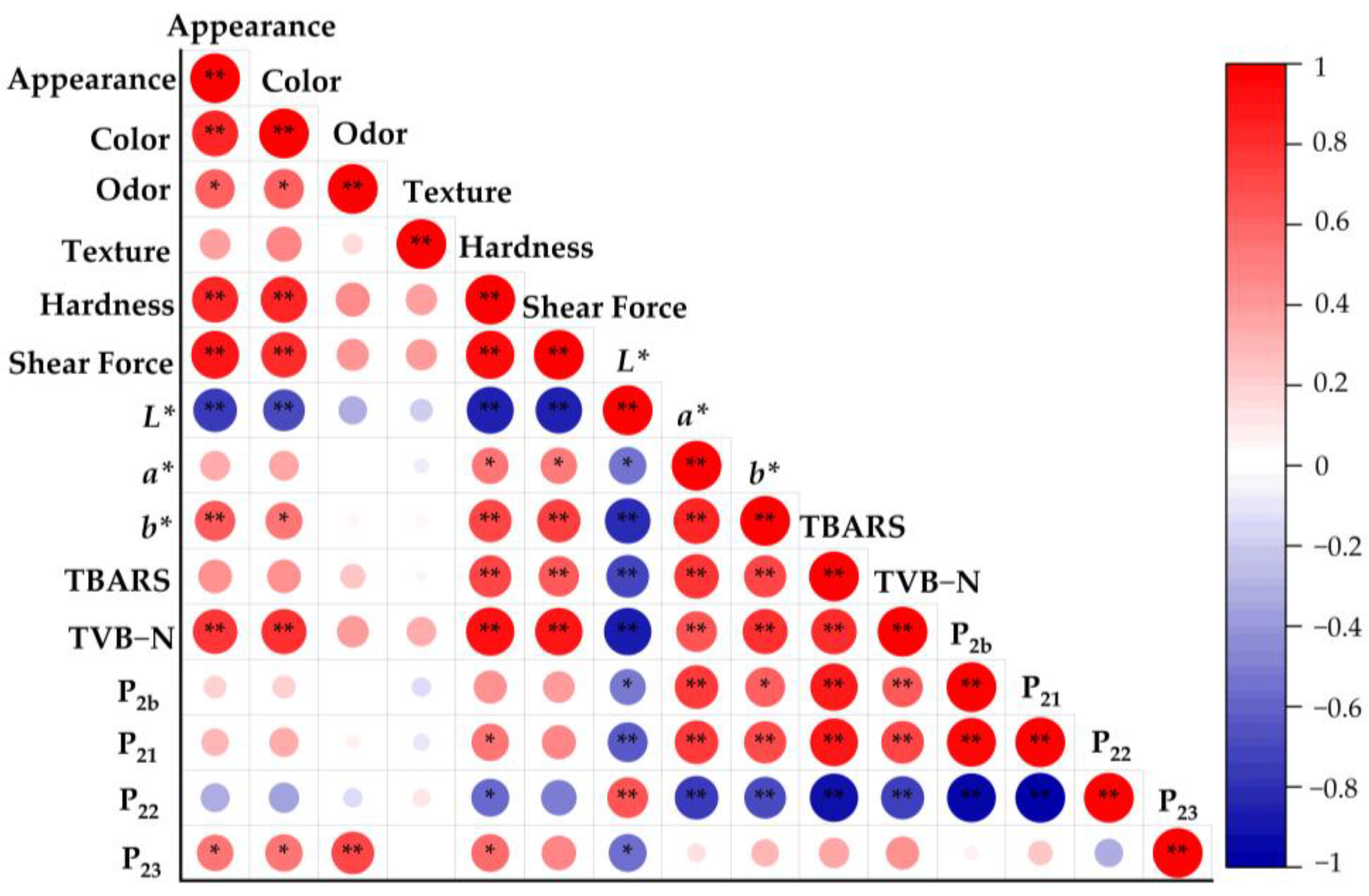
3.11. Correlation Analysis of Quality Indicators in Roasted Large Yellow Croaker Fillets with Different Water Content
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, W.; Li, L.; Xie, W.; Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Huang, W. Exploration of the current situation and development methods of China’s large yellow croaker aquaculture industry. China Fish. 2024, 11, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Yu, H.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. Quality enhancement of large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) during frozen (–18 °C) storage by spiral freezing. Cyta-J. Food 2021, 19, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Shi, L.; Ren, Z.; Hao, G.; Weng, W. Effect of transglutaminase concentration in curing solution on the physicochemical properties of salted large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Food Chem. X 2022, 14, 100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasul, M.G.; Yuan, C.; Yu, K.; Takaki, K.; Shah, A. Factors influencing the nutritional composition, quality and safety of dried fishery products. Food Res. 2022, 6, 444–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.P.; Duarah, P.; Purkait, M.K. Fundamentals of food roasting process. In High-Temperature Processing of Food Products; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 103–130. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Ma, J.; Pan, T.; Suleman, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D. Effects of roasting by charcoal, electric, microwave and superheated steam methods on (non)volatile compounds in oyster cuts of roasted lamb. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duppeti, H.; Manjabhatta, S.N.; Martin, A.; Kempaiah, B.B. Effects of different processing methods on the biochemical composition, color and non-volatile taste active compounds of whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Food Chem. Adv. 2022, 1, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.Z.; Che, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.H.; Qin, L. Improvement of flavor and inhibition of accompanying harmful substances in roasted fish by different tea pre-marinades. Food Chem. 2025, 479, 143781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; Su, L. Effects of different roasting methods on the quality of roasted large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Foods 2024, 13, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.S.; Oh, B.J.; Lee, J.H.; Yoon, Y.S.; Lee, H.I. Effects of various drying methods on physicochemical characteristics and textural features of yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis). Foods 2020, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Tang, M.; Dai, H.; Feng, X.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y. Dominating roles of protein conformation and water migration in fish muscle quality: The effect of freshness and heating process. Food Chem. 2022, 388, 132881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraha, B.; Admassu, H.; Mahmud, A.; Tsighe, N.; Shui, X.W.; Fang, Y. Effect of processing methods on nutritional and physico-chemical composition of fish: A review. MOJ Food Process. Technol. 2018, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, H.; Ma, G.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Pei, H.; Li, X.; Gao, L. Insights into flavor and key influencing factors of Maillard reaction products: A recent update. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 973677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, W.; Dong, S.; Jin, W.; Yang, Y.; Han, K.; Zha, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, M. Effect of different cooking conditions on the profiles of Maillard reaction products and nutrient composition of hairtail (Thichiurus lepturus) fillets. Food Res. Int. 2018, 103, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guan, Z.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ling, C. Effect of pretreatment on water migration and volatile components of heat pump dried tilapia fillets. Dry Technol. 2019, 38, 1828–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xia, X.; Yu, G. The Effect of frying conditions on the physical and chemical quality attributes of clearhead icefish (Protosalanx hyalocranius) during deep frying and air frying. Foods 2025, 14, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwin, C.; Labuza, T. Role of moisture in Maillard browning reaction rate in intermediate moisture foods: Comparing solvent phase and matrix properties. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copson, D.A.; Neumann, B.R.; Brody, A.L. High-frequency cooking, browning methods in microwave cooking. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1955, 3, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.; Peng, L.; Zhang, P. Understanding changes in moisture state, wheat gluten structure and oil penetration of breaded fish nuggets during frying. LWT 2024, 198, 115967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, F.; Cheng, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, D. Effects of combined roasting and steam cooking on NaCl reduction and quality changes in marinated salmon flesh as compared with roasting and water bath cooking. LWT 2023, 179, 114623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, H.R.; Sepulveda, C.A.; Garmyn, A.J.; Legako, J.F.; Miller, M.F. Effects of dry heat cooking method and quality grade on the composition and objective tenderness and juiciness of beef strip loin steaks. Meat Muscle Biol. 2019, 3, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.d.O.; Ribeiro, A.L.S.; Lima, K.M.d.O.; dos Santos, I.R.P.; de Almeida, B.S.; de Matos, M.F.R.; Krumreich, F.D.; Andrade, L.L.; Ruggiero, W.F.; Matos, L.C.P. Critical factors associated with Maillard reaction products in different meats: An integrative review. Food Control 2024, 168, 110960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwaniyi, O.O.; Dosumu, O.O.; Awolola, G.V. Effect of local processing methods (boiling, frying and roasting) on the amino acid composition of four marine fishes commonly consumed in nigeria. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Xie, J. Quality changes of Larimichthys crocea pretreated by ultrasonic-assisted immersion under cold storage at 4 °C. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 98, 106484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Pan, N.; Liu, S.; Su, Y.; Xiao, M.; Shi, W.; Liu, Z. The effects of five different drying methods on the quality of semi-dried takifugu obscurus fil-lets. LWT 2022, 161, 113340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Gao, P.; Yang, F.; Yu, D.; Xia, W.; Yu, D. Effects of different thermal methods and degrees on the flavor of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) fillets: Fatty acids, volatile flavor and taste compounds. Food Chem. 2024, 461, 140887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Su, Y.; Pan, N.; Liao, D.; Qiao, K.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z. Dynamic changes in the microbial composition and spoilage characteristics of refrigerated large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) during storage. Foods 2023, 12, 3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Wang, B.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Huang, X.; Qin, L. Integrated volatolomics and lipidomics analysis reveal the characteristic flavor formation mechanism in steamed large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Xu, M.; Su, Y.; Qiao, K.; Chen, X.; Chen, B.; Zhong, H.; et al. The effects of four different thawing methods on quality indicators of Amphioctopus neglectus. Foods 2024, 13, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. Analysis of key volatile compounds and quality properties of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) fillets during cold storage: Based on thermal desorption coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (TD-GC-MS). LWT 2023, 184, 115051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Ju, M.; Du, Y.; Wang, M.; Han, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, B.; Ritzoulis, C.; Pan, W. Changes in properties of nano protein particles (NPP) of fish muscle stored at 4 °C and its application in food quality assessment. LWT 2022, 155, 112968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, W.Y.; Ming, L.R.; Lei, W.S. Water distribution and key aroma compounds in the process of beef roasting. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 978622. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Jiang, P.; Feng, D.; Jin, M.; Qi, H. Characterization of flavor substances in cooking and seasoned cooking brown seaweeds by GC-IMS and E-nose. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, X.; Hu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, L. Research on flavor characteristics of beef cooked in tomato sour soup by gas chromatog-raphy-ion mobility spectrometry and electronic nose. LWT 2023, 179, 114646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Xu, H.; Jiang, X.; Sun, T.; Luo, Y.; Shi, W. Evaluation of aroma characteristics in grass carp mince as affected by different washing pro-cesses using an E-nose, HS-SPME-GC-MS, HS-GC-IMS, and sensory analysis. Food Res. Int. 2022, 158, 111584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Li, C.; Huang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Xiang, H.; Wang, D.; Feng, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, S. Identification of key physicochemical properties and volatile flavor compounds for the sensory formation of roasted tilapia. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiryousefi, M.R.; Mohebbi, M.; Khodaiyan, F. Applying an intelligent model and sensitivity analysis to inspect mass transfer kinetics, shrinkage and crust color changes of deep-fat fried ostrich meat cubes. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fang, C.; Luo, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liu, S. Effects of konjac oligo-glucomannan on the physicochemical properties of frozen surimi from red gurnard (Aspitrigla cuculus). Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-Y.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Yu, M.-M.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.-Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.-L.; Zhou, D.-Y. Effect of oxidation and Maillard reaction on color deterioration of ready-to-eat shrimps during storage. LWT 2020, 131, 109696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Cittadini, A.; Munekata, P.E.; Domínguez, R. Physicochemical properties of foal meat as affected by cooking methods. Meat Sci. 2015, 108, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, X.; Ruiz-Ramírez, J.; Arnau, J.; Gou, P. Texture parameters of dry-cured ham m. biceps femoris samples dried at different levels as a function of water activity and water content. Meat Sci. 2004, 69, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. Revealing the evolution of lipid extracts from tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) during cold storage: Based on lipid metabolism analysis via GC-Q-MS and characterization of lipid oxidation. LWT 2024, 201, 116268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, T.T.; Huang, Y.N.; Ren, S.T.; Jin, D.L.; Fu, J.J.; Guo, J.Y.; Chen, Y.W. Inhibitory effects of ultrasonic and rosmarinic acid on lipid oxidation and lipoxy-genase in large yellow croaker during cold storage. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 92, 106229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, P.; Tian, H.; Zhan, P. Advances in the formation and control methods of undesirable flavors in fish. Foods 2022, 11, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Liu, Q.; Ni, X.; Chen, C.; Deng, X.; Fang, Y.; Wang, X.; Shen, Q.; Yu, R. Lipidomics reveals the effect of hot-air drying on the quality characteristics and lipid oxidation of Tai Lake whitebait (Neosalanx taihuensis Chen). LWT 2024, 197, 115942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Hu, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, X. Coating effects of tea polyphenol and rosemary extract combined with chitosan on the storage quality of large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Food Control 2012, 25, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, X.; Liu, S.; Hong, P.; Zhou, C.; Zhong, S.; Zhu, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, K. Changes in protein and volatile flavor compounds of low-salt wet-marinated fermented Golden Pomfret during processing. Food Chem. 2024, 456, 140029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Huang, F.; Li, X.; Han, D.; Zhao, L.; Liang, H.; Rui, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C. Water status evolution of pork blocks at different cooking procedures: A two-dimensional LF-NMR T1–T2 relaxation study. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Chen, L.; Wang, C. Improvement of water retention quality of Beijing roast duck: Analysis from protein structure perspective. LWT 2023, 193, 115644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, K.; Jayathilakan, K.; Sajeevkumar, V.A. Chemistry of animal tissues. In Advances in Food Chemistry: Food Components, Processing and Preservation; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 385–437. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, X.; Li, X.; Deng, S.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, G.; Xu, Y.; Brennan, C.; Benjakul, S.; Ma, L. How lipids, as important endogenous nutrient components, affect the quality of aquatic products: An overview of lipid peroxidation and the interaction with proteins. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2025, 24, e70096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kang, D.; Zhang, W.; Lorenzo, J.M. Recent advantage of interactions of protein-flavor in foods: Perspective of theoretical models, protein properties and extrinsic factors. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shi, R.; Liu, W.; Xu, Z.; Mi, S.; Sang, Y.; Yu, W.; Wang, X. Effect of different thermal processing methods on sensory, nutritional, physicochemical and structural properties of Penaeus vannamei. Food Chem. 2023, 438, 138003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Zhao, Y. A feature selection strategy of E-nose data based on PCA coupled with Wilks Λ-statistic for discrimination of vinegar samples. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 2406–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantono, K.; Hamid, N.; Chadha, D.; Ma, Q.; Oey, I.; Farouk, M.M. Pulsed electric field (PEF) processing of chilled and frozen-thawed lamb meat cuts: Relationships between sensory characteristics and chemical composition of meat. Foods 2021, 10, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yu, Y.; Saleh, A.S.; Yang, X.; Ma, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Wang, Z. Characterization of aroma profiles of chinese four most famous traditional red-cooked chickens using GC–MS, GC-IMS, and E-nose. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173 Pt 1, 113335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, F.; Tang, Y.; Yu, B.; Chen, B.; Lu, L.; Yuan, L.; Wu, Z.; Chen, H. Monitoring changes in the volatile compounds of tea made from summer tea leaves by GC-IMS and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Foods 2022, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Abad, A. Lipid-derived flavours and off-flavours in food. In Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 182–192. ISBN 978-0-12-814045-1. [Google Scholar]
- Nancy, F.; Mathieu, D.; Huertas, P.J.F. Detection of furan and five alkylfurans, including 2-Pentylfuran, in various food matrices. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1622, 461119. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Liu, T.; Yang, C.; Yang, H.; Liu, D. Relationship between phospholipid molecules species and volatile compounds in grilled lambs during the heating process. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Cheng, S.; Sun, X.; Bai, Y.; Yu, X.; Zeng, X.; Hu, S.; Zhang, M.; Yue, J.; Xu, X.; et al. Combination of contact ultrasound and infrared radiation for improving the quality and flavor of air-dried beef during hot air drying. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 110, 107047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomac, A.; Cova, M.C.; Narvaiz, P.; Yeannes, M.I. Texture, color, lipid oxidation and sensory acceptability of gamma-irradiated marinated anchovy fillets. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2015, 106, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Liang, C.; Fang, F.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z. Impact of chilling rate on the evolution of volatile and non-volatile compounds in raw lamb meat during refrigeration. Foods 2021, 10, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, Q.; Liu, S.; Hong, P.; Zhou, C.; Zhong, S. Characterization of the effect of different cooking methods on volatile compounds in fish cakes using a combination of GC–MS and GC-IMS. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, D.; Zhong, X.; Pei, Z.; Tian, Y.; Xiang, D.; Cao, J.; Shen, X.; Li, C. Quality and protein degradation of golden pompano (Trachinotus blochii) fillets during four drying methods. LWT 2020, 130, 109638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Tan, Y.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y. Uncovering quality changes of salted bighead carp fillets during frozen storage: The potential role of time-dependent protein denaturation and oxidation. Food Chem. 2023, 414, 135714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, B.L.; da Costa, M.P.; da Silva Frasão, B.; da Silva, F.A.; Mársico, E.T.; da Silveira Alvares, T.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Instrumental texture parameters as freshness indicators in five farmed brazilian freshwater fish species. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 3589–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Grading Criteria |
|---|---|
| Appearance (10%) | The appearance is loose and incomplete |
| The appearance is slightly loose but complete, and the structure is tighter | |
| The appearance is complete, and the structure is tight | |
| Color (30%) | The fish is white in color, without the yellow color of roasting or black or dark brown in color; charred |
| The fish are pale yellow or dark brown in color | |
| The fish pieces are yellow and shiny | |
| Odor (30%) | The odor of fish is not obvious, and there is an unpleasant fishy odor or other peculiar odor |
| The fish has a strong flavor and no irritating odor or other peculiar odors | |
| The fish has a strong aroma and no other peculiar odor | |
| Texture (30%) | The meat is soft, chewy, less elastic, or hard |
| The meat is soft and slightly chewy | |
| Moderate hardness and chewiness; soft and not dry |
| L* | a* | b* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMC-77 | 69.43 ± 2.69 a | −2.97 ± 0.38 bc | 12.10 ± 1.60 c |
| BMC-70 | 69.18 ± 2.80 a | −3.65 ± 0.76 c | 9.27 ± 1.98 c |
| BMC-65 | 63.24 ± 1.35 b | −2.63 ± 0.42 bc | 16.29 ± 1.65 b |
| BMC-60 | 64.87 ± 1.21 b | −1.90 ± 1.29 b | 17.47 ± 3.38 b |
| BMC-55 | 64.87 ± 1.21 b | −0.40 ± 0.93 a | 22.59 ± 3.15 a |
| Grading Items | Appearance (10%) | Color (30%) | Odor (30%) | Texture (30%) | Total Score (9 Points) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMC-77 | 5.50 ± 1.04 c | 3.50 ± 0.54 b | 4.60 ± 1.11 b | 3.50 ± 0.81 b | 4.04 ± 0.46 c |
| BMC-70 | 6.00 ± 1.27 bc | 4.10 ± 0.66 b | 5.20 ± 1.53 ab | 6.00 ± 1.25 a | 5.18 ± 0.63 b |
| BMC-65 | 7.40 ± 1.11 ab | 6.80 ± 0.41 a | 7.20 ± 1.26 a | 5.20 ± 1.57 ab | 6.51 ± 0.58 a |
| BMC-60 | 8.20 ± 0.75 a | 7.80 ± 0.61 a | 6.40 ± 1.45 ab | 6.00 ± 1.72 a | 6.75 ± 0.85 a |
| BMC-55 | 7.90 ± 0.92 a | 6.70 ± 0.98 a | 5.60 ± 2.05 ab | 5.00 ± 1.71 ab | 5.90 ± 0.80 ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.; Liu, S.; Wen, P.; Lin, X.; Chen, X.; Su, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z. Effects of Different Water Contents on the Quality Characteristics of Roasted Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Fillets. Foods 2025, 14, 1638. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091638
Huang S, Liu S, Wen P, Lin X, Chen X, Su Y, Xie Y, Zheng H, Chen Y, Liu Z. Effects of Different Water Contents on the Quality Characteristics of Roasted Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Fillets. Foods. 2025; 14(9):1638. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091638
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Shuting, Shuji Liu, Ping Wen, Xiangyang Lin, Xiaoting Chen, Yongchang Su, Yuping Xie, Huawei Zheng, Yihui Chen, and Zhiyu Liu. 2025. "Effects of Different Water Contents on the Quality Characteristics of Roasted Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Fillets" Foods 14, no. 9: 1638. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091638
APA StyleHuang, S., Liu, S., Wen, P., Lin, X., Chen, X., Su, Y., Xie, Y., Zheng, H., Chen, Y., & Liu, Z. (2025). Effects of Different Water Contents on the Quality Characteristics of Roasted Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Fillets. Foods, 14(9), 1638. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091638







