Enhancement of Emulsifying Activity in Soy-Protein-Based Products by Partial Substitution with Zein Hydrolysates and Transglutaminase Addition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of ZH
2.2.2. Preparation of the SPI/ZH Conjugates from SPI and ZH with TGase Addition
2.2.3. SDS-PAGE
2.2.4. Measurement of Free Amino Group Contents
2.2.5. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) Analysis
2.2.6. Solubility
2.2.7. Analysis of Emulsifying Properties
2.2.8. Droplet Size Distribution and Zeta Potential of the Prepared Emulsions
2.2.9. Measurement of Surface Hydrophobicity
2.2.10. Apparent Viscosity of SPI and Its Modified Products Dispersions
2.2.11. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
3. Results and Discussion
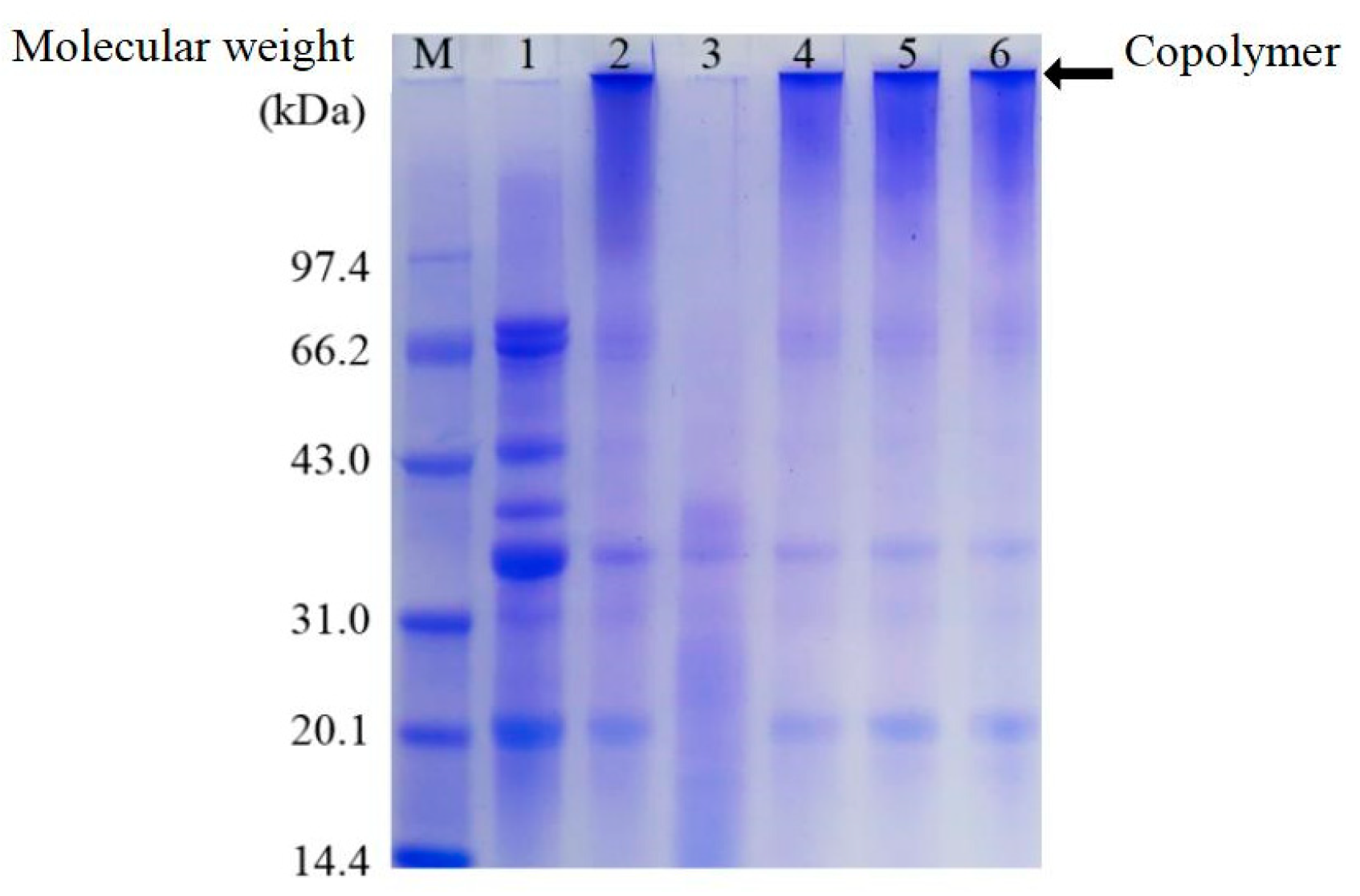
3.1. Analysis of Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
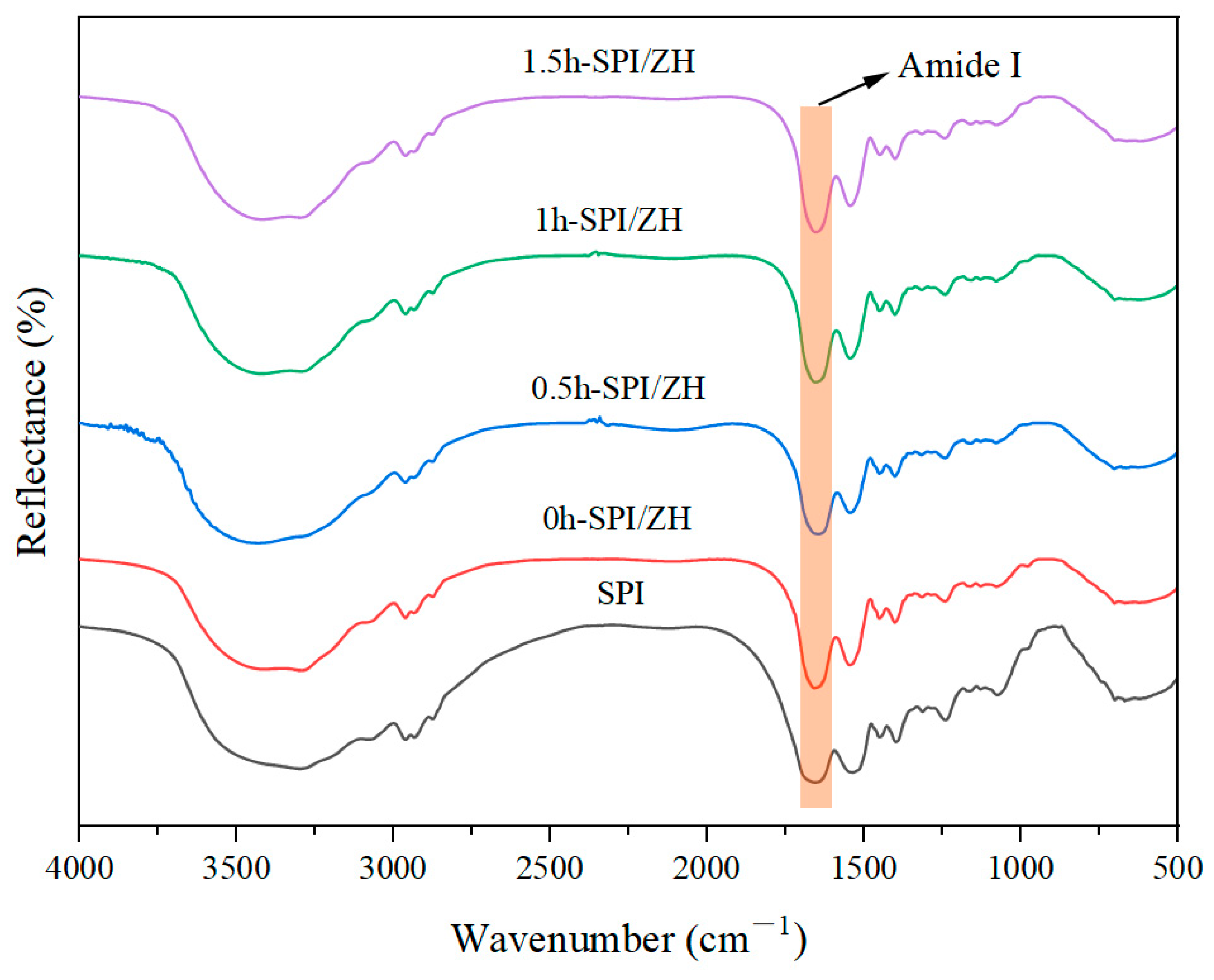
3.2. FT-IR Analysis
3.3. Alterations in Solubility, Emulsion Droplet Size, and Zeta Potential
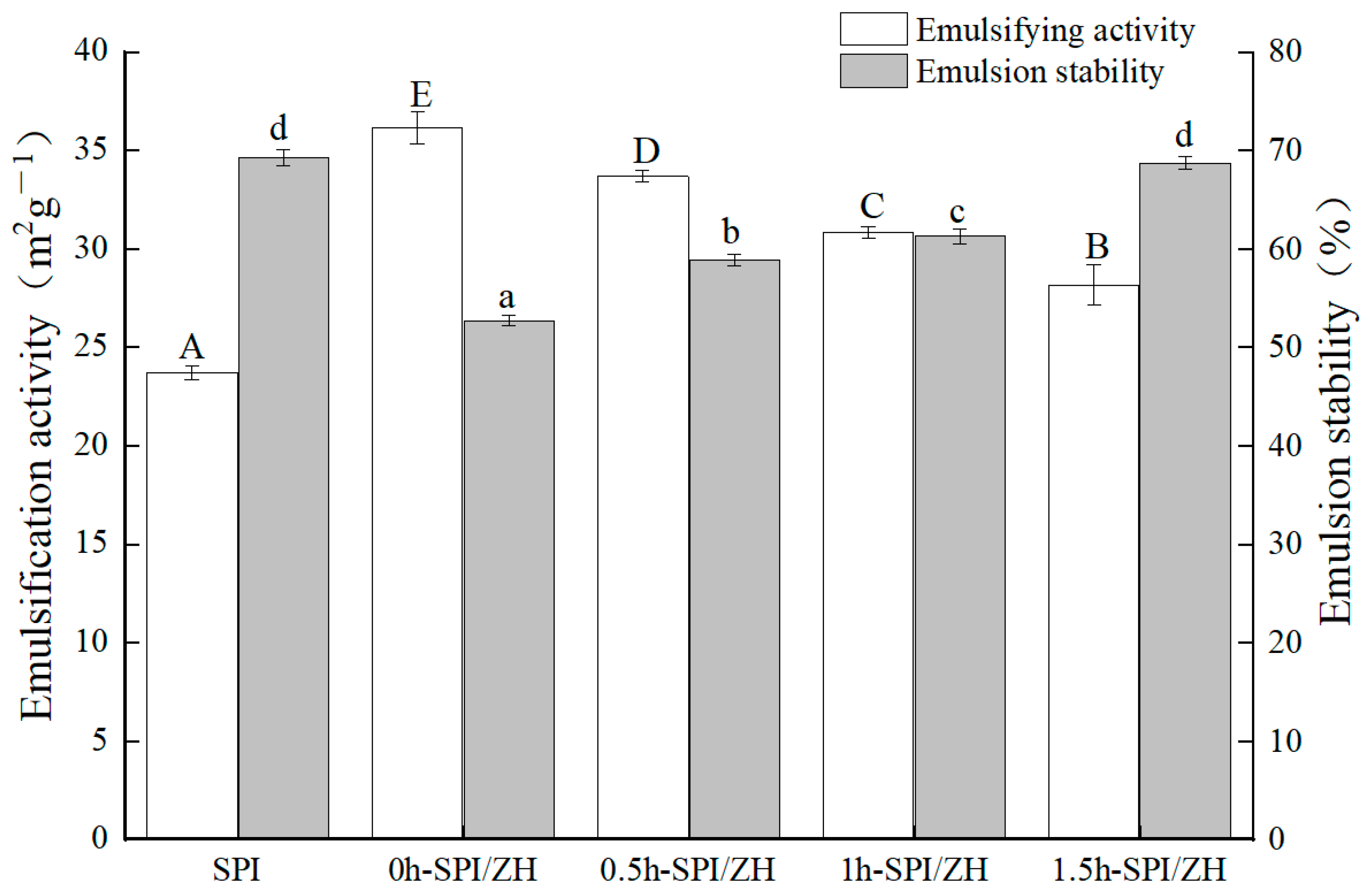
3.4. Emulsification
3.5. Surface Hydrophobicity
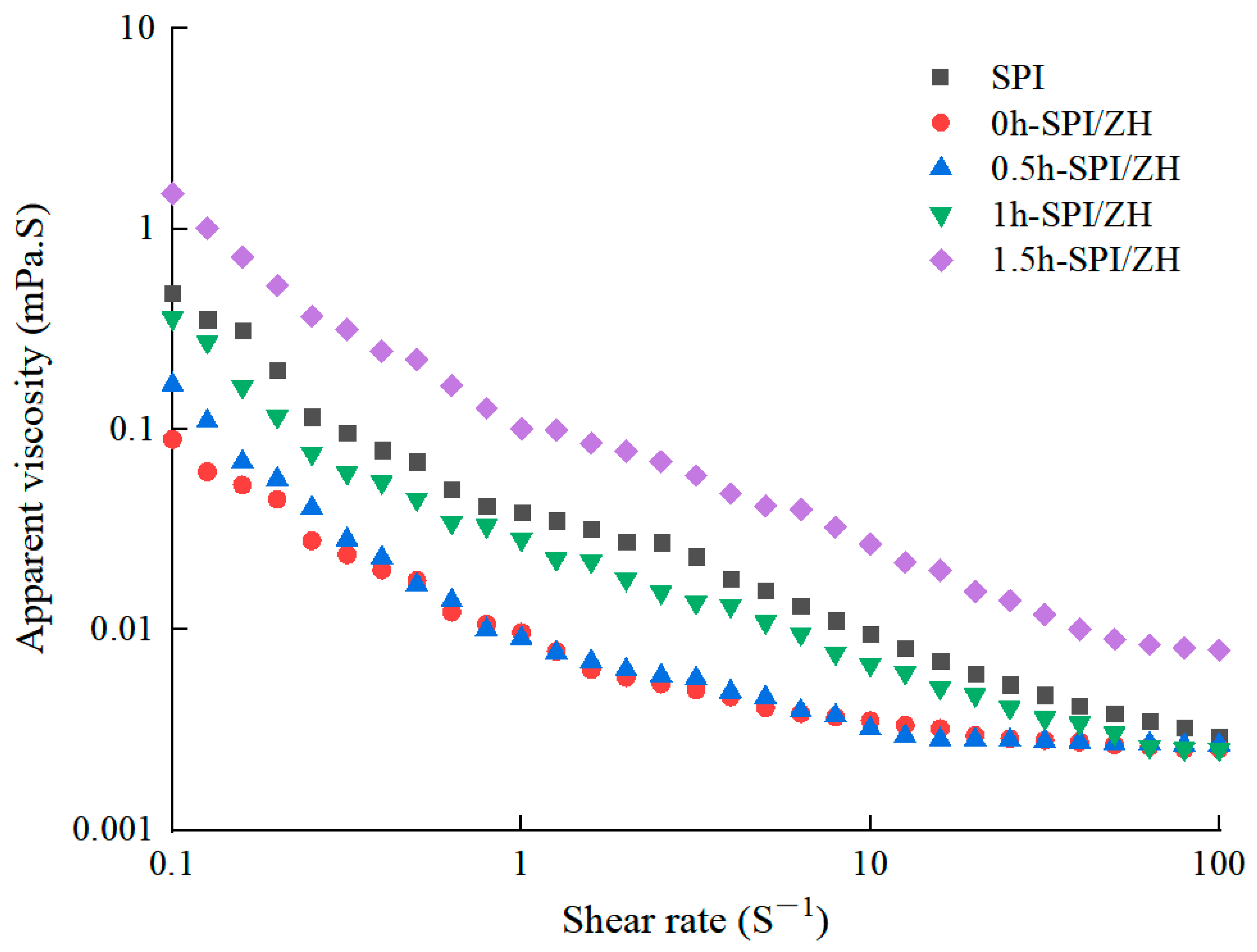
3.6. Apparent Viscosity of Protein Dispersions
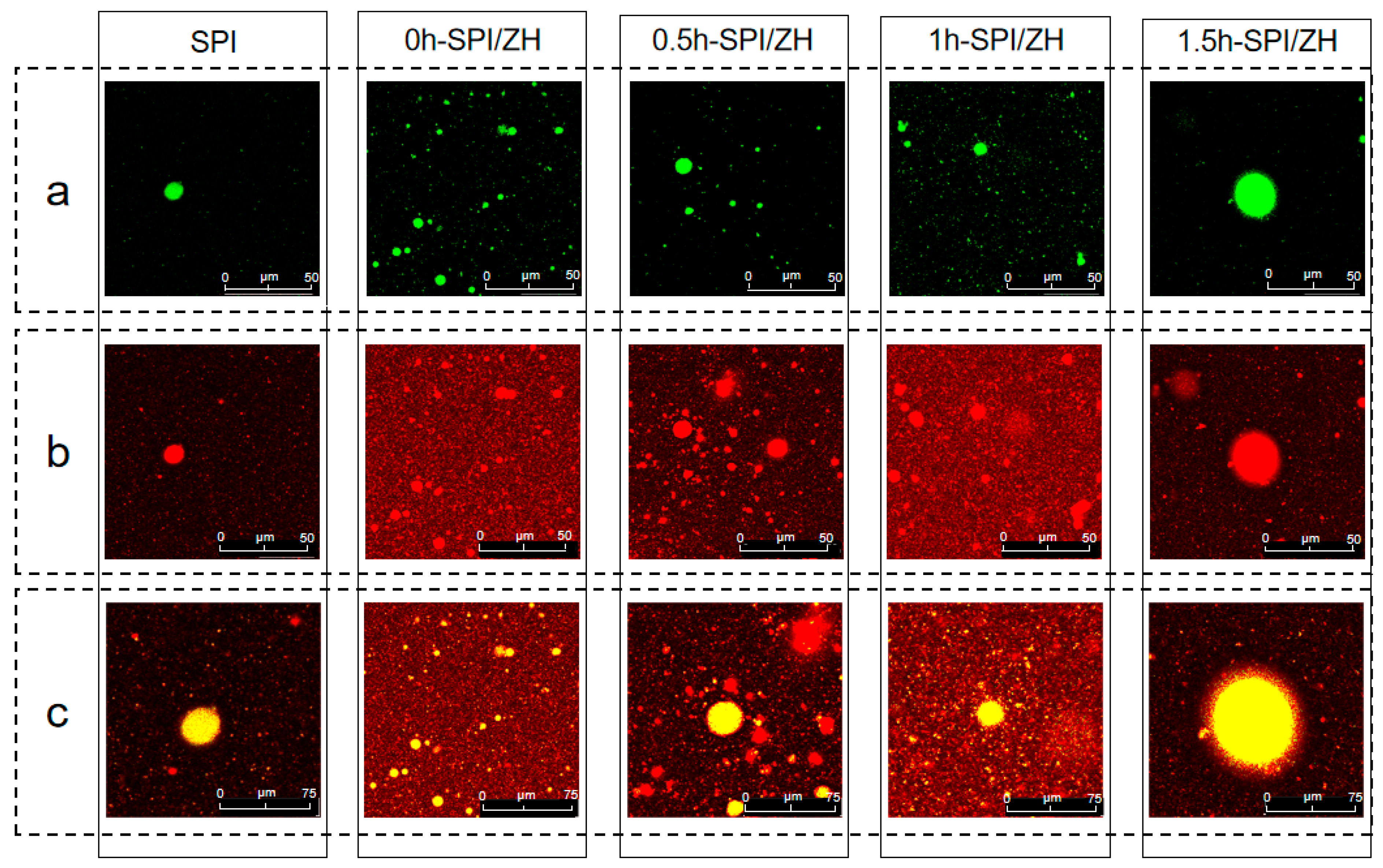
3.7. Adsorbed Proteins
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Imura, T.; Nakayama, M.; Taira, T.; Sakai, H.; Abe, M.; Kitamoto, D. Interfacial and emulsifying properties of soybean peptides with different degrees of hydrolysis. J. Oleo Sci. 2015, 64, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Han, X.; Li, Y.; Gong, J.Y.; Xiao, J.N.; Aziz, T.; Liu, S.W.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; He, G.H.; et al. Preparation and investigation of the processing characteristics of transglutaminase cross-linked soy protein isolate–whey protein polymer. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 15, 3165–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Cheryan, M. Zein: The industrial protein from corn. Ind. Crops Prod. 2001, 13, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.Y.; Zhao, J.R.; Jiang, L.Z.; Sui, X.N. Oil-water interfacial behavior of zein-soy protein composite nanoparticles in high internal phase Pickering emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 149, 109659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glusac, J.; Fishman, A. Enzymatic and chemical modification of zein for food application. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Q. Effect of acid and base treatments on structural, Theological, and antioxidant properties of oe-zein. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Liu, X.L.; Zheng, X.Q.; Qu, Y.; Shi, Y.G. Preparation of corn glycopeptides and evaluation of their antagonistic effects on alcohol-induced liver injury in rats. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 66, 103776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.T.; Miao, Y.; Fu, L.; Zhong, C. Stirring greatly improves transglutaminase-induced gelation of soy protein-stabilized emulsions. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 51, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.X.; Liu, C.; Lu, M.H.; Liu, Y.L.; Yin, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.H. Impact of enzymatic hydrolysis followed by transglutaminase-induced cross-linking on decreasing antigenicity and reserving partial interfacial properties of whey protein isolate. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, J.S.; Ren, J.Y.; Zhao, M.M. Modifications of soy protein isolates using combined extrusion pre-treatment and controlled enzymatic hydrolysis for improved emulsifying properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, L.Y.; Zhou, X.H.; Yun, F.; Zhang, G.L. Enzymatic synthesis of chitosan-gelatin antimicrobial copolymer and its characterisation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.Q.; Liu, X.L.; Yu, S.F.; Wang, X.J.; Ma, Y.Q.; Yang, S.; Jing, S.S. Effects of extrusion and starch removal pretreatment on zein proteins extracted from corn gluten meal. Cereal Chem. 2014, 91, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Zhang, Z.H.; Cui, Y.F.; Shi, J.H.; Sun, X.T.; Liu, Y.A.; Wang, X.B.; Xu, N. Optimization of enzymatic soy protein isolate-glucosamine conjugates to improve the freeze-thaw stability of emulsion. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 103, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaputri, P.B.; Feyzi, S.; Ismail, P.B. Transglutaminase-Induced Polymerization of Pea and Chickpea Protein to Enhance Functionality. Gels 2023, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Fu, J.F.; Ma, Y.; He, Y.T.; Fu, R.X.; Qayum, A.; Jiang, Z.M.; Wang, L.Z. Low temperature extrusion promotes transglutaminase cross-linking of whey protein isolate and enhances its emulsifying properties and water holding capacity. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 125, 107410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, S.; Uluko, H. Effect of ultrasound pretreatment on rennet-induced coagulation properties of goat’s milk. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.B.; Wu, N.N.; Yang, X.Q.; He, X.T.; Wang, L.J. Improvement of emulsifying properties of Maillard reaction products from β-conglycinin and dextran using controlled enzymatic hydrolysis. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 28, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udomrati, S.; Pantoa, T.; Sorndech, W.; Ploypetchara, T. Investigation of transglutaminase incubated condition on crosslink and rheological properties of soy protein isolate, and their effects in plant-based patty application. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 8811–8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.M.; Liu, Y.W.; Liu, A.J.; Wang, W.H. Improved thermal-stability and mechanical properties of type I collagen by crosslinking with casein, keratin and soy protein isolate using transglutaminase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wu, Y.Q.; Shan, Z.M.; Li, M.; Wen, X.; Ni, Y.Y. Effects of zein extractions on the structural properties of SPI-zein composite gels: Implications for gluten-free plant-based products. Food Chem. 2024, 452, 139562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, A.; Mitsuiki, M.; Motoki, M.; Ebisawa, K.; Suzuki, E. Relationship between the glass transition of soy protein and molecular structure. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3292–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.L.; Sun, X.H.; Yang, J.Q.; Ren, J.; Vardhanabhuti, B.; Liu, X.L.; Fu, Y. TGase-induced glycosylated soy protein products with limited enzymatic hydrolysis showed enhanced foaming property. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 2557–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H. Emulsifying properties of soy proteins: A critical review with emphasis on the role of conformational flexibility. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2636–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Cui, Q.; Wang, G.; Wang, G.R.; Liu, J.N.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.D.; Wang, X.B.; Jiang, L.Z. Relationship between surface functional properties and flexibility of soy protein isolate-glucose conjugates. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghribi, A.M.; Gafsi, I.M.; Blecker, C. Effect of drying methods on physico-chemical and functional properties of chickpea protein concentrates. J. Food Eng. 2015, 165, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Li, J.S.; Huang, G.X.; Yan, L.J. Predicting protein surface property with its surface hydrophobicity. Protein Pept. Lett. 2021, 28, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, J. Effects of alcalase hydrolysis combined with TGase-type glycosylation of self-assembled zein for curcumin delivery: Stability, bioavailability, and antioxidant properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 303, 140735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, D.; Conte, C.; d’Angelo, I.; Miro, A.; Ungaro, F.; Quaglia, F. Mucoadhesive zein/beta-cyclodextrin nanoparticles for the buccal delivery of curcumin. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, E.; Merino, L.M. Effect of sugars on the rheological properties of acid caseinate -stabilized emulsion gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 6, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.Y.; Liu, H.F.; Fu, M.; Zhao, X.H. Structure and property changes of soybean protein isolates resulted from the glycation and cross-linking by transglutaminase and a degraded chitosan. CyTA-J. Food 2016, 14, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.C.; Shi, L.F.; Ren, Z.Y.; Hao, G.X.; Weng, W.Y. Effects of microfluidization cycles on physicochemical properties of soy. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 130, 107684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, T.; Liu, C.; Guo, F.X.; Zhao, J. l-Histidine improves solubility and emulsifying properties of soy proteins under various ionic strengths. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 152, 112382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | α-Helix (%) | β-Sheet (%) | β-Turn (%) | Random Coil (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPI | 13.35 | 37.1 | 36.68 | 13.54 |
| 0 h-SPI/ZH | 14.28 | 42.34 | 30.17 | 13.21 |
| 0.5 h-SPI/ZH | 14.28 | 42.34 | 30.17 | 13.21 |
| 1 h-SPI/ZH | 13.04 | 37.25 | 36.32 | 13.39 |
| 1.5 h-SPI/ZH | 10.87 | 27 | 40.21 | 11.04 |
| Index | SPI | 0 h-SPI/ZH | 0.5 h-SPI/ZH | 1 h-SPI/ZH | 1.5 h-SPI/ZH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grafting degree (%) | 0 | 0 | 17.38 ± 0.20 c | 19.86 ± 0.28 b | 23.51 ± 0.32 a |
| Solubility (pH 7.5) | 53.9 ± 2.91 b | 59.4 ± 1.81 a | 57.6 ± 1.61 ab | 56.5 ± 0.90 ab | 55.7 ± 2.21 ab |
| Emulsion drop size (r.nm) | 64.73 ± 2.5 a | 74.87 ± 1.4 b | 78.01 ± 2.2 c | 80.22 ± 2.9 d | 80.79 ± 1.6 e |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −21.8 ± 0.8 b | −18.3 ± 0.7 a | −25.9 ± 1.2 c | −26.8 ± 1.1 c | −29.9 ± 0.9 d |
| Surface hydrophobicity | 53.53 ± 0.32 a | 57.31 ± 0.26 b | 60.13 ± 0.92 c | 66.66 ± 0.34 d | 72.21 ± 0.17 e |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Z.; Li, W.; Xue, Y.; Bo, L.; Ren, J.; Song, C. Enhancement of Emulsifying Activity in Soy-Protein-Based Products by Partial Substitution with Zein Hydrolysates and Transglutaminase Addition. Foods 2025, 14, 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081353
Guo Z, Li W, Xue Y, Bo L, Ren J, Song C. Enhancement of Emulsifying Activity in Soy-Protein-Based Products by Partial Substitution with Zein Hydrolysates and Transglutaminase Addition. Foods. 2025; 14(8):1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081353
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Zhihao, Weiyu Li, Yuan Xue, Liying Bo, Jian Ren, and Chunli Song. 2025. "Enhancement of Emulsifying Activity in Soy-Protein-Based Products by Partial Substitution with Zein Hydrolysates and Transglutaminase Addition" Foods 14, no. 8: 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081353
APA StyleGuo, Z., Li, W., Xue, Y., Bo, L., Ren, J., & Song, C. (2025). Enhancement of Emulsifying Activity in Soy-Protein-Based Products by Partial Substitution with Zein Hydrolysates and Transglutaminase Addition. Foods, 14(8), 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081353






