Rapid Covalent Bonding of Walnut Protein Isolates to EGCG: Unveiling the Ultrasound-Assisted Ratio Optimization, Binding Mechanism, and Structural–Functional Transformations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of WPI
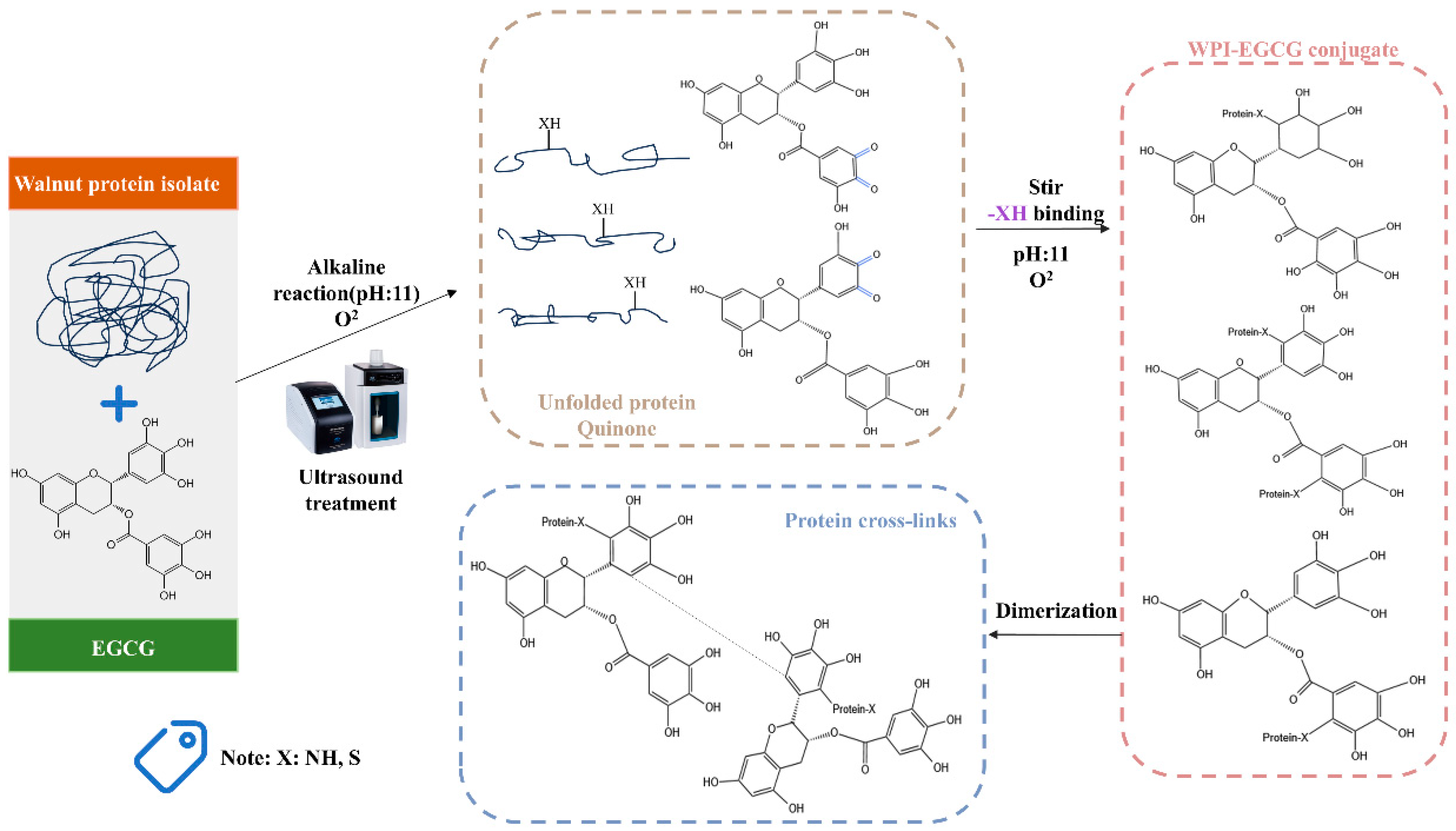
2.3. Preparation of WPI–EGCG Conjugates
2.4. Determination of Grafted Polyphenol Contents
2.5. Free Sulfhydryl Content
2.6. Free Amino Content
2.7. SDS-PAGE
2.8. Ultraviolet–Visible (UV–Vis) Spectra Analysis
2.9. Fluorescence Spectra Analysis
2.10. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
2.11. Determination of Particle Size and Zeta Potential
2.12. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.13. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Analysis
2.14. Protein Solubility
2.15. Determination of Emulsifying Properties
2.16. Molecular Docking
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
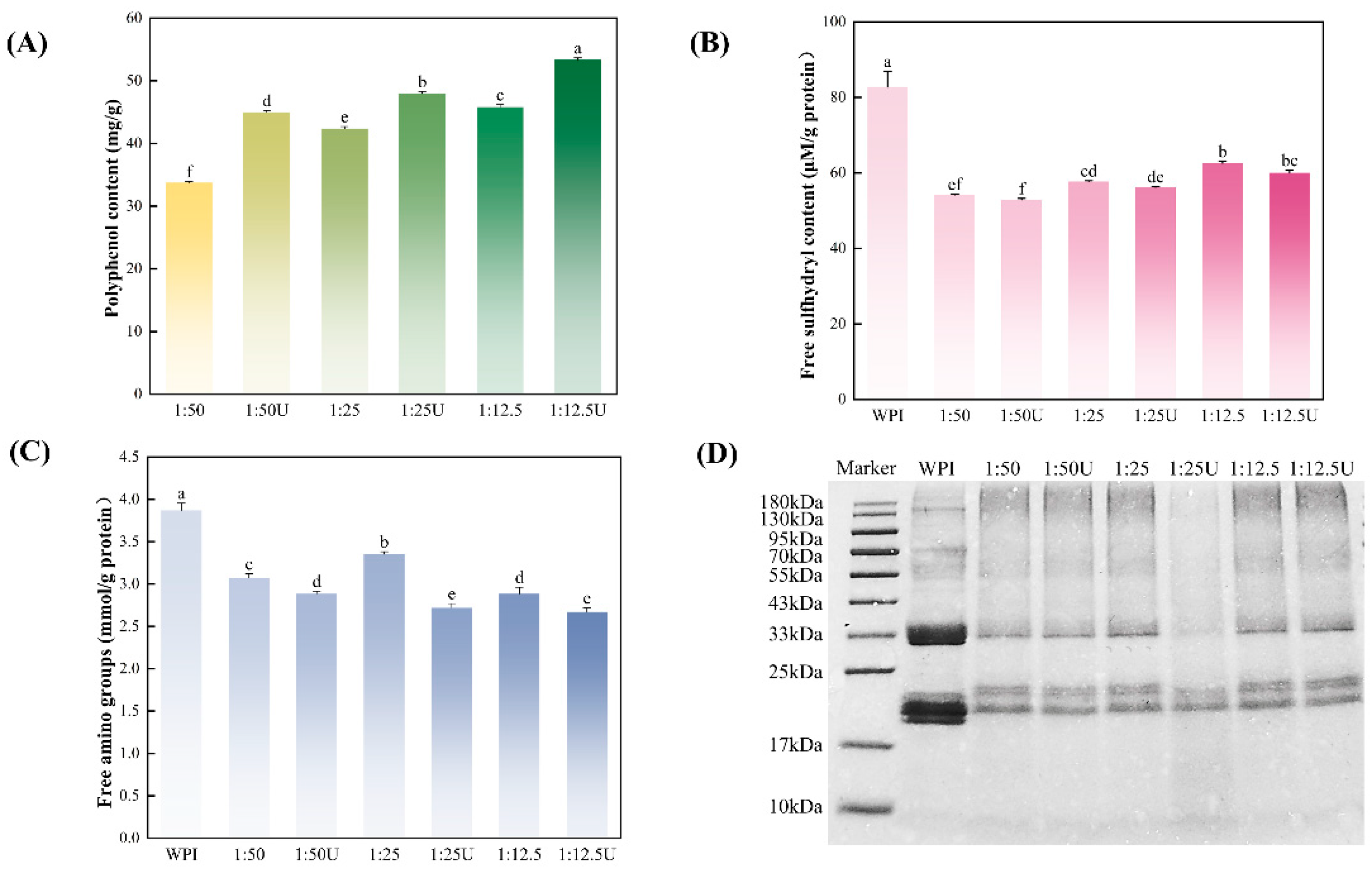
3.1. Polyphenol Contents
3.2. Free Sulfhydryl and Amino Contents Analysis
3.3. SDS-PAGE Analysis
3.4. UV–Vis Spectra
3.5. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis
3.6. FT-IR Analysis
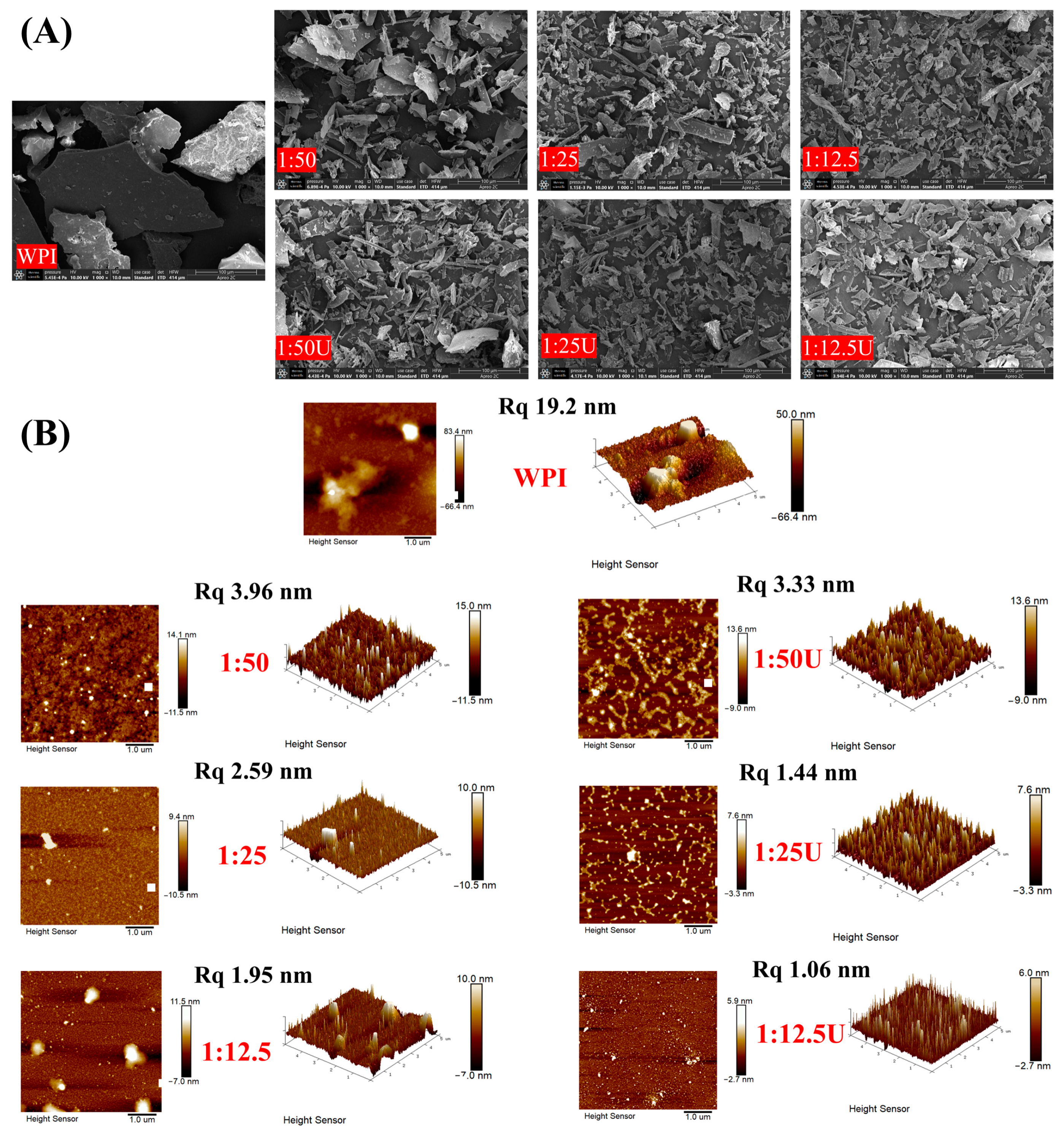
3.7. Morphological Characters
3.8. Surface Topography of WPI–EGCG Conjugates
3.9. Analysis of Particle Size and Zeta Potential
3.10. Solubility Analysis
3.11. Emulsifying Properties
3.12. Molecular Docking Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, H.; Shi, Y.; Bai, J.; Zou, G.; Wang, R.; Xu, H.; Wang, J.; Luo, A. Electron beam irradiation treatment driven structure-function relationships of walnut meal proteins and hydrolysates. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 155, 110234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, L.; Liu, G.; Liang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; et al. Walnut Protein: A Rising Source of High-Quality Protein and Its Updated Comprehensive Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 10525–10542. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Zhang, L.; Cao, M.; Guo, Y.; Mi, J.; Zhu, Z.; Song, Y.; Chang, M.; Liu, R.; Wang, X. Characterization and functional properties of walnut protein fibrils for enhanced bioaccessibility of CoQ10 and ALA. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 285, 138171. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Mao, X.; Zhang, C. Ultrasound and high-speed shear pretreatments of walnut meal protein: Structural and functional characterization and mechanistic investigation. LWT 2024, 210, 116820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poklar Ulrih, N. Analytical techniques for the study of polyphenol–protein interactions. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2144–2161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yan, C.; Lin, M.; He, C.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Z. The effects of conjugation of walnut protein isolate with polyphenols on protein solubility, antioxidant activity, and emulsifying properties. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111910. [Google Scholar]
- Kieserling, H.; de Bruijn, W.J.C.; Keppler, J.; Yang, J.; Sagu, S.T.; Güterbock, D.; Rawel, H.; Schwarz, K.; Vincken, J.-P.; Schieber, A.; et al. Protein-phenolic interactions and reactions: Discrepancies, challenges, and opportunities. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e70015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tan, B.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Sun, X. The phenolic profile of walnut meal protein isolate and interaction of phenolics with walnut protein. Food Res. Int. 2023, 170, 113042. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lv, J.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Jin, F.; Wang, F. Walnut protein isolate-epigallocatechin gallate nanoparticles: A functional carrier enhanced stability and antioxidant activity of lycopene. Food Res. Int. 2024, 189, 114536. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Zeng, Z.; McClements, D.J.; Gong, X.; Yu, P.; Xia, J.; Gong, D. A review of the structure, function, and application of plant-based protein-phenolic conjugates and complexes. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 1312–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.; Zia, M.B.; Naik, R.R.; Ho, K.K.H.Y.; Selomulya, C. Effects of polyphenols from Tasmannia lanceolata on structural, emulsifying, and antioxidant properties of pea protein. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Cui, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, L.; Li, M.; Tian, L.; Wu, X.; Jie, Y. A time-saving pH-ultrasonic-shifting method for insoluble pea protein isolate to encapsulate polyphenol: Binding mechanism, structure, and functional characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Yi, L.; Högger, P.; Arroo, R.; Bajpai, V.K.; Prieto, M.-A.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Wang, S.; Cao, H. Stability and antioxidant capacity of epigallocatechin gallate in Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bourvellec, C.; Renard, C.M.G.C. Interactions between Polyphenols and Macromolecules: Quantification Methods and Mechanisms. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 213–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, V.; Pavithra, R.; Koli, V.; Dattatrya, P.A.; Nikashini, T.; Ashika, R.; Nanje Gowda, N.A.; Sunil, C.K. Ultrasound modification of techno-functional, structural, and physico-chemical properties of legume proteins: A review. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.S.; Yang, X.Y.; Gong, T.; Hu, C.Y.; Shen, Y.H.; Meng, Y.H. Ultrasonic treatment improves physical and oxidative stabilities of walnut protein isolate-based emulsion by changing protein structure. LWT 2023, 173, 114269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodpran, T.; Benjakul, S.; Phatcharat, S. Effect of phenolic compounds on protein cross-linking and properties of film from fish myofibrillar protein. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lu, Y.; Xu, H.; Lin, D.; He, Z.; Wu, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z. Reducing the allergenic capacity of β-lactoglobulin by covalent conjugation with dietary polyphenols. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, F.C.; Porter, D.H.; Catignani, G.L.; Swaisgood, H.E. An o-phthalaldehyde spectrophotometric assay for proteinases. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 146, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Liu, G.; Huang, Y.-B.; Zeng, Q.-H.; Song, G.-S.; Hou, Y.; Li, L.; Hu, S.-Q. Role of N-terminal domain of HMW 1Dx5 in the functional and structural properties of wheat dough. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ma, Z.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Ban, Q.; Wang, X. Synergistic modification of structural and functional characteristics of whey protein isolate by soybean isoflavones non-covalent binding and succinylation treatment: A focus on emulsion stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 144, 108994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Niu, F.; Gu, L.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Zhou, B.; Wang, J.; Su, Y.; Yang, Y. Formation of fibrous or granular egg white protein microparticles and properties of the integrated emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X.; Zhang, C.; Hua, Y.; Chen, Y. Effect of high-speed shearing treatment on dehulled walnut proteins. LWT 2019, 116, 108500. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Mao, B.; Cui, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Tang, X.; Chen, W. Absorption, metabolism, bioactivity, and biotransformation of epigallocatechin gallate. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 6546–6566. [Google Scholar]
- Iscimen, E.M.; Dursun Capar, T.; McClements, D.J.; Yalcin, H.; Hayta, M. Ultrasound-assisted preparation of faba bean protein isolate-Vitis vinifera L. polyphenol extract conjugates: Structural and functional characterization. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 103041. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.-D.; Huang, L.; Meng, L.; Lin, Y.-F.; Xu, X.; Dong, M.-S. Soy protein isolate -(-)-epigallocatechin gallate conjugate: Covalent binding sites identification and IgE binding ability evaluation. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Kang, M.; Kou, T.; Yan, S.; Chen, T.; Gao, Y.; Qi, B.; Li, Y. Effects of three polyphenols with different numbers of phenolic hydroxyls on the structural and interfacial properties and lipid-protein co-oxidation of oil body emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 154, 110077. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, T.; Jing, H.; Zhang, F.; Obadi, M.; Xu, B. Evaluation of crossing-linking sites of egg white protein–polyphenol conjugates: Fabricated using a conventional and ultrasound-assisted free radical technique. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132606. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, N.; Lorentzen, L.G.; Davies, M.J. Reaction of quinones with proteins: Kinetics of adduct formation, effects on enzymatic activity and protein structure, and potential reversibility of modifications. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 137, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; Chen, J.; Fu, H.; Wang, N.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; Lu, S.; Dong, J.; Wang, Q.; Yan, H. Effects of fabrication of conjugates between different polyphenols and bovine bone proteins on their structural and functional properties. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102375. [Google Scholar]
- O’Sullivan, J.; Park, M.; Beevers, J. The effect of ultrasound upon the physicochemical and emulsifying properties of wheat and soy protein isolates. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 69, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; He, K.; Liu, X.; Ye, L.; Lin, X.; Ma, L.; Yang, P.; Wu, X. Modulating the allergenicity and functional properties of peanut protein by covalent conjugation with polyphenols. Food Chem. 2023, 415, 135733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.-H.; Ren, L.-Q.; Tang, T.-X.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Zhang, C.-X.; Ke, Y.-F.; Zhang, Y.; Muskat, M.N.; Cheng, X.-R. Effects of polyphenols from walnut pellicle on the structure and allergenicity of walnut globulin. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104381. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, H.-L.; Shang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Wu, J.; Gong, Z.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q. Effects of rosmarinic acid covalent conjugation on the allergenicity and functional properties of egg white protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 158, 110579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wang, Q.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Qi, B. Ultrasound-assisted preparation of protein-polyphenol conjugates and their structural and functional characteristics. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2023, 100, 106645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Lv, Y.; Wang, S.; Suo, Z.; Cheng, X.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Li, Z.; Feng, X. Inhibition of interaction between epigallocatechin-3-gallate and myofibrillar protein by cyclodextrin derivatives improves gel quality under oxidative stress. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Cao, J.; Tian, T.; Lyu, B.; Miao, L.; Lian, Z.; Cui, W.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. Changes in structure, rheological property and antioxidant activity of soy protein isolate fibrils by ultrasound pretreatment and EGCG. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, B.; Huang, X.; Teng, H.; Ai, C.; Chen, L. Ultrasound-assisted free radical modification on the structural and functional properties of ovalbumin-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) conjugates. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2023, 95, 106396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Xu, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, S.; Lin, X.; Xu, B.; Wu, X. Function, digestibility and allergenicity assessment of ovalbumin–EGCG conjugates. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 61, 103490. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Lin, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Ding, J. Covalent modification of soy protein hydrolysates by EGCG: Improves the emulsifying and antioxidant properties. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Xue, C.; Huang, Q. Covalent modification of zein with polyphenols: A feasible strategy to improve antioxidant activity and solubility. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 2965–2979. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Song, G.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, D.; Yuan, T.; Li, L.; He, G.; Yang, Q.; Xiao, G.; et al. Ultrasound-assisted assembly of β-lactoglobulin and chlorogenic acid for non covalent nanocomplex: Fabrication, characterization and potential biological function. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2022, 86, 106025. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Yu, X.; Zhou, C.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Ma, H. Effects of collagen and casein with phenolic compounds interactions on protein in vitro digestion and antioxidation. LWT 2020, 124, 109192. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Liang, Q.; Qu, W.; He, R.; Zhou, C.; Mahunu, G.K. Effects of ultrasound and ultrasound assisted alkaline pretreatments on the enzymolysis and structural characteristics of rice protein. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2016, 31, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, M.; Li, S.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Deng, Q.; Cravotto, G. Combination modes impact on the stability of β-carotene-loaded emulsion constructed by soy protein isolate, β-glucan and myricetin ternary complex. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113173. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, M.; Feng, X.; Yang, H.; Wu, X.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Teng, F. Comparison of soy protein isolate-(–)-epigallocatechin gallate complexes prepared by mixing, chemical polymerization, and ultrasound treatment. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2022, 90, 106172. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Zhou, H.; Lin, J.; Yin, X.; Xiong, T.; Peng, F. Interaction between pea protein isolate and quercetin: Effects on protein conformation and quercetin activity. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 7549–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawel, H.M.; Kroll, J.; Rohn, S. Reactions of phenolic substances with lysozyme—physicochemical characterisation and proteolytic digestion of the derivatives. Food Chem. 2001, 72, 59–71. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhang, C.; Meng, K.; Liang, F.; Shi, J. Covalent conjugation of pumpkin seed protein induction by epigallocatechin-3-gallate: Structural formation, functional and in vitro digestion properties. LWT 2025, 222, 117636. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, N.; Ye, S.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xu, J.; Pan, S.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Z. Effect of ultrasound treatment on interactions of whey protein isolate with rutin. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2023, 95, 106387. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.-W.; Yue, X.-J.; Yuan, X.-F.; Zhao, B. Covalent modification using hemp seed polyphenols improves the structural and functional properties of the hemp seed globulin. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103293. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, C.; Li, L. Modification mechanism of soybean protein isolate-soluble soy polysaccharide complex by EGCG through covalent and non-covalent interaction: Structural, interfacial, and functional properties. Food Chem. 2024, 448, 139033. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Zheng, M.; Tao, F.; Chen, W.; Huang, G.; Jiang, J. Effect of covalent modification by (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on physicochemical and functional properties of whey protein isolate. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Abdollahi, K.; Condict, L.; Hung, A.; Kasapis, S. Examination of β-lactoglobulin-ferulic acid complexation at elevated temperature using biochemical spectroscopy, proteomics and molecular dynamics. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 134, 108053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Residues Involved in Hydrogen Bonds | Residues Involved in Hydrophobic Contacts | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glutelin | –3.66 | Glu 2, Ser 6, Asp 4, Val 263, Asp 264 | Leu 5, Val 268, Leu 3, Phe 285, Gly 262, and Arg 266 |
| 11S globulin | –3.26 | Lys 36, Pro 30, Cys 35, Gln 424 | Phe 32, Gly 33, Gln 29, Arg 31, Phe 426, Glu 34, Asn 425, Pro 423, His 387, Asn 404, and Phe 405 |
| 2S albumin | –5.03 | Arg 34, Asp 28, Asn 31, Glu 27 | Asp 30, Arg 35, Glu 37, Gly 38, and Ile 29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Y.; Sun, L.; Gu, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Fan, X.; Ding, Y. Rapid Covalent Bonding of Walnut Protein Isolates to EGCG: Unveiling the Ultrasound-Assisted Ratio Optimization, Binding Mechanism, and Structural–Functional Transformations. Foods 2025, 14, 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071204
Wei Y, Sun L, Gu Y, Zhuang Y, Zhang G, Fan X, Ding Y. Rapid Covalent Bonding of Walnut Protein Isolates to EGCG: Unveiling the Ultrasound-Assisted Ratio Optimization, Binding Mechanism, and Structural–Functional Transformations. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071204
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Yuanyuan, Liping Sun, Ying Gu, Yongliang Zhuang, Gaopeng Zhang, Xuejing Fan, and Yangyue Ding. 2025. "Rapid Covalent Bonding of Walnut Protein Isolates to EGCG: Unveiling the Ultrasound-Assisted Ratio Optimization, Binding Mechanism, and Structural–Functional Transformations" Foods 14, no. 7: 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071204
APA StyleWei, Y., Sun, L., Gu, Y., Zhuang, Y., Zhang, G., Fan, X., & Ding, Y. (2025). Rapid Covalent Bonding of Walnut Protein Isolates to EGCG: Unveiling the Ultrasound-Assisted Ratio Optimization, Binding Mechanism, and Structural–Functional Transformations. Foods, 14(7), 1204. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071204







