Involvement of Anion-Specific Effects in Changes in the Gelation and Thermodynamic Properties of Calcium Alginate Hydrogel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Calcium Alginate Hydrogels
2.3. Gelation Time
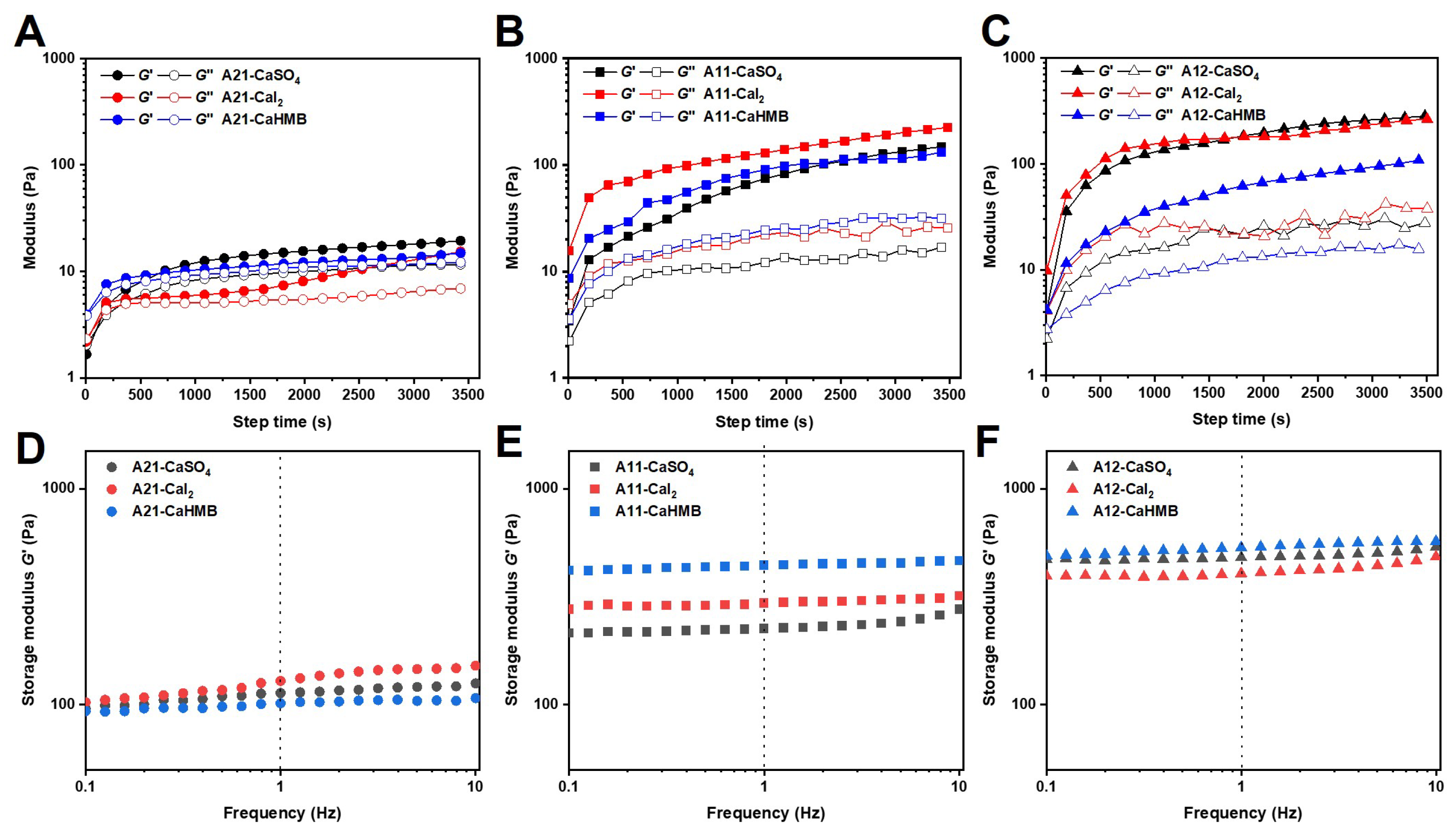
2.4. Rheology Tests
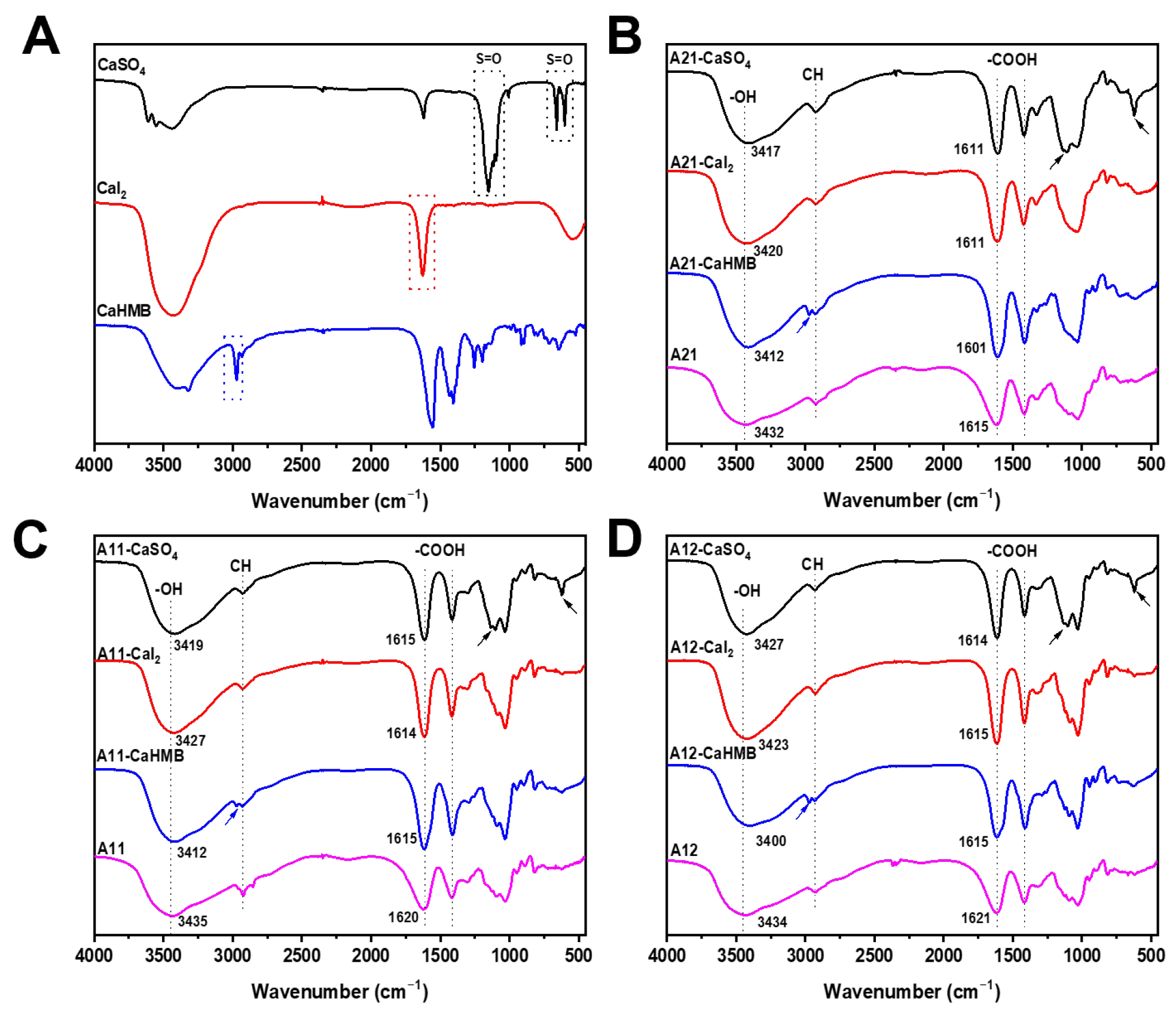
2.5. FTIR
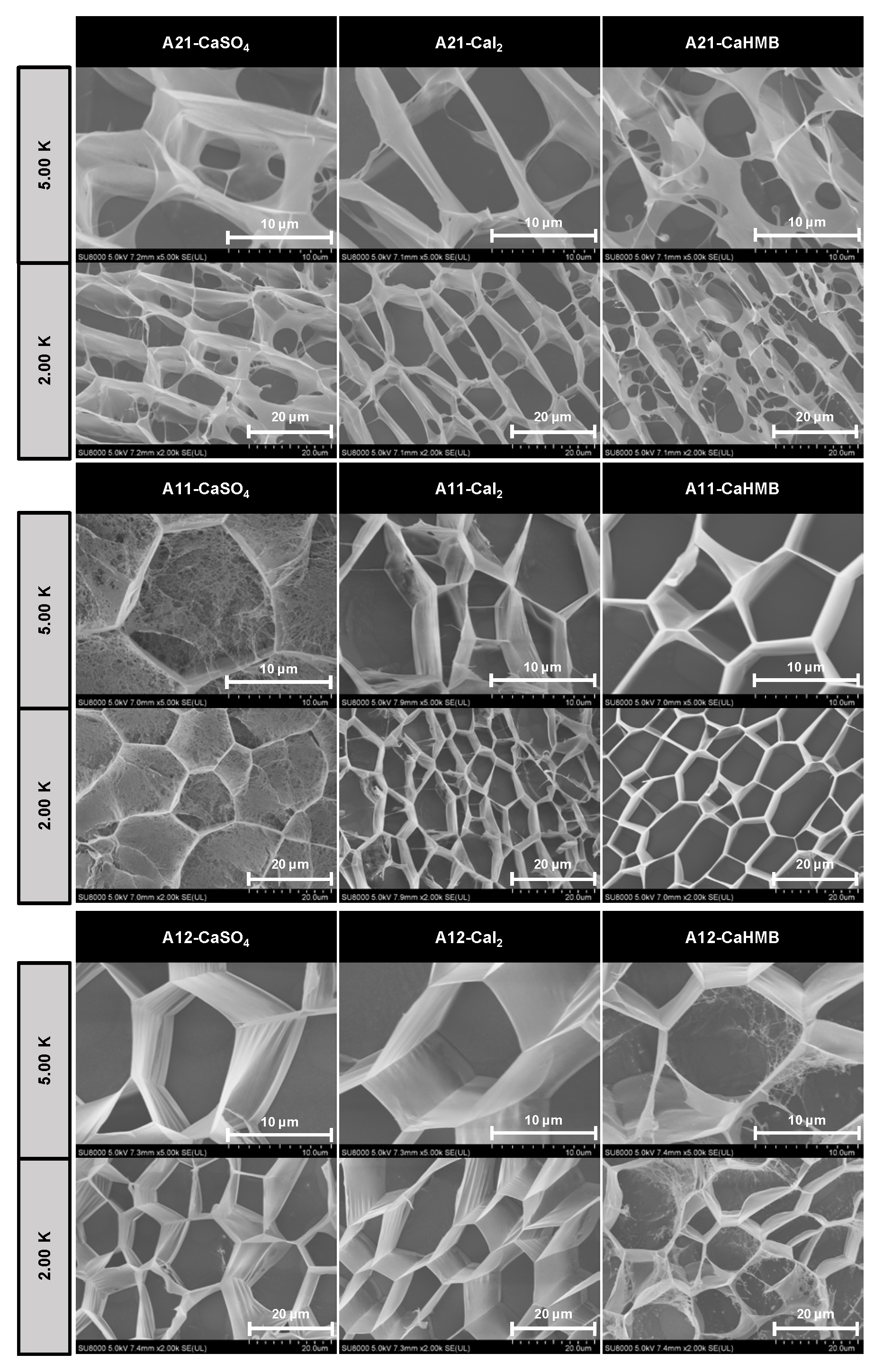
2.6. Cryo-SEM
2.7. LF-NMR Relaxometry
2.8. Thermodynamic Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
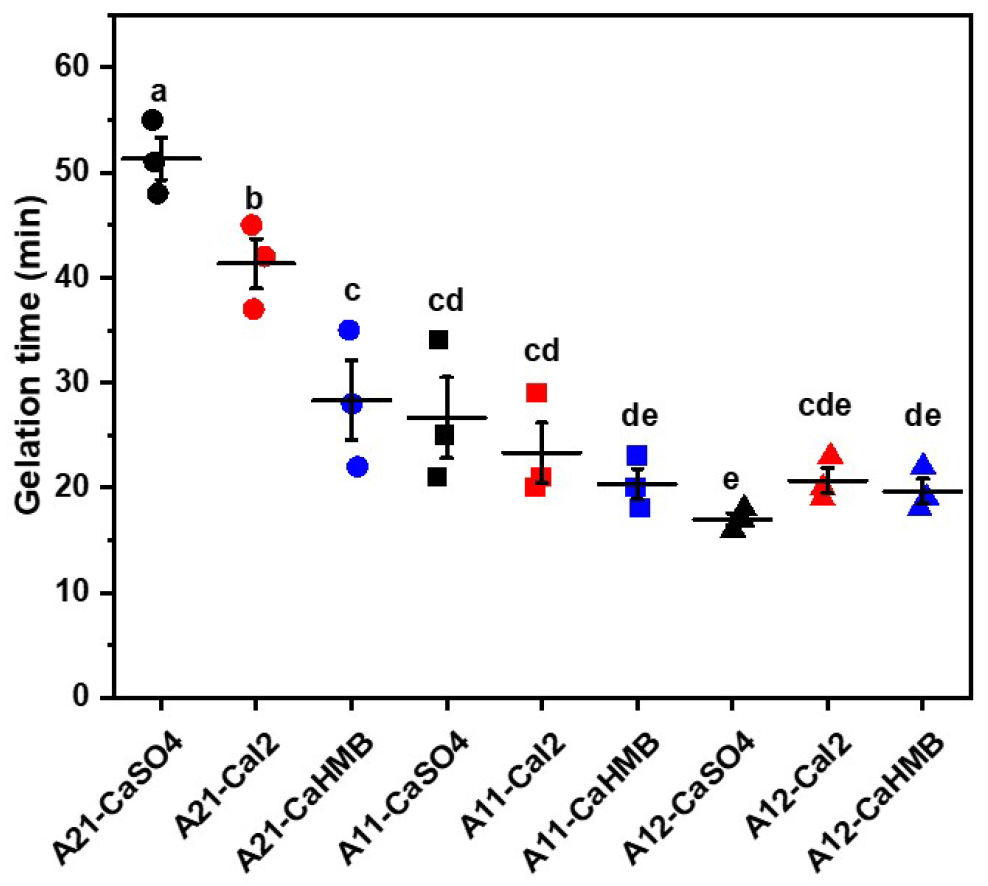
3.1. Effects of M/G Ratios and Calcium Salt Types on Gelation Time
3.2. Effects of the M/G Ratios and Calcium Salt Types on the Gelation Process
3.3. Effects of M/G Ratios and Calcium Salt Types on Chemical Structures
3.4. Effects of the M/G Ratios and Calcium Salt Types on Microstructure
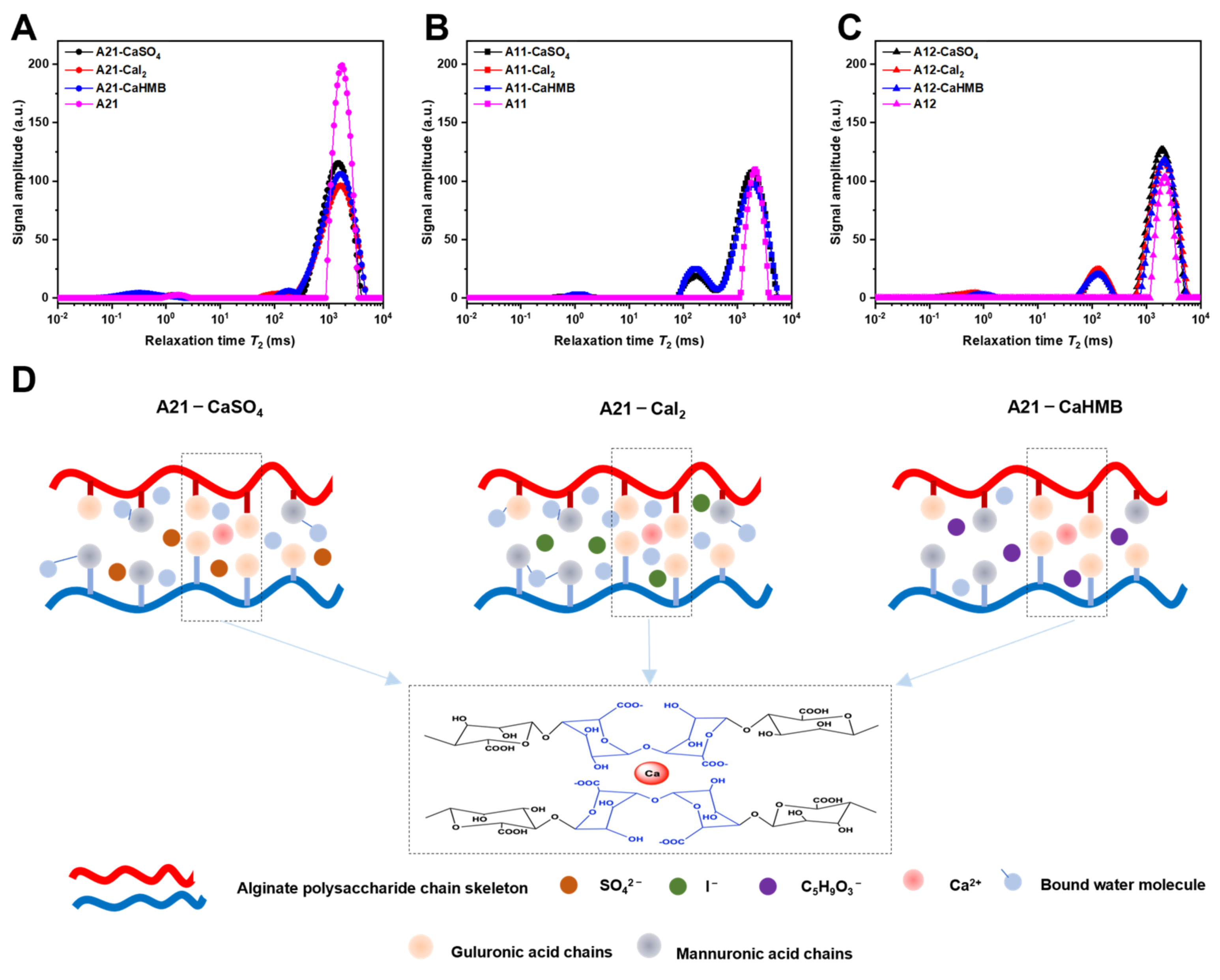
3.5. Effects of the M/G Ratios and Calcium Salt Types on Moisture Migration
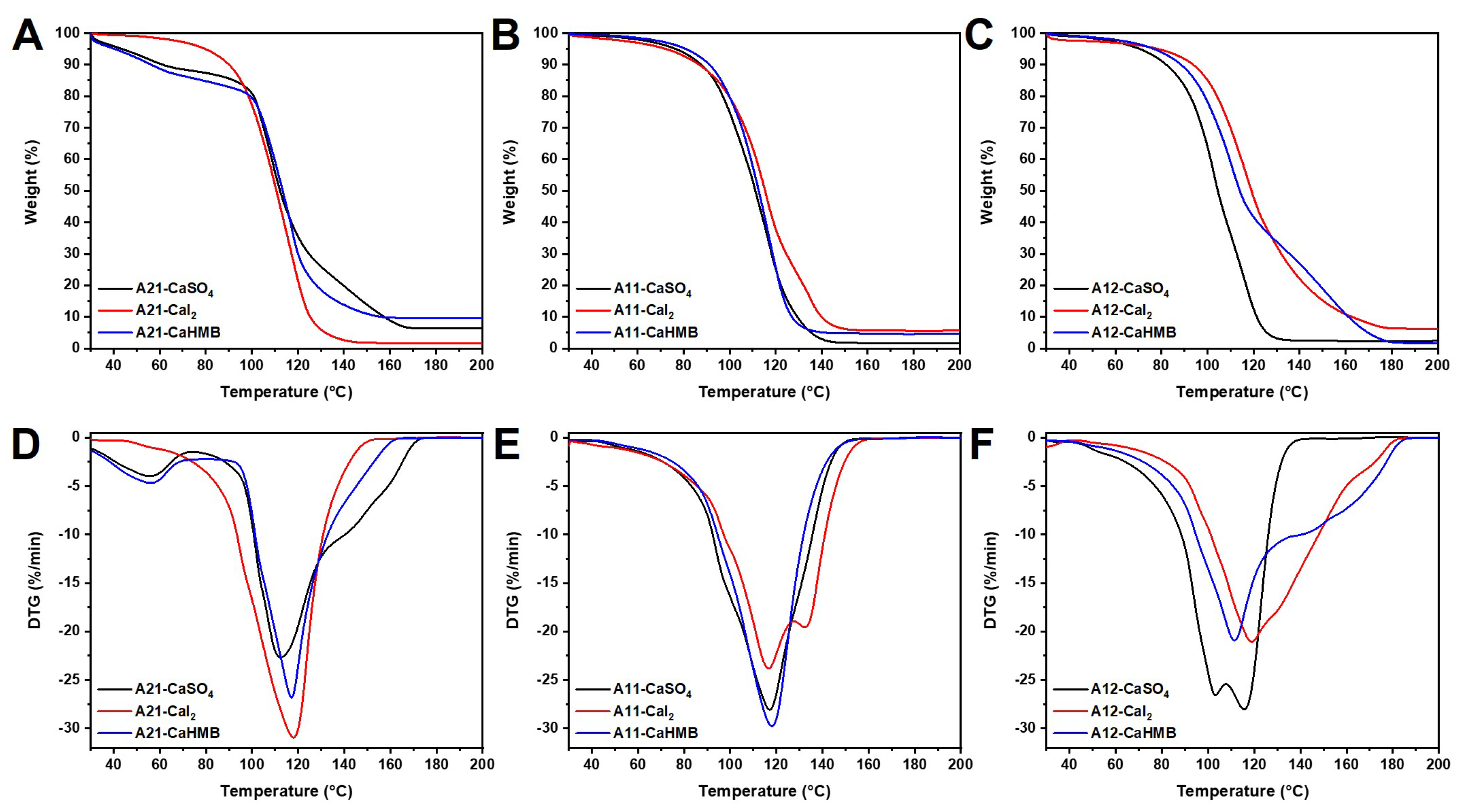
3.6. Effects of M/G Ratios and Calcium Salt Types on Thermodynamic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALG | alginate |
| CaHMB | calcium β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate |
| M/G ratios | mannuronic/guluronic acids ratios |
| LVR | linear viscoelastic region |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| cryo-SEM | cryo-scanning electron microscopy |
| LF-NMR | low-field NMR |
| CPMG | Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill sequence |
| T2 | transverse spin-spin |
| TGA | thermal gravimetric analysis |
| DTG | derivative thermogravimetric |
References
- Chen, B.; Ai, C.; He, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, L.; Teng, H. Preparation and structural characterization of chitosan-sodium alginate nanocapsules and their effects on the stability and antioxidant activity of blueberry anthocyanins. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, X.; Li, D.; Lai, X.; Liu, Y. Development of alginate-based hydrogels: Crosslinking strategies and biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, P.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, S. Recent advances in calcium alginate hydrogels encapsulating rejuvenator for asphalt self-healing. J. Road Eng. 2022, 2, 181–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traffano-Schiffo, M.V.; Aguirre-Calvo, T.R.; Navajas-Porras, B.; Avanza, M.V.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á.; Santagapita, P.R. In vitro digestion and fermentation of cowpea pod extracts and proteins loaded in Ca(II)-alginate hydrogels. Foods 2024, 13, 3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, S.; Donati, I. Comparative insights into the fundamental steps underlying gelation of plant and algal ionic polysaccharides: Pectate and alginate. Gels 2022, 8, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.W.; Hua, M.T.; Alsaid, Y.; Du, Y.J.; Ma, Y.F.; Zhao, Y.S.; Lo, C.Y.; Wang, C.R.; Wu, D.; Yao, B.W.; et al. Poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels with broad-range tunable mechanical properties via the Hofmeister effect. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzini, V.; Liu, G.; Craig, V.S. Probing the Hofmeister series beyond water: Specific-ion effects in non-aqueous solvents. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 222805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lu, S.; Chen, X.; Fang, Q.; Guan, X.; Qin, L.; Chen, C.; Zhao, C. Time-Salt type superposition and salt processing of poly (methacrylamide) hydrogel based on Hofmeister series. Macromolecules 2024, 57, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.H.; Ma, J.M.; Huang, C.X.; Lai, C.H.; Ling, Z.; Yong, Q. Effects of the Hofmeister anion series salts on the rheological properties of Sesbania cannabina galactomannan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 188, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatini, D.; Sarri, F.; Maltoni, P.; Ambrosi, M.; Carretti, E.; Ninham, B.W.; Lo Nostro, P. Specific ion effects in polysaccharide dispersions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, E.; Altemimi, A.B.; Roohi, R.; Hashemi, S.M.B.; Conte, F.L. Understanding starch gelatinization and rheology modeling of tapioca starch–NaCl/CaCl2 blends: Thermodynamic properties and gelatinization reaction kinetics during pre-and post-ultrasonication. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 272, 132865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, I.; Christensen, B.E. Alginate-metal cation interactions: Macromolecular approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 321, 121280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Hou, J.; Hu, B.; Shao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, D. Determination of calcium β-hydroxy-β-methyl butyrate content in milk and dairy products by solid-phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 132, 106362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.C.; Yan, J.N.; Wang, C.; Lai, B.; Zhang, L.C.; Wu, H.T. Construction and characterization of alginate/calcium β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate hydrogels: Effect of M/G ratios and calcium ion concentration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 133162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzini, V.; Craig, V.S. Specific-ion effects in non-aqueous systems. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 23, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Tang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Song, S. Hofmeister series: Insights of ion specificity from amphiphilic assembly and interface property. ACS omega 2020, 5, 6229–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Song, J.; Meng, D.; Li, J.; Shu, Y.; Wu, X. Effects of calcium salts on experimental characterizations of sodium alginate hydrogels and the drug release of electrospun naringin-loaded microspheres hybrid hydrogel scaffolds. Mater. Lett. 2023, 333, 133663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lai, B.; Yan, J.N.; Yambazi, M.H.; Wang, C.; Wu, H.T. Characterization of complex coacervation between chia seed gum and whey protein isolate: Effect of pH, protein/polysaccharide mass ratio and ionic strength. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 148, 109445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Rosenfeld, S.E.; McClements, D.J. Creation of plant-based meat analogs: Effects of calcium salt type on structure and texture of potato protein-alginate composite gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Marín, M.; Castro-Díaz, M.; Drage, T.C.; Maroto-Valer, M.M. Use of small-amplitude oscillatory shear rheometry to study the flow properties of pure and potassium-doped Li2ZrO3 sorbents during the sorption of CO2 at high temperatures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 73, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Park, H.; Park, W.H. Effect of pH and precursor salts on in situ formation of calcium phosphate nanoparticles in methylcellulose hydrogel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 191, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higham, A.K.; Bonino, C.A.; Raghavan, S.R.; Khan, S.A. Photo-activated ionic gelation of alginate hydrogel: Real-time rheological monitoring of the two-step crosslinking mechanism. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 4990–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.H.K.; Simon, C.G. Fast setting calcium phosphate-chitosan scaffold: Mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moody, C.T.; Brown, A.E.; Massaro, N.P.; Patel, A.S.; Agarwalla, P.A.; Simpson, A.M.; Brown, A.C.; Zheng, H.; Pierce, J.G.; Brudno, Y. Restoring carboxylates on highly modified alginates improves gelation, tissue retention and systemic capture. Acta Biomater. 2022, 138, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengsuk, N.; Laohakunjit, N.; Sanporkha, P.; Kaisangsri, N.; Selamassakul, O.; Ratanakhanokchai, K.; Uthairatanakij, A.; Waeonukul, R. Comparative physicochemical characteristics and in vitro protein digestibility of alginate/calcium salt restructured pork steak hydrolyzed with bromelain and addition of various hydrocolloids (low acyl gellan, low methoxy pectin and κ-carrageenan). Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Liu, P.; Qiu, Z.; Gitis, V.; Feng, H.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y.; Xiang, H.; Li, H. Hydrogen-bond dominated phosphorus uptake by chitosan-calcium alginate coated melamine foam in ecological floating beds. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 494, 153303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, N.; Sahare, P.D.; Lochab, S.P.; Kumar, P. TL and PL studies on CaSO4: Dy nanoparticles. Radiat. Meas. 2006, 41, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.Z.; Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Luo, X.J.; Zhang, H.B.; Yu, Z.Z. Highly conductive calcium ion-reinforced MXene/sodium alginate aerogel meshes by direct ink writing for electromagnetic interference shielding and Joule heating. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 135, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, C.; Yang, Q.; Pu, H.Y.; Cao, Y.A.; Ma, W.H.; Kuang, J.W.; Huang, J.R.; Xiong, Y.L. Textural characterization of calcium salts-induced mung bean starch-flaxseed protein composite gels as dysphagia food. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriamanantoanina, H.; Rinaudo, M. Relationship between the molecular structure of alginates and their gelation in acidic conditions. Polymer Int. 2010, 59, 1531–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, S.K.; Kouvelos, E.P.; Favvas, E.P.; Sapalidis, A.A.; Romanos, G.E.; Katsaros, F.K. Metal-carboxylate interactions in metal-alginate complexes studied with FTIR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Mascaraque, L.G.; Martínez-Sanz, M.; Hogan, S.A.; López-Rubio, A.; Brodkorb, A. Nano-and microstructural evolution of alginate beads in simulated gastrointestinal fluids. Impact of M/G ratio, molecular weight and pH. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaspers, M.; Rowan, A.E.; Kouwer, P.H.J. Tuning Hydrogel Mechanics Using the Hofmeister Effect. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 6503–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nokab, M.E.; Lasorsa, A.; Sebakhy, K.O.; Picchioni, F.; van der Wel, P.C.A. Solid-state NMR spectroscopy insights for resolving different water pools in alginate hydrogels. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 127, 107500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.Y.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Low-field NMR study of heat-induced gelation of pork myofibrillar proteins and its relationship with microstructural characteristics. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L.Y.; Wang, Y. Green double crosslinked starch-alginate hydrogel regulated by sustained calcium ion-gluconolactone release for human motion monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satriaji, K.P.; Garcia, C.V.; Kim, G.H.; Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T. Antibacterial bionanocomposite films based on CaSO4-crosslinked alginate and zinc oxide nanoparticles. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 24, 100510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoor, S.; Kassahun, S.K.; Kim, H. Selective adsorption of cationic dye by κ-carrageenan-potato starch bio-hydrogel: Kinetics, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281, 136377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Zheng, X.; Guo, R.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W. Biomass chitosan/sodium alginate colorimetric imprinting hydrogels with integrated capture and visualization detection for cadmium (II). Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 331, 121841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.J.; Liu, Y.; Cui, L.; Yan, C.; Zhu, P. Bio-based calcium alginate nonwoven fabrics: Flame retardant and thermal degradation properties. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 122, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Fernandes, R.; de Moura, M.R.; Glenn, G.M.; Aouada, F.A. Thermal, microstructural, and spectroscopic analysis of Ca2+ alginate/clay nanocomposite hydrogel beads. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 265, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachemaoui, M.; Mokhtar, A.; Mekki, A.; Zaoui, F.; Abdelkrim, S.; Hacini, S.; Boukoussa, B. Composites beads based on Fe3O4@ MCM-41 and calcium alginate for enhanced catalytic reduction of organic dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample | M/G Ratios | Mw (g/mol) | Polydispersity Mw/Mn |
|---|---|---|---|
| A21 | 2:1 | 667622 | 1.36 |
| A11 | 1:1 | 366279 | 1.01 |
| A12 | 1:2 | 450057 | 1.11 |
| Sample | νasym(COO−) | νsym(COO−) | Δν(COO−) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A21-CaSO4 | 1607 | 1419 | 188 |
| A21-CaI2 | 1611 | 1423 | 188 |
| A21-CaHMB | 1611 | 1416 | 195 |
| A21 | 1615 | 1417 | 198 |
| A11-CaSO4 | 1615 | 1416 | 199 |
| A11-CaI2 | 1614 | 1417 | 197 |
| A11-CaHMB | 1615 | 1412 | 203 |
| A11 | 1620 | 1417 | 203 |
| A12-CaSO4 | 1614 | 1416 | 198 |
| A12-CaI2 | 1615 | 1416 | 199 |
| A12-CaHMB | 1615 | 1412 | 203 |
| A12 | 1621 | 1417 | 204 |
| Sample | T21 | T22 | T23 |
|---|---|---|---|
| A21-CaSO4 | 1.55 ± 0.06 a | 170.37 ± 6.91 ab | 1465.76 ± 59.41 a |
| A21-CaI2 | 1.33 ± 0.19 b | 158.94 ± 6.44 b | 1607.91 ± 63.69 b |
| A21-CaHMB | 2.05 ± 0.17 c | 174.36 ± 6.91 a | 1607.91 ± 63.69 b |
| A21 | 1.74 ± 0.07 d | - | 1762.91 ± 0.00 c |
| A11-CaSO4 | 1.13 ± 0.16 a | 174.36 ± 6.91 a | 1847.41 ± 73.17 a |
| A11-CaI2 | 1.03 ± 0.15 a | 162.66 ± 6.44 ab | 1980.22 ± 78.43 b |
| A11-CaHMB | 1.14 ± 0.20 a | 158.94 ± 6.44 b | 2025.50 ± 0.00 bc |
| A11 | - | - | 2122.58 ± 84.07 c |
| A12-CaSO4 | 0.53 ± 0.06 a | 138.34 ± 5.61 a | 1847.41 ± 73.17 a |
| A12-CaI2 | 0.71 ± 0.08 b | 138.79 ± 14.94 ab | 2122.58 ± 84.07 b |
| A12-CaHMB | 0.93 ± 0.04 c | 123.22 ± 4.88 b | 2074.04 ± 84.07 b |
| A12 | - | - | 2122.58 ± 84.07 b |
| Sample | T5% (°C) | T10% (°C) | Tmax (°C) | Residue (%) at 200 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A21-CaSO4 | 46.0 ± 2.5 a | 61.3 ± 0.4 a | 112.0 ± 2.0 a | 4.3 ± 1.1 a |
| A21-CaI2 | 80.8 ± 1.5 b | 89.7 ± 0.5 b | 117.5 ± 1.4 b | 3.3 ± 1.9 a |
| A21-CaHMB | 39.8 ± 0.5 c | 55.2 ± 1.5 c | 117.0 ± 0.8 b | 6.3 ± 2.0 a |
| A11-CaSO4 | 76.7 ± 0.2 a | 88.3 ± 0.7 a | 117.3 ± 0.7 a | 3.0 ± 1.4 a |
| A11-CaI2 | 73.9 ± 2.5 a | 87.7 ± 1.0 a | 116.4 ± 1.4 a | 4.6 ± 1.0 a |
| A11-CaHMB | 79.9 ± 1.6 a | 90.7 ± 1.3 a | 118.0 ± 1.1 a | 4.5 ± 1.3 a |
| A12-CaSO4 | 72.6 ± 1.8 a | 83.4 ± 1.3 a | 115.1 ± 1.8 a | 3.7 ± 1.4 a |
| A12-CaI2 | 78.5 ± 2.2 a | 94.2 ± 1.6 b | 117.0 ± 1.5 a | 4.3 ± 1.0 a |
| A12-CaHMB | 76.1 ± 1.2 a | 88.7 ± 1.0 c | 113.4 ± 1.9 a | 2.8 ± 1.3 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Yan, J.; Wang, C.; Lai, B.; Dong, Y.; Wu, H. Involvement of Anion-Specific Effects in Changes in the Gelation and Thermodynamic Properties of Calcium Alginate Hydrogel. Foods 2025, 14, 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14040634
Wang Y, Li L, Liu J, Yan J, Wang C, Lai B, Dong Y, Wu H. Involvement of Anion-Specific Effects in Changes in the Gelation and Thermodynamic Properties of Calcium Alginate Hydrogel. Foods. 2025; 14(4):634. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14040634
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuqiao, Lin Li, Jiacheng Liu, Jianan Yan, Ce Wang, Bin Lai, Yu Dong, and Haitao Wu. 2025. "Involvement of Anion-Specific Effects in Changes in the Gelation and Thermodynamic Properties of Calcium Alginate Hydrogel" Foods 14, no. 4: 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14040634
APA StyleWang, Y., Li, L., Liu, J., Yan, J., Wang, C., Lai, B., Dong, Y., & Wu, H. (2025). Involvement of Anion-Specific Effects in Changes in the Gelation and Thermodynamic Properties of Calcium Alginate Hydrogel. Foods, 14(4), 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14040634







