Effects of Substituting Wheat with Waxy Barley Bran Flour on Physical Properties, Health Functionality, and Sensory Characteristics of Noodles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Particle-Size Measurements
2.3. Noodle Preparation
2.4. Imaging
2.5. Water Content
2.6. Color Analysis
2.7. Extensibility
2.8. Gluten Content
2.9. Texture Profile
2.10. Sensory Evaluation
2.11. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.12. β-Glucan Content, TPC, and Antioxidant Activity
2.12.1. β-Glucan Content
2.12.2. TPC
2.12.3. Antioxidant Activity
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of the Raw Materials Used in This Experiment
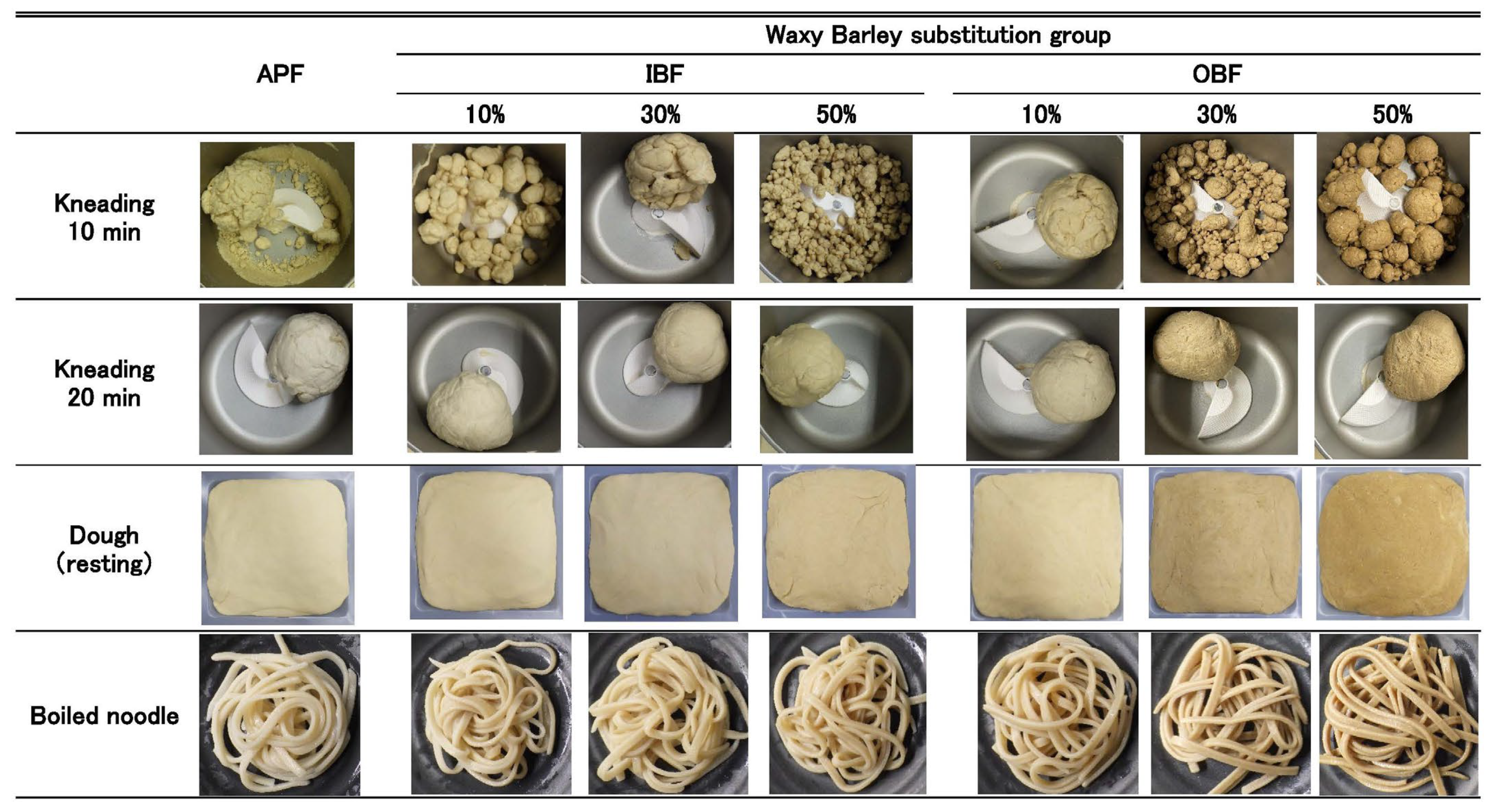
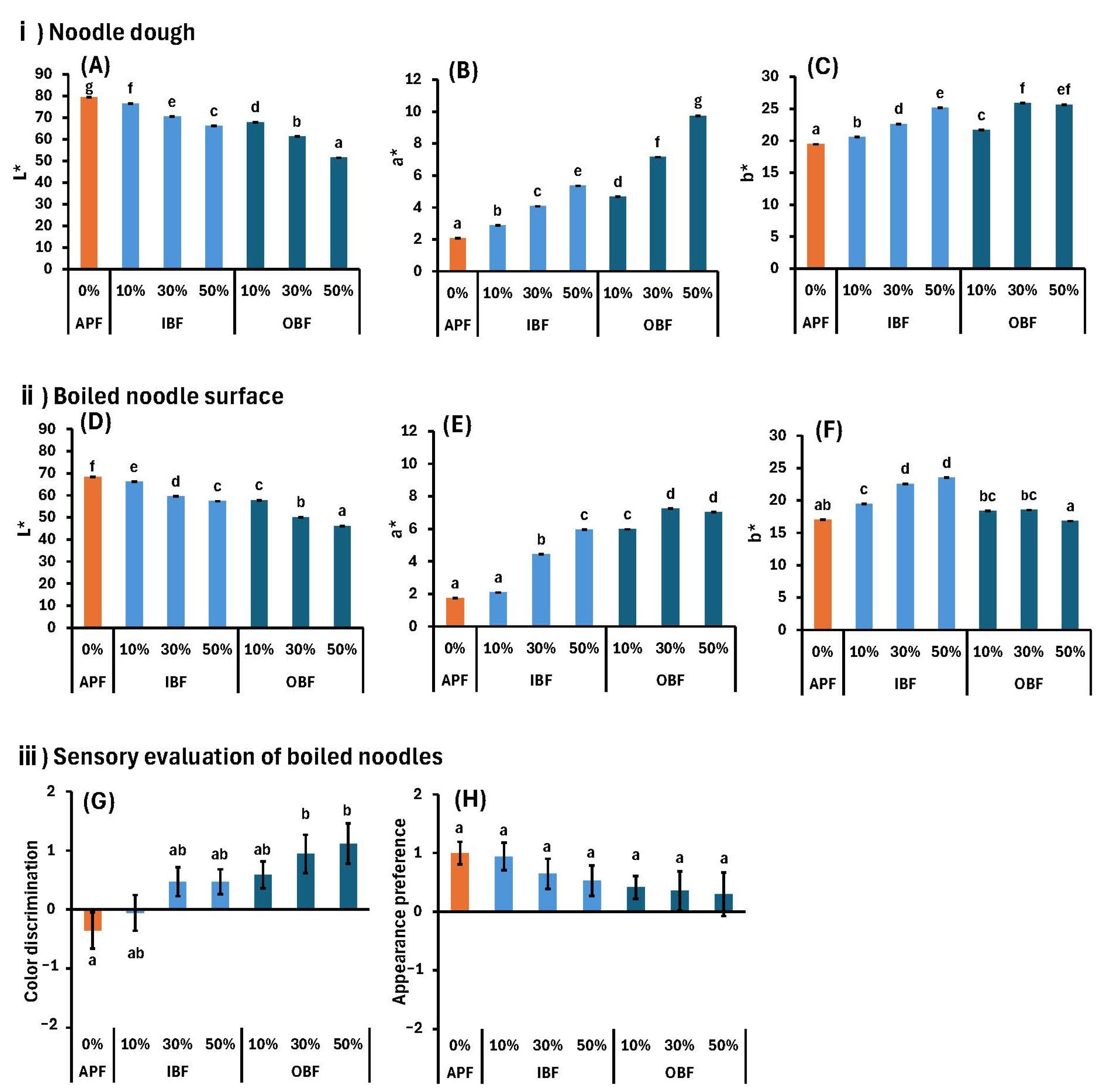
3.2. Effect of WB Bran Substitution on the Appearance of Doughs and Noodles
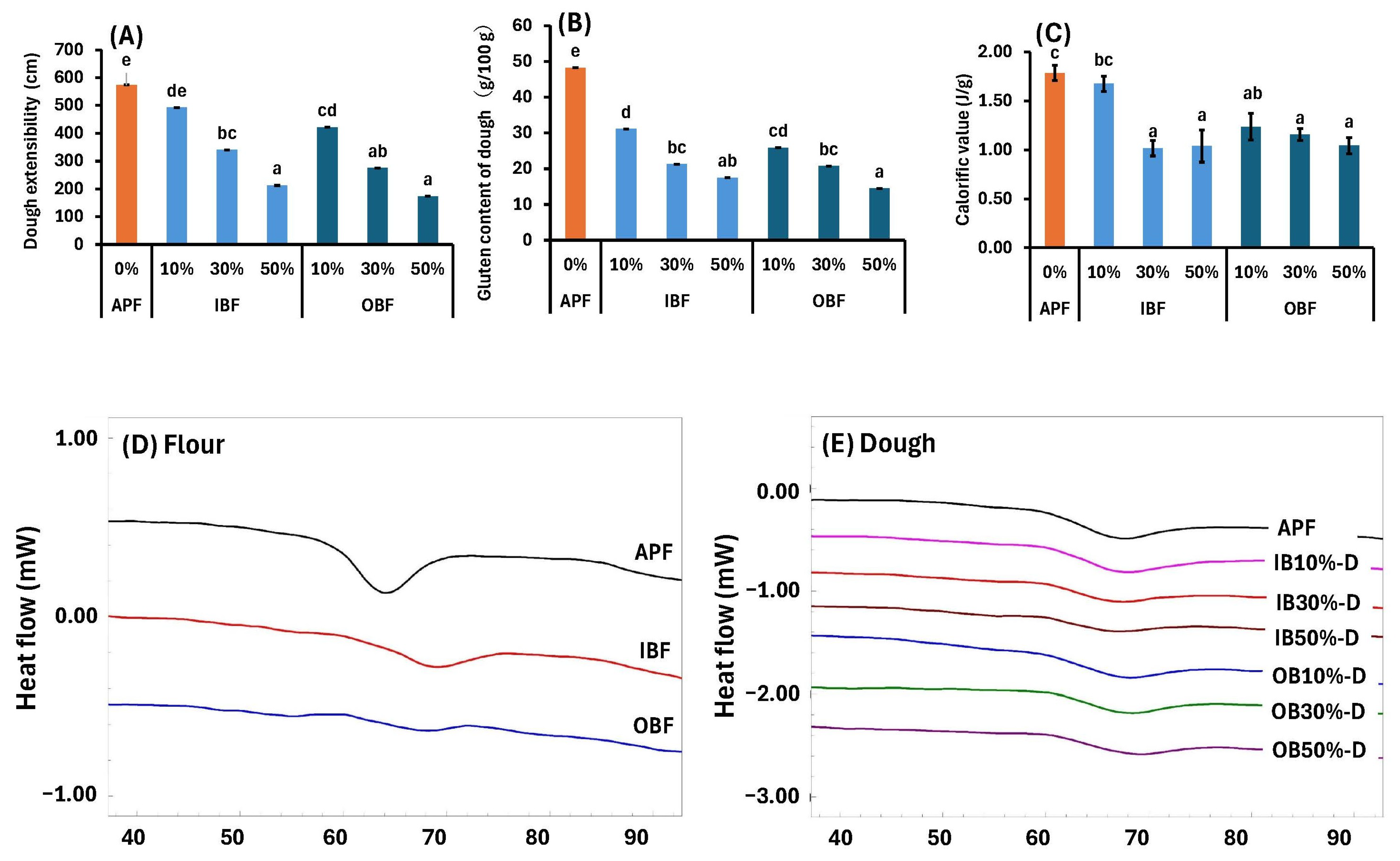
3.3. Effects of WB Bran Substitution on Water Content, Dough Extensibility, Gluten Content, and Thermal Properties of Dough
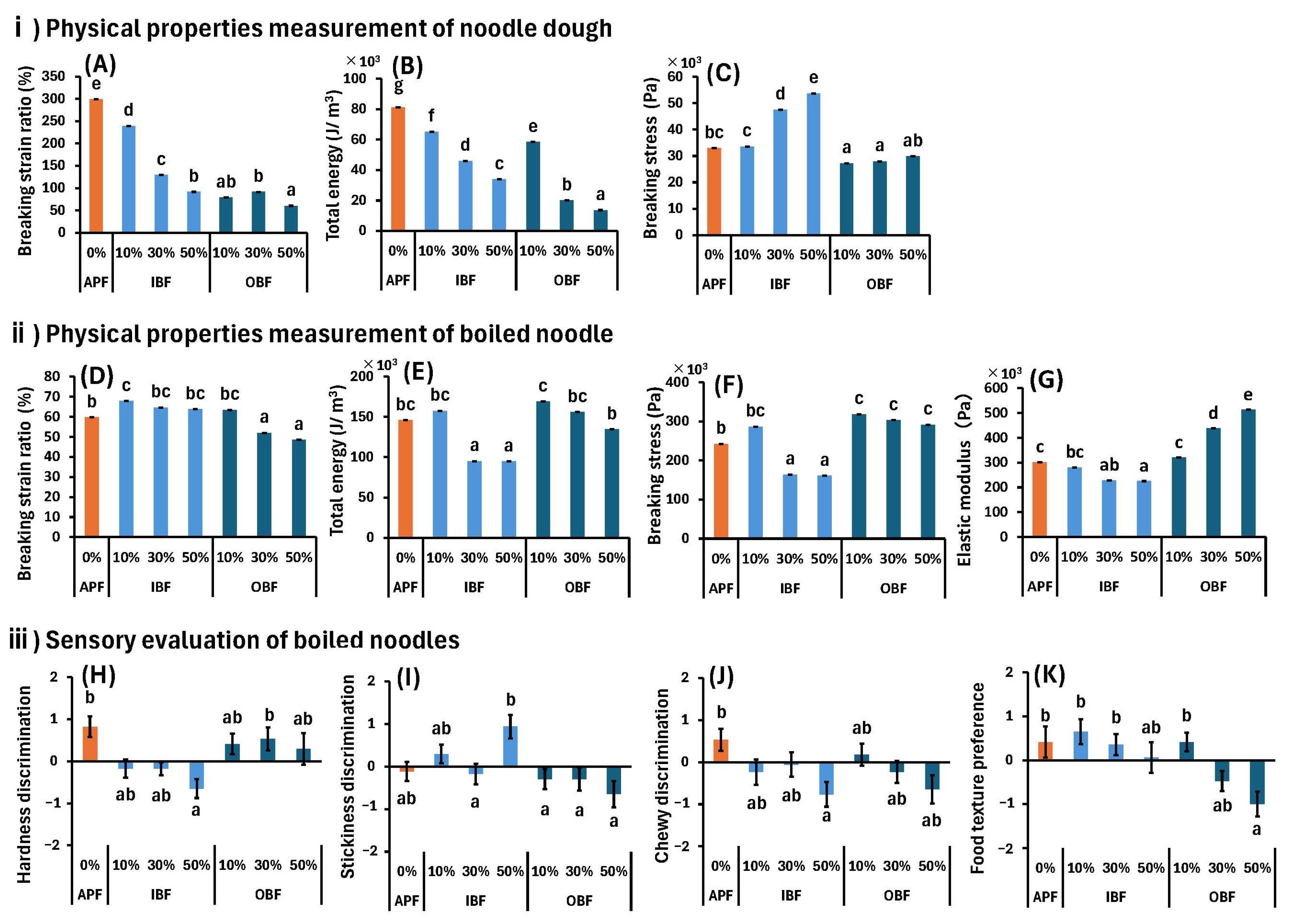
3.4. Effects of WB Bran Substitution on Physical Properties and Sensory Evaluation of Dough and Boiled Noodles
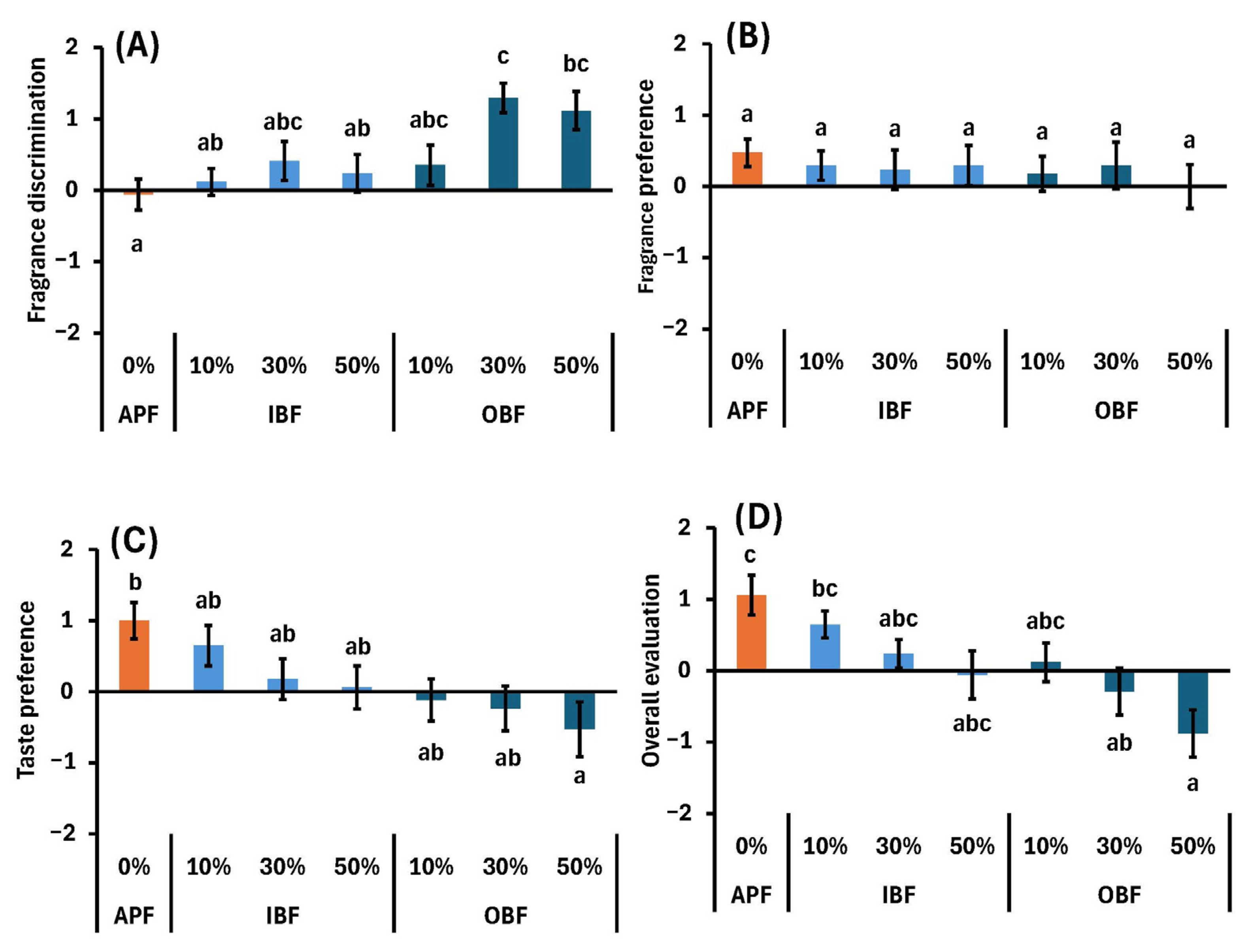
3.5. Effects of WB Bran Replacement on Aroma, Taste, and Overall Impression in Sensory Evaluations
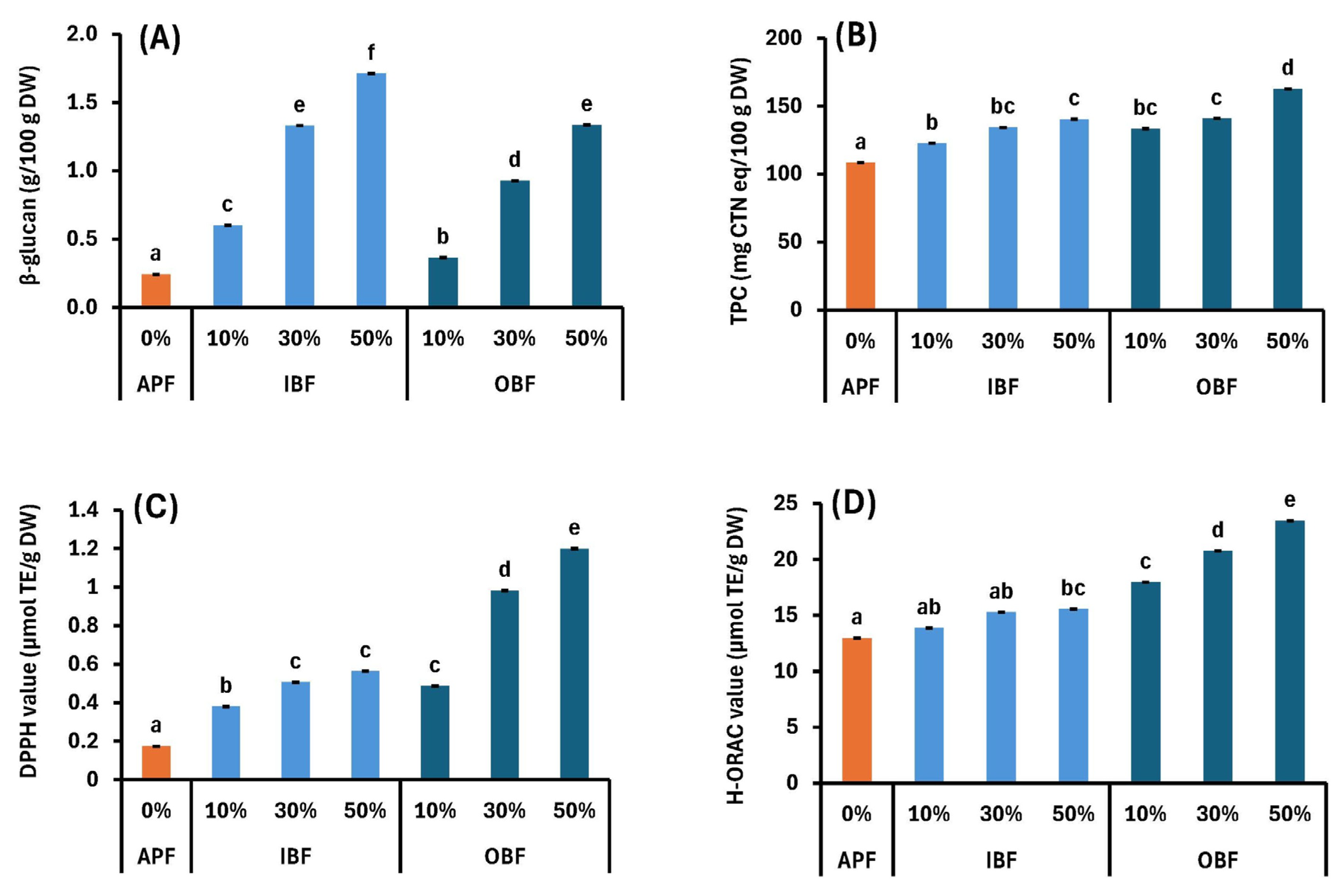
3.6. Effects of WB Bran Substitution on β-Glucan Content and Antioxidant Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.-L.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, M.-S.; Moon, Y.K. Barley β-glucan lowers serum cholesterol based on the up-regulation of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase activity and mRNA abundance in cholesterol-fed rats. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2003, 49, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messia, M.C.; De Arcangelis, E.; Candigliota, T.; Trivisonno, M.C.; Marconi, E. Production of ß-glucan enriched flour from waxy barley. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 93, 102989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullrich, S.; Clancy, J.; Eslick, R.; Lance, R. β-Glucan content and viscosity of extracts from waxy barley. J. Cereal Sci. 1986, 4, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuichi, T.; Abe, D.; Uchikawa, T.; Nagasaki, T.; Kanou, M.; Kasuga, J.; Matsumoto, S.; Tsurunaga, Y. Comparison of Nutritional Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Pulverized and Unutilized Portions of Waxy Barley. Foods 2023, 12, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.; Grafenauer, S. Oat and barley in the food supply and use of beta glucan health claims. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonooka, T. Breeding of Waxy Barley Cultivars in the National Barley Breeding Program of Japan. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. JARQ 2023, 57, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, S.V.; Storsley, J.; Thandapilly, S.J.; Ames, N.P. Lower 30 Minute Serum Insulin in Healthy Sprague-Dawley Rats Consuming Chips from Specific Barley Flour Blends. Cereal Chem. 2013, 90, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupton, J.R.; Robinson, M.C.; Morin, J.L. Cholesterol-lowering effect of barley bran flour and oil. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1994, 94, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamagawa, K.; Iizuka, S.; Fukushima, S.; Endo, Y.; Komiyama, Y. Antioxidative activity of polyphenol extracts from barley bran. J. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 44, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Fei, M.; Shi, C.; Tian, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Z.; Dong, H. Effect of particle size and addition level of wheat bran on quality of dry white Chinese noodles. J. Cereal Sci. 2011, 53, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Ma, S.; Wang, X.; Zheng, X. Improvement of Chinese noodle quality by supplementation with arabinoxylans from wheat bran. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gull, A.; Prasad, K.; Kumar, P. Nutritional, antioxidant, microstructural and pasting properties of functional pasta. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2018, 17, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanna, S.; Prabhasankar, P. A study on development of Gluten free pasta and its biochemical and immunological validation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Chi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, L.; Li, X. New insights into how starch structure synergistically affects the starch digestibility, texture, and flavor quality of rice noodles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 184, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, A.; Miura, M.; Ikeda, T.M.; Kaneko, S.; Kobayashi, R. Factors affecting rheological properties of barley flour-derived batter and dough examined from particle properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 129, 107645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Wei, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Luo, C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H. Effects of potato/wheat flours ratio on mixing properties of dough and quality of noodles. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 76, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chiang, J.; Tan, M.; Saw, L.; Xu, Y.; Ngan-Loong, M. Physicochemical properties of hydrothermally treated glutinous rice flour and xanthan gum mixture and its application in gluten-free noodles. J. Food Eng. 2016, 186, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udachan, I.; Sahoo, A. Quality evaluation of gluten free protein rich broken rice pasta. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhu, K.-X.; Sun, Q.-J.; Amza, T.; Guo, X.-N.; Zhou, H.-M. Quality characteristics, structural changes, and storage stability of semi-dried noodles induced by moderate dehydration: Understanding the quality changes in semi-dried noodles. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- β-Glucan Assay Kit (Mixed Linkage) Assay Protocol. Available online: https://prod-docs.megazyme.com/documents/Assay_Protocol/K-BGLU_DATA.pdf (accessed on 22 January 2025).
- AOAC International. AOAC Official Method 995.16;β-D-Glucan in Oats: Streamlined Enzymatic Method ; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cereals & Grains Association. AACC Approved Method 32–23.01; beta-Glucan Content of Barley and Oats—Rapid Enzymatic Procedure; Cereals & Grains Association: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2010; Available online: https://www.cerealsgrains.org/Pages/default.aspx (accessed on 22 January 2025).
- International Association for Cereal Sciences and Technology. ICC Standard Method No.166; Determination of ß-Glucan in Barley, Oat and Rye; International Association for Cereal Sciences and Technology: Vienna, Austria, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ainsworth, E.A.; Gillespie, K.M. Estimation of total phenolic content and other oxidation substrates in plant tissues using Folin–Ciocalteu reagent. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 875–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, J.; Oki, T.; Takebayashi, J.; Yamasaki, K.; Takano-Ishikawa, Y.; Hino, A.; Yasui, A. Method validation by interlaboratory studies of improved hydrophilic oxygen radical absorbance capacity methods for the determination of antioxidant capacities of antioxidant solutions and food extracts. Anal. Sci. 2012, 28, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsurunaga, Y.; Kanou, M.; Ikeura, H.; Makino, M.; Oowatari, Y.; Tsuchiya, I. Effect of different tea manufacturing methods on the antioxidant activity, functional components, and aroma compounds of Ocimum gratissimum. LWT 2022, 169, 114058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherno, N.; Gural, L.; Naidonov, O. Black wheat bran as a promising source of food fibres with an expanded spectrum of Functionalities. Grain Prod. Mix. Fodder’s 2020, 20, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ker, Y.-B.; Wu, H.-L.; Chen, K.-C.; Peng, R.Y. Nutrient composition of Chenopodium formosanum Koidz. bran: Fractionation and bioactivity of its soluble active polysaccharides. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach Knudsen, K.E.; Nørskov, N.P.; Bolvig, A.K.; Hedemann, M.S.; Laerke, H.N. Dietary fibers and associated phytochemicals in cereals. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, P.; Li, X. Sorption equilibrium moisture and isosteric heat of adsorption of Chinese dried wheat noodles. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2016, 67, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, P.J.; Stojiljkovic, M.J. The Kinetics of Drying Pasta with Added of Soya Flour. Int. J. Latest Eng. Sci. 2019, 2, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, M.; Yang, T.; Li, M.; Sun, Q. Dynamic distribution and transition of gluten proteins during noodle processing. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesiekierski, J.R. What is gluten? J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boita, E.R.; Oro, T.; Bressiani, J.; Santetti, G.S.; Bertolin, T.E.; Gutkoski, L.C. Rheological properties of wheat flour dough and pan bread with wheat bran. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 71, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Pi, J.; Zhang, G. The interaction between tea polyphenols and wheat gluten in dough formation and bread making. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 12827–12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.-W.; Ma, M.; Zhang, H.-H.; Li, M.; Sun, Q.-J. Progressive study of the effect of superfine green tea, soluble tea, and tea polyphenols on the physico-chemical and structural properties of wheat gluten in noodle system. Food Chem. 2020, 308, 125676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangopadhyay, N.; Harrison, S.M.; Brunton, N.P.; Hidalgo-Ruiz, J.L.; Gallagher, E.; Rai, D.K. Brans of the roller-milled barley fractions rich in polyphenols and health-promoting lipophilic molecules. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 83, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lan, Y.; Dang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, W.; Du, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, Z. Polyphenol profile and in vitro antioxidant and enzyme inhibitory activities of different solvent extracts of highland barley bran. Molecules 2023, 28, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verardo, V.; Cevoli, C.; Pasini, F.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; Marconi, E.; Fabbri, A.; Caboni, M.F. Analysis of oligomer proanthocyanidins in different barley genotypes using high-performance liquid chromatography–fluorescence detection–mass spectrometry and near-infrared methodologies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4130–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, A.L.; Bean, S.R.; Tilley, M.; Adrianos, S.L.; Awika, J.M. Interaction mechanisms of condensed tannins (proanthocyanidins) with wheat gluten proteins. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Robards, K.; Helliwell, S.; Blanchard, C. Effect of the addition of fatty acids on rice starch properties. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Ramos, D.; de Dios Figueroa-Cárdenas, J.; Véles-Medina, J.J.; Salazar, R. Physicochemical properties of nixtamalized black bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) flours. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-P.; Lai, H.-M. Bioactive compounds and antioxidative activity of colored rice bran. J. Food. Drug. Anal. 2016, 24, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izydorczyk, M.; Lagasse, S.; Hatcher, D.; Dexter, J.; Rossnagel, B. The enrichment of Asian noodles with fiber-rich fractions derived from roller milling of hull-less barley. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 2094–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemitsu, H.; Amako, M.; Sako, Y.; Kita, K.; Ozeki, T.; Inui, H.; Kitamura, S. Reducing the undesirable odor of barley by cooking with superheated steam. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4732–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Campos, J.; Escalona-Buendía, H.; Orozco-Avila, I.; Lugo-Cervantes, E.; Jaramillo-Flores, M.E. Dynamics of volatile and non-volatile compounds in cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.) during fermentation and drying processes using principal components analysis. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajarayasiri, J.; Chaiseri, S. Comparative study on aroma-active compounds in Thai, black and white glutinous rice varieties. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2008, 42, 715–722. [Google Scholar]
- Heiniö, R.-L.; Noort, M.; Katina, K.; Alam, S.A.; Sozer, N.; De Kock, H.L.; Hersleth, M.; Poutanen, K. Sensory characteristics of wholegrain and bran-rich cereal foods—A review. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2016, 47, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Liu, H.; Yang, C.; Xia, H.; Pan, D.; Yang, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Sun, G. Effects of different delivering matrices of β-glucan on lipids in mildly hypercholesterolaemic individuals: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozbulut, R.; Sanlier, N. Promising effects of β-glucans on glyceamic control in diabetes. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 83, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.; Fan, M.; Qian, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, G.; Zhang, H.; Qi, X.; Xu, M. Physiological functionalities and mechanisms of β-glucans. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Nie, Q.; Xie, M.; Yao, H.; Zhang, K.; Yin, J.; Nie, S. Protective effects of β-glucan isolated from highland barley on ethanol-induced gastric damage in rats and its benefits to mice gut conditions. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.M.; Hossain, R.; Herrera-Bravo, J.; Islam, M.T.; Atolani, O.; Adeyemi, O.S.; Owolodun, O.A.; Kambizi, L.; Daştan, S.D.; Calina, D. Natural antioxidants from some fruits, seeds, foods, natural products, and associated health benefits: An update. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 1657–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Gan, R.-Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, A.-N.; Xu, D.-P.; Li, H.-B. Antioxidant phytochemicals for the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases. Molecules 2015, 20, 21138–21156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, F.; Adnan, N.; Shuib, N.S.; Yusof, R.M. Antioxidants for Health Management. J. Intelek 2022, 17, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, J.H. Antioxidant nutrients: Current dietary recommendations and research update. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2000, 40, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
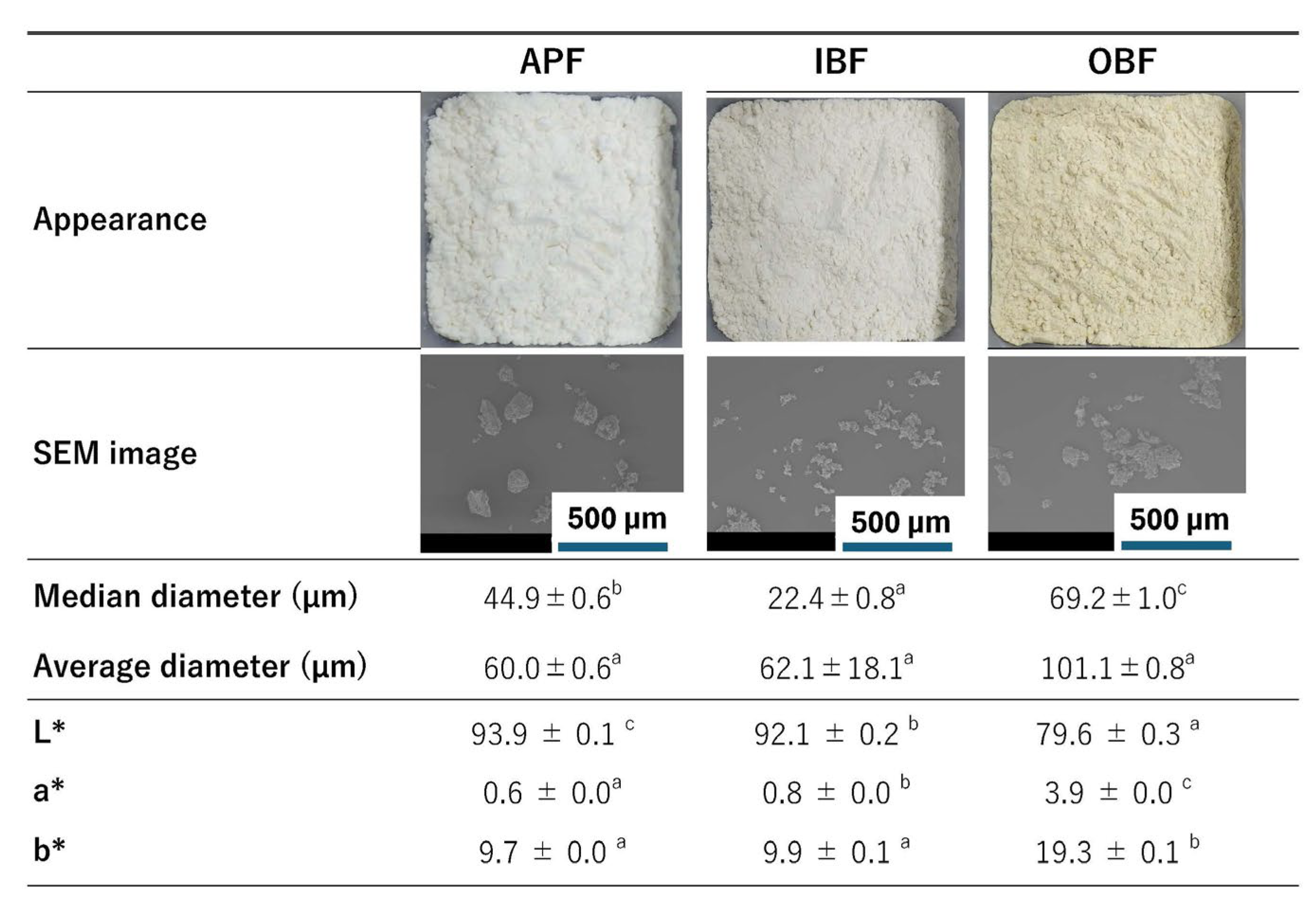
| Component | Unit | APF | IBF | OBF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy 1 | kcal/100 g | 350 | 370 | 402 |
| Protein 1 | g/100 g | 10.9 | 11.4 | 14.9 |
| Fat 1 | g/100 g | 1.6 | 4.5 | 9.5 |
| Carbohydrates 1 | g/100 g | 74.3 | 71.0 | 64.1 |
| Dietary fiber 1 | g/100 g | 2.7 | 9.1 | 20.6 |
| Ash 1 | g/100 g | 0.5 | 2.6 | 4.1 |
| β-glucan | g/100 g | 0.3 a | 4.8 c | 3.9 b |
| Sample | APF | IBF | OBF | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 30% | 50% | 10% | 30% | 50% | |||
| Dough | % | 36.66 ± 0.42 a | 38.57 ± 0.41 c | 37.66 ± 0.10 abc | 37.09 ± 0.07 ab | 38.28 ± 0.29 bc | 37.58 ± 0.09 abc | 37.33 ± 0.10 ab |
| Dried Noodle | % | 10.40 ± 0.02 c | 10.67 ± 0.05 d | 9.93 ± 0.07 b | 10.09 ± 0.06 b | 11.77 ± 0.06 e | 9.90 ± 0.04 b | 9.50 ± 0.01 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsurunaga, Y.; Uno, A.; Takahashi, T.; Furuichi, T. Effects of Substituting Wheat with Waxy Barley Bran Flour on Physical Properties, Health Functionality, and Sensory Characteristics of Noodles. Foods 2025, 14, 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030436
Tsurunaga Y, Uno A, Takahashi T, Furuichi T. Effects of Substituting Wheat with Waxy Barley Bran Flour on Physical Properties, Health Functionality, and Sensory Characteristics of Noodles. Foods. 2025; 14(3):436. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030436
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsurunaga, Yoko, Ayane Uno, Tetsuya Takahashi, and Tsugumi Furuichi. 2025. "Effects of Substituting Wheat with Waxy Barley Bran Flour on Physical Properties, Health Functionality, and Sensory Characteristics of Noodles" Foods 14, no. 3: 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030436
APA StyleTsurunaga, Y., Uno, A., Takahashi, T., & Furuichi, T. (2025). Effects of Substituting Wheat with Waxy Barley Bran Flour on Physical Properties, Health Functionality, and Sensory Characteristics of Noodles. Foods, 14(3), 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030436






