Modification of Structure, Pasting, and In Vitro Digestion Properties of Glutinous Rice Starch by Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Glutinous Rice Pretreatment, Fermentation, and Extraction of Starch
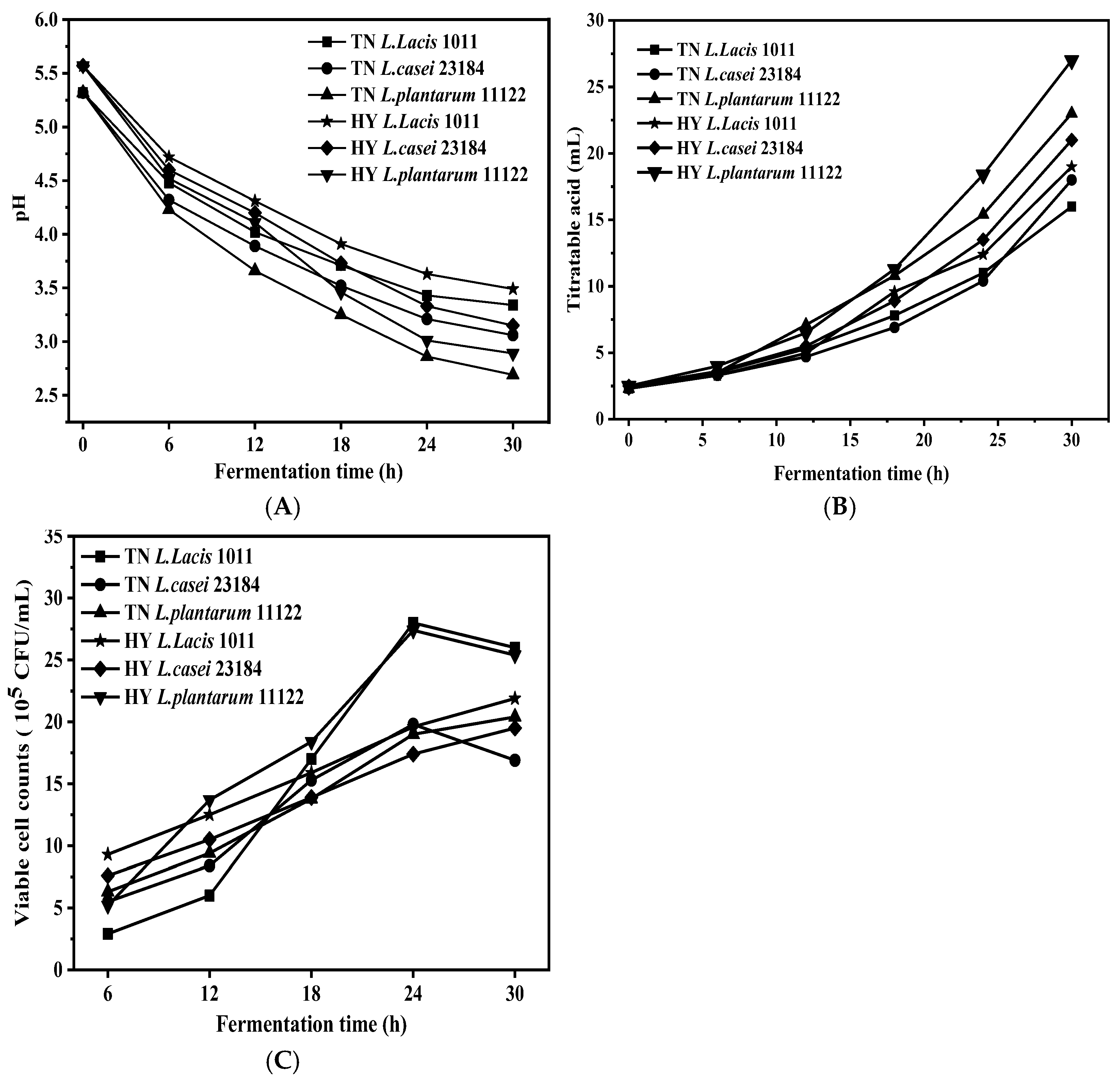
2.3. pH, Total Titratable Acidity, and Viable Cell Count
2.4. Amylopectin Chain Length Distribution
2.5. Total Molecular Size Distribution of Starch
2.6. Solid-State 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
2.7. Branching Degree
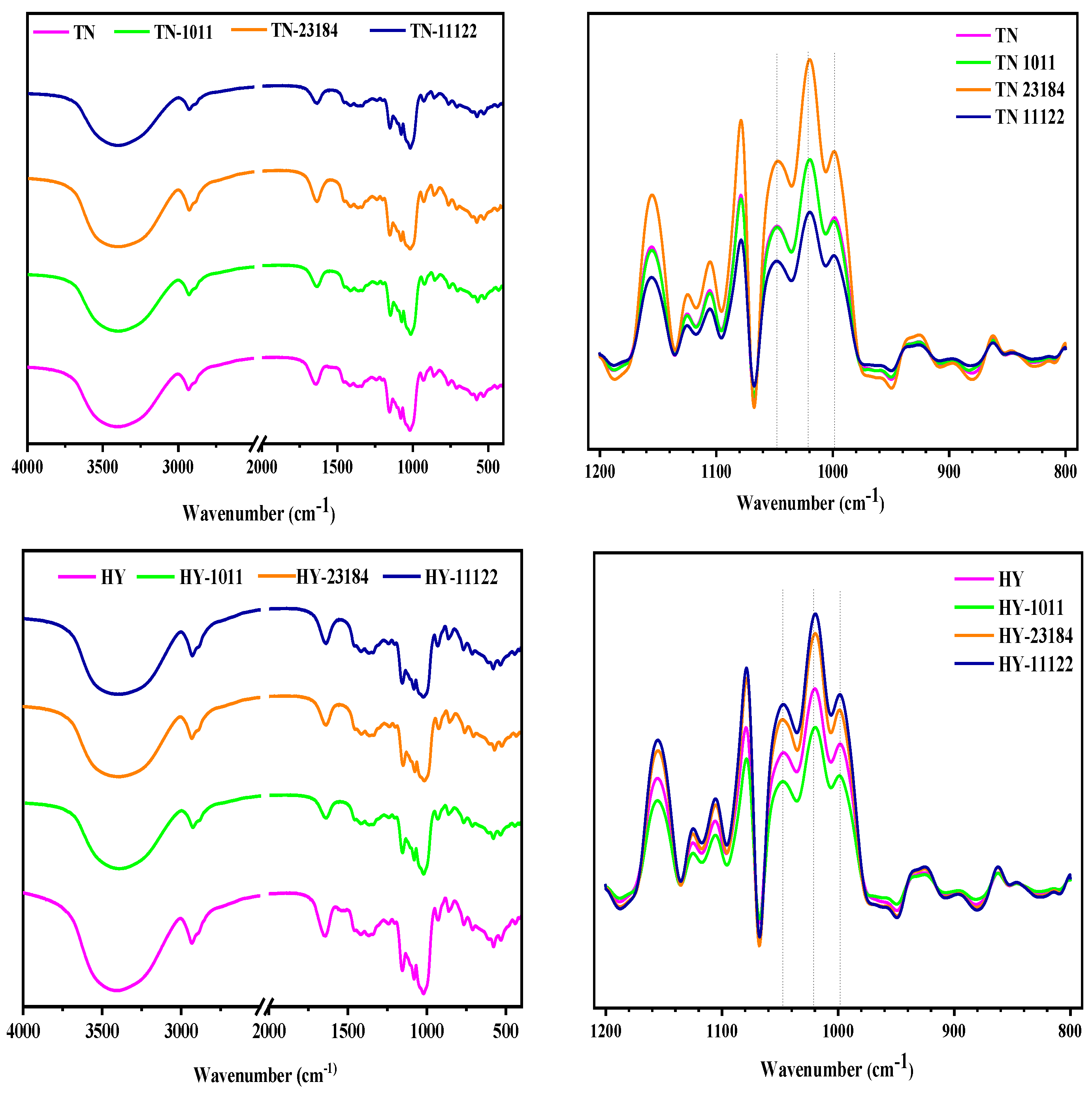
2.8. FTIR
2.9. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
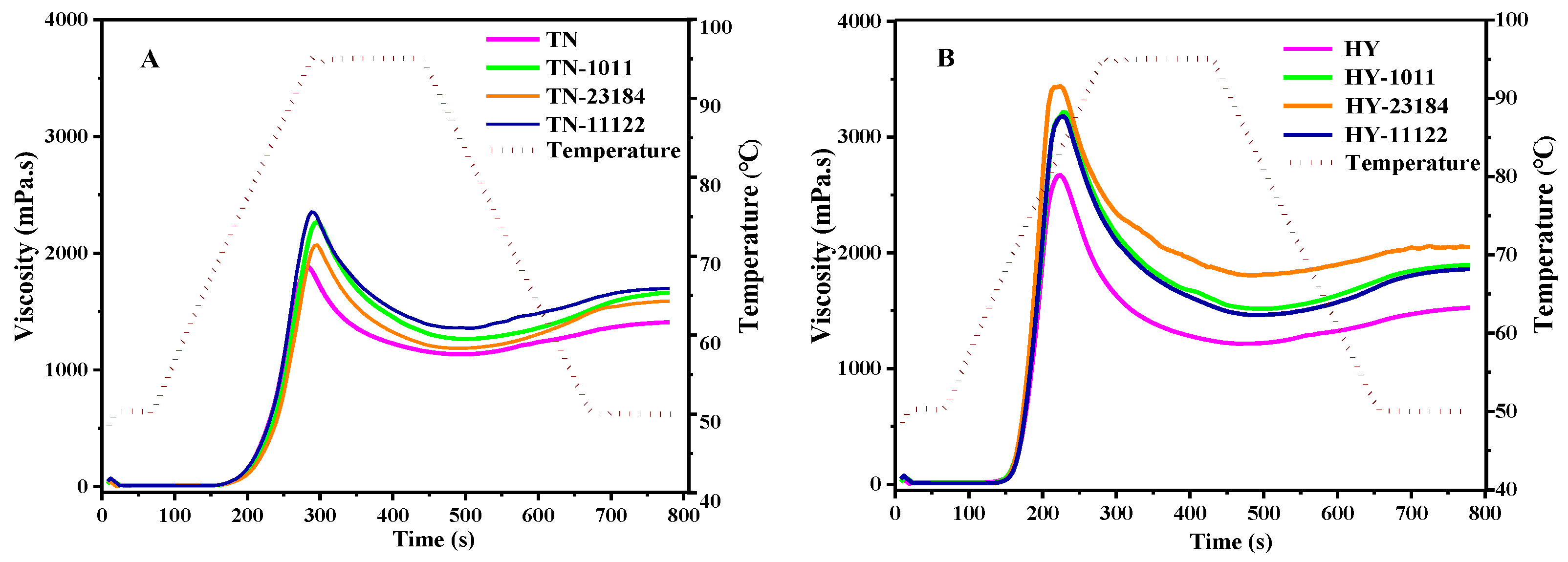
2.10. Pasting Properties
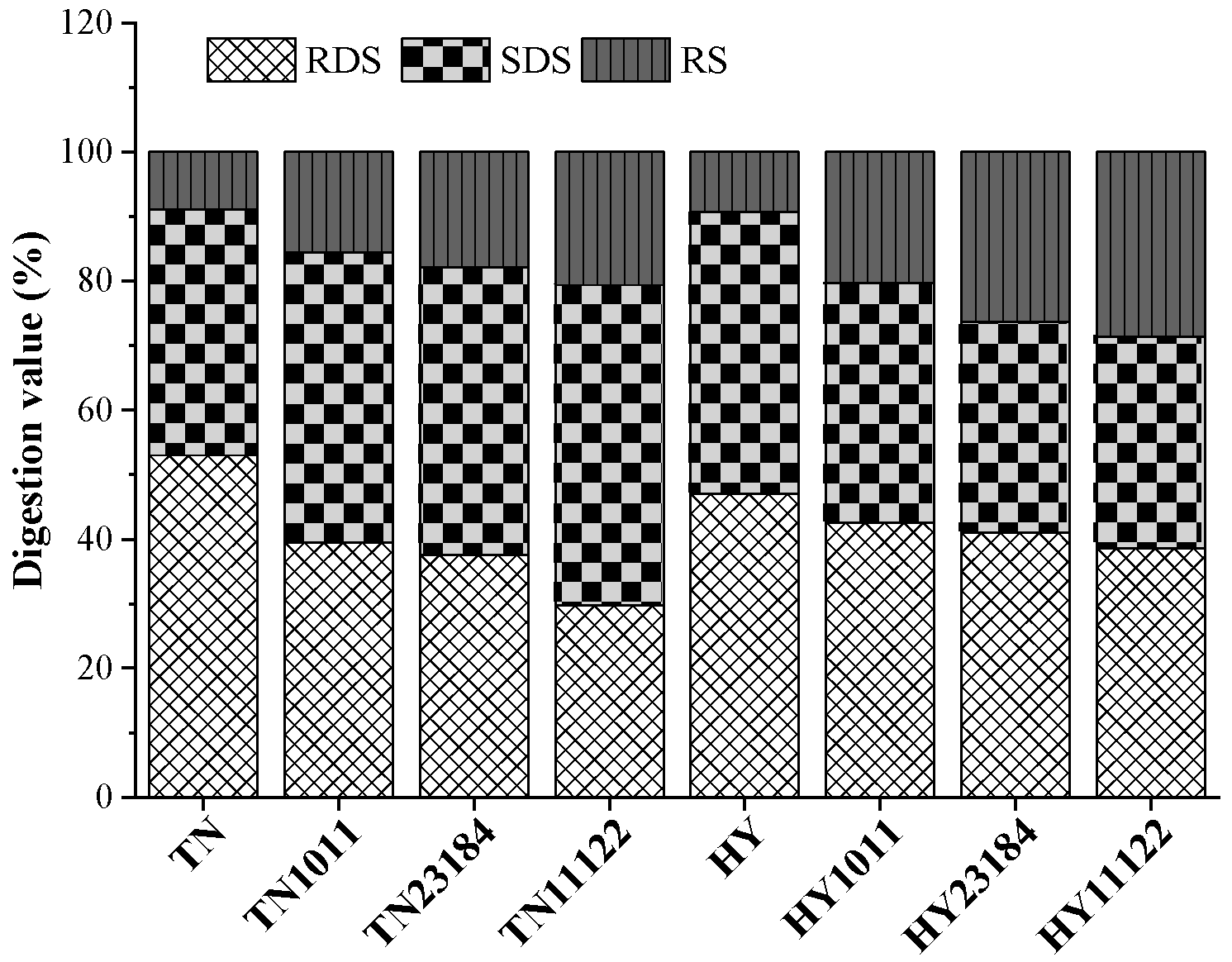
2.11. In Vitro Digestibility of Starch
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. pH Value, the Total Titratable Acidity, and Viable Cell Counts
3.2. Molecular Weight Distribution
3.3. Amylopectin Chain Length Distribution
3.4. Solid-State 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
3.5. X-Ray Diffraction Pattern and Crystallinity
3.6. Degree of Branching
3.7. Molecular Order by FTIR
3.8. Pasting Properties
3.9. Starch Digestibility Characteristics
3.10. Correlation Analysis and Principal Component Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LAB | Lactic Acid Bacteria |
| HY | Huaiyuannuo |
| TN2072 | Tenuo 2072 |
| TTA | Total titratable acidity |
| Mw | Weight average molecular weight |
| Rz | Radius of gyration |
| AM | Amorphous phase |
| RDS | Rapidly digestible starch |
| SDS | Slowly digestible starch |
| RS | Resistant starch |
References
- Liu, S.P.; Zhang, H.; Peng, J.L.; Yao, Z.; Han, X.; Liu, T.T.; Zhang, S.J.; Mao, J. Effects of degree of milling on japonica and glutinous rice used for huangjiu brewing physicochemical properties. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 183, 114825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincer, E.; Tekin, T. Fermentation of Commercial Resistant Starch Products by Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Various Foods. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2023, 66, e23230168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiseenko, K.V.; Glazunova, O.A.; Fedorova, T.V. Fermentation of Rice, Oat, and Wheat Flour by Pure Cultures of Common Starter Lactic Acid Bacteria: Growth Dynamics, Sensory Evaluation, and Functional Properties. Foods 2024, 13, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, P.; Petrov, K.; Stoyancheva, G. Starch-modifying enzymes of lactic acid bacteria—Structures, properties, and applications. Starch-Starke 2013, 65, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimini, A.; Morgante, L.; Moresi, M. Analyzing Cooking Efficiency of Gradoli Purgatory Beans: Effects of Dehulling, Malting, and Monovalent Carbonates. Foods 2024, 13, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barczynska, R.; Slizewska, K.; Jochym, K.; Kapusniak, J.; Libudzisz, Z. The tartaric acid-modified enzyme-resistant dextrin from potato starch as potential prebiotic. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Copeland, L. Effect of acid hydrolysis on starch structure and functionality: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1081–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Shi, Y.; Cong, T.; Liu, H.; Gao, Y. Preparation of lauric acid esterified starch by ethanol solvothermal process and its Pickering emulsion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 248, 125941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Jia, H.; Wang, B.; Ma, C.; He, F.; Fan, Q.; Liu, W. A Prospective Review on the Research Progress of Citric Acid Modified Starch. Foods 2023, 12, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, S.; Xiao, X. Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum dy-1 fermentation on multi-scale structure and physicochemical properties of barley starch. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 1923–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Xie, W.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, N.; Fan, H. Preparation of lactic acid bacteria compound starter cultures based on pasting properties and its improvement of glutinous rice flour and dough. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 2024, 2090–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Fan, H.; Wang, B.; Liu, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, N. Effects of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on the physicochemical and structural characteristics of starch in blends of glutinous and japonica rice. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 1623–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Hong, S.; Zhang, J.-R.; Liu, P.-H.; Li, S.; Wen, Z.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, G.; Habimana, O.; Shah, N.P.; et al. The effect of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on physicochemical properties of starch from fermented proso millet flour. Food Chem. 2024, 437, 137764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Fan, C.; Pan, C.; Zhang, F.; Hou, X.; Hui, M. Analysis of differences in physicochemical properties of different sorghum varieties and their influence on the selection of raw materials for winemaking. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Guo, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Wei, C. Comparative structure of starches from high-amylose maize inbred lines and their hybrids. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atichokudomchai, N.; Varavinit, S.; Chinachoti, P. A study of ordered structure in acid-modified tapioca starch by 13C CP/MAS solid-state NMR. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 58, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Li, X.; Boye, J.I. Molecular rearrangement of Laird lentil (Lens culinaris Medikus) starch during different processing treatments of the seeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boetje, L.; Lan, X.; van Dijken, J.; Woortman, A.J.; Popken, T.; Polhuis, M.; Loos, K. Starch ester film properties: The role of the casting temperature and starch its molecular weight and amylose content. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 316, 121043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Man, J.; Wei, C. Methods for Determining Relative Crystallinity of Plant Starch X-ray Powder Diffraction Spectra. Chin. Bull. Bot. 2012, 47, 278–285. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Yu, M.; Li, Y.; Zhu, S.; Huang, D. The synergistic effect of lactic acid bacteria fermentation combined with gluten on the starch digestive properties of highland barley. Food Biosci. 2024, 58, 103822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englyst, H.N.; Kingman, S.M.; Cummings, J.H. Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 46, S33–S50. [Google Scholar]
- Giraud, E.; Champailler, A.; Raimbault, M. Degradation of Raw Starch by a Wild Amylolytic Strain of Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 4319–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Östman, E. Fermentation as a Means of Optimizing the Glycaemic Index—Food Mechanisms and Metabolic Merits with Emphasis on Lactic Acid in Cereal Products. Ph.D. Thesis, Lund Institute of Technology, Lund, Sweden, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zimm, B.H. The Scattering of Light and the Radial Distribution Function of High Polymer Solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 1949, 16, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Chen, J.-R.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D.-H.; Ma, Z.-Q.; Ren, L.-K.; Wu, N.; Chen, F.-L.; Liu, X.-F.; Wang, B.; et al. Effects of fermentation on the structure and physical properties of glutinous proso millet starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Sun, X.; Du, Y.; Fang, Y.; Yang, W.; Hu, Q.; Pei, F. Effect of the starch structure fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum LB-1 and yeast on rheological and thermomechanical characteristics of dough. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benavent-Gil, Y.; Rosell, C.M. Morphological and physicochemical characterization of porous starches obtained from different botanical sources and amylolytic enzymes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wei, S.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Cui, L.; Wang, Y. The influence of cooperative fermentation on the structure, crystallinity, and rheological properties of buckwheat starch. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 8, 100670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanashiro, I.; Abe, J.-I.; Hizukuri, S. A periodic distribution of the chain length of amylopectin as revealed by high-performance anion-exchange chromatography. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 283, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Concha, B.B.S.; Agama-Acevedo, E.; Nuñez-Santiago, M.C.; Bello-Perez, L.A.; Garcia, H.S.; Alvarez-Ramirez, J. Acid hydrolysis of waxy starches with different granule size for nanocrystal production. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, Y.; Jiao, A.; Zhao, J.; Chen, X.; Wei, B.; Hu, X.; Wu, C.; Jin, Z.; Tian, Y. Impact of α-amylase combined with hydrochloric acid hydrolysis on structure and digestion of waxy rice starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 55, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.; Flanagan, B.M.; Halley, P.J.; Whittaker, A.K.; Gidley, M.J. A method for estimating the nature and relative proportions of amorphous, single, and double-helical components in starch granules by (13)C CP/MAS NMR. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Ma, M.; Sui, Z.; Corke, H. Lamellar structure changes in rice starch during α-amylase hydrolysis: Effect of starch granule surface and channel proteins. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, I.; Zhuo, G.-Y.; Chakraborty, I.; Melanthota, S.K.; Mal, S.S.; Sarmah, B.; Baruah, V.J.; Mahato, K.K.; Mazumder, N. Investigation of structural and physicochemical properties of rice starch with varied amylose content: A combined microscopy, spectroscopy, and thermal study. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Gui, Y.; Tao, H.; Zou, F.; Liu, P.; Janaswamy, S.; Cui, B. The effects of wheat amylose ratios on the structural and physicochemical properties of waxy rice starch using branching enzyme and glucoamylase. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhou, Q.; Li, E.; Yuan, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Gu, J. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on structure and physicochemical properties of “super” rice starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 239, 116237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello-Pérez, L.A.; Ottenhof, M.-A.; Agama-Acevedo, E.; Farhat, I.A. Effect of storage time on the retrogradation of banana starch extrudate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Yang, S.; Zhao, D.; Liu, J.; Wu, Q.; Yang, Q. Changes in Structural and Physicochemical Properties of Corn Flour after Fermentation with Lactobacillus plantarum Y1. Starch-Starke 2020, 72, 1900285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Sit, N. Modification of foxtail millet starch by combining physical, chemical and enzymatic methods. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 95, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Xu, R.; Zhan, J.; Chen, L.; Jin, Z.; Tian, Y. Pasting, rheology, and fine structure of starch for waxy rice powder with high-temperature baking. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.-Z.; Hamaker, B.R. Amylopectin Fine Structure and Rice Starch Paste Breakdown. J. Cereal Sci. 2001, 34, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Q.; Huang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Du, F.; Chen, Y.; Shen, J.; Luo, H.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Pueraria lobata starch regulates gut microbiota and alleviates high-fat high-cholesterol diet induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhu, H.; Yi, C.; Yuan, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Cheng, H. Digestibility of rice and structural changes of rice starch during fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 187, 115392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojarczuk, A.; Skąpska, S.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Marszałek, K. Health benefits of resistant starch: A review of the literature. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 93, 105094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamala, T.; Sreekantiah, K. Degradation of starchy substrates by a crude enzyme preparation and utilization of the hydrolysates for lactic fermentation. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1987, 9, 726–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Samples | Mw | Rz | PDI | Chain Length Distribution (%) | (A + B1)/(B2 + B3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ×105, kDa | (nm) | A | B1 | B2 | B3 | |||
| TN | 2.77 ± 0.10 ab | 333.95 ± 0.12 bc | 2.16 ± 0.09 a | 30.58 ± 0.73 b | 47.65 ± 0.52 b | 12.00 ± 0.05 c | 9.74 ± 0.25 a | 3.59 ± 0.03 b |
| TN1011 | 2.36 ± 0.07 c | 334.13 ± 0.31 b | 2.08 ± 0.13 a | 30.98 ± 0.32 b | 47.73 ± 0.44 b | 10.95 ± 0.12 d | 9.62 ± 0.12 a | 3.82 ± 0.13 a |
| TN23184 | 2.43 ± 0.05 b | 334.26 ± 0.21 b | 2.05 ± 0.08 a | 31.87 ± 0.19 ab | 47.72 ± 1.35 b | 11.03 ± 0.24 d | 9.54 ± 0.18 ab | 3.86 ± 0.11 a |
| TN11122 | 2.01 ± 0.04 d | 335.79 ± 0.36 a | 2.03 ± 0.14 a | 32.12 ± 0.06 a | 48.13 ± 0.16 b | 10.86 ± 0.18 d | 9.34 ± 0.11 b | 3.97 ± 0.08 a |
| HY | 2.96 ± 0.11 a | 333.58 ± 0.22 c | 2.21 ± 0.17 a | 24.13 ± 0.33 d | 51.16 ± 0.34 a | 15.63 ± 0.26 a | 8.26 ± 0.09 c | 3.18 ± 0.09 d |
| HY-1011 | 2.36 ± 0.06 c | 334.23 ± 0.34 b | 2.16 ± 0.09 a | 25.04 ± 0.26 cd | 51.23 ± 0.26 a | 14.83 ± 0.19 b | 8.11 ± 0.11 c | 3.32 ± 0.13 c |
| HY23184 | 2.43 ± 0.13 b | 335.63 ± 0.17 a | 2.13 ± 0.01 a | 25.33 ± 0.48 cd | 51.31 ± 0.12 a | 14.28 ± 0.25 b | 8.06 ± 0.09 cd | 3.43 ± 0.16 bc |
| HY11122 | 1.79 ± 0.02 d | 335.51 ± 0.06 a | 2.07 ± 0.06 a | 25.93 ± 0.14 c | 51.33 ± 1.09 a | 14.73 ± 0.09 b | 7.83 ± 0.17 d | 3.42 ± 0.14 bc |
| Sample | Crystallinity by XRD (%) | Double Helix by 13C-NMR (%) | Single Helix by 13C-NMR (%) | Amorphous by 13C-NMR (%) | Branching Degree (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN | 27.06 ± 0.16 e | 62.26 ± 0.36 b | 3.21 ± 0.09 b | 34.53 ± 0.17 ab | 11.53 ± 0.32 d |
| TN-1011 | 35.93 ± 0.25 b | 64.21 ± 0.21 a | 4.36 ± 0.05 ab | 31.43 ± 0.23 c | 13.21 ± 0.26 c |
| TN-23184 | 39.65 ± 0.09 a | 62.21 ± 0.42 b | 4.88 ± 0.09 ab | 32.91 ± 0.35 bc | 16.70 ± 0.41 b |
| TN-11122 | 39.15 ± 0.31 a | 64.55 ± 0.16 a | 5.43 ± 0.11 a | 30.02 ± 0.29 d | 18.05 ± 0.39 a |
| HY | 31.04 ± 0.19 d | 62.85 ± 0.09 b | 1.23 ± 0.03 c | 35.92 ± 0.18 a | 12.07 ± 0.55 d |
| HY-1011 | 33.01 ± 0.27 c | 63.39 ± 0.34 ab | 3.31 s ± 0.10 b | 33.00 ± 0.36 b | 14.25 ± 0.63 bc |
| HY-23184 | 38.12 ± 0.04 a | 64.27 ± 0.29 a | 2.84 ± 0.05 bc | 32.89 ± 0.32 bc | 16.07 ± 0.39 b |
| HY-11122 | 39.54 ± 0.11 a | 64.74 ± 0.18 a | 3.43 ± 0.03 b | 31.83 ± 0.29 c | 19.65 ± 0.21 a |
| Sample | DO (1047/1022 cm−1) | DD (995/1022 cm−1) |
|---|---|---|
| TN | 0.9316 ± 0.0008 d | 0.4895 ± 0.0003 e |
| TN-1011 | 0.9883 ± 0.0004 b | 0.5000 ± 0.0004 d |
| TN-23184 | 1.0377 ± 0.0007 a | 0.5179 ± 0.0005 d |
| TN-11122 | 1.0328 ± 0.0019 a | 0.5778 ± 0.0006 b |
| HY | 0.9600 ± 0.0003 c | 0.5509 ± 0.0012 c |
| HY-1011 | 0.9876 ± 0.0004 b | 0.5597 ± 0.0009 c |
| HY-23184 | 0.9614 ± 0.0002 c | 0.5984 ± 0.0008 b |
| HY-11122 | 0.9954 ± 0.0006 ab | 0.6532 ± 0.0003 a |
| Sample | PV (cP) | TV (cP) | BD (cP) | FV (cP) | SB (cP) | GT (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN | 1882 ± 43 f | 1135 ± 39 d | 747 ± 13 e | 1408 ± 17 e | 273 ± 9 c | 76.65 ± 0.13 b |
| TN-1011 | 2268 ± 66 d | 1265 ± 46 c | 1003 ± 16 c | 1662 ± 19 c | 397 ± 8 a | 77.4 ± 0.22 ab |
| TN-23184 | 2070 ± 39 e | 1168 ± 25 d | 884 ± 14 d | 1590 ± 25 cd | 404 ± 11 a | 78.38 ± 0.19 a |
| TN-11122 | 2143 ± 51 de | 1231 ± 23 c | 912 ± 11 cd | 1610 ± 29 cd | 379 ± 12 ab | 77.5 ± 0.23 ab |
| HY | 2673 ± 53 c | 1215 ± 31 c | 1458 ± 19 b | 1526 ± 33 d | 311 ± 9 b | 69.25 ± 0.12 c |
| HY-1011 | 3217 ± 62 b | 1518 ± 27 b | 1699 ± 29 a | 1895 ± 16 b | 377 ± 7 ab | 68.55 ± 0.09 d |
| HY-23184 | 3439 ± 49 a | 1805 ± 31 a | 1634 ± 14 a | 2049 ± 14 a | 244 ± 12 c | 68.55 ± 0.13 d |
| HY-11122 | 3182 ± 61 b | 1464 ± 26 b | 1718 ± 18 a | 1859 ± 12 b | 395 ± 11 a | 69.30 ± 0.17 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, D.; Zhang, J.; Shao, T.; Li, Y.; He, H.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Cao, R.; Li, A.; Du, X. Modification of Structure, Pasting, and In Vitro Digestion Properties of Glutinous Rice Starch by Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation. Foods 2025, 14, 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030367
Shao D, Zhang J, Shao T, Li Y, He H, Wang Y, Ma J, Cao R, Li A, Du X. Modification of Structure, Pasting, and In Vitro Digestion Properties of Glutinous Rice Starch by Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation. Foods. 2025; 14(3):367. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030367
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Dongliang, Jigang Zhang, Tiantian Shao, Yuhui Li, Hongkui He, Yanli Wang, Jintong Ma, Runjie Cao, Anjun Li, and Xianfeng Du. 2025. "Modification of Structure, Pasting, and In Vitro Digestion Properties of Glutinous Rice Starch by Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation" Foods 14, no. 3: 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030367
APA StyleShao, D., Zhang, J., Shao, T., Li, Y., He, H., Wang, Y., Ma, J., Cao, R., Li, A., & Du, X. (2025). Modification of Structure, Pasting, and In Vitro Digestion Properties of Glutinous Rice Starch by Different Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation. Foods, 14(3), 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14030367




