Mycotoxins Co-Exposure Risk Assessment in Coix Seed: Contamination Levels and Safety for Dietary Consumption and Medicinal Intake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical and Standards
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. QuEChERS Sample Preparation
2.4. Decoction Sample Preparation
2.5. Mycotoxins Determination by HPLC-MS/MS
2.6. Method Validation
2.7. Risk Assessment
2.8. Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) Estimation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
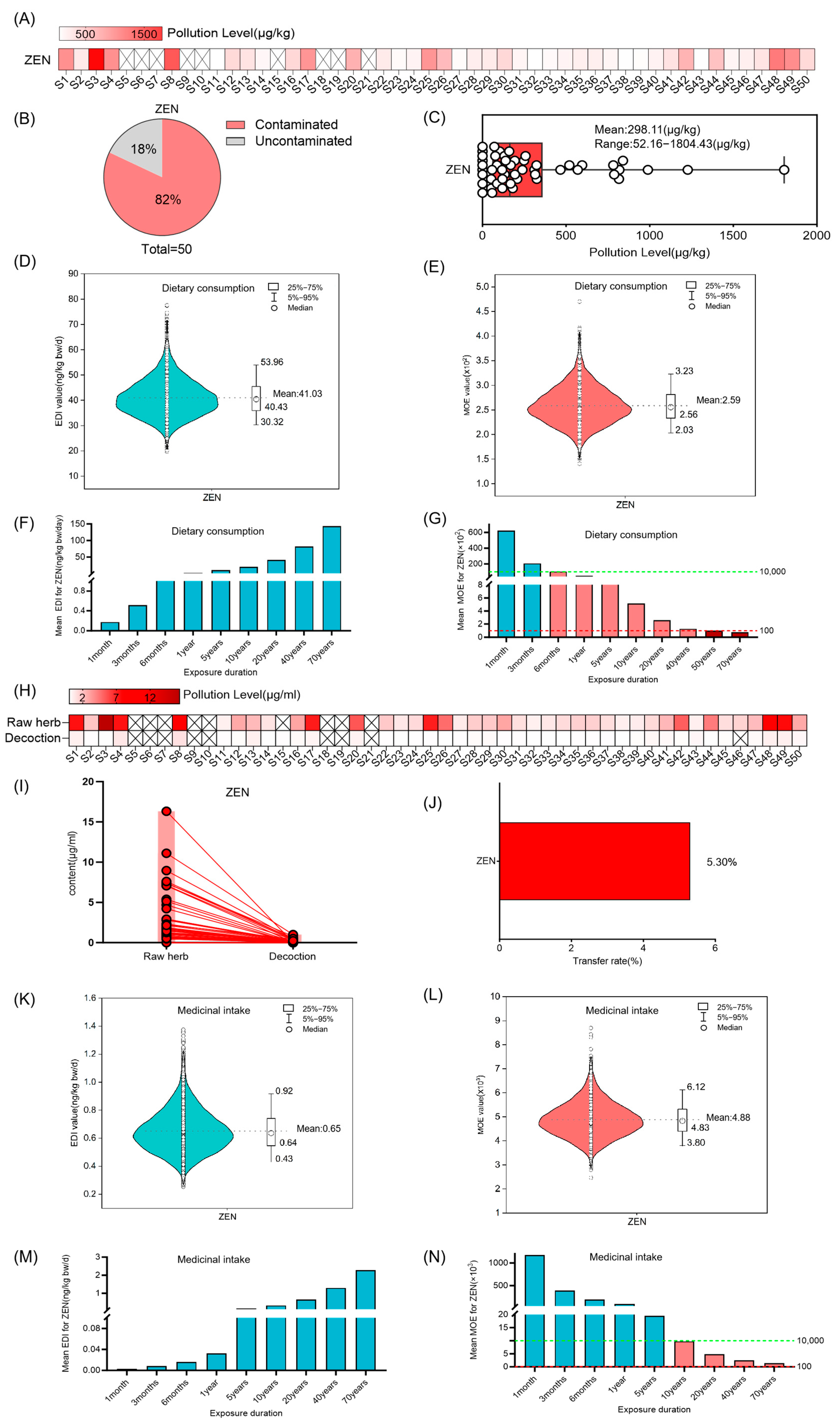
3.1. Risk Assessment for ZEN in Coix Seed for Dietary Consumption and Medicinal Intake
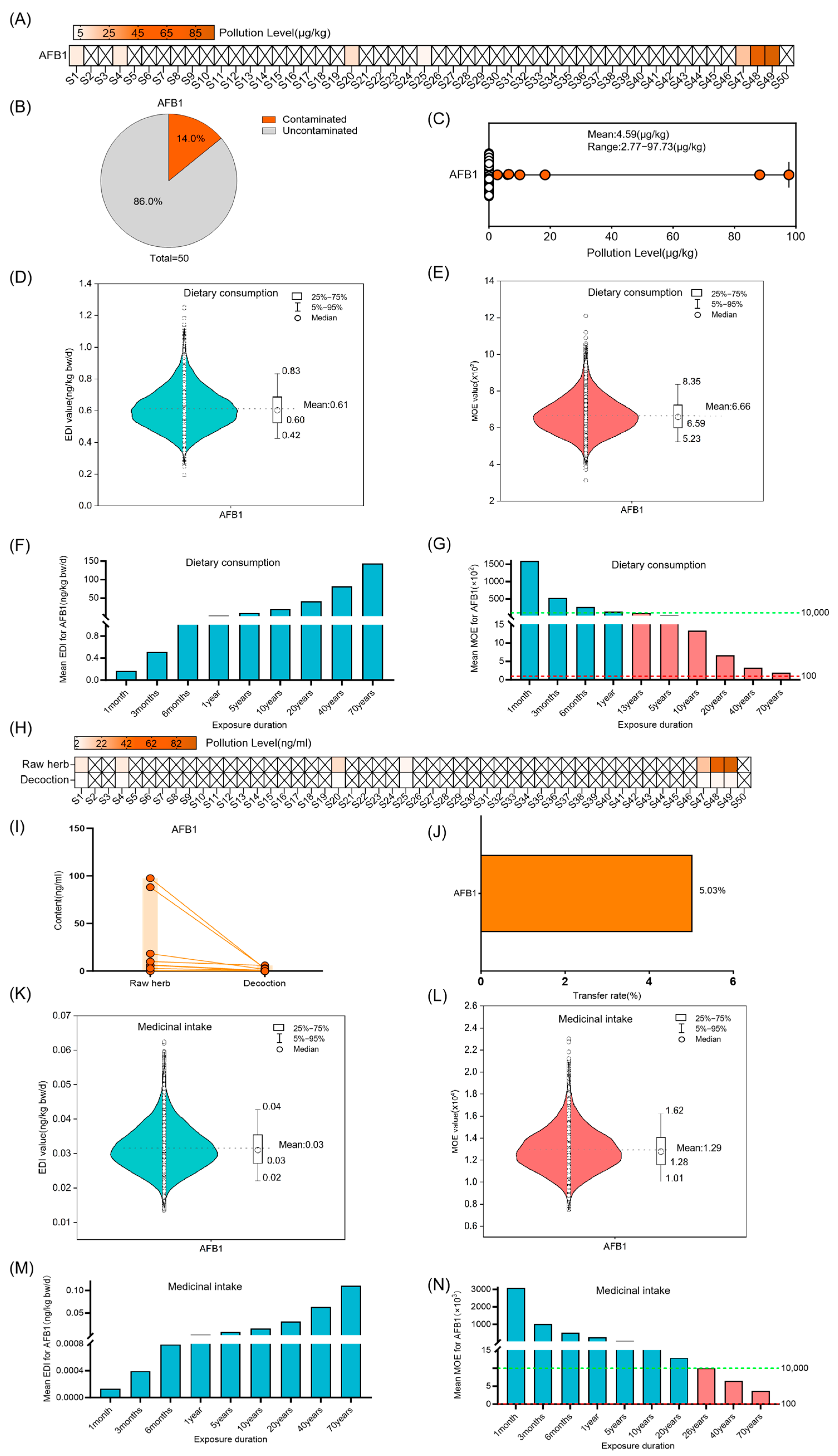
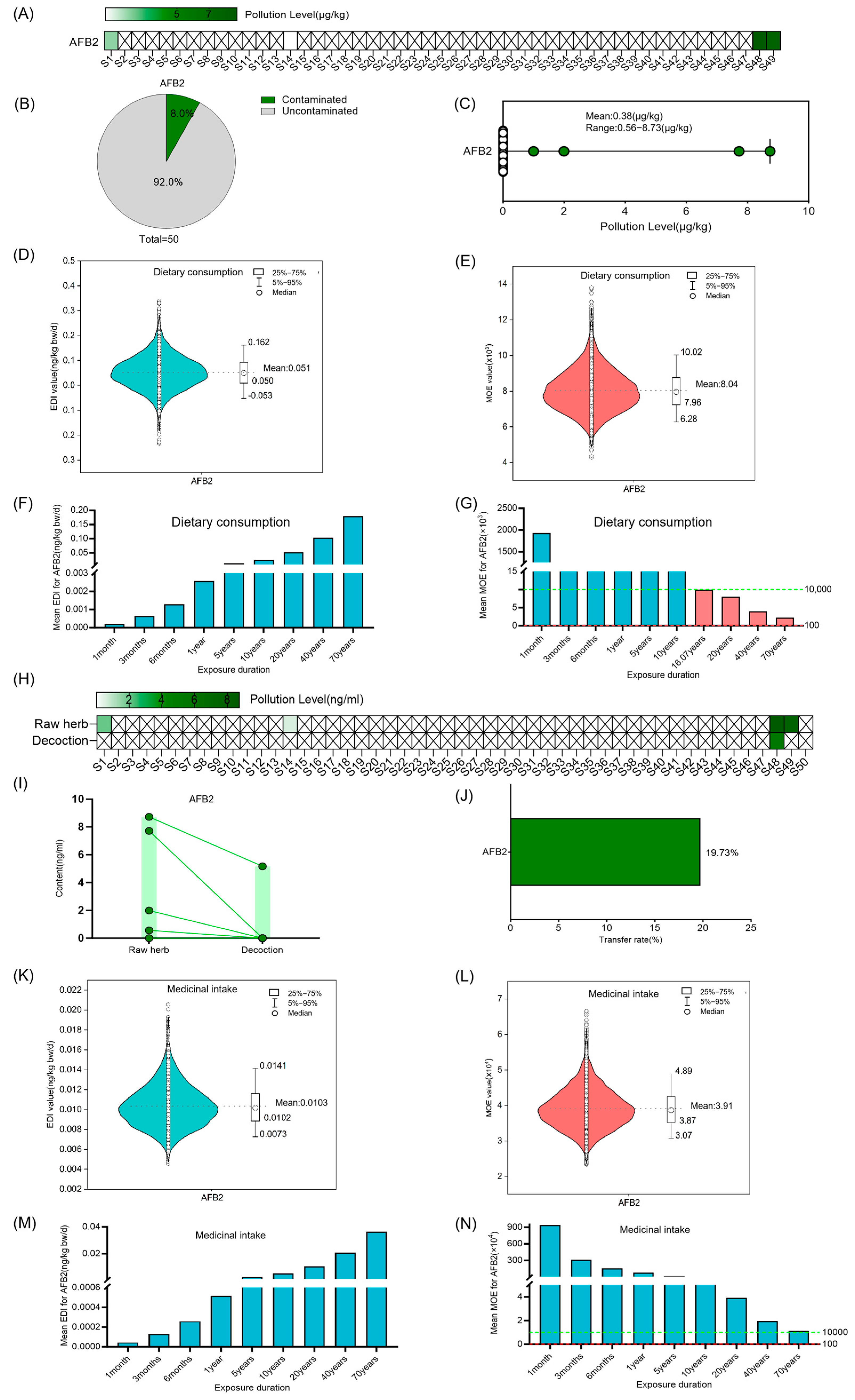
3.2. Risk Assessment for AFs in Coix Seed for Dietary Consumption and Medicinal Intake
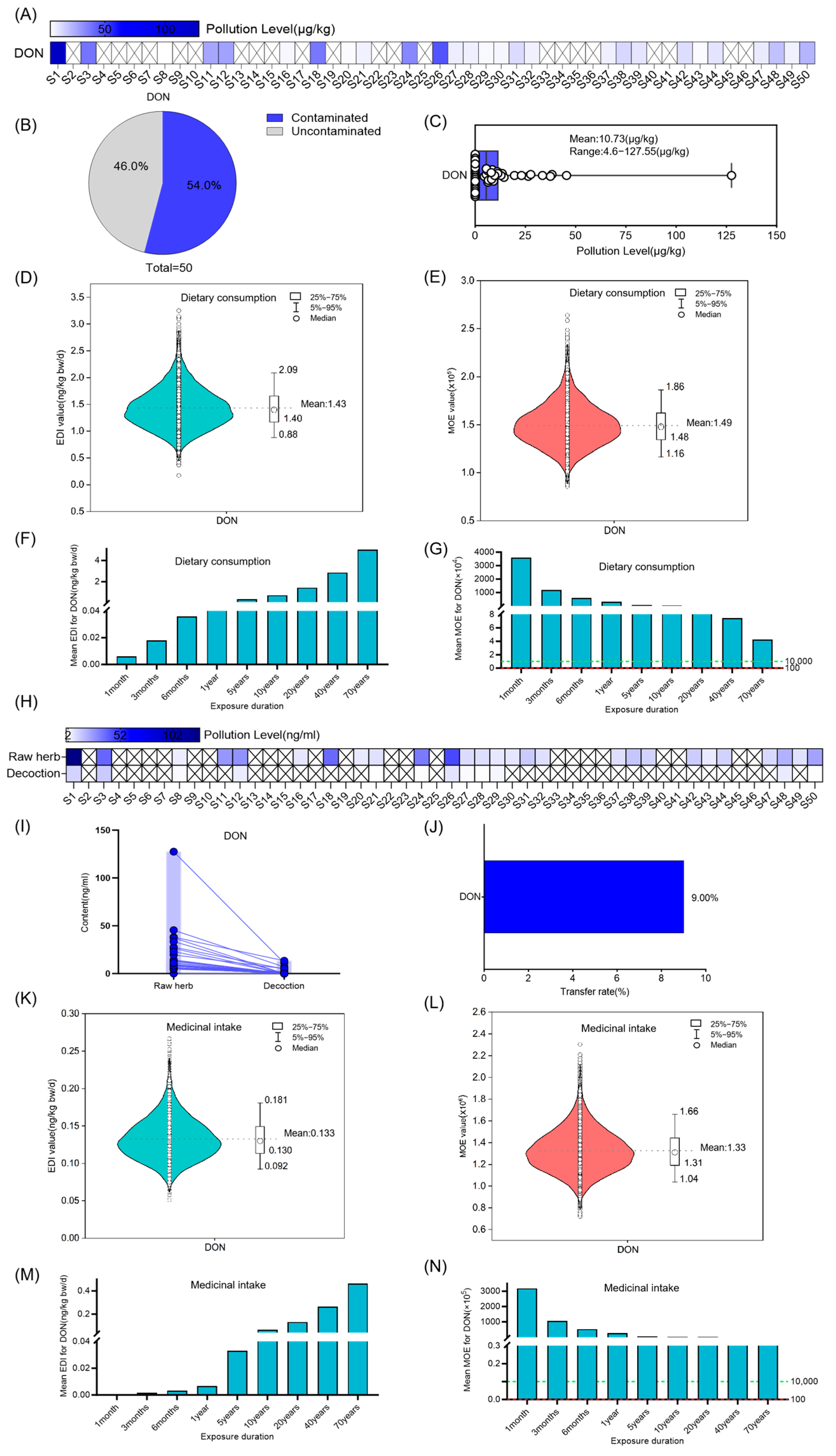
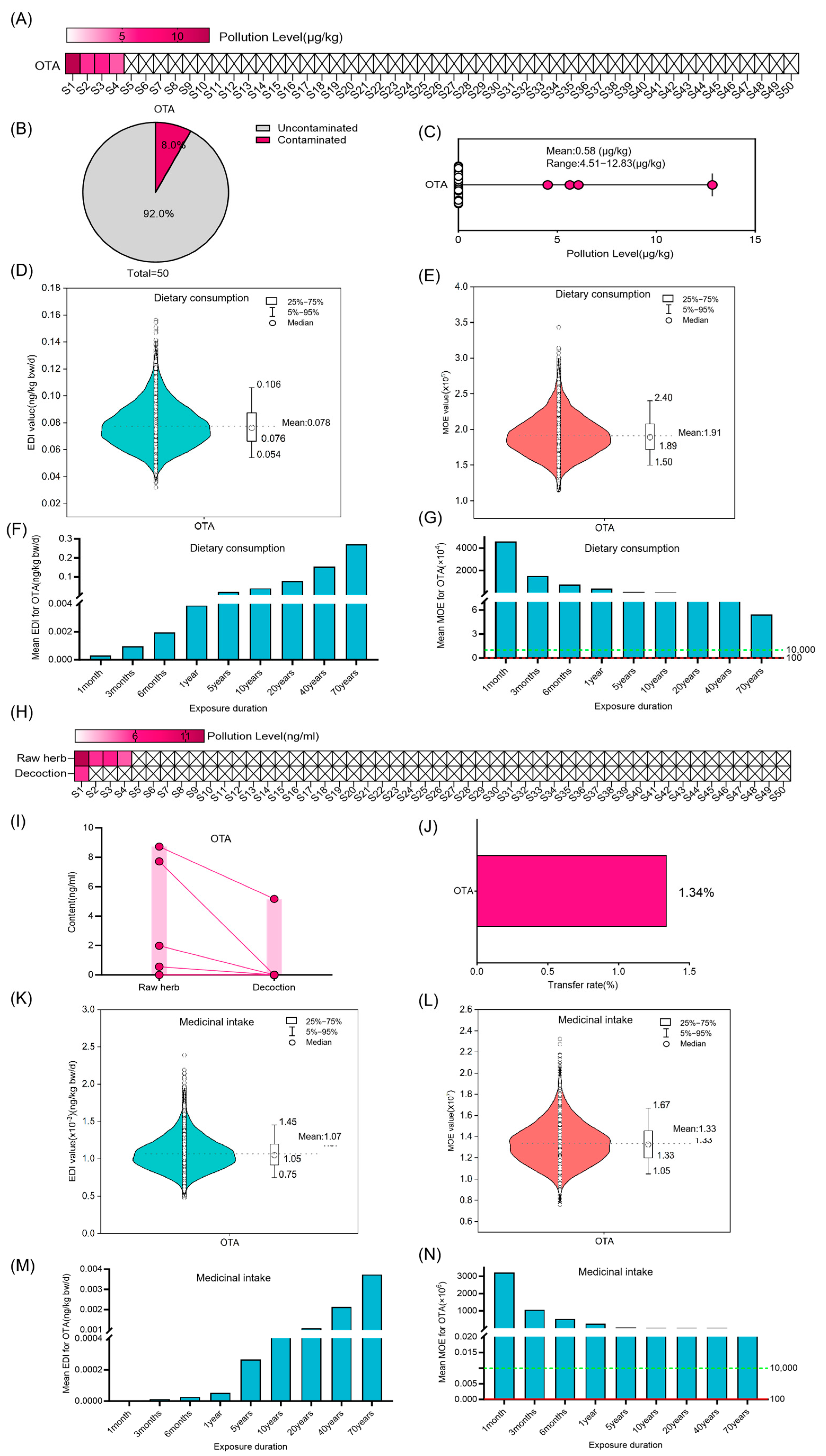
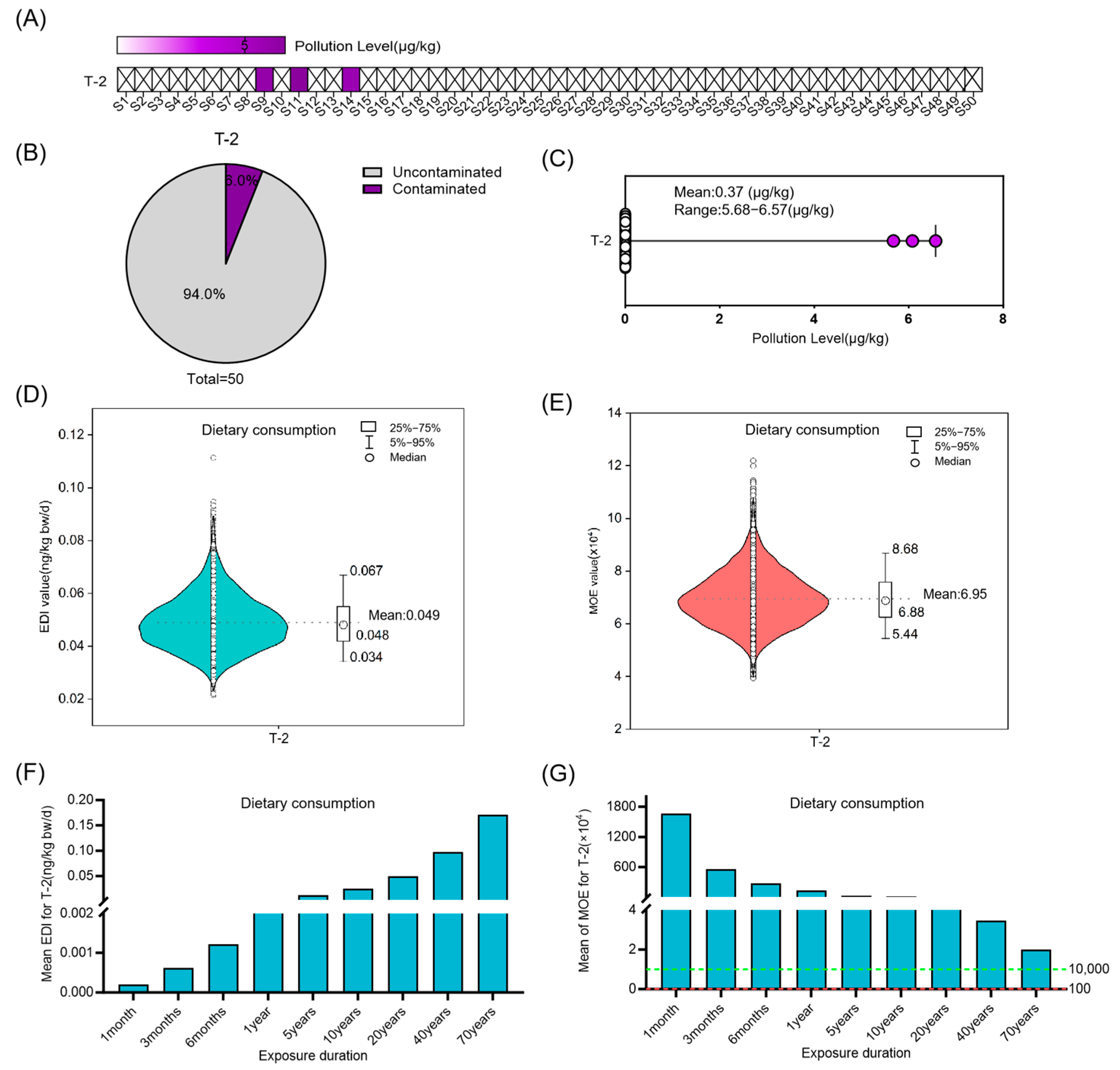
3.3. Risk Assessment for ST, DON OTA and T-2 in Coix Seed for Dietary Consumption and Medicinal Intake
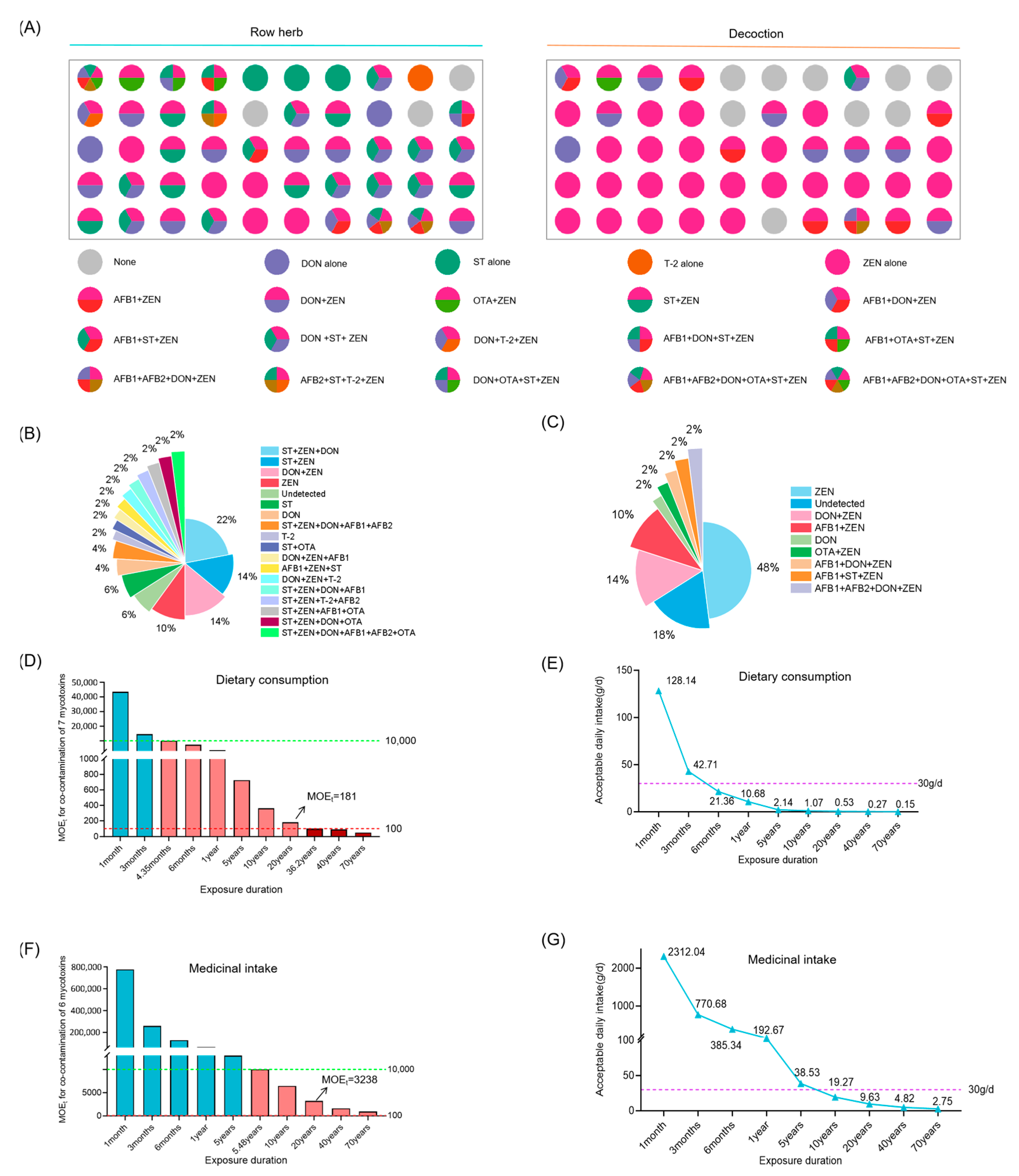
3.4. Risk Assessment of Multi-Mycotoxin Co-Exposure in Coix Seed for Dietary Consumption and Medicinal Intake
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADI | Acceptable daily intake |
| AFB1 | Aflatoxin B1 |
| AFB2 | Aflatoxin B2 |
| Afs | Aflatoxins |
| AY | Average Life Expectancy (Year) |
| BMDL10 | Benchmark Dose Lower Confidence Limit (for a 10% response) |
| BW | Average Body Weight |
| DON | Deoxynivalenol |
| ED | Exposure Duration |
| EDI | Estimated Daily Intake |
| HT-2 | HT-2 Toxin |
| IC | Daily intake of Coix seed |
| LOD | Limit of Detection |
| LOQ | Limit of Quantification |
| MD | Mycotoxin Content in Decoction |
| MOE | Margin of Exposure |
| MR | Mycotoxin Content in Raw Material |
| MRM | Multiple Reaction Monitoring |
| NOAEL | No-Observed-Adverse-Effect Level |
| OTA | Ochratoxin A |
| ST | Sterigmatocystin |
| T-2 | T-2 Toxin |
| ZEN | Zearalenone |
References
- Li, H.; Peng, L.; Yin, F.; Fang, J.; Cai, L.; Zhang, C.; Xiang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sheng, H.; et al. Research on Coix seed as a food and medicinal resource, it’s chemical components and their pharmacological activities: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319 Pt 3, 117309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, S.; Guo, C.; Dong, X.; Li, Q.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L. The Differences of Nutrient Components in Edible and Feeding Coix Seed at Different Developmental Stages Based on a Combined Analysis of Metabolomics. Molecules 2023, 28, 3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Yang, Y.; He, L.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Zeng, X. Flavor, physicochemical properties, and storage stability of P. lobata-coix seed fermented beverage produced by A. aegerita. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Ji, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, S. Mechanisms of Coix Seed Compositions in the Treatment of Spleen Deficiency and Wet Dampness Zheng. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 14, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Zhu, W.; Ge, W.; Li, C. Research on the effect of spleen-invigorating and anti-swelling active ingredients in crude and processed coix seed based on Spectrum—Effects relationship combined with chemometrics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 205, 114350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wu, S.; Jiang, Q.; Jiao, J. Therapeutic efficacy of Roujin formula in managing fibromyalgia patients with liver depression and spleen deficiency syndrome: A single-blinded randomized controlled trial. Sci. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2025, 3, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.F.; Peng, Y.; Pan, X.; Yan, J.; Li, X.D.; Liao, Z.Y.; Cheng, J.P.; Gao, A.J.; Yao, X.; Ruan, J.J.; et al. Adlay, an ancient functional plant with nutritional quality, improves human health. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1019375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ye, J.; Xuan, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, S. Development and validation of a rapid and efficient method for simultaneous determination of mycotoxins in coix seed using one-step extraction and UHPLC-HRMS. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2021, 38, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.; Chang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Bai, Y.; Qiu, G.; Pang, G.; Wang, K.; Zhao, M.; et al. Simultaneous determination of pesticides, mycotoxins and ferulic acid in Angelica sinensis by GC/LC-Q-TOF/MS. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1737, 465437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; Wallace, H. Risk assessment of aflatoxins in food. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Scientific Opinion on the risks for public health related to the presence of zearalenone in food. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Deoxynivalenol in food and feed: Occurrence and exposure. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutsen, H.K.; Barregård, L.; Bignami, M.; Brüschweiler, B.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cottrill, B.; Dinovi, M.; Edler, L.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; et al. Appropriateness to set a group health based guidance value for T2 and HT2 toxin and its modified forms. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarik, Y.; Boyetey, S.T.; Aikins, A.R.; Mutocheluh, M. Effect of Ochratoxin A (OTA) on the Immune System: A Systematic Review. Toxins 2025, 17, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui-Klimke, T.R.; Wu, F. Ochratoxin A and human health risk: A review of the evidence. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1860–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Rajput, S.A.; Al Zoubi, O.M.; Wang, S.; Qi, D. Effect of zearalenone on aflatoxin B1-induced intestinal and ovarian toxicity in pregnant and lactating rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 258, 114976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, K.; Huang, R.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, A.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L. Development of a Reliable ic-ELISA with a Robust Antimatrix Interference Capability Based on QuEChERS Technology for the Rapid Detection of Zearalenone in Edible and Medical Coix Seeds and Subsequent Risk Assessments. Foods 2022, 11, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Xu, W.; Ni, L.; Chen, H.; Hu, X.; Lin, H. Development of a sensitive simultaneous analytical method for 26 targeted mycotoxins in coix seed and Monte Carlo simulation-based exposure risk assessment for local population. Food Chem. 2024, 435, 137563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Li, Y.; Long, N.; Xu, Q.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L.; Kong, W. Multi-mycotoxin detection and human exposure risk assessment in medicinal foods. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kuang, F.; Liu, C.; Ma, K.; Liu, T.; Zhao, M.; Lv, G.; Huang, H. Contamination and Health Risk Assessment of Multiple Mycotoxins in Edible and Medicinal Plants. Toxins 2023, 15, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Ying, X.; Hu, Q.; Wang, X.; Ji, S.; Cai, Q. Exposure assessment and risk-based limit levels evaluation of ochratoxin A in Astragali Radix in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 237, 113517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dou, X.W.; Zhang, C.; Logrieco, A.F.; Yang, M.H. A Review of Current Methods for Analysis of Mycotoxins in Herbal Medicines. Toxins 2018, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, A.C.; Weaver, D.M.; Adams, N.; Yiannikouris, A. Co-Occurrence of 35 Mycotoxins: A Seven-Year Survey of Corn Grain and Corn Silage in the United States. Toxins 2021, 13, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Attiya, W.; Hassan, Z.U.; Al-Thani, R.; Jaoua, S. Prevalence of toxigenic fungi and mycotoxins in Arabic coffee (Coffea arabica): Protective role of traditional coffee roasting, brewing and bacterial volatiles. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Su, D.; Yuan, Q.; Xiao, C.; Hu, M.; Guo, L.; Kang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, T. Simultaneous detection of multiple mycotoxins in Radix Dipsaci and estimation of exposure risk for consumers. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, M.; Freitas, A.; Barbosa, J.; Ramos, F. Mycotoxins in Portuguese Agricultural Maize Fields and Dairy Farms. Toxins 2024, 16, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.W.; Yang, C.G.; Jiang, W.K.; Zhang, J.Q.; Yuan, Q.S.; Zhang, H.X.; Liu, X.; Wen, N.T.; Zhou, T. Methods for synchronous detection of 14 mycotoxins in Pseudostellariae Radix and investigation on its contamination. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2022, 47, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.J.; Lambert, J.C.; Thayer, K.; Dorne, J.C.M. Sourcing data on chemical properties and hazard data from the US-EPA CompTox Chemicals Dashboard: A practical guide for human risk assessment. Environ. Int. 2021, 154, 106566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Su, B.; Yan, X.; Geng, C.; Lian, T.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y. Studies of Mycotoxins in Medicinal Plants Conducted Worldwide over the Last Decade: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Exposure Risk Assessment. Phytomedicine 2024, 128, 155367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsauliya, K.; Yahavi, C.; Pandey, A.; Bhateria, M.; Sonker, A.K.; Pandey, H.; Sharma, M.; Singh, S.P. Co-occurrence of mycotoxins: A review on bioanalytical methods for simultaneous analysis in human biological samples, mixture toxicity and risk assessment strategies. Toxicon 2022, 218, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Scientific opinion on the risk for public and animal health related to the presence of sterigmatocystin in food and feed. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malir, F.; Pickova, D.; Toman, J.; Grosse, Y.; Ostry, V. Hazard characterisation for significant mycotoxins in food. Mycotoxin Res. 2023, 39, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Evaluation of the increase of risk for public health related to a possible temporary derogation from the maximum level of deoxynivalenol, zearalenone and fumonisins for maize and maize products. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Feng, R.; Hu, Q.; Mao, X.; Zhou, H. Contamination Status and Health Risk Assessment of 73 Mycotoxins in Four Edible and Medicinal Plants Using an Optimized QuEChERS Pretreatment Coupled with LC-MS/MS. Toxins 2025, 17, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.L.; Wang, M.M.; Ma, Z.Y.; Raza, M.; Zhao, P.; Liang, J.M.; Gao, M.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, J.W.; Hu, D.M.; et al. Fusarium diversity associated with diseased cereals in China, with an updated phylogenomic assessment of the genus. Stud. Mycol. 2023, 104, 87–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, B.; Marin, S.; Kiaitsi, E.; Magan, N.; Verheecke-Vaessen, C.; Cervini, C.; Rubio-Lopez, F.; Garcia-Cela, E. Fusarium graminearum and zearalenone in wheat: A water activity-temperature model. Fungal Biol. 2025, 129, 101572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhai, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Jia, Q.; Liang, Z.; Wang, D. Genome-wide analysis of the HSP20 gene family and its response to heat and drought stress in Coix (Coix lacryma-jobi L.). BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, B. Optimization for the Production of Deoxynivalenoland Zearalenone by Fusarium graminearum UsingResponse Surface Methodology. Toxins 2017, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piontek, M.; Łuszczyńska, K.; Lechów, H. Occurrence of the Toxin-Producing Aspergillus versicolor Tiraboschi in Residential Buildings. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gündüz, A.; Yalçın, E.; Çavuşoğlu, K. Combined toxic effects of aflatoxin B(2) and the protective role of resveratrol in Swiss albino mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleadin, J.; Frece, J.; Markov, K. Mycotoxins in food and feed. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2019, 89, 297–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Guo, X.; Liang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, G.; Liang, C.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, S.; Dong, L. Occurrence of fungi and mycotoxins in herbal medicines and rapid detection of toxin-producing fungi. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 122082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Safety evaluation of certain contaminants in food. Prepared by the Sixty-fourth meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). FAO Food Nutr. Pap. 2006, 82, 1–778. [Google Scholar]
- Alassane-Kpembi, I.; Schatzmayr, G.; Taranu, I.; Marin, D.; Puel, O.; Oswald, I.P. Mycotoxins co-contamination: Methodological aspects and biological relevance of combined toxicity studies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3489–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, F.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Zhao, S.; Guan, X.; Li, D. Close association between the synergistic toxicity of zearalenone-deoxynivalenol combination and microRNA221-mediated PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling in HepG2 cells. Toxicology 2022, 468, 153104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Liu, W.; Zhao, L.; Cao, L.; Shen, Z. Low doses of individual and combined deoxynivalenol and zearalenone in naturally moldy diets impair intestinal functions via inducing inflammation and disrupting epithelial barrier in the intestine of piglets. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 333, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Zhang, N.; Qi, D. In vitro investigation of individual and combined cytotoxic effects of aflatoxin B1 and other selected mycotoxins on the cell line porcine kidney 15. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 65, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Zheng, N.; Fan, C.; Cheng, M.; Wang, S.; Jabar, A.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J. Effects of aflatoxin B1 combined with ochratoxin A and/or zearalenone on metabolism, immune function, and antioxidant status in lactating dairy goats. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, J.; Sun, Y.; Ji, H.; Liu, F.; Peng, X.; Zhong, Y.; Geng, F.; Nie, S. In vitro digestion of eight types of wholegrains and their dietary recommendations for different populations. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Luo, X.; Liu, J.; Yao, M.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Huang, L.; Sun, X. Promoting international acceptance of clinical studies about traditional Chinese medicine interventions. Sci. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2025, 3, 10-1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, Y.; Wang, H.; Ying, G.; Yang, M.; Wang, Z.; Kong, W.; Yang, S. Transfer rates of aflatoxins from herbal medicines to decoctions determined by an optimized high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection method. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 70, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Tong, X.; Lu, F.; Mao, W.; Fu, L.; Deng, L.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; et al. The effect of coix seed on the nutritional status of peritoneal dialysis patients: A pilot study. Complement. Ther. Med. 2014, 22, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.D.; Yuan, L.; Lu, D.D.; Yang, Y.T.; Xu, D.J.; Che, M.Y.; Nan, Y. Anti-tumor effect of coix seed based on the theory of medicinal and food homology. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 14, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Wang, L.; Yuan, Q.; Guo, L.; Kang, C.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, C.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, T. Mycotoxins Co-Exposure Risk Assessment in Coix Seed: Contamination Levels and Safety for Dietary Consumption and Medicinal Intake. Foods 2025, 14, 3965. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223965
Han Y, Wang L, Yuan Q, Guo L, Kang C, Yang Y, Xiao C, Yang C, Zhang J, Zhou T. Mycotoxins Co-Exposure Risk Assessment in Coix Seed: Contamination Levels and Safety for Dietary Consumption and Medicinal Intake. Foods. 2025; 14(22):3965. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223965
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yue, Lulu Wang, Qingsong Yuan, Lanping Guo, Chuanzhi Kang, Ye Yang, Chenghong Xiao, Changgui Yang, Jinqiang Zhang, and Tao Zhou. 2025. "Mycotoxins Co-Exposure Risk Assessment in Coix Seed: Contamination Levels and Safety for Dietary Consumption and Medicinal Intake" Foods 14, no. 22: 3965. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223965
APA StyleHan, Y., Wang, L., Yuan, Q., Guo, L., Kang, C., Yang, Y., Xiao, C., Yang, C., Zhang, J., & Zhou, T. (2025). Mycotoxins Co-Exposure Risk Assessment in Coix Seed: Contamination Levels and Safety for Dietary Consumption and Medicinal Intake. Foods, 14(22), 3965. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223965






