Effects of Treatment Methods on the Formation, Structure, and Functional Properties of Soy Protein Amyloid Fibrils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of SPAF
2.3. Characteristics of SPAF
2.3.1. FTIR
2.3.2. ThT Fluorescence
2.3.3. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
2.3.4. SEM
2.3.5. H0
2.3.6. XRD
2.3.7. Dityrosine
2.3.8. Thermal Stability
2.3.9. Solubility
2.3.10. Turbidity
2.3.11. Free Sulfhydryl Groups (Free-SH), Total Sulfhydryl (Total-SH), and Disulfide Bonds (S–S)
2.3.12. EAI and ESI
2.3.13. FC and FS
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
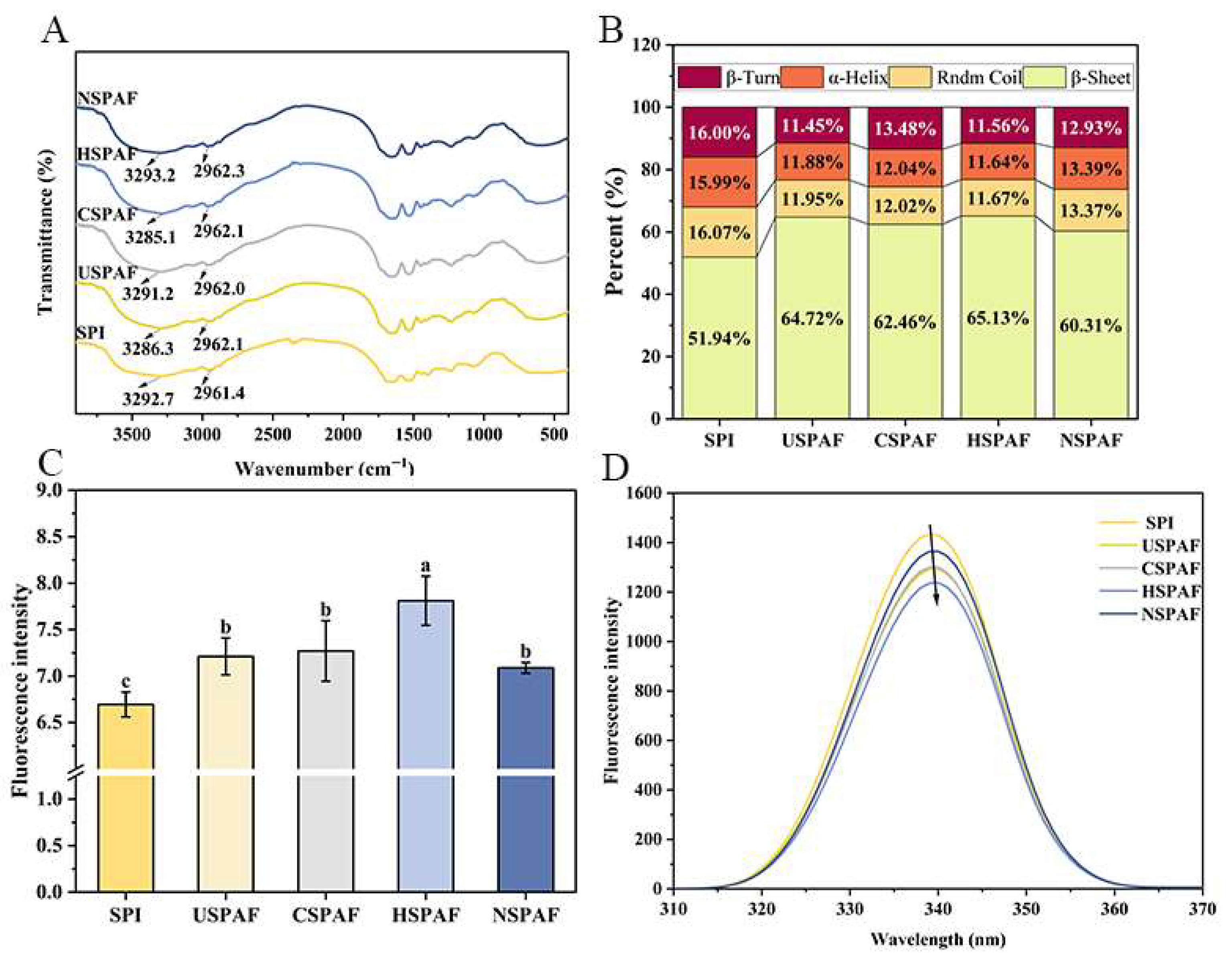
3.1. FTIR Analysis
3.2. ThT Fluorescence Analysis
3.3. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis
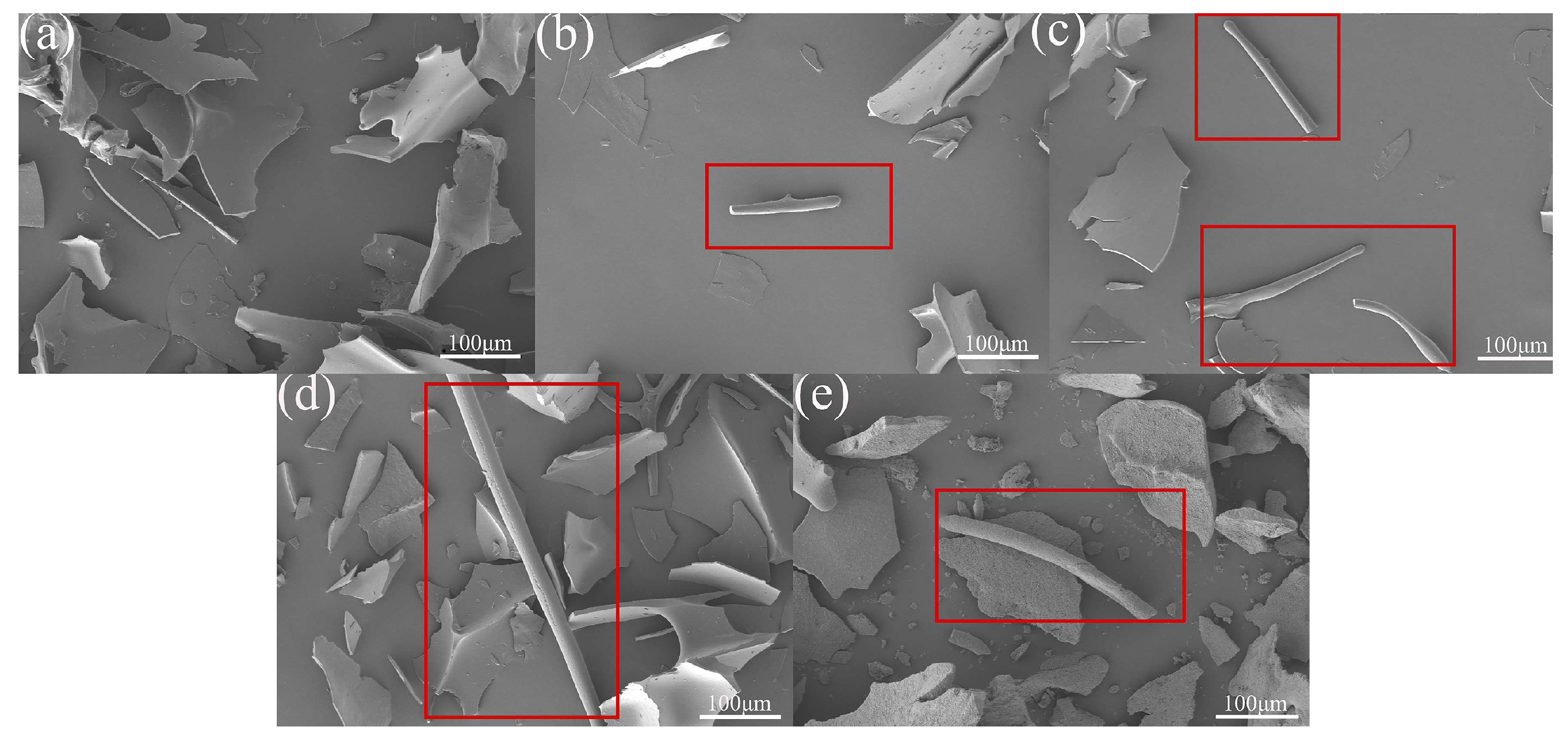
3.4. SEM Analysis
3.5. H0 Analysis
3.6. XRD Analysis
3.7. Dityrosine Analysis
3.8. Thermal Stability Analysis
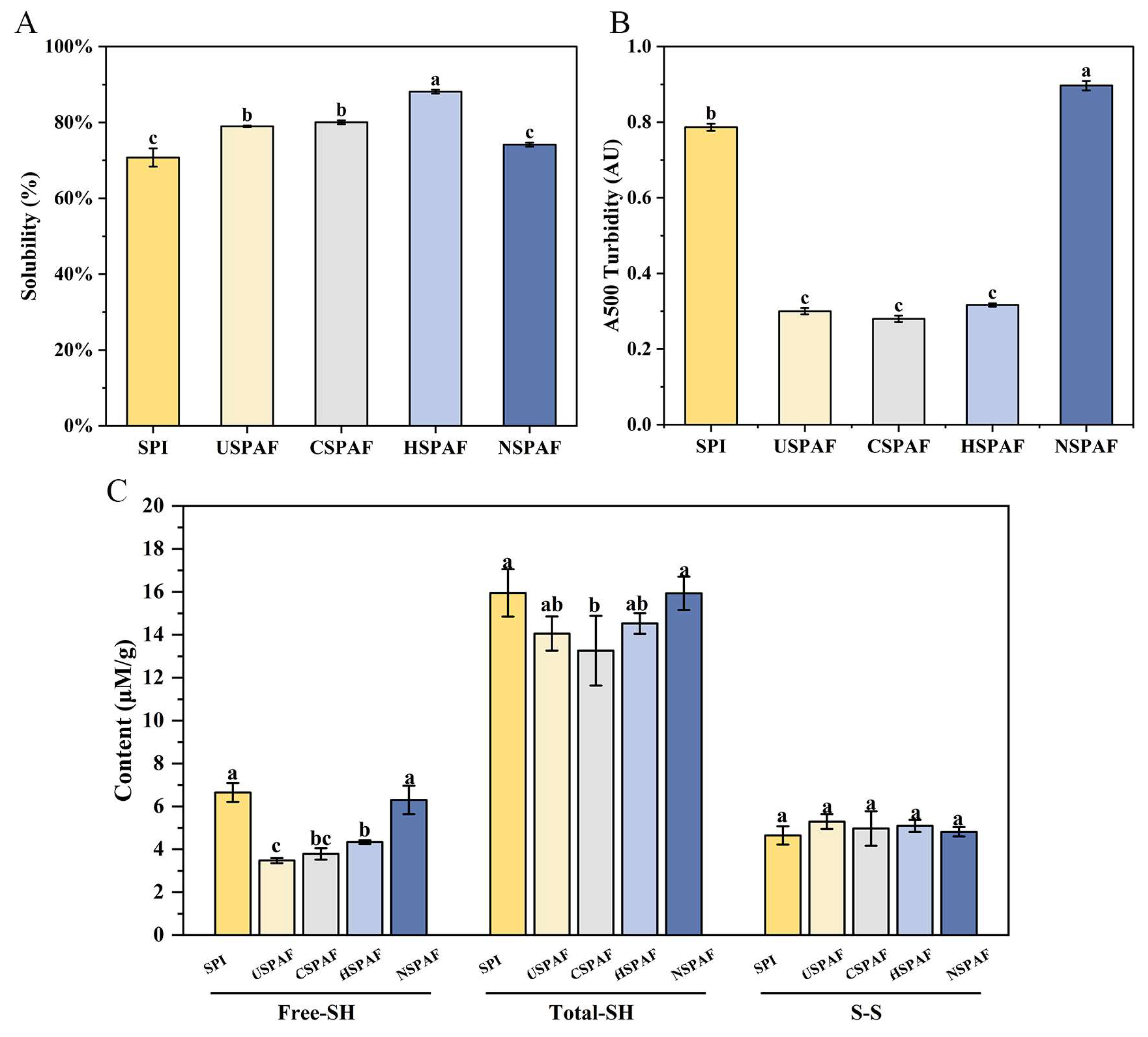
3.9. Solubility Analysis
3.10. Turbidity Analysis
3.11. Free-SH, Total-SH, and S–S Analysis
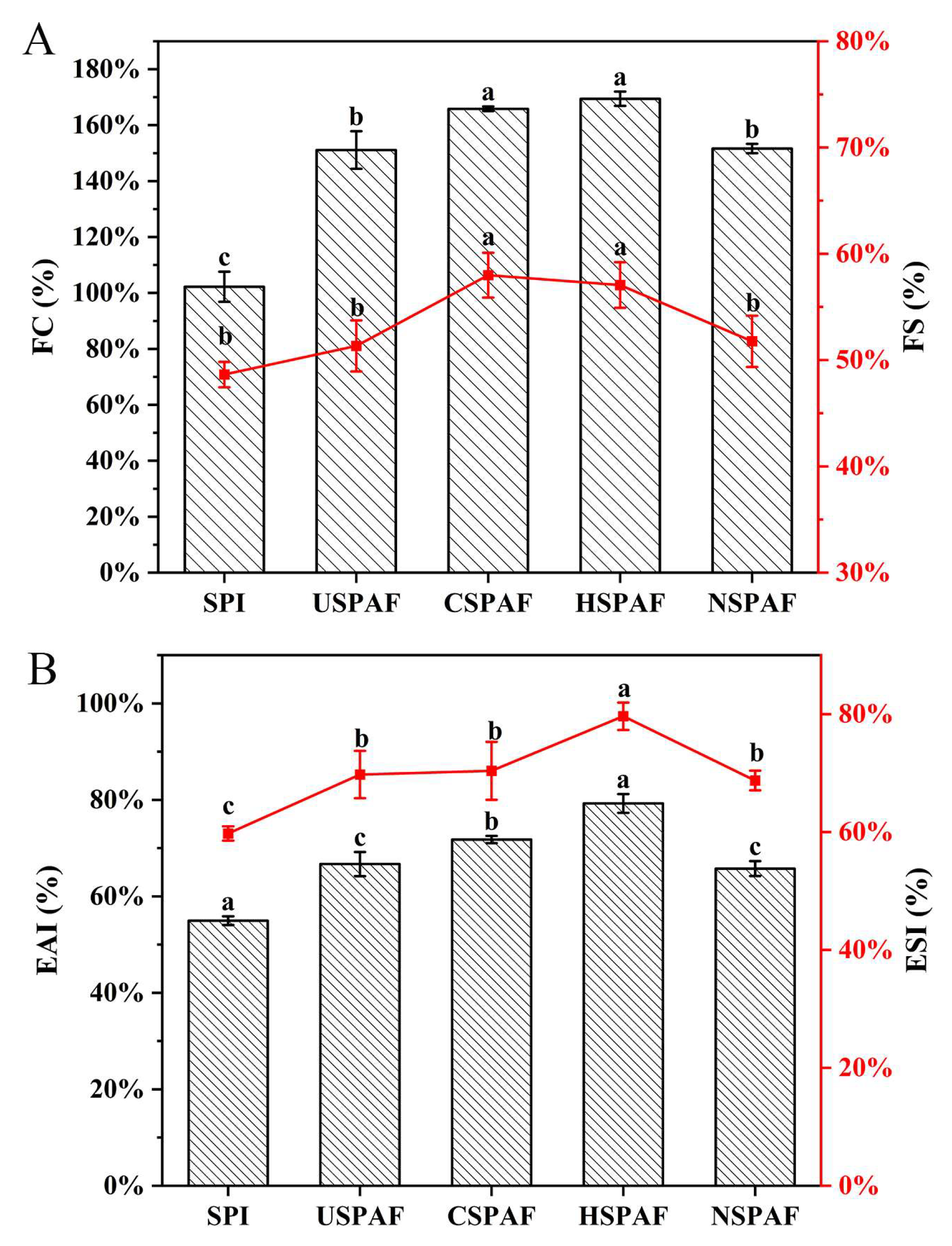
3.12. FC and FS Analysis
3.13. EAI and ESI Analysis
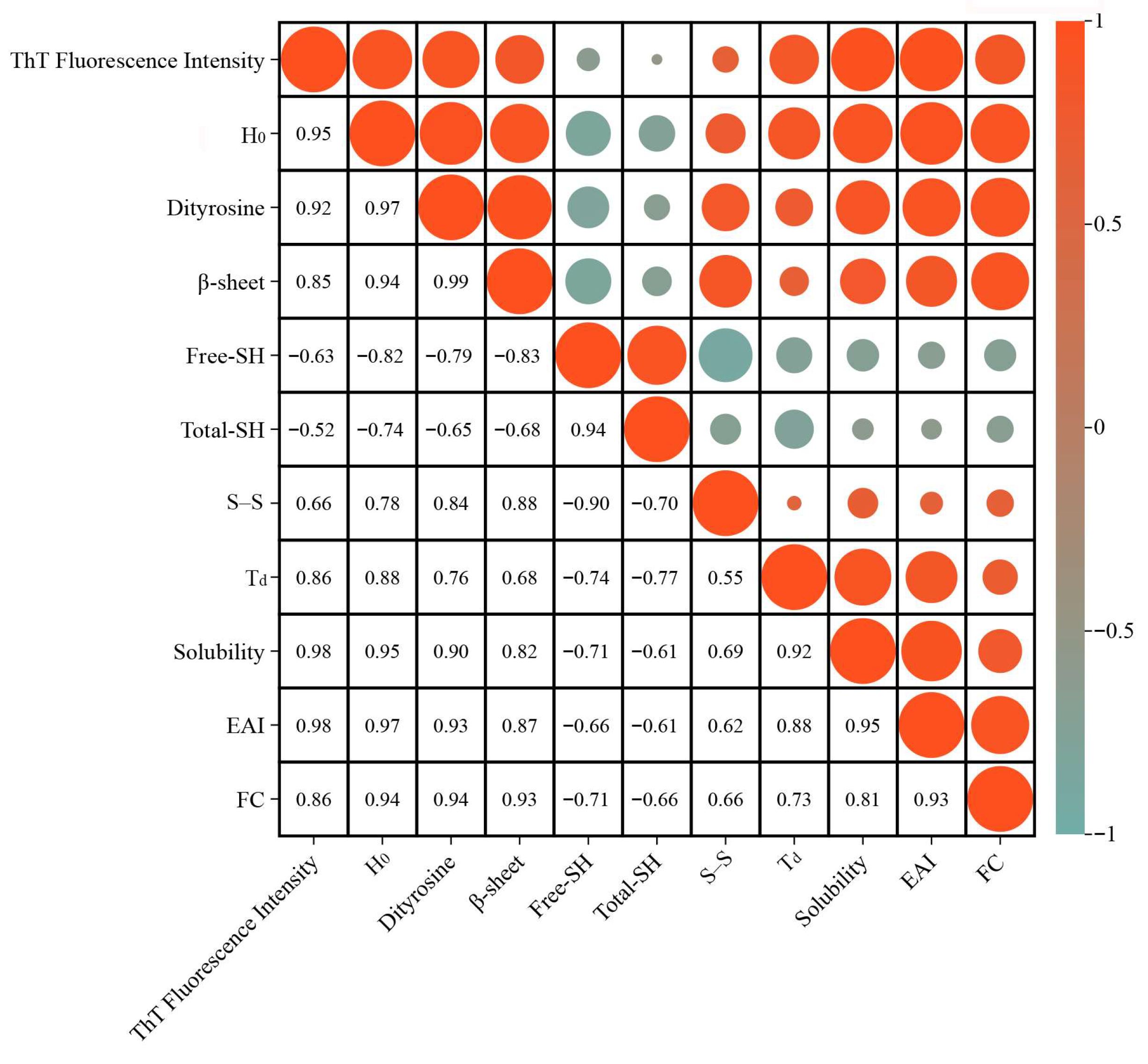
3.14. Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, S.T.; Tan, S.S.; Tan, C.X. Soy protein, bioactive peptides, and isoflavones: A review of their safety and health benefits. PharmaNutrition 2023, 25, 100352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, X. The Beneficial Effects of Soybean Proteins and Peptides on Chronic Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, L.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Influence of ultrasound-assisted ionic liquid pretreatments on the functional properties of soy protein hydrolysates. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 73, 105546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Wei, Z.; Xue, C. Protein fibrils from different food sources: A review of fibrillation conditions, properties, applications and research trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 121, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Mezzenga, R. Food protein amyloid fibrils: Origin, structure, formation, characterization, applications and health implications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 269, 334–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Geng, H.; Xue, W.; Chen, Z. Assembly behavior, structural characterization and rheological properties of legume proteins based amyloid fibrils. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wijaya, W.; Cheng, Y.; Xiao, J.; Huang, Q. Hydrogels assembled from ovotransferrin fibrils and xanthan gum as dihydromyricetin delivery vehicles. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, M.; Everett, D.W.; Huang, M.; Zhai, Y.; Li, T.; Fu, Y. Amyloid fibrils for β-carotene delivery—Influence of self-assembled structures on binding and in vitro release behavior. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Wang, Z.; Bai, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, X.; Luo, S.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, Z. Ultrasound‒treated soy protein fibrils: A potential vehicle for curcumin with improved water solubility, antioxidant activity and sustained‒release property. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 143, 108929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tang, P.; Liu, C.; Tan, Y.; Liu, T.; Cheng, J.; Aadil, R.M.; Liu, X. Promoting ovalbumin amyloid fibrils formation by cold plasma treatment and improving its emulsifying properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 158, 110531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, J. Multiscale analysis based on amorphous and fibrillated aggregates of fava bean proteins: Mechanism of regulation of aggregation morphology and its functional properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2026, 170, 111652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akharume, F.U.; Aluko, R.E.; Adedeji, A.A. Modification of plant proteins for improved functionality: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 198–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, H.; Hasegawa, K.; Yoshimura, Y.; Goto, Y. Acceleration of the depolymerization of amyloid β fibrils by ultrasonication. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Proteins Proteom. 2013, 1834, 2480–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, R.; Varidi, M.J.; Varidi, M.; Hadizadeh, F. Improvement of heat-induced nanofibrils formation of soy protein isolate through NaCl and microwave. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 139, 108443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xu, Z.; Sui, X. Elucidating the modulatory influence of Hofmeister divalent ions on the structural dynamics and rheological properties of soy protein amyloid fibrils. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 151, 109871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Qi, G.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.S.; Qiu, D.; Li, Y. Formation and physicochemical properties of amyloid fibrils from soy protein. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Li, L. Synergistic treatment of pH and ultrasound promotes the formation of insoluble soy protein hydrolysate nanofibrils. Food Chem. 2025, 470, 142659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xue, X.; Guo, P.; Dong, S. Mechanism of zein self-assembly fibrillation induced via plasma-assisted acid-heat treatment: Influence of the fibrillation degree. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2025, 100, 103909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, G.; Yang, T.; Gao, B.; Yang, J.; Guo, L.; Fan, F. Effect of cold plasma treatment time on walnut protein isolate: Revealing structural changes and improving functional properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 311, 143693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Hu, H.; Rasulov, F.; Bi, D.; Huang, X.; Pan, S. Formation of amyloid fibrils from soy protein hydrolysate: Effects of selective proteolysis on β-conglycinin. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Formation, structure and functional characteristics of amyloid fibrils formed based on soy protein isolates. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yuan, G.; Yang, T.; Gao, B.; Lu, Y.; Yang, J.; Guo, L.; Ma, Q.; Fan, F. Modifying the Structural and Functional Properties of Walnut Glutenin Through Atmospheric Cold Plasma Treatment: Evaluation of Treatment Times Effects. Foods 2025, 14, 2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Jiang, D.; Liu, X.; Cheng, J.; Aadil, R.M.; Liu, Z. Reduction of antigenicity and emulsibility improvement of ovalbumin by dielectric-barrier discharge plasma treatment induced structure modification. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 92, 103602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Cui, C.; Wang, W.; Dong, K. Modification of soy protein isolate by glutaminase for nanocomplexation with curcumin. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadian, M.; Madadlou, A. Characterization of fibrillated antioxidant whey protein hydrolysate and comparison with fibrillated protein solution. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Liu, X.; Gao, Q.; Gong, S.; Li, J.; Shi, S.Q. Multiple hydrogen bonding enables strong, tough, and recyclable soy protein films. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 7680–7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Fan, F.; Xu, X.; Liang, Y. Interactions of black and green tea polyphenols with whole milk. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Luo, S.; Zhong, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Z. Gelation properties of transglutaminase-induced soy protein isolate and wheat gluten mixture with ultrahigh pressure pretreatment. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oboroceanu, D.; Wang, L.; Brodkorb, A.; Magner, E.; Auty, M.A. Characterization of β-lactoglobulin fibrillar assembly using atomic force microscopy, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and in situ Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3667–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Jiang, B.; Xu, J.; Sun, Z. Formation of whey protein isolate nanofibrils by endoproteinase GluC and their emulsifying properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Cao, J.; Tian, T.; Lyu, B.; Miao, L.; Lian, Z.; Cui, W.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. Changes in structure, rheological property and antioxidant activity of soy protein isolate fibrils by ultrasound pretreatment and EGCG. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Xu, H.; Li, B.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, L. Inhibition or improvement for acidic subunits fibril aggregation formation from β-conglycinin, glycinin and basic subunits. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 70, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Shao, P.; Sun, Q.; Pu, C.; Tang, W. Relationship between the emulsifying properties and formation time of rice bran protein fibrils. LWT 2020, 122, 108985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Ding, X.; Dai, C.; Ma, H. Changes in the structure and dissociation of soybean protein isolate induced by ultrasound-assisted acid pretreatment. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Fu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, T.; Shi, Y.; Xie, H.; Li, Y.; Su, H.; Li, Z. Application of whey protein isolate fibrils in encapsulation and protection of β-carotene. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoisier, A.; Vilgis, T.A.; Aguilera, J.M. Effect of cysteine addition and heat treatment on the properties and microstructure of a calcium-induced whey protein cold-set gel. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2019, 1, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Li Chan, E.C.; Wan, L.; Tian, M.; Pan, S. The effect of high intensity ultrasonic pre-treatment on the properties of soybean protein isolate gel induced by calcium sulfate. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Peng, L.; Cao, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Dou, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, C. Insights into Cold Plasma Treatment on the Cereal and Legume Proteins Modification: Principle, Mechanism, and Application. Foods 2024, 13, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, A.; Luan, B.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, B.; Zhang, B. Exploring changes in aggregation and gel network morphology of soybean protein isolate induced by pH, NaCl, and temperature in view of interactions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 132911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Huang, Q. Impact of covalent or non-covalent bound epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) on assembly, physicochemical characteristics and digestion of ovotransferrin fibrils. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; He, C.; Woo, M.W.; Xiong, H.; Hu, J.; Zhao, Q. Formation of fibrils derived from whey protein isolate: Structural characteristics and protease resistance. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 8106–8115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwald, J.; Riek, R. Biology of Amyloid: Structure, Function, and Regulation. Structure 2010, 18, 1244–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, S.; Kumar, Y.; Saxena, D.C. Functional, thermal and structural properties of fractionated protein from waste banana peel. Food Chem. X 2022, 13, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Li, L. Effects of ultrasound pretreatment on functional property, antioxidant activity, and digestibility of soy protein isolate nanofibrils. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 90, 106193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, F.; Xu, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Mu, D.; Li, X.; Luo, S.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, Z. Effects of NaCl concentration and temperature on fibrillation, structure, and functional properties of soy protein isolate fibril dispersions. LWT 2021, 149, 111862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiel, S.; Grinberg, O.; Perkas, N.; Charmet, J.; Kepner, H.; Gedanken, A. Forming nanoparticles of water-soluble ionic molecules and embedding them into polymer and glass substrates. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 3, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Ge, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Shi, Y.; Le, G. Dityrosine in food: A review of its occurrence, health effects, detection methods, and mitigation strategies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 355–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Pan, J.; Hu, X.; Zhu, M.; Gong, D.; Zhang, G. A combination of alkaline pH-shifting/acidic pH and thermal treatments improves the solubility and emulsification properties of wheat glutenin. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolder, S.G.; Sagis, L.M.; Venema, P.; van der Linden, E. Effect of stirring and seeding on whey protein fibril formation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5661–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbour, M.; He, R.; Mintah, B.; Xiang, J.; Ma, H. Changes in functionalities, conformational characteristics and antioxidative capacities of sunflower protein by controlled enzymolysis and ultrasonication action. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, R.A.; Furtado, G.d.F.; Netto, F.M.; Cunha, R.L. Assessing the potential of whey protein fibril as emulsifier. J. Food Eng. 2018, 223, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Zhu, J.; Peng, X.; Feng, J.; Dong, H.; Tong, X.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L. Effects of CaCl2 concentration on fibrils formation and characteristics of soybean protein isolate and β-conglycinin/glycinin. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 142, 108769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Du, Y.; Chen, H. Evaluation of the impact of stirring on the formation, structural changes and rheological properties of ovalbumin fibrils. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 128, 107615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Chen, F.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, B.; Guo, Y. Cysteine Thiol-Based Oxidative Post-Translational Modifications Fine-Tune Protein Functions in Plants. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oboroceanu, D.; Wang, L.; Magner, E.; Auty, M.A.E. Fibrillization of whey proteins improves foaming capacity and foam stability at low protein concentrations. J. Food Eng. 2014, 121, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rullier, B.; Axelos, M.A.; Langevin, D.; Novales, B. β-Lactoglobulin aggregates in foam films: Effect of the concentration and size of the protein aggregates. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 343, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, A.; Báez, G.D.; Busti, P.A.; Ballerini, G.A.; Delorenzi, N.J. Effects of heat-treated β-lactoglobulin and its aggregates on foaming properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Hu, M.; Du, X.; Liao, Y.; Yan, S.; Zhang, S.; Qi, B.; Li, Y. Correlating structure and emulsification of soybean protein isolate: Synergism between low-pH-shifting treatment and ultrasonication improves emulsifying properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 646, 128963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Deng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Han, L.; Ma, Q.; Guo, L.; Fan, F. Effects of Treatment Methods on the Formation, Structure, and Functional Properties of Soy Protein Amyloid Fibrils. Foods 2025, 14, 3835. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223835
Zhang Q, Deng Y, Lu Y, Han L, Ma Q, Guo L, Fan F. Effects of Treatment Methods on the Formation, Structure, and Functional Properties of Soy Protein Amyloid Fibrils. Foods. 2025; 14(22):3835. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223835
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qian, Yanmei Deng, Yanling Lu, Long Han, Qian Ma, Lei Guo, and Fangyu Fan. 2025. "Effects of Treatment Methods on the Formation, Structure, and Functional Properties of Soy Protein Amyloid Fibrils" Foods 14, no. 22: 3835. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223835
APA StyleZhang, Q., Deng, Y., Lu, Y., Han, L., Ma, Q., Guo, L., & Fan, F. (2025). Effects of Treatment Methods on the Formation, Structure, and Functional Properties of Soy Protein Amyloid Fibrils. Foods, 14(22), 3835. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223835




