Tailored Fermentation of Large Yellow Croaker Surimi Balls with Direct Vat Set Starters: Effects on Physicochemical and Sensory Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Fermented Large Yellow Croaker Surimi Balls
2.3. Determination of pH and Moisture Content
2.4. Color Measurement
2.5. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
2.6. Sensory Evaluation
2.7. Determination of Free Amino Acid Content
2.8. Determination of Flavor Nucleotide Content
2.9. Umami Assessment
2.10. Determination of Malondialdehyde (MDA), Carbonyl and Sulfhydryl Content
2.11. Determination of Sodium (Na+) and Potassium (K+)
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Different Starter Cultures on pH Value, Moisture Content and Color of Fermented Surimi Balls
3.2. Effects of Different Starter Cultures on Texture Properties of Fermented Surimi Balls
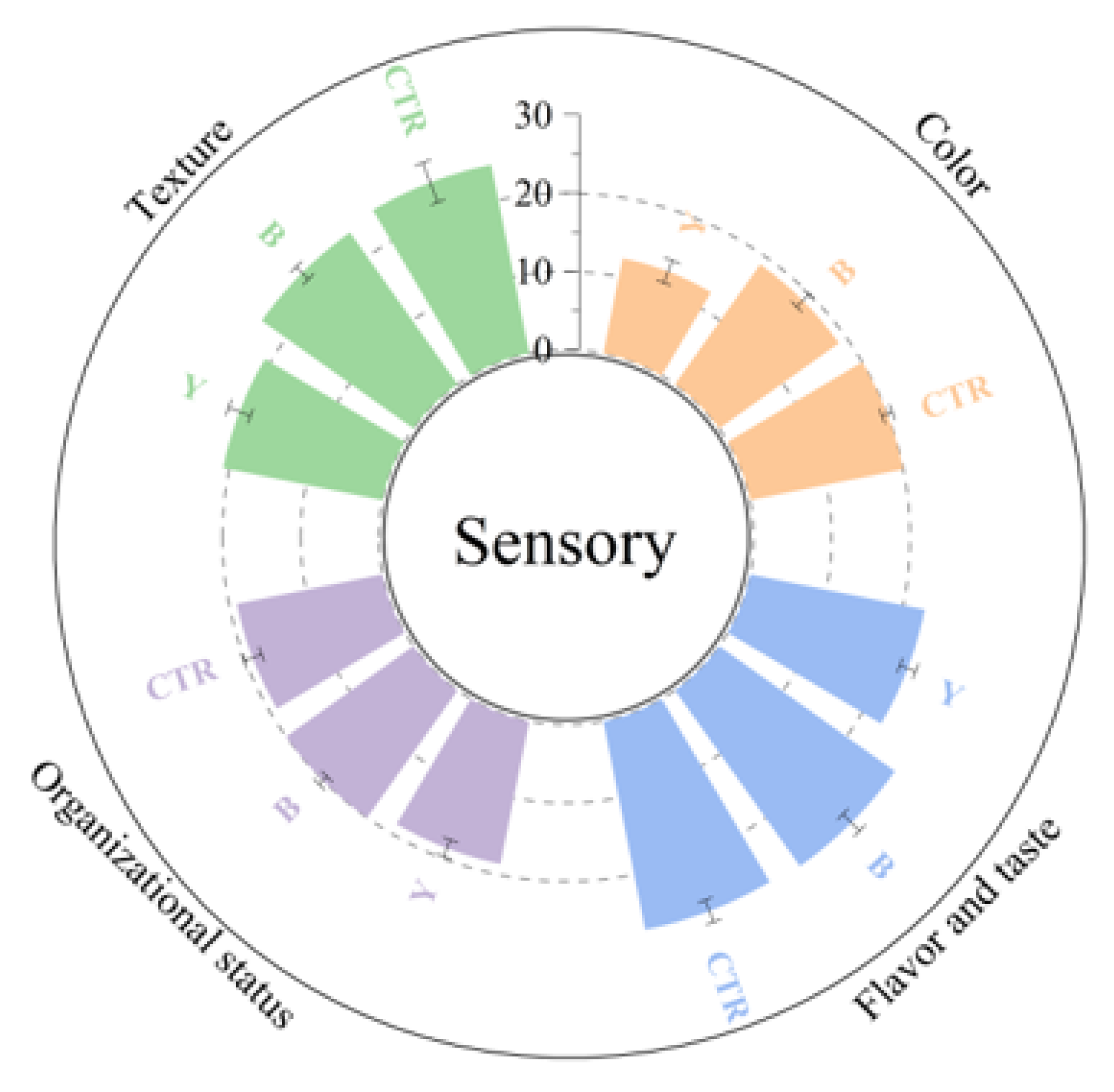
3.3. Effects of Different Starter Cultures on Sensory Properties of Fermented Surimi Balls
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Physical and Chemical Indicators
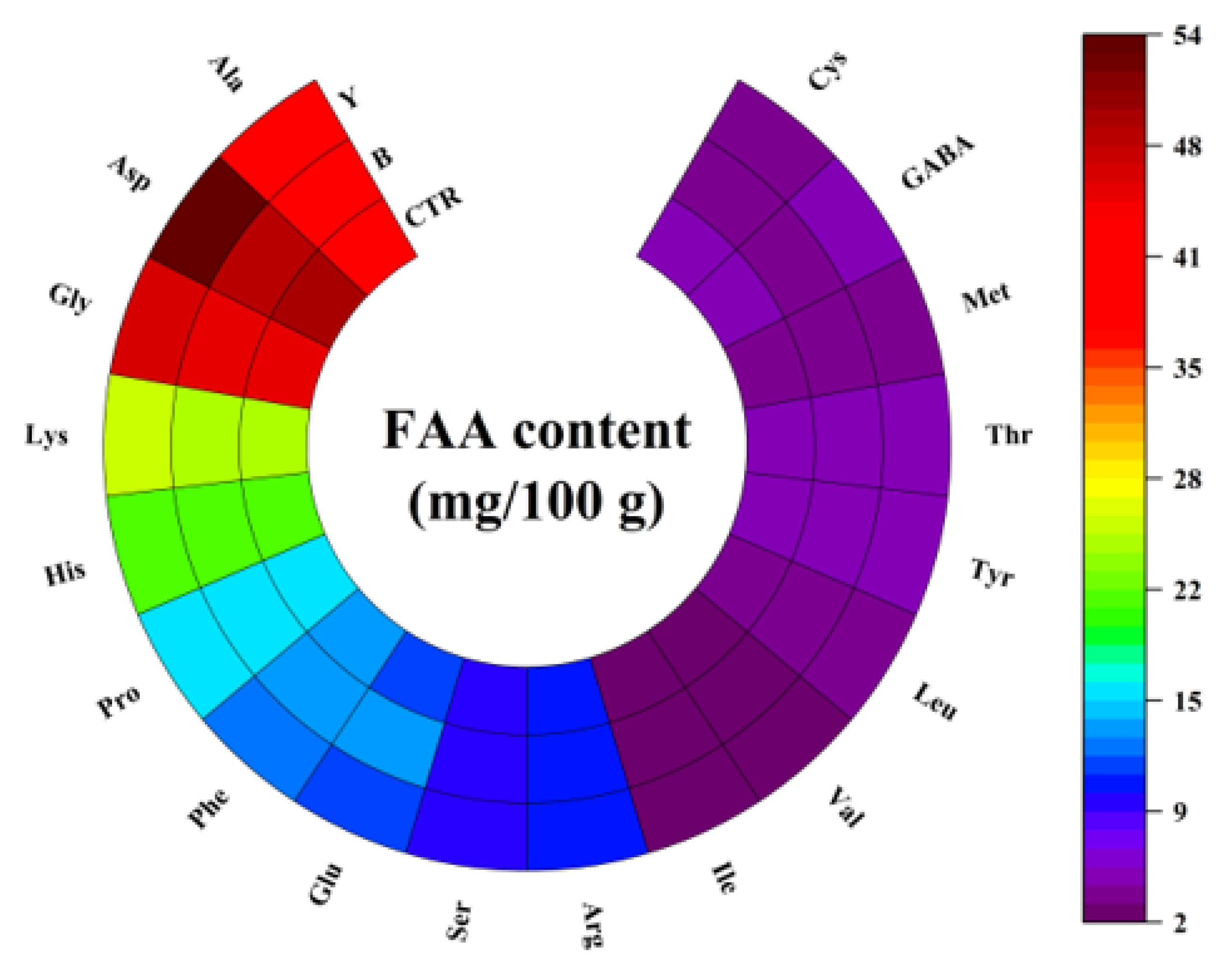
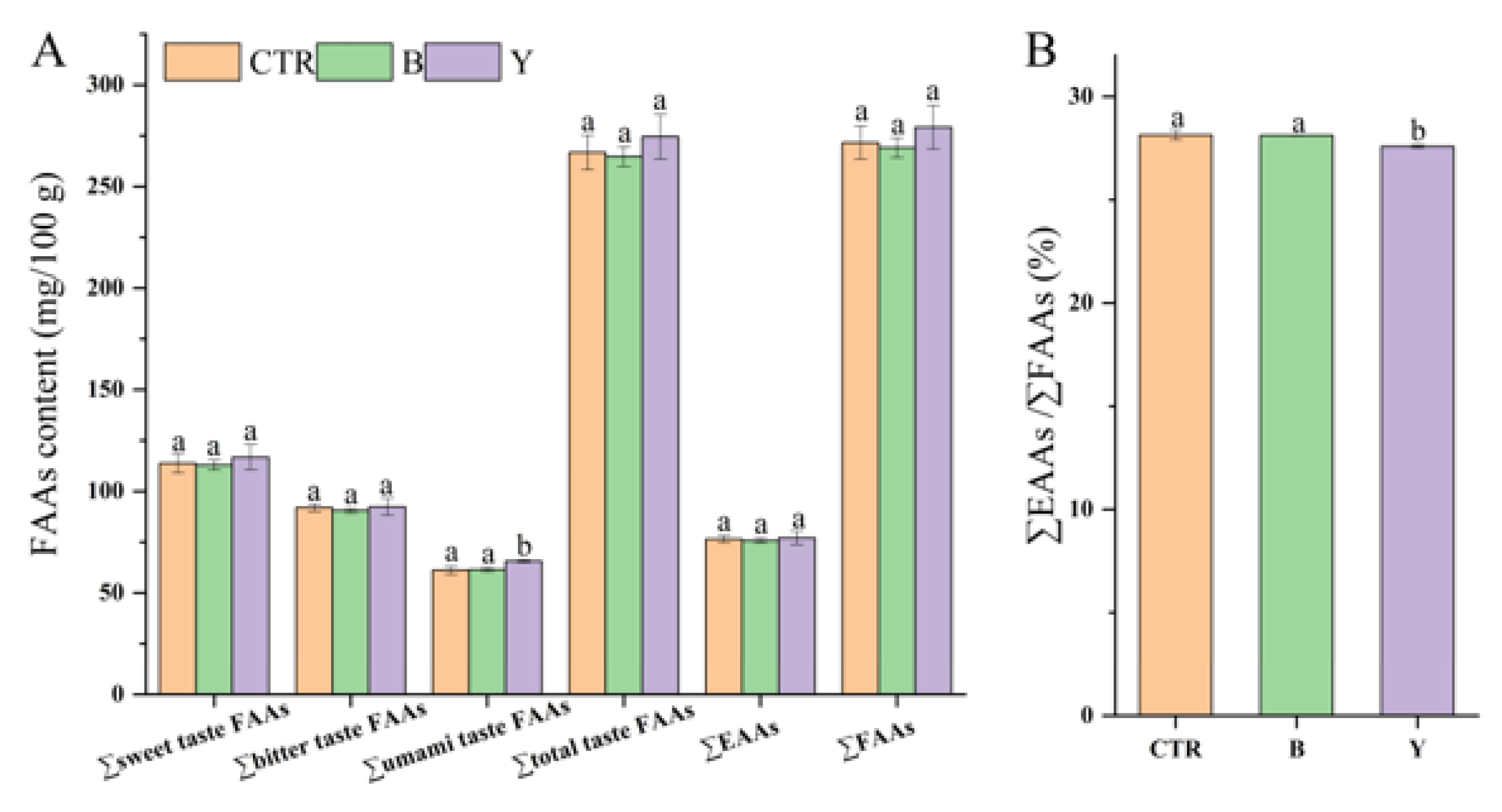
3.5. Effects of Different Starter Cultures on Free Amino Acid Contents of Fermented Surimi Balls
3.6. Effects of Different Starter Cultures on Flavor Nucleotides and Taste Activity Values of Fermented Surimi Balls
3.7. Effects of Different Starter Cultures on MDA, Carbonyl and Sulfhydryl Content of Fermented Surimi Balls
3.8. Effects of Different Starter Cultures on Na+ and K+ Content of Fermented Surimi Balls
3.9. Correlation Analysis of Water-Soluble Indicators
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
| Index | Evaluation Standards | Score |
|---|---|---|
| Color | light white, glossy | 15~20 |
| gray white or slightly yellowish, with a slight luster | 8~14 | |
| light yellow, slightly glossy or dull | 1~7 | |
| Organizational status | smooth surface, compact cut surface, no or minimal pores | 15~20 |
| relatively smooth surface, basically compact cut surface, a few small pores | 8~14 | |
| surface roughness, loose cutting surface, numerous pores or dense pores | 1~7 | |
| Texture | good elasticity and chewiness | 21~30 |
| moderate elasticity, moderate chewiness | 11~20 | |
| poor or no elasticity, poor chewiness | 1~10 | |
| Flavor and taste | rich or moderate fermentation flavor, distinct fresh taste of fish, no fishy smell, harmonious aroma, delicious | 21~30 |
| plain fermentation flavor, plain fresh taste of fish, light fishy smell, average taste | 11~20 | |
| slightly sour or absent fermentation flavor, no fresh taste of fish, obvious fishy smell, poor taste | 1~10 |
Appendix A.2
| Index | CTR | B | Y |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color | 20.03 ± 0.71 b | 18.80 ± 1.10 b | 12.41 ± 1.52 a |
| Organizational status | 19.02 ± 1.22 a | 20.07 ± 0.71 a | 18.61 ± 1.14 a |
| Texture | 24.60 ± 2.70 b | 23.83 ± 1.10 ab | 20.80 ± 1.48 a |
| Flavor and taste | 27.22 ± 1.48 b | 27.61 ± 1.52 b | 22.84 ± 1.10 a |
| Total score | 90.88 ± 6.12 b | 90.32 ± 4.41 b | 74.66 ± 5.24 a |
References
- Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, J.C.; Jing, Y. Larimichthys crocea (large yellow croaker): A bibliometric study. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y. Paradigm shift of fish nutrition and feed:the necessity revealed by the application of formulated feed in Micropterus salmoides and Larimichthys crocea farming. J. Fish. China 2024, 48, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Lan, H.; Zhang, J.H.; Gao, Y.P.; Deng, S.G. Comparative analysis of quality and flavor profiles in raw and pre-cooked large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) meat post freezing and reheating. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.W.; Jiang, L.H.; Song, W.H.; Zheng, J.L.; Liu, Y.F.; Chen, S.; Yan, X.J. Skeletal muscle feature of different populations in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea): From an epigenetic point of view. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1403861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BAO, T. Large yellow croaker industry in China: Production, market and prospect. Chin. Fish. Econ. 2024, 42, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.J.; Jiang, W.T.; Chen, X.; Wu, J.H.; Huang, J.L.; Cai, X.X.; Wang, S.Y. Investigation on the quality regulating mechanism of antifreeze peptides on frozen surimi: From macro to micro. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.C.; He, W.J.; Dai, W.L.; Xie, X.B.; Pan, Y.B.; Tang, X.L.; Zheng, R.C.; Zhou, X.X. Quality and flavor development of solid-state fermented surimi with Actinomucor elegans: A perspective on the impacts of carbon and nitrogen sources. Food Chem. 2024, 447, 139053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Lin, C.X.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Q.; Meng, J.; He, L.P.; Deng, L.; Zeng, X.F. Exploring the bacterial community for starters in traditional high-salt fermented Chinese fish (Suanyu). Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, G.T.; Bi, Y.C.; Liu, S. Fermented fish products: Balancing tradition and innovation for improved quality. Foods 2024, 13, 2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laranjo, M.; Potes, M.E.; Elias, M. Role of starter cultures on the safety of fermented meat products. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, K.; Yao, Y.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhou, T.M.; Zeng, X.M.; Zhang, M.; Ke, W.X.; He, H.; Li, C.B. Effect of probiotic Bacillus cereus DM423 on the flavor formation of fermented sausage. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebroy, S.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W. Properties and acceptability of Som-fug, a Thai fermented fish mince, inoculated with lactic acid bacteria starters. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; Wang, C.H.; Deng, J.C.; Wang, D.; Huang, H.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chen, S.J. Inhibition of biogenic amines in fermented tilapia surimi by collaborative fermentation of Latilactobacillus sakei and Pediococcus acidilactici. Foods 2024, 13, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; Chen, S.J.; Huang, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.Q. Improvement mechanism of volatile flavor in fermented tilapia surimi by cooperative fermentation of Pediococcus acidilactici and Latilactobacillus sakei: Quantization of microbial contribution through influence of genus. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 139239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, H.J.; Yang, L.; Liu, S.Y.; Shi, J.L.; Xie, Z.H.; He, Z.F. Effect of commercial direct vat set cultures on the quality of fermented sausages. Food Ferment. Ind. 2023, 49, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Yang, S.H.; Deng, C.H.; Lin, X.; Kong, H.; Song, Y.L.; Liang, Z.W.; Tang, J.; Liu, L.; Xiong, H.; et al. Preparation of a novel biofilm directed vat set (DVS) starter and its preliminary application in pickled radish. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 224, 117815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.Y.; Liu, C.R.; Dong, Y.L.; Hu, R.F.; Liu, X.J. Preparation of direct-vat Weissella cibaria products. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2023, 45, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, L.; Tamime, A.Y.; Muir, D.D. Rheology and sensory profiling of set-type fermented milks made with different commercial probiotic and yoghurt starter cultures. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2003, 56, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.Q.; Zhang, X.T.; Jin, Q.W.; Liu, L.J.; Meng, X.C. Effect of lactic acid bacteria starter cultures on the quality of multigrain dough and steamed bread. Food Sci. 2023, 44, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, G.; Ma, W.; Jin, G. Preparation and application of directed vat set indigenous freeze-drying Lentilactobacillus hilgardii Q19 starter in winemaking. Foods 2023, 12, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yousaf, M.; Liu, D.M. Improvement of physicochemical properties and flavour of pickled radish through the use of a direct-vat set starter consisting of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 6272–6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, B.; Shi, L.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, F.; Xiong, Y.; Li, F.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yin, Z. Changes in the objective indices related to meat quality of porcine Longissimus dorsi induced by different thawing methods. Foods 2024, 13, 3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patinho, I.; Selani, M.M.; Saldaña, E.; Bortoluzzi, A.C.T.; Rios-Mera, J.D.; da Silva, C.M.; Kushida, M.M.; Contreras-Castillo, C.J. Agaricus bisporus mushroom as partial fat replacer improves the sensory quality maintaining the instrumental characteristics of beef burger. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.Y.; Shi, T.; Zhang, W.; Kong, Y.F.; Yuan, L.; Gao, R.C. Improvement of gel properties of low salt surimi using low-dose l-arginine combined with oxidized caffeic acid. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 145, 111303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.J.; Wang, N.X.; Li, C.; Liu, H.; Wu, X.P. Process optimization of preparation of meatball of pelteobagrus fulvidraco and lentinus edodes using multi strain mixed fermentation. Food Ind. 2017, 38, 162–166. Available online: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/spgy201707043 (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Siddiqi, R.A.; Singh, T.P.; Rani, M.; Sogi, D.S.; Bhat, M.A. Diversity in grain, flour, amino acid composition, protein profiling, and proportion of total flour proteins of different wheat cultivars of north India. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Luo, Y.H.; Wang, P.P.; Zhao, M.Y.; Li, L.; Hu, X.S.; Chen, F. Simultaneous determination of free amino acids in Pu-erh tea and their changes during fermentation. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.C.; Hou, H. Characteristic flavor of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) and white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) induced by thermal treatment. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 132074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Li, J.; Song, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D.; Wang, Q.Z.; Jiang, C.Y.; Li, L.; Fu, Z.Y.; Jiang, P.F. Effects of different thermal cooking methods on the characteristic taste and flavor compounds of Solen grandis meat. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 217, 117439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.181-2016; Determination of Malondialdehyde in Food. National Food Safety Standard: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Wang, Z.M.; He, Z.F.; Emara, A.M.; Gan, X.; Li, H.J. Effects of malondialdehyde as a byproduct of lipid oxidation on protein oxidation in rabbit meat. Food Chem. 2019, 288, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.T.; Li, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhu, B.W.; Luo, Y.K. Changes in chemical interactions and gel properties of heat-induced surimi gels from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) fillets during setting and heating: Effects of different washing solutions. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 75, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Zhou, X.S.; Zhao, M.M.; Yang, B. Effect of thermal treatment on the enzymatic hydrolysis of chicken proteins. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2009, 10, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.91-2017; Determination of Potassium and Sodium in Food. National Food Safety Standard: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Ngapo, T.M.; Wilkinson, B.H.P.; Chong, R. 1,5-glucono-δ-lactone-induced gelation of myofibrillar protein at chilled temperatures. Meat Sci. 1996, 42, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.Y.; Gao, P.; Xia, W.S.; Xu, Y.S. Effects of inoculation of Lactiplantibacillus pentosus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on quality of low-salt fermented bream. South China Fish. Sci. 2022, 18, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Yang, H.Y.; Ying, X.; Ying, K.; Niu, X.H.; Li, H.; Lv, Y. Effects of different yeasts on sourdough starter and bread quality and flavor. Food Sci. 2023, 44, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Guo, C.; Lin, L.; Si, Y.; Gao, X.; Xu, D.; Jia, R.; Yang, W. Combined use of rheology, LF-NMR, and MRI for characterizing the gel properties of hairtail surimi with potato starch. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2020, 13, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S. Formulation Optimization of fish balls added with tomato pomace for improved overall texture quality as determined by dimension reduction analysis. Meat Res. 2020, 34, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wen, R.; Wang, Y.; Qin, L.; Kong, B. Quality characteristics and flavor profile of Harbin dry sausages inoculated with lactic acid bacteria and Staphylococcus xylosus. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 114, 108392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnzle, M.; Schwab, C. Bacterial Polysaccharides: Current Innovations and Future Trends; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2009; pp. 263–278. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, R.A.; Hunt, M.C. Current research in meat color. Meat Sci. 2005, 71, 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Zhang, H.P. Application of probiogenomics in screening and functional evaluation of probiotics lactic acid bacteria. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 24, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Boekel, M.A.J.S. Formation of flavour compounds in the Maillard reaction. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Huo, J.; Cheng, H.; Yi, C.P. Research progress on quality enhancement of rice bread. Food Mach. 2025, 41, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Holley, R.A. Factors Influencing gel formation by myofibrillar proteins in muscle foods. Compr. Rev. Food. Sci. Food Saf. 2010, 10, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Fan, W.Q.; Song, S.; Shu, Y. Research progress on salt reduction and salt substitution in meat products. Hans J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2025, 14, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Ke, C.; Li, L. Physicochemical, rheological and digestive characteristics of soy protein isolate gel induced by lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Eng. 2021, 292, 110243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, Q.; Sheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Rui, X. The effects of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on protein gelation and gastrointestinal digestive characteristics from four pulses. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2023, 44, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.X. Research progress on the effect of wheat bran dietary fiber on dough properties. J. Henan Univ. Technol. 2020, 41, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.; Yu, X.Y.; Shen, S.; Li, P.; Xiong, S.B. Effect of yeast extract on properties of surimi gel. Meat Res. 2019, 33, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Bravo, N.; Wells, J.M.; Margolles, A.; Ruas-Madiedo, P. Interactions of surface exopolysaccharides from Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus within the intestinal environment. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Ye, H.; Chen, J.Y.; Guo, N.; Fang, X.; Lu, X. Study on physicochemical properties and flavor changes of different protein components during fermentation of soybean yogurt. Food Ferment. Ind. 2024, 50, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Li, J.; Gong, X.; Cao, Y.; Lu, X. Study on deodorization process of tilapia enzymatic hydrolysate by yeast fermentation and its volatile componets. Food Res. Dev. 2021, 42, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozorio, L.; Passerini, A.B.S.; Silva, A.P.C.d.; Braga, A.R.C.; Perrechil, F. Designing plant-based foods: Biopolymer gelation for enhanced texture and functionality. Foods 2025, 14, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.M.; Cui, Y.L.; Yue, F.F.; Liu, L.H.; Shan, Y.Y.; Liu, B.F.; Zhou, Y.; Lü, X. Exopolysaccharides produced by lactic acid bacteria and Bifidobacteria: Structures, physiochemical functions and applications in the food industry. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 475–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.S.; Ferreira, C.; Pereira, J.O.; Pintado, M.E.; Carvalho, A.P. Spent brewer’s yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) as a potential source of bioactive peptides: An overview. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasri, R.; Abdelhedi, O.; Nasri, M.; Jridi, M. Fermented protein hydrolysates: Biological activities and applications. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Hong, T.N.; Shen, G.H.; Gu, Y.T.; Guo, Y.Z.; Han, J. Amino acid profiles and nutritional evaluation of fresh sweet–waxy corn from three different regions of China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.M.; Wu, Y.; Lv, P.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Q. Effect of different lactic acid bacteria inoculation fermentation on the physicochemical characteristics and flavor of Chinese cabbage pickles. Food Ferment. Ind. 2024, 50, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, X.B.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, F.B.; Jie, G. Taste characteristics analysis of compound umami products based on free amino acids and sensory evaluation of umami taste. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2023, 44, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, G.P.; Zhang, J.H.; Lu, J. Changes in ATP-related compound contents and freshness. Food Sci. 2014, 35, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niki, E.; Yoshida, Y.; Saito, Y.; Noguchi, N. Lipid peroxidation: Mechanisms, inhibition, and biological effects. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 338, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noonpakdee, W.; Sitthimonchai, S.; Panyim, S.; Lertsiri, S. Expression of the catalase gene katA in starter culture Lactobacillus plantarum TISTR850 tolerates oxidative stress and reduces lipid oxidation in fermented meat product. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 95, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Bao, Y.L.; Hua, X.Q.; Zhang, K.P.; Wang, F.M.; Tian, J.J.; Jin, Y. Lactic acid bacteria: A review of their inhibitory effect on harmful microbes and effect on flavor characteristics of fermented meat products. Food Sci. 2023, 44, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.Y.; Tian, J.J.; Jing, Z.B.; Zhao, L.H.; Zhang, K.P.; Jin, Y. Progress in understanding the antioxidant regulation system of lactic acid bacteria. Food Sci. 2018, 39, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Kong, B.; Sun, Q.; Dong, F.; Liu, Q. Antioxidant potential of a unique LAB culture isolated from Harbin dry sausage: In vitro and in a sausage model. Meat Sci. 2015, 110, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.L.; Ayed, C.; Wang, W.L.; Liu, Y. Sensory-guided analysis of key taste-active compounds in pufferfish (Takifugu obscurus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13809–13816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, S.; Methven, L.; Cheng, Q. Role of taste receptors in salty taste perception of minerals and amino acids and developments in salt reduction strategies: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 65, 3444–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.M.; Tian, Y.Y.; Lin, Y.M.; Maeda, H.; Yamashita, T.; Yu, K.F.; Takaki, K.; Yuan, C.H. Condition-dependent adenosine monophosphate decomposition pathways in striated adductor muscle from Japanese scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis). J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jia, S.L.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, X.X.; Ding, Y.T. Formation mechanisms of reactive carbonyl species from fatty acids in dry-cured fish during storage in the presence of free radicals. J. Future Foods 2021, 1, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.Y.; Guo, X.H.; Dong, H.; Du, F.; Li, B.F. Characteristic flavor analysis of Pandalus borealis head seasoning basic materials under different processes. China Condiment 2023, 48, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; You, J.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Liao, T.; Huang, Q.L.; Xiong, S.B.; Yin, T. Insight into the mechanism on texture change of Wuchang bream muscle during live transportation using a UPLC-QTOF-MS based metabolomics method. Food Chem. 2023, 398, 133796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Sample | pH | Moisture Content (%) | Color | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | W | |||
| CTR | 7.26 ± 0.06 c | 70.91 ± 0.11 b | 84.72 ± 1.26 b | −0.59 ± 0.07 a | 8.17 ± 0.71 a | 82.63 ± 0.94 b |
| B | 6.93 ± 0.03 b | 69.41 ± 0.46 a | 83.45 ± 2.52 ab | 0.36 ± 0.04 b | 11.70 ± 1.05 b | 79.66 ± 2.11 a |
| Y | 6.76 ± 0.04 a | 71.46 ± 0.11 b | 81.59 ± 1.95 a | 1.83 ± 0.14 c | 8.86 ± 0.72 a | 79.45 ± 1.76 a |
| Texture Index | CTR | B | Y |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (g) | 1748.99 ± 15.23 a | 2238.74 ± 144.97 b | 2741.85 ± 52.05 c |
| Adhesiveness (g·s) | −0.800 ± 0.024 b | −8.49 ± 0.770 a | −0.415 ± 0.036 b |
| Springiness | 0.883 ± 0.020 a | 0.904 ± 0.030 a | 0.880 ± 0.020 a |
| Cohesiveness | 0.757 ± 0.017 b | 0.634 ± 0.056 a | 0.708 ± 0.036 ab |
| Gumminess | 1324.33 ± 35.86 a | 1449.48 ± 101.54 a | 1942.22 ± 127.46 b |
| Chewiness | 1162.52 ± 40.48 a | 1305.46 ± 73.18 a | 1818.14 ± 176.31 b |
| Resilience | 0.438 ± 0.016 b | 0.440 ± 0.023 b | 0.374 ± 0.024 a |
| Sample | IMP | AMP | EUC (%) | Content (mg/100 g) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (mg/100 g) | TAV | Content (mg/100 g) | TAV | ATP | ADP | HXR | HX | ||
| CTR | 78.44 ± 1.81 a | 3.14 | 0.181 ± 0.011 a | 0.004 | 1.53 | 2.80 ± 0.34 b | 11.98 ± 1.65 b | 60.49 ± 5.56 b | 9.59 ± 0.91 a |
| B | 78.95 ± 4.19 a | 3.16 | 0.285 ± 0.003 b | 0.006 | 1.66 | 2.42 ± 0.13 b | 11.84 ± 0.63 b | 40.44 ± 1.50 a | 12.47 ± 0.72 b |
| Y | 76.08 ± 5.05 a | 3.04 | 0.760 ± 0.021 c | 0.015 | 1.47 | 1.77 ± 0.22 a | 2.28 ± 0.07 a | 50.20 ± 4.39 ab | 23.88 ± 4.39 c |
| Sample | Na+ | K+ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (mg/100 g) | TAV | Content (mg/100 g) | TAV | |
| CTR | 674.33 ± 6.13 a | 75.34 | 43.72 ± 2.34 a | 3.16 |
| B | 886.30 ± 5.26 c | 99.03 | 107.35 ± 9.40 b | 7.75 |
| Y | 851.26 ± 13.12 b | 95.11 | 107.34 ± 7.00 b | 7.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Deng, Y.; Chen, S.; Yao, R.; Li, S.; Ye, P.; Wang, R.; Saleh, A.S.M.; Li, J. Tailored Fermentation of Large Yellow Croaker Surimi Balls with Direct Vat Set Starters: Effects on Physicochemical and Sensory Properties. Foods 2025, 14, 3825. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223825
Liu S, Deng Y, Chen S, Yao R, Li S, Ye P, Wang R, Saleh ASM, Li J. Tailored Fermentation of Large Yellow Croaker Surimi Balls with Direct Vat Set Starters: Effects on Physicochemical and Sensory Properties. Foods. 2025; 14(22):3825. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223825
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shumin, Yijia Deng, Shengjun Chen, Ruosong Yao, Shuangping Li, Peiyi Ye, Rundong Wang, Ahmed S. M. Saleh, and Jianrong Li. 2025. "Tailored Fermentation of Large Yellow Croaker Surimi Balls with Direct Vat Set Starters: Effects on Physicochemical and Sensory Properties" Foods 14, no. 22: 3825. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223825
APA StyleLiu, S., Deng, Y., Chen, S., Yao, R., Li, S., Ye, P., Wang, R., Saleh, A. S. M., & Li, J. (2025). Tailored Fermentation of Large Yellow Croaker Surimi Balls with Direct Vat Set Starters: Effects on Physicochemical and Sensory Properties. Foods, 14(22), 3825. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223825







