Preparation, Structural Characterization, and Calcium Supplementation Activity of Lycium barbarum Peptide–Calcium Derived from Bovine Bones
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
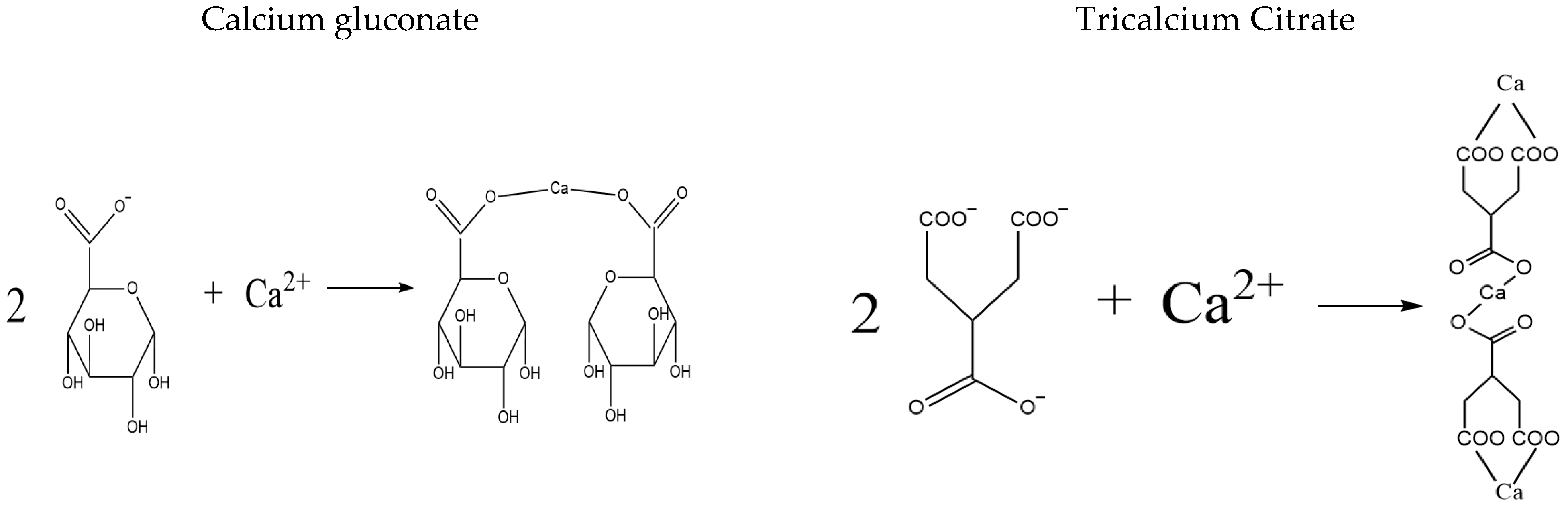
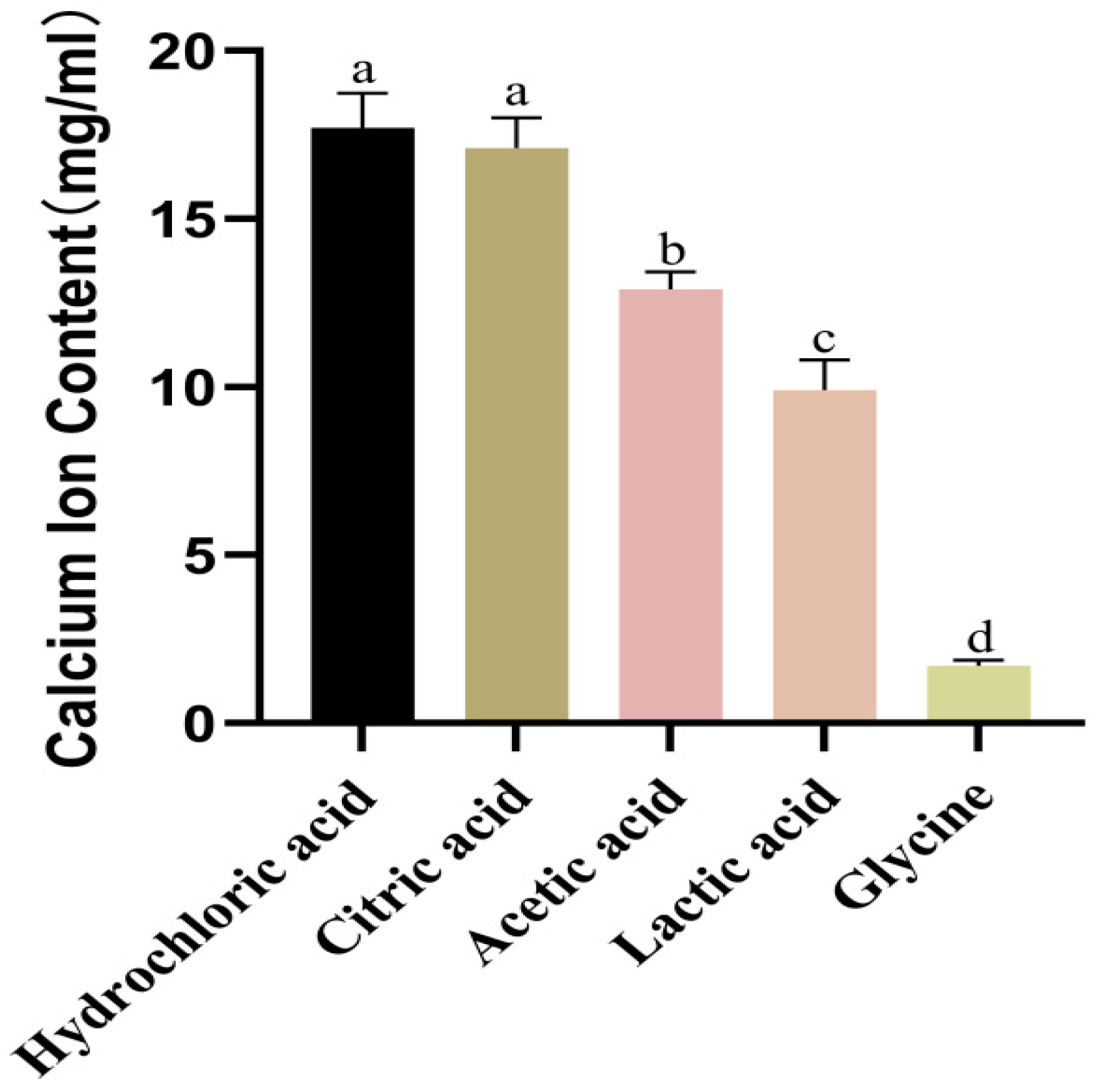
2.2. Screening of Acid Reagents
2.3. Optimization of Calcium Extraction by Adapting Single-Factor Experiments
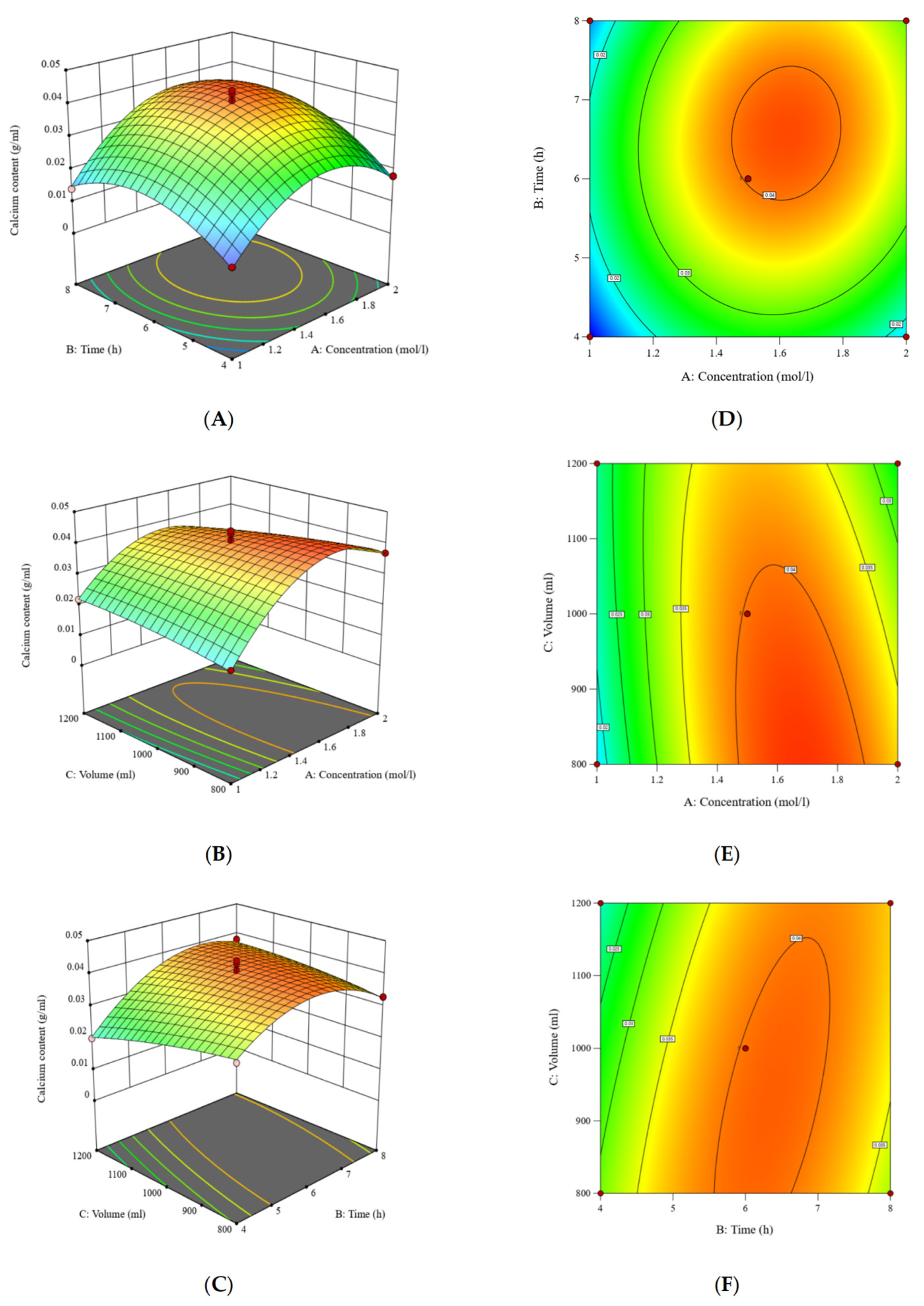
2.4. Optimization of Calcium Extraction Using Response Surface Methodology
2.5. Preparation of Peptide–Calcium Chelate (LBP-Ca)
2.6. Structural Characterization
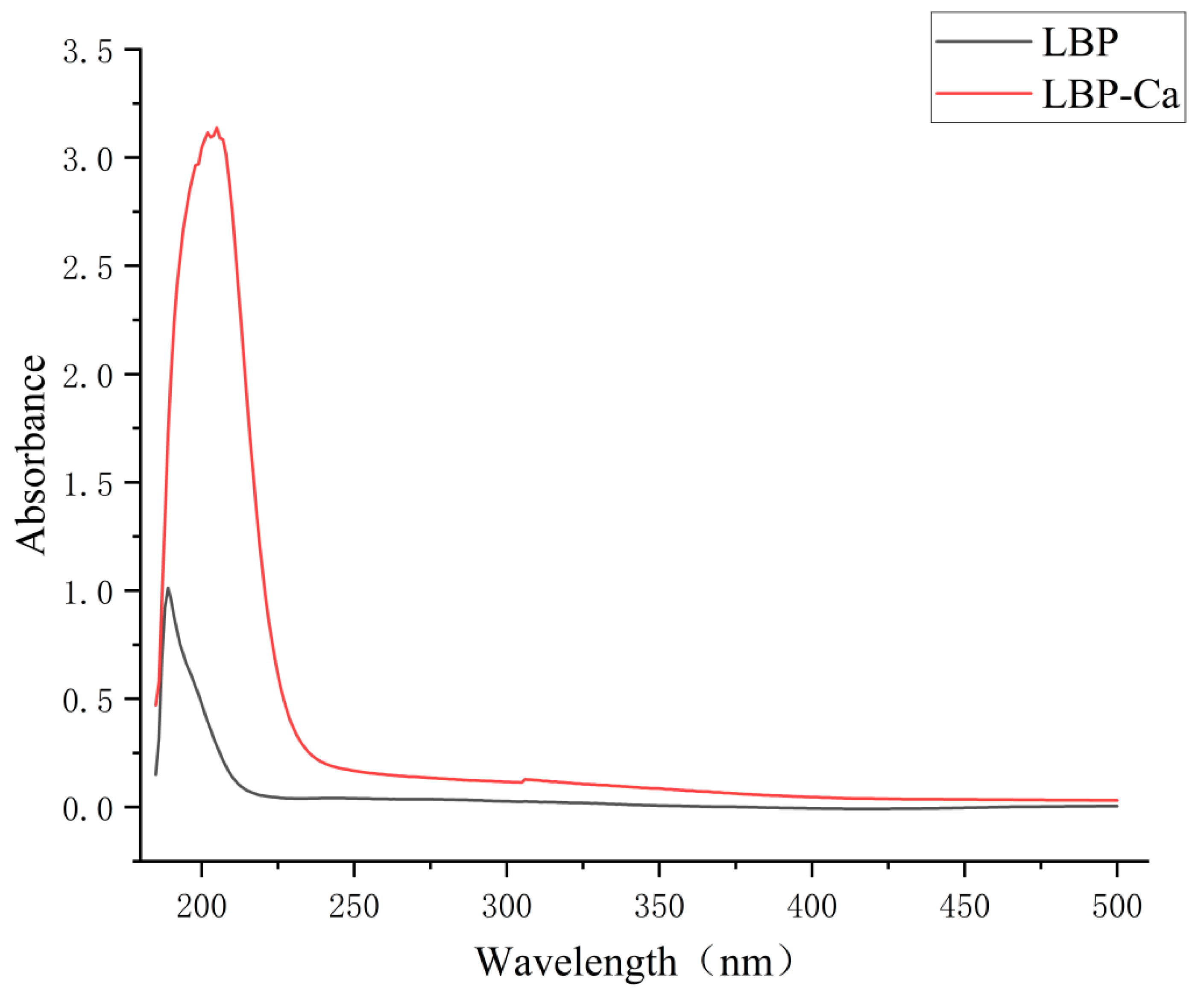
2.6.1. UV-Vis Spectroscopy Analysis
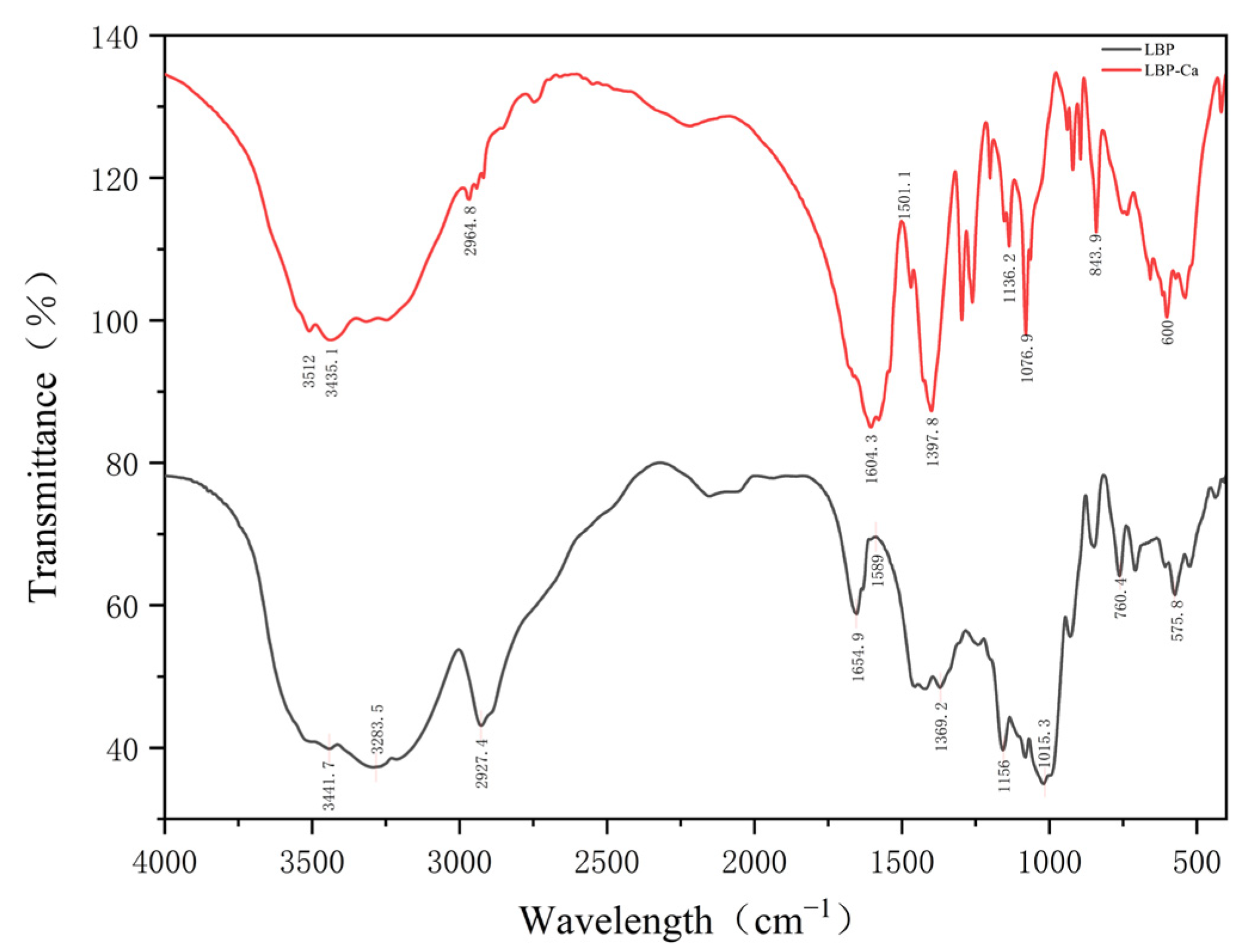
2.6.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
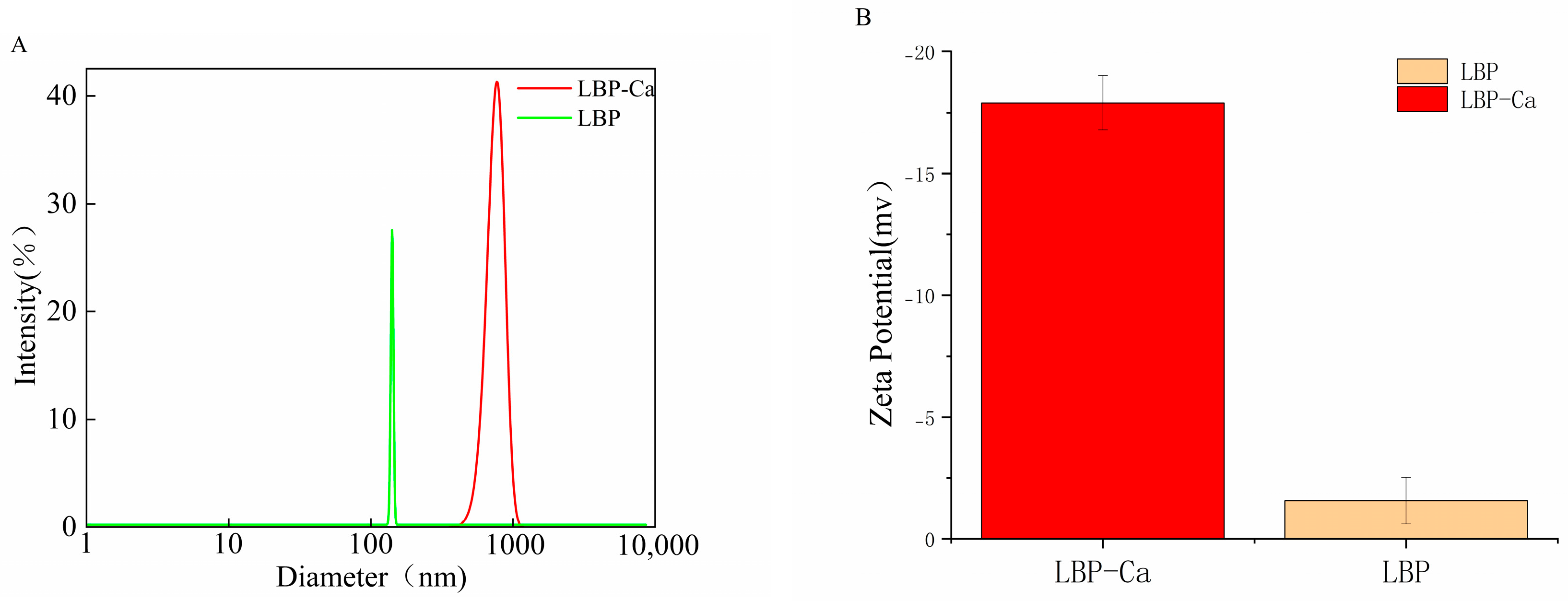
2.6.3. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Analysis
2.6.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy Observation
2.7. Animal Experiment
2.7.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.7.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.8. Femur Morphometric Analysis
2.9. Bone Densitometry Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Determination of Optimal Acid Reagents
3.2. The Optimization of Extraction Conditions of the Acid Treatment Process
3.3. Optimization of Calcium Extraction Using Response Surface Methodology
3.4. Structural Characterization
3.4.1. UV-Vis Spectroscopy Analysis
3.4.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.4.3. Particle Size and Zeta Potential
3.4.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy Observation
3.5. Effects of Different Calcium Supplements on Serum Biochemical Parameters
3.6. Effects of Different Calcium Supplements on Femur Parameters
3.6.1. Femur Length and Femur Index
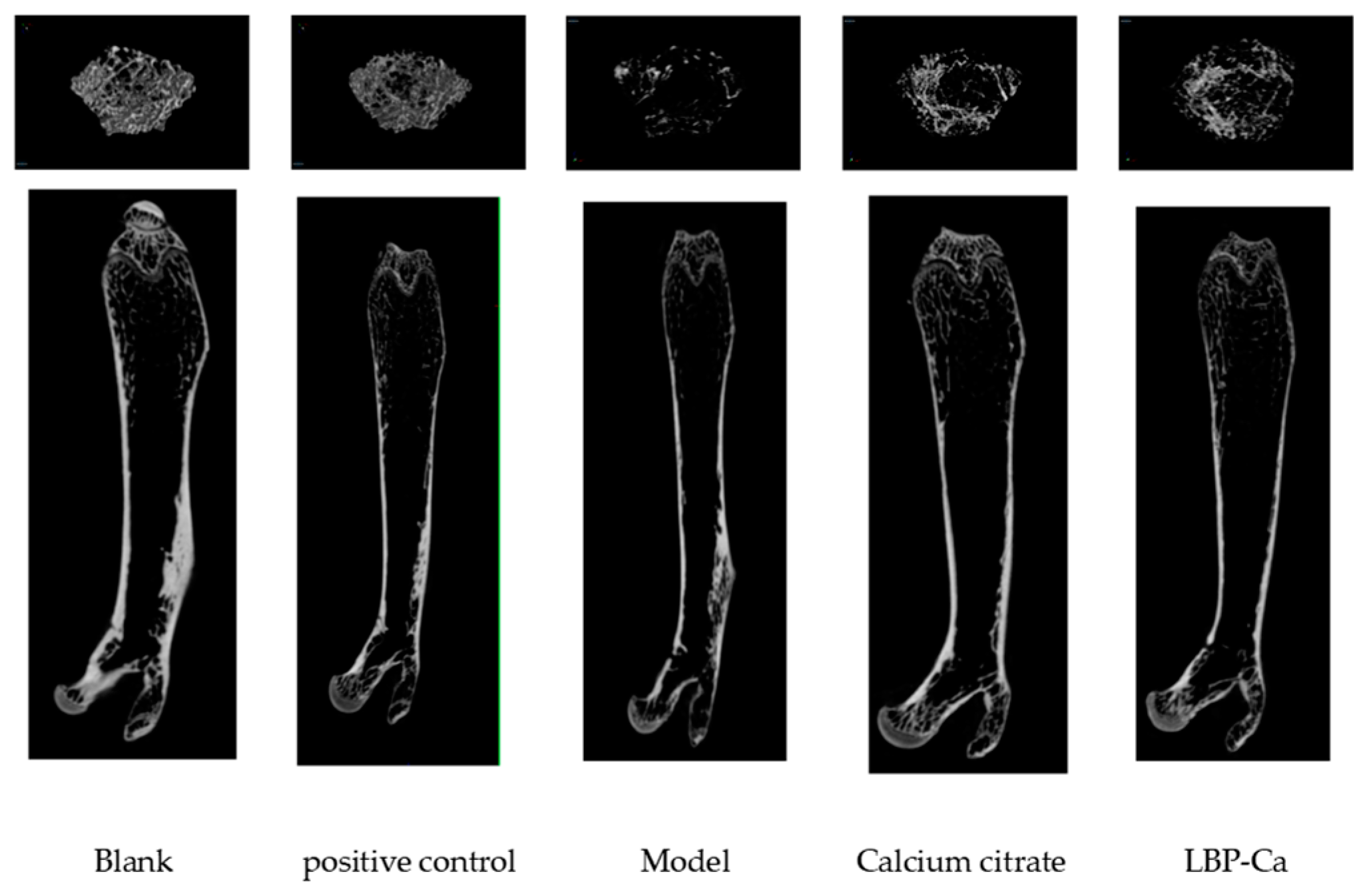
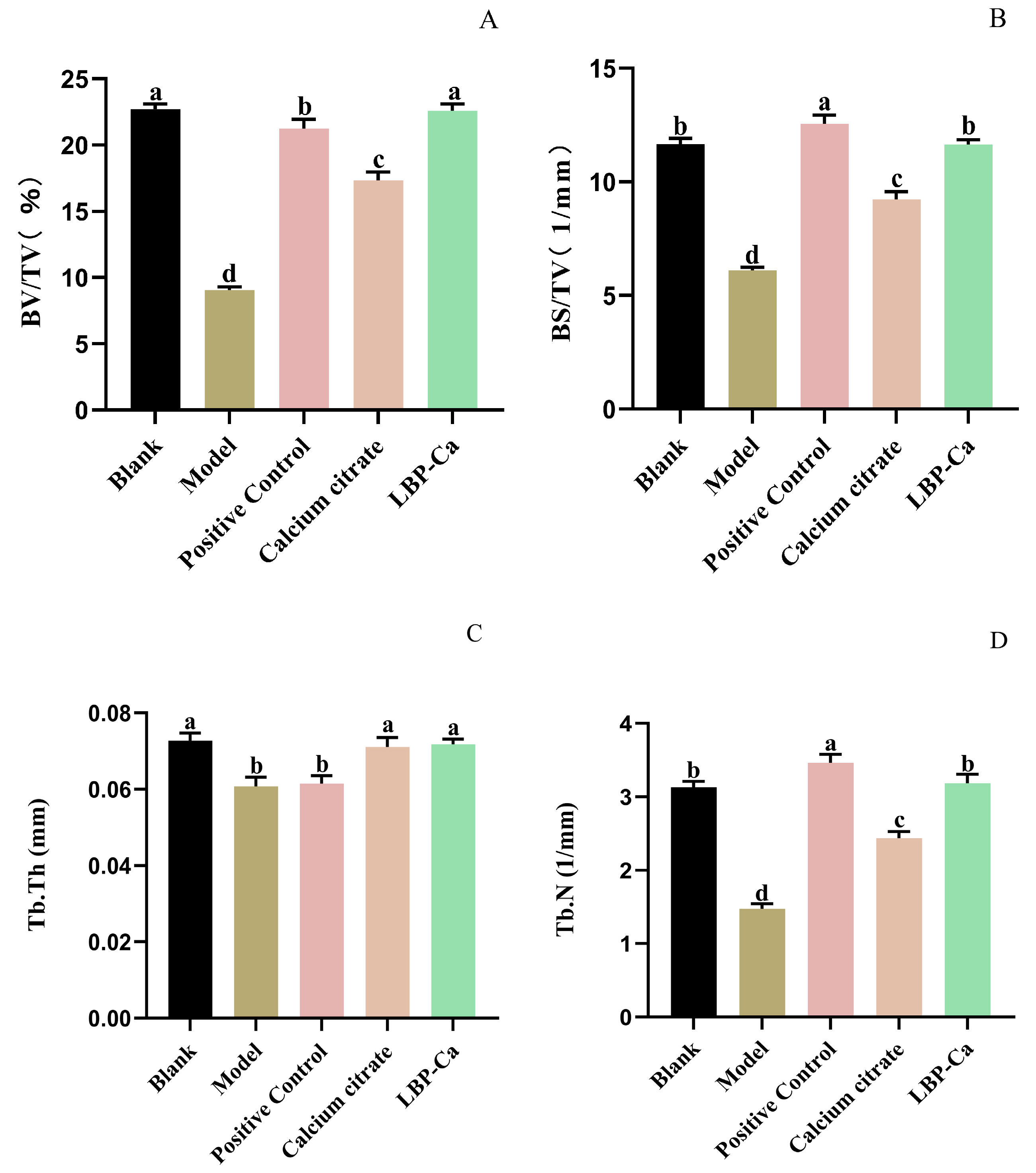
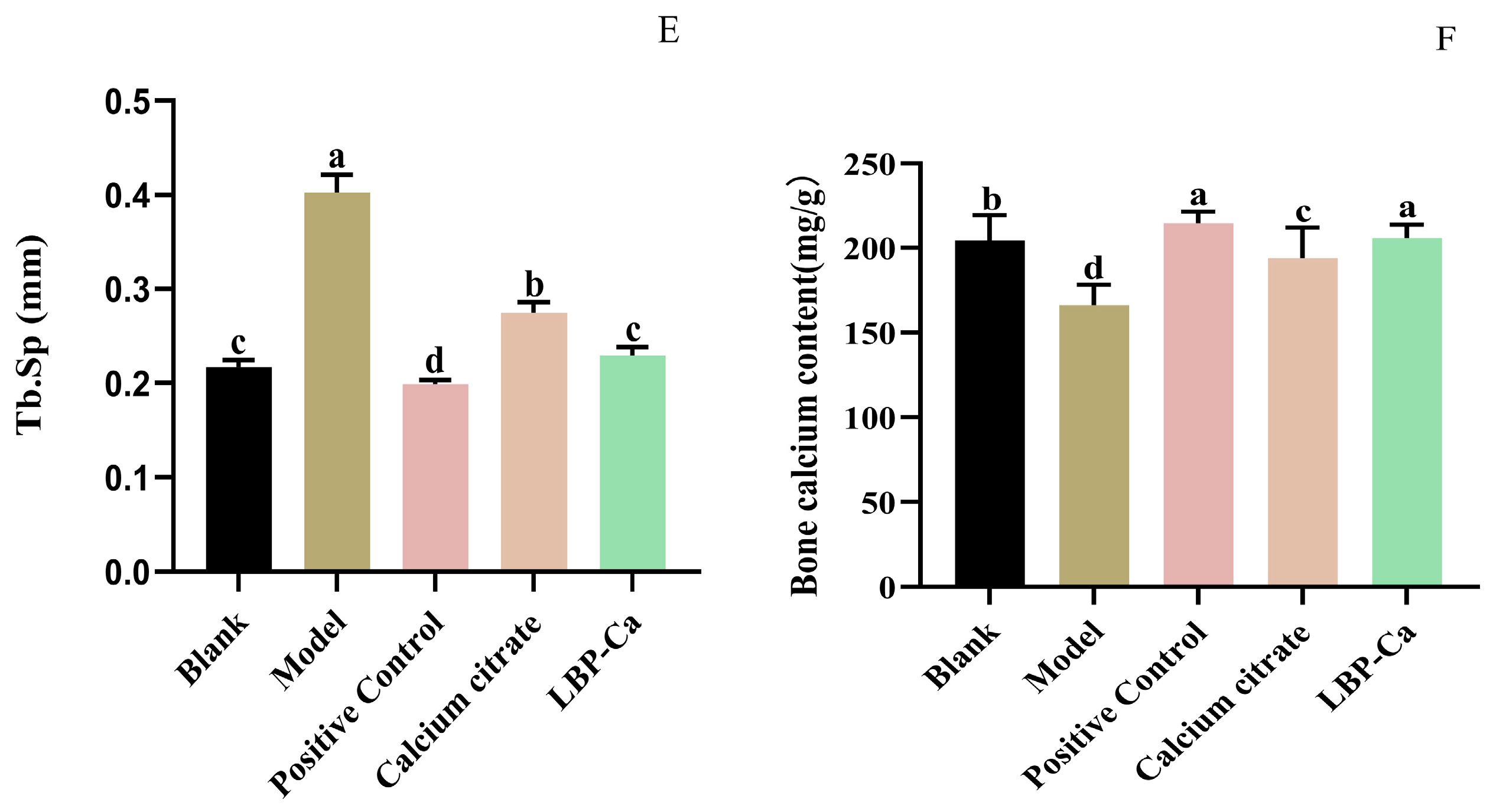
3.6.2. Micro-CT Analysis of Bone Microstructure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, M.; Liu, K. Calcium Supplements and Structure–Activity Relationship of Peptide-Calcium Chelates: A Review. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passarelli, S.; Free, C.M.; Shepon, A.; Beal, T.; Batis, C.; Golden, C.D. Global Estimation of Dietary Micronutrient Inadequacies: A Modelling Analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2024, 12, e1590–e1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, B.; Ding, G. Nutrition Transition and Related Health Challenges over Decades in China. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Gao, Z. Novel Technologies in Utilization of Byproducts of Animal Food Processing: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3420–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezenova, N.Y.; Agafonova, S.V.; Mezenova, O.Y.; Baidalinova, L.S.; Grimm, T. Obtaining and Estimating the Potential of Protein Nutraceuticals from Highly Mineralized Collagen-Containing Beef Raw Materials. Teopuя u npaкmuкa nepepaбomкu мяca 2021, 6, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limeneh, D.Y.; Tesfaye, T.; Ayele, M.; Husien, N.M.; Ferede, E.; Haile, A.; Mengie, W.; Abuhay, A.; Gelebo, G.G.; Gibril, M. A Comprehensive Review on Utilization of Slaughterhouse by-Product: Current Status and Prospect. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, X. Comparative Evaluation of Bone Chars Derived from Bovine Parts: Physicochemical Properties and Copper Sorption Behavior. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambros, M.; Tran, T.; Fei, Q.; Nicolaou, M. Citric Acid: A Multifunctional Pharmaceutical Excipient. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodall, C.M.; Gomes, K.V.; Voigt, A.; Sundmacher, K.; Wilcox, J. Tuning Acid Extraction of Magnesium and Calcium from Platinum Group Metal Tailings for Co 2 Conversion and Storage. RSC Sustain. 2024, 2, 3320–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, K.A.; Winpenny, R.E.; Saiani, A.; Miller, A.F.; Herrick, A.L.; Watson, R.E. Citric Acid is More Effective Than Sodium Thiosulfate in Chelating Calcium in a Dissolution Model of Calcinosis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.; Werner, E.; Erbes, H.-J.; Larrat, V.; Kaltwasser, J. Intestinal Calcium Absorption from Different Calcium Preparations: Influence of Anion and Solubility. Osteoporos. Int. 1996, 6, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Tang, N. Enhanced Solubility and Calcium Absorption of Calcium Gluconate and Calcium Citrate in the Presence of Aspartic Acid and Glutamic Acid. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 410, 125573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavrusova, M.; Skibsted, L.H. Calcium Nutrition. Bioavailability and Fortification. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Straub, D.A. Calcium Supplementation in Clinical Practice: A Review of Forms, Doses, and Indications. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2007, 22, 286–296. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Qi, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Richel, A. Preparation of a Cattle Bone Collagen Peptide–Calcium Chelate by the Ultrasound Method and Its Structural Characterization, Stability Analysis, and Bioactivity on Mc3t3-E1 Cells. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, X. The Formation, Structural Characteristics, Absorption Pathways and Bioavailability of Calcium–Peptide Chelates. Foods 2022, 11, 2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, P.; Xiong, Y.; Yu, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhao, L. Effect of Chlorella Pyrenoidosa Protein Hydrolysate-Calcium Chelate on Calcium Absorption Metabolism and Gut Microbiota Composition in Low-Calcium Diet-Fed Rats. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 348. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, J.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, K.; Kong, X.; Du, M.; Wang, Z.; Xu, B.; Cheng, Y. Isolation, Characterization, and Molecular Docking Analyses of Novel Calcium-Chelating Peptide from Soy Yogurt and the Study of Its Calcium Chelation Mechanism. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 2939–2948. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Alexa, E.-A.; Liu, G.; Berisha, A.; Walsh, R.; Kelleher, R. Lycium Barbarum for Health and Longevity: A Review of Its Biological Significance. Obesities 2025, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Jia, W.; Zhu, J. Advanced Functional Materials as Reliable Tools for Capturing Food-Derived Peptides to Optimize the Peptidomics Pre-Treatment Enrichment Workflow. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2025, 24, e13395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard’s GB 5009.92-2016; National Food Safety Standard for the Determination of Calcium in Foods. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; You, J.; Hu, X. Characterization of Collagen Peptide-Calcium Chelate and Its Promotion of Calcium Absorption in Vitro and in Vivo. Food Biosci. 2025, 66, 106150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Yang, Q.; Lin, J.; Fu, N.; Wang, S. A Specific Peptide with Calcium-Binding Capacity from Defatted Schizochytrium sp. Protein Hydrolysates and the Molecular Properties. Molecules 2017, 22, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Sun, Z.; Sun, J.; Liu, F.; Du, L.; Wang, D. Preparation and Characterization of Polylactic Acid Nanofiber Films Loading Perilla Essential Oil for Antibacterial Packaging of Chilled Chicken. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B.; Hao, Z. Preparation and Characterization of Sesame Peptide-Calcium Chelate with Different Molecular Weight. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 2198–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Wang, Y.; Bao, Z.; Cui, P.; Wang, S.; Lin, S. Calcium Binding to Herring Egg Phosphopeptides: Binding Characteristics, Conformational Structure and Intermolecular Forces. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Ahn, D.U.; Li, S.; Liu, W.; Yi, S.; Huang, X. Effects of Phosvitin Phosphopeptide-Ca Complex Prepared by Efficient Enzymatic Hydrolysis on Calcium Absorption and Bone Deposition of Mice. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, J.; Pei, H.; Shi, M.; Chen, W.; Zong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Du, R.; He, Z. Structural Characterisation of Deer Sinew Peptides as Calcium Carriers, Their Promotion of Mc3t3-E1 Cell Proliferation and Their Effect on Bone Deposition in Mice. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 2587–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Huang, Q.; Huang, S.; Lin, J.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Hong, J.; Rao, P. Novel Peptide with a Specific Calcium-Binding Capacity from Whey Protein Hydrolysate and the Possible Chelating Mode. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10274–10282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, R.C. Spectroscopy of Metal-Ion Complexes with Peptide-Related Ligands. Gas-Phase IR Spectrosc. Struct. Biol. Mol. 2015, 364, 183–223. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza Alizadeh, A.; Hosseini, H.; Mohseni, M.; Eskandari, S.; Sohrabvandi, S.; Hosseini, M.J.; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Mohammadi-Kamrood, M.; Nahavandi, S. Analytic and Chemometric Assessments of the Native Probiotic Bacteria and Inulin Effects on Bioremediation of Lead Salts. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 5142–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minisha, S.; Johnson, J.; Mohammad Wabaidur, S.; Gupta, J.K.; Aftab, S.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Lai, W.-C. Synthesis and Characterizations of Fe-Doped Nio Nanoparticles and Their Potential Photocatalytic Dye Degradation Activities. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Jin, Z.; Li, D.; Yin, H.; Lin, S. An Exploration of the Calcium-Binding Mode of Egg White Peptide, Asp-His-Thr-Lys-Glu, and in Vitro Calcium Absorption Studies of Peptide–Calcium Complex. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9782–9789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Bai, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z. Casein Phosphopeptide Calcium Chelation: Preparation Optimization, in Vitro Gastrointestinal Simulated Digestion, and Peptide Fragment Exploration. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Li, J.; Hu, X.; Chen, S.; Huang, H.; Wu, Y.; Li, Z. Potential Dietary Calcium Supplement: Calcium-Chelating Peptides and Peptide-Calcium Complexes Derived from Blue Food Proteins. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 145, 104364. [Google Scholar]
- Shkembi, B.; Huppertz, T. Calcium Absorption from Food Products: Food Matrix Effects. Nutrients 2021, 14, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, R.; Wang, Q.; Yan, Z. Corrosion in the Food and Beverage Industry. In Industrial Corrosion: Fundamentals, Failure, Analysis and Prevention; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 183–203. [Google Scholar]
- Anyasi, T.; Jideani, A.; Edokpayi, J.; Anokwuru, C. Application of Organic Acids in Food Preservation. In Organic Acids, Characteristics, Properties and Synthesis; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed. Scientific Opinion on the Safety and Efficacy of Citric Acid When Used as a Technological Additive (Preservative) for All Animal Species. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Książek, E. Citric Acid: Properties, Microbial Production, and Applications in Industries. Molecules 2023, 29, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narimani, L.; Lee, V.S.; Alias, Y.; Manan, N.S.; Woi, P.M. Rational Design of a Fluorescent Chromophore as a Calcium Receptor Via DFT and Multivariate Approaches. Molecules 2022, 27, 6248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armas, A.; Sonois, V.; Mothes, E.; Mazarguil, H.; Faller, P. Zinc(II) Binds to the Neuroprotective Peptide Humanin. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2006, 100, 1672–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Ono, T.-A. Chelator-Induced Disappearance of Carboxylate Stretching Vibrational Modes in S2/S1 FTIR Spectrum in Oxygen-Evolving Complex of Photosystem II. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 14061–14068. [Google Scholar]
- Berzina-Cimdina, L.; Borodajenko, N. Research of Calcium Phosphates Using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Infrared Spectrosc.-Mater. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2012, 12, 251–263. [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi, Y.; Noguchi, T. Drastic Changes in the Ligand Structure of the Oxygen-Evolving Mn Cluster Upon Ca2+ Depletion as Revealed by FTIR Difference Spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Bioenerg. 2007, 1767, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Du, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xu, B.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, T.; Gan, J. Calcium-Binding Properties, Stability, and Osteogenic Ability of Phosphorylated Soy Peptide-Calcium Chelate. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1129548. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, P. Preparation and Characterization of Caseinophosphopeptides Mineral Complexes; National Dairy Research Institute: Karnal, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Wang, D.; Sun, L.; Su, R.; Corazzin, M.; Sun, X.; Dou, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, L.; Su, L. Isolation, Purification and Structure Identification of a Calcium-Binding Peptide from Sheep Bone Protein Hydrolysate. Foods 2022, 11, 2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Fu, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhu, H.; Yu, Y.; Feng, X.; Sun, Y.; Dai, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z. Calcium-Chelating Peptides from Rabbit Bone Collagen: Characterization, Identification and Mechanism Elucidation. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Amakye, W.K.; Xiao, G.; Liu, X.; Ren, J.; Wang, M. Intestinal Absorptivity-Increasing Effects of Sodium N-[8-(2-Hydroxybenzoyl) Amino]-Caprylate on Food-Derived Bioactive Peptide. Food Chem. 2023, 401, 134059. [Google Scholar]
- Kellett, G.L. Alternative Perspective on Intestinal Calcium Absorption: Proposed Complementary Actions of Cav1. 3 and Trpv6. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 347–370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Lao, L.; Deng, Y.; Li, Z.; Liao, W.; Duan, S.; Xiao, S.; Cao, Y.; Miao, J. Preparation, Characterization, and Osteogenic Activity Mechanism of Casein Phosphopeptide-Calcium Chelate. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 960228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Du, R.; Liu, J.; He, Z.; Pei, H. Emerging Therapies for Osteoporosis: A Narrative Review of Multifaceted Interventions Involving Plant-and Animal-Derived Bioactive Peptides. Aging Adv. 2025, 2, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
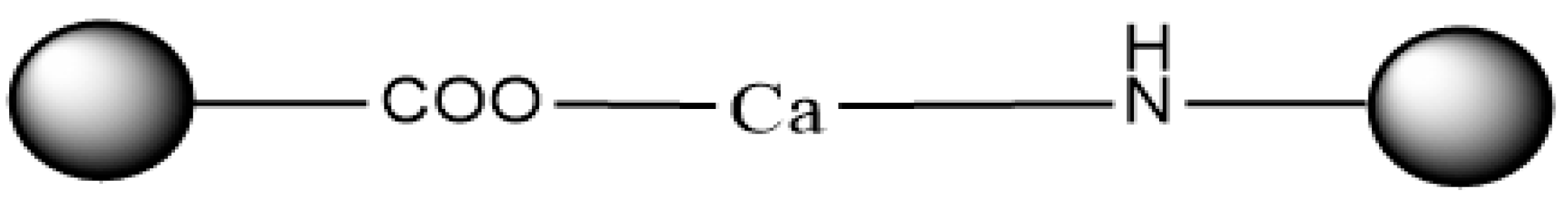


| Run | Citric Acid Concentration (mol/L) | Extraction Time (h) | Material-to-Liquid Ratio | Calcium Extraction Yield (g/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 4 | 1:10 | 0.010 |
| 2 | 2 | 4 | 1:10 | 0.018 |
| 3 | 1 | 8 | 1:10 | 0.014 |
| 4 | 2 | 8 | 1:10 | 0.030 |
| 5 | 1 | 6 | 1:8 | 0.018 |
| 6 | 2 | 6 | 1:8 | 0.037 |
| 7 | 1 | 6 | 1:12 | 0.022 |
| 8 | 2 | 6 | 1:12 | 0.026 |
| 9 | 1.5 | 4 | 1:8 | 0.030 |
| 10 | 1.5 | 8 | 1:8 | 0.033 |
| 11 | 1.5 | 4 | 1:12 | 0.020 |
| 12 | 1.5 | 8 | 1:12 | 0.038 |
| 13 | 1.5 | 6 | 1:10 | 0.041 |
| 14 | 1.5 | 6 | 1:10 | 0.035 |
| 15 | 1.5 | 6 | 1:10 | 0.043 |
| 16 | 1.5 | 6 | 1:10 | 0.038 |
| 17 | 1.5 | 6 | 1:10 | 0.044 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Meansquare | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 0.0018 | 9 | 0.0002 | 23.28 | 0.0002 |
| X1 | 0.0003 | 1 | 0.0003 | 33.01 | 0.0007 |
| X2 | 0.0002 | 1 | 0.0002 | 20.46 | 0.0027 |
| X3 | 0.0000 | 1 | 0.0000 | 2.15 | 0.1858 |
| X1X2 | 0.0000 | 1 | 0.0000 | 1.91 | 0.2091 |
| X1X3 | 0.0001 | 1 | 0.0001 | 6.73 | 0.0358 |
| X2X3 | 0.0001 | 1 | 0.0001 | 6.73 | 0.0358 |
| X12 | 0.0008 | 1 | 0.0008 | 89.72 | <0.0001 |
| X22 | 0.0003 | 1 | 0.0003 | 39.43 | 0.0004 |
| X32 | 5.095 × 10−6 | 1 | 5.095 × 10−6 | 0.6091 | 0.4607 |
| Residual | 0.0001 | 7 | 8.364 × 10−6 | ||
| Lack of Fit | 3.750 × 10−6 | 3 | 1.250 × 10−6 | 0.0912 | 0.9610 |
| Pure Error | 0.0001 | 4 | 0.0000 | ||
| Cor Total | 0.0018 | 16 | |||
| R2 = 0.9677 R2Adj = 0.9261 R2pre = 0.9196 Adeq Precision = 13.8404 C.V.% = 9.89% | |||||
| Water-Extracted Bovine Bones | Acid-Extracted Bovine Bones | LBP-Ca | Calcium Gluconate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium content (mg/mL) | 2 | 44 | 20 | 11 |
| Group | Serum Calcium (μmol/dL) | ALP Activity (U/mL) | Serum Protein (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 98.2 ± 18.7 b | 0.08 ± 0.01 a | 38.5 ± 0.3 a |
| Model | 57.0 ± 24.1 c | 0.47 ± 0.06 c | 38.2 ± 0.5 a |
| Positive Control | 114.5 ± 19.8 a | 0.21 ± 0.04 ab | 38.6 ± 0.4 a |
| Calcium citrate | 105.8 ± 22.3 b | 0.17 ± 0.03 ab | 38.4 ± 0.3 a |
| LBP-Ca | 123.0 ± 24.5 a | 0.15 ± 0.02 ab | 38.3 ± 0.4 a |
| Group | Femur Length (mm) | Femur Index |
|---|---|---|
| Blank | 16.72 ± 0.45 b | 4.30 ± 0.50 b |
| Model | 15.43 ± 0.32 a | 4.06 ± 0.50 c |
| Positive Control | 16.46 ± 0.30 b | 4.56 ± 0.60 a |
| Calcium citrate | 16.05 ± 0.25 ab | 4.55 ± 0.50 a |
| LBP-Ca | 16.68 ± 0.50 b | 4.11 ± 0.60 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Cai, J.; Liu, L.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhong, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Ye, Q. Preparation, Structural Characterization, and Calcium Supplementation Activity of Lycium barbarum Peptide–Calcium Derived from Bovine Bones. Foods 2025, 14, 3812. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223812
Wang L, Cai J, Liu L, Zhu S, Chen Y, Xu M, Zhong J, Li J, Zhang L, Ye Q. Preparation, Structural Characterization, and Calcium Supplementation Activity of Lycium barbarum Peptide–Calcium Derived from Bovine Bones. Foods. 2025; 14(22):3812. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223812
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Long, Jia Cai, Lin Liu, Shunpeng Zhu, Yangxi Chen, Min Xu, Jie Zhong, Jiaxin Li, Liang Zhang, and Qiang Ye. 2025. "Preparation, Structural Characterization, and Calcium Supplementation Activity of Lycium barbarum Peptide–Calcium Derived from Bovine Bones" Foods 14, no. 22: 3812. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223812
APA StyleWang, L., Cai, J., Liu, L., Zhu, S., Chen, Y., Xu, M., Zhong, J., Li, J., Zhang, L., & Ye, Q. (2025). Preparation, Structural Characterization, and Calcium Supplementation Activity of Lycium barbarum Peptide–Calcium Derived from Bovine Bones. Foods, 14(22), 3812. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14223812







