Characterization and Discrimination of Pure Standards of Phenolic Compounds Using FTIR Spectroscopy in the Terahertz Range
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Standards
2.2. Experimental Setup
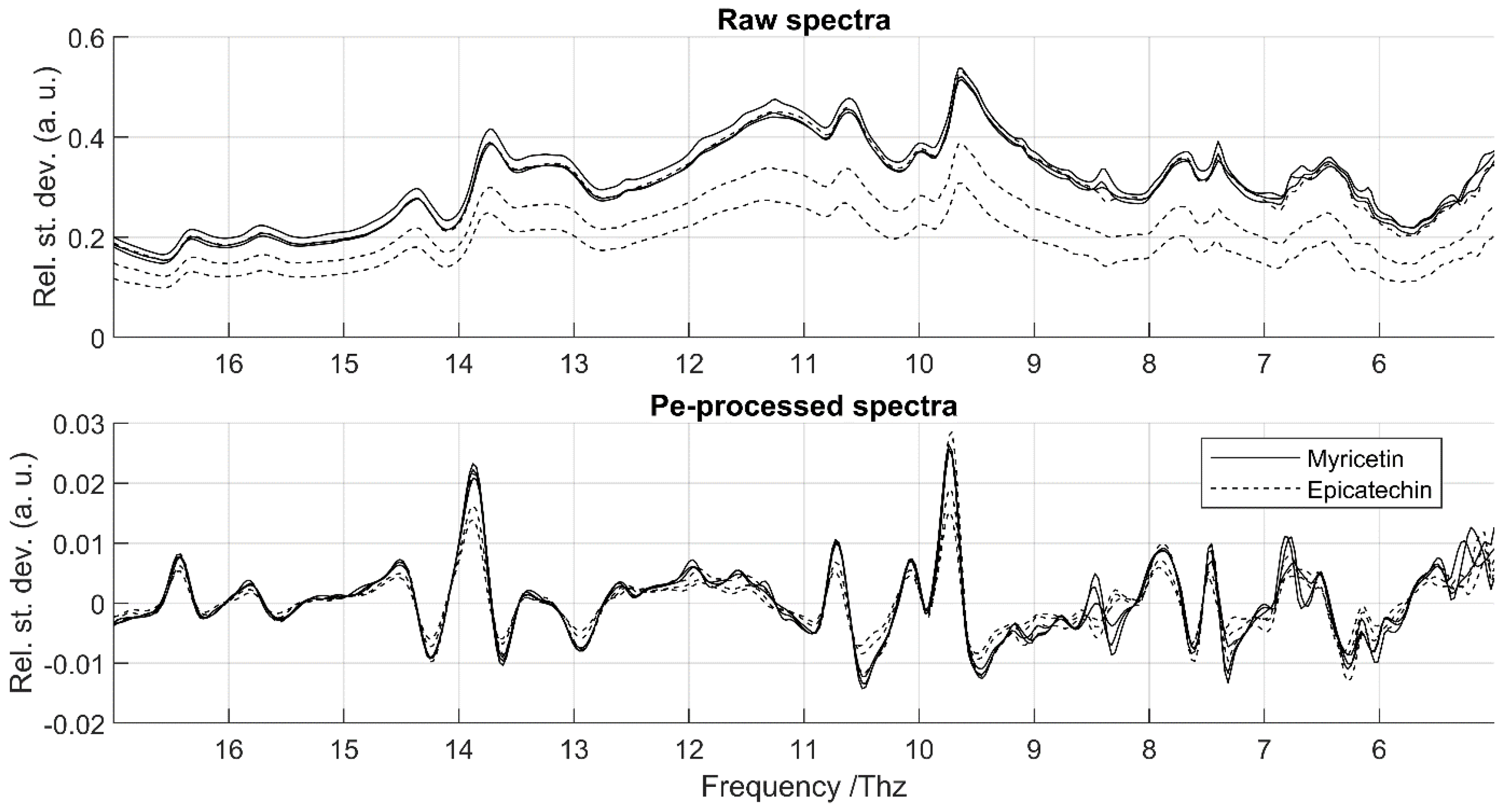
2.3. Spectral Pre-Processing
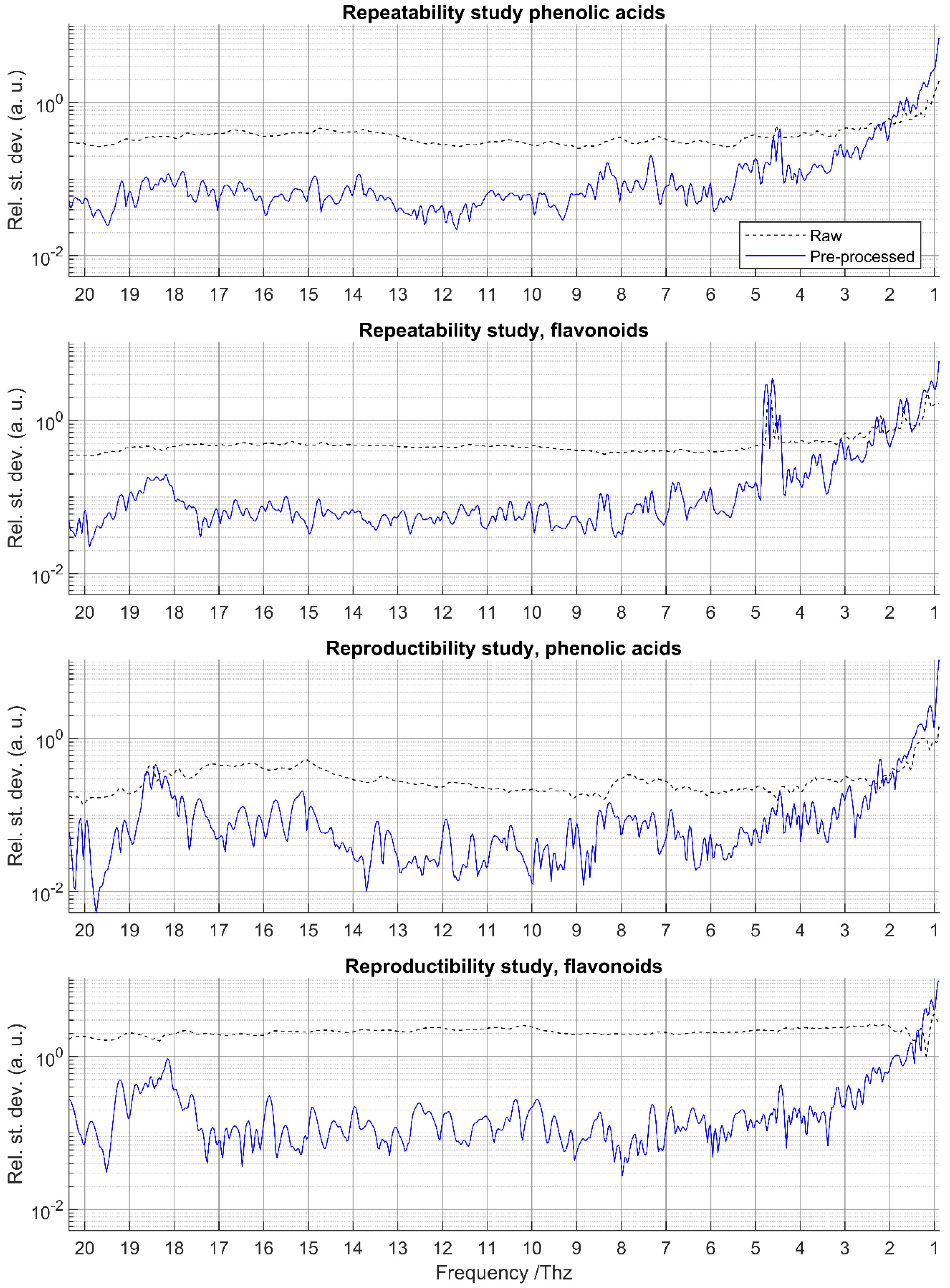
2.4. Assessment of Repeatability and Time-Reproducibility
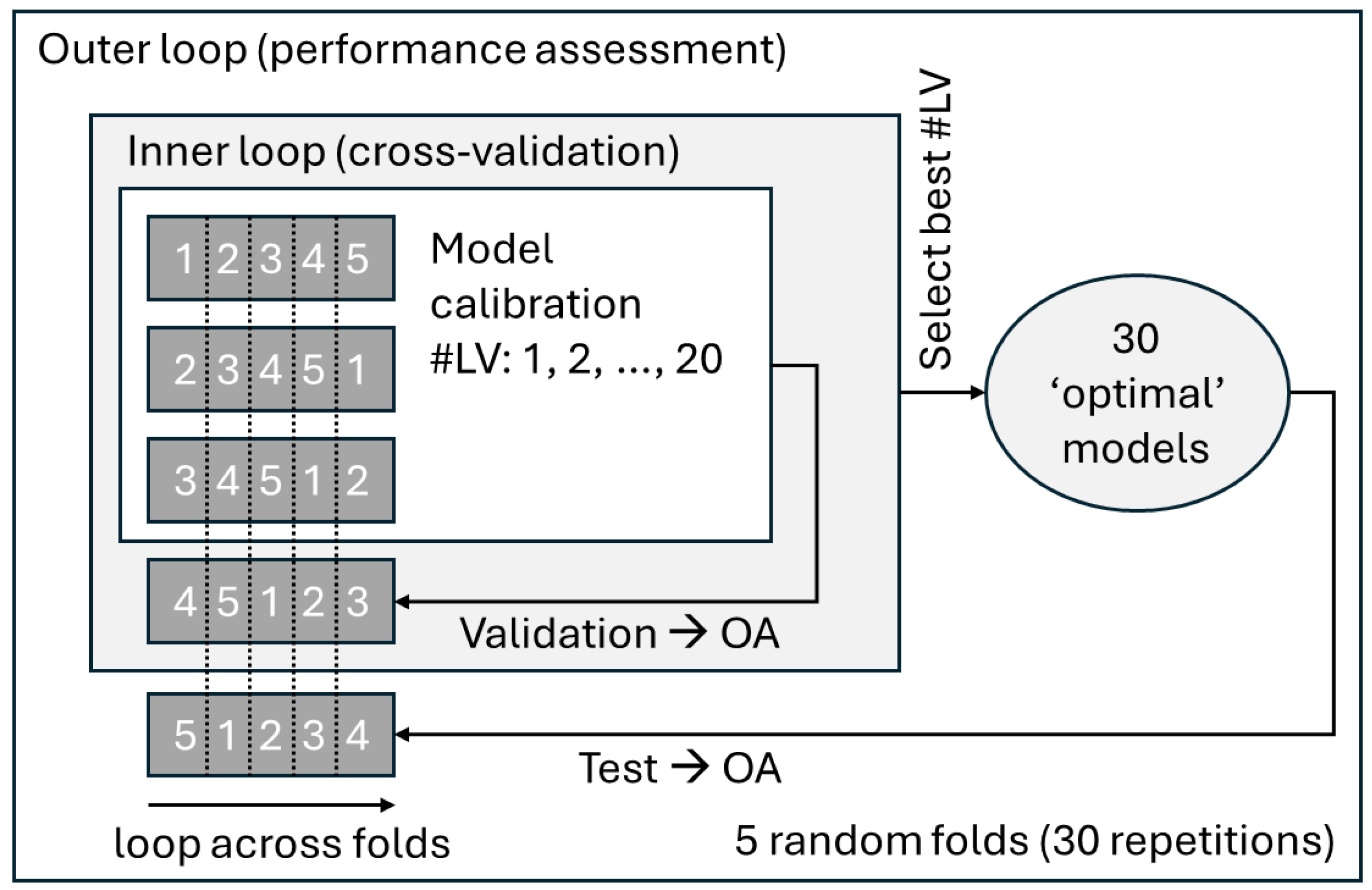
2.5. Predictive Classification Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Data Cleaning
3.2. Repeatability and Time-Reproducibility
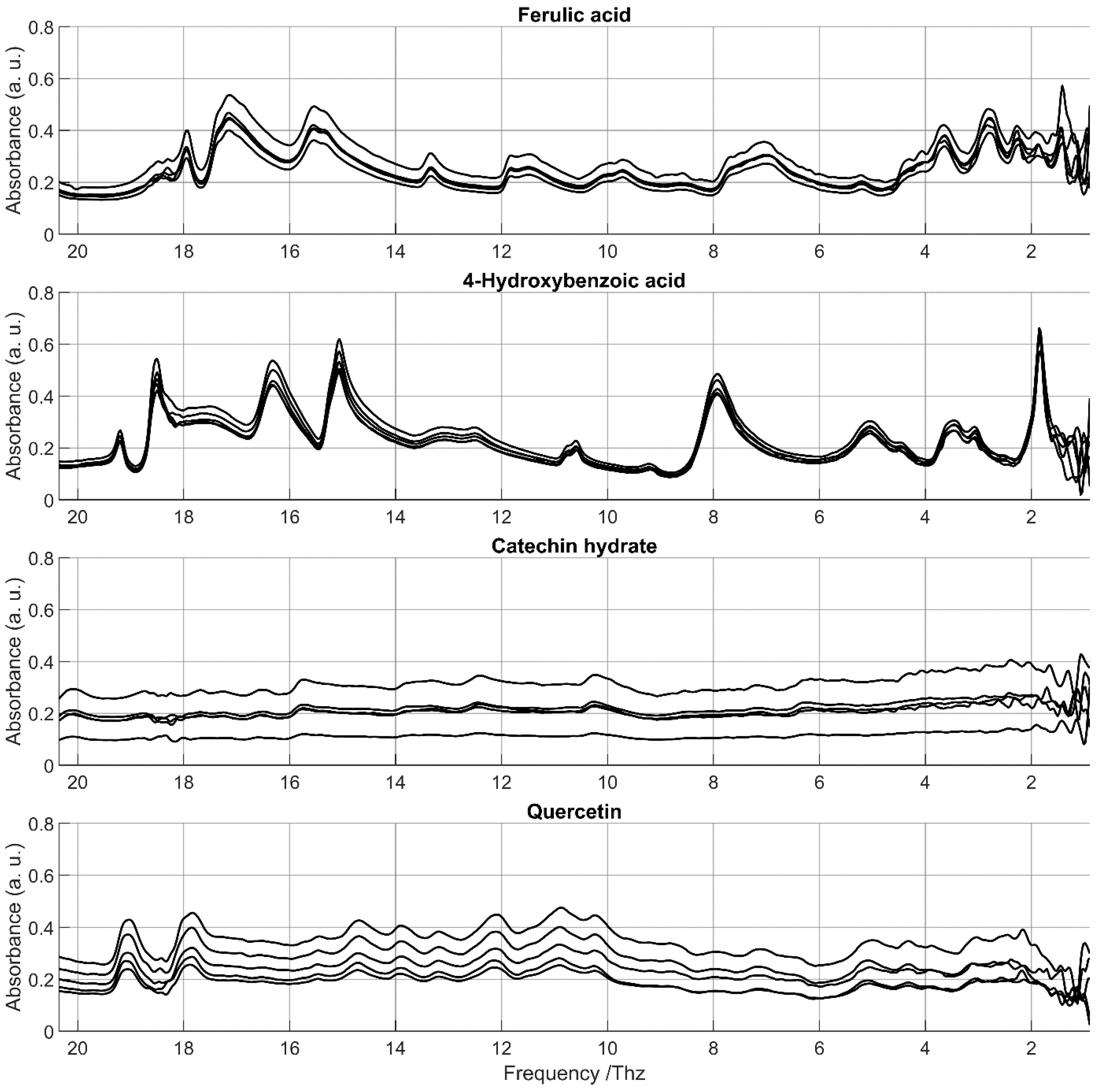
3.3. FIR Characterization of Phenolic Compounds
3.3.1. Phenolic Acids
3.3.2. Flavonoids
3.4. Predictive Classification Modeling
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| PC | Phenolic compound |
| THz | Terahertz |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| GC | Gas chromatography |
| GC–MS | Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
| MIR | Mid infrared |
| FIR | Far infrared |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| PLS-DA | Partial least squares discriminant analysis |
| LV | Latent variable |
| CS# | Case study # |
| R# | Range # |
References
- Li, A.N.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.J.; Xu, X.R.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, H.B. Resources and biological activities of natural polyphenols. Nutrients 2014, 6, 6020–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, P.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, Y. A Brief Review of Phenolic Compounds Identified from Plants: Their Extraction, Analysis, and Biological Activity. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2022, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alara, O.R.; Abdurahman, N.H.; Ukaegbu, C.I. Extraction of phenolic compounds: A review. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Huang, Q.; Fu, Z.; Lu, Y. Analysis of Flavonoid Compounds by Terahertz Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 18134–18141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.B.; Walsh, K.B.; Naiker, M.; Ameer, K. The Use of Infrared Spectroscopy for the Quantification of Bioactive Compounds in Food: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, O.; Compère, G.; Larondelle, Y.; Pompeu, D.; Rogez, H.; Baeten, V. Phenolic compound explorer: A mid-infrared spectroscopy database. Vib. Spectrosc. 2017, 92, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, Y. Infrared Spectroscopy—Mid-infrared, Near-infrared, and Far-infrared/Terahertz Spectroscopy. Anal. Sci. 2021, 37, 1193–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, P.Y.; Tani, M.; Usami, M.; Kono, S.; Kersting, R.; Zhang, X.C. A direct comparison between terahertz time-domain spectroscopy and far-infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 2357–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsah-Hejri, L.; Akbari, E.; Toudeshki, A.; Homayouni, T.; Alizadeh, A.; Ehsani, R. Terahertz spectroscopy and imaging: A review on agricultural applications. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 177, 105628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Bai, X.; Wei, M.; Jiang, H.; Xu, L. Terahertz Spectroscopy for Food Quality Assessment: A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2025, 14, 2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.H.; Otani, C. Terahertz spectroscopy technology as an innovative technique for food: Current state-of-the-Art research advances. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2523–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, B.B.; Spiteller, M. On the chemical identification and determination of flavonoids in solid-state. Talanta 2012, 94, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Liu, C.; Qu, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zheng, L. Discrimination and Measurements of Three Flavonols with Similar Structure Using Terahertz Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2018, 39, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompeu, D.R.; Larondelle, Y.; Rogez, H.; Abbas, O.; Pierna, J.A.F.; Baeten, V. Characterization and discrimination of phenolic compounds using Fourier transform Raman spectroscopy and chemometric tools. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. Environ. 2018, 22, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, S.; Marles, R.J. Monocyclic phenolic acids; hydroxy- and polyhydroxybenzoic acids: Occurrence and recent bioactivity studies. Molecules 2010, 15, 7985–8005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Zhao, G.; Wang, H. Terahertz spectrum of gallic acid. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Optical Instruments and Technology: Optoelectronic Information Security, Shanghai, China, 19–22 October 2009; Volume 7512, p. 75120E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Zhao, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, X.; Li, W. Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy of four hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives. J. Biol. Phys. 2006, 32, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Liang, D.; Yin, X. Terahertz spectral vibrational properties and weak interactions analysis of caffeic acid and ferulic acid. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1270, 133960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wan, J.; Zhu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, W. Using terahertz spectroscopy to quantify bioactive flavonoids in Moxa Wool as predictor of rheumatoid arthritis treatment outcomes. Phytomedicine 2024, 133, 155927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.H.; Otani, C.; Ogawa, Y. Innovatively identifying naringin and hesperidin by using terahertz spectroscopy and evaluating flavonoids extracts from waste orange peels by coupling with multivariate analysis. Food Control 2022, 137, 108897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsah-Hejri, L.; Hajeb, P.; Ara, P.; Ehsani, R.J. A Comprehensive review on food applications of Terahertz Spectroscopy and Imaging. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1563–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Family | Class | Phenolic Compound |
|---|---|---|
| Phenolic acid | Hydroxybenzoic acid | gentisic acid 1,2,3; ellagic acid 1,2,3; syringic acid 1,2,3; vanillic acid 1,2,3, gallic acid 1,2; salicylic acid 2; 4-hydroxybenzoic acid 2,3; protocatechuic acid 2,3; |
| Hydroxycinnamic acid | caffeic acid 1,2,3; chlorogenic acid 1,2; sinapic acid 2; ferulic acid 2; 2-coumaric acid 2,3; | |
| Flavonoid | Flavanol | catechin 3; catechin hydrate 1; epicatechin 3; epigallocatechin 3; epicatechin gallate 3; epigallocatechin gallate 3; |
| Flavonol | quercetin anhydrous 2; quercetin dihydrate 1; quercetin-3-b-D-glucoside 2; quercetin 1; rutin hydrate 2; rutin 3; kaempferol 2; myricetin 2; isorhamnetin 3; | |
| Anthocyanin | cyanidin chloride 3; keracyanin chloride 3; kuromanin chloride 3; myrtillin chloride 3; | |
| Dihydrochalcone | phloretin 2; phlorizin 2; | |
| Flavone | luteolin 1,3; | |
| Flavanone | eriodictyol 2; bavachinin 3; | |
| Isoflavone | genistein 3; daidzein 3; |
| Phenolic Compound | Family | Class | Supplier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ferulic acid | Phenolic acid | Hydroxycinnamic acid | Sigma-Aldrich |
| 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | Phenolic acid | Hydroxybenzoic acid | Extrasynthese |
| Catechin hydrate | Flavonoid | Flavanol | VWR |
| Quercetin | Flavonoid | Flavonol | Sigma-Aldrich |
| R0 | R1 | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS1 CS2 CS3 | 0.964 (0.692–1.000) | 0.985 (0.872–1.000) | 0.987 (0.872–1.000) |
| 0.972 (0.769–1.000) | 0.979 (0.923–1.000) | 0.995 (0.962–1.000) | |
| 0.974 (0.692–1.000) | 0.874 (0.692–1.000) | 0.892 (0.538–1.000) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pissard, A.; Baeten, V.; Arnould, Q.; Rogez, H.; Stevens, F. Characterization and Discrimination of Pure Standards of Phenolic Compounds Using FTIR Spectroscopy in the Terahertz Range. Foods 2025, 14, 3737. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213737
Pissard A, Baeten V, Arnould Q, Rogez H, Stevens F. Characterization and Discrimination of Pure Standards of Phenolic Compounds Using FTIR Spectroscopy in the Terahertz Range. Foods. 2025; 14(21):3737. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213737
Chicago/Turabian StylePissard, Audrey, Vincent Baeten, Quentin Arnould, Hervé Rogez, and François Stevens. 2025. "Characterization and Discrimination of Pure Standards of Phenolic Compounds Using FTIR Spectroscopy in the Terahertz Range" Foods 14, no. 21: 3737. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213737
APA StylePissard, A., Baeten, V., Arnould, Q., Rogez, H., & Stevens, F. (2025). Characterization and Discrimination of Pure Standards of Phenolic Compounds Using FTIR Spectroscopy in the Terahertz Range. Foods, 14(21), 3737. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213737







