Qualitative Characteristics of Semolina–Pulse Flour Mixes and Related Breads
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wheat Flours and Origin of Pulses
2.2. Milling Process and Composition of Mixed Flours with Pulses
2.3. Determination of Moisture, Ash, and Color Characteristics in Flours and Breads
2.4. Water- and Oil-Binding Capacity of Flours
2.5. Rheological Analyses
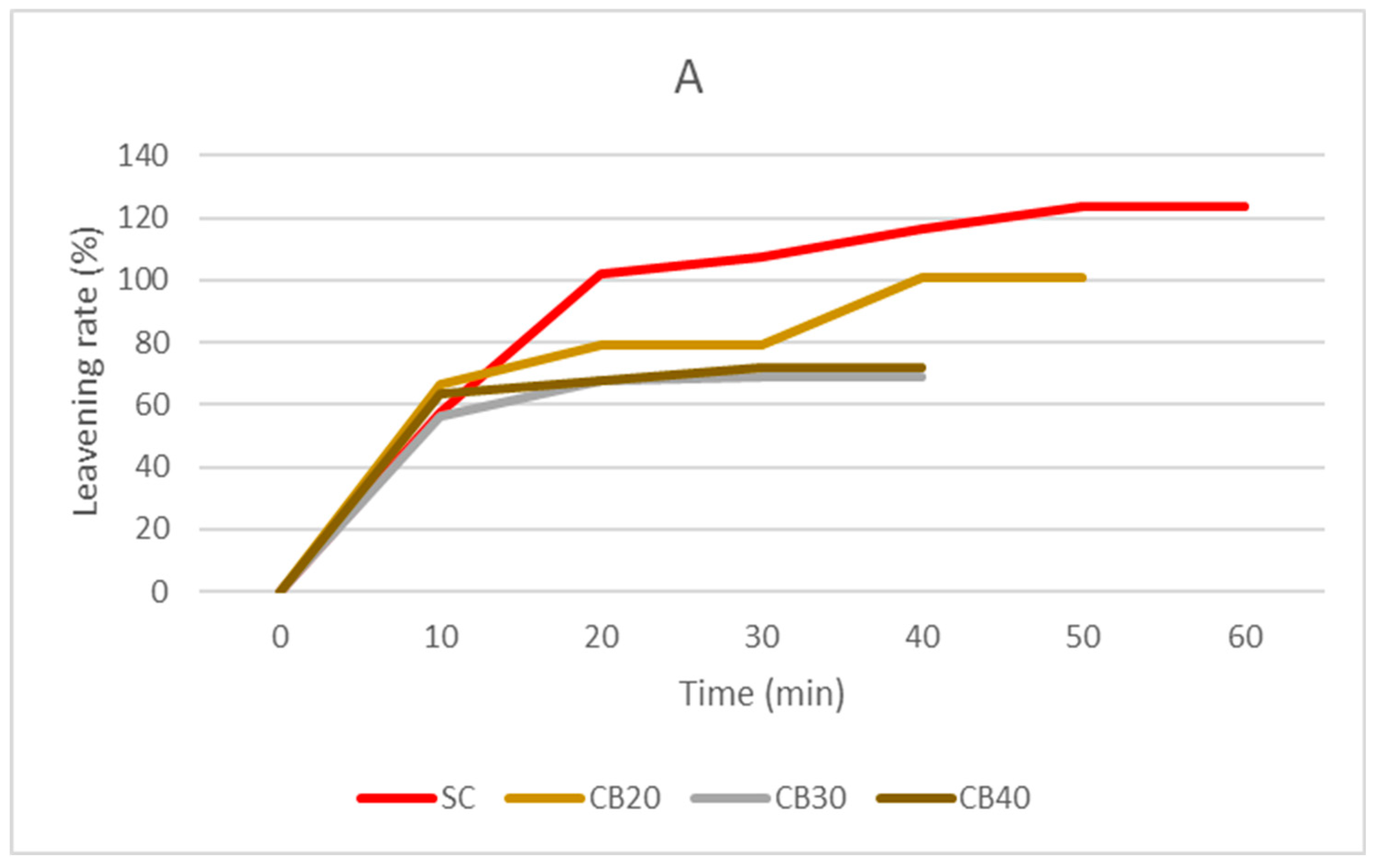
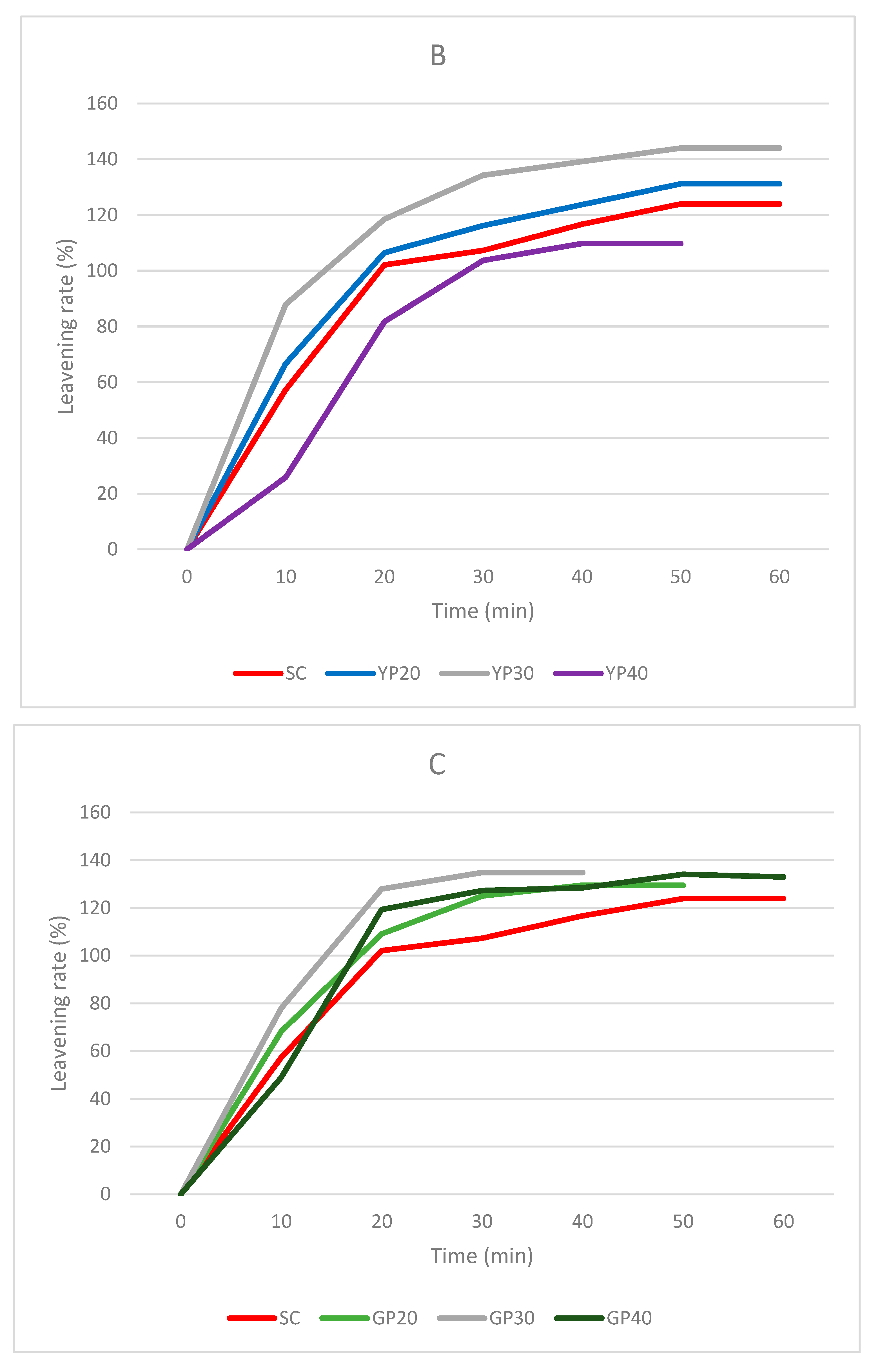
2.6. Leavening Test
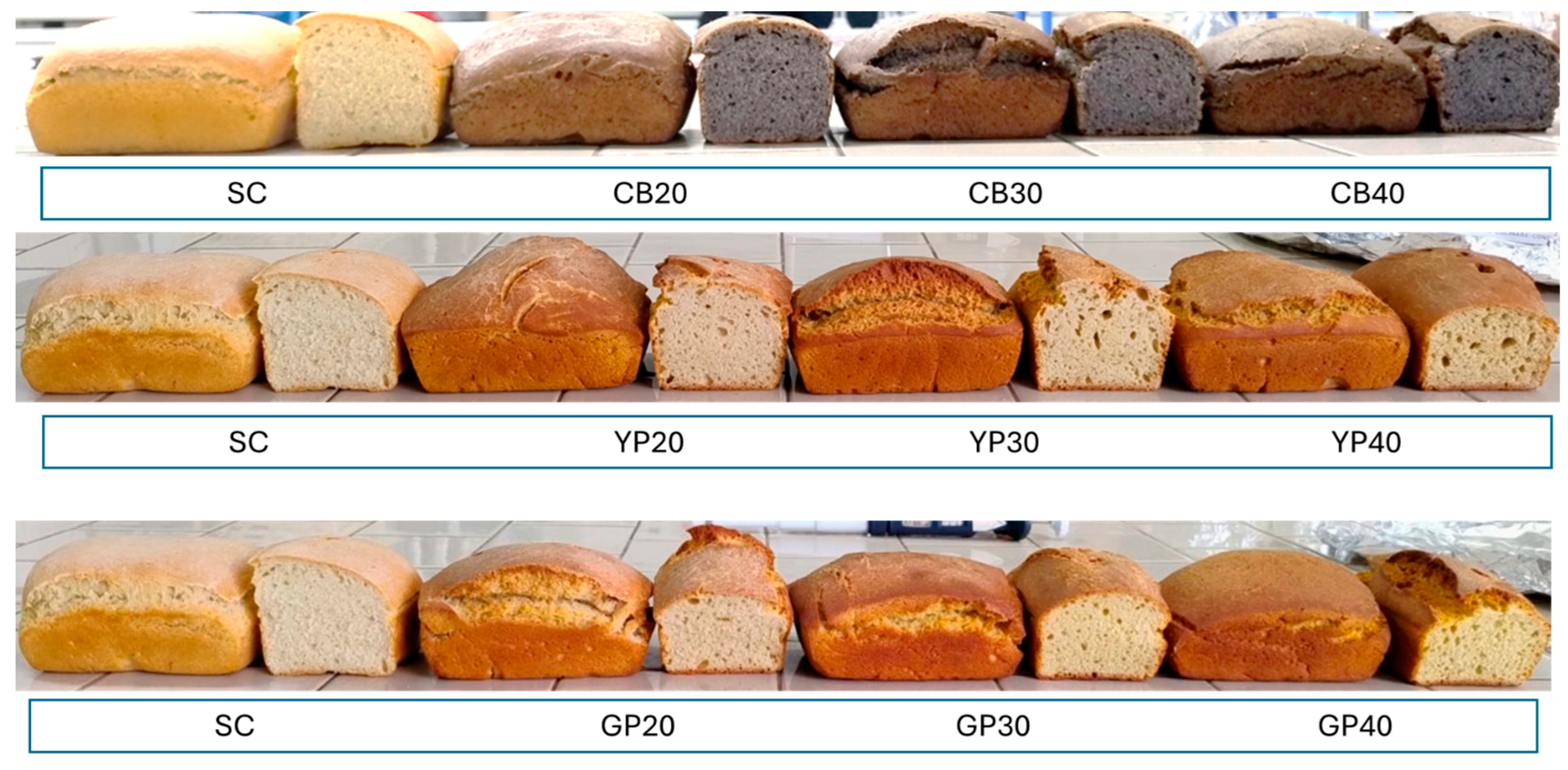
2.7. Bread Production
2.8. Physical Properties of Bread and Texture Profile Analyses (TPA)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
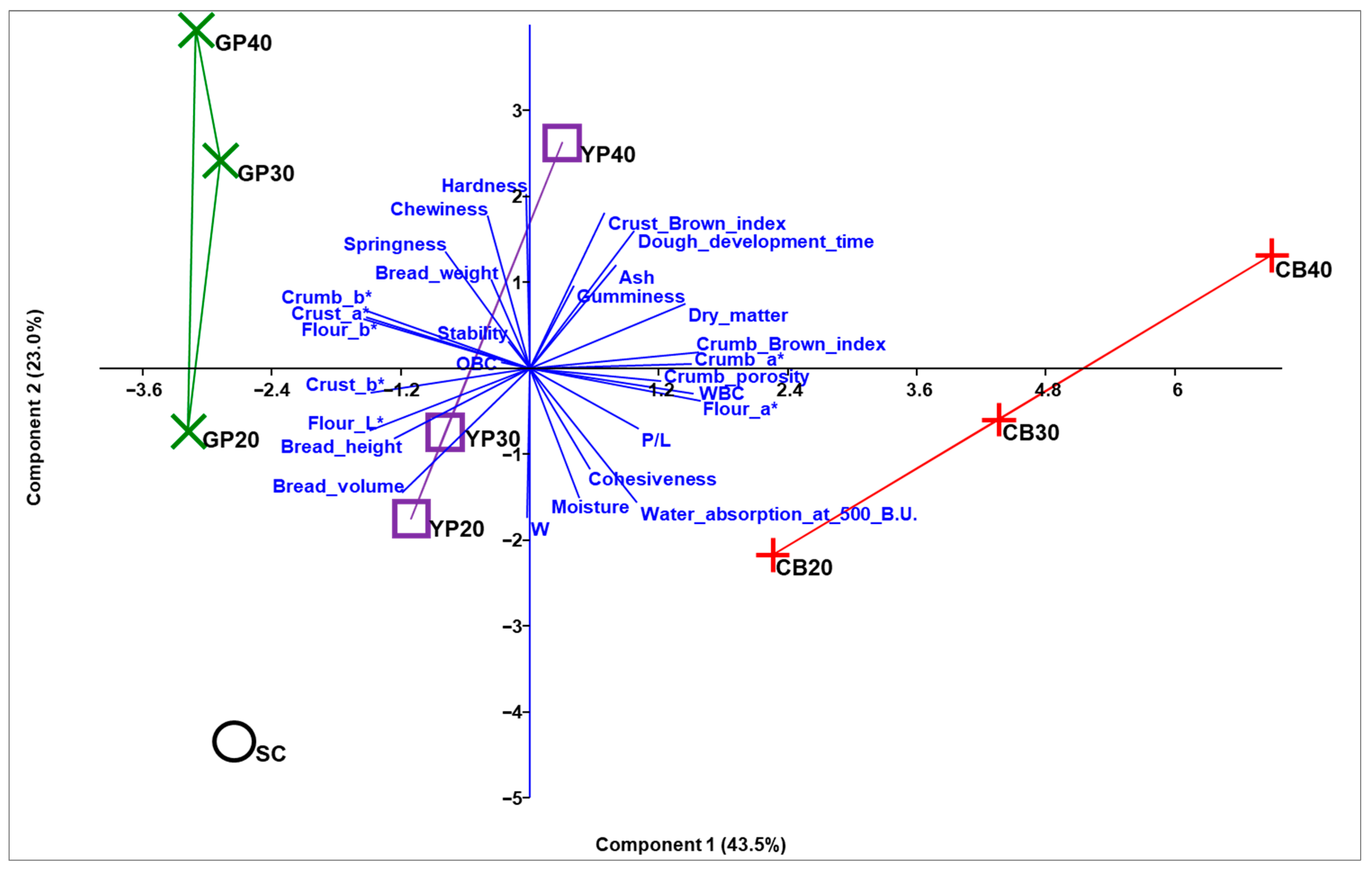
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical Analyses of Flours
3.2. Technological Analysis of Doughs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spina, A.; De Benedetti, S.; Heinzl, G.C.; Ceravolo, G.; Magni, C.; Emide, D.; Castorina, G.; Consonni, G.; Canale, M.; Scarafoni, A. Biochemical characterization of the seed quality of a collection of white lupin landraces from Southern Italy. Plants 2024, 13, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaraluce, G.; Bentivoglio, D.; Finco, A. Circular economy for a sustainable agri-food supply chain: A review for current trends and future pathways. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.; Donovan, J.; Topple, C. Achieving sustainability in food manufacturing operations and their supply chains: Key insights from a systematic literature review. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 28, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, A.; Scarangella, M.; Canale, M.; Sanfilippo, R.; Giannone, V.; Summo, C.; Pasqualone, A. Nutritional features of flour blends composed of durum wheat and lupin. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 4812–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Królak, M.; Górska-Warsewicz, H.; Mądra-Sawicka, M.; Rejman, K.; Żakowska-Biemans, S.; Szlachciuk, J.; Czeczotko, M.; Kwiatkowski, B.; Zaremba, R.; Wojtaszek, M. Towards sustainable innovation in the bakery sector—An example of fibre-enriched bread. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melini, V.; Melini, F.; Luziatelli, F.; Ruzzi, M. Functional ingredients from agri-food waste: Effect of inclusion thereof on phenolic compound content and bioaccessibility in bakery products. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spina, A.; Summo, C.; Timpanaro, N.; Canale, M.; Sanfilippo, R.; Amenta, M.; Strano, M.C.; Allegra, M.; Papa, M.; Pasqualone, A. Lupin as ingredient in durum wheat breadmaking: Physicochemical properties of flour blends and bread quality. Foods 2024, 13, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jian, C. Sustainable plant-based ingredients as wheat flour substitutes in bread making. npj Sci. Food 2022, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Araiza, O.; Boukid, F.; Suo, X.; Wang, S.; Vittadini, E. Pretreated green pea flour as wheat flour substitutes in composite bread making. Foods 2023, 12, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutroneo, S.; Petrusan, J.I.; Stolzenberger, R.; Zurlini, C.; Tedeschi, T. Formulation of new sourdough bread prototypes fortified with non-compliant chickpea and pea residues. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1351443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setia, R.; Dai, Z.; Nickerson, M.T.; Sopiwnyk, E.; Malcolmson, L.; Ai, Y. Properties and bread-baking performance of wheat flour composited with germinated pulse flours. Cereal Chem. 2020, 97, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaadaoui, A.; Elyadini, M.; Hamal, A. Legumes as preventive nutraceuticals for chronic diseases. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 45: Legume Agriculture and Biotechnology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, R.; Phillips, E.M.; Campbell, A. Legumes: Health benefits and culinary approaches to increase intake. Clin. Diabetes 2015, 33, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duodu, K.G.; Minnaar, A. Legume composite flours and baked goods: Nutritional, functional, sensory, and phytochemical qualities. In Flour and Breads and Their Fortification in Health and Disease Prevention; Academic Press: London, UK, 2011; pp. 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, J.; Malalgoda, M.; Storsley, J.; Malunga, L.; Netticadan, T.; Thandapilly, S.J. Health benefits of cereal grain- and pulse-derived proteins. Molecules 2022, 27, 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boye, J.; Zare, F.; Pletch, A. Pulse proteins: Processing, characterization, functional properties and applications in food and feed. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, F.; Boye, J.I.; Simpson, B.K. Bioactive proteins and peptides in pulse crops: Pea, chickpea and lentil. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miñarro, B.; Albanell, E.; Aguilar, N.; Guamis, B.; Capellas, M. Effect of legume flours on baking characteristics of gluten-free bread. J. Cereal Sci. 2012, 56, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, R.; Sissons, M. Durum wheat products, couscous. In Wheat Quality for Improving Processing and Human Health; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 347–367. [Google Scholar]
- Brescia, M.A.; Sacco, D.; Sgaramella, A.; Pasqualone, A.; Simeone, R.; Peri, G.; Sacco, A. Characterisation of different typical Italian breads by means of traditional, spectroscopic and image analyses. Food Chem. 2017, 104, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebben, L.; Shen, Y.; Li, Y. Improvers and functional ingredients in whole wheat bread: A review of their effects on dough properties and bread quality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 81, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbica, A.; Belović, M.; Tomić, J. Novel breads of non-wheat flours. Food Chem. 2019, 282, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turfani, V.; Narducci, V.; Durazzo, A.; Galli, V.; Carcea, M. Technological, nutritional and functional properties of wheat bread enriched with lentil or carob flours. LWT 2017, 78, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, A.; Marti, A. Using pulses in baked products: Lights, shadows, and potential solutions. Foods 2019, 8, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojňanská, T.; Musilová, J.; Vollmannová, A. Effects of adding legume flours on the rheological and breadmaking properties of dough. Foods 2021, 10, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierotti, G.; Dazzi, C.; Raimondi, S. Carta Dei Suoli Della Sicilia (Soil Map of Sicily); Regione Siciliana, Assessorato Territorio e Ambiente: Palermo, Italy, 1988. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Method 935.25; AOAC International: Arlington, WA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 2171:2007; Cereals, Pulses and By-Products—Determination of Ash Yield by Incineration. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Sanfilippo, R.; Canale, M.; Dugo, G.; Oliveri, C.; Scarangella, M.; Strano, M.C.; Amenta, M.; Crupi, A.; Spina, A. Effects of partial replacement of durum wheat re-milled semolina with bean flour on physico-chemical and technological features of doughs and breads during storage. Plants 2023, 12, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC. Approved Methods of Analysis, 11th ed.; The American Association of Cereal Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- UNI 10453:1995; Durum Wheat and Semolina. Determination of Rheological Characteristics by Alveograph. Ente Italiano di Normazione: Milan, Italy, 1995.
- Canale, M.; Spina, A.; Summo, C.; Strano, M.C.; Bizzini, M.; Allegra, M.; Sanfilippo, R.; Amenta, M.; Pasqualone, A. Waste from artichoke processing industry: Reuse in bread-making and evaluation of the physico-chemical characteristics of the final product. Plants 2022, 11, 3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, M.; Sanfilippo, R.; Strano, M.C.; Bavaro, A.R.; Amenta, M.; Bizzini, M.; Spina, A. Technological properties of inulin-enriched doughs and breads, influence on short-term storage and glycemic response. Foods 2024, 13, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallmann, H. Porentabelle, 4th ed.; Verlag Moritz Schäfer: Detmold, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Rózylo, R.; Laskowski, J. Predicting bread quality (bread loaf volume and crumb texture). Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2011, 61, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Millar, K.A.; Gallagher, E.; Burke, R.; McCarthy, S.; Barry-Ryan, C. Proximate composition and anti-nutritional factors of fava-bean (Vicia faba), green-pea and yellow-pea (Pisum sativum) flour. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 82, 103233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribéreau, S.; Aryee, A.N.; Tanvier, S.; Han, J.; Boye, J.I. Composition, digestibility, and functional properties of yellow pea as affected by processing. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiq, M.; Ravi, R.; Harte, J.B.; Dolan, K.D. Physical and functional characteristics of selected dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) flours. LWT 2010, 43, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.; Pathak, K.; Das, P.; Baruah, A.R.; Kalita, H.; Baishya, S. Nutritional evaluation of few grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) genotypes of Assam. Indian J. Agric. Biochem. 2022, 35, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannone, V.; Giarnetti, M.; Spina, A.; Todaro, A.; Pecorino, B.; Summo, C.; Pasqualone, A. Physico-chemical properties and sensory profile of durum wheat Dittaino PDO bread and quality of re-milled semolina used for its production. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójtowicz, A.; Mościcki, L. Influence of legume type and addition level on quality characteristics, texture and microstructure of enriched precooked pasta. LWT 2014, 59, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekipoor, R.; Johnson, S.K.; Bhattarai, R.R. Lupin kernel fibre: Nutritional composition, processing methods, physicochemical properties, consumer acceptability and health effects of its enriched products. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Boye, J.I.; Simpson, B.K.; Prasher, S.O.; Monpetit, D.; Malcolmson, L. Thermal processing effects on the functional properties and microstructure of lentil, chickpea, and pea flours. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2534–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, M.; Handa, S.; Mridula, D.; Singh, R.K. Physicochemical, functional and rheological properties of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) flour as influenced by particle size. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuma, B.; Admasu, H.; Leta, S. Characterization of physicochemical, functional, and pasting properties of flours made from wheat, grass pea, anchote, and blends. Int. J. Food Eng. Technol. 2023, 7, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Norton, R.S. Metabolic changes induced during adaptation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to a water stress. Arch. Microbiol. 1991, 156, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, A.A.; Ross, K.A.; Lukow, O.M.; Fulcher, R.G.; Arntfield, S.D. Influence of added bean flour (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) on some physical and nutritional properties of wheat flour tortillas. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondor, M.; Guévremont, E.; Villeneuve, S. Processing, characterization and bread-making potential of malted yellow peas. Food Biosci. 2014, 7, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacak-Pietrzak, G.; Sujka, K.; Księżak, J.; Bojarszczuk, J.; Dziki, D. Sourdough wheat bread enriched with grass pea and lupine seed flour: Physicochemical and sensory properties. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atudorei, D.; Atudorei, O.; Codină, G.G. Dough rheological properties, microstructure and bread quality of wheat-germinated bean composite flour. Foods 2021, 10, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndife, J.; Abdulraheem, L.O.; Zakari, U.M. Evaluation of the nutritional and sensory quality of functional breads produced from whole wheat and soya bean flour blends. Afr. J. Food Sci. 2011, 5, 466–472. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava, C.; Chakraborty, S. Bread from wheat flour partially replaced by fermented chickpea flour: Optimizing the formulation and fuzzy analysis of sensory data. LWT 2018, 90, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaani, M. Characterization of whole wheat bread reformulated with pea and soy protein isolates. Int. J. Nutr. Pharmacol. Neurol. Dis. 2020, 10, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elleuch, M.; Bedigian, D.; Roiseux, O.; Besbes, S.; Blecker, C.; Attia, H. Dietary fibre and fibre-rich by-products of food processing: Characterisation, technological functionality and commercial applications: A review. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peressini, D.; Sensidoni, A. Effect of soluble dietary fibre addition on rheological and breadmaking properties of wheat doughs. J. Cereal Sci. 2009, 49, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladugula, M.P.; Smith, B.; Morris, C.F.; Kiszonas, A. Incorporation of yellow pea flour into white pan bread. Cereal Chem. 2021, 98, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsiou, K.; Sacharidis, D.D.; Matsakidou, A.; Biliaderis, C.G.; Lazaridou, A. Impact of roasted yellow split pea flour on dough rheology and quality of fortified wheat breads. Foods 2021, 10, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Particle Size Distribution (%) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ø (μm) | SC | CB | YP | GP | CB20 | CB30 | CB40 | YP20 | YP30 | YP40 | GB20 | GB30 | GB40 |
| >300 | 0.1 | 6.2 | 6.0 | 2.2 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 1.2 |
| 200–300 | 0.5 | 35.0 | 29.0 | 6.8 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.6 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 1.8 |
| 180–200 | 31.4 | 47.2 | 51.0 | 29.0 | 44.0 | 45.0 | 46.5 | 40.7 | 38.0 | 40.0 | 30.0 | 26.0 | 27.0 |
| 160–180 | 48.0 | 9.3 | 8.0 | 41.0 | 35.0 | 38.0 | 31.0 | 42.0 | 40.6 | 39.7 | 43.2 | 52.7 | 56.8 |
| <160 | 20.0 | 2.3 | 6.0 | 21.0 | 19.0 | 15.0 | 20.0 | 16.0 | 20.4 | 18.3 | 24.8 | 19.3 | 13.2 |
| Bread Type | Flour (g) | Bean (g) | Yellow Pea (g) | Grass Pea (g) | NaCl (g) | Water (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC | 100 | - | - | - | 2.2 | 62.70 |
| CB20 | 80 | 20 | - | - | 2.2 | 63.95 |
| CB30 | 70 | 30 | - | - | 2.2 | 64.10 |
| CB40 | 60 | 40 | - | - | 2.2 | 64.25 |
| YP20 | 80 | - | 20 | - | 2.2 | 63.80 |
| YP30 | 70 | - | 30 | - | 2.2 | 63.50 |
| YP40 | 60 | - | 40 | - | 2.2 | 61.55 |
| GP20 | 80 | - | - | 20 | 2.2 | 62.15 |
| GP30 | 70 | - | - | 30 | 2.2 | 59.50 |
| GP40 | 60 | - | - | 40 | 2.2 | 56.15 |
| Sample | Dry Matter (g/100 g) | Ash (g/100 g d.m.) | L* | a* | b* | ΔE | WBC (g H2O/g d.m.) | OBC (g Oil/g d.m.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC | 88.93 ± 0.12 c | 0.79 ± 0.01 g | 87.60 ± 0.55 ab | −1.91 ± 0.08 e | 16.48 ± 0.20 f | 0.0 | 1.73 ± 0.06 bc | 2.76 ± 0.35 |
| CB20 | 90.08 ± 0.45 abc | 1.62 ± 0.02 d | 85.82 ± 0.01 bcd | −1.50 ± 0.01 c | 10.81 ± 0.03 g | 6.0 | 1.92 ± 0.05 abc | 2.44 ± 0.07 |
| CB30 | 90.73 ± 0.23 ab | 1.91 ± 0.04 c | 84.48 ± 0.01 de | −1.05 ± 0.02 b | 8.20 ± 0.01 h | 8.9 | 2.06 ± 0.06 ab | 2.61 ± 0.11 |
| CB40 | 91.01 ± 0.06 a | 2.29 ± 0.01 b | 83.47 ± 0.07 e | −0.50 ± 0.03 a | 5.41 ± 0.01 i | 11.9 | 2.19 ± 0.02 a | 2.54 ± 0.11 |
| YP20 | 89.68 ± 0.06 bc | 1.81 ± 0.01 c | 87.76 ± 0.01 a | −1.82 ± 0.06 de | 17.58 ± 0.01 e | 1.1 | 1.74 ± 0.01 bc | 2.41 ± 0.10 |
| YP30 | 90.03 ± 0.01 abc | 2.31 ± 0.02 b | 85.79 ± 0.04 bcd | −1.74 ± 0.01 cde | 18.65 ± 0.06 d | 2.8 | 1.69 ± 0.05 bc | 2.59 ± 0.13 |
| YP40 | 90.58 ± 0.03 ab | 2.87 ± 0.01 a | 85.34 ± 0.63 cde | −1.65 ± 0.00 cd | 19.30 ± 0.01 c | 3.6 | 1.65 ± 0.06 c | 2.45 ± 0.19 |
| GP20 | 89.70 ± 0.14 bc | 1.31 ± 0.01 f | 87.79 ± 0.04 a | −2.46 ± 0.00 f | 19.91 ± 0.01 b | 3.5 | 1.71 ± 0.02 bc | 2.37 ± 0.04 |
| GP30 | 89.59 ± 0.13 bc | 1.54 ± 0.01 e | 87.03 ± 0.01 abc | −2.50 ± 0.02 f | 20.97 ± 0.03 a | 4.6 | 1.71 ± 0.04 bc | 2.67 ± 0.01 |
| GP40 | 89.53 ± 0.06 bc | 1.68 ± 0.02 d | 86.47 ± 0.03 abc | −2.48 ± 0.01 f | 20.84 ± 0.00 a | 4.5 | 1.65 ± 0.11 c | 2.66 ± 0.12 |
| Farinograph | Alveograph | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Development Time (min) | Stability (min) | Water Absorption at 500 B.U. (%) | W (10−4 × J) | P/L |
| SC | 1.80 ± 0.00 d | 2.70 ± 0.28 bc | 62.70 ± 0.1 ab | 246.00 ± 8.49 a | 5.25 ± 0.05 a |
| CB20 | 4.15 ± 0.64 bc | 4.35 ± 0.64 ab | 63.95 ± 0.49 a | 167.50 ± 7.78 b | 2.61 ± 0.17 c |
| CB30 | 4.50 ± 0.28 abc | 3.05 ± 0.28 ab | 64.10 ± 0.14 a | 117.50 ± 3.54 c | 3.49 ± 0.12 b |
| CB40 | 6.40 ± 0.00 a | 3.90 ± 0.00 ab | 64.25 ± 0.64 a | 74.50 ± 4.95 de | 5.91 ± 0.22 a |
| YP20 | 1.70 ± 0.14 d | 4.00 ± 0.14 ab | 63.80 ± 0.57 a | 58.00 ± 1.41 fg | 1.33 ± 0.00 d |
| YP30 | 3.30 ± 0.14 cd | 3.05 ± 0.14 ab | 63.50 ± 0.14 a | 36.00 ± 0.00 gh | 1.31 ± 0.08 d |
| YP40 | 4.60 ± 0.42 abc | 1.25 ± 0.42 c | 61.55 ± 0.64 ab | 21.00 ± 0.00 h | 2.43 ± 0.00 c |
| GP20 | 1.70 ± 0.14 d | 3.95 ± 0.14 ab | 62.15 ± 0.21 ab | 101.00 ± 0.00 cd | 1.47 ± 0.17 d |
| GP30 | 4.00 ± 0.42 bc | 4.15 ± 0.42 ab | 59.50 ± 1.98 bc | 65.50 ± 0.71 e | 1.19 ± 0.04 d |
| GP40 | 5.70 ± 0.00 ab | 5.05 ± 0.00 a | 56.15 ± 0.35 c | 49.00 ± 0.00 fgh | 1.41 ± 0.02 d |
| Sample | Moisture (g/100 g) | Volume (cm3) | Height (mm) | Weight (g) | Porosity (1–8) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC | 33.79 ± 0.40 ab | 276.25 ± 1.77 a | 55.25 ± 1.77 ab | 152.70 ± 1.34 a | 6.75 ± 0.14 ab |
| CB20 | 36.03 ± 0.30 a | 250.00 ± 7.07 ab | 52.95 ± 1.91 ab | 154.44 ± 0.09 a | 6.50 ± 0.01 ab |
| CB30 | 32.38 ± 0.88 ab | 232.50 ± 7.07 bc | 52.35 ± 1.34 ab | 152.62 ± 0.17 a | 7.00 ± 0.01 ab |
| CB40 | 33.20 ± 0.45 ab | 208.75 ± 1.77 c | 50.05 ± 1.91 b | 152.75 ± 1.27 a | 7.75 ± 0.05 a |
| YP20 | 34.01 ± 0.48 ab | 243.75 ± 1.77 b | 56.15 ± 1.34 a | 149.25 ± 2.68 a | 6.25 ± 0.01 ab |
| YP30 | 34.51 ± 0.59 ab | 251.25 ± 5.30 ab | 54.20 ± 0.71 ab | 152.09 ± 4.35 a | 5.75 ± 0.01 b |
| YP40 | 33.60 ± 0.08 ab | 230.00 ± 3.54 bc | 50.65 ± 1.48 ab | 154.44 ± 1.20 a | 6.00 ± 0.01 b |
| GP20 | 32.72 ± 0.26 ab | 252.50 ± 7.07 ab | 56.35 ± 0.07 a | 155.12 ± 1.87 a | 6.00 ± 0.03 b |
| GP30 | 31.59 ± 0.81 b | 246.25 ± 1.77 ab | 53.00 ± 0.71 ab | 155.69 ± 0.83 a | 6.00 ± 0.04 b |
| GP40 | 30.75 ± 0.57 b | 238.75 ± 2.12 bc | 55.50 ± 2.12 ab | 154.36 ± 0.36 a | 6.50 ± 0.02 ab |
| Crust | Crumb | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Brown Index (100 − L*) | a* | b* | ΔE | Brown Index (100 − L*) | a* | b* | ΔE |
| SC | 40.62 ± 0.59 c | 11.85 ± 0.25 ab | 27.52 ± 0.34 a | 0.0 | 26.88 ± 0.47 d | −2.05 ± 0.01 d | 19.18 ± 0.16 d | 0.0 |
| CB20 | 54.69 ± 0.42 ab | 7.80 ± 0.45 bc | 13.76 ± 0.00 bcd | 1.0 | 55.04 ± 1.12 b | 2.59 ± 0.11 a | 4.92 ± 0.04 e | 0.7 |
| CB30 | 57.11 ± 2.11 ab | 6.08 ± 0.69 c | 12.61 ± 0.91 cd | 20.3 | 60.49 ± 1.48 ab | 2.92 ± 0.23 a | 4.24 ± 0.49 e | 30.9 |
| CB40 | 59.91 ± 2.35 a | 5.48 ± 0.29 c | 11.29 ± 0.56 d | 19.7 | 64.45 ± 0.98 a | 2.55 ± 0.2 a | 2.36 ± 0.21 e | 32.4 |
| YP20 | 52.76 ± 1.80 ab | 11.96 ± 0.54 a | 21.21 ± 2.16 abc | 22.4 | 38.38 ± 0.71 c | 0.30 ± 0.33 bc | 20.72 ± 0.11 cd | 37.9 |
| YP30 | 55.08 ± 1.66 ab | 13.29 ± 0.04 a | 23.11 ± 1.05 a | 23.4 | 39.52 ± 0.67 c | 0.80 ± 0.17 b | 22.01 ± 0.39 bcd | 35.8 |
| YP40 | 55.82 ± 0.67 ab | 13.31 ± 0.55 a | 23.05 ± 1.36 a | 26.8 | 38.17 ± 1.65 c | 1.05 ± 0.04 b | 22.55 ± 0.28 bcd | 41.8 |
| GP20 | 48.58 ± 0.74 bc | 13.09 ± 0.76 a | 24.14 ± 2.26 a | 25.0 | 33.36 ± 0.18 cd | −1.44 ± 0.08 d | 23.46 ± 0.98 abc | 40.5 |
| GP30 | 58.75 ± 1.53 a | 13.96 ± 1.05 a | 21.81 ± 1.14 ab | 11.6 | 32.77 ± 0.52 cd | −1.42 ± 0.20 d | 24.63 ± 1.19 ab | 12.0 |
| GP40 | 60.15 ± 0.98 a | 14.26 ± 0.52 a | 21.43 ± 0.00 ab | 15.3 | 38.48 ± 1.78 c | −0.78 ± 0.19 cd | 27.03 ± 0.00 a | 11.0 |
| Sample | Hardness (N) | Springness | Gumminess (N) | Chewiness (N · mm) | Resilience |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC | 16.10 ± 2.69 c | 1.11 ± 0.14 c | 126.41 ± 1.54 e | 130.60 ± 2.05 g | 0.64 ± 0.01 ab |
| CB20 | 15.85 ± 2.62 c | 1.00 ± 0.01 c | 59.16 ± 2.73 g | 60.98 ± 1.05 i | 0.37 ± 0.01 ab |
| CB30 | 20.25 ± 0.21 bc | 0.84 ± 0.01 c | 124.18 ± 0.64 e | 102.79 ± 0.35 h | 0.52 ± 0.24 ab |
| CB40 | 24.00 ± 0.42 abc | 0.98 ± 0.05 c | 244.41 ± 4.79 a | 234.15 ± 1.40 c | 0.67 ± 0.00 a |
| YP20 | 16.40 ± 0.14 c | 0.98 ± 0.01 c | 181.14 ± 0.94 c | 180.00 ± 2.85 e | 0.69 ± 0.02 a |
| YP30 | 21.70 ± 0.14 abc | 0.96 ± 0.1 c | 83.66 ± 0.67 f | 81.24 ± 2.79 i | 0.63 ± 0.14 ab |
| YP40 | 30.45 ± 0.92 a | 0.92 ± 0.01 c | 217.42 ± 1.34 b | 198.24 ± 0.55 d | 0.39 ± 0.04 ab |
| GP20 | 21.10 ± 1.98 abc | 1.00 ± 0.03 c | 160.85 ± 3.70 d | 159.66 ± 0.60 f | 0.36 ± 0.03 ab |
| GP30 | 26.85 ± 0.64 ab | 1.58 ± 0.04 b | 159.78 ± 1.87 d | 252.95 ± 0.49 b | 0.39 ± 0.01 ab |
| GP40 | 25.15 ± 0.78 abc | 2.50 ± 0.02 a | 130.29 ± 1.03 e | 325.74 ± 0.52 a | 0.30 ± 0.04 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Canale, M.; Sanfilippo, R.; Moscaritolo, S.; Fiore, M.C.; Strano, M.C.; Allegra, M.; Fascella, G.; Gugliuzza, G.; Spina, A. Qualitative Characteristics of Semolina–Pulse Flour Mixes and Related Breads. Foods 2025, 14, 3720. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213720
Canale M, Sanfilippo R, Moscaritolo S, Fiore MC, Strano MC, Allegra M, Fascella G, Gugliuzza G, Spina A. Qualitative Characteristics of Semolina–Pulse Flour Mixes and Related Breads. Foods. 2025; 14(21):3720. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213720
Chicago/Turabian StyleCanale, Michele, Rosalia Sanfilippo, Salvatore Moscaritolo, Maria Carola Fiore, Maria Concetta Strano, Maria Allegra, Giancarlo Fascella, Giovanni Gugliuzza, and Alfio Spina. 2025. "Qualitative Characteristics of Semolina–Pulse Flour Mixes and Related Breads" Foods 14, no. 21: 3720. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213720
APA StyleCanale, M., Sanfilippo, R., Moscaritolo, S., Fiore, M. C., Strano, M. C., Allegra, M., Fascella, G., Gugliuzza, G., & Spina, A. (2025). Qualitative Characteristics of Semolina–Pulse Flour Mixes and Related Breads. Foods, 14(21), 3720. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14213720








